074241205adf47c2862c0a07fa7a0f47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Image Processing for Interventional MRI Derek Hill Professor of Medical Imaging Sciences King’s College London
Image Processing for Interventional MRI Derek Hill Professor of Medical Imaging Sciences King’s College London
 Image Processing for Interventional MRI Derek Hill Professor of Medical Imaging Sciences University College London
Image Processing for Interventional MRI Derek Hill Professor of Medical Imaging Sciences University College London
 The team • • • Kawal Rhode Marc Miquel Redha Berboutkah David Atkinson Maxime Sermesant Rado Andriantsimiavona • Kate Mc. Leish • Sebastian Kozerke • • Reza Razavi Vivek Muthurangu Sanjeet Hegde Jas Gill Pier Lambraise Cliff Bucknall Eric Rosenthal Shaqueel Qureshi
The team • • • Kawal Rhode Marc Miquel Redha Berboutkah David Atkinson Maxime Sermesant Rado Andriantsimiavona • Kate Mc. Leish • Sebastian Kozerke • • Reza Razavi Vivek Muthurangu Sanjeet Hegde Jas Gill Pier Lambraise Cliff Bucknall Eric Rosenthal Shaqueel Qureshi
 Context • Interventional MRI provides particular opportunities and challenges for image analysis. – Hostile environment for computers – “real time” requirements – Link between acquisition and analysis
Context • Interventional MRI provides particular opportunities and challenges for image analysis. – Hostile environment for computers – “real time” requirements – Link between acquisition and analysis
 Overview • • Background to XMR guided interventions Integrating x-ray and MRI Automatic cathether tracking Integration of image analysis in acquisition
Overview • • Background to XMR guided interventions Integrating x-ray and MRI Automatic cathether tracking Integration of image analysis in acquisition
 XMR • X-ray + cylindrical bore MRI in the same room • Becoming main platform for MR guided interventions – Resection control in neurosurgery – Endovascular procedures • Not ideal for percutaneous procedures
XMR • X-ray + cylindrical bore MRI in the same room • Becoming main platform for MR guided interventions – Resection control in neurosurgery – Endovascular procedures • Not ideal for percutaneous procedures
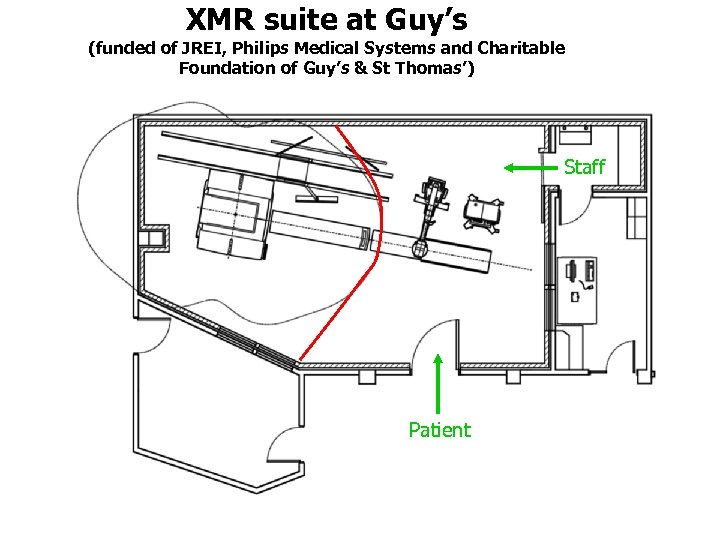 XMR suite at Guy’s (funded of JREI, Philips Medical Systems and Charitable Foundation of Guy’s & St Thomas’) Staff Patient
XMR suite at Guy’s (funded of JREI, Philips Medical Systems and Charitable Foundation of Guy’s & St Thomas’) Staff Patient
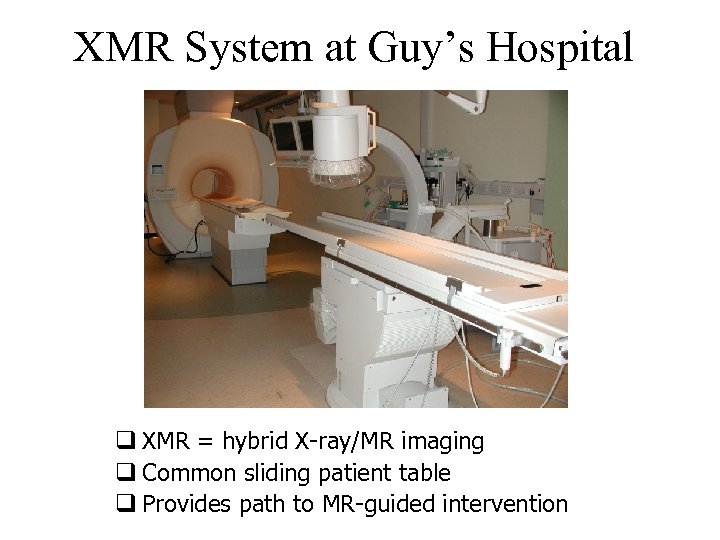 XMR System at Guy’s Hospital q XMR = hybrid X-ray/MR imaging q Common sliding patient table q Provides path to MR-guided intervention
XMR System at Guy’s Hospital q XMR = hybrid X-ray/MR imaging q Common sliding patient table q Provides path to MR-guided intervention
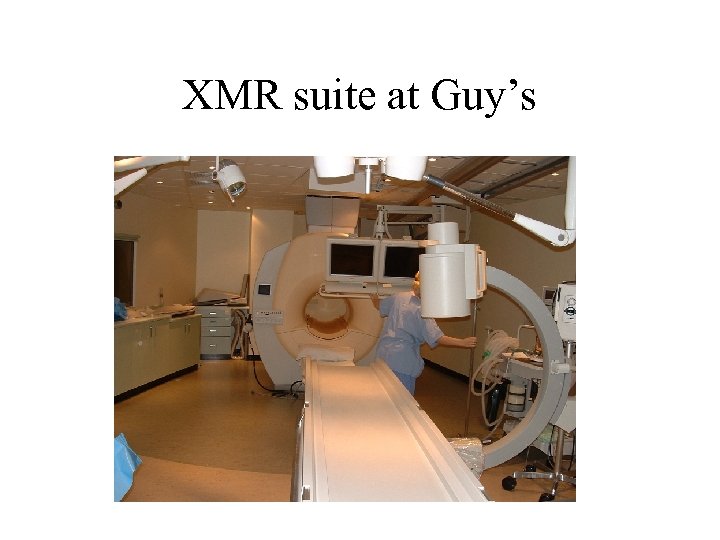 XMR suite at Guy’s
XMR suite at Guy’s
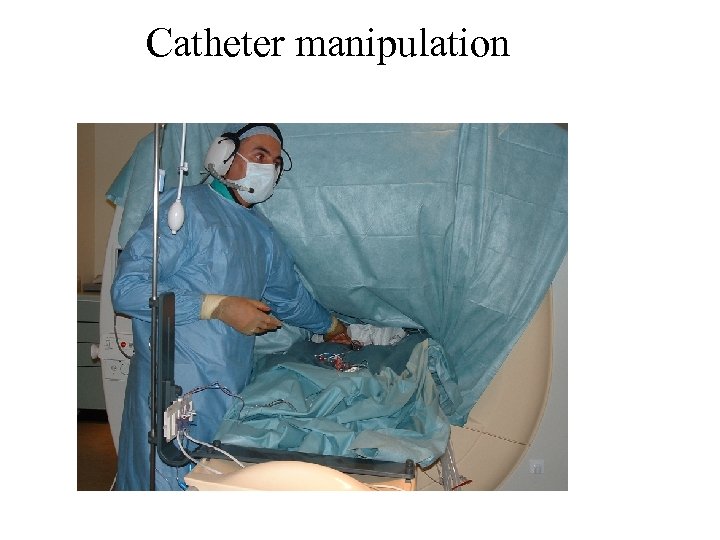 Catheter manipulation
Catheter manipulation
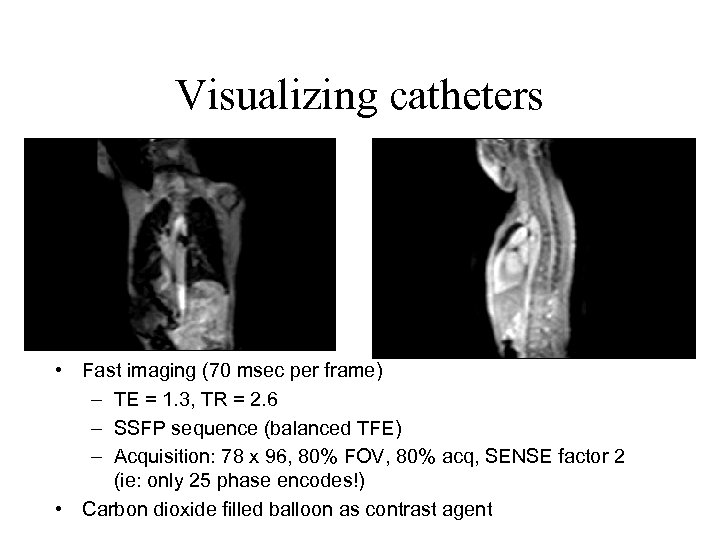 Visualizing catheters • Fast imaging (70 msec per frame) – TE = 1. 3, TR = 2. 6 – SSFP sequence (balanced TFE) – Acquisition: 78 x 96, 80% FOV, 80% acq, SENSE factor 2 (ie: only 25 phase encodes!) • Carbon dioxide filled balloon as contrast agent
Visualizing catheters • Fast imaging (70 msec per frame) – TE = 1. 3, TR = 2. 6 – SSFP sequence (balanced TFE) – Acquisition: 78 x 96, 80% FOV, 80% acq, SENSE factor 2 (ie: only 25 phase encodes!) • Carbon dioxide filled balloon as contrast agent
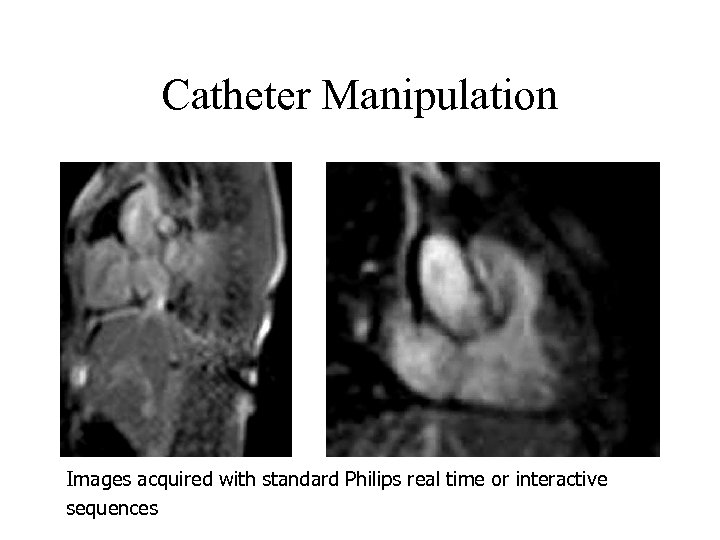 Catheter Manipulation Images acquired with standard Philips real time or interactive sequences
Catheter Manipulation Images acquired with standard Philips real time or interactive sequences
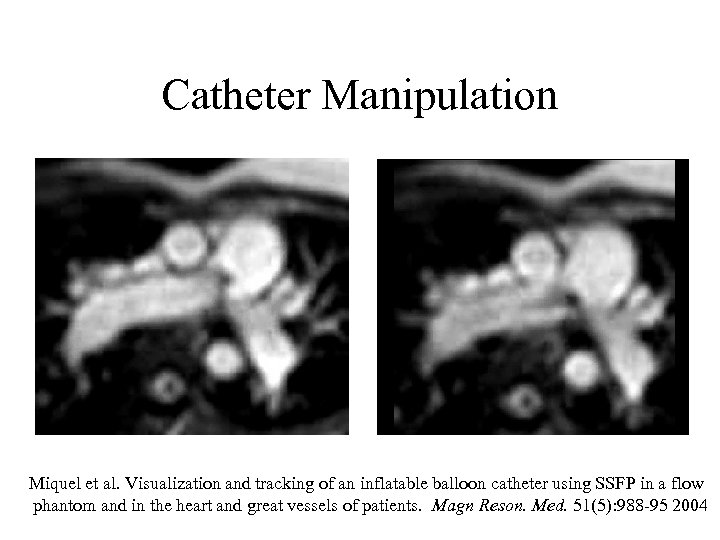 Catheter Manipulation Miquel et al. Visualization and tracking of an inflatable balloon catheter using SSFP in a flow phantom and in the heart and great vessels of patients. Magn Reson. Med. 51(5): 988 -95 2004
Catheter Manipulation Miquel et al. Visualization and tracking of an inflatable balloon catheter using SSFP in a flow phantom and in the heart and great vessels of patients. Magn Reson. Med. 51(5): 988 -95 2004

 Integrating x-ray and MRI • XMR provide rapid transfer between modalities • No capability to integrate the images • X-ray and MRI provide complementary information • Combined x-ray and MR has value in complex interventions eg: electrophysiology
Integrating x-ray and MRI • XMR provide rapid transfer between modalities • No capability to integrate the images • X-ray and MRI provide complementary information • Combined x-ray and MR has value in complex interventions eg: electrophysiology
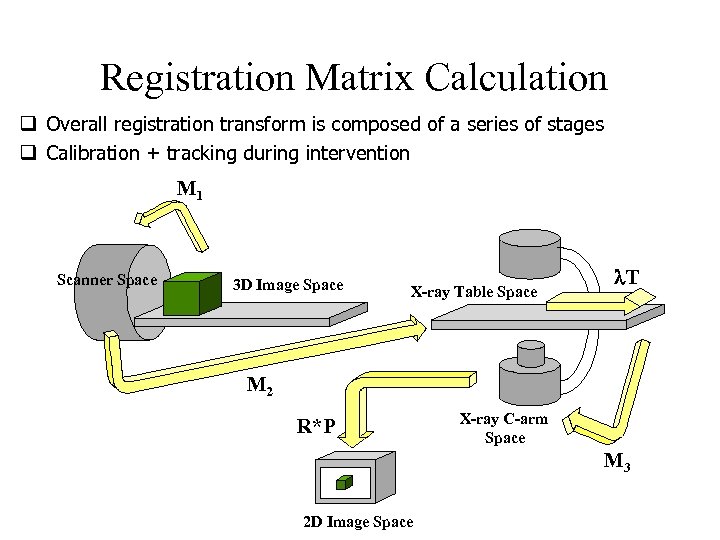 Registration Matrix Calculation q Overall registration transform is composed of a series of stages q Calibration + tracking during intervention M 1 Scanner Space 3 D Image Space X-ray Table Space T M 2 R*P X-ray C-arm Space M 3 2 D Image Space
Registration Matrix Calculation q Overall registration transform is composed of a series of stages q Calibration + tracking during intervention M 1 Scanner Space 3 D Image Space X-ray Table Space T M 2 R*P X-ray C-arm Space M 3 2 D Image Space
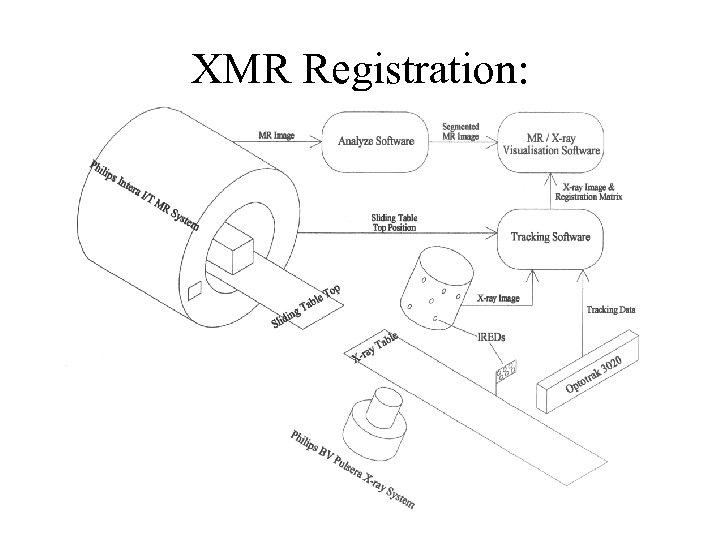 XMR Registration: Software Overview
XMR Registration: Software Overview
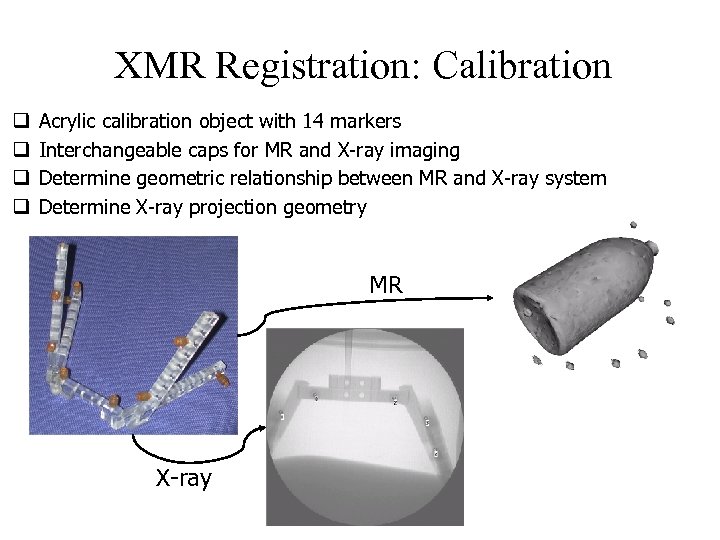 XMR Registration: Calibration q q Acrylic calibration object with 14 markers Interchangeable caps for MR and X-ray imaging Determine geometric relationship between MR and X-ray system Determine X-ray projection geometry MR X-ray
XMR Registration: Calibration q q Acrylic calibration object with 14 markers Interchangeable caps for MR and X-ray imaging Determine geometric relationship between MR and X-ray system Determine X-ray projection geometry MR X-ray
 Calibration (1) Fixing flange for sliding table. (2) Saline-filled acrylic half cylinder with 20 divot cap markers in a helical arrangement. (3) Slot in acrylic base plate to allow sliding of half cylinder. (4) & (5) End stops. (6) Fixing to allow MR surface coil attachment
Calibration (1) Fixing flange for sliding table. (2) Saline-filled acrylic half cylinder with 20 divot cap markers in a helical arrangement. (3) Slot in acrylic base plate to allow sliding of half cylinder. (4) & (5) End stops. (6) Fixing to allow MR surface coil attachment
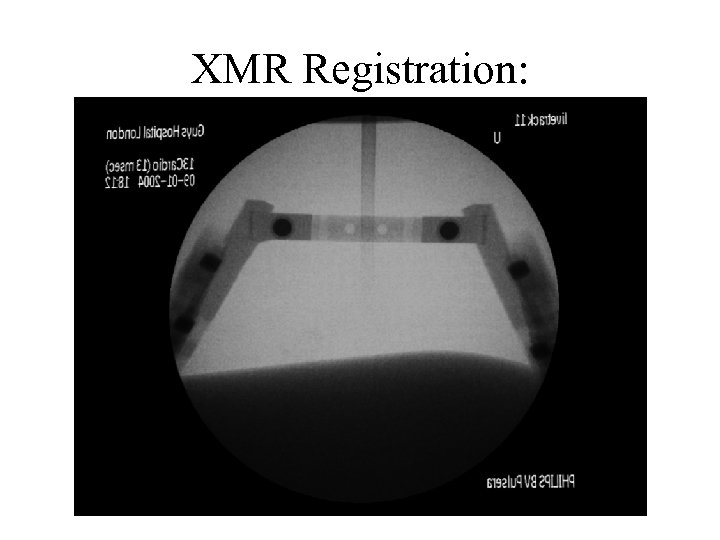 XMR Registration: MR Overlay on X-Ray
XMR Registration: MR Overlay on X-Ray
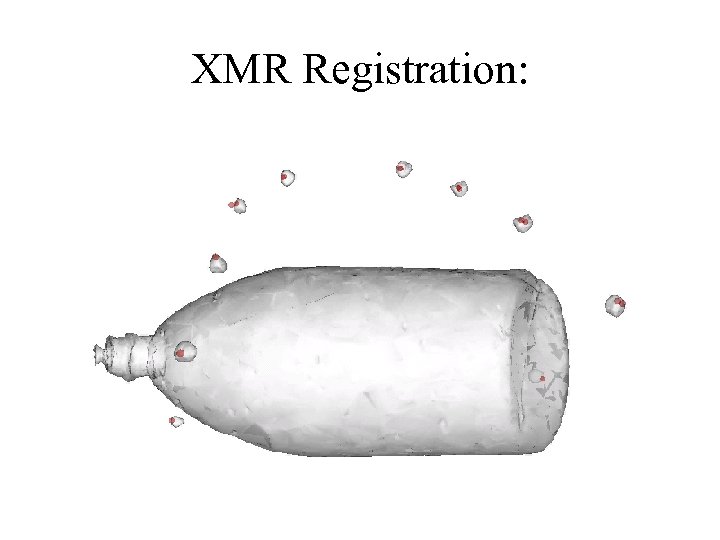 XMR Registration: 3 D Reconstruction
XMR Registration: 3 D Reconstruction
 XMR Registration: Phantom Validation q. T 1 -weighted MR volume + 5 pairs of tracked x-ray images using calibration object as a phantom q 2 D RMS Error = 4. 2 mm (n=35), Range = 1. 4 to 8. 0 mm q 3 D RMS Error = 4. 6 mm (n=17), Range = 1. 7 to 9. 0 mm
XMR Registration: Phantom Validation q. T 1 -weighted MR volume + 5 pairs of tracked x-ray images using calibration object as a phantom q 2 D RMS Error = 4. 2 mm (n=35), Range = 1. 4 to 8. 0 mm q 3 D RMS Error = 4. 6 mm (n=17), Range = 1. 7 to 9. 0 mm

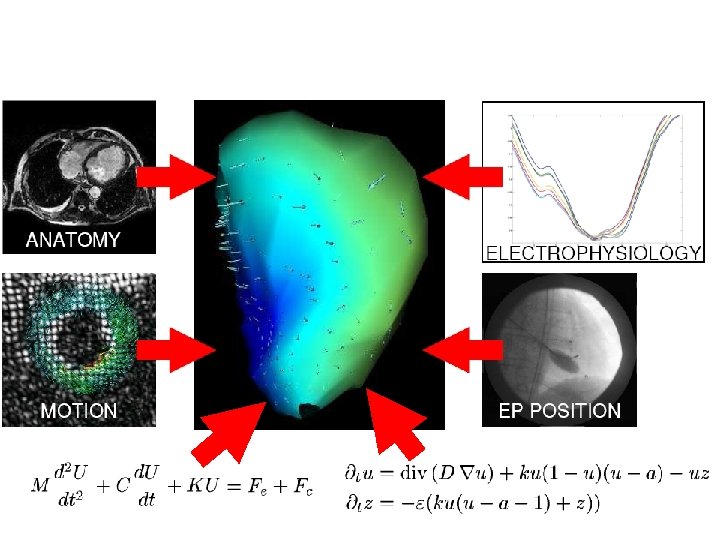
 Clinical Example • Patient undergoing electrophysiology study prior to RF ablation of heart rhythm abnormality
Clinical Example • Patient undergoing electrophysiology study prior to RF ablation of heart rhythm abnormality
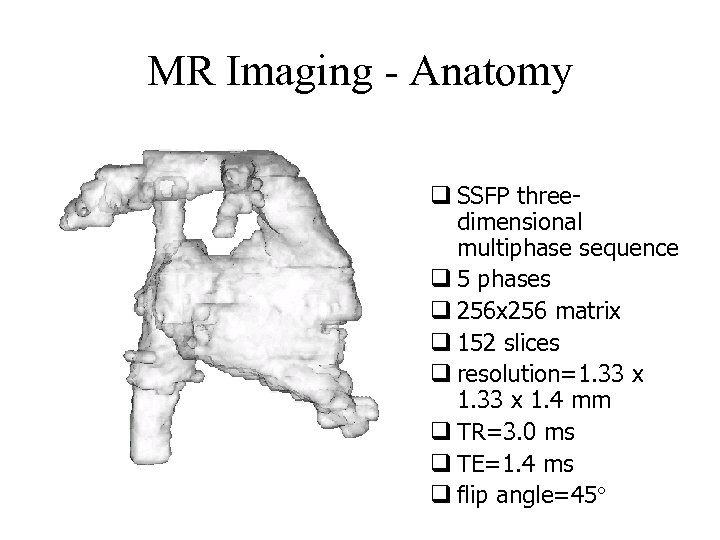 MR Imaging - Anatomy q SSFP threedimensional multiphase sequence q 5 phases q 256 x 256 matrix q 152 slices q resolution=1. 33 x 1. 4 mm q TR=3. 0 ms q TE=1. 4 ms q flip angle=45
MR Imaging - Anatomy q SSFP threedimensional multiphase sequence q 5 phases q 256 x 256 matrix q 152 slices q resolution=1. 33 x 1. 4 mm q TR=3. 0 ms q TE=1. 4 ms q flip angle=45
 MR Imaging - Motion q SPAMM tagged imaging sequence q 59 phases SA & 50 phases LA q 256 x 256 matrix q 11 slices SA & 4 slices LA q resolution=1. 33 x 8. 0 mm q TR=11. 0 ms q TE=3. 5 ms q flip angle=13 q tag spacing=8 mm
MR Imaging - Motion q SPAMM tagged imaging sequence q 59 phases SA & 50 phases LA q 256 x 256 matrix q 11 slices SA & 4 slices LA q resolution=1. 33 x 8. 0 mm q TR=11. 0 ms q TE=3. 5 ms q flip angle=13 q tag spacing=8 mm
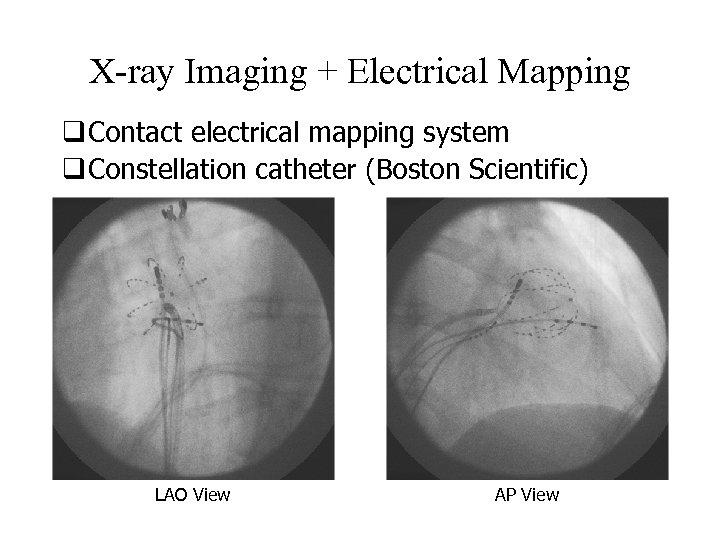 X-ray Imaging + Electrical Mapping q Contact electrical mapping system q Constellation catheter (Boston Scientific) LAO View AP View
X-ray Imaging + Electrical Mapping q Contact electrical mapping system q Constellation catheter (Boston Scientific) LAO View AP View
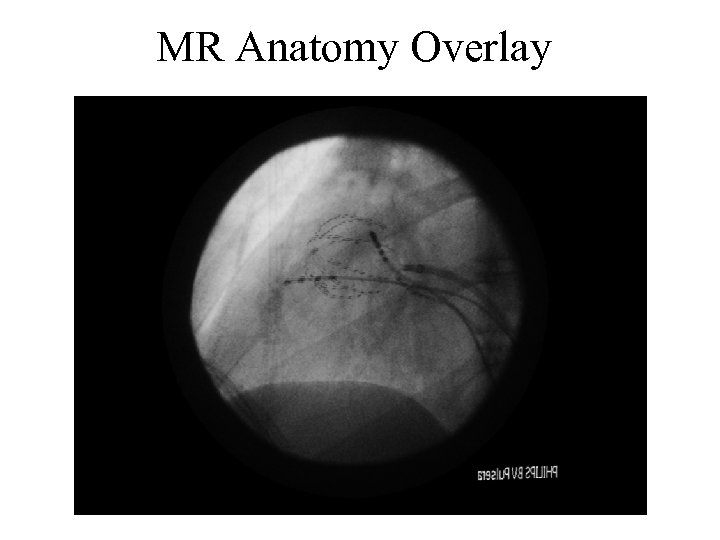 MR Anatomy Overlay
MR Anatomy Overlay
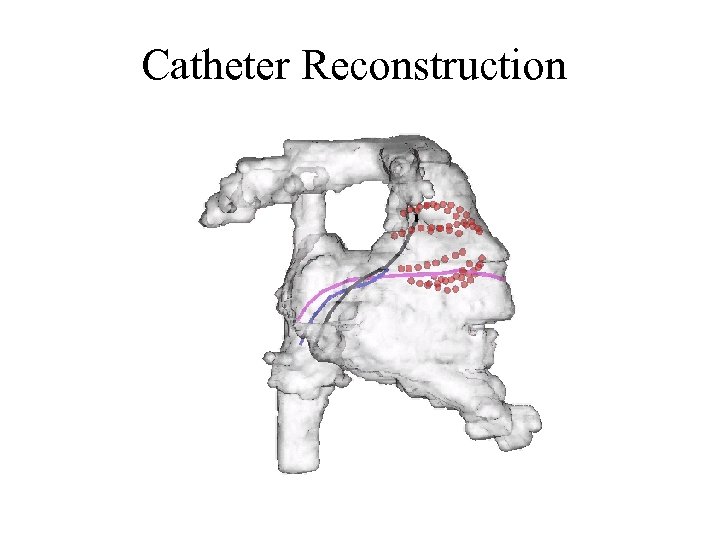 Catheter Reconstruction
Catheter Reconstruction
 Refining the Registration q Errors due to limitations of registration technique and patient motion q Basket point cloud meshed q Rigid surface-to-image registration used to realign the basket mesh
Refining the Registration q Errors due to limitations of registration technique and patient motion q Basket point cloud meshed q Rigid surface-to-image registration used to realign the basket mesh
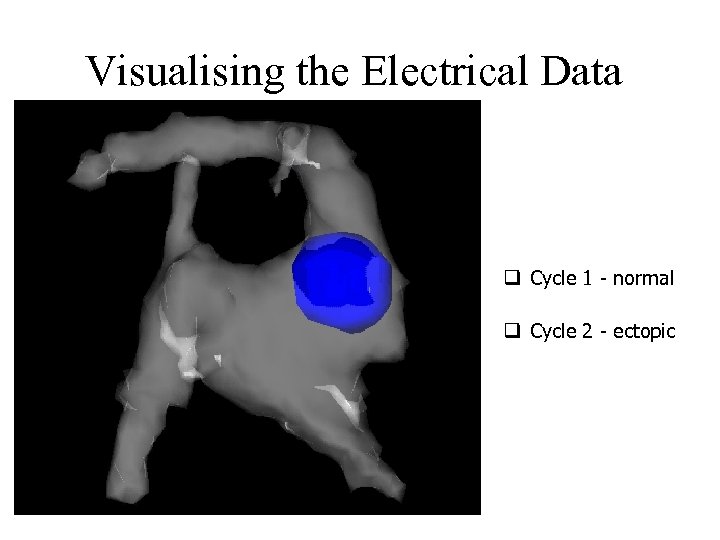 Visualising the Electrical Data q Cycle 1 - normal q Cycle 2 - ectopic
Visualising the Electrical Data q Cycle 1 - normal q Cycle 2 - ectopic
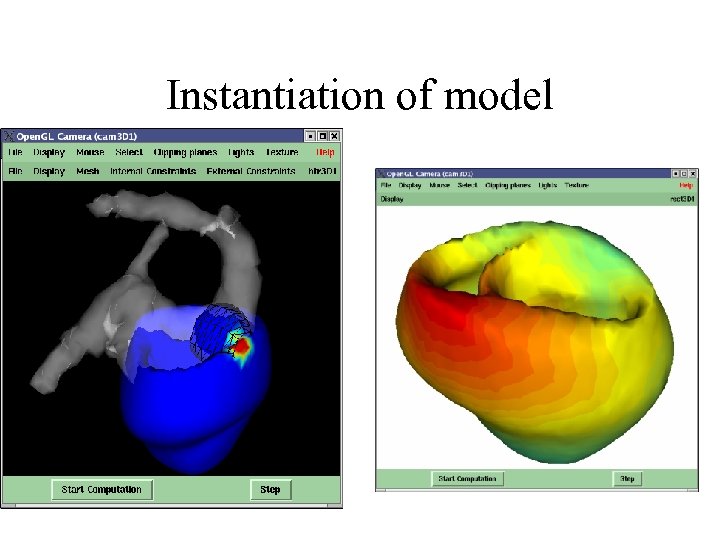 Instantiation of model
Instantiation of model
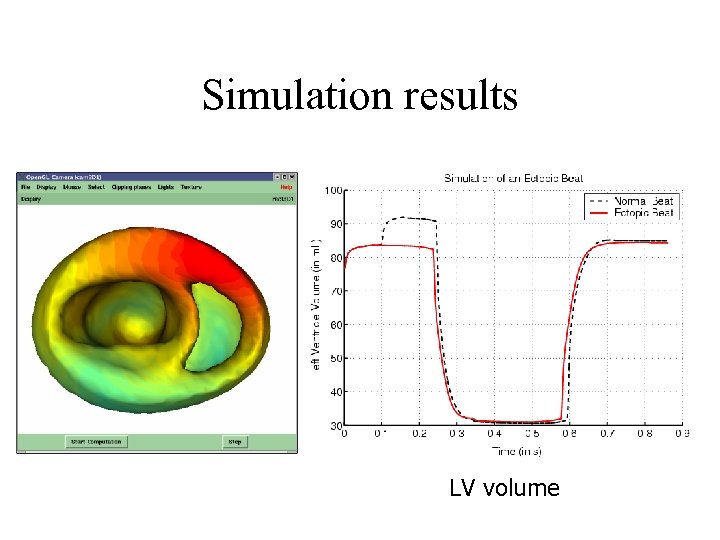 Simulation results LV volume
Simulation results LV volume
 Catheters re-visited • Essential properties of catheters – Clearly visible – Safe • mechanically • electrically • Magnetically • Desirable properties – Automatic localization – Tip and length visible • CO 2 filled balloon catheters are safe • Tip location ambiguous • Length not visible • Cannot be localized automatically
Catheters re-visited • Essential properties of catheters – Clearly visible – Safe • mechanically • electrically • Magnetically • Desirable properties – Automatic localization – Tip and length visible • CO 2 filled balloon catheters are safe • Tip location ambiguous • Length not visible • Cannot be localized automatically
 Is there an image analysis solution? • Find catheter automatically in modulus image? • Is it easier to find in a phase image?
Is there an image analysis solution? • Find catheter automatically in modulus image? • Is it easier to find in a phase image?
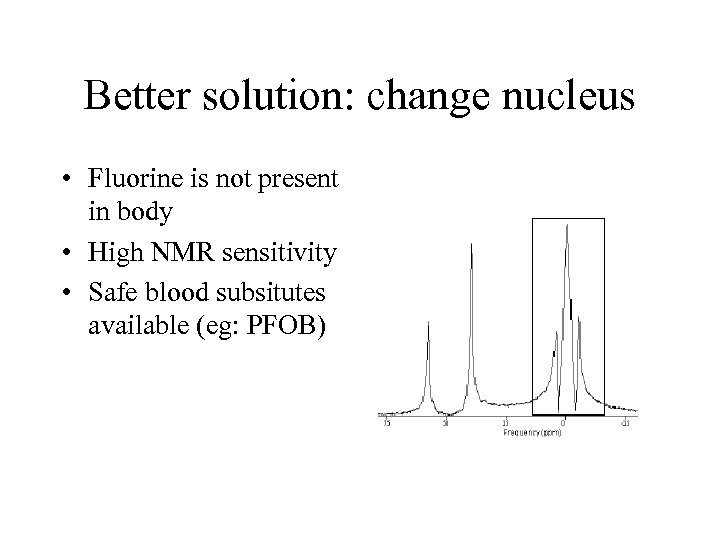 Better solution: change nucleus • Fluorine is not present in body • High NMR sensitivity • Safe blood subsitutes available (eg: PFOB)
Better solution: change nucleus • Fluorine is not present in body • High NMR sensitivity • Safe blood subsitutes available (eg: PFOB)
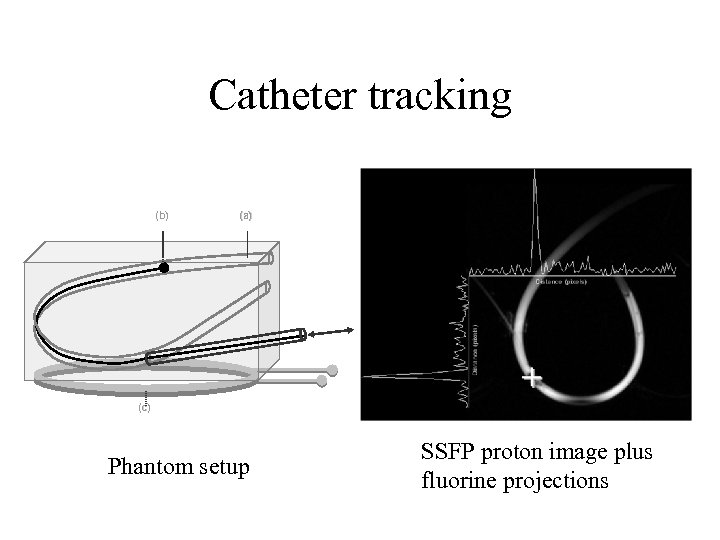 Catheter tracking (b) (a) (c) Phantom setup SSFP proton image plus fluorine projections
Catheter tracking (b) (a) (c) Phantom setup SSFP proton image plus fluorine projections
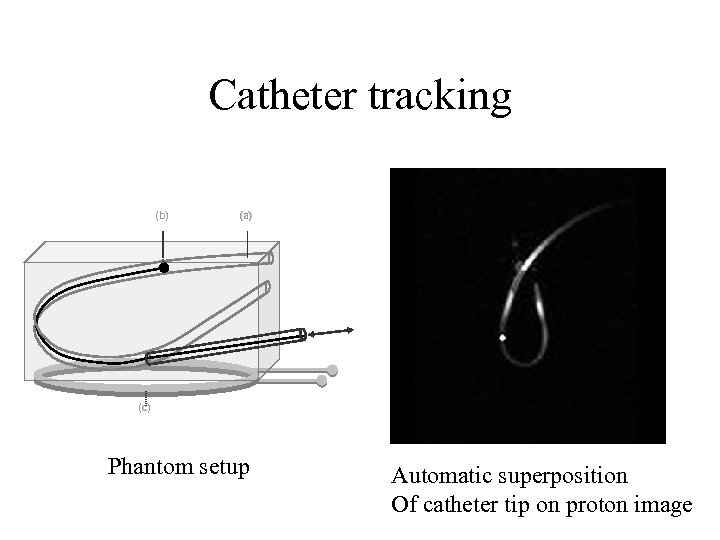 Catheter tracking (b) (a) (c) Phantom setup Automatic superposition Of catheter tip on proton image
Catheter tracking (b) (a) (c) Phantom setup Automatic superposition Of catheter tip on proton image
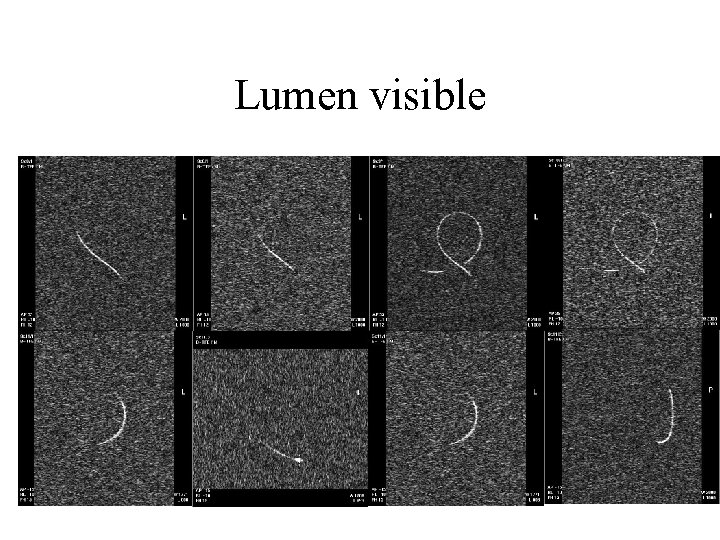 Lumen visible
Lumen visible
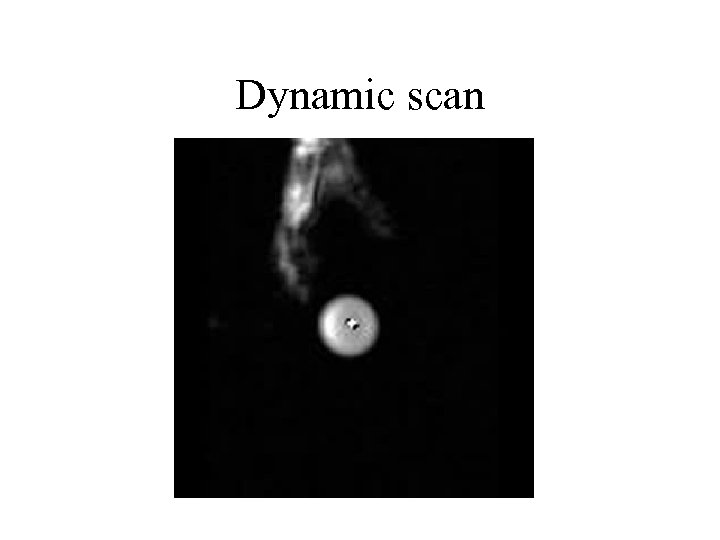 Dynamic scan
Dynamic scan
 Catheter Tracking and Visualization Using 19 F Nuclear Magnetic Resonance • Sebastian Kozerke 1, 2, Sanjeet Hegde 3, Tobias Schaeffter 4, Rolf Lamerichs 5, Reza Razavi 3, Derek L. Hill 2 Magn. Reson. Med. 2004 (in press)
Catheter Tracking and Visualization Using 19 F Nuclear Magnetic Resonance • Sebastian Kozerke 1, 2, Sanjeet Hegde 3, Tobias Schaeffter 4, Rolf Lamerichs 5, Reza Razavi 3, Derek L. Hill 2 Magn. Reson. Med. 2004 (in press)
 Image analysis combined with acquisition • Real time MRI can provide high temporal resolution, but low quality • Can we subsequently combine real time images to generate high image quality?
Image analysis combined with acquisition • Real time MRI can provide high temporal resolution, but low quality • Can we subsequently combine real time images to generate high image quality?
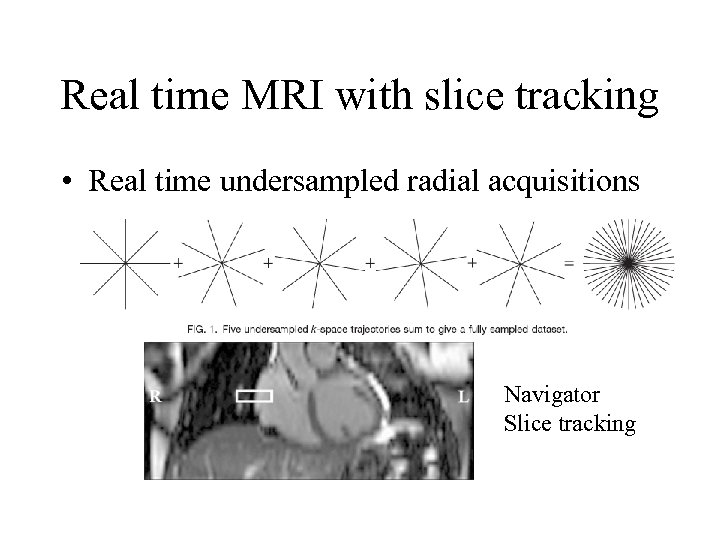 Real time MRI with slice tracking • Real time undersampled radial acquisitions Navigator Slice tracking
Real time MRI with slice tracking • Real time undersampled radial acquisitions Navigator Slice tracking
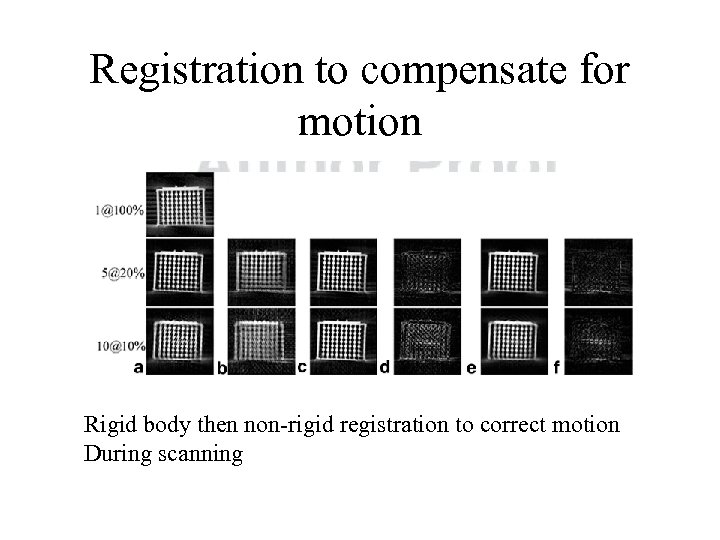 Registration to compensate for motion Rigid body then non-rigid registration to correct motion During scanning
Registration to compensate for motion Rigid body then non-rigid registration to correct motion During scanning
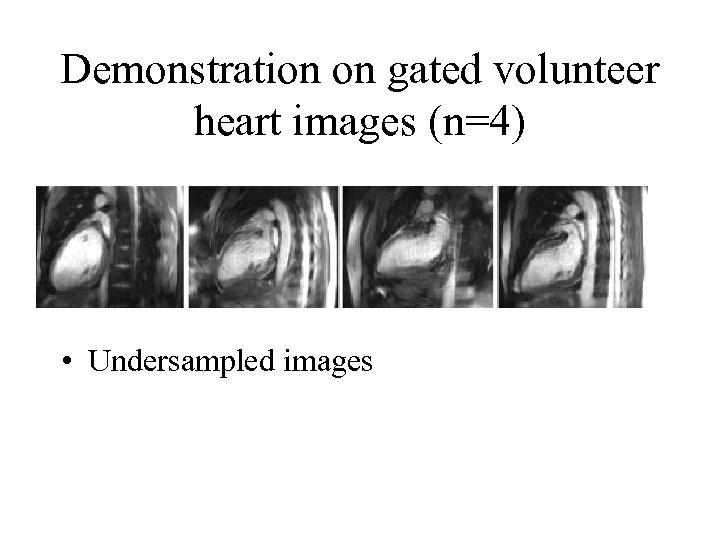 Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Undersampled images
Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Undersampled images
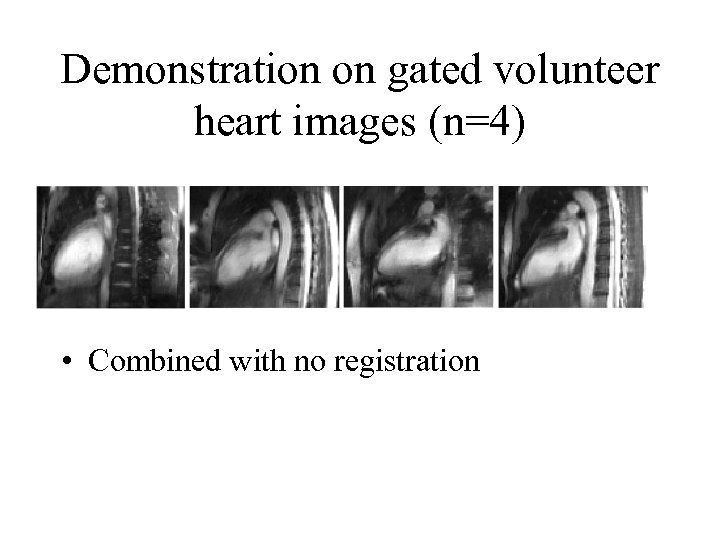 Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Combined with no registration
Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Combined with no registration
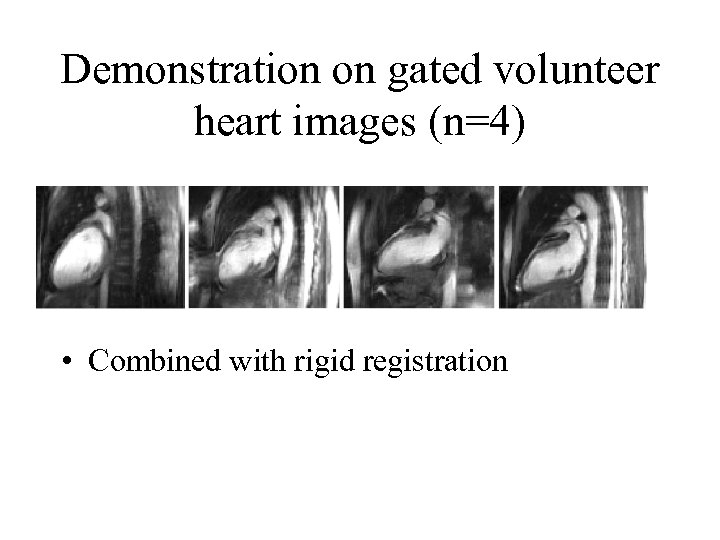 Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Combined with rigid registration
Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Combined with rigid registration
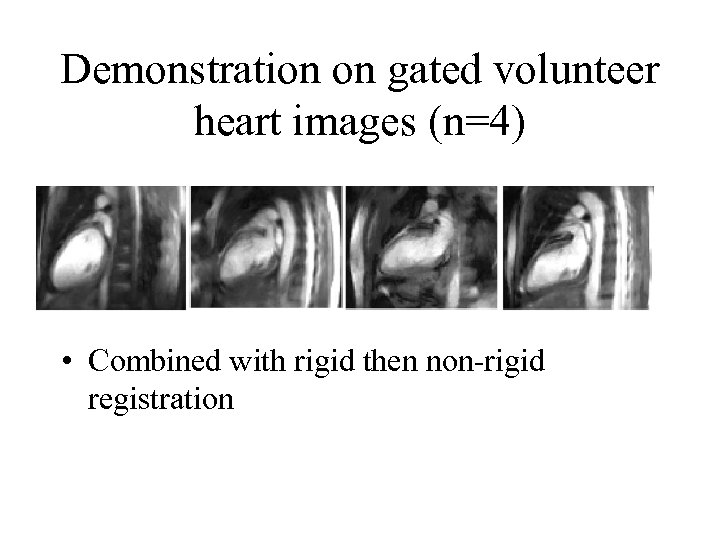 Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Combined with rigid then non-rigid registration
Demonstration on gated volunteer heart images (n=4) • Combined with rigid then non-rigid registration

 Conclusions • Interventional MRI is fertile area for image analysis • • Real time requirements New applications (eg: RF ablation) Improving guidance Novel acquisition and reconstruction incorporating image analysis
Conclusions • Interventional MRI is fertile area for image analysis • • Real time requirements New applications (eg: RF ablation) Improving guidance Novel acquisition and reconstruction incorporating image analysis


