week-1.1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 21
 IITU Operating systems { introduction IS&MM Department Lecture 1. 1 tutor: Naimanov Yerbol email: yerbol. naimanov@gmail. com
IITU Operating systems { introduction IS&MM Department Lecture 1. 1 tutor: Naimanov Yerbol email: yerbol. naimanov@gmail. com
 Overview • • 2 Structure of computer systems. What is software, types of software. What is an operating system, types of OS. Introduction to UNIX operating system.
Overview • • 2 Structure of computer systems. What is software, types of software. What is an operating system, types of OS. Introduction to UNIX operating system.
 Structure of computer systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components, which are the electronic devices and electromechanical devices, such as the processors, memory modules, disk units, keyboard, screen, and other devices. Software components, such as the application programs, operating system, and other programs. 3
Structure of computer systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components, which are the electronic devices and electromechanical devices, such as the processors, memory modules, disk units, keyboard, screen, and other devices. Software components, such as the application programs, operating system, and other programs. 3
 Structure of computer systems The basic structure of a computer normally consists of one or more of the following hardware components: - The CPU or the central processing unit, also called the processor - RAM or random access memory, also known as main memory - The massive storage devices, which store large amounts of data and programs in permanent form - The I/O devices or input/output units - The system bus, which provides interconnections for all components of the system 4
Structure of computer systems The basic structure of a computer normally consists of one or more of the following hardware components: - The CPU or the central processing unit, also called the processor - RAM or random access memory, also known as main memory - The massive storage devices, which store large amounts of data and programs in permanent form - The I/O devices or input/output units - The system bus, which provides interconnections for all components of the system 4
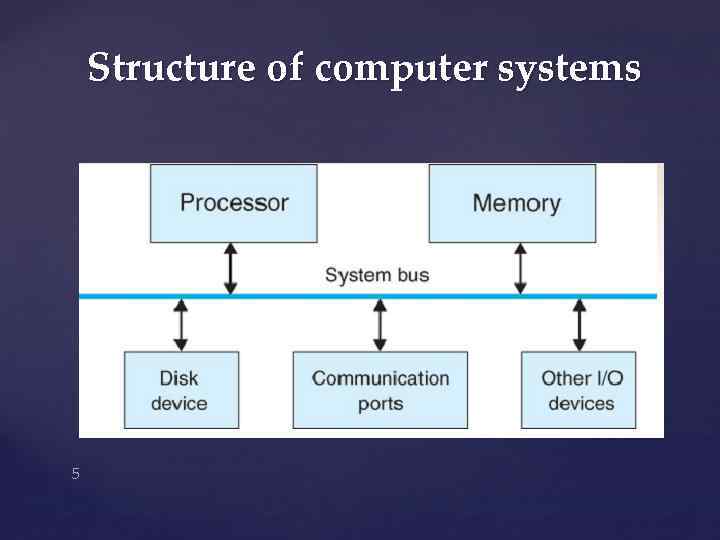 Structure of computer systems 5
Structure of computer systems 5
 Software • A program is a sequence of instructions to be executed in the computer for the purpose of carrying out some specific task. • The software components are the collection of programs that execute in the computer. • Two general types of software components are: - System software 6 - Application software
Software • A program is a sequence of instructions to be executed in the computer for the purpose of carrying out some specific task. • The software components are the collection of programs that execute in the computer. • Two general types of software components are: - System software 6 - Application software
 Types of software • The system software is the set of programs that control the activities and functions of the various hardware components. • The system software forms an environment for the programmers to develop and execute their programs (known as application software). • Application programs are developed by 7 individuals and organizations for solving specific problems.
Types of software • The system software is the set of programs that control the activities and functions of the various hardware components. • The system software forms an environment for the programmers to develop and execute their programs (known as application software). • Application programs are developed by 7 individuals and organizations for solving specific problems.
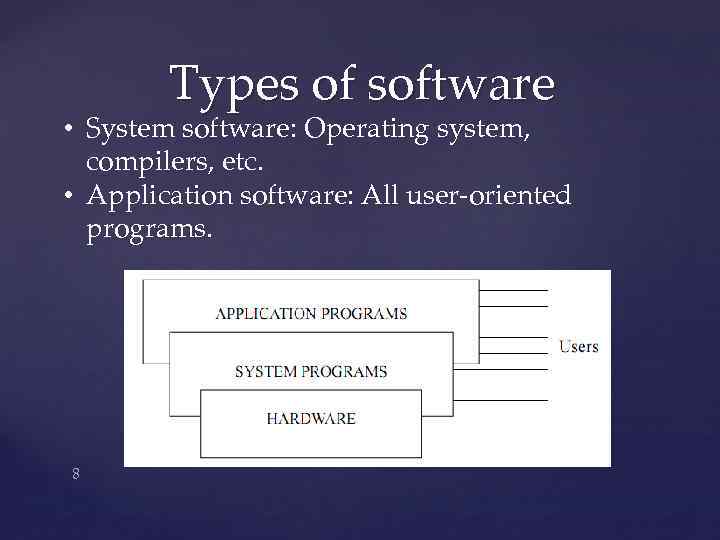 Types of software • System software: Operating system, compilers, etc. • Application software: All user-oriented programs. 8
Types of software • System software: Operating system, compilers, etc. • Application software: All user-oriented programs. 8
 What is an operating system? • A large and complex software component for the operation and control of the computer system. • It acts as an intermediary between a user and the computer system. • Examples of OS: Unix, MS Windows, Mac OS, Solaris, Linux, etc. 9
What is an operating system? • A large and complex software component for the operation and control of the computer system. • It acts as an intermediary between a user and the computer system. • Examples of OS: Unix, MS Windows, Mac OS, Solaris, Linux, etc. 9
 OS and programs • Operating systems provide a software platform on top of which other "application" programs can run. • The application programs must be written to run on a particular operating system. • So, your choice of operating system determines what application software you can run. 10
OS and programs • Operating systems provide a software platform on top of which other "application" programs can run. • The application programs must be written to run on a particular operating system. • So, your choice of operating system determines what application software you can run. 10
 Operating system user interfaces • Three levels of interface: • 1) Graphics GUI (icons, windows, buttons) • 2) Command level (shell) • 3) System calls (invoked from user programs) 11
Operating system user interfaces • Three levels of interface: • 1) Graphics GUI (icons, windows, buttons) • 2) Command level (shell) • 3) System calls (invoked from user programs) 11
 Types of OS • Generally, there are four types, based on the type of computer they control and the sort of applications they support. • 1) Single-user, single task: this type manages the computer so that one user can effectively do one thing at a time. 12
Types of OS • Generally, there are four types, based on the type of computer they control and the sort of applications they support. • 1) Single-user, single task: this type manages the computer so that one user can effectively do one thing at a time. 12
 Types of OS • 2) Multi-user, multi-task: allows two or more users to run programs at the same time. Some operating systems permit hundreds or even thousands of concurrent users. 13
Types of OS • 2) Multi-user, multi-task: allows two or more users to run programs at the same time. Some operating systems permit hundreds or even thousands of concurrent users. 13
 Types of OS • 3) Real Time Operating Systems: used to control machinery, scientific instruments, and industrial systems. • Resources are managed so that a particular operation executes precisely the same every time. 14
Types of OS • 3) Real Time Operating Systems: used to control machinery, scientific instruments, and industrial systems. • Resources are managed so that a particular operation executes precisely the same every time. 14
 Types of OS • 4) Single-user, Multi-tasking: operating systems that will let a single user have several programs in operation at the same time. 15
Types of OS • 4) Single-user, Multi-tasking: operating systems that will let a single user have several programs in operation at the same time. 15
 What is UNIX? • UNIX is an operating system which was first developed in the 1960 s, and has been under constant development ever since. It is a multi -user, multi-tasking system for servers, desktops and laptops. • There are many different versions of UNIX, although they share common similarities. The most popular varieties of UNIX are Sun Solaris, GNU/Linux, and Mac. OS X. 16
What is UNIX? • UNIX is an operating system which was first developed in the 1960 s, and has been under constant development ever since. It is a multi -user, multi-tasking system for servers, desktops and laptops. • There are many different versions of UNIX, although they share common similarities. The most popular varieties of UNIX are Sun Solaris, GNU/Linux, and Mac. OS X. 16
 What is UNIX? • The UNIX operating system is made up of three parts; the kernel, the shell and the programs. • The kernel of UNIX is the hub of the operating system: it allocates time and memory to programs and handles the filestore and communications in response to system calls. • The shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel. When a user logs in, the login program checks the username and password, and then starts another program called the shell. The shell is a 17 command line interpreter.
What is UNIX? • The UNIX operating system is made up of three parts; the kernel, the shell and the programs. • The kernel of UNIX is the hub of the operating system: it allocates time and memory to programs and handles the filestore and communications in response to system calls. • The shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel. When a user logs in, the login program checks the username and password, and then starts another program called the shell. The shell is a 17 command line interpreter.
 What is UNIX? • As an illustration of the way that the shell and the kernel work together, suppose a user types rm myfile (which has the effect of removing the file “myfile”). The shell searches the filestore for the file containing the program rm, and then requests the kernel, through system calls, to execute the program “rm” on “myfile”. When the process rm myfile has finished running, the shell then returns the UNIX prompt to the user, indicating that it is waiting for further commands. 18
What is UNIX? • As an illustration of the way that the shell and the kernel work together, suppose a user types rm myfile (which has the effect of removing the file “myfile”). The shell searches the filestore for the file containing the program rm, and then requests the kernel, through system calls, to execute the program “rm” on “myfile”. When the process rm myfile has finished running, the shell then returns the UNIX prompt to the user, indicating that it is waiting for further commands. 18
 What is Linux? • A freely available version of the UNIX operating system • Started by Linus Torvalds in 1991 • Programmers from around the world contribute code 19
What is Linux? • A freely available version of the UNIX operating system • Started by Linus Torvalds in 1991 • Programmers from around the world contribute code 19
 Next Lecture: • Linux file system structure, users. 20
Next Lecture: • Linux file system structure, users. 20
 Thanks for attention! 21
Thanks for attention! 21


