11e1a04d321b678cece57d446c582eae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Il Calcolo Scientifico a Padova e nel Veneto Padova, 24 Giugno 2008 Il CINECA e il Calcolo Scientifico Giovanni Erbacci Coordinatore Gruppo Supercalcolo CINECA g. erbacci@cineca. it CINECA Casalecchio di Reno (BO) Via Magnanelli 6/3, 40033 Casalecchio di Reno | 051 6171411 | www. cineca. it © CINECA -24 giugno 2008
Il Calcolo Scientifico a Padova e nel Veneto Padova, 24 Giugno 2008 Il CINECA e il Calcolo Scientifico Giovanni Erbacci Coordinatore Gruppo Supercalcolo CINECA g. erbacci@cineca. it CINECA Casalecchio di Reno (BO) Via Magnanelli 6/3, 40033 Casalecchio di Reno | 051 6171411 | www. cineca. it © CINECA -24 giugno 2008
 The CINECA Consortium • Consortium of 32 Italian Universities, CNR, MIUR, OGS • Private non for Profit Organization • Founded in 1969 by Ministry of Public Education now under the control of Italian Ministry of University and Research • Main activities: – Promote the use of the most advanced information processing systems to support public and private scientific and technological research – Services both for universities and private enterprises and Ministry © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 2
The CINECA Consortium • Consortium of 32 Italian Universities, CNR, MIUR, OGS • Private non for Profit Organization • Founded in 1969 by Ministry of Public Education now under the control of Italian Ministry of University and Research • Main activities: – Promote the use of the most advanced information processing systems to support public and private scientific and technological research – Services both for universities and private enterprises and Ministry © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 2
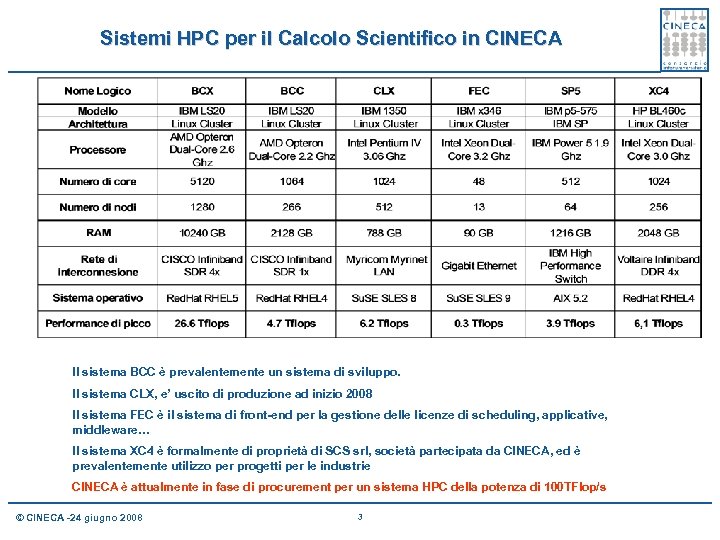 Sistemi HPC per il Calcolo Scientifico in CINECA Il sistema BCC è prevalentemente un sistema di sviluppo. Il sistema CLX, e’ uscito di produzione ad inizio 2008 Il sistema FEC è il sistema di front-end per la gestione delle licenze di scheduling, applicative, middleware… Il sistema XC 4 è formalmente di proprietà di SCS srl, società partecipata da CINECA, ed è prevalentemente utilizzo per progetti per le industrie CINECA è attualmente in fase di procurement per un sistema HPC della potenza di 100 TFlop/s © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 3
Sistemi HPC per il Calcolo Scientifico in CINECA Il sistema BCC è prevalentemente un sistema di sviluppo. Il sistema CLX, e’ uscito di produzione ad inizio 2008 Il sistema FEC è il sistema di front-end per la gestione delle licenze di scheduling, applicative, middleware… Il sistema XC 4 è formalmente di proprietà di SCS srl, società partecipata da CINECA, ed è prevalentemente utilizzo per progetti per le industrie CINECA è attualmente in fase di procurement per un sistema HPC della potenza di 100 TFlop/s © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 3
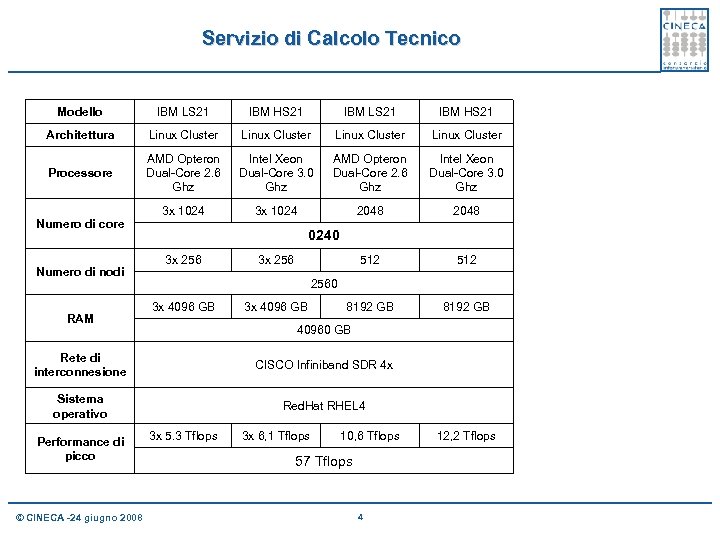 Servizio di Calcolo Tecnico Modello IBM LS 21 IBM HS 21 Architettura Linux Cluster Processore AMD Opteron Dual-Core 2. 6 Ghz Intel Xeon Dual-Core 3. 0 Ghz 3 x 1024 2048 512 8192 GB Numero di core Numero di nodi RAM 0240 3 x 256 2560 3 x 4096 GB 40960 GB Rete di interconnesione CISCO Infiniband SDR 4 x Sistema operativo Red. Hat RHEL 4 Performance di picco © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 3 x 5. 3 Tflops 3 x 6, 1 Tflops 10, 6 Tflops 57 Tflops 4 12, 2 Tflops
Servizio di Calcolo Tecnico Modello IBM LS 21 IBM HS 21 Architettura Linux Cluster Processore AMD Opteron Dual-Core 2. 6 Ghz Intel Xeon Dual-Core 3. 0 Ghz 3 x 1024 2048 512 8192 GB Numero di core Numero di nodi RAM 0240 3 x 256 2560 3 x 4096 GB 40960 GB Rete di interconnesione CISCO Infiniband SDR 4 x Sistema operativo Red. Hat RHEL 4 Performance di picco © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 3 x 5. 3 Tflops 3 x 6, 1 Tflops 10, 6 Tflops 57 Tflops 4 12, 2 Tflops
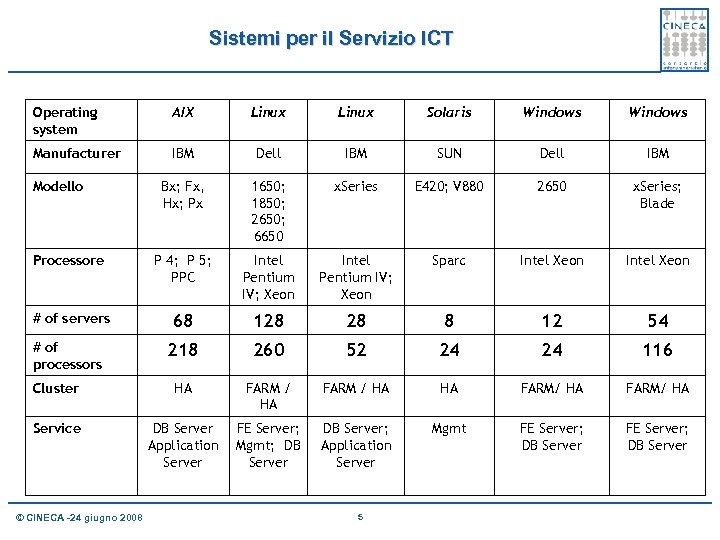 Sistemi per il Servizio ICT Operating system AIX Linux Solaris Windows Manufacturer IBM Dell IBM SUN Dell IBM Bx; Fx, Hx; Px 1650; 1850; 2650; 6650 x. Series E 420; V 880 2650 x. Series; Blade Processore P 4; P 5; PPC Intel Pentium IV; Xeon Sparc Intel Xeon # of servers 68 128 28 8 12 54 # of processors 218 260 52 24 24 116 Cluster HA FARM / HA HA FARM/ HA Service DB Server Application Server FE Server; Mgmt; DB Server; Application Server Mgmt FE Server; DB Server Modello © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 5
Sistemi per il Servizio ICT Operating system AIX Linux Solaris Windows Manufacturer IBM Dell IBM SUN Dell IBM Bx; Fx, Hx; Px 1650; 1850; 2650; 6650 x. Series E 420; V 880 2650 x. Series; Blade Processore P 4; P 5; PPC Intel Pentium IV; Xeon Sparc Intel Xeon # of servers 68 128 28 8 12 54 # of processors 218 260 52 24 24 116 Cluster HA FARM / HA HA FARM/ HA Service DB Server Application Server FE Server; Mgmt; DB Server; Application Server Mgmt FE Server; DB Server Modello © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 5
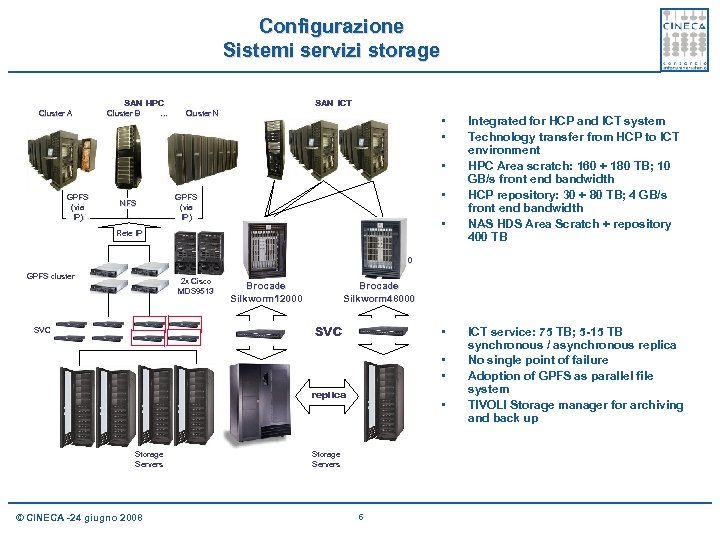 Configurazione Sistemi servizi storage Cluster A SAN HPC Cluster B … SAN ICT Cluster N • • • GPFS (via IP) NFS • GPFS (via IP) • Rete IP Integrated for HCP and ICT system Technology transfer from HCP to ICT environment HPC Area scratch: 160 + 180 TB; 10 GB/s front end bandwidth HCP repository: 30 + 80 TB; 4 GB/s front end bandwidth NAS HDS Area Scratch + repository 400 TB Brocade Silkworm 2800 GPFS cluster 2 x Cisco MDS 9513 Brocade Silkworm 12000 Brocade Silkworm 48000 SVC • • • replica Storage Servers © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 • Storage Servers 6 ICT service: 75 TB; 5 -15 TB synchronous / asynchronous replica No single point of failure Adoption of GPFS as parallel file system TIVOLI Storage manager for archiving and back up
Configurazione Sistemi servizi storage Cluster A SAN HPC Cluster B … SAN ICT Cluster N • • • GPFS (via IP) NFS • GPFS (via IP) • Rete IP Integrated for HCP and ICT system Technology transfer from HCP to ICT environment HPC Area scratch: 160 + 180 TB; 10 GB/s front end bandwidth HCP repository: 30 + 80 TB; 4 GB/s front end bandwidth NAS HDS Area Scratch + repository 400 TB Brocade Silkworm 2800 GPFS cluster 2 x Cisco MDS 9513 Brocade Silkworm 12000 Brocade Silkworm 48000 SVC • • • replica Storage Servers © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 • Storage Servers 6 ICT service: 75 TB; 5 -15 TB synchronous / asynchronous replica No single point of failure Adoption of GPFS as parallel file system TIVOLI Storage manager for archiving and back up
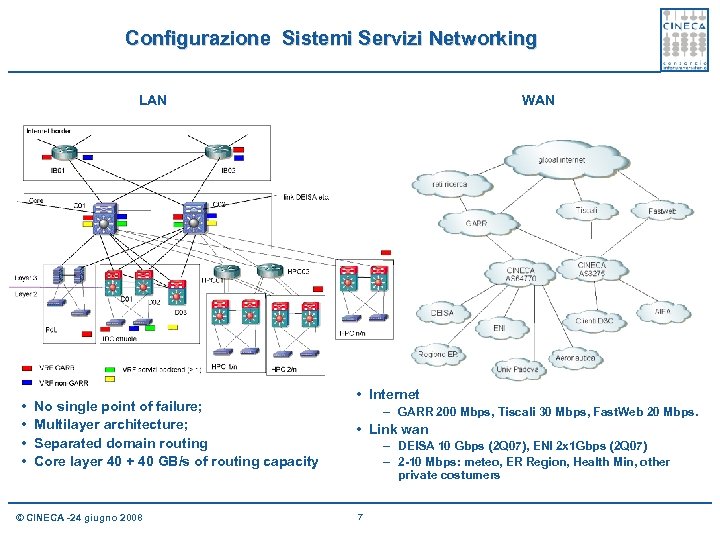 Configurazione Sistemi Servizi Networking LAN • • No single point of failure; Multilayer architecture; Separated domain routing Core layer 40 + 40 GB/s of routing capacity © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 WAN • Internet – GARR 200 Mbps, Tiscali 30 Mbps, Fast. Web 20 Mbps. • Link wan – DEISA 10 Gbps (2 Q 07), ENI 2 x 1 Gbps (2 Q 07) – 2 -10 Mbps: meteo, ER Region, Health Min, other private costumers 7
Configurazione Sistemi Servizi Networking LAN • • No single point of failure; Multilayer architecture; Separated domain routing Core layer 40 + 40 GB/s of routing capacity © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 WAN • Internet – GARR 200 Mbps, Tiscali 30 Mbps, Fast. Web 20 Mbps. • Link wan – DEISA 10 Gbps (2 Q 07), ENI 2 x 1 Gbps (2 Q 07) – 2 -10 Mbps: meteo, ER Region, Health Min, other private costumers 7
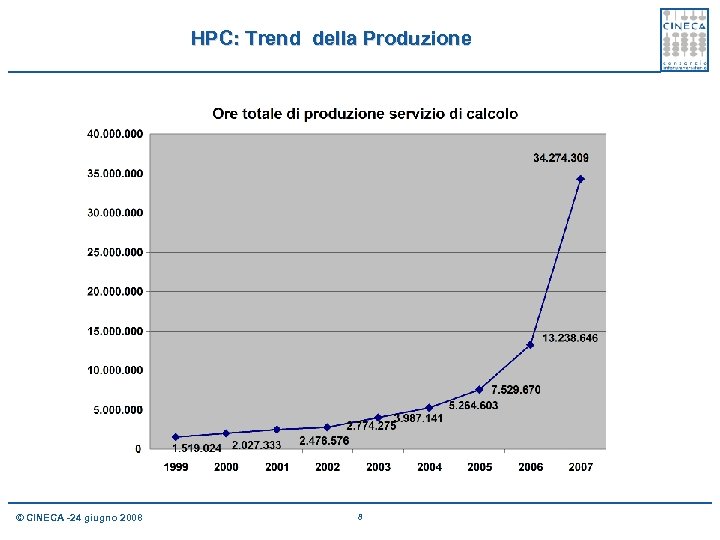 HPC: Trend della Produzione © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 8
HPC: Trend della Produzione © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 8
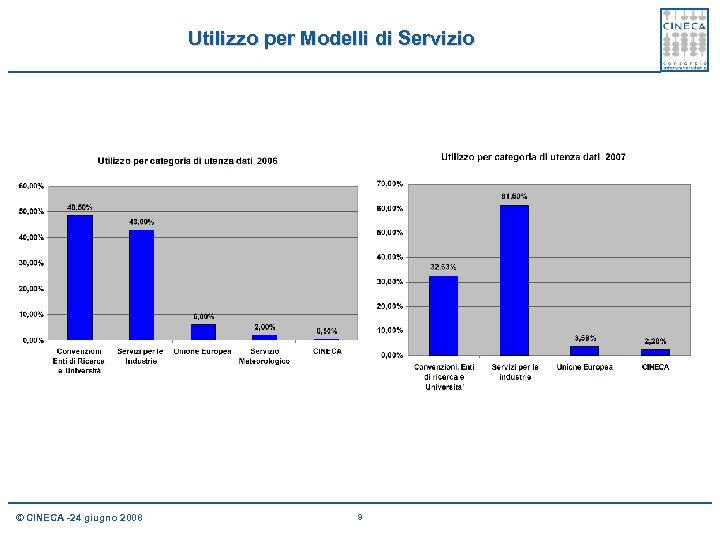 Utilizzo per Modelli di Servizio © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 9
Utilizzo per Modelli di Servizio © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 9
 Scuole Estive Scuola Estiva di Calcolo Parallelo Scuola Specialisicta di Calcolo Parallelo Scuola Estiva di Visualizzazione scientifca Scuola Specialistica di Visualizzazione Scientifica © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 10
Scuole Estive Scuola Estiva di Calcolo Parallelo Scuola Specialisicta di Calcolo Parallelo Scuola Estiva di Visualizzazione scientifca Scuola Specialistica di Visualizzazione Scientifica © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 10
 Oltre le Scuole Estive Programma di Stage in CINECA della durata di 3 mesi durante il quale gli studenti, seguiti dagli esperti del gruppo Supercalcolo, hanno Dal 2005 il CINECA, a completamento dell’attività di formazione nell’ambito HPC, finanzia 2 borse di dottorato sui temi delle metodologie innovative del calcolo parallelo e delle scienze computazionali. © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 11
Oltre le Scuole Estive Programma di Stage in CINECA della durata di 3 mesi durante il quale gli studenti, seguiti dagli esperti del gruppo Supercalcolo, hanno Dal 2005 il CINECA, a completamento dell’attività di formazione nell’ambito HPC, finanzia 2 borse di dottorato sui temi delle metodologie innovative del calcolo parallelo e delle scienze computazionali. © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 11
 Accesso alle risorse • Convenzioni con Istituti Nazionali: – INAF, – INFM-CNR, – OGS, – SISSA, – INSTM, – ICTP • Contratti a forfait • Programma di Grant • Franchigie per le Università consorziate e CNR © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 12
Accesso alle risorse • Convenzioni con Istituti Nazionali: – INAF, – INFM-CNR, – OGS, – SISSA, – INSTM, – ICTP • Contratti a forfait • Programma di Grant • Franchigie per le Università consorziate e CNR © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 12
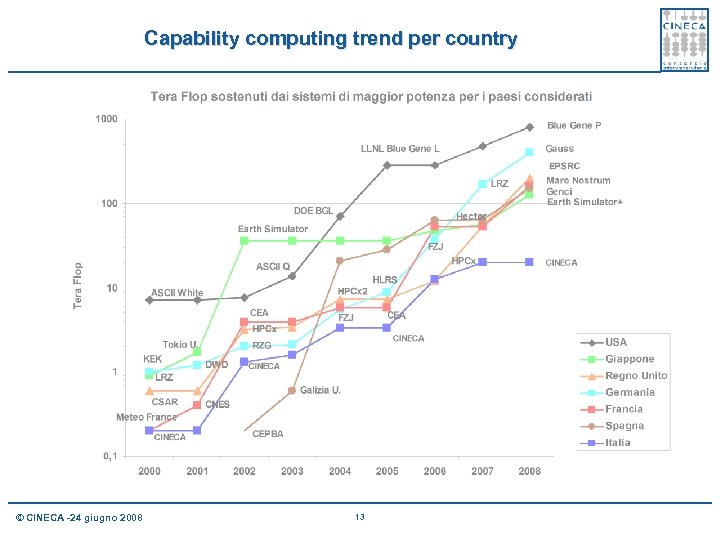 Capability computing trend per country © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 13
Capability computing trend per country © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 13
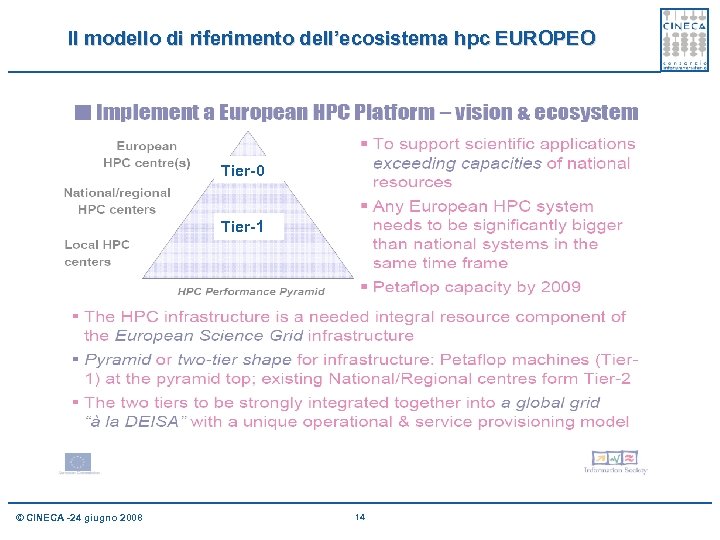 Il modello di riferimento dell’ecosistema hpc EUROPEO Tier-0 Tier-1 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 14
Il modello di riferimento dell’ecosistema hpc EUROPEO Tier-0 Tier-1 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 14
 PRACE Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe Partnership at State Member Level Italy represented by CINECA delegated by the MUR in collaboration with CNR / INFM € 10 Mio EU funded project to define the implementation plan State Member in kind funding for the computing infrastructure implementation, EU co found the transnational access © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 15
PRACE Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe Partnership at State Member Level Italy represented by CINECA delegated by the MUR in collaboration with CNR / INFM € 10 Mio EU funded project to define the implementation plan State Member in kind funding for the computing infrastructure implementation, EU co found the transnational access © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 15
 PRACE Consortium Members 1 (Coord. ) Forschungszentrum Juelich Gmb. H GAUSS Germany 2 Grand Equipement national pour le Calcul I. GENCI France 3 Engineering and Phys. Sciences Research C. EPSRC United Kingdom 4 Barcelona Supercomputing Center BSC Spain 5 CSC Scientific Computing Ltd. CSC Finland 6 ETH Zürich - CSCS ETHZ Switzerland 7 Netherlands Computing Facilities Foundation NCF Netherlands 8 Joh. Kepler Universitaet Linz GUP Austria 9 Swedish National Infrastructure for Comp. SNIC Sweden 10 CINECA Consorzio Interuniversitario MUR Italy 11 Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Centre PSNC Poland 12 UNINETT Sigma AS SIGMA Norway 13 Greek Research and Technology Network GRNET Greece 14 Universidade de Coimbra UC-LCA Portugal © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 16
PRACE Consortium Members 1 (Coord. ) Forschungszentrum Juelich Gmb. H GAUSS Germany 2 Grand Equipement national pour le Calcul I. GENCI France 3 Engineering and Phys. Sciences Research C. EPSRC United Kingdom 4 Barcelona Supercomputing Center BSC Spain 5 CSC Scientific Computing Ltd. CSC Finland 6 ETH Zürich - CSCS ETHZ Switzerland 7 Netherlands Computing Facilities Foundation NCF Netherlands 8 Joh. Kepler Universitaet Linz GUP Austria 9 Swedish National Infrastructure for Comp. SNIC Sweden 10 CINECA Consorzio Interuniversitario MUR Italy 11 Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Centre PSNC Poland 12 UNINETT Sigma AS SIGMA Norway 13 Greek Research and Technology Network GRNET Greece 14 Universidade de Coimbra UC-LCA Portugal © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 16
 Prace Workplane outline • Preparation of the RI as a single legal entity – Legal form and governance structure, funding, procurement, and usage strategy, Peer Review process – HPC Ecosystem links: European and national HPC infrastructures e. g. DEISA, HPC-Europa, the ESFRI projects, EGEE and EGI, communities, vendors and user industries, … • Prepare operation of petascale systems in 2009/2010 – Deployment and benchmarking of prototypes – Porting, optimising, petascaling of applications – Start a process of technology development and assessment for future multi-petascale systems • PRACE will cooperate with other EU projects in these areas – Utilising existing technologies e. g. from DEISA – Confirmed: DEISA, HPC-Europa, EGI © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 17
Prace Workplane outline • Preparation of the RI as a single legal entity – Legal form and governance structure, funding, procurement, and usage strategy, Peer Review process – HPC Ecosystem links: European and national HPC infrastructures e. g. DEISA, HPC-Europa, the ESFRI projects, EGEE and EGI, communities, vendors and user industries, … • Prepare operation of petascale systems in 2009/2010 – Deployment and benchmarking of prototypes – Porting, optimising, petascaling of applications – Start a process of technology development and assessment for future multi-petascale systems • PRACE will cooperate with other EU projects in these areas – Utilising existing technologies e. g. from DEISA – Confirmed: DEISA, HPC-Europa, EGI © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 17
 The DEISA Consortium • Project Initialization in 2002 • • DEISA Start on 1 st of May 2004 with eight partners (CSC, CINECA, EPCC, ECMWF, FZJ, IDRIS, RZG, SARA) Three new partners joined (BSC, HLRS, LRZ) • e. DEISA Start on 1 st of June 2005 • • DEISA End on 30 th of April 2008 e. DEISA End on 31 st of May 2008 • Start of DEISA 2 on 1 st of May 2008 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 18
The DEISA Consortium • Project Initialization in 2002 • • DEISA Start on 1 st of May 2004 with eight partners (CSC, CINECA, EPCC, ECMWF, FZJ, IDRIS, RZG, SARA) Three new partners joined (BSC, HLRS, LRZ) • e. DEISA Start on 1 st of June 2005 • • DEISA End on 30 th of April 2008 e. DEISA End on 31 st of May 2008 • Start of DEISA 2 on 1 st of May 2008 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 18
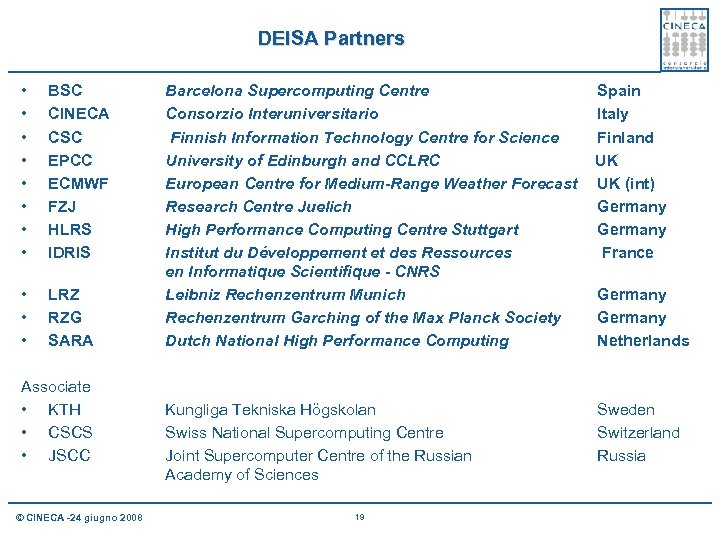 DEISA Partners • • BSC CINECA CSC EPCC ECMWF FZJ HLRS IDRIS • • • LRZ RZG SARA Associate • KTH • CSCS • JSCC © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 Barcelona Supercomputing Centre Consorzio Interuniversitario Finnish Information Technology Centre for Science University of Edinburgh and CCLRC European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast Research Centre Juelich High Performance Computing Centre Stuttgart Institut du Développement et des Ressources en Informatique Scientifique - CNRS Leibniz Rechenzentrum Munich Rechenzentrum Garching of the Max Planck Society Dutch National High Performance Computing Spain Italy Finland UK UK (int) Germany France Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan Swiss National Supercomputing Centre Joint Supercomputer Centre of the Russian Academy of Sciences Sweden Switzerland Russia 19 Germany Netherlands
DEISA Partners • • BSC CINECA CSC EPCC ECMWF FZJ HLRS IDRIS • • • LRZ RZG SARA Associate • KTH • CSCS • JSCC © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 Barcelona Supercomputing Centre Consorzio Interuniversitario Finnish Information Technology Centre for Science University of Edinburgh and CCLRC European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast Research Centre Juelich High Performance Computing Centre Stuttgart Institut du Développement et des Ressources en Informatique Scientifique - CNRS Leibniz Rechenzentrum Munich Rechenzentrum Garching of the Max Planck Society Dutch National High Performance Computing Spain Italy Finland UK UK (int) Germany France Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan Swiss National Supercomputing Centre Joint Supercomputer Centre of the Russian Academy of Sciences Sweden Switzerland Russia 19 Germany Netherlands
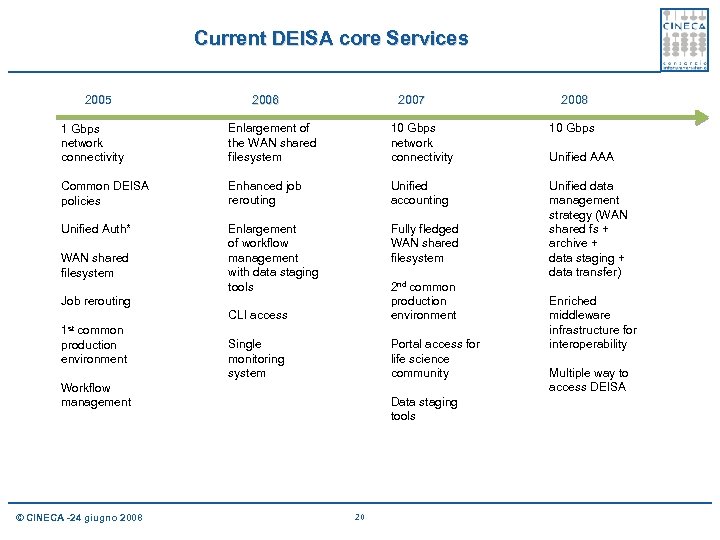 Current DEISA core Services 2005 2007 2006 2008 1 Gbps network connectivity Enlargement of the WAN shared filesystem 10 Gbps network connectivity 10 Gbps Common DEISA policies Enhanced job rerouting Unified accounting Unified Auth* Enlargement of workflow management with data staging tools Fully fledged WAN shared filesystem Unified data management strategy (WAN shared fs + archive + data staging + data transfer) WAN shared filesystem CLI access 2 nd common production environment Single monitoring system Portal access for life science community Job rerouting 1 st common production environment Workflow management © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 Data staging tools 20 Unified AAA Enriched middleware infrastructure for interoperability Multiple way to access DEISA
Current DEISA core Services 2005 2007 2006 2008 1 Gbps network connectivity Enlargement of the WAN shared filesystem 10 Gbps network connectivity 10 Gbps Common DEISA policies Enhanced job rerouting Unified accounting Unified Auth* Enlargement of workflow management with data staging tools Fully fledged WAN shared filesystem Unified data management strategy (WAN shared fs + archive + data staging + data transfer) WAN shared filesystem CLI access 2 nd common production environment Single monitoring system Portal access for life science community Job rerouting 1 st common production environment Workflow management © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 Data staging tools 20 Unified AAA Enriched middleware infrastructure for interoperability Multiple way to access DEISA
 DEISA 2 _ Objectives • Continuation and achievement of the persistency of the DEISA infrastructure – Network – Technology (Global file System, Middleware, …) – Operations • Improvement of technologies • Advance computational sciences in Europe in the supercomputing area • Collaboration with other projects (PRACE, HCP-Europa) and other European HPC centres and communities (ITER, Climate Community, Europhysiome, …) © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 21
DEISA 2 _ Objectives • Continuation and achievement of the persistency of the DEISA infrastructure – Network – Technology (Global file System, Middleware, …) – Operations • Improvement of technologies • Advance computational sciences in Europe in the supercomputing area • Collaboration with other projects (PRACE, HCP-Europa) and other European HPC centres and communities (ITER, Climate Community, Europhysiome, …) © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 21
 DECI: DEISA Extreme Computing Initiative DECI call 2005 51 proposals, 12 European countries involved 30 mio cpu-h requested 29 proposals accepted, 12 mio cpu-h DECI call 2006 41 proposals, 12 European countries involved 28 mio cpu-h requested 23 proposals accepted, 12 mio cpu-h DECI call 2007 63 proposals, 14 European countries involved ((US, Canada, Brazil, Israel) 30 mio cpu-h requested 45 proposal accepted, 20 mio cpu-h 15 European countries so far involved in DECI: Austria Greece Poland Sweden © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 Finland Hungary Portugal Switzerland France Italy Russia UK 22 Germany Netherlands Spain
DECI: DEISA Extreme Computing Initiative DECI call 2005 51 proposals, 12 European countries involved 30 mio cpu-h requested 29 proposals accepted, 12 mio cpu-h DECI call 2006 41 proposals, 12 European countries involved 28 mio cpu-h requested 23 proposals accepted, 12 mio cpu-h DECI call 2007 63 proposals, 14 European countries involved ((US, Canada, Brazil, Israel) 30 mio cpu-h requested 45 proposal accepted, 20 mio cpu-h 15 European countries so far involved in DECI: Austria Greece Poland Sweden © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 Finland Hungary Portugal Switzerland France Italy Russia UK 22 Germany Netherlands Spain
 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 23
© CINECA -24 giugno 2008 23
 The HPC-Europa Consortium • CINECA, Italy Consorzio Interuniversitario di Calcolo, Bologna • EPCC (HPCx), United Kingdom Edinburgh Parallel Computing Centre • BSC, Spain Barcelona Supercomputing Centre • HLRS, Germany High Performance Computing Centre, Stuttgart • IDRIS, France Institut du Développement et des Ressources en Informatique Scientifique, Paris • SARA, Netherlands Stichting Academisch Rekencentrum Amsterdam • PSNC, Poland Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Centre • PARALLAB, Norway HPC Laboratory, Bergen • TCD, Ireland Trinity Centre for HPC, Dublin • CASPUR, Italy Consorzio Interuniversitario, Roma • NTUA, Greece National Technical University of Athens © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 24
The HPC-Europa Consortium • CINECA, Italy Consorzio Interuniversitario di Calcolo, Bologna • EPCC (HPCx), United Kingdom Edinburgh Parallel Computing Centre • BSC, Spain Barcelona Supercomputing Centre • HLRS, Germany High Performance Computing Centre, Stuttgart • IDRIS, France Institut du Développement et des Ressources en Informatique Scientifique, Paris • SARA, Netherlands Stichting Academisch Rekencentrum Amsterdam • PSNC, Poland Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Centre • PARALLAB, Norway HPC Laboratory, Bergen • TCD, Ireland Trinity Centre for HPC, Dublin • CASPUR, Italy Consorzio Interuniversitario, Roma • NTUA, Greece National Technical University of Athens © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 24
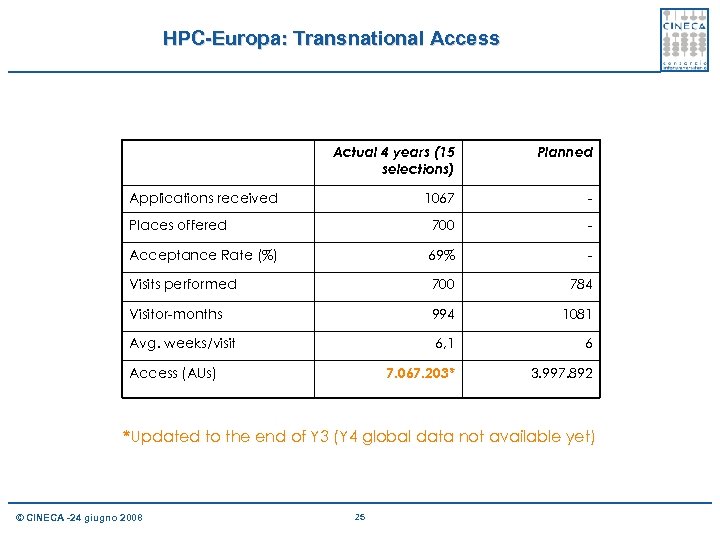 HPC-Europa: Transnational Access Actual 4 years (15 selections) Planned 1067 - Places offered 700 - Acceptance Rate (%) 69% - Visits performed 700 784 Visitor-months 994 1081 Avg. weeks/visit 6, 1 6 7. 067. 203* 3. 997. 892 Applications received Access (AUs) *Updated to the end of Y 3 (Y 4 global data not available yet) © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 25
HPC-Europa: Transnational Access Actual 4 years (15 selections) Planned 1067 - Places offered 700 - Acceptance Rate (%) 69% - Visits performed 700 784 Visitor-months 994 1081 Avg. weeks/visit 6, 1 6 7. 067. 203* 3. 997. 892 Applications received Access (AUs) *Updated to the end of Y 3 (Y 4 global data not available yet) © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 25
 HPC-Europa and the Future • FP 7 Capacities: Infrastructures INFRA-2007 -3. 6: Support to ensure the continuity of FP 6 actions Ø HPC-EUROPA++ • FP 7 -INFRASTRUCTURES-2008 -1 29 November 2007 - 29 February 2008 Ø HPC-EUROPA 2 ØJanuary 1, 2009 – December 31 2012 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 26
HPC-Europa and the Future • FP 7 Capacities: Infrastructures INFRA-2007 -3. 6: Support to ensure the continuity of FP 6 actions Ø HPC-EUROPA++ • FP 7 -INFRASTRUCTURES-2008 -1 29 November 2007 - 29 February 2008 Ø HPC-EUROPA 2 ØJanuary 1, 2009 – December 31 2012 © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 26
 Alcuni spunti di riflessione • CINECA è in fase di procurement per un sistema da 100 Tflop/s che si porrà come il sistema di riferimento nazionale per il capability computing (HPC per progetti challenge) • Il sistema BCX a 5120 core sarà invece il sistema di riferimento per il Capacity Computing • Finalizzazione di una azione utile a rendere disponibile al sistema nazionale della ricerca una infrastruttura per il calcolo scientifico in grado di competere con il resto del mondo e utile a riportare l’Italia in un contesto di rilevanza mondiale • Mantenere una rilevanza europea in termini di potenza di calcolo in modo da cogliere le opportunità che si presenteranno nel Settimo Programma quadro: Tier 0 (Calcolatore Europeo) e Tier 1 (Calcolatori Nazionali alla DEISA) e Tier 2 (Centri Regionali) • E’ importante l’interazione e l’integrazione sinergica con i centri HPC locali, regionali e tematici (Tier 2) • Nuove metodologie algoritmiche innovative e scalabili (enormi quantità di dati) • Sviluppo di metodologie algoritmiche e porting di applicazioni a supporto della ricerca accademica e dell’industria • Supporto alla ricerca scientifica e industriale tramite un programma di grant ad hoc • Programma di formazione su metodologie innovative a supporto della ricerca accademica e industriale • Favorire la partecipazione a progetti europei anche in sinergia con l’Industria © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 27
Alcuni spunti di riflessione • CINECA è in fase di procurement per un sistema da 100 Tflop/s che si porrà come il sistema di riferimento nazionale per il capability computing (HPC per progetti challenge) • Il sistema BCX a 5120 core sarà invece il sistema di riferimento per il Capacity Computing • Finalizzazione di una azione utile a rendere disponibile al sistema nazionale della ricerca una infrastruttura per il calcolo scientifico in grado di competere con il resto del mondo e utile a riportare l’Italia in un contesto di rilevanza mondiale • Mantenere una rilevanza europea in termini di potenza di calcolo in modo da cogliere le opportunità che si presenteranno nel Settimo Programma quadro: Tier 0 (Calcolatore Europeo) e Tier 1 (Calcolatori Nazionali alla DEISA) e Tier 2 (Centri Regionali) • E’ importante l’interazione e l’integrazione sinergica con i centri HPC locali, regionali e tematici (Tier 2) • Nuove metodologie algoritmiche innovative e scalabili (enormi quantità di dati) • Sviluppo di metodologie algoritmiche e porting di applicazioni a supporto della ricerca accademica e dell’industria • Supporto alla ricerca scientifica e industriale tramite un programma di grant ad hoc • Programma di formazione su metodologie innovative a supporto della ricerca accademica e industriale • Favorire la partecipazione a progetti europei anche in sinergia con l’Industria © CINECA -24 giugno 2008 27


