9332130d22b2092907d4f2499eaf3371.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Image Segmentation Region growing & Contour following Hyeun-gu Choi Advisor: Dr. Harvey Rhody Center for Imaging Science
Image Segmentation Region growing & Contour following Hyeun-gu Choi Advisor: Dr. Harvey Rhody Center for Imaging Science
 Background • Definition of image segmentation – Subdivides an image into its constituent parts or objects. • Region growing – Based on similarity of gray-level values • Contour following – Based on discontinuity of gray-level values 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Background • Definition of image segmentation – Subdivides an image into its constituent parts or objects. • Region growing – Based on similarity of gray-level values • Contour following – Based on discontinuity of gray-level values 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Detection of discontinuity • Gradient operators - First derivative(Sobel) – Zero value - constant gray level – Positive value - transition from dark region to light region – Negative value - transition from light region to dark region 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Detection of discontinuity • Gradient operators - First derivative(Sobel) – Zero value - constant gray level – Positive value - transition from dark region to light region – Negative value - transition from light region to dark region 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Detection of discontinuity • Gradient operators - Second derivative (Laplacian) – Positive value - dark region – Negative value - light region – This operator is good for deciding whether a pixel is on the dark or light side of an edge. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Detection of discontinuity • Gradient operators - Second derivative (Laplacian) – Positive value - dark region – Negative value - light region – This operator is good for deciding whether a pixel is on the dark or light side of an edge. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Application of these operators(1) • Threshold Selection Based on Boundary Characteristics T: Threshold value s(x, y): result image 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Application of these operators(1) • Threshold Selection Based on Boundary Characteristics T: Threshold value s(x, y): result image 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Examples of derivative operator Original image with background picture Segmented image without background by Sobel and Laplacian operator 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Examples of derivative operator Original image with background picture Segmented image without background by Sobel and Laplacian operator 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
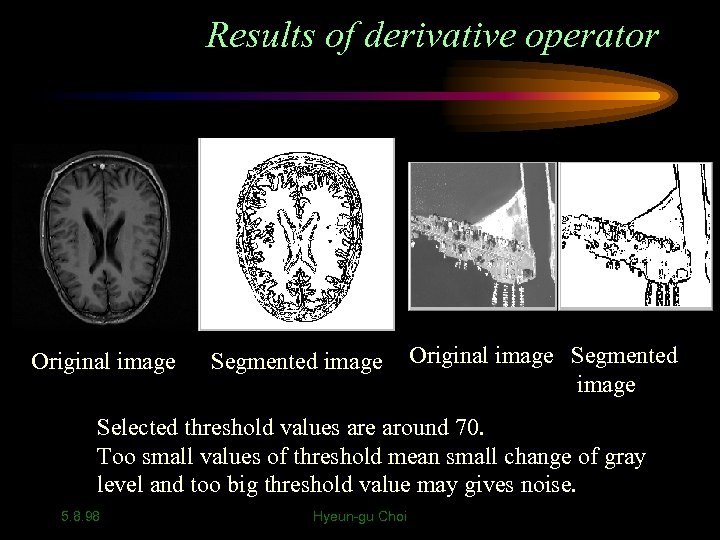 Results of derivative operator Original image Segmented image Selected threshold values are around 70. Too small values of threshold mean small change of gray level and too big threshold value may gives noise. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Results of derivative operator Original image Segmented image Selected threshold values are around 70. Too small values of threshold mean small change of gray level and too big threshold value may gives noise. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Segmentation by thresholding • Simple Global Thresholding – Simply select a threshold value between peak values from a histogram plot and set zero below than threshold and set 255 greater than threshold. – Disadvantage: lost a lot of data information and there is no guarantee of grouped (wellseparated) histogram. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Segmentation by thresholding • Simple Global Thresholding – Simply select a threshold value between peak values from a histogram plot and set zero below than threshold and set 255 greater than threshold. – Disadvantage: lost a lot of data information and there is no guarantee of grouped (wellseparated) histogram. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Segmentation by thresholding • Multiple Thresholding – Select useful region by selecting two thresholds – Simple and very good results – Disadvantage - No guarantee for grouped histogram. Not good for automated system because user should decide threshold value 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Segmentation by thresholding • Multiple Thresholding – Select useful region by selecting two thresholds – Simple and very good results – Disadvantage - No guarantee for grouped histogram. Not good for automated system because user should decide threshold value 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
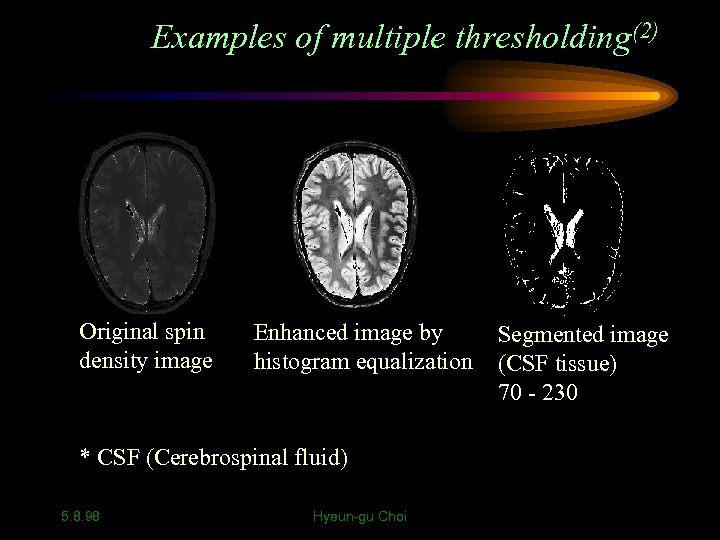 Examples of multiple thresholding(2) Original spin density image Enhanced image by histogram equalization * CSF (Cerebrospinal fluid) 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi Segmented image (CSF tissue) 70 - 230
Examples of multiple thresholding(2) Original spin density image Enhanced image by histogram equalization * CSF (Cerebrospinal fluid) 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi Segmented image (CSF tissue) 70 - 230
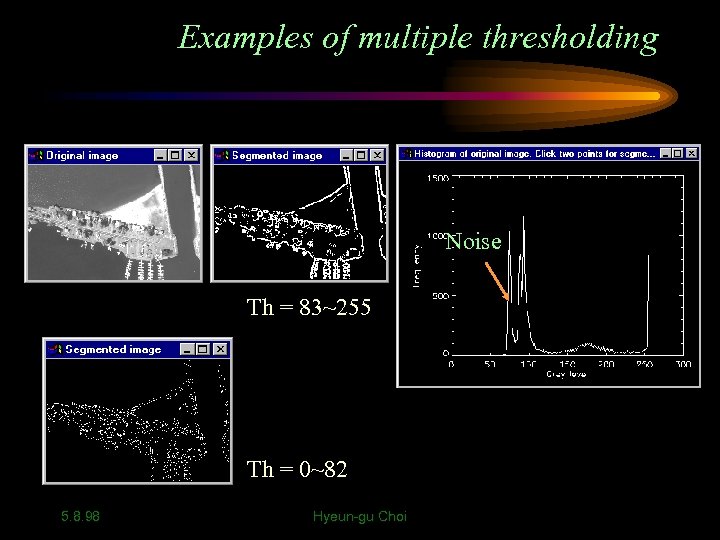 Examples of multiple thresholding Noise Th = 83~255 Th = 0~82 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Examples of multiple thresholding Noise Th = 83~255 Th = 0~82 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Label Region algorithm • Basic Concept – Scan through an image pixel by pixel – Compare the gray value of center pixel with those of top and left pixels. – If compared gray values are the same, those pixels are categorized to one group. – After scanning all pixels, pixels with the same gray level value will be grouped. • Disadvantage - Very vulnerable to noise. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Label Region algorithm • Basic Concept – Scan through an image pixel by pixel – Compare the gray value of center pixel with those of top and left pixels. – If compared gray values are the same, those pixels are categorized to one group. – After scanning all pixels, pixels with the same gray level value will be grouped. • Disadvantage - Very vulnerable to noise. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
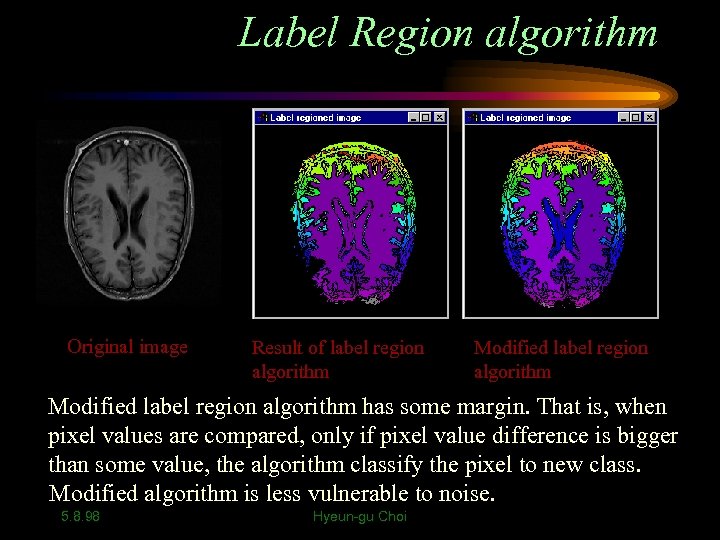 Label Region algorithm Original image Result of label region algorithm Modified label region algorithm has some margin. That is, when pixel values are compared, only if pixel value difference is bigger than some value, the algorithm classify the pixel to new class. Modified algorithm is less vulnerable to noise. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Label Region algorithm Original image Result of label region algorithm Modified label region algorithm has some margin. That is, when pixel values are compared, only if pixel value difference is bigger than some value, the algorithm classify the pixel to new class. Modified algorithm is less vulnerable to noise. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
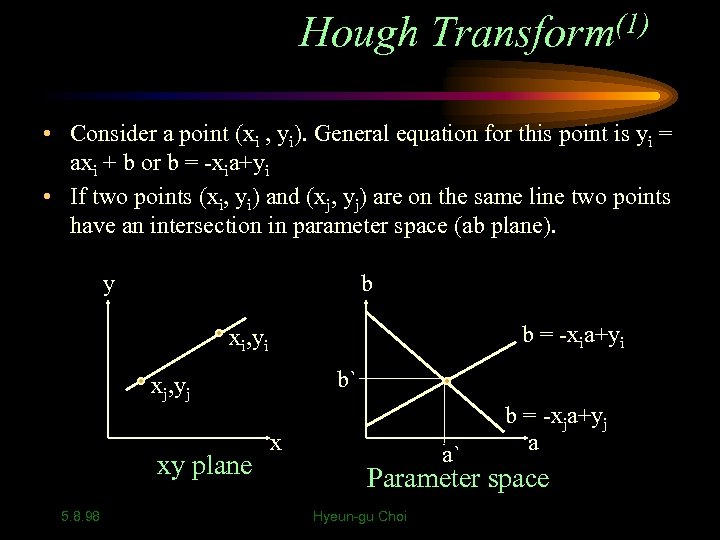 Hough Transform(1) • Consider a point (xi , yi). General equation for this point is yi = axi + b or b = -xia+yi • If two points (xi, yi) and (xj, yj) are on the same line two points have an intersection in parameter space (ab plane). y b b = -xia+yi xi, yi b` xj, yj xy plane 5. 8. 98 x a` b = -xja+yj a Parameter space Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform(1) • Consider a point (xi , yi). General equation for this point is yi = axi + b or b = -xia+yi • If two points (xi, yi) and (xj, yj) are on the same line two points have an intersection in parameter space (ab plane). y b b = -xia+yi xi, yi b` xj, yj xy plane 5. 8. 98 x a` b = -xja+yj a Parameter space Hyeun-gu Choi
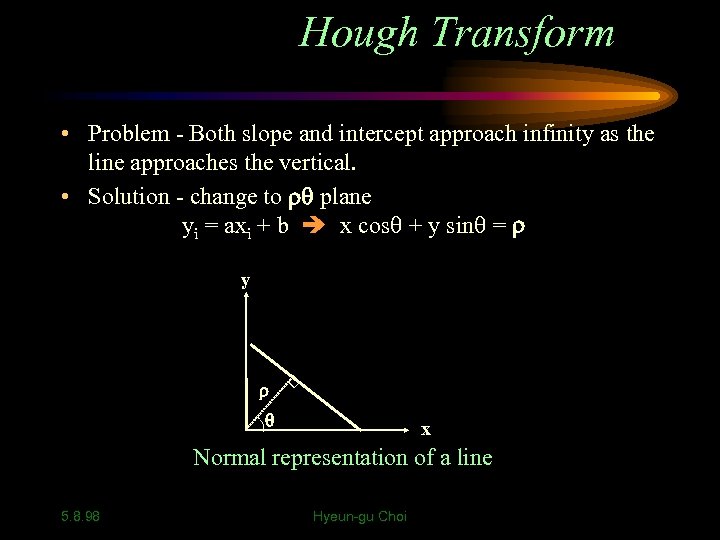 Hough Transform • Problem - Both slope and intercept approach infinity as the line approaches the vertical. • Solution - change to plane yi = axi + b x cos + y sin = y x Normal representation of a line 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform • Problem - Both slope and intercept approach infinity as the line approaches the vertical. • Solution - change to plane yi = axi + b x cos + y sin = y x Normal representation of a line 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
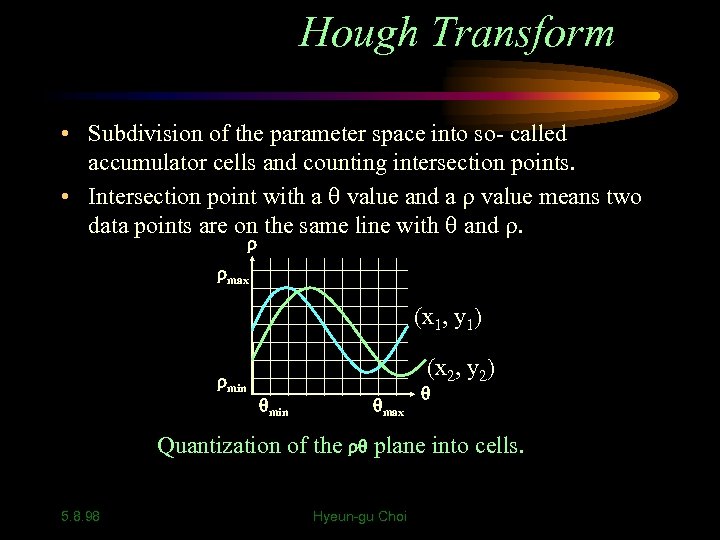 Hough Transform • Subdivision of the parameter space into so- called accumulator cells and counting intersection points. • Intersection point with a value and a value means two data points are on the same line with and . max (x 1, y 1) min (x 2, y 2) min max Quantization of the plane into cells. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform • Subdivision of the parameter space into so- called accumulator cells and counting intersection points. • Intersection point with a value and a value means two data points are on the same line with and . max (x 1, y 1) min (x 2, y 2) min max Quantization of the plane into cells. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
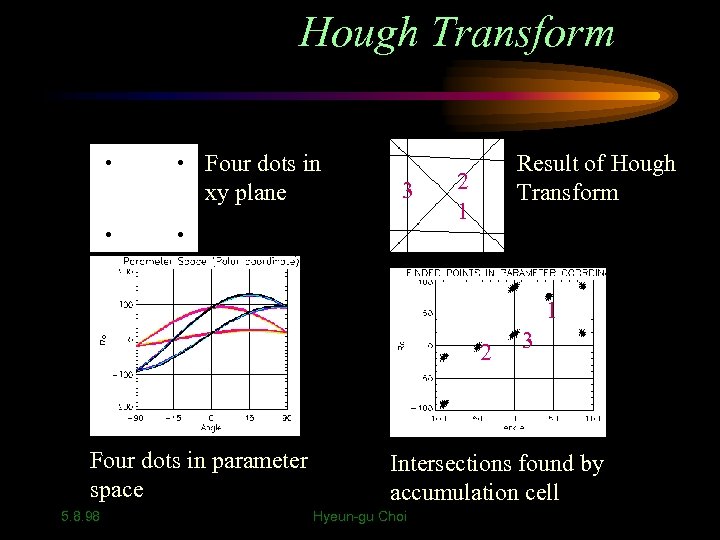 Hough Transform Four dots in xy plane 3 Result of Hough Transform 2 1 1 2 Four dots in parameter space 5. 8. 98 3 Intersections found by accumulation cell Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform Four dots in xy plane 3 Result of Hough Transform 2 1 1 2 Four dots in parameter space 5. 8. 98 3 Intersections found by accumulation cell Hyeun-gu Choi
 Hough Transform • Disadvantage of Hough Transform – Vulnerable to noise – Difficult to find lines in complicated images – Difficult to change the shape which looking for • Line : y = ax + b • Circle : (x-C 1)2 + (y-C 2)2 = C 3 3 Dim parameter space – Long processing time • About 25 minutes for 192 x 128 size image by Pentium 166 MHz, 48 Mbyte RAM 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform • Disadvantage of Hough Transform – Vulnerable to noise – Difficult to find lines in complicated images – Difficult to change the shape which looking for • Line : y = ax + b • Circle : (x-C 1)2 + (y-C 2)2 = C 3 3 Dim parameter space – Long processing time • About 25 minutes for 192 x 128 size image by Pentium 166 MHz, 48 Mbyte RAM 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
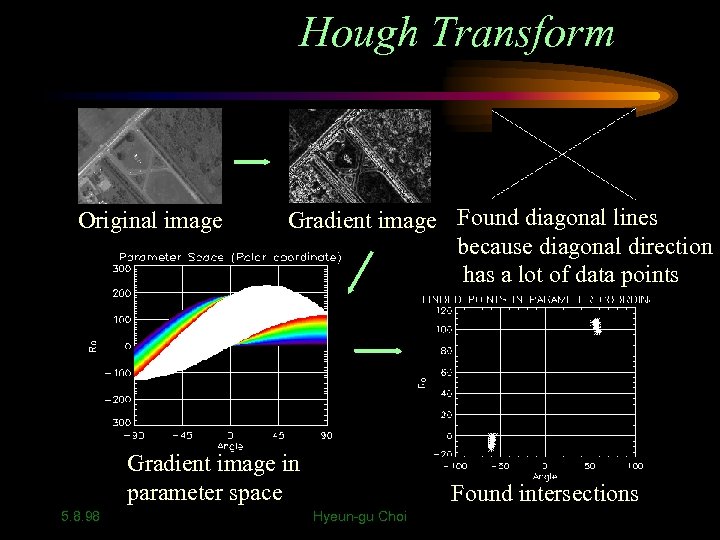 Hough Transform Original image Gradient image Found diagonal lines because diagonal direction has a lot of data points Gradient image in parameter space 5. 8. 98 Found intersections Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform Original image Gradient image Found diagonal lines because diagonal direction has a lot of data points Gradient image in parameter space 5. 8. 98 Found intersections Hyeun-gu Choi
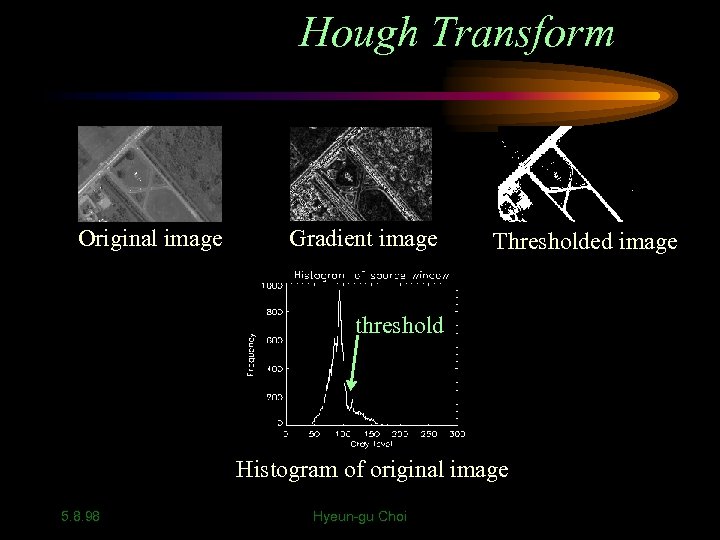 Hough Transform Original image Gradient image Thresholded image threshold Histogram of original image 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform Original image Gradient image Thresholded image threshold Histogram of original image 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
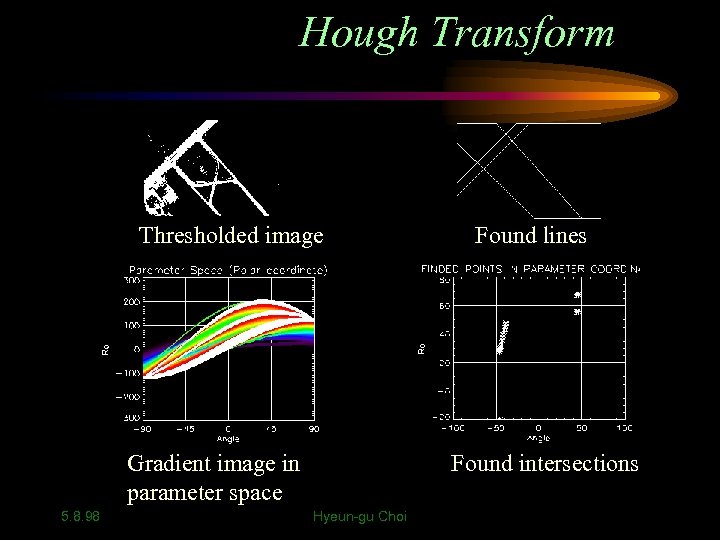 Hough Transform Thresholded image Gradient image in parameter space 5. 8. 98 Found lines Found intersections Hyeun-gu Choi
Hough Transform Thresholded image Gradient image in parameter space 5. 8. 98 Found lines Found intersections Hyeun-gu Choi
 Graphic User Interface (Widget) • A graphic user interface is created for demonstration of segmentation methods in IDL (Interactive Data Language). • Widget interface is consisted of five image windows and one plot window. • 11 full down main menus. • Advantage - Easy to organize many algorithms and easy to modify. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Graphic User Interface (Widget) • A graphic user interface is created for demonstration of segmentation methods in IDL (Interactive Data Language). • Widget interface is consisted of five image windows and one plot window. • 11 full down main menus. • Advantage - Easy to organize many algorithms and easy to modify. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
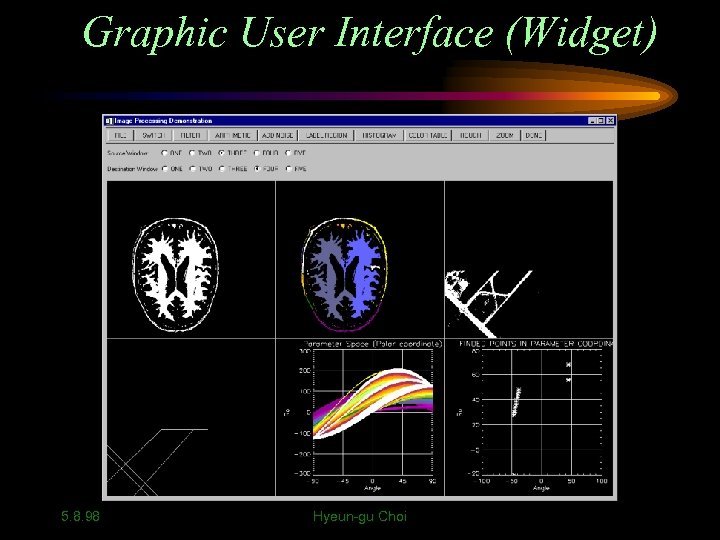 Graphic User Interface (Widget) 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Graphic User Interface (Widget) 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Graphic User Interface (Widget) • Main menus and sub menus – Files • New - Get an new image. • Save Image – Switch - User can switch two windows – Filter • High pass, low pass, unsharp, laplacian, vertical edges, horizontal edges, sobel, median, and custom. – Arithmetic - Add and subtract two windows. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Graphic User Interface (Widget) • Main menus and sub menus – Files • New - Get an new image. • Save Image – Switch - User can switch two windows – Filter • High pass, low pass, unsharp, laplacian, vertical edges, horizontal edges, sobel, median, and custom. – Arithmetic - Add and subtract two windows. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Graphic User Interface (Widget) – Add Noise – Label Region • Label region (IDL library) and Modified label region – Histogram • Histogram of source window, Histogram equalization, one threshold, and two thresholds – Color table - Emphasize the processed image. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Graphic User Interface (Widget) – Add Noise – Label Region • Label region (IDL library) and Modified label region – Histogram • Histogram of source window, Histogram equalization, one threshold, and two thresholds – Color table - Emphasize the processed image. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
 Graphic User Interface (Widget) – Hough • Manual - User can choose intersections by clicking in parameter space. • Auto - Computer do the whole process. – Zoom - Zoom in an image with several magnification (2 x, 3 x, 4 x). – Done - Finish the interface. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Graphic User Interface (Widget) – Hough • Manual - User can choose intersections by clicking in parameter space. • Auto - Computer do the whole process. – Zoom - Zoom in an image with several magnification (2 x, 3 x, 4 x). – Done - Finish the interface. 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
![Reference • (1) Gonzalez, Rafael C. and Woods, Richard E. [1992] “Digital Image Processing” Reference • (1) Gonzalez, Rafael C. and Woods, Richard E. [1992] “Digital Image Processing”](https://present5.com/presentation/9332130d22b2092907d4f2499eaf3371/image-27.jpg) Reference • (1) Gonzalez, Rafael C. and Woods, Richard E. [1992] “Digital Image Processing” Addison. Wesley Publishing Company • (2) Lynn M. Fletcher, John B. Barsotti, Joseph P. Hornak [1993] “A Multispectral Analysis of Brain Tissues” Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 29: 623 -630 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi
Reference • (1) Gonzalez, Rafael C. and Woods, Richard E. [1992] “Digital Image Processing” Addison. Wesley Publishing Company • (2) Lynn M. Fletcher, John B. Barsotti, Joseph P. Hornak [1993] “A Multispectral Analysis of Brain Tissues” Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 29: 623 -630 5. 8. 98 Hyeun-gu Choi


