5952add9f342b3219a7045de3a6a4368.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Image Information Retrieval Shaw-Ming Yang IST 497 E 12/05/02
Image Information Retrieval Shaw-Ming Yang IST 497 E 12/05/02
 Overview n J. R. Smith and S. -F. Chang, Visually Searching the Web for Content, IEEE Multimedia. July - Sept, 1997, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 1220; part of paper also in Columbia University CTR Technical Report # 45996 -25, 1996. n Introduction: 5 -min Recap Webseek n ¨ ¨ n What is Webseek? Data Collection Process Subject Classification Process Search and Retrieval Process Conclusion
Overview n J. R. Smith and S. -F. Chang, Visually Searching the Web for Content, IEEE Multimedia. July - Sept, 1997, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 1220; part of paper also in Columbia University CTR Technical Report # 45996 -25, 1996. n Introduction: 5 -min Recap Webseek n ¨ ¨ n What is Webseek? Data Collection Process Subject Classification Process Search and Retrieval Process Conclusion

 5 -min Recap n Why is Image IR important? ¨ “a picture is worth a 1000 words” ¨ Alternative form of communication ¨ Not everything can be described in text; Not everything can be described in images ¨ Popular medium of information on the Internet
5 -min Recap n Why is Image IR important? ¨ “a picture is worth a 1000 words” ¨ Alternative form of communication ¨ Not everything can be described in text; Not everything can be described in images ¨ Popular medium of information on the Internet
 5 -min Recap n Visual Feature Extraction ¨ What is the best way to represent all data contained in an image empirically? n Multi-Dimensional Indexing ¨ What is the best way to scale large size image collections? n Retrieval System Design
5 -min Recap n Visual Feature Extraction ¨ What is the best way to represent all data contained in an image empirically? n Multi-Dimensional Indexing ¨ What is the best way to scale large size image collections? n Retrieval System Design
 What is Webseek? n n “Web. SEEK is a Content- Based Image and Video Search and Catalog Tool for the Web. Search through more than 650, 000 images and videos. ” (Advent Project) Developed by The Advent Project at Columbia University ¨ Founded 1995 ¨ Foster industrial collaboration between researchers and media technology
What is Webseek? n n “Web. SEEK is a Content- Based Image and Video Search and Catalog Tool for the Web. Search through more than 650, 000 images and videos. ” (Advent Project) Developed by The Advent Project at Columbia University ¨ Founded 1995 ¨ Foster industrial collaboration between researchers and media technology
 What is Webseek? n More Specifically… Uses multiple agents to automatically analyze, index, and assign images/videos to subject classes ¨ Uses both visual content and text for cataloging and searching ¨ n Features ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Searching using image content-based techniques Query modification using content-based relevance feedback Automated collection of visual information Compact presentation of images and videos for displaying query results Image and video subject search and navigation Text-based searching Search results lists manipulations n n intersection, subtraction and concatenation. http: //www. ctr. columbia. edu/webseek
What is Webseek? n More Specifically… Uses multiple agents to automatically analyze, index, and assign images/videos to subject classes ¨ Uses both visual content and text for cataloging and searching ¨ n Features ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Searching using image content-based techniques Query modification using content-based relevance feedback Automated collection of visual information Compact presentation of images and videos for displaying query results Image and video subject search and navigation Text-based searching Search results lists manipulations n n intersection, subtraction and concatenation. http: //www. ctr. columbia. edu/webseek
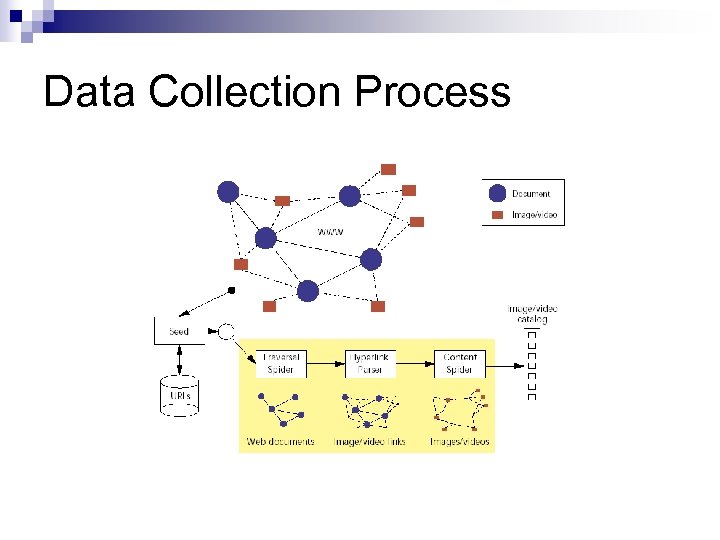
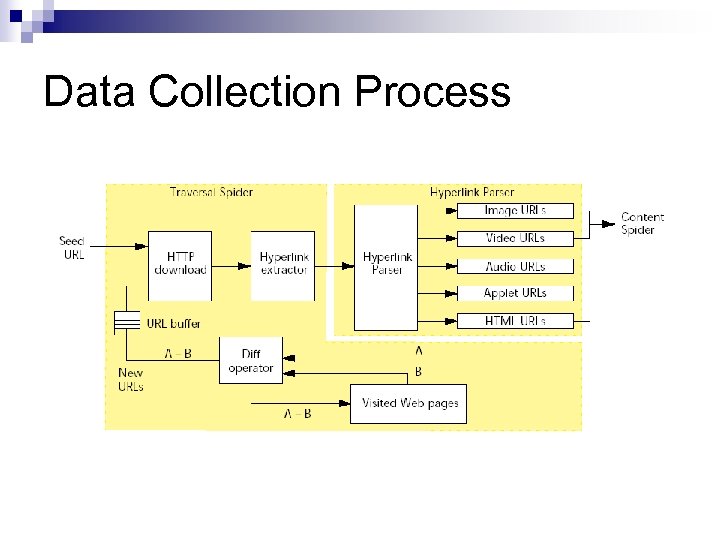
 Data Collection Process n Autonomous “spiders” ¨ Traversal Spider – “assembles lists of candidate Web documents that may include images, videos, or hyperlinks to them” ¨ Hyperlink Parser – “which extracts the Web addresses of images and videos” ¨ Content Spider – “which retrieves, analyzes, and iconifies the images and videos”
Data Collection Process n Autonomous “spiders” ¨ Traversal Spider – “assembles lists of candidate Web documents that may include images, videos, or hyperlinks to them” ¨ Hyperlink Parser – “which extracts the Web addresses of images and videos” ¨ Content Spider – “which retrieves, analyzes, and iconifies the images and videos”
 Data Collection Process
Data Collection Process
 Data Collection Process
Data Collection Process
 Data Collection Process n Content Spider Functions ¨ “extracts visual features that allow for content-based searching, browsing, and grouping” ¨ “extracts other attributes such as width, height, number of frames, type of visual data” n Color histogram ¨ “generates an icon, or motion icon, which sufficiently compacts and represents the visual information to be used for browsing and displaying query results” n Compression algorithms
Data Collection Process n Content Spider Functions ¨ “extracts visual features that allow for content-based searching, browsing, and grouping” ¨ “extracts other attributes such as width, height, number of frames, type of visual data” n Color histogram ¨ “generates an icon, or motion icon, which sufficiently compacts and represents the visual information to be used for browsing and displaying query results” n Compression algorithms
 Subject Classification Process n “text provides clues about the semantic content of visual information” ¨ URL ¨ File n name Text clues can be found in HTML syntax ¨
Subject Classification Process n “text provides clues about the semantic content of visual information” ¨ URL ¨ File n name Text clues can be found in HTML syntax ¨ ¨ [hyperlink text]
 Subject Classification Process n Term extraction Extracted from URLs, alt tags, hyperlink text by removing nonalpha characters ¨ Fkey (URL) = Fchop (“animals/domestic-beasts 1/dog 37”) = “animals, ” “domestic, ” “beasts, ” “dog. ” ¨ n Dictionary name extraction ¨ n Fdir (URL) = “animals/domestic-beasts. ” Key-term dictionary Terms and Dictionary names are used to create t*k terms ¨ t*k terms identified semantically related to subject classes sm ¨ Mkm: t*k sm ¨
Subject Classification Process n Term extraction Extracted from URLs, alt tags, hyperlink text by removing nonalpha characters ¨ Fkey (URL) = Fchop (“animals/domestic-beasts 1/dog 37”) = “animals, ” “domestic, ” “beasts, ” “dog. ” ¨ n Dictionary name extraction ¨ n Fdir (URL) = “animals/domestic-beasts. ” Key-term dictionary Terms and Dictionary names are used to create t*k terms ¨ t*k terms identified semantically related to subject classes sm ¨ Mkm: t*k sm ¨
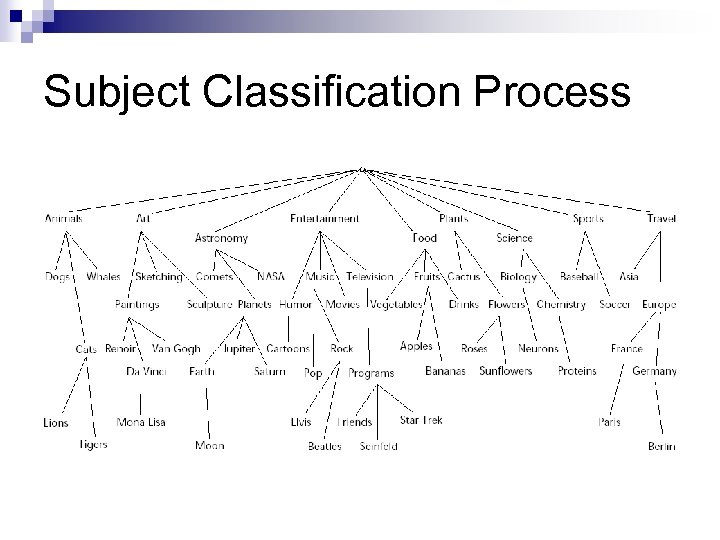 Subject Classification Process
Subject Classification Process
 Search and Retrieval Process n Search results list manipulation ¨A = Query (Term = “sunset”) ¨ Returns Query A results ¨ Select Query B from Query A results ¨ B = Query (Term = “nature”) ¨ C = A ∩ B = Query (Term = “sunset” and Term = “nature”)
Search and Retrieval Process n Search results list manipulation ¨A = Query (Term = “sunset”) ¨ Returns Query A results ¨ Select Query B from Query A results ¨ B = Query (Term = “nature”) ¨ C = A ∩ B = Query (Term = “sunset” and Term = “nature”)
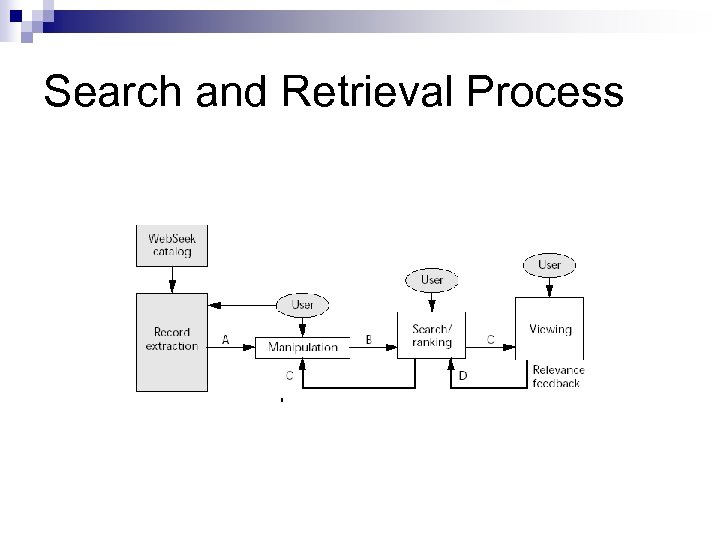 Search and Retrieval Process
Search and Retrieval Process
 Search and Retrieval Process
Search and Retrieval Process
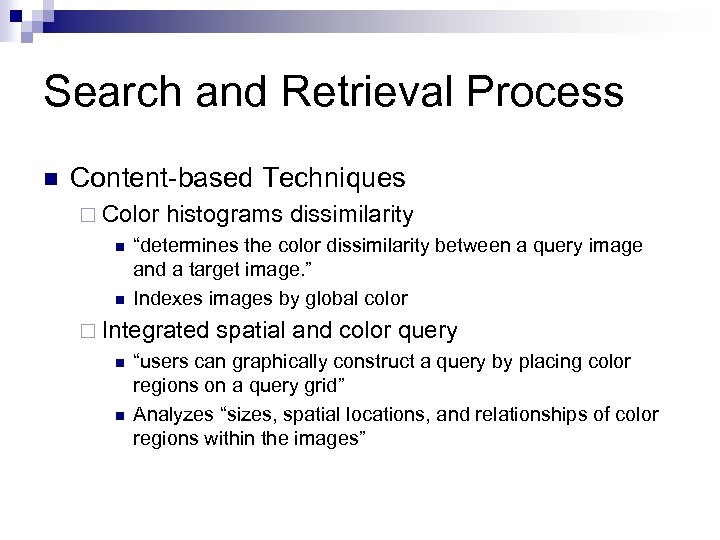 Search and Retrieval Process n Content-based Techniques ¨ Color n n histograms dissimilarity “determines the color dissimilarity between a query image and a target image. ” Indexes images by global color ¨ Integrated n n spatial and color query “users can graphically construct a query by placing color regions on a query grid” Analyzes “sizes, spatial locations, and relationships of color regions within the images”
Search and Retrieval Process n Content-based Techniques ¨ Color n n histograms dissimilarity “determines the color dissimilarity between a query image and a target image. ” Indexes images by global color ¨ Integrated n n spatial and color query “users can graphically construct a query by placing color regions on a query grid” Analyzes “sizes, spatial locations, and relationships of color regions within the images”
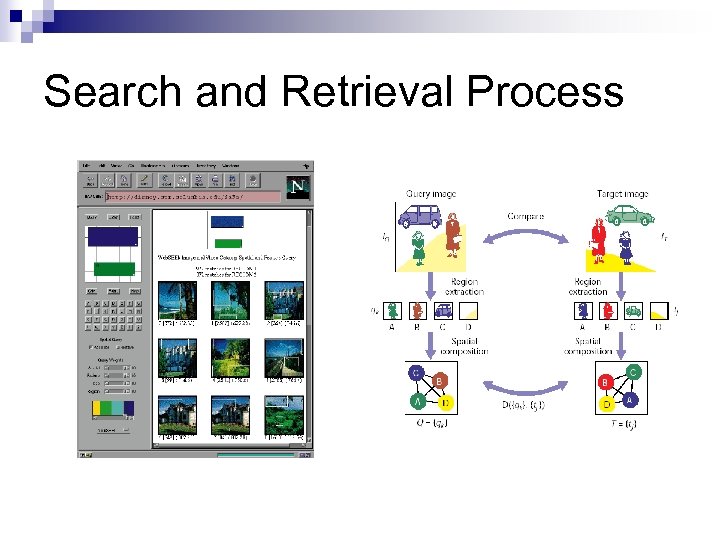 Search and Retrieval Process
Search and Retrieval Process
 Conclusion n n Many similarities exist between traditional text-based IR systems and content-based IR systems Although text-based IR systems have been relatively successful, CBIR still has many barriers to overcome. Visual Feature Extraction ¨ Multi-Dimensional Indexing ¨ Retrieval System Design ¨ n Although the discussed article is 5 years old, recent studies show Image IR research and development trends continue to focus on similar issues.
Conclusion n n Many similarities exist between traditional text-based IR systems and content-based IR systems Although text-based IR systems have been relatively successful, CBIR still has many barriers to overcome. Visual Feature Extraction ¨ Multi-Dimensional Indexing ¨ Retrieval System Design ¨ n Although the discussed article is 5 years old, recent studies show Image IR research and development trends continue to focus on similar issues.
 Conclusion n Future research directions ¨ Involving humans ¨ Identify high-level features n in the R&D process concepts with low-level visual Finger print, human face ¨ Web oriented ¨ High dimensional indexing ¨ Performance evaluation criterion and standard ¨ Integration of Database and Computer Vision resources testbed
Conclusion n Future research directions ¨ Involving humans ¨ Identify high-level features n in the R&D process concepts with low-level visual Finger print, human face ¨ Web oriented ¨ High dimensional indexing ¨ Performance evaluation criterion and standard ¨ Integration of Database and Computer Vision resources testbed
 Bibliography n n n (2002) Image Retrieval. Retrieved: November 6, 2002, from: http: //140. 120. 7. 1/~yloug/images/Image_Retrieval. PDF. Feng, X. (2002) Content-based Image Retrieval. Retrieved: November 6, 2002, from: http: //www. cse. ucsc. edu/classes/ee 264/Winter 02/xgfeng. ppt. J. R. Smith and S. -F. Chang, Visually Searching the Web for Content, IEEE Multimedia. July - Sept, 1997, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 12 -20; part of paper also in Columbia University CTR Technical Report # 45996 -25, 1996. Rui, Y. , Huang, T. S. , & Chang, S. F. (1999). Image Retrieval: Current Techniques, Promising Directions and Open Issues. Vaidya, D. (2002) Visual Information Retrieval. Retrieved: November 6, 2002, from: http: //www-isl. ece. arizona. edu/islpresentations/VISUAL%20 INFORMATION%20 RETRIEVAL. ppt Note: All images and quoted content are from J. R. Smith and S. -F. Chang’s Visually Searching the Web for Content.
Bibliography n n n (2002) Image Retrieval. Retrieved: November 6, 2002, from: http: //140. 120. 7. 1/~yloug/images/Image_Retrieval. PDF. Feng, X. (2002) Content-based Image Retrieval. Retrieved: November 6, 2002, from: http: //www. cse. ucsc. edu/classes/ee 264/Winter 02/xgfeng. ppt. J. R. Smith and S. -F. Chang, Visually Searching the Web for Content, IEEE Multimedia. July - Sept, 1997, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 12 -20; part of paper also in Columbia University CTR Technical Report # 45996 -25, 1996. Rui, Y. , Huang, T. S. , & Chang, S. F. (1999). Image Retrieval: Current Techniques, Promising Directions and Open Issues. Vaidya, D. (2002) Visual Information Retrieval. Retrieved: November 6, 2002, from: http: //www-isl. ece. arizona. edu/islpresentations/VISUAL%20 INFORMATION%20 RETRIEVAL. ppt Note: All images and quoted content are from J. R. Smith and S. -F. Chang’s Visually Searching the Web for Content.


