05cc028859cc48090c49fab7bda8e306.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

 Image Reconstruction from Projections J. Anthony Parker, MD Ph. D Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, Massachusetts Caveat Lector Tony_Parker@BIDMC. Harvard. edu
Image Reconstruction from Projections J. Anthony Parker, MD Ph. D Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, Massachusetts Caveat Lector Tony_Parker@BIDMC. Harvard. edu
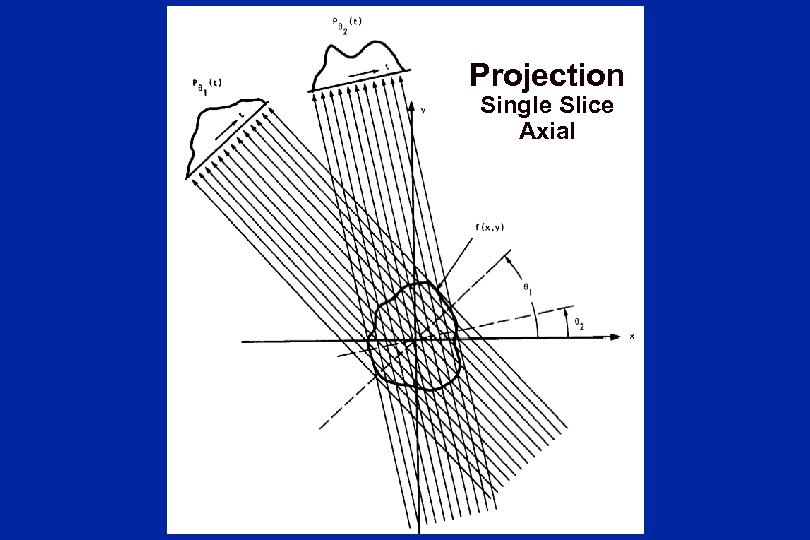 Projection Single Slice Axial
Projection Single Slice Axial
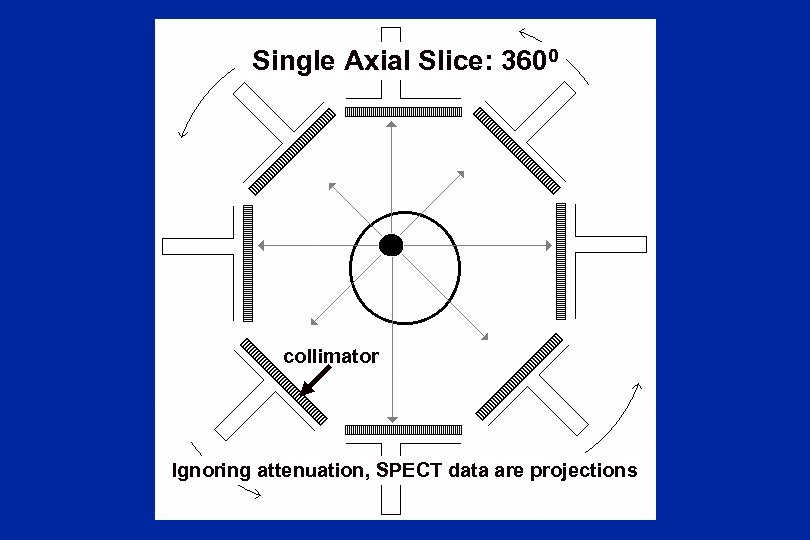 Single Axial Slice: 3600 collimator Ignoring attenuation, SPECT data are projections
Single Axial Slice: 3600 collimator Ignoring attenuation, SPECT data are projections
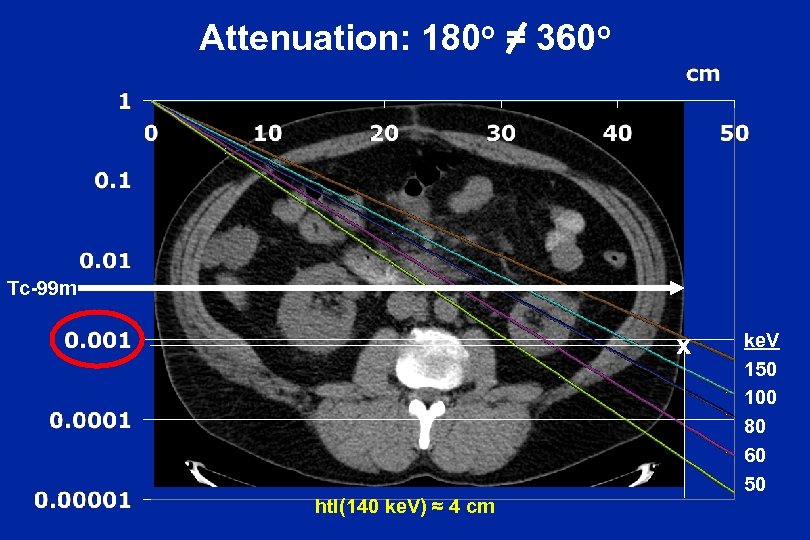 Attenuation: 180 o = 360 o Tc-99 m x htl(140 ke. V) ≈ 4 cm ke. V 150 100 80 60 50
Attenuation: 180 o = 360 o Tc-99 m x htl(140 ke. V) ≈ 4 cm ke. V 150 100 80 60 50
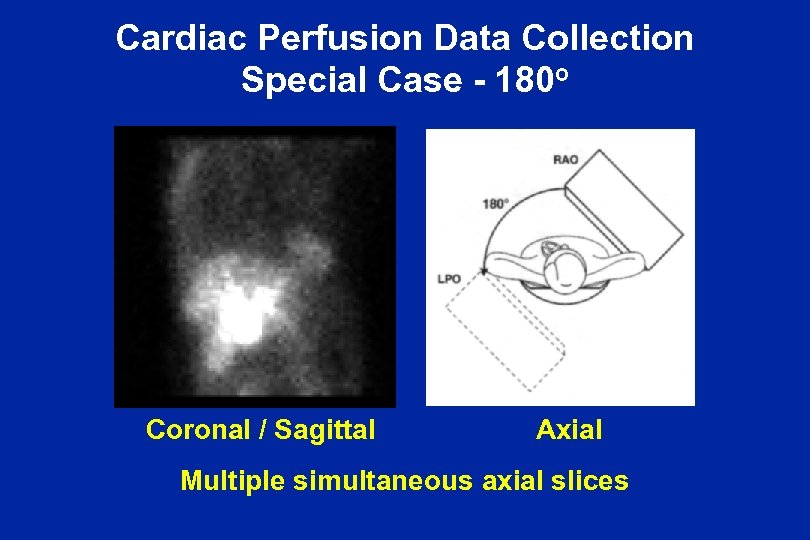 Cardiac Perfusion Data Collection Special Case - 180 o Coronal / Sagittal Axial Multiple simultaneous axial slices
Cardiac Perfusion Data Collection Special Case - 180 o Coronal / Sagittal Axial Multiple simultaneous axial slices
 Dual-Head General-Purpose Gamma Camera: 900 “Cardiac” Position 1 2 2 heads: 900 rotation = 1800 data
Dual-Head General-Purpose Gamma Camera: 900 “Cardiac” Position 1 2 2 heads: 900 rotation = 1800 data
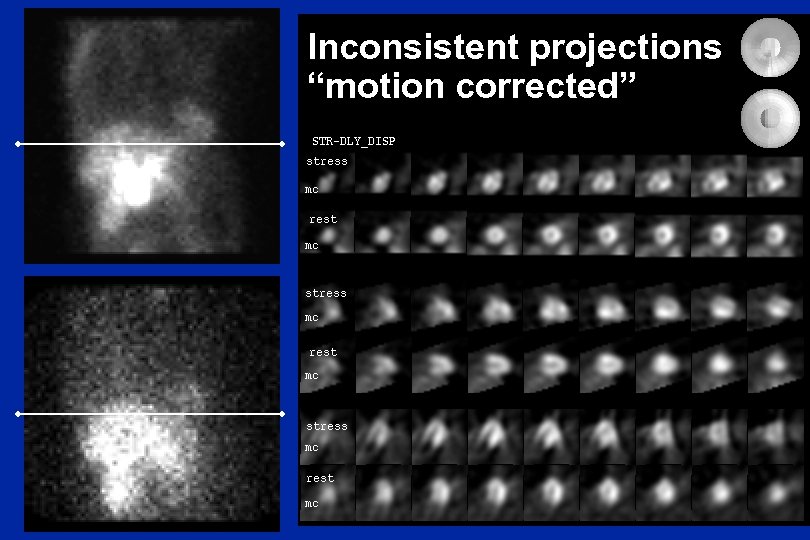 Inconsistent projections “motion corrected”
Inconsistent projections “motion corrected”
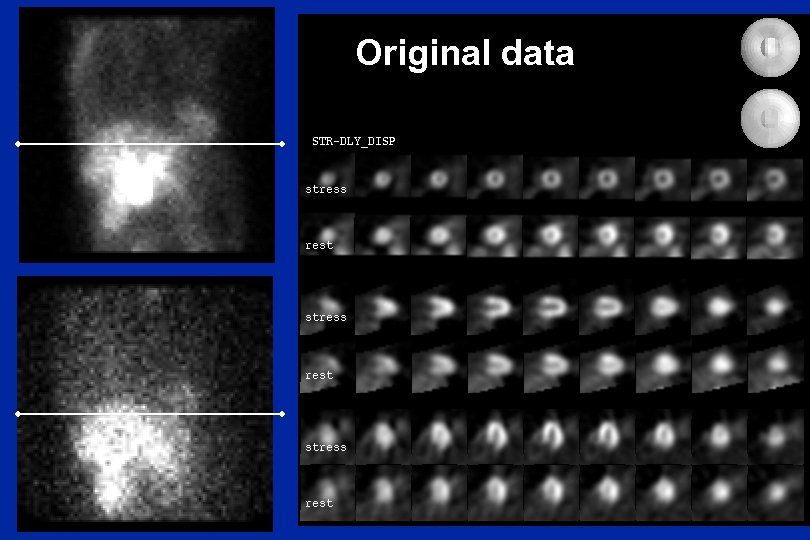 Original data
Original data
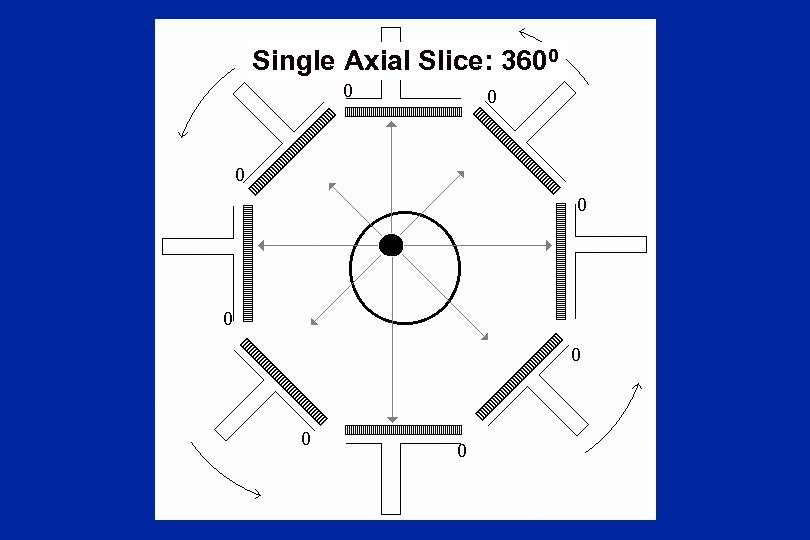 Single Axial Slice: 3600 0 0 0 0
Single Axial Slice: 3600 0 0 0 0
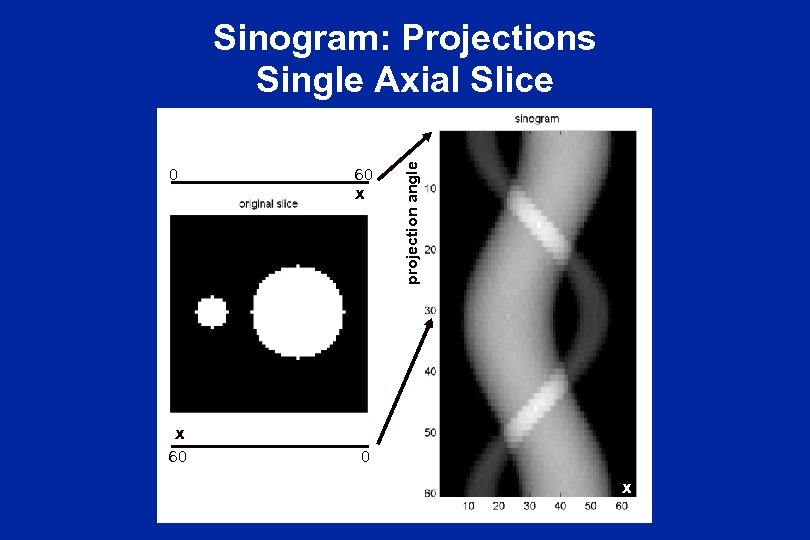 0 60 x projection angle Sinogram: Projections Single Axial Slice x 60 0 x
0 60 x projection angle Sinogram: Projections Single Axial Slice x 60 0 x
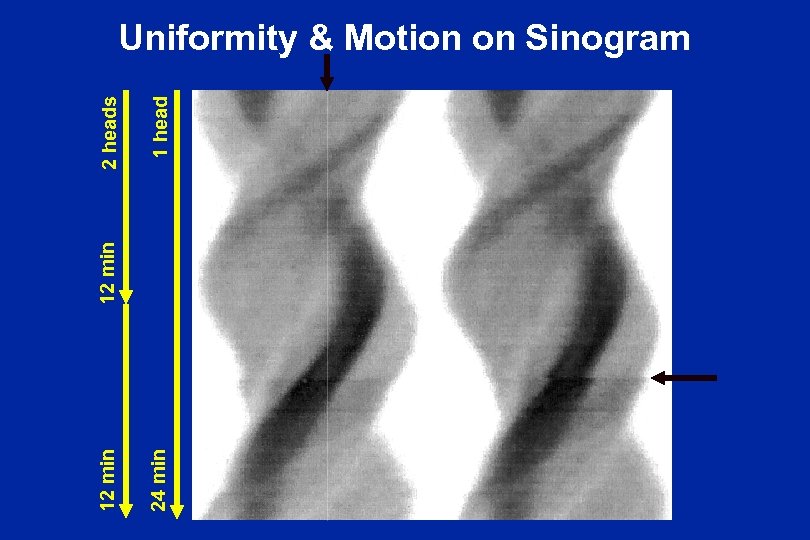 1 head 24 min 12 min 2 heads Uniformity & Motion on Sinogram
1 head 24 min 12 min 2 heads Uniformity & Motion on Sinogram
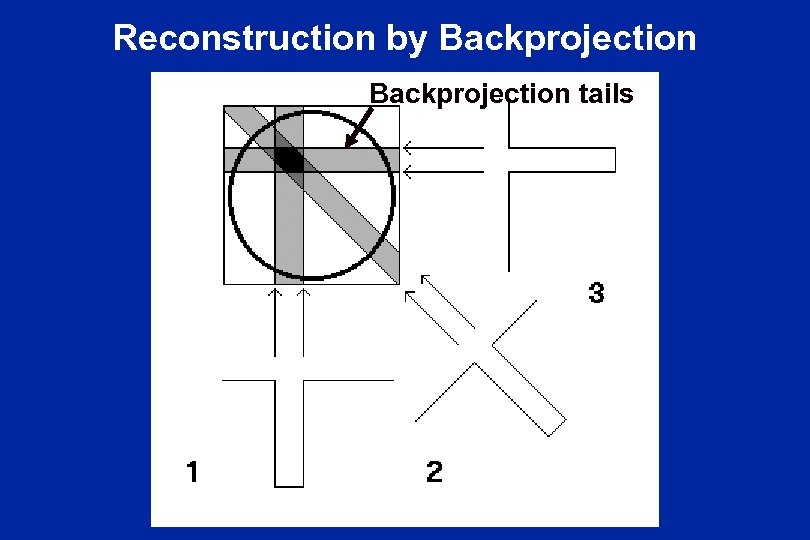 Reconstruction by Backprojection tails
Reconstruction by Backprojection tails
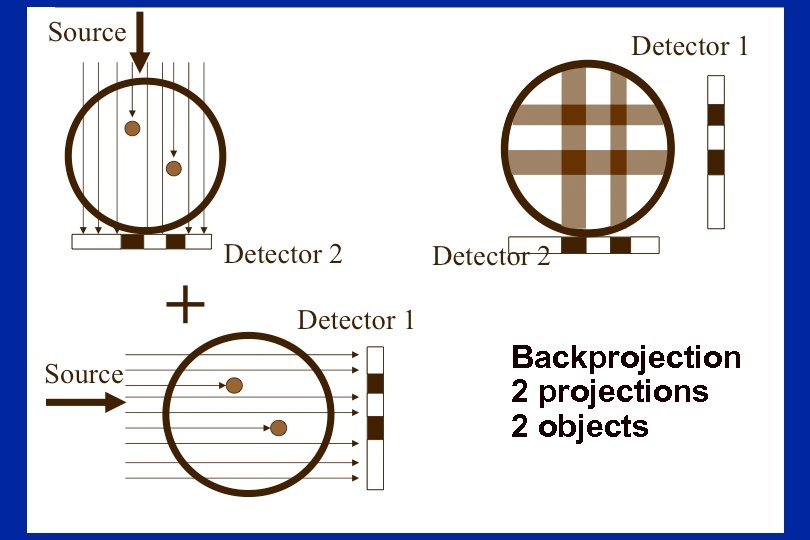 Backprojection 2 projections 2 objects
Backprojection 2 projections 2 objects
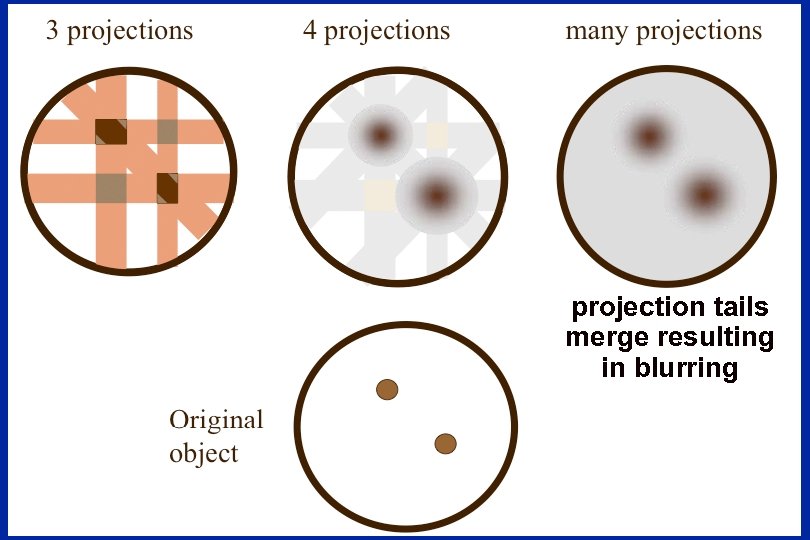 projection tails merge resulting in blurring
projection tails merge resulting in blurring
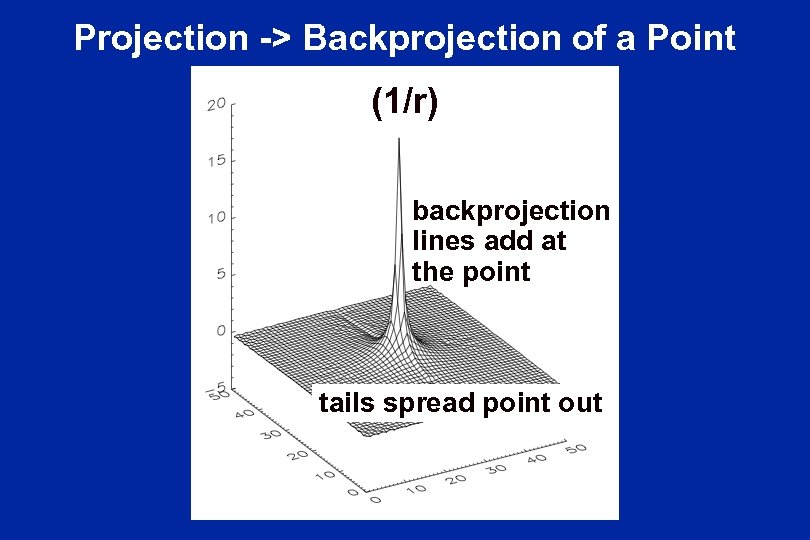 Projection -> Backprojection of a Point (1/r) backprojection lines add at the point tails spread point out
Projection -> Backprojection of a Point (1/r) backprojection lines add at the point tails spread point out
 Projection -> Backprojection
Projection -> Backprojection
 Projection->Backprojection Smooths or “blurs” the image (Low pass filter) ((Convolution with 1/r)) Nuclear Medicine physics Square law detector adds pixels -> always blurs Different from MRI (phase)
Projection->Backprojection Smooths or “blurs” the image (Low pass filter) ((Convolution with 1/r)) Nuclear Medicine physics Square law detector adds pixels -> always blurs Different from MRI (phase)
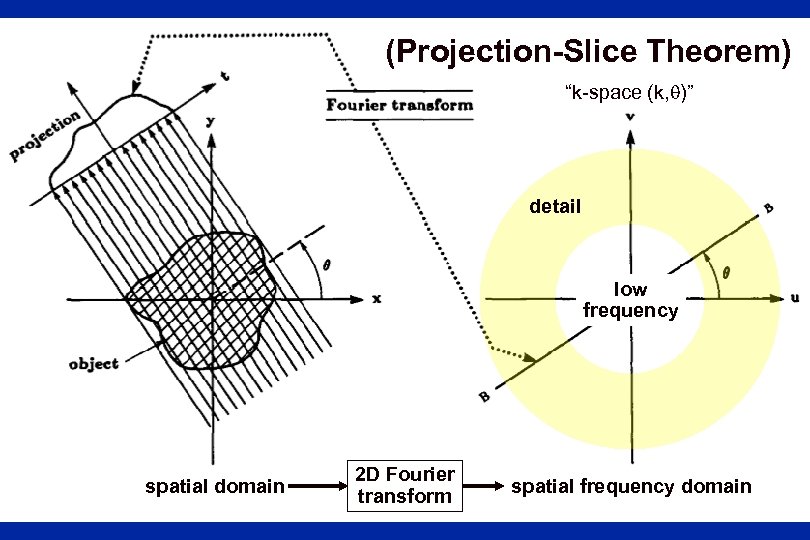 (Projection-Slice Theorem) “k-space (k, )” detail low frequency spatial domain 2 D Fourier transform spatial frequency domain
(Projection-Slice Theorem) “k-space (k, )” detail low frequency spatial domain 2 D Fourier transform spatial frequency domain
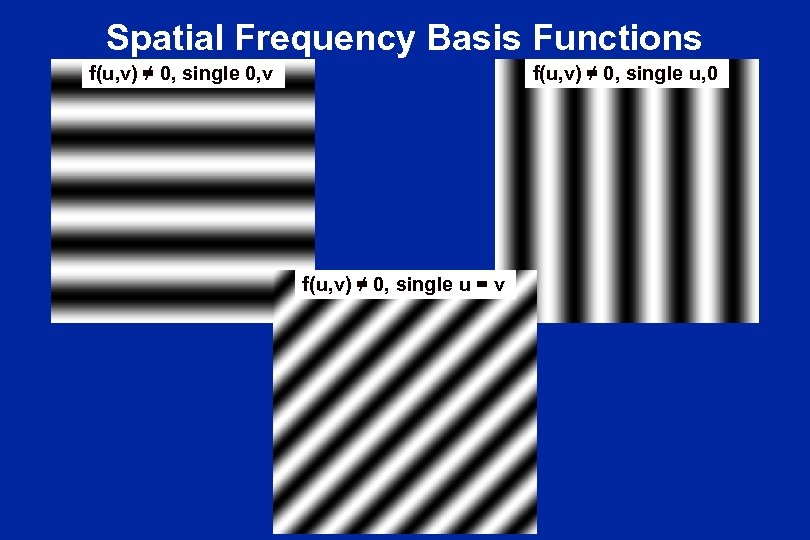 Spatial Frequency Basis Functions f(u, v) ≠ 0, single 0, v f(u, v) ≠ 0, single u, 0 f(u, v) ≠ 0, single u = v
Spatial Frequency Basis Functions f(u, v) ≠ 0, single 0, v f(u, v) ≠ 0, single u, 0 f(u, v) ≠ 0, single u = v
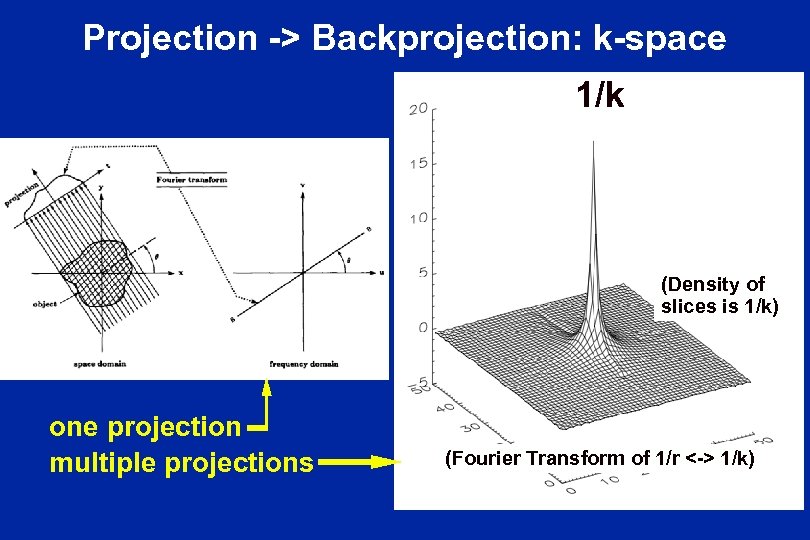 Projection -> Backprojection: k-space 1/k (Density of slices is 1/k) one projection multiple projections (Fourier Transform of 1/r <-> 1/k)
Projection -> Backprojection: k-space 1/k (Density of slices is 1/k) one projection multiple projections (Fourier Transform of 1/r <-> 1/k)
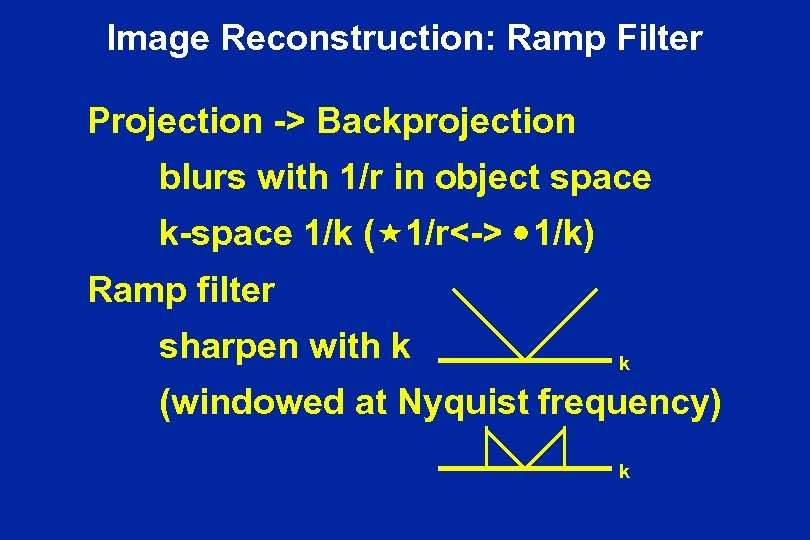 Image Reconstruction: Ramp Filter Projection -> Backprojection blurs with 1/r in object space k-space 1/k ( 1/r<-> 1/k) Ramp filter sharpen with k k (windowed at Nyquist frequency) k
Image Reconstruction: Ramp Filter Projection -> Backprojection blurs with 1/r in object space k-space 1/k ( 1/r<-> 1/k) Ramp filter sharpen with k k (windowed at Nyquist frequency) k
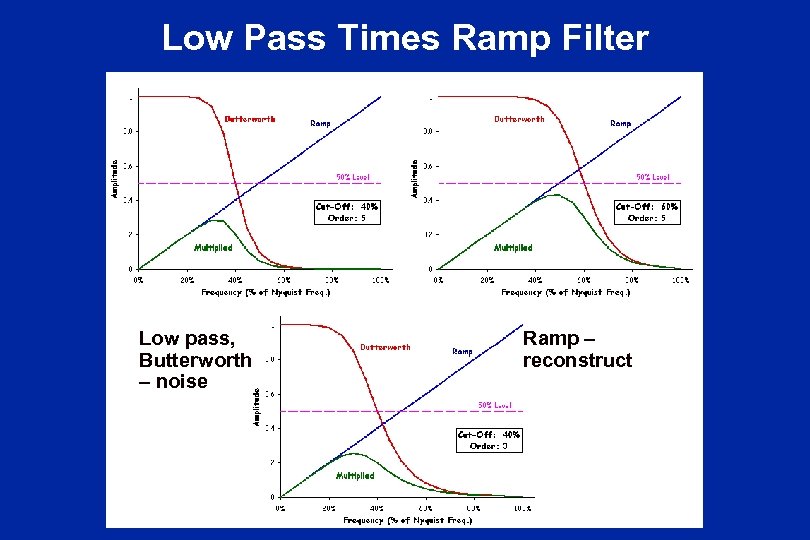 Low Pass Times Ramp Filter Low pass, Butterworth – noise Ramp – reconstruct
Low Pass Times Ramp Filter Low pass, Butterworth – noise Ramp – reconstruct
 What’s Good about FPB Ramp filter exactly reconstructs projection Efficient (Linear shift invariant) (FFT is order of n log(n) n = number of pixels) “Easily” understood
What’s Good about FPB Ramp filter exactly reconstructs projection Efficient (Linear shift invariant) (FFT is order of n log(n) n = number of pixels) “Easily” understood
 New Cardiac Cameras Solid state - CZT: $$$, energy resolution scatter rejection, dual isotope Pixelated detector: count rate & potential high resolution poorer uniformity Non-uniform sampling: sensitivity potential for artifacts Special purpose design closer to patient: system resolution upright: ameliorates diaphragmatic attenuation
New Cardiac Cameras Solid state - CZT: $$$, energy resolution scatter rejection, dual isotope Pixelated detector: count rate & potential high resolution poorer uniformity Non-uniform sampling: sensitivity potential for artifacts Special purpose design closer to patient: system resolution upright: ameliorates diaphragmatic attenuation
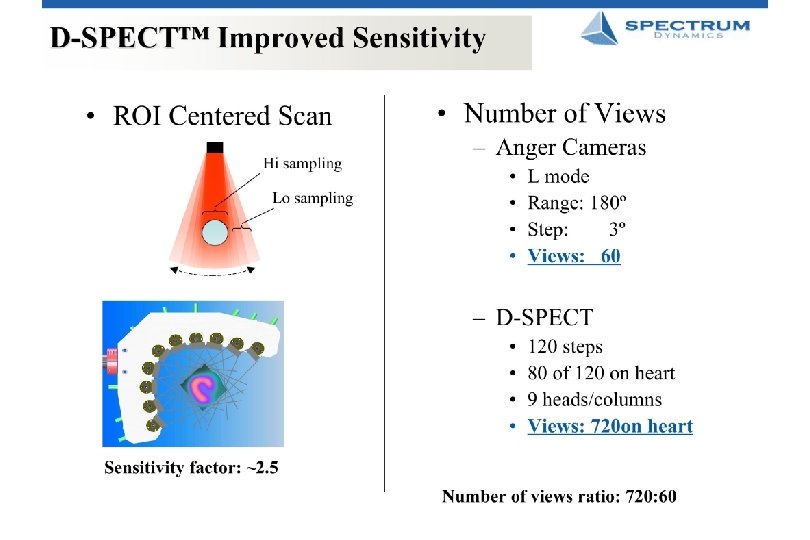
 Collimator Resolution* Single photon imaging (i. e. not PET) Collimators: image formation Sensitivity / resolution trade-off Resolution recovery hype “Low resolution, high sensitivity -> image processing = high resolution” Reality - ameliorates low resolution Steve Moore: “Resolution: data = target object” Can do quick, low resolution image * not resolution from reduced distance due to design
Collimator Resolution* Single photon imaging (i. e. not PET) Collimators: image formation Sensitivity / resolution trade-off Resolution recovery hype “Low resolution, high sensitivity -> image processing = high resolution” Reality - ameliorates low resolution Steve Moore: “Resolution: data = target object” Can do quick, low resolution image * not resolution from reduced distance due to design
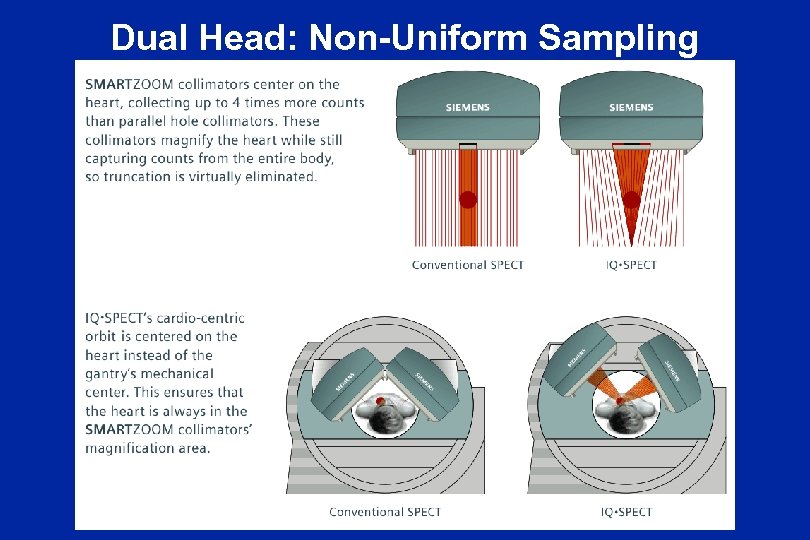 Dual Head: Non-Uniform Sampling
Dual Head: Non-Uniform Sampling
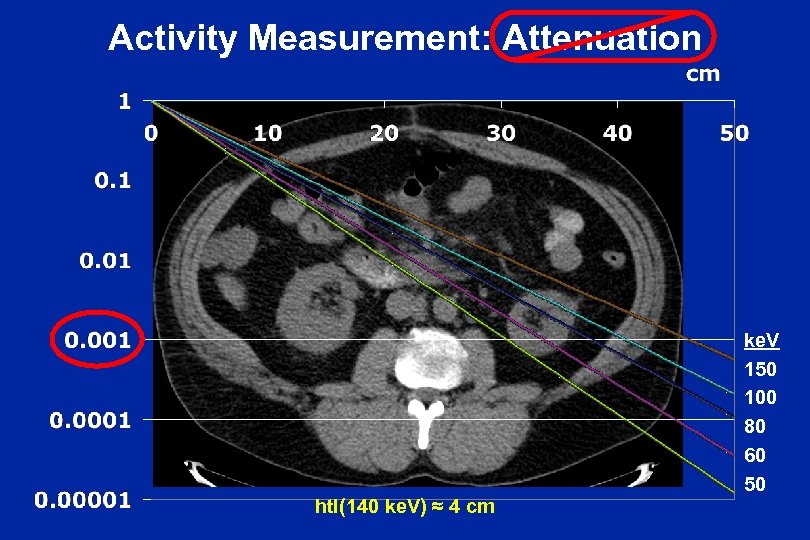 Activity Measurement: Attenuation htl(140 ke. V) ≈ 4 cm ke. V 150 100 80 60 50
Activity Measurement: Attenuation htl(140 ke. V) ≈ 4 cm ke. V 150 100 80 60 50
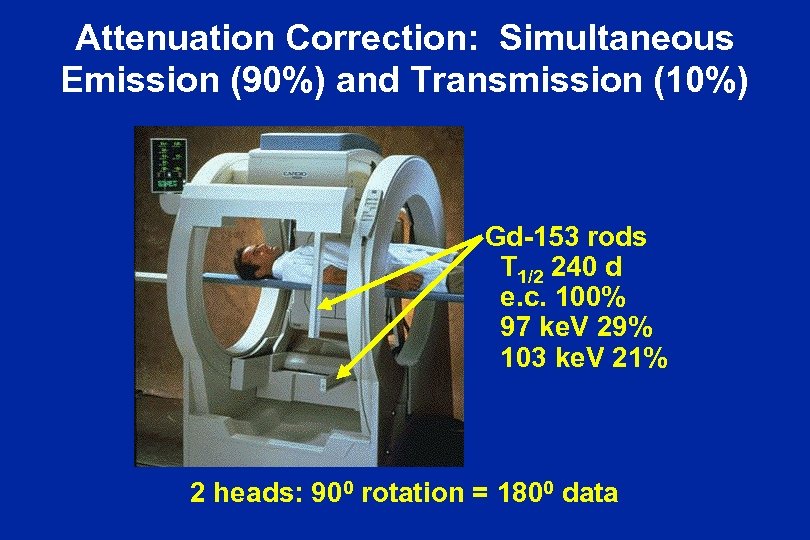 Attenuation Correction: Simultaneous Emission (90%) and Transmission (10%) Gd-153 rods T 1/2 240 d e. c. 100% 97 ke. V 29% 103 ke. V 21% 2 heads: 900 rotation = 1800 data
Attenuation Correction: Simultaneous Emission (90%) and Transmission (10%) Gd-153 rods T 1/2 240 d e. c. 100% 97 ke. V 29% 103 ke. V 21% 2 heads: 900 rotation = 1800 data
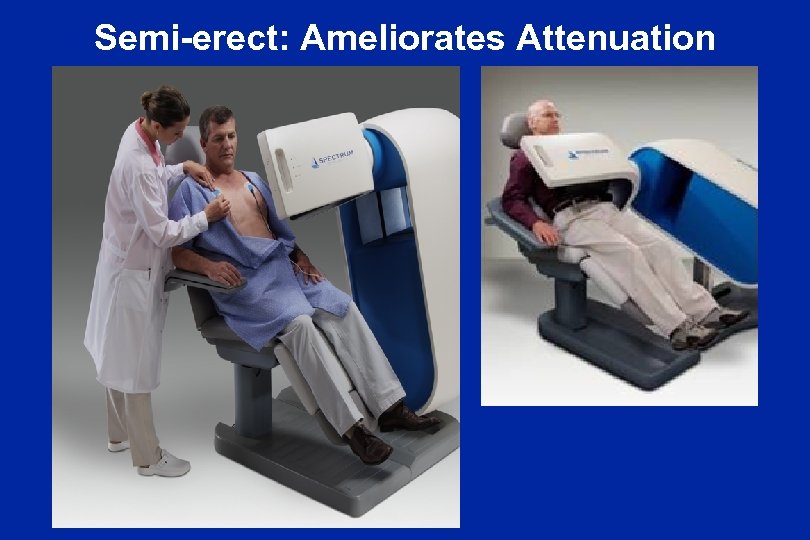 Semi-erect: Ameliorates Attenuation
Semi-erect: Ameliorates Attenuation
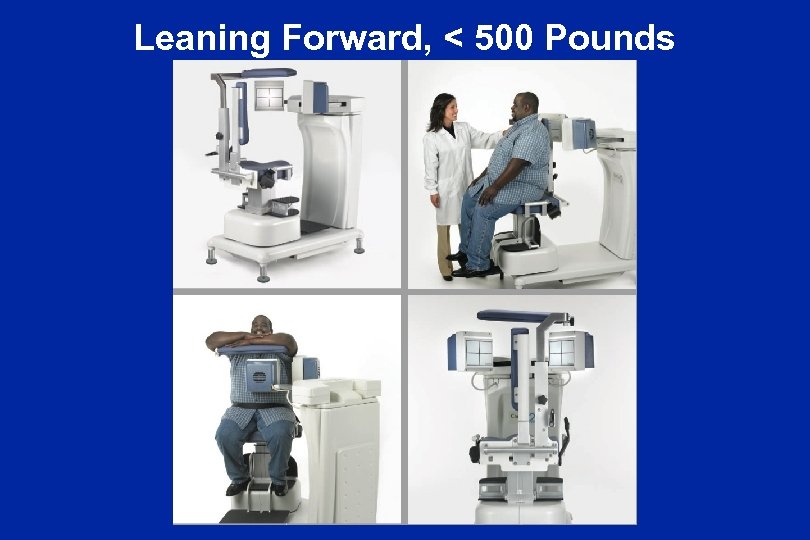 Leaning Forward, < 500 Pounds
Leaning Forward, < 500 Pounds
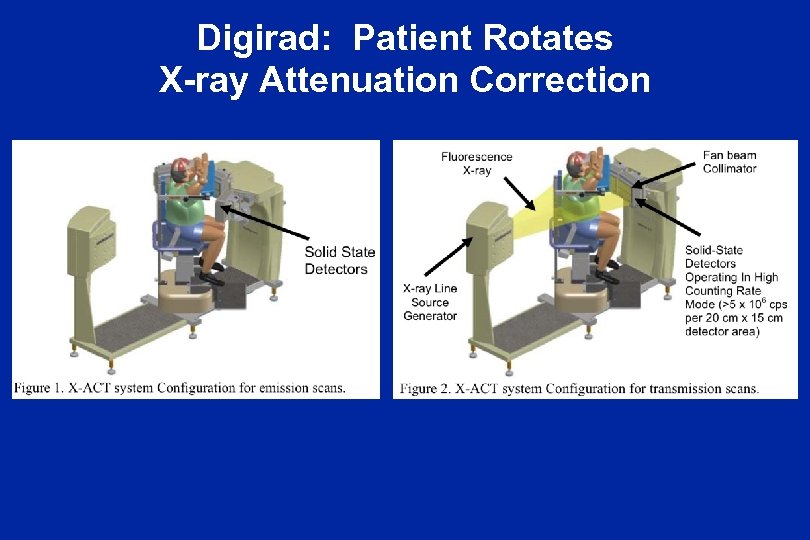 Digirad: Patient Rotates X-ray Attenuation Correction
Digirad: Patient Rotates X-ray Attenuation Correction
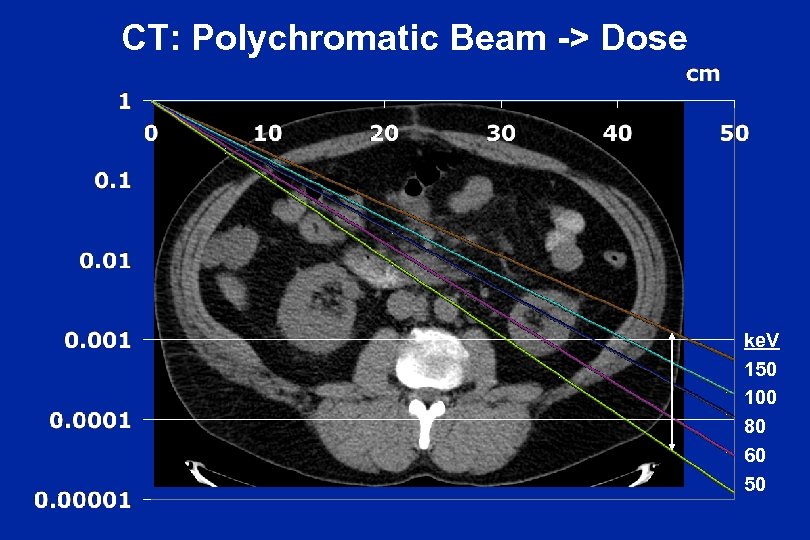 CT: Polychromatic Beam -> Dose ke. V 150 100 80 60 50
CT: Polychromatic Beam -> Dose ke. V 150 100 80 60 50
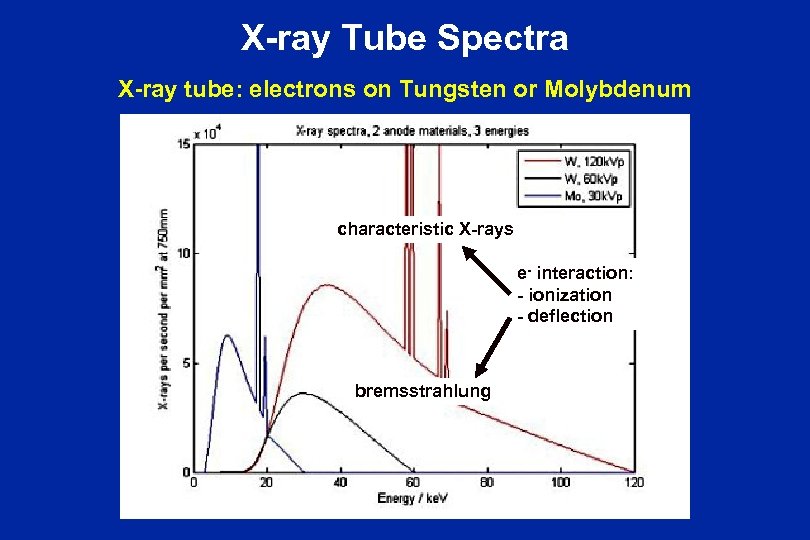 X-ray Tube Spectra X-ray tube: electrons on Tungsten or Molybdenum characteristic X-rays e- interaction: - ionization - deflection bremsstrahlung
X-ray Tube Spectra X-ray tube: electrons on Tungsten or Molybdenum characteristic X-rays e- interaction: - ionization - deflection bremsstrahlung
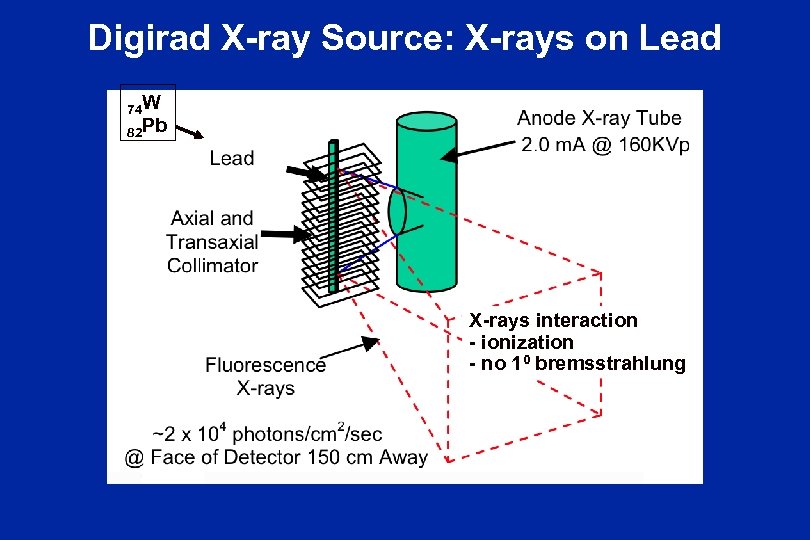 Digirad X-ray Source: X-rays on Lead 74 W 82 Pb X-rays interaction - ionization - no 10 bremsstrahlung
Digirad X-ray Source: X-rays on Lead 74 W 82 Pb X-rays interaction - ionization - no 10 bremsstrahlung
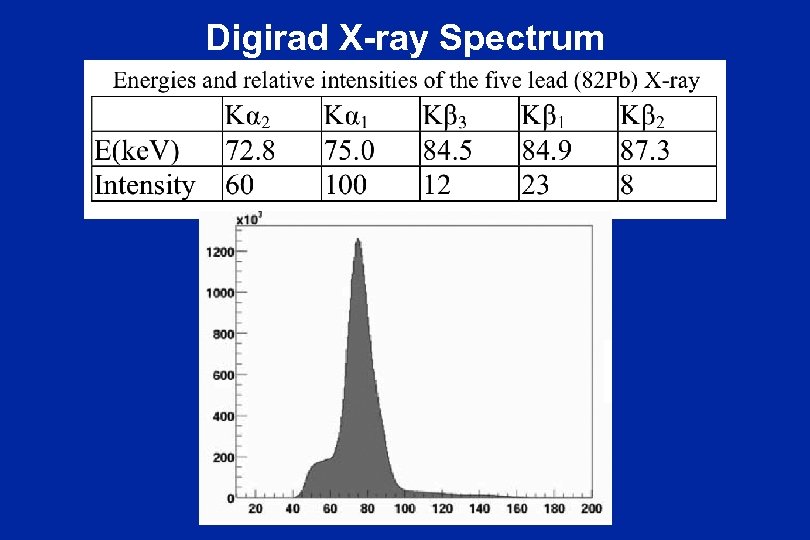 Digirad X-ray Spectrum
Digirad X-ray Spectrum
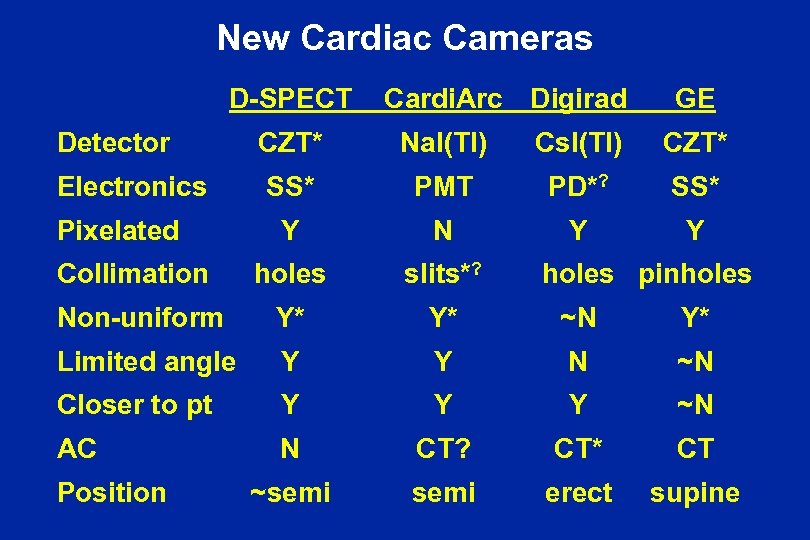 New Cardiac Cameras D-SPECT Detector Cardi. Arc Digirad GE CZT* Na. I(Tl) Cs. I(Tl) CZT* SS* PMT PD*? SS* Y N Y Y Collimation holes slits*? Non-uniform Y* Y* ~N Y* Limited angle Y Y N ~N Closer to pt Y Y Y ~N AC N CT? CT* CT ~semi erect supine Electronics Pixelated Position holes pinholes
New Cardiac Cameras D-SPECT Detector Cardi. Arc Digirad GE CZT* Na. I(Tl) Cs. I(Tl) CZT* SS* PMT PD*? SS* Y N Y Y Collimation holes slits*? Non-uniform Y* Y* ~N Y* Limited angle Y Y N ~N Closer to pt Y Y Y ~N AC N CT? CT* CT ~semi erect supine Electronics Pixelated Position holes pinholes
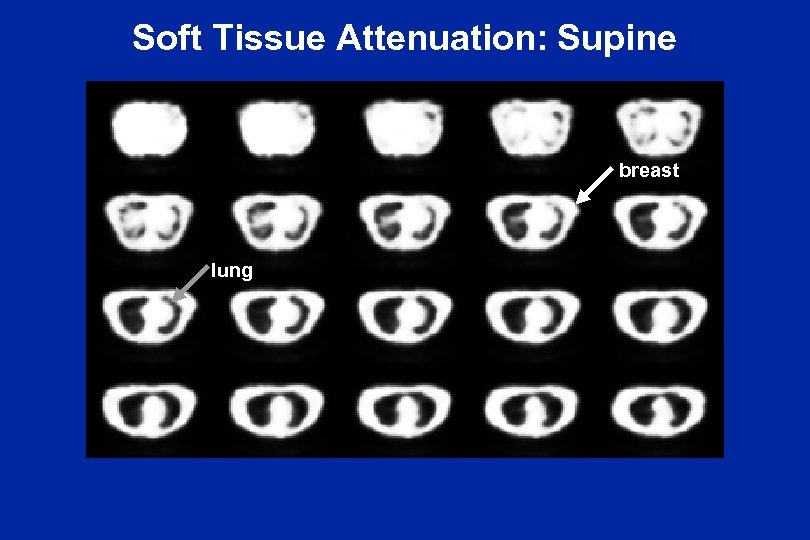 Soft Tissue Attenuation: Supine breast lung
Soft Tissue Attenuation: Supine breast lung
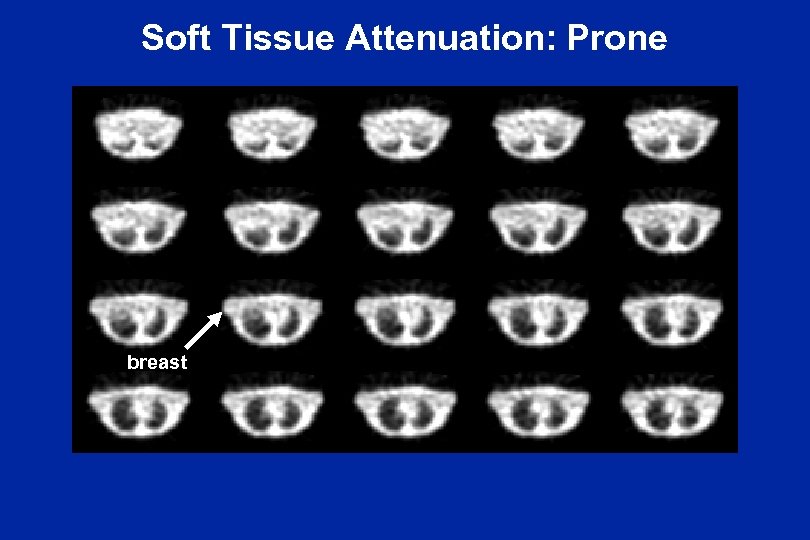 Soft Tissue Attenuation: Prone breast
Soft Tissue Attenuation: Prone breast
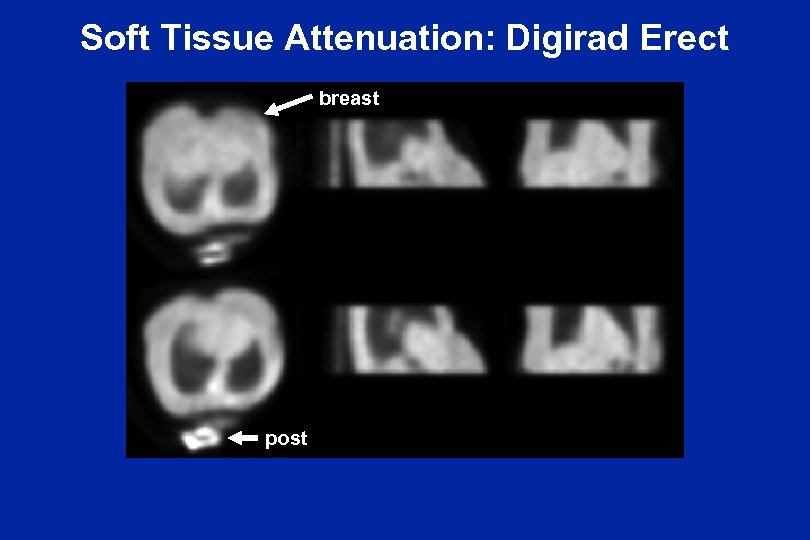 Soft Tissue Attenuation: Digirad Erect breast post
Soft Tissue Attenuation: Digirad Erect breast post
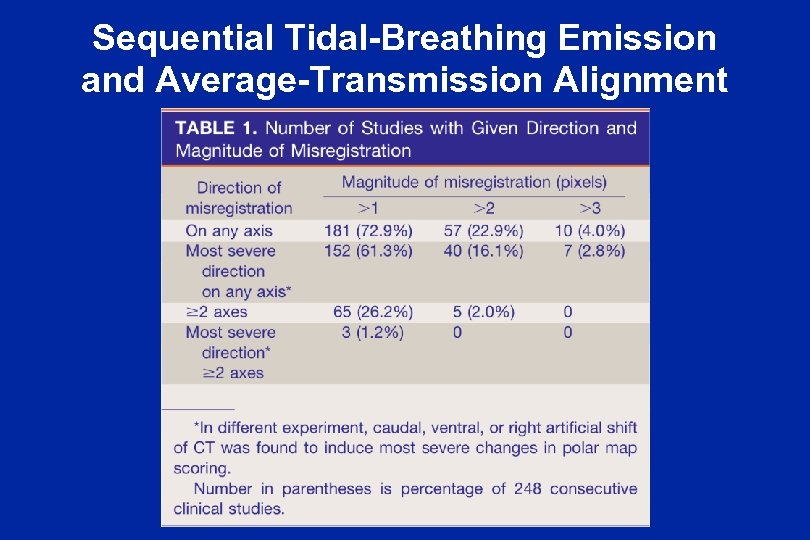 Sequential Tidal-Breathing Emission and Average-Transmission Alignment
Sequential Tidal-Breathing Emission and Average-Transmission Alignment
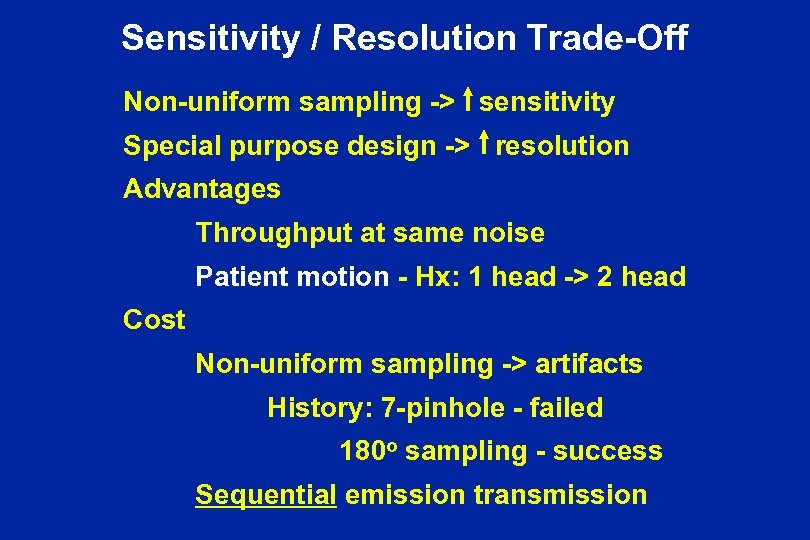 Sensitivity / Resolution Trade-Off Non-uniform sampling -> sensitivity Special purpose design -> resolution Advantages Throughput at same noise Patient motion - Hx: 1 head -> 2 head Cost Non-uniform sampling -> artifacts History: 7 -pinhole - failed 180 o sampling - success Sequential emission transmission
Sensitivity / Resolution Trade-Off Non-uniform sampling -> sensitivity Special purpose design -> resolution Advantages Throughput at same noise Patient motion - Hx: 1 head -> 2 head Cost Non-uniform sampling -> artifacts History: 7 -pinhole - failed 180 o sampling - success Sequential emission transmission
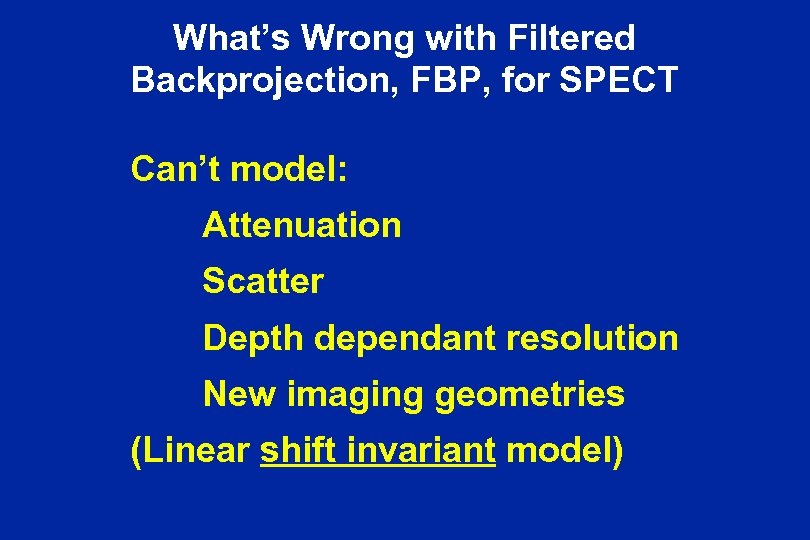 What’s Wrong with Filtered Backprojection, FBP, for SPECT Can’t model: Attenuation Scatter Depth dependant resolution New imaging geometries (Linear shift invariant model)
What’s Wrong with Filtered Backprojection, FBP, for SPECT Can’t model: Attenuation Scatter Depth dependant resolution New imaging geometries (Linear shift invariant model)
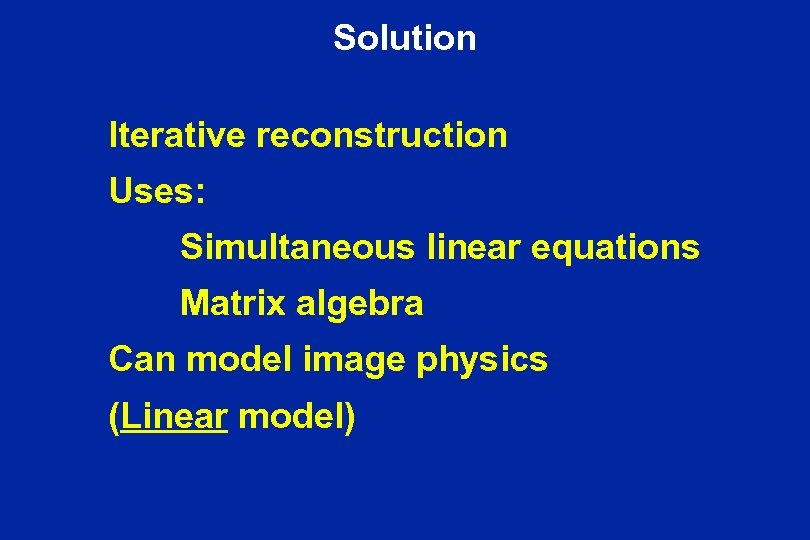 Solution Iterative reconstruction Uses: Simultaneous linear equations Matrix algebra Can model image physics (Linear model)
Solution Iterative reconstruction Uses: Simultaneous linear equations Matrix algebra Can model image physics (Linear model)
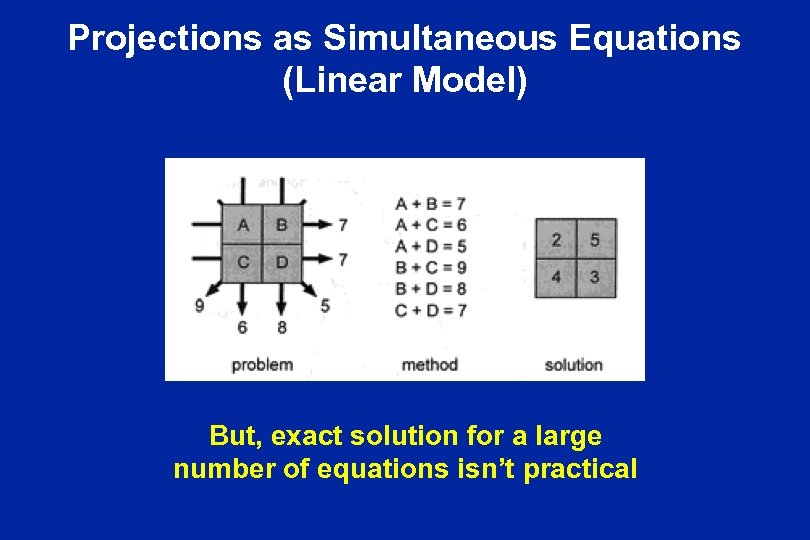 Projections as Simultaneous Equations (Linear Model) But, exact solution for a large number of equations isn’t practical
Projections as Simultaneous Equations (Linear Model) But, exact solution for a large number of equations isn’t practical
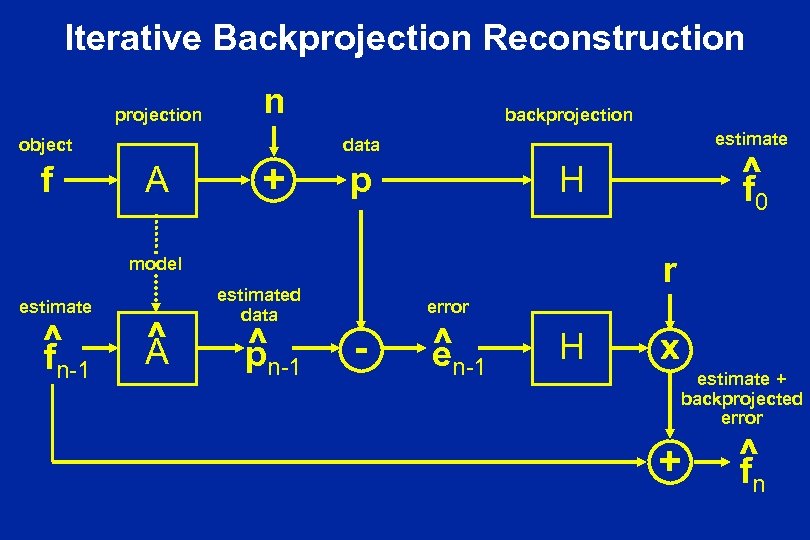 Iterative Backprojection Reconstruction projection n object f backprojection estimate data A + p ^ f n-1 ^ A estimated data ^ pn-1 0 r model estimate ^ f H error - ^n-1 e H x estimate + backprojected error + ^ f n
Iterative Backprojection Reconstruction projection n object f backprojection estimate data A + p ^ f n-1 ^ A estimated data ^ pn-1 0 r model estimate ^ f H error - ^n-1 e H x estimate + backprojected error + ^ f n
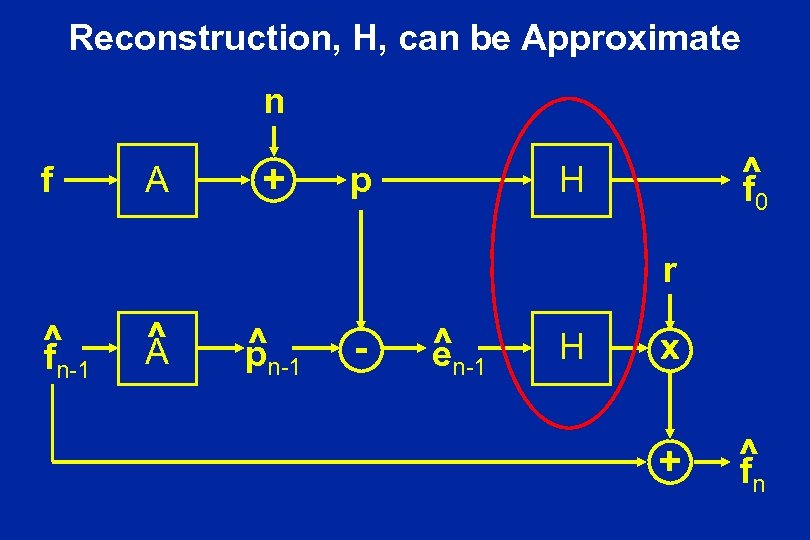 Reconstruction, H, can be Approximate n f A + p ^ f H 0 r ^ f n-1 ^ A ^ pn-1 - ^n-1 e H x + ^ f n
Reconstruction, H, can be Approximate n f A + p ^ f H 0 r ^ f n-1 ^ A ^ pn-1 - ^n-1 e H x + ^ f n
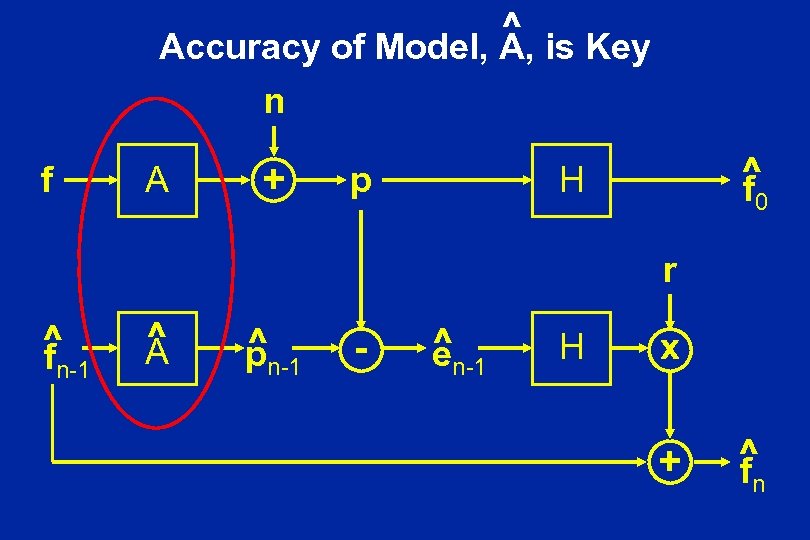 ^ is Key Accuracy of Model, A, n f A + p ^ f H 0 r ^ f n-1 ^ A ^ pn-1 - ^n-1 e H x + ^ f n
^ is Key Accuracy of Model, A, n f A + p ^ f H 0 r ^ f n-1 ^ A ^ pn-1 - ^n-1 e H x + ^ f n
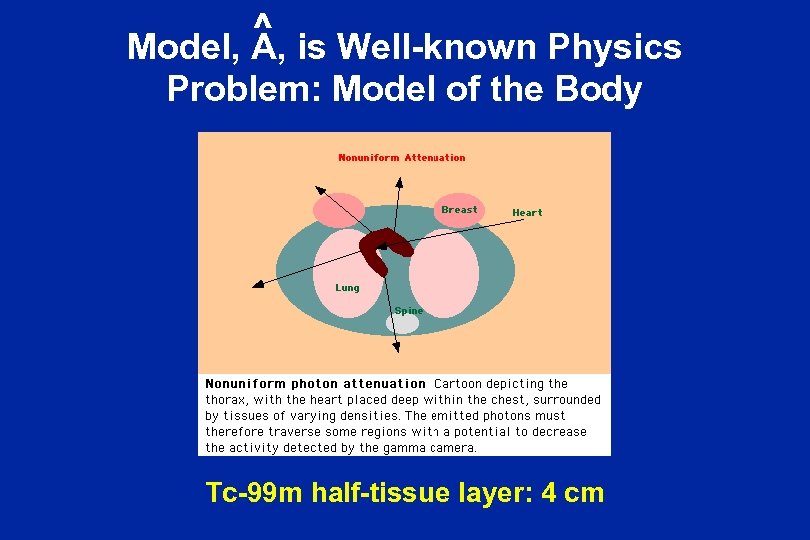 ^ is Well-known Physics Model, A, Problem: Model of the Body Tc-99 m half-tissue layer: 4 cm
^ is Well-known Physics Model, A, Problem: Model of the Body Tc-99 m half-tissue layer: 4 cm
 Attenuation Map Gd-153 Transmission Map adds noise to reconstruction and can introduce artifacts
Attenuation Map Gd-153 Transmission Map adds noise to reconstruction and can introduce artifacts
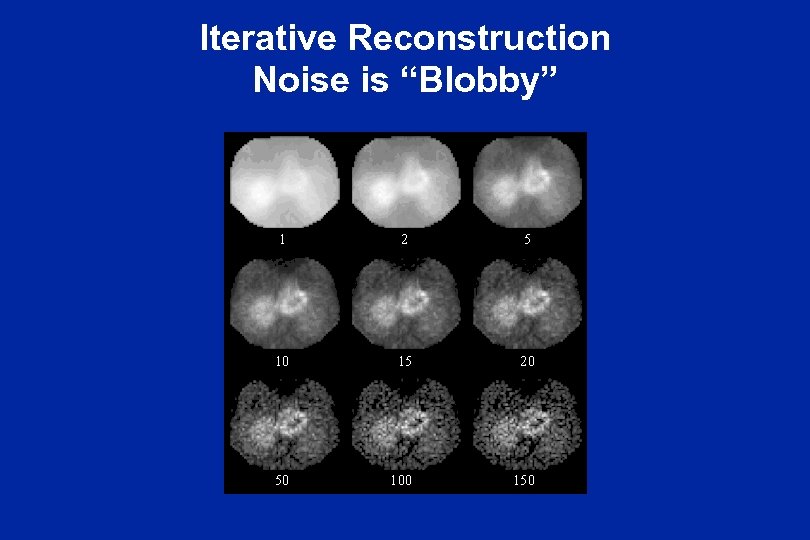 Iterative Reconstruction Noise is “Blobby”
Iterative Reconstruction Noise is “Blobby”
 What’s Good About Iterative Reconstruction Able to model: Data collection, including new geometries Attenuation Scatter Depth dependant resolution Fairly efficient given current computers (Iterative solution, e. g. EM, reasonable) (OSEM is even better) ((OSEM has about 1/nsubsets of EM iterations))
What’s Good About Iterative Reconstruction Able to model: Data collection, including new geometries Attenuation Scatter Depth dependant resolution Fairly efficient given current computers (Iterative solution, e. g. EM, reasonable) (OSEM is even better) ((OSEM has about 1/nsubsets of EM iterations))
 What’s Wrong with Iterative Reconstruction (Complicated by ill conditioned model) ((Estimating projections not object)) Noise character bad for oncology To model attenuation & scatter - need to measure attenuation - adds noise
What’s Wrong with Iterative Reconstruction (Complicated by ill conditioned model) ((Estimating projections not object)) Noise character bad for oncology To model attenuation & scatter - need to measure attenuation - adds noise
 Conclusions Filtered backprojection, FBP Efficient (Models noise) “Easy” to understand Iterative reconstruction, OSEM Moderately efficient Models noise, attenuation, scatter, depth dependant resolution, and new cameras
Conclusions Filtered backprojection, FBP Efficient (Models noise) “Easy” to understand Iterative reconstruction, OSEM Moderately efficient Models noise, attenuation, scatter, depth dependant resolution, and new cameras
 Applause
Applause


