eff87265de393587e4f30f11c101bf97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

Immigrants, Industry and the City

Background of Industrial Revolution • • War of 1812 Transportation Revolution Textiles Artificial Power Mechanization of Production Replaceable Parts Factory Production Destruction of the Artisan Class

Thomas Edison • Creates – Lightbulb – DC Electricity Generation – Image and sound recording • Innovator in creation of research labs

Inventing Technology • Chemistry – Charles Goodyear (Vulcanization of Rubber) -1839 – John Wesley Hyatt--Celluloid--1863 – Leo Hendrik Baekeland -- Bakelite -- 1909 – Du. Pont Corporation • Information Technology – Typewriter, Telephone, Rotary Printing Press, Telegraph

Rising Industry • Agriculture – $1. 5 billion in 1870; $7. 5 billion by 1919 – 50% of workers in 1870; 31% by 1910 • Fuels – Coal, Oil, Wood – Electrical Generation • Infrastructure – 240, 000 miles of Rail by 1910
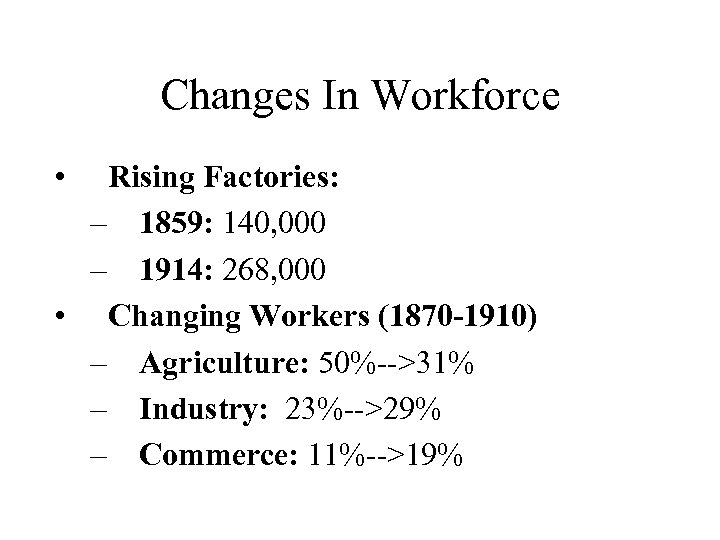
Changes In Workforce • Rising Factories: – 1859: 140, 000 – 1914: 268, 000 • Changing Workers (1870 -1910) – Agriculture: 50%-->31% – Industry: 23%-->29% – Commerce: 11%-->19%
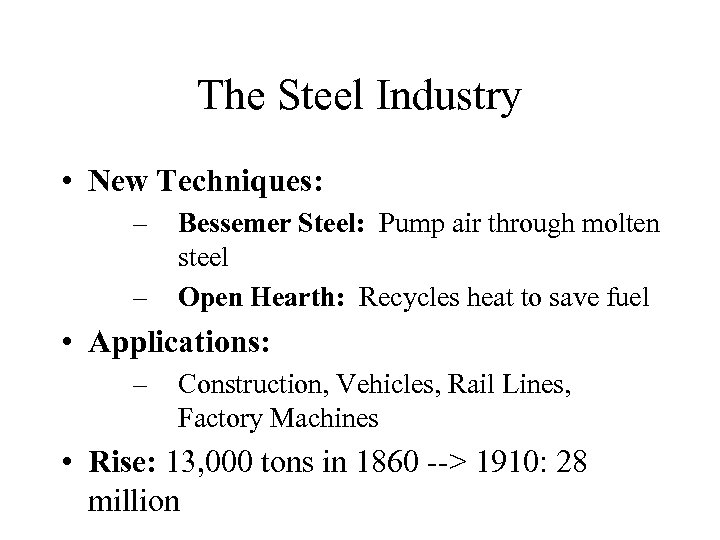
The Steel Industry • New Techniques: – – Bessemer Steel: Pump air through molten steel Open Hearth: Recycles heat to save fuel • Applications: – Construction, Vehicles, Rail Lines, Factory Machines • Rise: 13, 000 tons in 1860 --> 1910: 28 million

Meatpacking • Chicago Union Stock Yards (1865) – – – • 475 acres with internal rail lines and roads Millions of cattle and pigs a year Adjacent plants could pack year round by storing meat in refrigerator rooms Refrigerator cars hauled meat to other cities

The Chicago Union Stockyard

Grain Processing • Chicago Board of Trade— 1850 – – Standardizes grain quality grades Grain storage now works like a bank for money • • – Deposit grain in storage Write 'checks' to pay out grain to others Civil War leads to the 'futures' trade

Rise of Breakfast Cereal • • 'Granula'—granulated wheat, soak overnight, 1863 Quaker Oats man registered, 1877 – • • The Cereal Box, 1887 Grape Nuts, C. W. Post, 1897 Toasted Corn Flakes, W. K. Kellogg, 1906

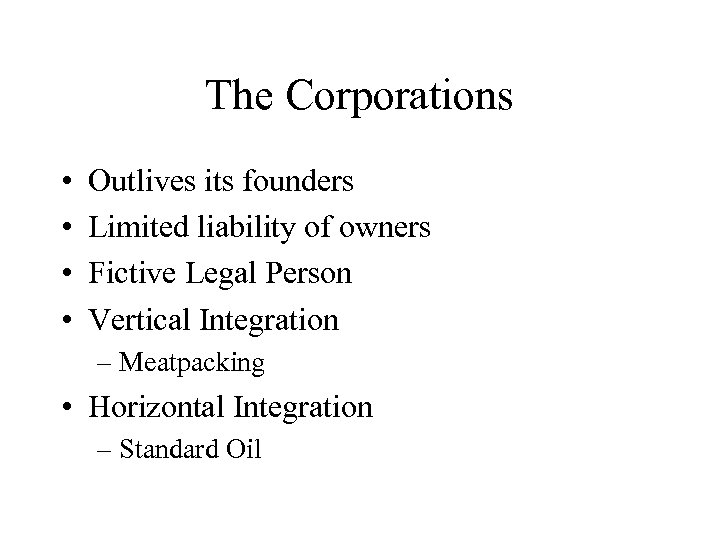
The Corporations • • Outlives its founders Limited liability of owners Fictive Legal Person Vertical Integration – Meatpacking • Horizontal Integration – Standard Oil

Financing the Industrial Revolution • • • Greenbacks Silver Rise of Wall Street Bonds Mergers – Pools – Trusts – Holding Companies

Changes in Retailing • Fixed Prices Replace Haggling • General Store—cheap but narrow range of goods • Department Store – – – Broad range of goods Offers special services (warranties, bridal registry, home delivery, etc. ) Leads to rise of the Chain Stores

Rise of the Department Store • • • 1846: The Marble Palace 1858: W. H. Macy's and Lord and Taylor's Might occupy an entire city block

Rise of the Mail Order Houses • • Enables rural Americans to buy anything by mail 1872—Aaron Montgomery Ward's first catalog sent out

Creation of Modern Labor Force • By 1900, 19 of 27 million worked for wages – Factories destroyed independent artisans • Everyone in family worked to survive – Wages were below survival level • Job Conditions Unsafe: 30, 000 railworkers alone died every year • Work Insecurity: Few worked year round – Many had to move a lot for work • Long Hours: 12 hours a day, 6 days a week

Female Labor • 1880: 2. 6 of 17. 4 million workers are women • 1900: 85% of female labor are unmarried and 25 or younger • No Family Wage • Inadequate Female Wages (25 -50% of what men made)

Limited Professions • Teachers • Nurses • Social Work – Social Housekeeping • Domestics

Child Labor • 4% of non-farm workforce in 1900 • Due to inadequacy of Adult Wages • Protests begin in 1890

Women’s Entertainments

Business Ethics: The Self-Made Man • Horatio Alger Novels—Work hard and improve yourself and you will flourish • This appeals to many Americans • Strong American belief in selfimprovement, self-denial to accumulate wealth, and desire for personal property

Business Ethics: Crush Everyone Else • Laisez Faire—Government stay out of business! • Social Darwinism—CRUSH THE WEAK AND GROW STRONG – An excuse to be evil • Contradictions: – – – Big Businesses had hard to overcome edge Businesses loved government help--for them. Businessmen hated competition and loved monopolies. . . if they ran them.

Andrew Carnegie • • Immigrant (Scot) Factory Work → Massive Steel Empire Gives away most of fortune Urges 'Intelligent Philanthropy'

The Gospel of Wealth • • Written by Andrew Carnegie Advocated intelligent philanthrophy Creation of institutions of self-improvement Discouraged redistribution of wealth and poverty assistance charities • Rejected leaving your fortune to your kids – Say no to Paris Hilton, etc.
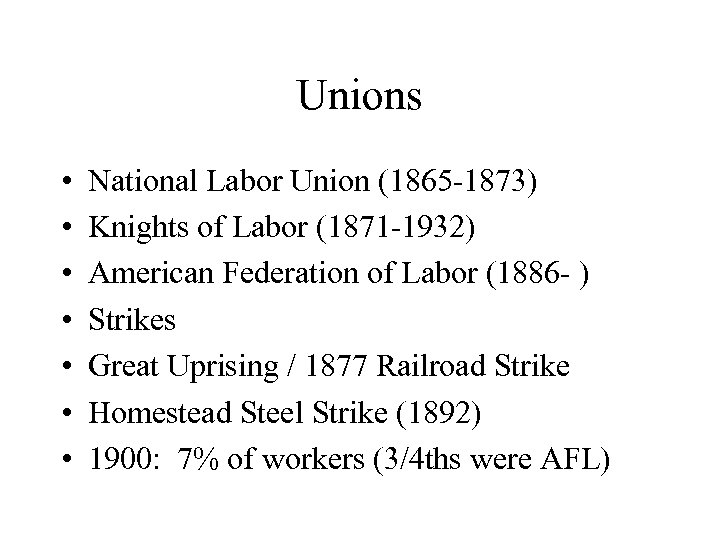
Unions • • National Labor Union (1865 -1873) Knights of Labor (1871 -1932) American Federation of Labor (1886 - ) Strikes Great Uprising / 1877 Railroad Strike Homestead Steel Strike (1892) 1900: 7% of workers (3/4 ths were AFL)

Supreme Court Backs Big Business • Slaughterhouse Cases (1873) • Munn vs. Illinois (1877) • Santa Clar Co. V. Southern Pacific Railroad (1886) • Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific Railroad Company vs. Illinois (1886) • Pollock v. Farmers Loan and Trust Company (1895)

First Efforts at Regulation • Interstate Commerce Commission (1887) – 1897 Maximum Freight Rates Case • Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) – United States vs. E. C. Knight (1895)
Immigration

Immigrants: Western US • Japanese: 50, 000 by 1900 – Farm Labor • Chinese: 125, 000 by 1882 – Mining, Railroads, and Support Businesses – Called California ‘Gold Mountain’ – “Chinese Food”

Chinese Gold Miners

Eastern US Immigration • • • Italians Jews Slavs Greeks Many are Catholic or Greek Orthodox

Greek Immigrants in Ethnic Dress

Immigrant Communities • • Women’s Roles Ghettos / Ethnic Neighborhoods Religion and Fraternal Organizations Linguistic Enclaves

Italian Society Parade

Internal Migration • The Push West – 1900: The Frontier Closes • “The Great Migration” – Moving North – Work Opportunities – Ghettos – Communal Institutions

The American City: Growth • 1860: 25 million Rural / 6. 2 mil Urban • 1910: 50 million Rural / 42 mil Urban – 3 Cities: 1 million + – 5: 500, 000 - 999, 000 • New Immigrants • Rural Migration

The American City: Neighborhood Specialization • Districting • Suburbs • Urban Transportation: – Streetcards – Elevated Rail – Electric Streetcar – Subways – Effects

Problems • Wastes – Improved Sewage – 1910: 10 out of 42 million Americans have access to clean water • Tenements – Poorly made – Poorly insulated – No fire codes – Cramped

Crime • • Mostly Urban Murders Quadruple (Lead? ) Slums Prostitution – Regulators – White Slavery Panic – Anti-Vice Crusaders

Political Machines • • • Urban Immigrants Bosses Corruption Social Services Upper Class Protest

New Urban Architecture • • Technology Skyscrapers Style Louis Sullivan

Education • • • Innovators Country vs. City Rise of High Schools Classical vs. Modern Curricula Assimilation Universities – Land Grant and Co-Ed Universities

Sports: Baseball • 1840: NYC Area • Pro Ball: 1869 --Cincinnati Red Stockings • National League (1880 s) - 8 million spectators / year • 1899: American League • 1903: First World Series (Boston Americans (AL) vs Pittsburgh Pirates (NL), 5 -3 games.

Entertainment • • • Theatre: Melodrama --> Realism Music Orchestras Black Music (Ragtime) New Theatre Forms
Motion Pictures • Thomas Edison (1890 s) • 1895: First projected movies • 1903: Great Train Robbery -- First full story • 1905: 3, 000 movie theatres • 1914: 13, 000 movie theatres / 5 -7 million patrons a day

Sports • • Urban Need for Exercise and Entertainment Basketball (1891) Bicycling (1890 s) Blue Laws Boxing (Jack Johnson 1908) Football Male Dominated
eff87265de393587e4f30f11c101bf97.ppt