7dbe584cb740b931013a9d119cac40ed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Implementing Six Sigma Quality at Better Body Manufacturing D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control

Overview D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control ABC Incorporated (ABC) is not achieving Six Sigma quality levels for all critical Body-Side Sub-Assembly dimensions as requested by their customers. Ensure that all critical body-side subassembly dimensions are within Six Sigma quality levels of < 3. 4 DPM. Cp ³ 2. 0 and Cpk ³ 1. 67. • Determined the correlation between body side and assembly dimensions. • Evaluated the significance of Tonnage > 935 for ASM_7 Y & ASM_8 Y. • Conducted a DOE for Clamp position for ASM_9 Y & ASM_10 Y. • Change tonnage to > 935 to correct ASM_7 Y and ASM_8 Y • Set clamp position to location 2 for ASM_9 Y and ASM_10 Y • Re-machine A-pillar die to correct A_3 Y and ASM_3 Y 2

Problem Statement & The Goal D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control ABC Incorporated’s customer wants ABC to apply Six Sigma problem solving methodology to insure that the body side subassembly is achieving Six Sigma quality levels of less than 3. 4 defects per million for all critical body side subassembly dimensions. ABC needs an improvement strategy that minimizes the rework costs while achieving the desired quality objective. ABC’s goal is to produce module subassemblies that meet the customer requirements and not necessarily to insure that every individual stamped component within the assembly meets it original print specifications – sub-system optimizations vs. local optimization. A-Pillar Reinforcement + B-Pillar Reinforcement Body Side Outer + 3
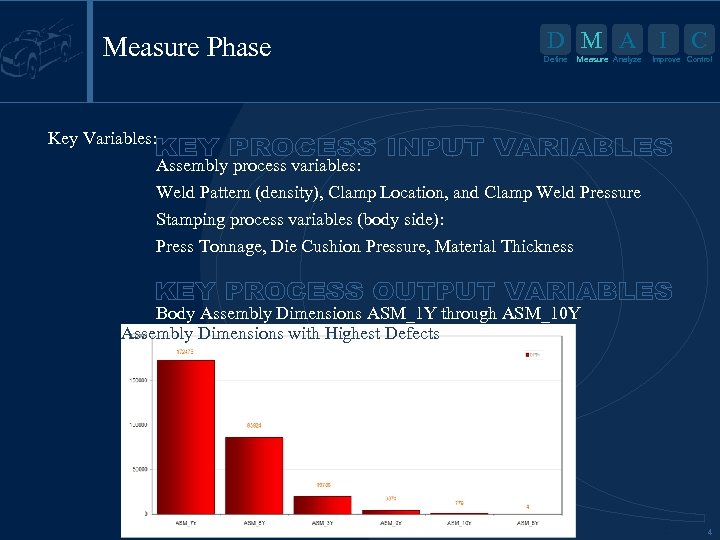
Measure Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Key Variables: Assembly process variables: Weld Pattern (density), Clamp Location, and Clamp Weld Pressure Stamping process variables (body side): Press Tonnage, Die Cushion Pressure, Material Thickness Body Assembly Dimensions ASM_1 Y through ASM_10 Y Assembly Dimensions with Highest Defects 4

Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Resolution alternatives (based upon past experience): 1. Make adjustments to assembly process settings 2. Reduce variation of components through better control of stamping process input variables 3. Rework stamping dies to shift component mean deviation that is off target and causing assembly defects Target Performance Level: All ten critical assembly dimensions at Six Sigma quality level of £ 3. 4 DPM. Cp ³ 2. 0 and Cpk ³ 1. 67 Fish Bone and P-Diagrams: Understanding potential causes of defects. From this we pick the assembly and component dimensions that require further analysis 5
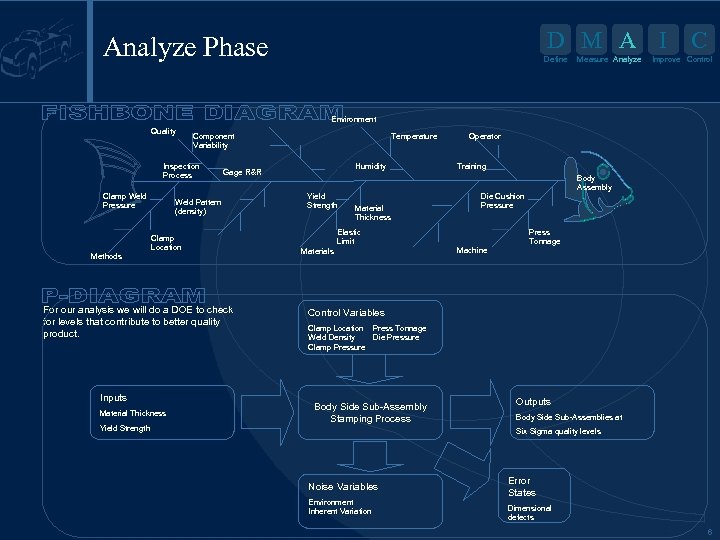
D M A I Analyze Phase Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Environment Quality Component Variability Inspection Process Clamp Weld Pressure Methods Clamp Location For our analysis we will do a DOE to check for levels that contribute to better quality product. Material Thickness Yield Strength Humidity Gage R&R Weld Pattern (density) Inputs Temperature Yield Strength Material Thickness Elastic Limit Materials Operator Training Body Assembly Die Cushion Pressure Machine Press Tonnage Control Variables Clamp Location Press Tonnage Weld Density Die Pressure Clamp Pressure Body Side Sub-Assembly Stamping Process Outputs Body Side Sub-Assemblies at Six Sigma quality levels Noise Variables Environment Inherent Variation Error States Dimensional defects 6
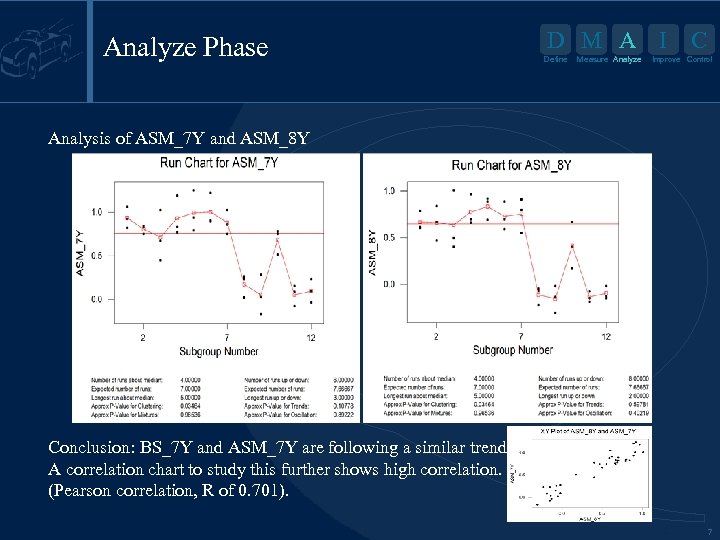
Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Analysis of ASM_7 Y and ASM_8 Y Conclusion: BS_7 Y and ASM_7 Y are following a similar trend. A correlation chart to study this further shows high correlation. (Pearson correlation, R of 0. 701). 7
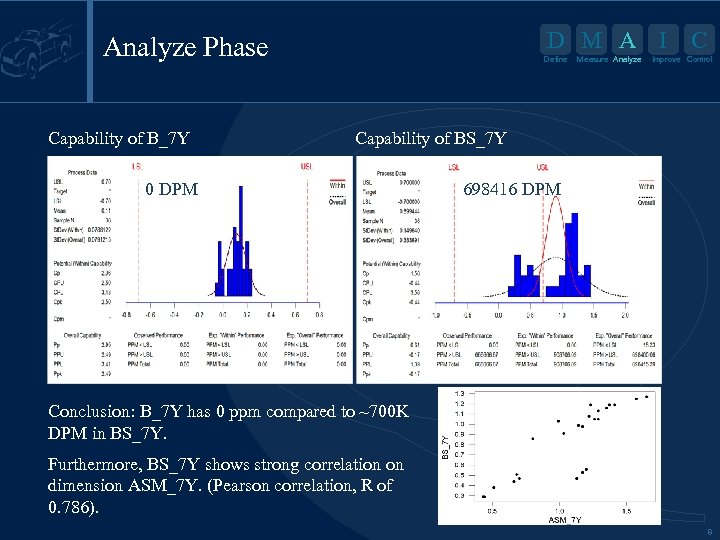
D M A I Analyze Phase Capability of B_7 Y Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Capability of BS_7 Y 0 DPM 698416 DPM Conclusion: B_7 Y has 0 ppm compared to ~700 K DPM in BS_7 Y. Furthermore, BS_7 Y shows strong correlation on dimension ASM_7 Y. (Pearson correlation, R of 0. 786). 8
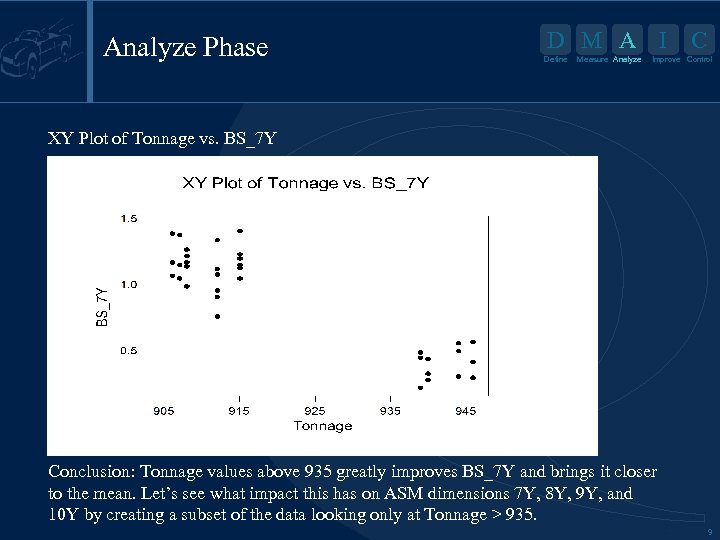
Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control XY Plot of Tonnage vs. BS_7 Y Conclusion: Tonnage values above 935 greatly improves BS_7 Y and brings it closer to the mean. Let’s see what impact this has on ASM dimensions 7 Y, 8 Y, 9 Y, and 10 Y by creating a subset of the data looking only at Tonnage > 935. 9
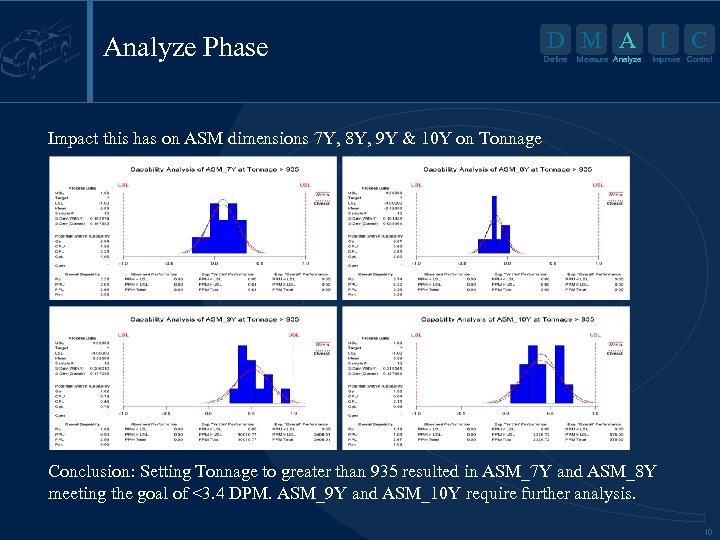
Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Impact this has on ASM dimensions 7 Y, 8 Y, 9 Y & 10 Y on Tonnage Conclusion: Setting Tonnage to greater than 935 resulted in ASM_7 Y and ASM_8 Y meeting the goal of <3. 4 DPM. ASM_9 Y and ASM_10 Y require further analysis. 10

Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control DOE for Response Variable ASM_9 Y • DOE factorial analysis shows Clamp Position is the only significant factor in determining ASM_9 Y dimension DOE Response Optimization for ASM_9 Y • Set Clamp Position to Location 2 (level 1) • Optimizer recommends setting Weld Density to 1. 33 weld per inch (level 1), but this appears to be a robust parameter, which could be changed for the benefit of process without reducing quality if processing time or cost shows a benefit. • Optimizer recommends setting Clamp Pressure to 2100 psi (level 1), but this appears to be a robust parameter, which could be changed for the benefit of process without reducing quality if processing time or cost shows a benefit. • Run additional tests at recommended settings to confirm results • Weld Density and Clamp Pressure are robust parameters and can be set to optimize the process capability to maximum level and lowest cost. 11

Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control DOE for Response Variable ASM_10 Y • DOE factorial analysis shows Clamp Position is also the only significant factor in determining ASM_10 Y dimension DOE Response Optimization for ASM_10 Y • Setting clamp to location 2 also improves ASM_10 Y • Recommend same settings used to improve ASM_9 Y to improve process capability which also allows for no changes to machine setup and helps reduce possible process concerns • Run additional tests at recommended settings to confirm results • Weld Density and Clamp Pressure are robust parameters and can be set to optimize the process capability to maximum level and lowest cost. 12

Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control DOE for Response Variable ASM_3 Y • DOE factorial analysis shows that no factors are significant • Response Optimization shows no solution for response optimizer Observe Process Capability of A_3 Y and BS_3 Y • ASM_3 Y and A_3 Y have a similar mean shift in the -Y direction Correlation of Output Variables • No dimensional correlations appear to exist between ASM_3 Y and A_3 Y or BS_3 Y Stepwise Regression Analysis of BS_3 Y • Tonnage and Die Pressure appear to be significant in determining dimension BS_3 Y • Tonnage values < 920 may improve BS_3 Y • Die Pressure appears to have no clear correlation to BS_3 Y 13
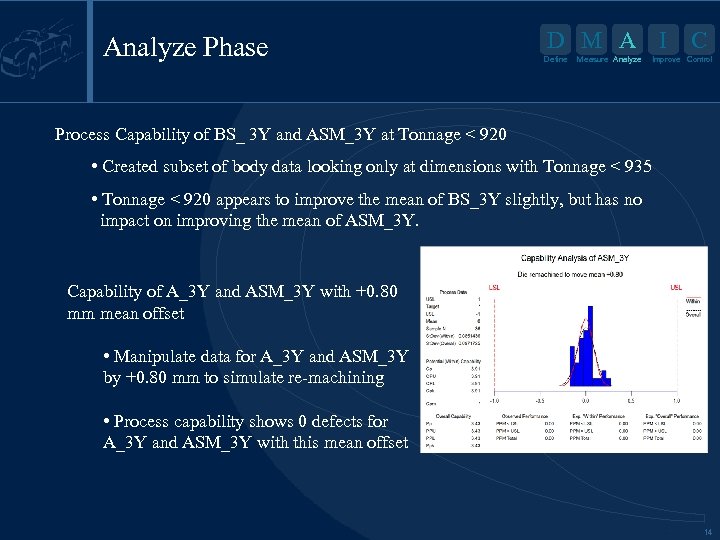
Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Process Capability of BS_ 3 Y and ASM_3 Y at Tonnage < 920 • Created subset of body data looking only at dimensions with Tonnage < 935 • Tonnage < 920 appears to improve the mean of BS_3 Y slightly, but has no impact on improving the mean of ASM_3 Y. Capability of A_3 Y and ASM_3 Y with +0. 80 mm mean offset • Manipulate data for A_3 Y and ASM_3 Y by +0. 80 mm to simulate re-machining • Process capability shows 0 defects for A_3 Y and ASM_3 Y with this mean offset 14

Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Conclusions • From the analysis of ASM_7 Y and ASM_8 Y we can conclude that: • Setting tonnage > 935 results in ASM_7 Y and ASM_8 Y meeting the goal • Analyzing ASM_9 Y and ASM_10 Y helps determine that: • Setting clamp position to location 2, weld density to 1 weld every 1. 33” and clamp pressure to 2000 psi helps with dimensions ASM_9 Y and ASM_10 Y • Analyzing ASM_3 Y helps us conclude that: • Re-machine A-Pillar die to move A_3 Y to nominal – which could cause BS_3 Y to shift towards nominal – effectively shifting ASM_3 Y to nominal 15
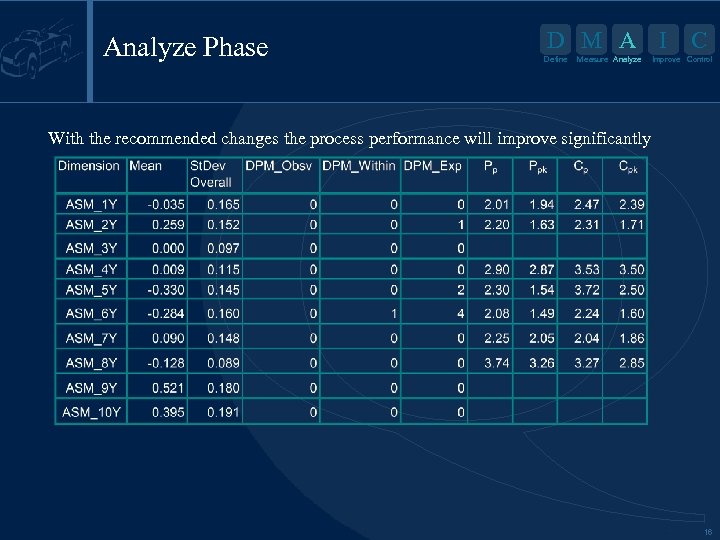
Analyze Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control With the recommended changes the process performance will improve significantly 16

Improve Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Recommendations for improving the process: • Set Tonnage to above 935 to improve ASM_7 Y & ASM_8 Y • Set Clamp to Location 2 to improve ASM_9 Y & ASM_10 Y • Re-machine the A-Pillar die to move the mean of A_3 Y to nominal which in turn will move ASM_3 Y to nominal Implement the above recommendations and run additional samples to verify results. 17

Control Phase D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control Recommended controls : • Implement a gauge on the body side component press to monitor tonnage • Implement an alarm and shut-off feature on the body side press if tonnage falls below 935 tons • Implement poke-yoke clamping fixture that ensures clamp is always in Position 2 • Establish an affordable control plan for ongoing monitoring of the 10 critical assembly dimensions. 18

Summary D M A I Define Measure Analyze C Improve Control ABC Incorporated is not achieving Six Sigma quality levels for all critical Body-Side Sub-Assembly dimensions as requested by their customers. BBM needs to apply Six Sigma problem solving methodology to establish an improvement strategy that minimizes rework costs, yet achieves the desired quality objective. Bring the key process output variables within Six Sigma quality level of < 3. 4 DPM. Cp ³ 2. 0 and Cpk ³ 1. 67 • Set Tonnage to above 935 to improve ASM_7 Y & ASM_8 Y • Set Clamp to Location 2 to improve ASM_9 Y & ASM_10 Y • Re-machine the A-Pillar die to move the mean of A_3 Y to nominal • Implement a gauge on the body side component press to monitor tonnage • Implement an alarm & shut-off feature on body side press if tonnage falls below 935 • Implement poke-yoke clamping fixture that ensures clamp is always in Position 2 • Establish control plan for ongoing monitoring of the 10 critical assembly dimensions. 19
7dbe584cb740b931013a9d119cac40ed.ppt