b5c33df94e70251ce313ff64826e5590.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 IIS Security 101 Jeni Li for WNUG/CCC April 1, 2004
IIS Security 101 Jeni Li for WNUG/CCC April 1, 2004
 Please be polite n n This file is being shared on the Web in raw Power. Point format. I put a lot of time into creating and commenting this file. For permission to share it outside of ASU, or to use it in presentations, please contact me first. Thanks!
Please be polite n n This file is being shared on the Web in raw Power. Point format. I put a lot of time into creating and commenting this file. For permission to share it outside of ASU, or to use it in presentations, please contact me first. Thanks!
 Who am I n n n n Web geek at ASU Polytechnic campus Tri-campus veteran Author of IIS item for 2002/3 SANS Top 20 Local mentor for SANS Board member of Infra. Gard and HTCIA Member of MCC IA Advisory Board Member of Infosec Academy Advisory Board Somewhat of an Apache bigot
Who am I n n n n Web geek at ASU Polytechnic campus Tri-campus veteran Author of IIS item for 2002/3 SANS Top 20 Local mentor for SANS Board member of Infra. Gard and HTCIA Member of MCC IA Advisory Board Member of Infosec Academy Advisory Board Somewhat of an Apache bigot
 What we’ll cover this morning n n Common types of attacks against Web servers A layered (host-based) defense against those attacks Three tools used to secure IIS What’s different about IIS 6
What we’ll cover this morning n n Common types of attacks against Web servers A layered (host-based) defense against those attacks Three tools used to secure IIS What’s different about IIS 6
 Common types of attacks n Directory traversal – GET /scripts/. . /winnt/system 32/cmd. exe /c+dir – GET /scripts/. . %5 c. . /winnt/system 32/cmd. exe /c+dir n Examples – Code Blue, Nimda – Socket 80 n Effects – Unauthorized file access – Execution of arbitrary commands
Common types of attacks n Directory traversal – GET /scripts/. . /winnt/system 32/cmd. exe /c+dir – GET /scripts/. . %5 c. . /winnt/system 32/cmd. exe /c+dir n Examples – Code Blue, Nimda – Socket 80 n Effects – Unauthorized file access – Execution of arbitrary commands
 Common types of attacks n Buffer overflows – Long requests with machine code embedded n Example – Web. DAV ntdll. dll exploit n Effects – Denial of service – Execution of arbitrary code
Common types of attacks n Buffer overflows – Long requests with machine code embedded n Example – Web. DAV ntdll. dll exploit n Effects – Denial of service – Execution of arbitrary code
 Common types of attacks n Preprocessor exploits – Requests for. idq, . printer, et cetera – Requests with unusual HTTP verbs; e. g. , PUT n Examples – Code Red, Code Red II n Effects – Denial of service – Execution of arbitrary commands
Common types of attacks n Preprocessor exploits – Requests for. idq, . printer, et cetera – Requests with unusual HTTP verbs; e. g. , PUT n Examples – Code Red, Code Red II n Effects – Denial of service – Execution of arbitrary commands
 Common types of attacks n Application exploits – Requests for executables you’re not using n Examples – newdsn. exe, ism. dll – Sample applications – Anything in /iisadmin or /MSADC n Effects – Denial of service – Unauthorized file access – Execution of arbitrary commands
Common types of attacks n Application exploits – Requests for executables you’re not using n Examples – newdsn. exe, ism. dll – Sample applications – Anything in /iisadmin or /MSADC n Effects – Denial of service – Unauthorized file access – Execution of arbitrary commands
 Layers of defense n Harden the OS – – Use Gold Standard or similar templates Eliminate unnecessary services Set appropriate file space permissions Patch, patch
Layers of defense n Harden the OS – – Use Gold Standard or similar templates Eliminate unnecessary services Set appropriate file space permissions Patch, patch
 Layers of defense n Strip down the Web service – – Move document root and Web log directories Eliminate unnecessary mappings Eliminate sample applications Disable Web. DAV unless it’s an absolute requirement
Layers of defense n Strip down the Web service – – Move document root and Web log directories Eliminate unnecessary mappings Eliminate sample applications Disable Web. DAV unless it’s an absolute requirement
 Layers of defense n Restrict file and URL access – Deny Web user access to certain system files – Set document directory permissions according to the principle of least privilege – Disallow known bad extensions (or, if you can, only allow known good ones) – Resolve URLs completely, then filter them
Layers of defense n Restrict file and URL access – Deny Web user access to certain system files – Set document directory permissions according to the principle of least privilege – Disallow known bad extensions (or, if you can, only allow known good ones) – Resolve URLs completely, then filter them
 Layers of defense n Hide in plain sight – Bind the Web service to the FQDN – Eliminate the Server header – Modify or eliminate the content-location header – Conceal the existence of preprocessed content
Layers of defense n Hide in plain sight – Bind the Web service to the FQDN – Eliminate the Server header – Modify or eliminate the content-location header – Conceal the existence of preprocessed content
 Layers of defense n Keep an eye on it – – Spikes in disk usage Unusual or unexpected network traffic Interesting log entries Audit the right stuff
Layers of defense n Keep an eye on it – – Spikes in disk usage Unusual or unexpected network traffic Interesting log entries Audit the right stuff
 Sound like a lot of work? ? ?
Sound like a lot of work? ? ?
 Three wonderful tools n n Security Configuration & Analysis snap-in IIS Lockdown Wizard URLScan filter. . . plus a little bit of manual labor
Three wonderful tools n n Security Configuration & Analysis snap-in IIS Lockdown Wizard URLScan filter. . . plus a little bit of manual labor
 SCAT snap-in n Configure security-related settings according to predefined templates (no regedit required!) n Good templates available from NSA, NIST, and Center for Internet Security (www. cisecurity. org) n Review/approve/deny changes before applying Can create/modify your own templates Note: Group policy n n
SCAT snap-in n Configure security-related settings according to predefined templates (no regedit required!) n Good templates available from NSA, NIST, and Center for Internet Security (www. cisecurity. org) n Review/approve/deny changes before applying Can create/modify your own templates Note: Group policy n n
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 ASU’s login warning banner
ASU’s login warning banner
 Back to using SCAT
Back to using SCAT
 Using SCAT
Using SCAT
 IIS Lockdown Wizard n www. microsoft. com/technet/security/tools/locktool. mspx n Role-based configuration Enable/disable/remove inetinfo services Remove sample applications Enable/disable built-in ISAPI mappings Set restrictive permissions on system files n n – e. g. , cmd. exe, tftp. exe – includes dllcache directory n Install URLScan
IIS Lockdown Wizard n www. microsoft. com/technet/security/tools/locktool. mspx n Role-based configuration Enable/disable/remove inetinfo services Remove sample applications Enable/disable built-in ISAPI mappings Set restrictive permissions on system files n n – e. g. , cmd. exe, tftp. exe – includes dllcache directory n Install URLScan
 Using IIS Lockdown
Using IIS Lockdown
 Using IIS Lockdown
Using IIS Lockdown
 Using IIS Lockdown
Using IIS Lockdown
 Using IIS Lockdown
Using IIS Lockdown
 Using IIS Lockdown
Using IIS Lockdown
 Using IIS Lockdown
Using IIS Lockdown
 URLScan n n n c: winntsystem 32inetsrvurlscan. ini Extensions to allow/disallow HTTP verbs to allow/disallow URL character patterns to disallow Resolve Unicoded URLs Modify or remove the Server header
URLScan n n n c: winntsystem 32inetsrvurlscan. ini Extensions to allow/disallow HTTP verbs to allow/disallow URL character patterns to disallow Resolve Unicoded URLs Modify or remove the Server header
 Manual labor: Bind to FQDN
Manual labor: Bind to FQDN
 Conceal interactive content
Conceal interactive content
 Eliminate revealing headers
Eliminate revealing headers
 OK, so what about IIS 6? n n Performance Security Upgrade issues Gotchas
OK, so what about IIS 6? n n Performance Security Upgrade issues Gotchas
 Performance!! n n n Delivers files 90% faster than IIS 5 Built-in HTTP compression faster, better Application isolation faster Application pool recycling Cleaner separation of user, kernel modes
Performance!! n n n Delivers files 90% faster than IIS 5 Built-in HTTP compression faster, better Application isolation faster Application pool recycling Cleaner separation of user, kernel modes
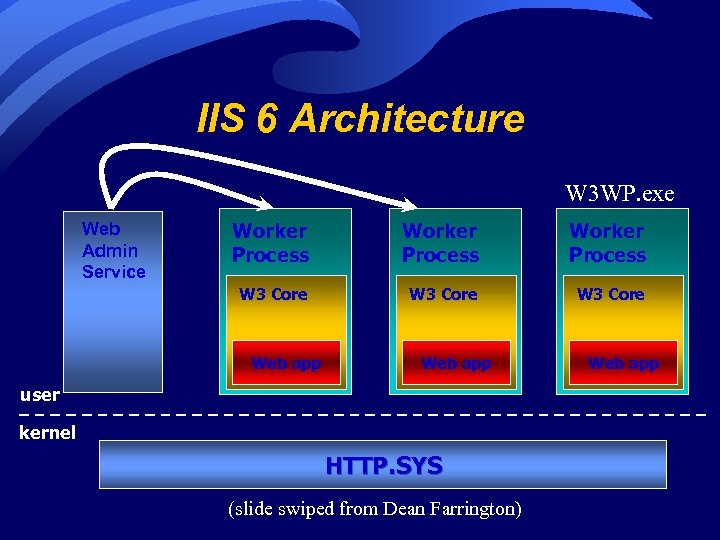 IIS 6 Architecture W 3 WP. exe Web Admin Service Worker Process W 3 Core Web app Worker Recycle Process time! W 3 Core Web app user kernel HTTP. SYS (slide swiped from Dean Farrington) Worker Process W 3 Core Web app
IIS 6 Architecture W 3 WP. exe Web Admin Service Worker Process W 3 Core Web app Worker Recycle Process time! W 3 Core Web app user kernel HTTP. SYS (slide swiped from Dean Farrington) Worker Process W 3 Core Web app
 Security n Not installed by default – And install can be disabled via Group Policy n Runs without SYSTEM context, hallelujah! – Restricted Network. Service user n n n Clean default install - static HTML only IIS_WPG group for application pool userids URL authorization – Role-based user access to URLs, not just files and directories
Security n Not installed by default – And install can be disabled via Group Policy n Runs without SYSTEM context, hallelujah! – Restricted Network. Service user n n n Clean default install - static HTML only IIS_WPG group for application pool userids URL authorization – Role-based user access to URLs, not just files and directories
 Some other new features n n Total. NET domination Authentication –. NET Passport authentication – Advanced Digest authentication n Cryptography – SSL 3 support – Support for third-party Crypto. API providers
Some other new features n n Total. NET domination Authentication –. NET Passport authentication – Advanced Digest authentication n Cryptography – SSL 3 support – Support for third-party Crypto. API providers
 Upgrade issues n New permissions settings may affect applications that write to Web space n No Lockdown Wizard pre-upgrade ==> Web service disabled on upgrade n Anecdotes indicating lots of trouble
Upgrade issues n New permissions settings may affect applications that write to Web space n No Lockdown Wizard pre-upgrade ==> Web service disabled on upgrade n Anecdotes indicating lots of trouble
 Gotchas n Windows 2003 Web Edition – Stripped-down, single-function server F e. g. , can’t be a DC, CA, or VPN gateway – Supports a limited amount of RAM (2 GB) – Does not include Internet Connection Filtering
Gotchas n Windows 2003 Web Edition – Stripped-down, single-function server F e. g. , can’t be a DC, CA, or VPN gateway – Supports a limited amount of RAM (2 GB) – Does not include Internet Connection Filtering
 Gotchas n Remote administration – Multiple vulnerabilities already – Not enabled by default, thank goodness n inetinfo. exe is still there – – ftp, smtp, nntp IIS 5 isolation mode Runs with SYSTEM context May be enabled by default on upgrades
Gotchas n Remote administration – Multiple vulnerabilities already – Not enabled by default, thank goodness n inetinfo. exe is still there – – ftp, smtp, nntp IIS 5 isolation mode Runs with SYSTEM context May be enabled by default on upgrades
 IIS 5 isolation mode
IIS 5 isolation mode
 Questions? ? jeni. li@asu. edu
Questions? ? jeni. li@asu. edu


