5dcc4879fed56ee6df9f75504b2b1973.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 IIIIIIIII Point of care testing (POCT) Dr K. A. C. Wickramaratne
IIIIIIIII Point of care testing (POCT) Dr K. A. C. Wickramaratne
 Definition Goals of POCT Uses Is it a rapid test? Tests available Advantages Disadvantages Management issues How to assure quality Accreditation of POCT
Definition Goals of POCT Uses Is it a rapid test? Tests available Advantages Disadvantages Management issues How to assure quality Accreditation of POCT
 What is POCT ? Analytical test performed outside the laboratory by health care providers Performance of tests –“bed side” “POCT is medical testing at or near the site of care. ” “Point‐of‐care testing (POCT) refers to any testing conducted outside a lab, in a hospital, in a clinic or by a health care organization providing ambulatory care.
What is POCT ? Analytical test performed outside the laboratory by health care providers Performance of tests –“bed side” “POCT is medical testing at or near the site of care. ” “Point‐of‐care testing (POCT) refers to any testing conducted outside a lab, in a hospital, in a clinic or by a health care organization providing ambulatory care.
 Goals of POCT Improve quality of patient care Enhance efficiency of patient care Increase physician and patient satisfaction Improve patient education Decrease liability risk ? ? Minimize burden at central level
Goals of POCT Improve quality of patient care Enhance efficiency of patient care Increase physician and patient satisfaction Improve patient education Decrease liability risk ? ? Minimize burden at central level
 Where POCT is used? ICU, Accident and emergency department Operating theatres Dialysis units, Neonatal units OPD, casualty wards, domestic care (health care team) Other special treatment centers – DF Mass disasters
Where POCT is used? ICU, Accident and emergency department Operating theatres Dialysis units, Neonatal units OPD, casualty wards, domestic care (health care team) Other special treatment centers – DF Mass disasters
 Does the POCT need to be an instrument‐free dipstick or RDT? • Widely used ASSURED criteria for rapid tests by WHO: S = sensitive S = specific U = user friendly ‐simple to perform R = robust and rapid (results available in less than 30 minutes) E = equipment free A = affordable D = deliverable to those who need the test • The type of device does not define a POCT test. POCT range from simplest dipsticks to sophisticated automated molecular tests on portable analysers and imaging systems.
Does the POCT need to be an instrument‐free dipstick or RDT? • Widely used ASSURED criteria for rapid tests by WHO: S = sensitive S = specific U = user friendly ‐simple to perform R = robust and rapid (results available in less than 30 minutes) E = equipment free A = affordable D = deliverable to those who need the test • The type of device does not define a POCT test. POCT range from simplest dipsticks to sophisticated automated molecular tests on portable analysers and imaging systems.

 What tests available? POCT ranges between three levels of complexity, simple procedures ‐ capillary urine glucose testing, dipstick moderate‐complexity microscopy or procedures ‐ of urine high‐complexity procedures ‐ PCR, TEG, resonant micro sensing platform for ultrasonic characterization of blood coagulation.
What tests available? POCT ranges between three levels of complexity, simple procedures ‐ capillary urine glucose testing, dipstick moderate‐complexity microscopy or procedures ‐ of urine high‐complexity procedures ‐ PCR, TEG, resonant micro sensing platform for ultrasonic characterization of blood coagulation.
 Advantages Identify critical diagnosis / screen quickly Evidence available on site Speed – less turnaround time ! Smaller sample volume – less waste Full time equivalent (FTI) Impact doctor patient confidence Improved cost outcome and patient education saving – (not always !)
Advantages Identify critical diagnosis / screen quickly Evidence available on site Speed – less turnaround time ! Smaller sample volume – less waste Full time equivalent (FTI) Impact doctor patient confidence Improved cost outcome and patient education saving – (not always !)
 Disadvantages Lower accuracy and precision – future can be promising Less skilled personnel to perform tests – can be trained Higher supply cost ‐ ? ? Lack of comparability – need standardization Lack of data systems - Difficulty in assuring quality- Difficulty in managing testing-
Disadvantages Lower accuracy and precision – future can be promising Less skilled personnel to perform tests – can be trained Higher supply cost ‐ ? ? Lack of comparability – need standardization Lack of data systems - Difficulty in assuring quality- Difficulty in managing testing-
 Management issues Who should perform ? Responsibility ? Ward staff or Laboratory Documentation and monitoring Doctor or a nursing officer - training Test results not linked to devices, no printouts, no signatures, no validation ! Maintenance
Management issues Who should perform ? Responsibility ? Ward staff or Laboratory Documentation and monitoring Doctor or a nursing officer - training Test results not linked to devices, no printouts, no signatures, no validation ! Maintenance
 Quality assurance – Test calibration – metrological traceability IQC ‐ Very difficult – Test method – validation – ? Compared with gold standard ? EQA – not available freely Market driven concerns Highly competitive and rapidly evolving The device available today may not be usable next year Repetition in both POCT and central – test duplication
Quality assurance – Test calibration – metrological traceability IQC ‐ Very difficult – Test method – validation – ? Compared with gold standard ? EQA – not available freely Market driven concerns Highly competitive and rapidly evolving The device available today may not be usable next year Repetition in both POCT and central – test duplication
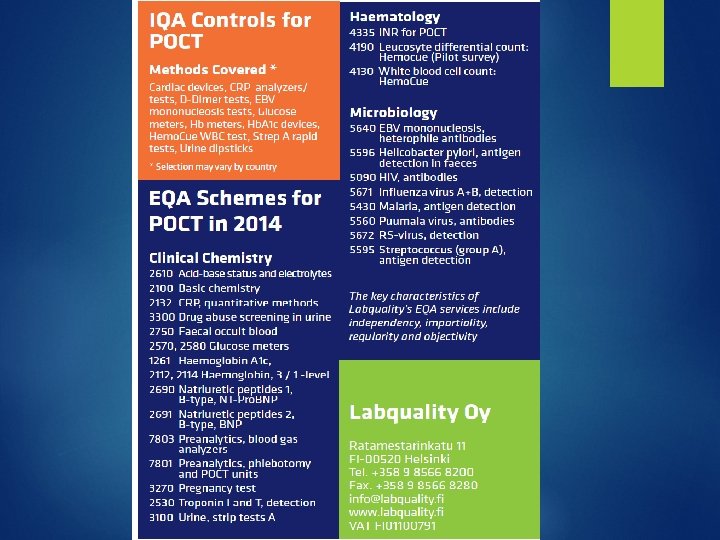
 How to assure quality Selection of a validated method with traceability method with a reasonable accuracy, precision and measurement uncertainty Selection of a method with ability to monitor performance (IQC and EQA) Setting up POCT management team Training of personnel Establishing documentation system Preparation of SOPs/manuals
How to assure quality Selection of a validated method with traceability method with a reasonable accuracy, precision and measurement uncertainty Selection of a method with ability to monitor performance (IQC and EQA) Setting up POCT management team Training of personnel Establishing documentation system Preparation of SOPs/manuals


 Accreditation of POCT. ! § Accreditation as per ISO 22870 ; Point of care testing requirements for quality and competence § Similar to ISO 15189 § All the requirements of ISO 15189 and ISO 22870 § Management requirements § § QMS, quality objectives, preventive, corrective , review Technical requirements § Personnel , training, accommodation and environment, equipment, pre ‐ examination, post examination. . .
Accreditation of POCT. ! § Accreditation as per ISO 22870 ; Point of care testing requirements for quality and competence § Similar to ISO 15189 § All the requirements of ISO 15189 and ISO 22870 § Management requirements § § QMS, quality objectives, preventive, corrective , review Technical requirements § Personnel , training, accommodation and environment, equipment, pre ‐ examination, post examination. . .
 Thank you
Thank you


