32d898cf8fc27bea8e63a9d07b7ea747.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Import Export Clearance Procedures Presented by: Mr. Em Khin Vorac Deputy Director General Customs and Excise Department Imperial Garden June 30, 2008 1
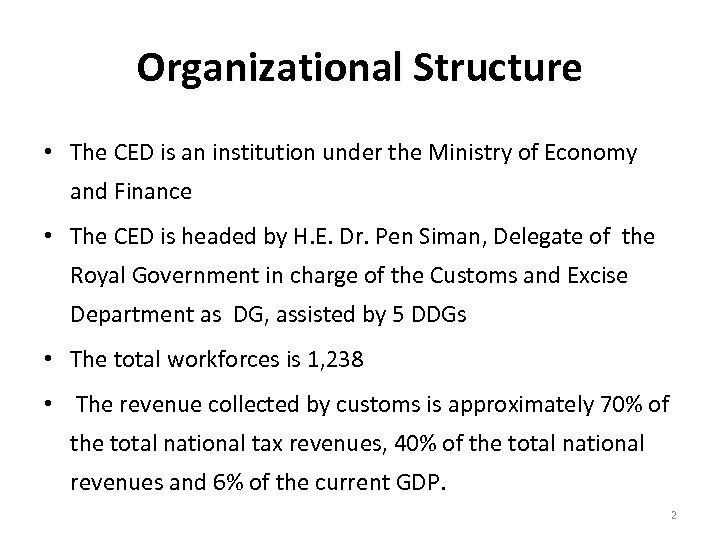
Organizational Structure • The CED is an institution under the Ministry of Economy and Finance • The CED is headed by H. E. Dr. Pen Siman, Delegate of the Royal Government in charge of the Customs and Excise Department as DG, assisted by 5 DDGs • The total workforces is 1, 238 • The revenue collected by customs is approximately 70% of the total national tax revenues, 40% of the total national revenues and 6% of the current GDP. 2
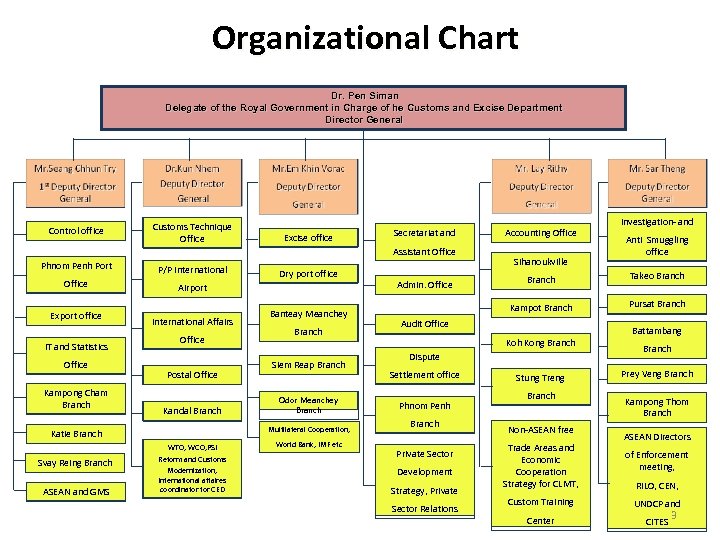
Organizational Chart Dr. Pen Siman Delegate of the Royal Government in Charge of he Customs and Excise Department Director General Control office Customs Technique Office Excise office Secretariat and Assistant Office Phnom Penh Port P/P International Office Airport Export office IT and Statistics Office Kampong Cham Branch International Affairs Office Postal Office Kandal Branch ASEAN and GMS Banteay Meanchey Branch Siem Reap Branch Odor Meanchey Branch Multilateral Cooperation, Katie Branch Svay Reing Branch Dry port office WTO, WCO, PSI Reform and Customs Modernization, International affaires coordinator for CED World Bank, IMF etc Accounting Office Sihanoukville Investigation- and Anti Smuggling office Branch Takeo Branch Kampot Branch Admin. Office Pursat Branch Audit Office Koh Kong Branch Dispute Settlement office Phnom Penh Branch Private Sector Development Strategy, Private Sector Relations Stung Treng Branch Non-ASEAN free Trade Areas and Economic Cooperation Strategy for CLMT, Battambang Branch Prey Veng Branch Kampong Thom Branch ASEAN Directors of Enforcement meeting, RILO, CEN, Custom Training UNDCP and Center CITES 3

Legal Instruments • Law on Customs and its supporting regulations, • Law on Investment and Sub-decree implementing the law on Investment, • Law on Taxation (Tax Department), • Other relevant laws and regulations. 4

Roles of the CED As a member of the WCO, CED has very similar roles with other customs administrations: • International trade facilitation • Revenue collection( duties, taxes, and other charges) • Anti- smuggling and combating of all of customs frauds • Compilation of trade statistics, analysis of trade patterns, and provision of recommendations to policy makers • Society protection by securing the supply chain. 5

Customs Clearance Procedures • The CED started to implement the ASYCUDA project since May 2006 as its application of electronic clearance system. The Project is divided into 3 phases namely: Development of Prototype, Pilot Site, and Roll-out project. • The pilot project at the Sihanoukville Port Customs (2 nd phase) since May 1 st, 2008. • The roll-out stage (3 rd phase) which is planned to start from late 2008 is the extension of ASYCUDA system to other main customs offices such as Airport, River port, Dry ports, and Export Office etc. 6
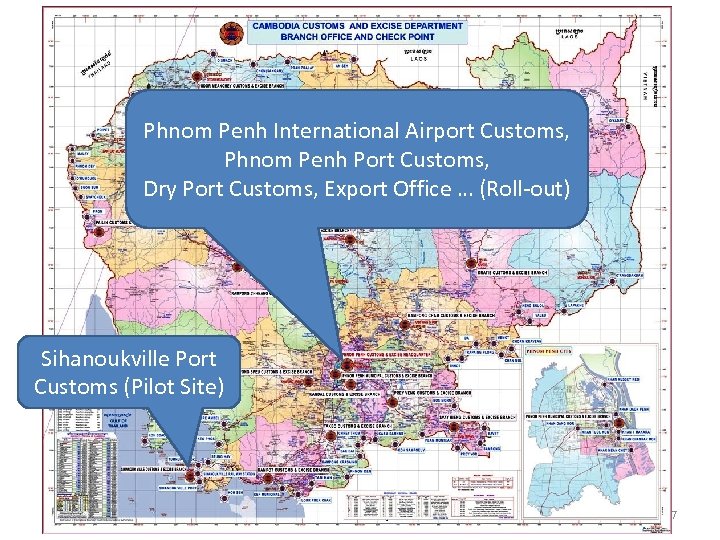
Phnom Penh International Airport Customs, Phnom Penh Port Customs, Dry Port Customs, Export Office … (Roll-out) Sihanoukville Port Customs (Pilot Site) 7

Customs Clearance Procedures • The current status (June 2008): – Electronic clearance: Sihanoukville port customs office. – Manual clearance: All customs offices other than Sihanoukville port customs office 8
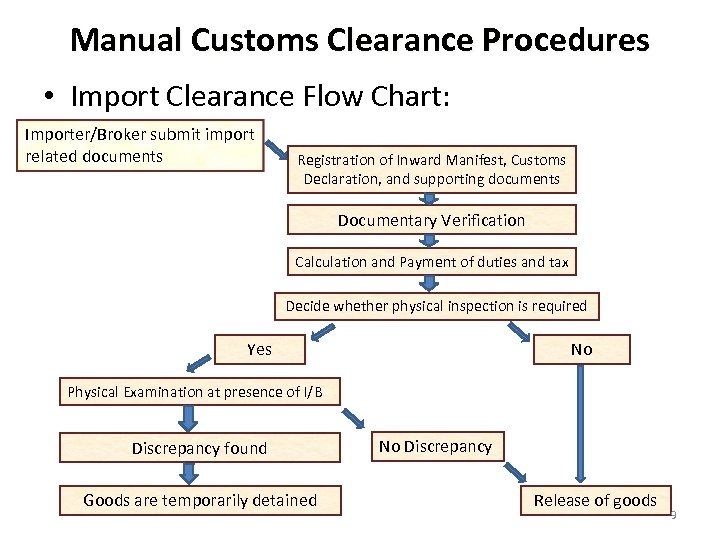
Manual Customs Clearance Procedures • Import Clearance Flow Chart: Importer/Broker submit import related documents Registration of Inward Manifest, Customs Declaration, and supporting documents Documentary Verification Calculation and Payment of duties and tax Decide whether physical inspection is required Yes No Physical Examination at presence of I/B Discrepancy found Goods are temporarily detained No Discrepancy Release of goods 9
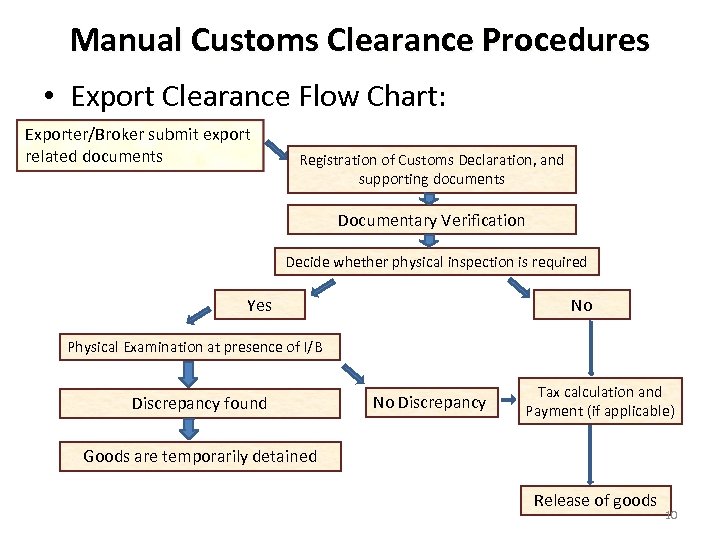
Manual Customs Clearance Procedures • Export Clearance Flow Chart: Exporter/Broker submit export related documents Registration of Customs Declaration, and supporting documents Documentary Verification Decide whether physical inspection is required Yes No Physical Examination at presence of I/B Discrepancy found No Discrepancy Tax calculation and Payment (if applicable) Goods are temporarily detained Release of goods 10
Electronic Customs Clearance Procedures through Automated System for Customs Data (ASYCUDA) Import Clearance Flow Chart 11
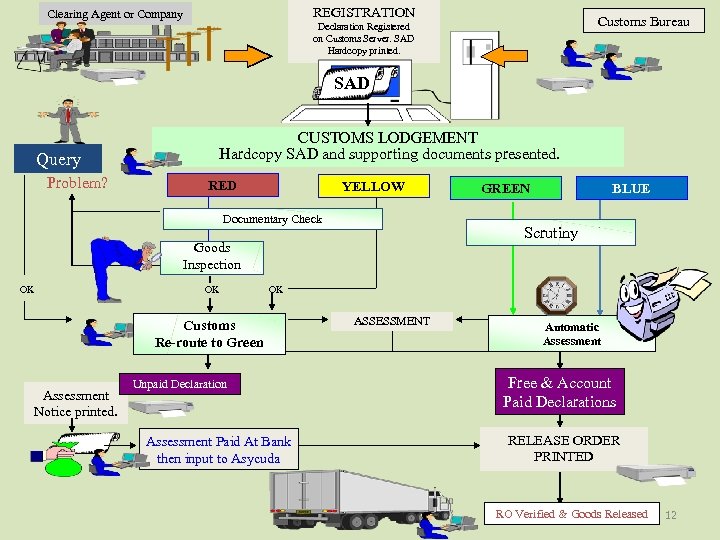
REGISTRATION Clearing Agent or Company Customs Bureau Declaration Registered on Customs Server. SAD Hardcopy printed. SAD Query Problem? CUSTOMS LODGEMENT Hardcopy SAD and supporting documents presented. RED YELLOW Documentary Check OK OK Customs Re-route to Green Assessment Notice printed. BLUE Scrutiny Goods Inspection OK GREEN Unpaid Declaration Assessment Paid At Bank then input to Asycuda ASSESSMENT Automatic Assessment Free & Account Paid Declarations RELEASE ORDER PRINTED RO Verified & Goods Released 12

Person eligible for Customs Clearance • According to Ministerial Prakas Nº 115 Dated February 15, 2008 on Establishing and Functioning of Customs Brokers, persons who are eligible for clearing imported/exported goods from customs are: – Importer/Exporter (Owner of imported/exported goods or his/her representative) – Customs brokers (legal person or individual) authorized by the MEF. 13

Customs Clearance Procedures • Where can the imported goods be declared for importation and exportation? – In any customs check-point, – For CEPT goods (originating in ASEAN Countries), customs declarations shall be lodged at 8 green lanes: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Sihanoukville port Phnom Penh International Airport Phnom Penh port Dry Ports Bavet (Cambodia-Vietnam border) Phnom Den (Cambodia-Vietnam border) Poi Pet (Cambodia-Thailand border) Excise Office 14

Customs Clearance Procedures • What are necessary documents to be attached to Customs Declaration? 1. Invoice 2. Packing List 3. VAT Certificate and Patent of previous year 4. Letter of attorney 5. Pre-shipment Inspection certificate (If applicable) 6. Customs Permit (If applicable) 7. Other necessary documents (If required) 15

Customs Clearance Procedures • Customs Permit: The Customs Permit will be issued only for importing or exporting of goods under: – preferential treatment of duties and taxes, – suspension regime, – Prohibited and restricted for the following reasons: National Security; Public order and standard of decency and morality; The protection of human, animal or plant life or health; The protection of national treasures of artistic, historic or archaeological value; • The conservation of natural resources; • The compliance with the provisions of any legislation of The Kingdom of Cambodia currently in force; • The fulfillment of obligations under the Charter of the United Nations. • • 16
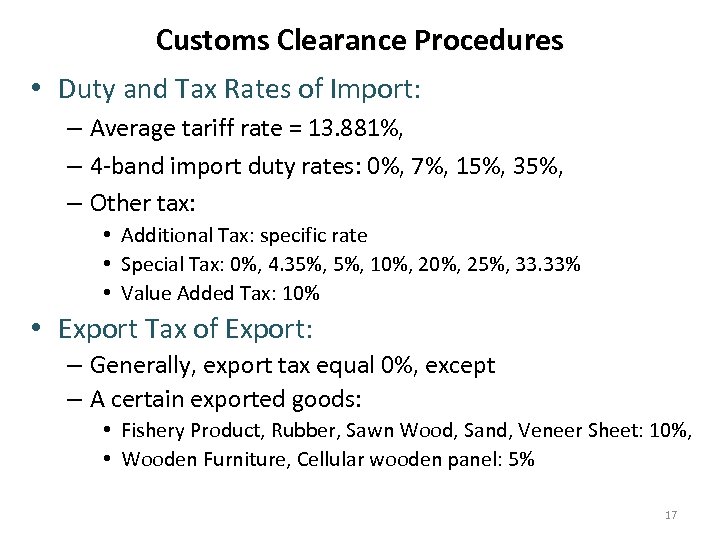
Customs Clearance Procedures • Duty and Tax Rates of Import: – Average tariff rate = 13. 881%, – 4 -band import duty rates: 0%, 7%, 15%, 35%, – Other tax: • Additional Tax: specific rate • Special Tax: 0%, 4. 35%, 10%, 25%, 33. 33% • Value Added Tax: 10% • Export Tax of Export: – Generally, export tax equal 0%, except – A certain exported goods: • Fishery Product, Rubber, Sawn Wood, Sand, Veneer Sheet: 10%, • Wooden Furniture, Cellular wooden panel: 5% 17
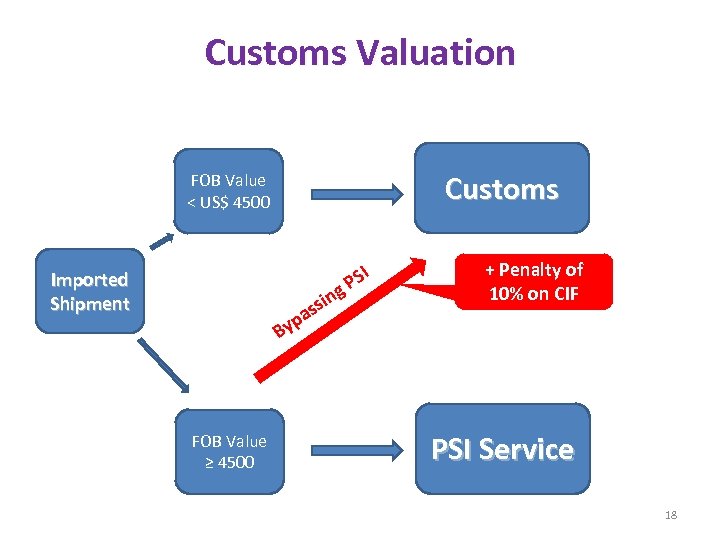
Customs Valuation Customs FOB Value < US$ 4500 Imported Shipment s pa y I PS g sin + Penalty of 10% on CIF B FOB Value ≥ 4500 PSI Service 18
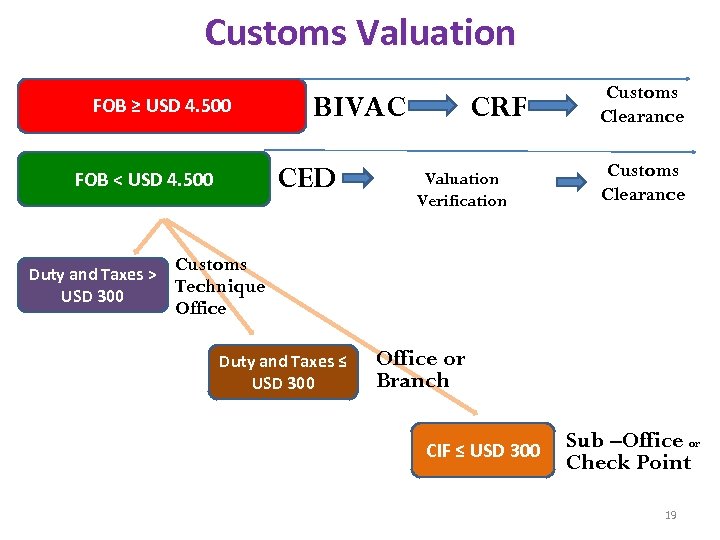
Customs Valuation FOB ≥ USD 4. 500 CED FOB < USD 4. 500 Duty and Taxes > USD 300 BIVAC CRF Valuation Verification Customs Clearance Customs Technique Office Duty and Taxes ≤ USD 300 Office or Branch CIF ≤ USD 300 Sub –Office or Check Point 19
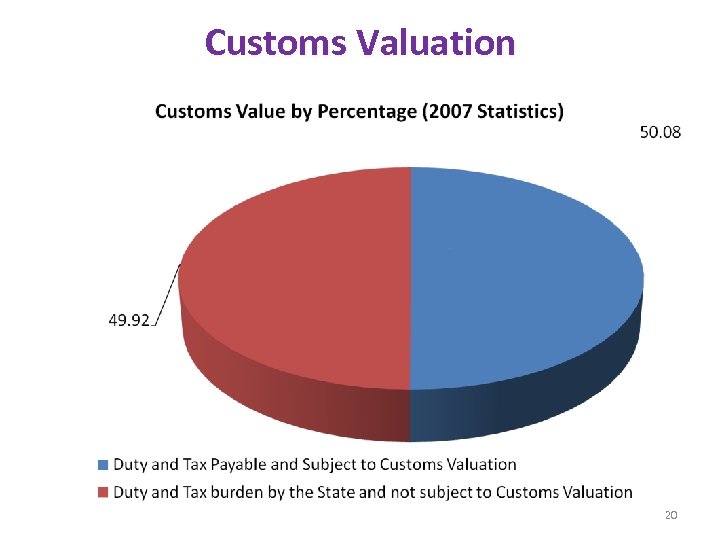
Customs Valuation 20
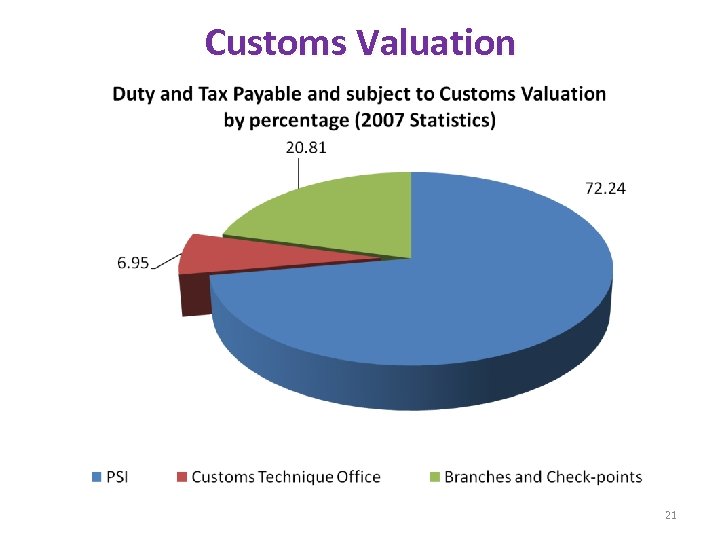
Customs Valuation 21
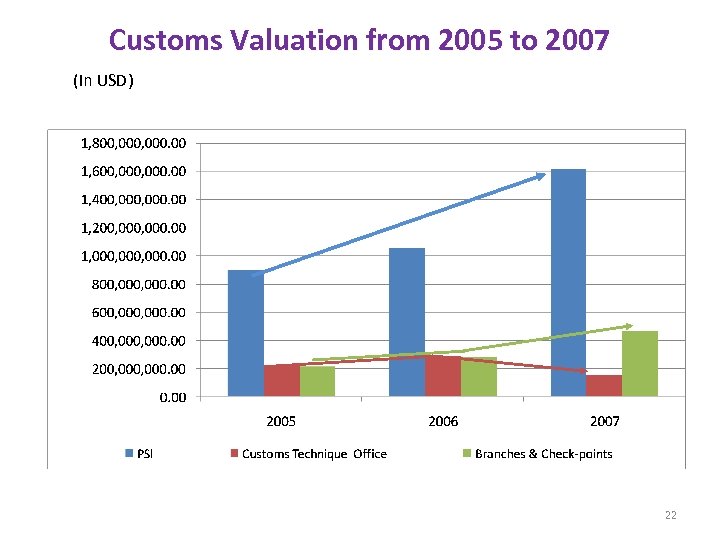
Customs Valuation from 2005 to 2007 (In USD) 22

Risk Management • How imported/exported goods are selected for physical inspection? – Before implementation of Risk Management, goods are chosen for inspection based on decision made by customs chief – Customs Risk Management and Audit Office (CRMAO) was established in 2006 and officially started its operation in May 2007. – Main responsibility of the CRMAO is to develop Selectivity Criteria for Risk Management purpose. 23

Risk Management • How imported/exported goods are selected for physical inspection? – So far, 9 Selectivity Criteria have been developed – Sub-decree 209 dated Dec 31 st, 2008 issues a National List of Prohibited and Restricted Goods – Imported/exported goods are selected by ASYCUDA into Red or Yellow or Blue or Green channels based on the above 9 Selectivity Criteria and the list of P & R Goods, – In manual environment where ASYCUDA System is not available, the above 9 Selectivity Criteria and the list of P & R Goods will also be used for determining whether imported/exported goods shall subject to physical inspection or not. 24

Risk Management • Under technical Assistance from JICA, CRMAO has developed 9 selectivity criteria as follows: 1. New Importer 2. New Items 3. Unknown Importer 4. High Customs Duty and Tax Amount 5. High Customs Duty Rate 6. High Customs Value 7. GSP Applicable goods 8. High Risk Country of Origin 9. Rank of Trader 25

Risk Management • Criterion No. 9 - Rank of Trader: Ø Is a general criterion for measuring risk level of each importer/exporter, Ø Is established base on 28 risk indicators, Ø Is divided into 5 levels: Rank 1, Rank 2, Rank 3, Rank 4, and Rank 5 which means Very low risk, Low risk, Medium risk, High risk, and Very high risk. 26

Risk Management • Selectivity Management System: Ø A software for managing all intelligent information and for updating Selectivity Criteria, Ø Collect information from different sources: Intelligent Unit, Anti-smuggling and Investigation Office, Customs Statistics System, ASYCUDA (Examination Results), Customs Offensive Records, Ø Periodically amend or update Selectivity Criteria and establish instructions for implementing those selectivity criteria. 27

Question ? 28
32d898cf8fc27bea8e63a9d07b7ea747.ppt