881df20eaefb695eff22e19e3afd7c79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Illinois Institute of Technology CS 487 Software Engineering Analysis Modeling Instructor David Lash CS 48704 -1/31
Illinois Institute of Technology CS 487 Software Engineering Analysis Modeling Instructor David Lash CS 48704 -1/31
 Illinois Institute of Technology This level of modeling is the very highest level. The basic input-processing-output template. CS 48704 -2/31
Illinois Institute of Technology This level of modeling is the very highest level. The basic input-processing-output template. CS 48704 -2/31
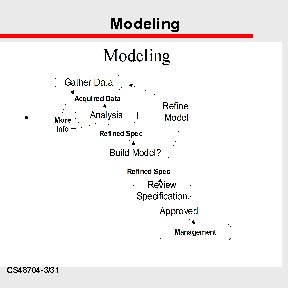 Modeling CS 48704 -3/31
Modeling CS 48704 -3/31
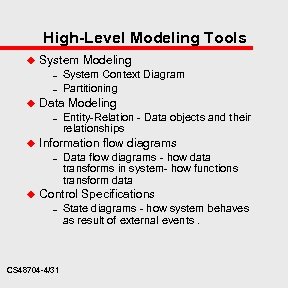 High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – u Data Modeling – u Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships Information flow diagrams – u System Context Diagram Partitioning Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – CS 48704 -4/31 State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events.
High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – u Data Modeling – u Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships Information flow diagrams – u System Context Diagram Partitioning Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – CS 48704 -4/31 State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events.
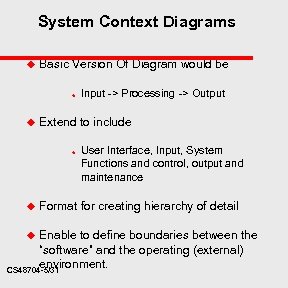 System Context Diagrams u Basic Version Of Diagram would be u u Extend to include u u Input -> Processing -> Output User Interface, Input, System Functions and control, output and maintenance Format for creating hierarchy of detail Enable to define boundaries between the “software” and the operating (external) environment. CS 48704 -5/31 u
System Context Diagrams u Basic Version Of Diagram would be u u Extend to include u u Input -> Processing -> Output User Interface, Input, System Functions and control, output and maintenance Format for creating hierarchy of detail Enable to define boundaries between the “software” and the operating (external) environment. CS 48704 -5/31 u
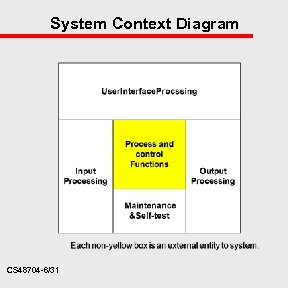 System Context Diagram CS 48704 -6/31
System Context Diagram CS 48704 -6/31
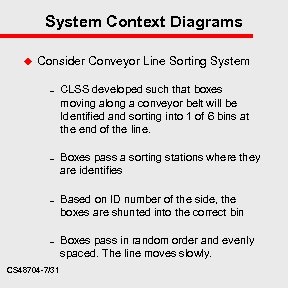 System Context Diagrams u Consider Conveyor Line Sorting System – – CS 48704 -7/31 CLSS developed such that boxes moving along a conveyor belt will be Identified and sorting into 1 of 6 bins at the end of the line. Boxes pass a sorting stations where they are identifies Based on ID number of the side, the boxes are shunted into the correct bin Boxes pass in random order and evenly spaced. The line moves slowly.
System Context Diagrams u Consider Conveyor Line Sorting System – – CS 48704 -7/31 CLSS developed such that boxes moving along a conveyor belt will be Identified and sorting into 1 of 6 bins at the end of the line. Boxes pass a sorting stations where they are identifies Based on ID number of the side, the boxes are shunted into the correct bin Boxes pass in random order and evenly spaced. The line moves slowly.
 System Context Diagrams - CLSS u Consider Conveyor Line Sorting System - II – – Has a PC sorting stn site. Boxes moving along conveyor belt identified and stored into 1 of 6 boxes at end of line. Boxes have bar code on side. PC execs software, interacts with bar code rdr and conveyor line monitoring equipment (to get speed of line) stores parts numbers sorted and interacts with operator sends signals to shunting hardware – sends CS 48704 -8/31 out reports and communicates with server in factory floor. (pg 265)
System Context Diagrams - CLSS u Consider Conveyor Line Sorting System - II – – Has a PC sorting stn site. Boxes moving along conveyor belt identified and stored into 1 of 6 boxes at end of line. Boxes have bar code on side. PC execs software, interacts with bar code rdr and conveyor line monitoring equipment (to get speed of line) stores parts numbers sorted and interacts with operator sends signals to shunting hardware – sends CS 48704 -8/31 out reports and communicates with server in factory floor. (pg 265)
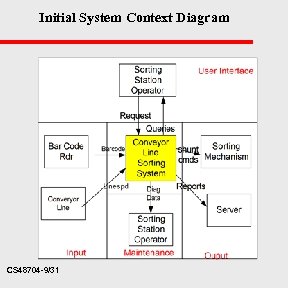 Initial System Context Diagram CS 48704 -9/31
Initial System Context Diagram CS 48704 -9/31
 Refine Into a System Flow Diagram u Page 265 shows refined diagram – – Look at important lines of data and control flow. Might be the top level of a series of SFDs that are later developed (See page 266. CS 48704 -10/31
Refine Into a System Flow Diagram u Page 265 shows refined diagram – – Look at important lines of data and control flow. Might be the top level of a series of SFDs that are later developed (See page 266. CS 48704 -10/31
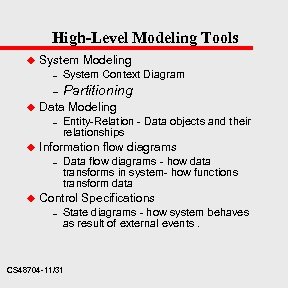 High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – u System Context Diagram Partitioning Data Modeling – u Information flow diagrams – u Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events. CS 48704 -11/31
High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – u System Context Diagram Partitioning Data Modeling – u Information flow diagrams – u Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events. CS 48704 -11/31
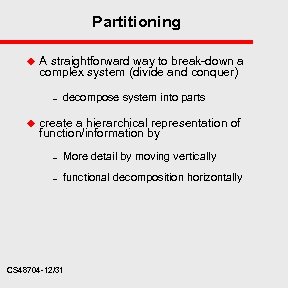 Partitioning u A straightforward way to break-down a complex system (divide and conquer) – u decompose system into parts create a hierarchical representation of function/information by – More detail by moving vertically – functional decomposition horizontally CS 48704 -12/31
Partitioning u A straightforward way to break-down a complex system (divide and conquer) – u decompose system into parts create a hierarchical representation of function/information by – More detail by moving vertically – functional decomposition horizontally CS 48704 -12/31
 Partitioning - Home Safe u Specification From Requirements gathering (interview) – – HS monitors sensors, interacts with owner via keypad (via control pad) Control pad can be program and config system Master passwd is programmed for arming and alarming system. Phone numbers are input for dialing out for help. When sensor event, alarm then after T time, dial phone number and downloads event info (sensor, time, type of event). Repeat every 20 seconds CS 48704 -13/31
Partitioning - Home Safe u Specification From Requirements gathering (interview) – – HS monitors sensors, interacts with owner via keypad (via control pad) Control pad can be program and config system Master passwd is programmed for arming and alarming system. Phone numbers are input for dialing out for help. When sensor event, alarm then after T time, dial phone number and downloads event info (sensor, time, type of event). Repeat every 20 seconds CS 48704 -13/31
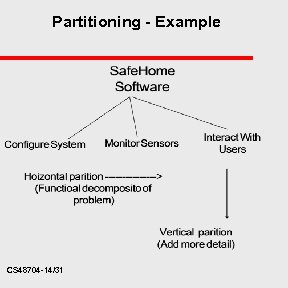 Partitioning - Example CS 48704 -14/31
Partitioning - Example CS 48704 -14/31
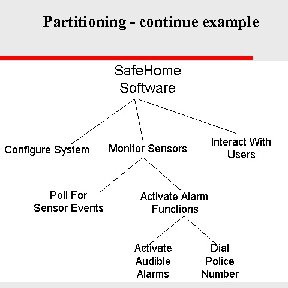 Partitioning - continue example CS 48704 -15/31
Partitioning - continue example CS 48704 -15/31
 High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – System Context Diagram Partitioning u Data Modeling - (See page 301 diag) – Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships u Information flow diagrams – u Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events. CS 48704 -16/31
High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – System Context Diagram Partitioning u Data Modeling - (See page 301 diag) – Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships u Information flow diagrams – u Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events. CS 48704 -16/31
 Data Modeling u DM answers questions like: – – – u What are data objects in the system What are the Data Objects made of How are they related One common method is the ERD - Has the following pieces: – – – Data Object: representation of something with attributes E. g. , Width (1 property) VS dimension (HGt, width) Relationship: The nature of the connection between data Objects. . Attributes: properties that describe the object CS 48704 -17/31
Data Modeling u DM answers questions like: – – – u What are data objects in the system What are the Data Objects made of How are they related One common method is the ERD - Has the following pieces: – – – Data Object: representation of something with attributes E. g. , Width (1 property) VS dimension (HGt, width) Relationship: The nature of the connection between data Objects. . Attributes: properties that describe the object CS 48704 -17/31
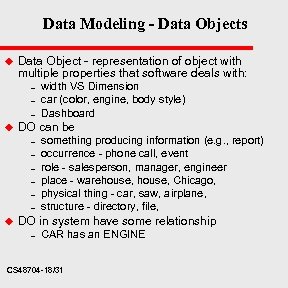 Data Modeling - Data Objects u Data Object - representation of object with multiple properties that software deals with: – – – u DO can be – – – u width VS Dimension car (color, engine, body style) Dashboard something producing information (e. g. , report) occurrence - phone call, event role - salesperson, manager, engineer place - warehouse, Chicago, physical thing - car, saw, airplane, structure - directory, file, DO in system have some relationship – CAR has an ENGINE CS 48704 -18/31
Data Modeling - Data Objects u Data Object - representation of object with multiple properties that software deals with: – – – u DO can be – – – u width VS Dimension car (color, engine, body style) Dashboard something producing information (e. g. , report) occurrence - phone call, event role - salesperson, manager, engineer place - warehouse, Chicago, physical thing - car, saw, airplane, structure - directory, file, DO in system have some relationship – CAR has an ENGINE CS 48704 -18/31
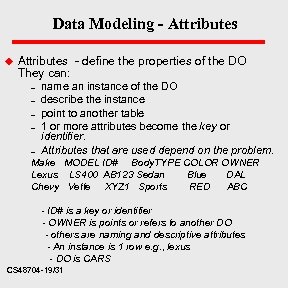 Data Modeling - Attributes u Attributes - define the properties of the DO They can: – – – name an instance of the DO describe the instance point to another table 1 or more attributes become the key or identifier. Attributes that are used depend on the problem. Make MODEL ID# Body. TYPE COLOR OWNER Lexus LS 400 AB 123 Sedan Blue DAL Chevy Vette XYZ 1 Sports RED ABC - ID# is a key or identifier - OWNER is points or refers to another DO - others are naming and descriptive attributes - An instance is 1 row e. g. , lexus - DO is CARS CS 48704 -19/31
Data Modeling - Attributes u Attributes - define the properties of the DO They can: – – – name an instance of the DO describe the instance point to another table 1 or more attributes become the key or identifier. Attributes that are used depend on the problem. Make MODEL ID# Body. TYPE COLOR OWNER Lexus LS 400 AB 123 Sedan Blue DAL Chevy Vette XYZ 1 Sports RED ABC - ID# is a key or identifier - OWNER is points or refers to another DO - others are naming and descriptive attributes - An instance is 1 row e. g. , lexus - DO is CARS CS 48704 -19/31
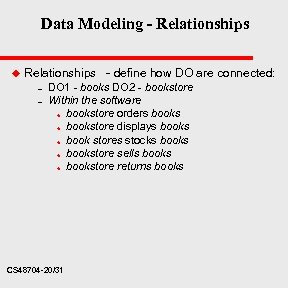 Data Modeling - Relationships u Relationships - define how DO are connected: – – DO 1 - books DO 2 - bookstore Within the software bookstore orders bookstore displays book stores stocks bookstore sells bookstore returns books u u u CS 48704 -20/31
Data Modeling - Relationships u Relationships - define how DO are connected: – – DO 1 - books DO 2 - bookstore Within the software bookstore orders bookstore displays book stores stocks bookstore sells bookstore returns books u u u CS 48704 -20/31
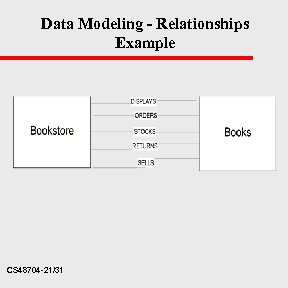 Data Modeling - Relationships Example CS 48704 -21/31
Data Modeling - Relationships Example CS 48704 -21/31
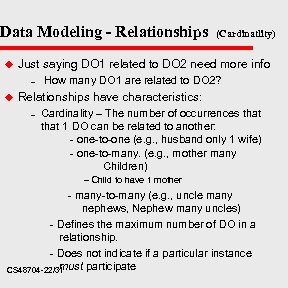 Data Modeling - Relationships u Just saying DO 1 related to DO 2 need more info – u (Cardinatlity) How many DO 1 are related to DO 2? Relationships have characteristics: – Cardinality – The number of occurrences that 1 DO can be related to another: - one-to-one (e. g. , husband only 1 wife) - one-to-many. (e. g. , mother many Children) – Child to have 1 mother - many-to-many (e. g. , uncle many nephews, Nephew many uncles) - Defines the maximum number of DO in a relationship. - Does not indicate if a particular instance must participate CS 48704 -22/31
Data Modeling - Relationships u Just saying DO 1 related to DO 2 need more info – u (Cardinatlity) How many DO 1 are related to DO 2? Relationships have characteristics: – Cardinality – The number of occurrences that 1 DO can be related to another: - one-to-one (e. g. , husband only 1 wife) - one-to-many. (e. g. , mother many Children) – Child to have 1 mother - many-to-many (e. g. , uncle many nephews, Nephew many uncles) - Defines the maximum number of DO in a relationship. - Does not indicate if a particular instance must participate CS 48704 -22/31
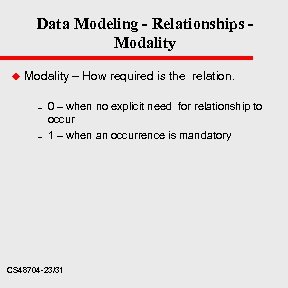 Data Modeling - Relationships Modality u Modality – How required is the relation. – – 0 – when no explicit need for relationship to occur 1 – when an occurrence is mandatory CS 48704 -23/31
Data Modeling - Relationships Modality u Modality – How required is the relation. – – 0 – when no explicit need for relationship to occur 1 – when an occurrence is mandatory CS 48704 -23/31
 ERD u u Cornerstone of the Data Model Diagram the DO, Relationships and attributes CS 48704 -24/31
ERD u u Cornerstone of the Data Model Diagram the DO, Relationships and attributes CS 48704 -24/31
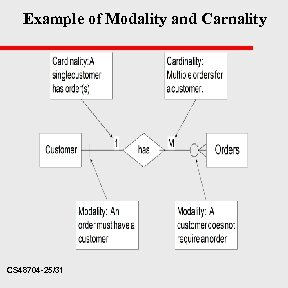 Example of Modality and Carnality CS 48704 -25/31
Example of Modality and Carnality CS 48704 -25/31
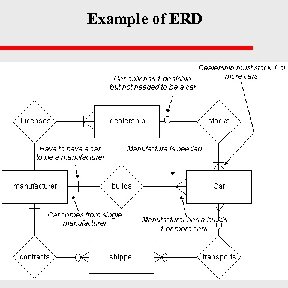 Example of ERD CS 48704 -26/31
Example of ERD CS 48704 -26/31
 ERD II example - Homesafe u u u u Enables homeowner (HW) to config security system (SS), during install HS monitors all sensors connected to SS HS interacts with HW via Keypad on cntl panel (CP) CP is used to program system Each sensor (SEN) is assigned a # and type A master passwd is programmed, Tel number are input for dialing on Sensor event (SEN) on SEN event, alarm invoked & SS dials phone number, and gives info to (MS) monitoring Service CP has keyboard input stuff CS 48704 -27/31
ERD II example - Homesafe u u u u Enables homeowner (HW) to config security system (SS), during install HS monitors all sensors connected to SS HS interacts with HW via Keypad on cntl panel (CP) CP is used to program system Each sensor (SEN) is assigned a # and type A master passwd is programmed, Tel number are input for dialing on Sensor event (SEN) on SEN event, alarm invoked & SS dials phone number, and gives info to (MS) monitoring Service CP has keyboard input stuff CS 48704 -27/31
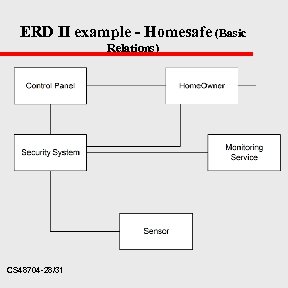 ERD II example - Homesafe (Basic Relations) CS 48704 -28/31
ERD II example - Homesafe (Basic Relations) CS 48704 -28/31
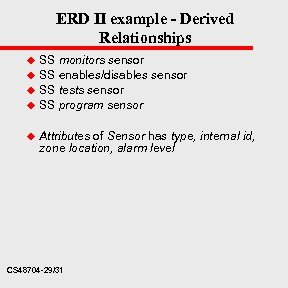 ERD II example - Derived Relationships u u u SS monitors sensor SS enables/disables sensor SS tests sensor SS program sensor Attributes of Sensor has type, internal id, zone location, alarm level CS 48704 -29/31
ERD II example - Derived Relationships u u u SS monitors sensor SS enables/disables sensor SS tests sensor SS program sensor Attributes of Sensor has type, internal id, zone location, alarm level CS 48704 -29/31
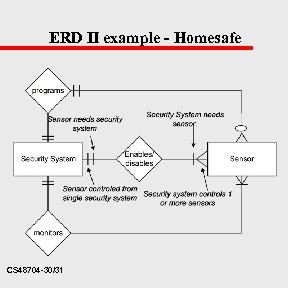 ERD II example - Homesafe CS 48704 -30/31
ERD II example - Homesafe CS 48704 -30/31
 High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – System Context Diagram Partitioning u Data Modeling – Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships u Information flow diagrams – u Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events. CS 48704 -31/31
High-Level Modeling Tools u System Modeling – – System Context Diagram Partitioning u Data Modeling – Entity-Relation - Data objects and their relationships u Information flow diagrams – u Data flow diagrams - how data transforms in system- how functions transform data Control Specifications – State diagrams - how system behaves as result of external events. CS 48704 -31/31


