1c1213298e439cebc207ee080a344cf4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Implementing universal Lynch Syndrome screening in a large healthcare system
Implementing universal Lynch Syndrome screening in a large healthcare system
 1. Getting started 2. Challenges with infrastructure 3. Overcoming barriers
1. Getting started 2. Challenges with infrastructure 3. Overcoming barriers
 1. Getting Started • The goal of universal Lynch Syndrome screening is to provide a population based approach to identify individuals at increased cancer risk resulting in: – Enhanced surveillance – Early cancer detection – Decreased disease-specific mortality – Overall cost savings due to earlier detection and prevention of cancer.
1. Getting Started • The goal of universal Lynch Syndrome screening is to provide a population based approach to identify individuals at increased cancer risk resulting in: – Enhanced surveillance – Early cancer detection – Decreased disease-specific mortality – Overall cost savings due to earlier detection and prevention of cancer.
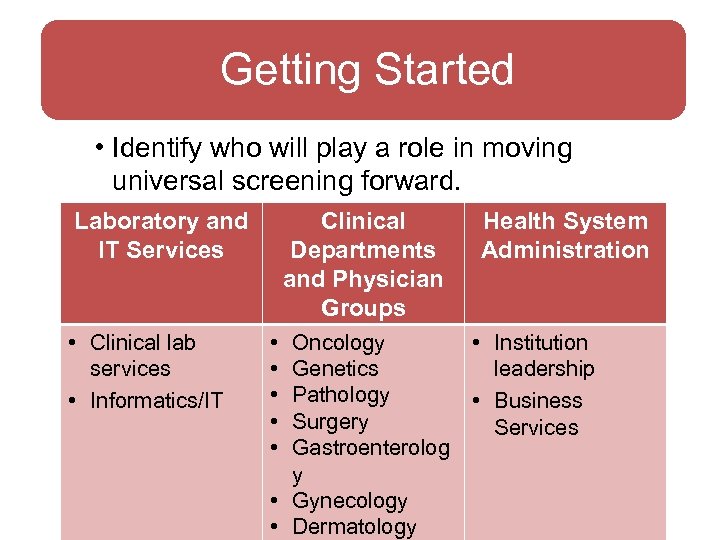 Getting Started • Identify who will play a role in moving universal screening forward. Laboratory and IT Services • Clinical lab services • Informatics/IT Clinical Departments and Physician Groups • • • Health System Administration Oncology • Institution Genetics leadership Pathology • Business Surgery Services Gastroenterolog y • Gynecology • Dermatology
Getting Started • Identify who will play a role in moving universal screening forward. Laboratory and IT Services • Clinical lab services • Informatics/IT Clinical Departments and Physician Groups • • • Health System Administration Oncology • Institution Genetics leadership Pathology • Business Surgery Services Gastroenterolog y • Gynecology • Dermatology
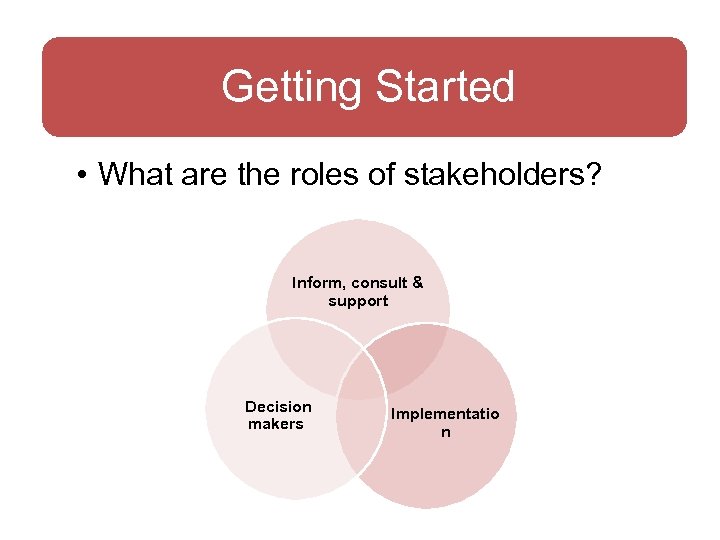 Getting Started • What are the roles of stakeholders? Inform, consult & support Decision makers Implementatio n
Getting Started • What are the roles of stakeholders? Inform, consult & support Decision makers Implementatio n
 Getting Started • Consider what information is relevant to each stakeholder group and foster communication around the benefits to the healthcare system, clinicians, and patients. — Administrators — Clinical providers (e. g. , oncologist, surgeon, pathologist, and geneticist) — Laboratory and IT Services
Getting Started • Consider what information is relevant to each stakeholder group and foster communication around the benefits to the healthcare system, clinicians, and patients. — Administrators — Clinical providers (e. g. , oncologist, surgeon, pathologist, and geneticist) — Laboratory and IT Services
 Getting Started • Administrators (business services, institutions) — Goal of universal screening — Clinical overview of Lynch Syndrome — Community standard for MSI/IHC testing — Cost benefit, both short term and long term perspectives for institutions
Getting Started • Administrators (business services, institutions) — Goal of universal screening — Clinical overview of Lynch Syndrome — Community standard for MSI/IHC testing — Cost benefit, both short term and long term perspectives for institutions
 Getting Started • Clinical providers (oncologist, surgeon, pathologist, and geneticist) — Evolving national and international standards — Evidence based data showing improved patient outcomes from universal Lynch syndrome screening testing — Examples of clinical management algorithms
Getting Started • Clinical providers (oncologist, surgeon, pathologist, and geneticist) — Evolving national and international standards — Evidence based data showing improved patient outcomes from universal Lynch syndrome screening testing — Examples of clinical management algorithms
 Getting Started • Laboratory and IT Services — Lynch Syndrome diagnostic and tumor testing criteria recommendations — Evolving standards for universal testing
Getting Started • Laboratory and IT Services — Lynch Syndrome diagnostic and tumor testing criteria recommendations — Evolving standards for universal testing
 Getting Started • EGAPP recommendations for screening www. egappreviews. org/docs/EGAPPWGLynch. Rec. pdf Resources to inform stakeholde rs • Journal articles www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/pmc/articles/PMC 292936 5 www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/pubmed/23674164 • Examples of algorithms describing tumor screening processes http: //jco. ascopubs. org/content/30/10/1024. full • Power. Point presentations with focus on benefits of Lynch Syndrome screening
Getting Started • EGAPP recommendations for screening www. egappreviews. org/docs/EGAPPWGLynch. Rec. pdf Resources to inform stakeholde rs • Journal articles www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/pmc/articles/PMC 292936 5 www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/pubmed/23674164 • Examples of algorithms describing tumor screening processes http: //jco. ascopubs. org/content/30/10/1024. full • Power. Point presentations with focus on benefits of Lynch Syndrome screening
 2. Challenges with infrastructure Identifying and understand challenges in a large healthcare system from communication with stakeholders • System culture - how new program decisions are made? – Evidence based review- does the science support the decision? – Financial impact (Prevention vs. Treatment) – New technology required?
2. Challenges with infrastructure Identifying and understand challenges in a large healthcare system from communication with stakeholders • System culture - how new program decisions are made? – Evidence based review- does the science support the decision? – Financial impact (Prevention vs. Treatment) – New technology required?
 Challenges with infrastructure • What resources are needed during: – Development – Implementation – Ongoing • From lab order through results management, what departments will be most impacted? – Pathology: Accommodating increased specimen management for testing – Laboratory/ IT: Increased resources for developing and implementing universal screening – Genetics: Increased resources during development as well as an potential change in
Challenges with infrastructure • What resources are needed during: – Development – Implementation – Ongoing • From lab order through results management, what departments will be most impacted? – Pathology: Accommodating increased specimen management for testing – Laboratory/ IT: Increased resources for developing and implementing universal screening – Genetics: Increased resources during development as well as an potential change in
 Challenges with infrastructure • How does a new process get integrated into complex, well established workflows? – What is the existing workflow for Lynch Syndrome screening? – Who are the owners of the current workflow? – Anticipate resistance to change! – Training requirements when new system is established.
Challenges with infrastructure • How does a new process get integrated into complex, well established workflows? – What is the existing workflow for Lynch Syndrome screening? – Who are the owners of the current workflow? – Anticipate resistance to change! – Training requirements when new system is established.
 Challenges with infrastructure Laboratory, pathology, and IT services require high level of commitment for process development. • Engage identified leaders who will manage the development for the laboratory flow • Determine pathology specimen flow from surgery to pathology laboratory – Specimen management by Inpatient pathologist and tech staff – Specimen management by Regional Lab
Challenges with infrastructure Laboratory, pathology, and IT services require high level of commitment for process development. • Engage identified leaders who will manage the development for the laboratory flow • Determine pathology specimen flow from surgery to pathology laboratory – Specimen management by Inpatient pathologist and tech staff – Specimen management by Regional Lab
 Challenges with infrastructure Laboratory/Pathology • Design detailed work flow — Engage IT for programing of automated orders in computerized pathology system — Flow design of Lynch syndrome screening to complete with IT, lab, and genetics stakeholders — Identify training needs to ensure implementation processes are followed — Test the processes – QC from start to finish
Challenges with infrastructure Laboratory/Pathology • Design detailed work flow — Engage IT for programing of automated orders in computerized pathology system — Flow design of Lynch syndrome screening to complete with IT, lab, and genetics stakeholders — Identify training needs to ensure implementation processes are followed — Test the processes – QC from start to finish
 Challenges with infrastructure Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – Consistency in receiving results from testing lab – Incorporation of results into medical record – Appropriate providers informed of results – Disclosure of results to patient – Coordination of appropriate reflex testing – Lynch syndrome screening billing processes – Genetic counseling for patient as indicated – Workflow should maximize patient
Challenges with infrastructure Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – Consistency in receiving results from testing lab – Incorporation of results into medical record – Appropriate providers informed of results – Disclosure of results to patient – Coordination of appropriate reflex testing – Lynch syndrome screening billing processes – Genetic counseling for patient as indicated – Workflow should maximize patient
 3. Overcoming barriers Frequent communication before, during, and after implementation • Identify and address problems as they arise — Pathologist work load impact- delay in specimen review, and sending to central laboratory causes delay for patient receiving results — Identifying need for training with lab staff • Communicate with stakeholders after implementation has begun to: — Provide opportunity for feedback — Assess need for changes — Inform and keep engaged
3. Overcoming barriers Frequent communication before, during, and after implementation • Identify and address problems as they arise — Pathologist work load impact- delay in specimen review, and sending to central laboratory causes delay for patient receiving results — Identifying need for training with lab staff • Communicate with stakeholders after implementation has begun to: — Provide opportunity for feedback — Assess need for changes — Inform and keep engaged
 Overcoming barriers • Elements for successful Lynch screening implementation: — — — Identify decision makers Engage stakeholders Provide information to inform and facilitate buy-in Meet with key personnel to develop the implementation plan Keep channels of communication going during the process to ensure implementation plan is progressing — When hurdles arise- look to stakeholders and key personnel to assist with resolution of the problem • Ongoing communication is a must with: — — Pathology Laboratory, IT Genetics Surgery
Overcoming barriers • Elements for successful Lynch screening implementation: — — — Identify decision makers Engage stakeholders Provide information to inform and facilitate buy-in Meet with key personnel to develop the implementation plan Keep channels of communication going during the process to ensure implementation plan is progressing — When hurdles arise- look to stakeholders and key personnel to assist with resolution of the problem • Ongoing communication is a must with: — — Pathology Laboratory, IT Genetics Surgery
 Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Consistency in receiving results from testing lab » Will they be mailed/faxed/incorporated into electronic medical record? » A point person or department is essential as is a consistent method of sending/receiving results. Incorporation of results into medical record » Where in the chart will the results go? » Will they be incorporated into the original pathology report? » They should be in the same place for each patient to ensure consistency and ease of locating results.
Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Consistency in receiving results from testing lab » Will they be mailed/faxed/incorporated into electronic medical record? » A point person or department is essential as is a consistent method of sending/receiving results. Incorporation of results into medical record » Where in the chart will the results go? » Will they be incorporated into the original pathology report? » They should be in the same place for each patient to ensure consistency and ease of locating results.
 Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Appropriate providers informed of results » How do providers involved in care typically receive lab results? » Consider routing results directly to relevant stakeholders, holding a case conference with stakeholders for all screen positive cases, etc. Disclosure of results to patient » How will results be disclosed to patient? » Letter or phone call with appropriate stakeholder; determine if all results or only abnormal results will be provided to patients etc.
Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Appropriate providers informed of results » How do providers involved in care typically receive lab results? » Consider routing results directly to relevant stakeholders, holding a case conference with stakeholders for all screen positive cases, etc. Disclosure of results to patient » How will results be disclosed to patient? » Letter or phone call with appropriate stakeholder; determine if all results or only abnormal results will be provided to patients etc.
 Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Coordination of appropriate reflex testing » Who will be involved? What consenting may be indicated? » Consider how current workflows could be modified. » Consider which stakeholders should be closely involved with this task. Lynch syndrome screening billing processes » What are the current billing processes/barriers? » Is an order in the EMR necessary for billing purposes? » Determine how will this impact workflow for a
Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Coordination of appropriate reflex testing » Who will be involved? What consenting may be indicated? » Consider how current workflows could be modified. » Consider which stakeholders should be closely involved with this task. Lynch syndrome screening billing processes » What are the current billing processes/barriers? » Is an order in the EMR necessary for billing purposes? » Determine how will this impact workflow for a
 Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Genetic counseling for patient as indicated » Consider patient education handouts for screen positive cases (prior to reflex testing if available). » Comprehensive Lynch syndrome screening program should consider genetic counseling of high risk cases if resources are available. » What will the patient population be in a more formal Genetics clinic setting once screening is in place? How will this impact clinic workflow? Workflow should maximize patient compliance » EGAPP cost-effective analyses are based on appropriate at risk family members receiving cancer surveillance. » Strive to obtain patient compliance data to track screening implementation process successes.
Overcoming barriers Genetics – Lynch screening test results • Development of appropriate work flow for results and patient education – – Genetic counseling for patient as indicated » Consider patient education handouts for screen positive cases (prior to reflex testing if available). » Comprehensive Lynch syndrome screening program should consider genetic counseling of high risk cases if resources are available. » What will the patient population be in a more formal Genetics clinic setting once screening is in place? How will this impact clinic workflow? Workflow should maximize patient compliance » EGAPP cost-effective analyses are based on appropriate at risk family members receiving cancer surveillance. » Strive to obtain patient compliance data to track screening implementation process successes.


