43a92bba6b9b342c6841ca36a643954d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
 IFIP-UNU ADVANCED COURSE ON NETWORKING AND SECURITY Module II-Wireless Communications Section 2 The IEEE 802. 11 Protocol 2 -1
IFIP-UNU ADVANCED COURSE ON NETWORKING AND SECURITY Module II-Wireless Communications Section 2 The IEEE 802. 11 Protocol 2 -1
 Learning Objectives • Identify the IEEE 802. standards. • Identify the IEEE 802. 11 standards. • Understand the MAC and PHY layers of 802. 11 • Identify which client operating systems are supported. • Determine the status of a client card by observing the indicator lights. • Install and configure a Cisco Aironet PC Card. 2 -2
Learning Objectives • Identify the IEEE 802. standards. • Identify the IEEE 802. 11 standards. • Understand the MAC and PHY layers of 802. 11 • Identify which client operating systems are supported. • Determine the status of a client card by observing the indicator lights. • Install and configure a Cisco Aironet PC Card. 2 -2
 Overview This chapter will cover the IEEE 802. 11 WLAN (WLAN) standards in detail, including data link and physical layer specifications. Throughout this module and this course, the terms IEEE and 802 are used often. This module provides a short overview of IEEE and the 802 committee. The MAC and physical layer services that have been standardized will be discussed. Finally, client adapters, driver types, and client support will also be discussed. 2 -3
Overview This chapter will cover the IEEE 802. 11 WLAN (WLAN) standards in detail, including data link and physical layer specifications. Throughout this module and this course, the terms IEEE and 802 are used often. This module provides a short overview of IEEE and the 802 committee. The MAC and physical layer services that have been standardized will be discussed. Finally, client adapters, driver types, and client support will also be discussed. 2 -3
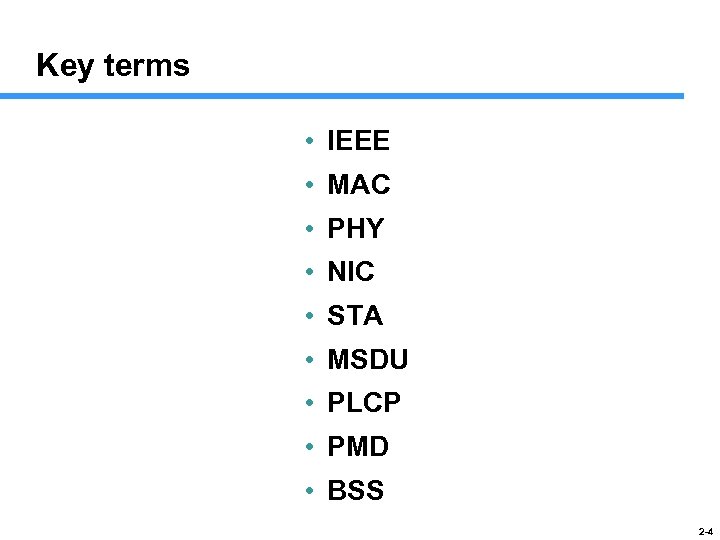 Key terms • IEEE • MAC • PHY • NIC • STA • MSDU • PLCP • PMD • BSS 2 -4
Key terms • IEEE • MAC • PHY • NIC • STA • MSDU • PLCP • PMD • BSS 2 -4
 802. 11 Standards 2 -5
802. 11 Standards 2 -5
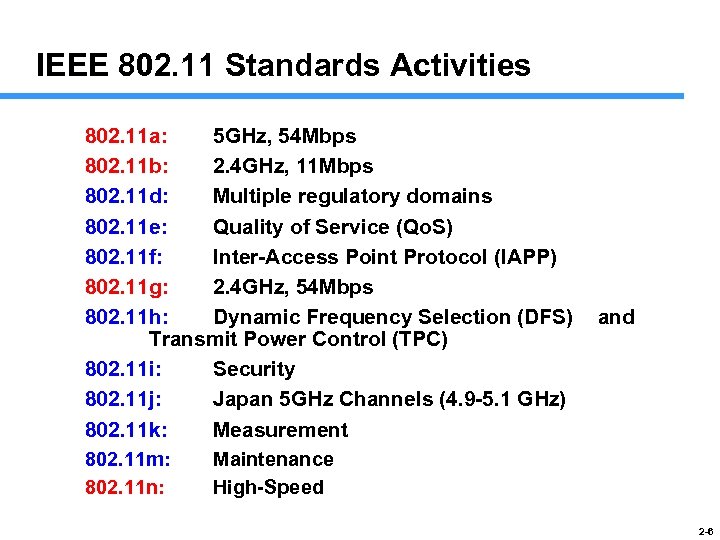 IEEE 802. 11 Standards Activities 802. 11 a: 5 GHz, 54 Mbps 802. 11 b: 2. 4 GHz, 11 Mbps 802. 11 d: Multiple regulatory domains 802. 11 e: Quality of Service (Qo. S) 802. 11 f: Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP) 802. 11 g: 2. 4 GHz, 54 Mbps 802. 11 h: Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) Transmit Power Control (TPC) 802. 11 i: Security 802. 11 j: Japan 5 GHz Channels (4. 9 -5. 1 GHz) 802. 11 k: Measurement 802. 11 m: Maintenance 802. 11 n: High-Speed and 2 -6
IEEE 802. 11 Standards Activities 802. 11 a: 5 GHz, 54 Mbps 802. 11 b: 2. 4 GHz, 11 Mbps 802. 11 d: Multiple regulatory domains 802. 11 e: Quality of Service (Qo. S) 802. 11 f: Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP) 802. 11 g: 2. 4 GHz, 54 Mbps 802. 11 h: Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) Transmit Power Control (TPC) 802. 11 i: Security 802. 11 j: Japan 5 GHz Channels (4. 9 -5. 1 GHz) 802. 11 k: Measurement 802. 11 m: Maintenance 802. 11 n: High-Speed and 2 -6
 802. 11 a / 5 GHz Band Data rates supported: 54, 48, 36, 24, 12, and 6 Mbps • Client will automatically “downshift” to lower data rate when it gets further from AP 23 Countries have approved the use of 802. 11 a products: • U. S. Australia Austria Denmark France Sweden New Zealand Singapore Taiwan Argentina • U. K. Germany Norway Portugal Canada Belgium Netherlands Poland Switzerland Mexico Ireland Japan Finland 802. 11 h will ultimately permit worldwide usage of WLANs @ 5 GHz • Transmit Power Control (TPC) • Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) 5. 470 -5. 725 GHz band being opened up (11 more channels) • This new 5. 47 -5. 725 GHz band, plus 5. 25 -5. 35 GHz UNII-2 band, will require DFS • Current UNII-2 products in the market will likely be grandfathered (i. e. no DFS) 5 GHz band has more channels than 2. 4 GHz band • UNII-1 + UNII-2 = 8 channels (plus 11 future channels) vs. 3 channels for 2. 4 GHz • However, depending on distance between AP’s, you may only be able to use half of the 5 GHz channels due to adjacent channel interference 5 GHz band subject to less interference than 2. 4 GHz band • However, 2. 4 GHz interference not a major problem in most business environments 2 -7
802. 11 a / 5 GHz Band Data rates supported: 54, 48, 36, 24, 12, and 6 Mbps • Client will automatically “downshift” to lower data rate when it gets further from AP 23 Countries have approved the use of 802. 11 a products: • U. S. Australia Austria Denmark France Sweden New Zealand Singapore Taiwan Argentina • U. K. Germany Norway Portugal Canada Belgium Netherlands Poland Switzerland Mexico Ireland Japan Finland 802. 11 h will ultimately permit worldwide usage of WLANs @ 5 GHz • Transmit Power Control (TPC) • Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) 5. 470 -5. 725 GHz band being opened up (11 more channels) • This new 5. 47 -5. 725 GHz band, plus 5. 25 -5. 35 GHz UNII-2 band, will require DFS • Current UNII-2 products in the market will likely be grandfathered (i. e. no DFS) 5 GHz band has more channels than 2. 4 GHz band • UNII-1 + UNII-2 = 8 channels (plus 11 future channels) vs. 3 channels for 2. 4 GHz • However, depending on distance between AP’s, you may only be able to use half of the 5 GHz channels due to adjacent channel interference 5 GHz band subject to less interference than 2. 4 GHz band • However, 2. 4 GHz interference not a major problem in most business environments 2 -7
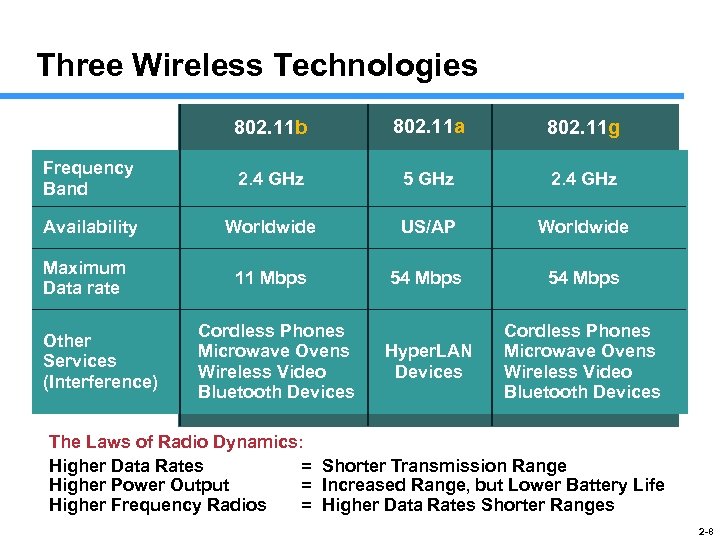 Three Wireless Technologies 802. 11 b 802. 11 a 802. 11 g Frequency Band 2. 4 GHz 5 GHz 2. 4 GHz Availability Worldwide US/AP Worldwide 11 Mbps 54 Mbps Hyper. LAN Devices Cordless Phones Microwave Ovens Wireless Video Bluetooth Devices Maximum Data rate Other Services (Interference) Cordless Phones Microwave Ovens Wireless Video Bluetooth Devices The Laws of Radio Dynamics: Higher Data Rates = Shorter Transmission Range Higher Power Output = Increased Range, but Lower Battery Life Higher Frequency Radios = Higher Data Rates Shorter Ranges 2 -8
Three Wireless Technologies 802. 11 b 802. 11 a 802. 11 g Frequency Band 2. 4 GHz 5 GHz 2. 4 GHz Availability Worldwide US/AP Worldwide 11 Mbps 54 Mbps Hyper. LAN Devices Cordless Phones Microwave Ovens Wireless Video Bluetooth Devices Maximum Data rate Other Services (Interference) Cordless Phones Microwave Ovens Wireless Video Bluetooth Devices The Laws of Radio Dynamics: Higher Data Rates = Shorter Transmission Range Higher Power Output = Increased Range, but Lower Battery Life Higher Frequency Radios = Higher Data Rates Shorter Ranges 2 -8
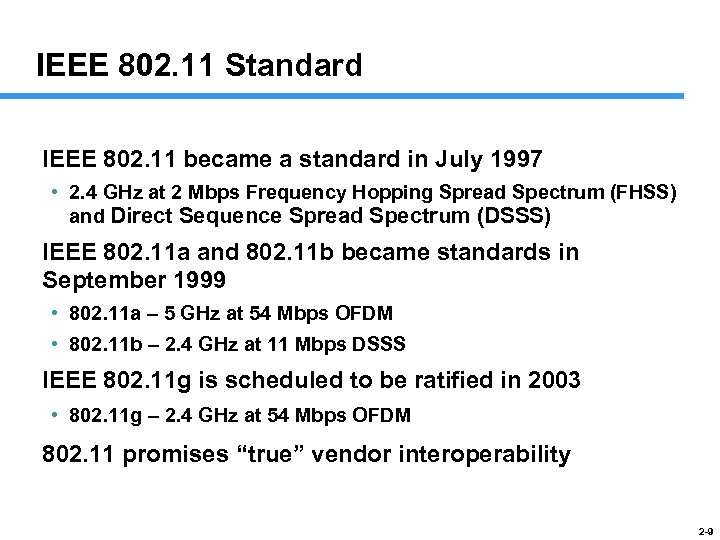 IEEE 802. 11 Standard IEEE 802. 11 became a standard in July 1997 • 2. 4 GHz at 2 Mbps Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) IEEE 802. 11 a and 802. 11 b became standards in September 1999 • 802. 11 a – 5 GHz at 54 Mbps OFDM • 802. 11 b – 2. 4 GHz at 11 Mbps DSSS IEEE 802. 11 g is scheduled to be ratified in 2003 • 802. 11 g – 2. 4 GHz at 54 Mbps OFDM 802. 11 promises “true” vendor interoperability 2 -9
IEEE 802. 11 Standard IEEE 802. 11 became a standard in July 1997 • 2. 4 GHz at 2 Mbps Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) IEEE 802. 11 a and 802. 11 b became standards in September 1999 • 802. 11 a – 5 GHz at 54 Mbps OFDM • 802. 11 b – 2. 4 GHz at 11 Mbps DSSS IEEE 802. 11 g is scheduled to be ratified in 2003 • 802. 11 g – 2. 4 GHz at 54 Mbps OFDM 802. 11 promises “true” vendor interoperability 2 -9
 Standards and Organizations 2 -10
Standards and Organizations 2 -10
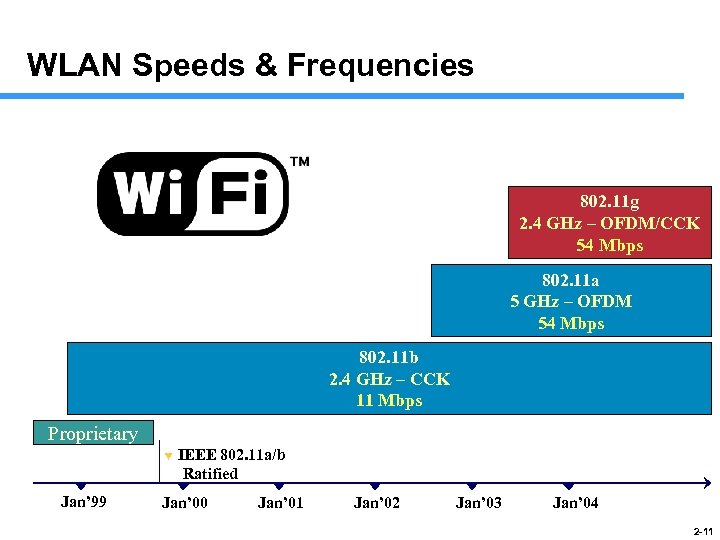 WLAN Speeds & Frequencies 802. 11 g 2. 4 GHz – OFDM/CCK 54 Mbps 802. 11 a 5 GHz – OFDM 54 Mbps 802. 11 b 2. 4 GHz – CCK 11 Mbps Proprietary Jan’ 99 IEEE 802. 11 a/b Ratified Jan’ 00 Jan’ 01 Jan’ 02 Jan’ 03 Jan’ 04 2 -11
WLAN Speeds & Frequencies 802. 11 g 2. 4 GHz – OFDM/CCK 54 Mbps 802. 11 a 5 GHz – OFDM 54 Mbps 802. 11 b 2. 4 GHz – CCK 11 Mbps Proprietary Jan’ 99 IEEE 802. 11 a/b Ratified Jan’ 00 Jan’ 01 Jan’ 02 Jan’ 03 Jan’ 04 2 -11
 What Is WLAN RF Technology? Data sent over the air waves Two-way radio communications (half duplex) Same radio frequency for sending & receiving (transceiver) No licensing required for Cisco Aironet Wireless products (in most countries) 2 -12
What Is WLAN RF Technology? Data sent over the air waves Two-way radio communications (half duplex) Same radio frequency for sending & receiving (transceiver) No licensing required for Cisco Aironet Wireless products (in most countries) 2 -12
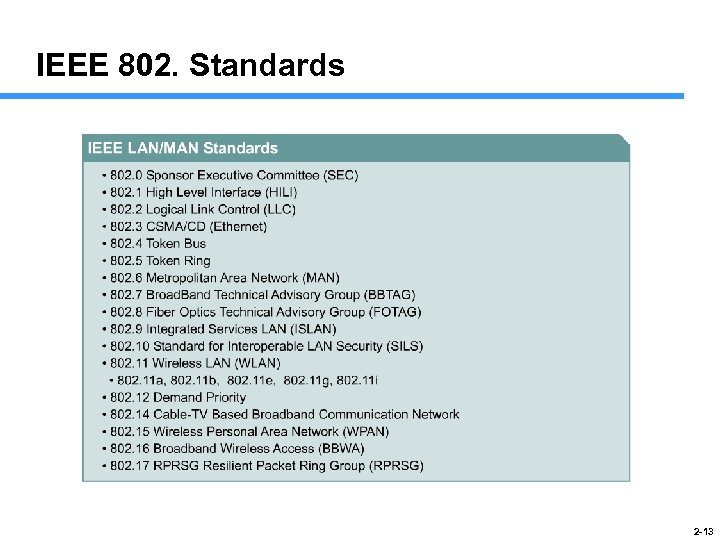 IEEE 802. Standards 2 -13
IEEE 802. Standards 2 -13
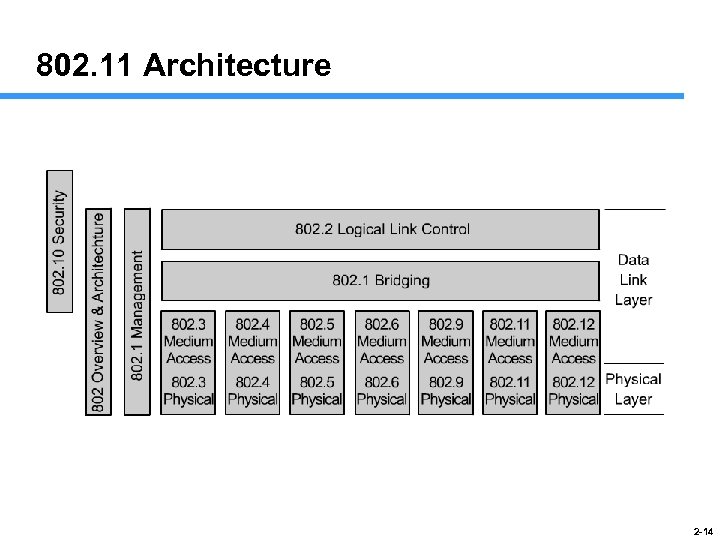 802. 11 Architecture 2 -14
802. 11 Architecture 2 -14
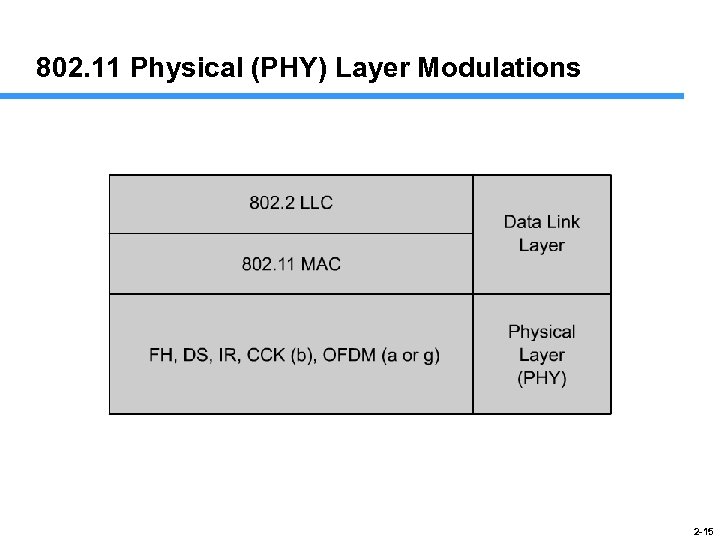 802. 11 Physical (PHY) Layer Modulations 2 -15
802. 11 Physical (PHY) Layer Modulations 2 -15
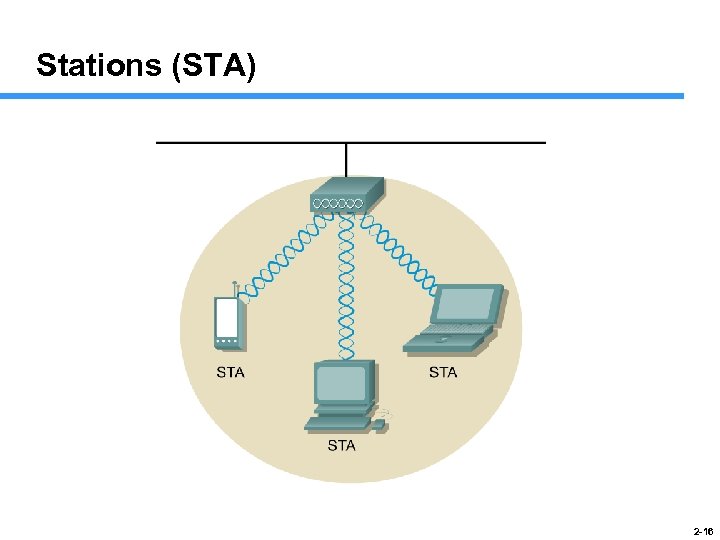 Stations (STA) 2 -16
Stations (STA) 2 -16
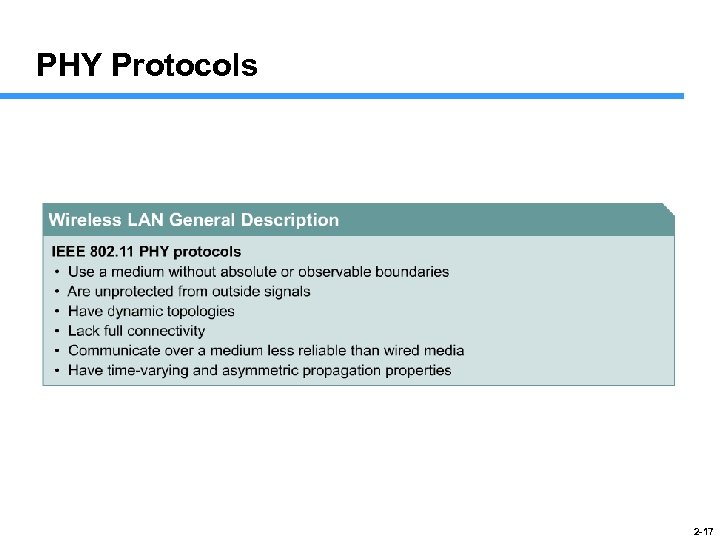 PHY Protocols 2 -17
PHY Protocols 2 -17
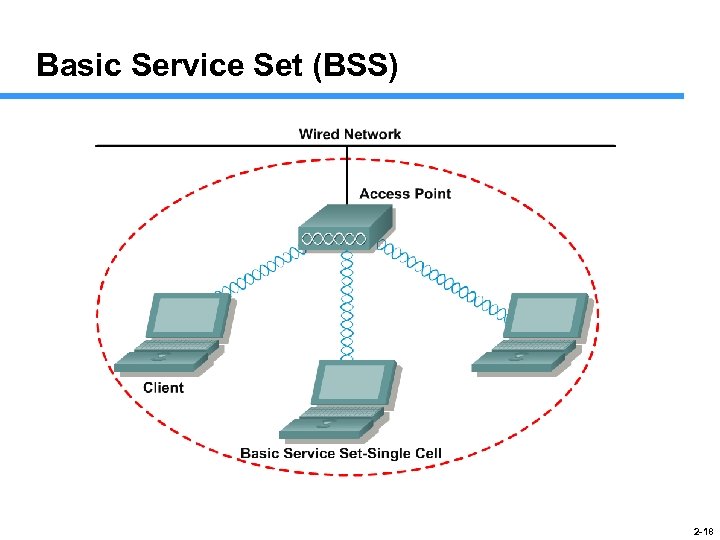 Basic Service Set (BSS) 2 -18
Basic Service Set (BSS) 2 -18
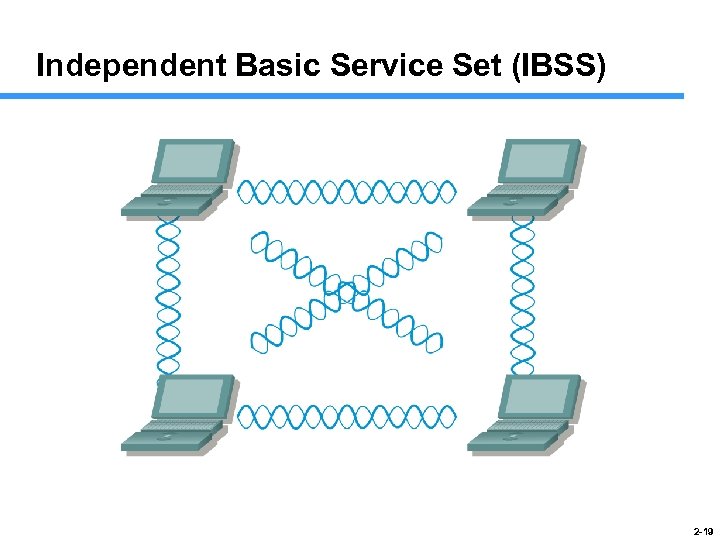 Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) 2 -19
Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) 2 -19
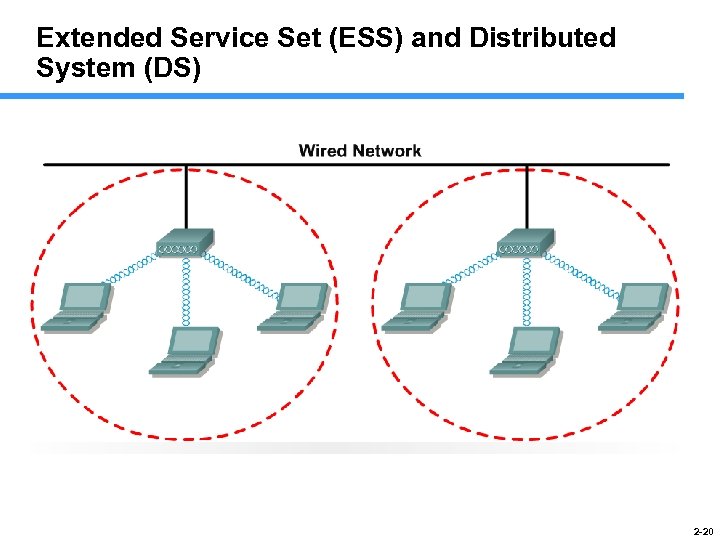 Extended Service Set (ESS) and Distributed System (DS) 2 -20
Extended Service Set (ESS) and Distributed System (DS) 2 -20
 MAC Layer 2 -21
MAC Layer 2 -21
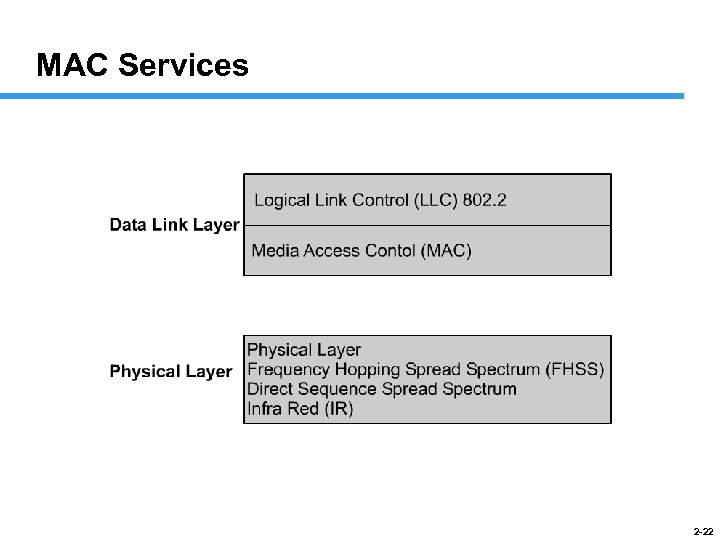 MAC Services 2 -22
MAC Services 2 -22
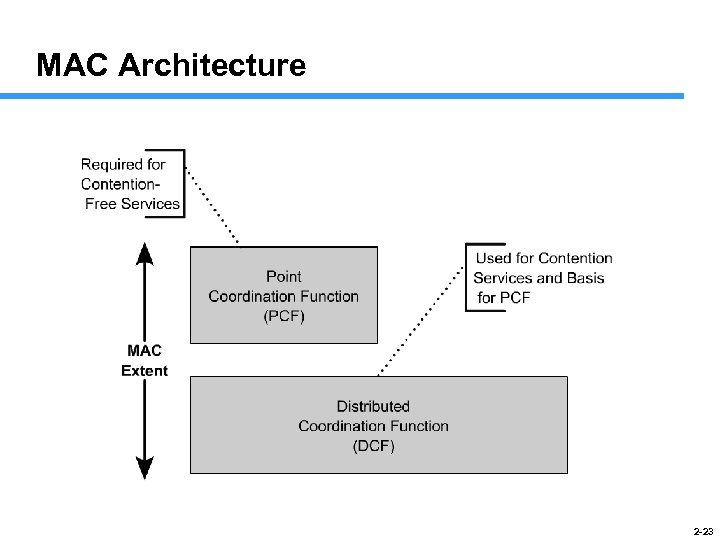 MAC Architecture 2 -23
MAC Architecture 2 -23
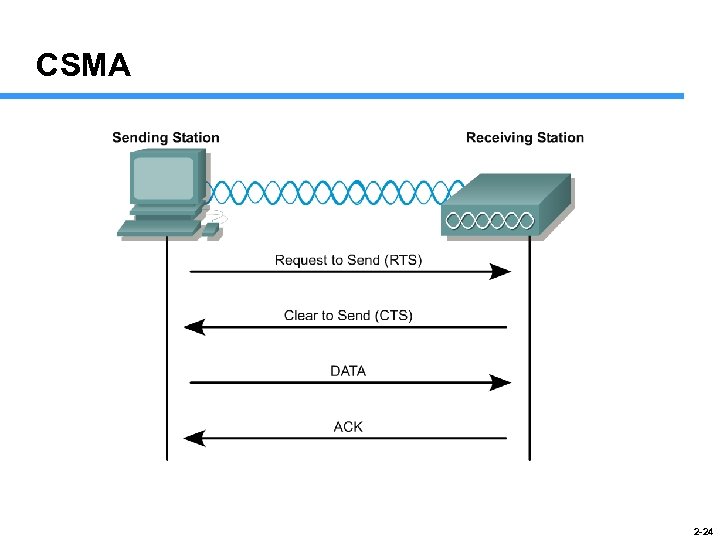 CSMA 2 -24
CSMA 2 -24
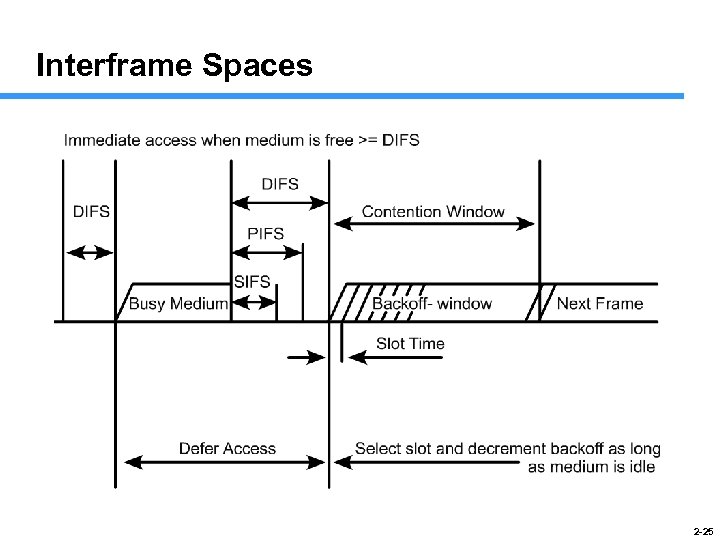 Interframe Spaces 2 -25
Interframe Spaces 2 -25
 PHY Layer 2 -26
PHY Layer 2 -26
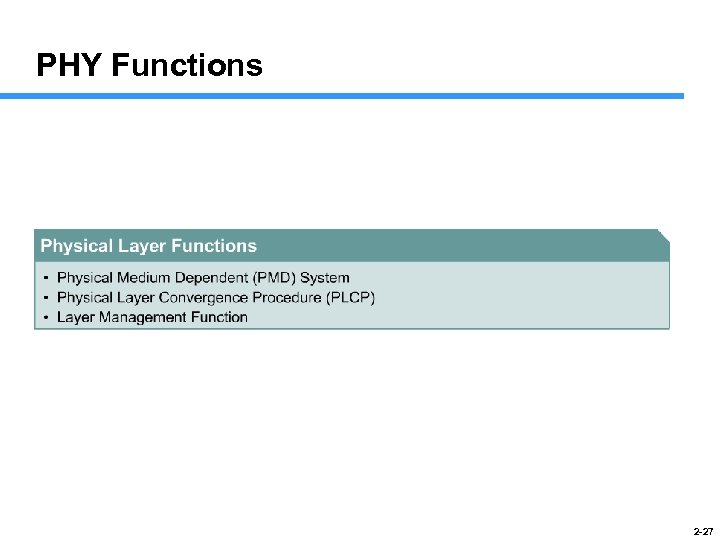 PHY Functions 2 -27
PHY Functions 2 -27
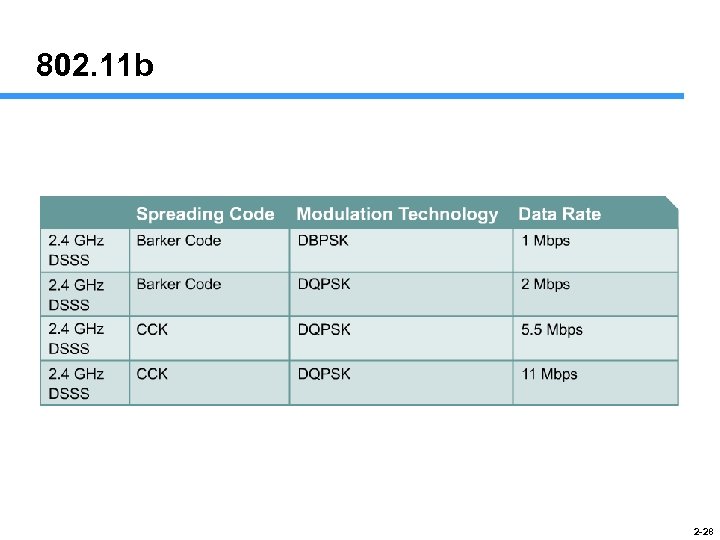 802. 11 b 2 -28
802. 11 b 2 -28
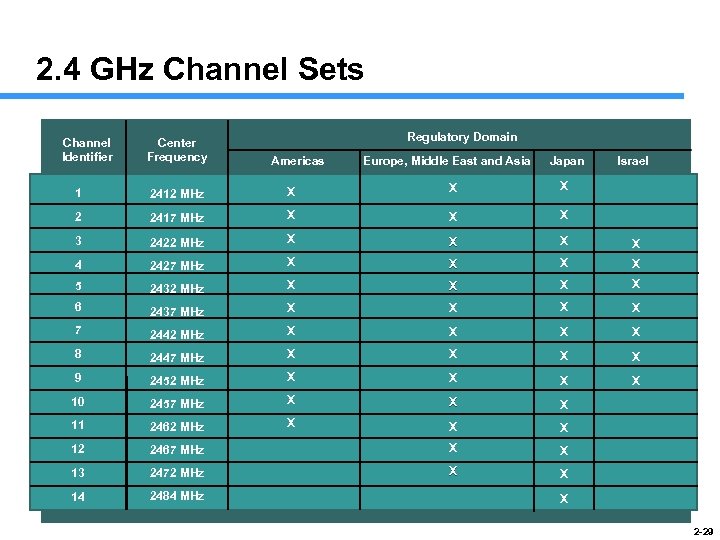 2. 4 GHz Channel Sets Channel Identifier Center Frequency Regulatory Domain Americas Europe, Middle East and Asia Japan Israel 1 2412 MHz X X X 2 2417 MHz X X X 3 2422 MHz X X 4 2427 MHz X X 5 2432 MHz X X 6 2437 MHz X X 7 2442 MHz X X 8 2447 MHz X X 9 2452 MHz X X 10 2457 MHz X X X 11 2462 MHz X X X 12 2467 MHz X X 13 2472 MHz X X 14 2484 MHz X 2 -29
2. 4 GHz Channel Sets Channel Identifier Center Frequency Regulatory Domain Americas Europe, Middle East and Asia Japan Israel 1 2412 MHz X X X 2 2417 MHz X X X 3 2422 MHz X X 4 2427 MHz X X 5 2432 MHz X X 6 2437 MHz X X 7 2442 MHz X X 8 2447 MHz X X 9 2452 MHz X X 10 2457 MHz X X X 11 2462 MHz X X X 12 2467 MHz X X 13 2472 MHz X X 14 2484 MHz X 2 -29
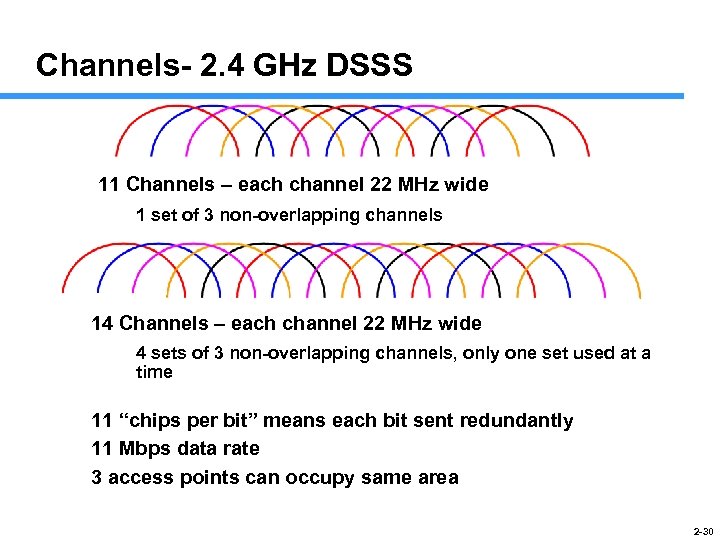 Channels- 2. 4 GHz DSSS 11 Channels – each channel 22 MHz wide 1 set of 3 non-overlapping channels 14 Channels – each channel 22 MHz wide 4 sets of 3 non-overlapping channels, only one set used at a time 11 “chips per bit” means each bit sent redundantly 11 Mbps data rate 3 access points can occupy same area 2 -30
Channels- 2. 4 GHz DSSS 11 Channels – each channel 22 MHz wide 1 set of 3 non-overlapping channels 14 Channels – each channel 22 MHz wide 4 sets of 3 non-overlapping channels, only one set used at a time 11 “chips per bit” means each bit sent redundantly 11 Mbps data rate 3 access points can occupy same area 2 -30
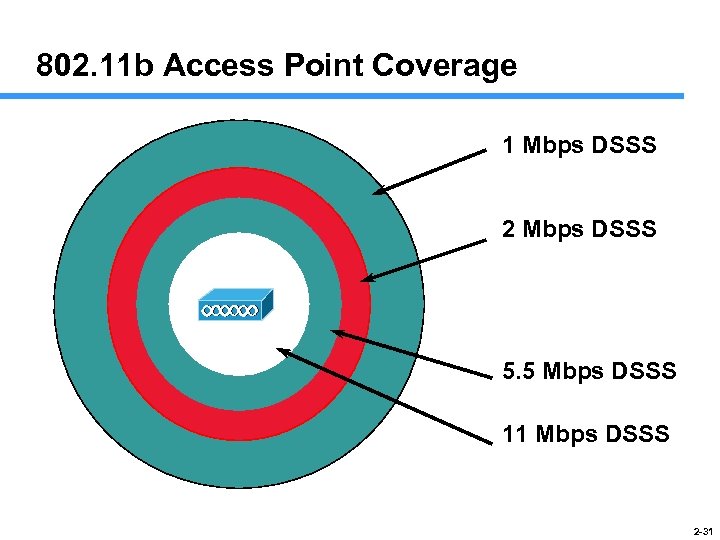 802. 11 b Access Point Coverage 1 Mbps DSSS 2 Mbps DSSS 5. 5 Mbps DSSS 11 Mbps DSSS 2 -31
802. 11 b Access Point Coverage 1 Mbps DSSS 2 Mbps DSSS 5. 5 Mbps DSSS 11 Mbps DSSS 2 -31
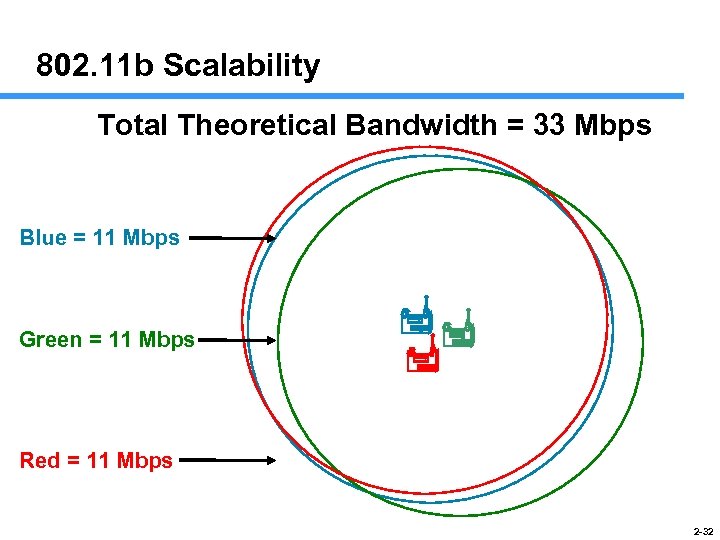 802. 11 b Scalability Total Theoretical Bandwidth = 33 Mbps Blue = 11 Mbps Green = 11 Mbps Red = 11 Mbps 2 -32
802. 11 b Scalability Total Theoretical Bandwidth = 33 Mbps Blue = 11 Mbps Green = 11 Mbps Red = 11 Mbps 2 -32
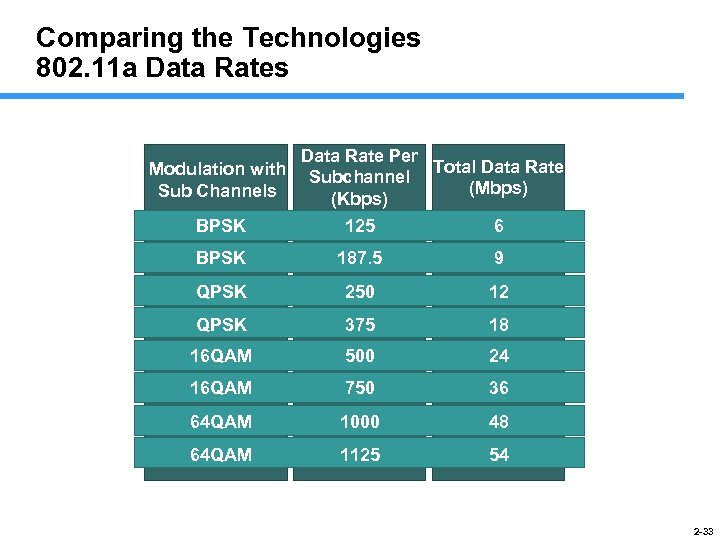 Comparing the Technologies 802. 11 a Data Rates Modulation with Sub Channels BPSK Data Rate Per Total Data Rate Subchannel (Mbps) (Kbps) 125 6 BPSK 187. 5 9 QPSK 250 12 QPSK 375 18 16 QAM 500 24 16 QAM 750 36 64 QAM 1000 48 64 QAM 1125 54 2 -33
Comparing the Technologies 802. 11 a Data Rates Modulation with Sub Channels BPSK Data Rate Per Total Data Rate Subchannel (Mbps) (Kbps) 125 6 BPSK 187. 5 9 QPSK 250 12 QPSK 375 18 16 QAM 500 24 16 QAM 750 36 64 QAM 1000 48 64 QAM 1125 54 2 -33
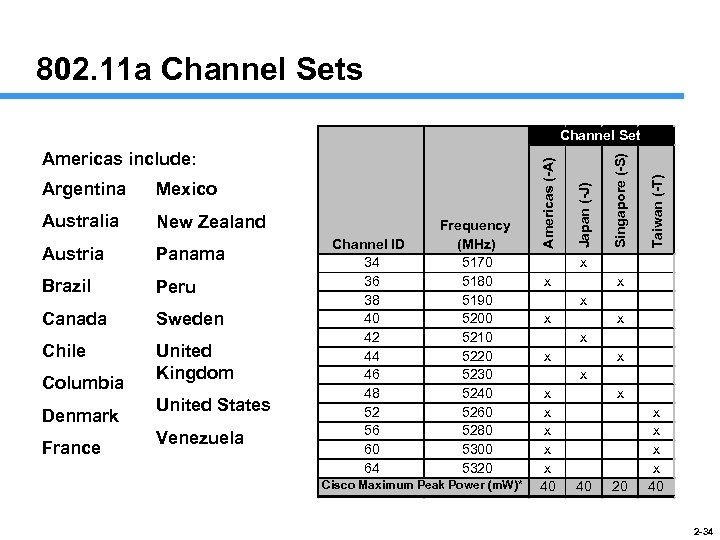 802. 11 a Channel Sets Australia New Zealand Austria Panama Brazil Peru Canada Sweden Chile Columbia Denmark France United Kingdom United States Venezuela Channel ID 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 52 56 60 64 Frequency (MHz) 5170 5180 5190 5200 5210 5220 5230 5240 5260 5280 5300 5320 Cisco Maximum Peak Power (m. W)* Taiwan (-T) Mexico Singapore (-S) Argentina Japan (-J) Americas include: Americas (-A) Channel Set x x x x 40 20 x x 40 2 -34
802. 11 a Channel Sets Australia New Zealand Austria Panama Brazil Peru Canada Sweden Chile Columbia Denmark France United Kingdom United States Venezuela Channel ID 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 52 56 60 64 Frequency (MHz) 5170 5180 5190 5200 5210 5220 5230 5240 5260 5280 5300 5320 Cisco Maximum Peak Power (m. W)* Taiwan (-T) Mexico Singapore (-S) Argentina Japan (-J) Americas include: Americas (-A) Channel Set x x x x 40 20 x x 40 2 -34
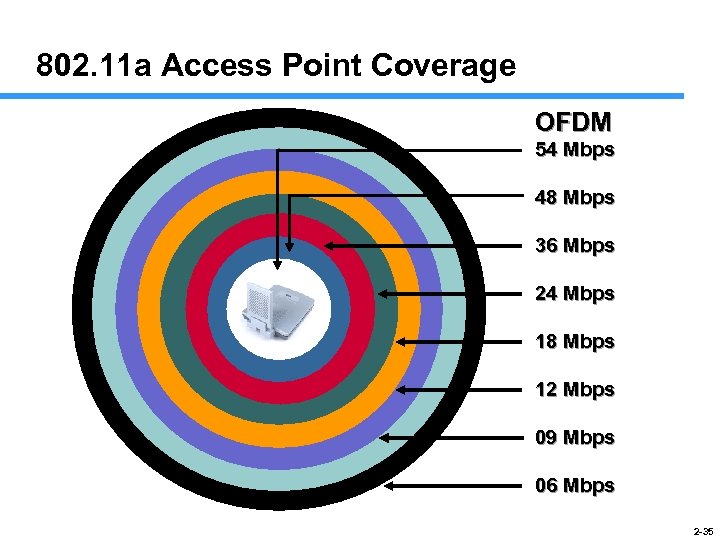 802. 11 a Access Point Coverage OFDM 54 Mbps 48 Mbps 36 Mbps 24 Mbps 18 Mbps 12 Mbps 09 Mbps 06 Mbps 2 -35
802. 11 a Access Point Coverage OFDM 54 Mbps 48 Mbps 36 Mbps 24 Mbps 18 Mbps 12 Mbps 09 Mbps 06 Mbps 2 -35
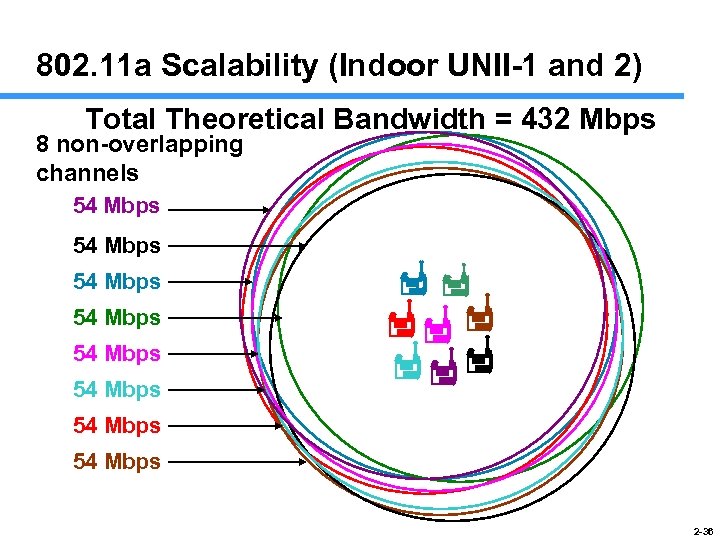 802. 11 a Scalability (Indoor UNII-1 and 2) Total Theoretical Bandwidth = 432 Mbps 8 non-overlapping channels 54 Mbps 54 Mbps 2 -36
802. 11 a Scalability (Indoor UNII-1 and 2) Total Theoretical Bandwidth = 432 Mbps 8 non-overlapping channels 54 Mbps 54 Mbps 2 -36
 Client Adapters 2 -37
Client Adapters 2 -37
 Cisco Aironet 802. 11 b Client Adapters 2. 4 GHz • 802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Include • PC Card • PCI Card • LMC Card • Mini PCI 2 -38
Cisco Aironet 802. 11 b Client Adapters 2. 4 GHz • 802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Include • PC Card • PCI Card • LMC Card • Mini PCI 2 -38
 802. 11 b PC Card 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Rate Shifting • 1, 2, 5. 5, and 11 Mbps Fixed data rates • User configurable option Integrated Antenna PCMCIA interface Transmit power settings: • 100 m. W, 50 m. W, 30 m. W, 20 m. W, 10 m. W, 5 m. W, and 1 m. W 2 -39
802. 11 b PC Card 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Rate Shifting • 1, 2, 5. 5, and 11 Mbps Fixed data rates • User configurable option Integrated Antenna PCMCIA interface Transmit power settings: • 100 m. W, 50 m. W, 30 m. W, 20 m. W, 10 m. W, 5 m. W, and 1 m. W 2 -39
 802. 11 b LMC Card 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Rate Shifting • 1, 2, 5. 5, and 11 Mbps Fixed data rates • User configurable option PCMCIA interface Transmit power settings: • 100 m. W, 50 m. W, 30 m. W, 20 m. W, 10 m. W, 5 m. W, and 1 m. W 2 -40
802. 11 b LMC Card 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Rate Shifting • 1, 2, 5. 5, and 11 Mbps Fixed data rates • User configurable option PCMCIA interface Transmit power settings: • 100 m. W, 50 m. W, 30 m. W, 20 m. W, 10 m. W, 5 m. W, and 1 m. W 2 -40
 802. 11 b PCI Card 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Rate Shifting • 1, 2, 5. 5, and 11 Mbps Fixed data rates • User configurable option RP-TNC Connector PCMCIA interface Transmit power settings: • 100 m. W, 50 m. W, 30 m. W, 20 m. W, 10 m. W, 5 m. W, and 1 m. W 2 -41
802. 11 b PCI Card 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b • 11 Mbps Rate Shifting • 1, 2, 5. 5, and 11 Mbps Fixed data rates • User configurable option RP-TNC Connector PCMCIA interface Transmit power settings: • 100 m. W, 50 m. W, 30 m. W, 20 m. W, 10 m. W, 5 m. W, and 1 m. W 2 -41
 802. 11 b Mini PCI Adapter 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b embedded wireless for notebooks 100 m. W transmit power Must order through PC manufactures (not orderable directly through Cisco) 2 -42
802. 11 b Mini PCI Adapter 2. 4 GHz/802. 11 b embedded wireless for notebooks 100 m. W transmit power Must order through PC manufactures (not orderable directly through Cisco) 2 -42
 802. 11 a Card. Bus 2 Client Adapter 5 GHz/802. 11 a • 54 Mbps Rate Shifting • 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, or 54 Fixed data rates • User configurable option 5 d. Bi Patch Antenna Card. Bus interface Transmit power settings: • 20 m. W, 10 m. W, and 5 m. W 2 -43
802. 11 a Card. Bus 2 Client Adapter 5 GHz/802. 11 a • 54 Mbps Rate Shifting • 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, or 54 Fixed data rates • User configurable option 5 d. Bi Patch Antenna Card. Bus interface Transmit power settings: • 20 m. W, 10 m. W, and 5 m. W 2 -43
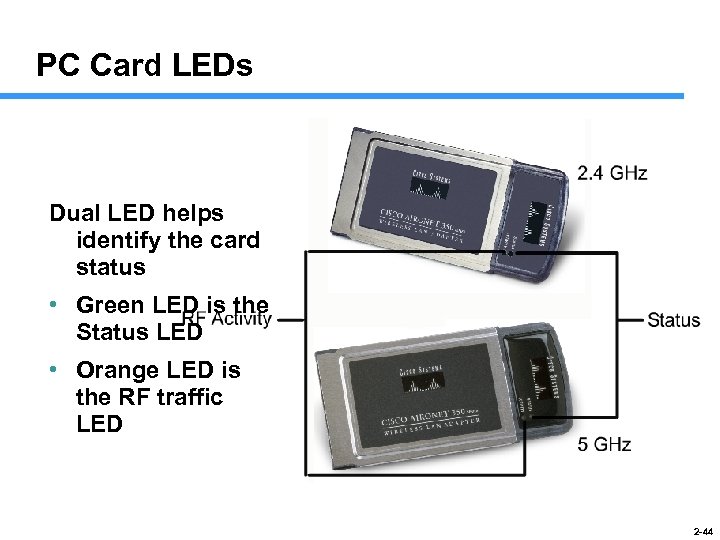 PC Card LEDs Dual LED helps identify the card status • Green LED is the Status LED • Orange LED is the RF traffic LED 2 -44
PC Card LEDs Dual LED helps identify the card status • Green LED is the Status LED • Orange LED is the RF traffic LED 2 -44
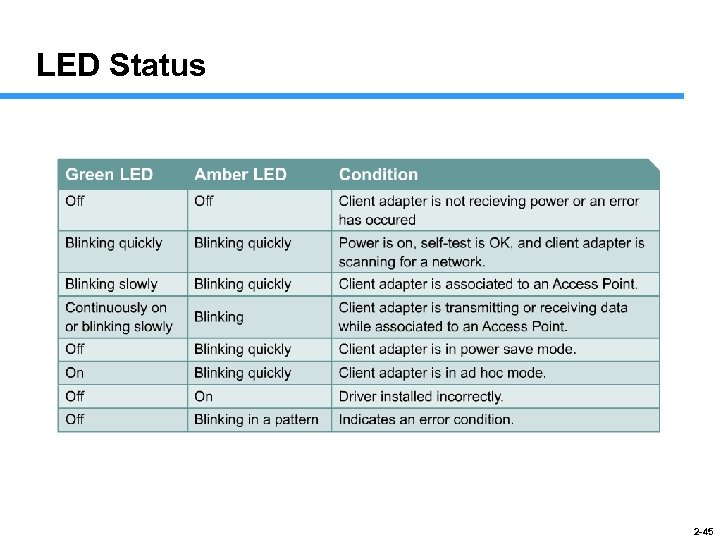 LED Status 2 -45
LED Status 2 -45
 Windows Drivers 2 -46
Windows Drivers 2 -46
 Linux and Macintosh Drivers 2 -47
Linux and Macintosh Drivers 2 -47
 Downloading Drivers and Software 2 -48
Downloading Drivers and Software 2 -48
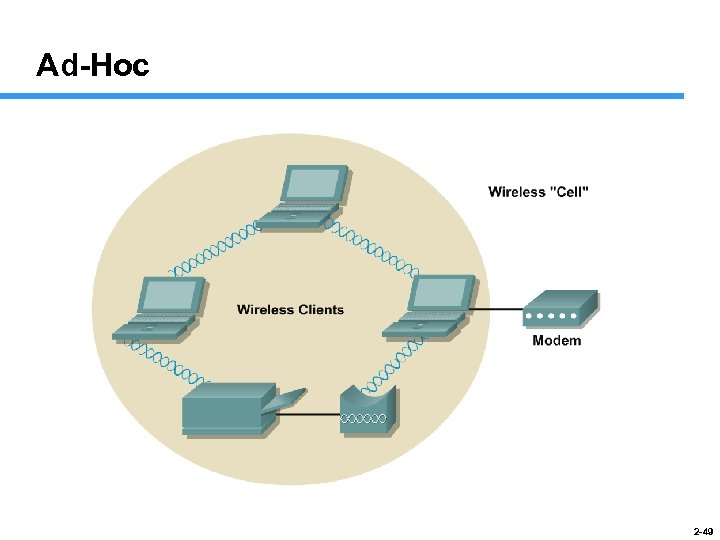 Ad-Hoc 2 -49
Ad-Hoc 2 -49
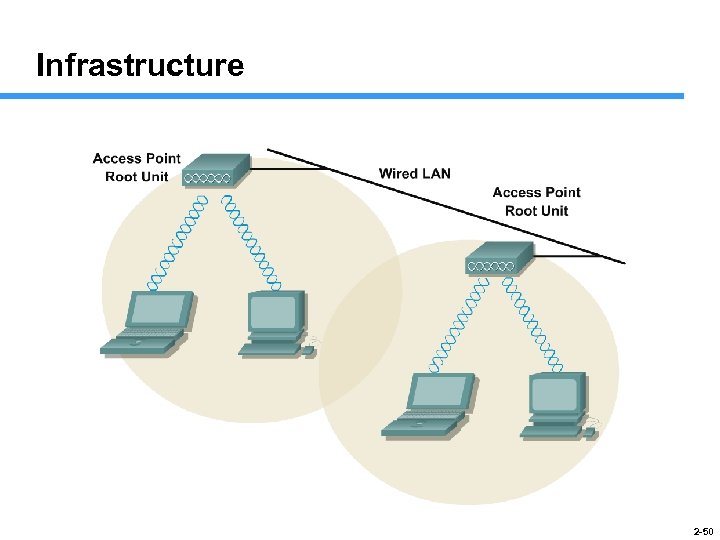 Infrastructure 2 -50
Infrastructure 2 -50
 Aironet Client Utility (ACU) 2 -51
Aironet Client Utility (ACU) 2 -51
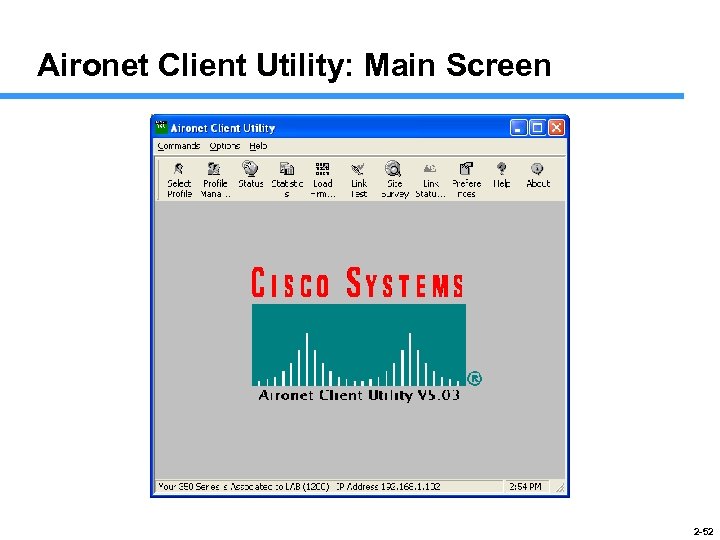 Aironet Client Utility: Main Screen 2 -52
Aironet Client Utility: Main Screen 2 -52
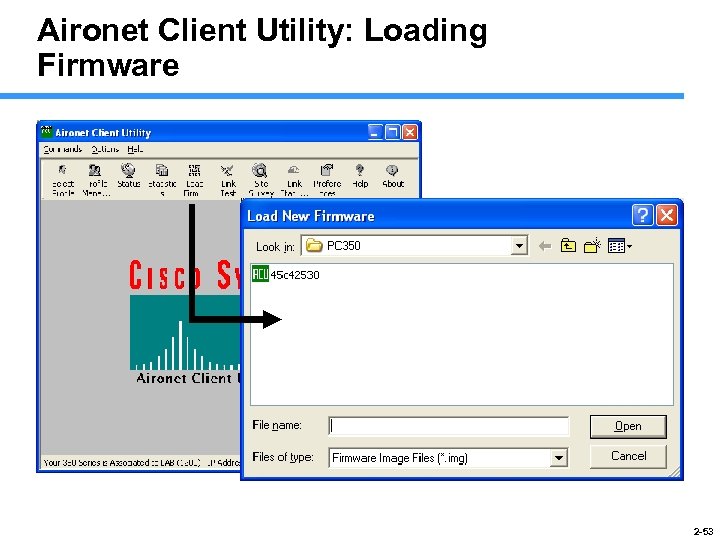 Aironet Client Utility: Loading Firmware 2 -53
Aironet Client Utility: Loading Firmware 2 -53
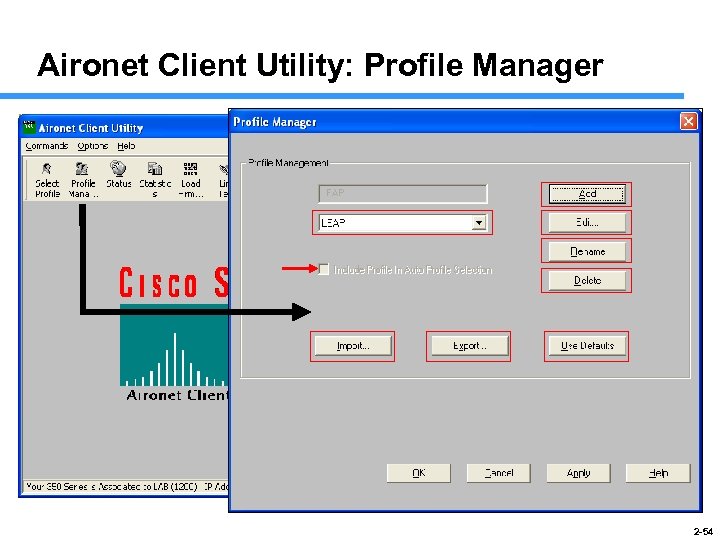 Aironet Client Utility: Profile Manager 2 -54
Aironet Client Utility: Profile Manager 2 -54
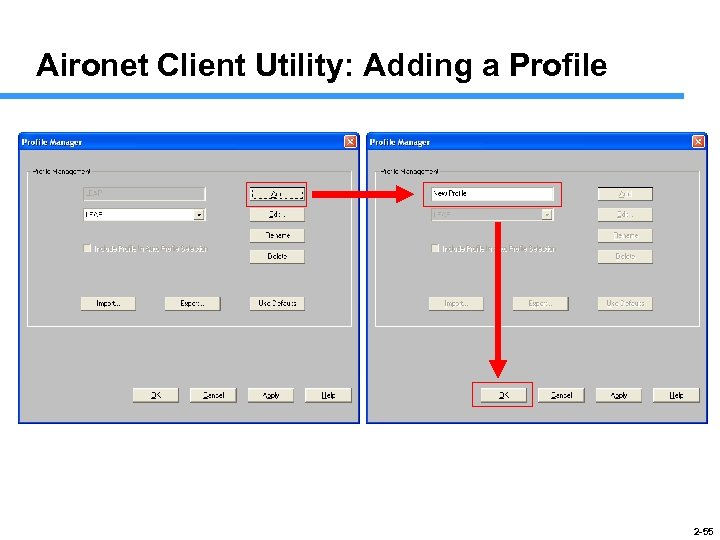 Aironet Client Utility: Adding a Profile 2 -55
Aironet Client Utility: Adding a Profile 2 -55
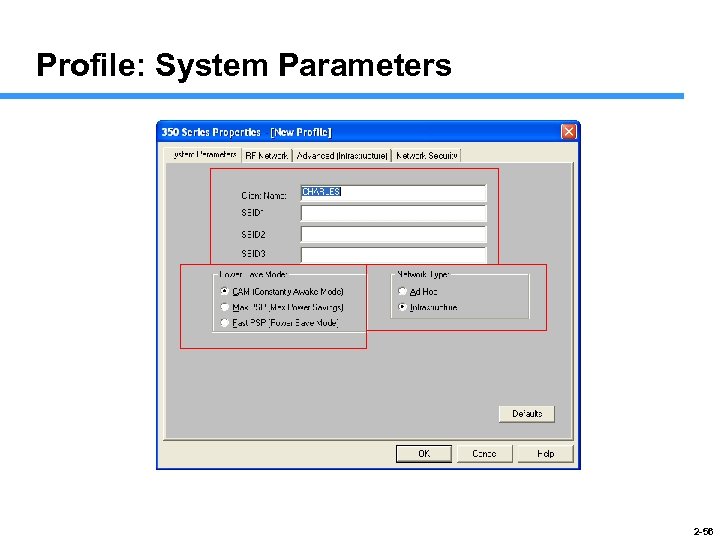 Profile: System Parameters 2 -56
Profile: System Parameters 2 -56
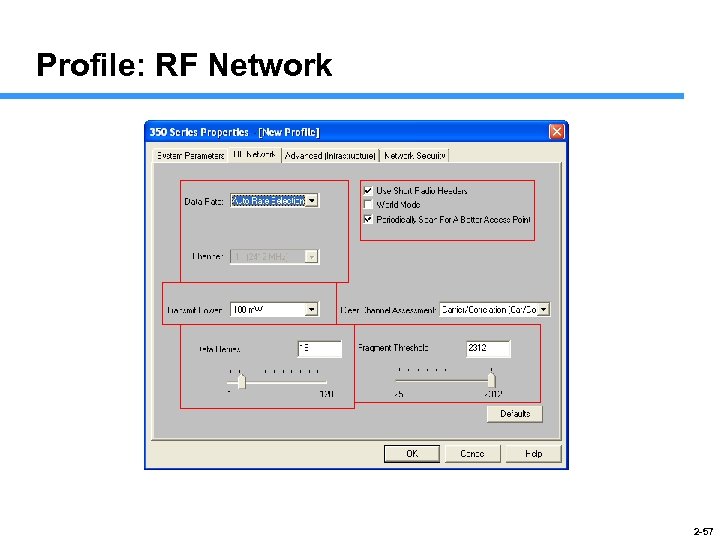 Profile: RF Network 2 -57
Profile: RF Network 2 -57
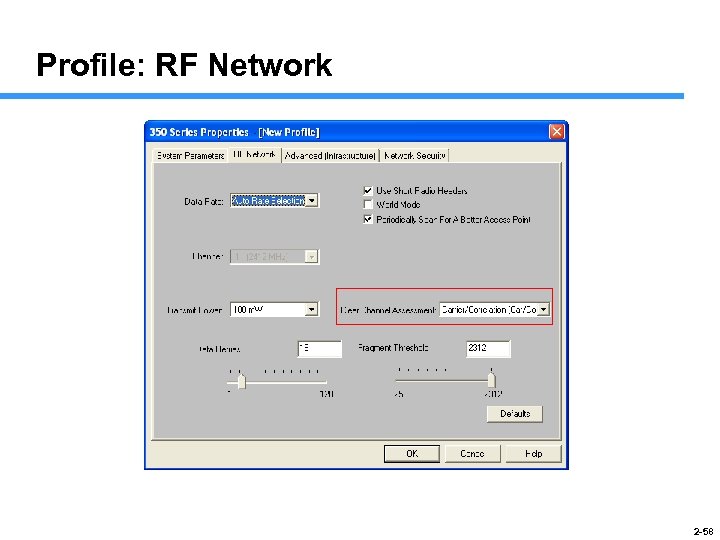 Profile: RF Network 2 -58
Profile: RF Network 2 -58
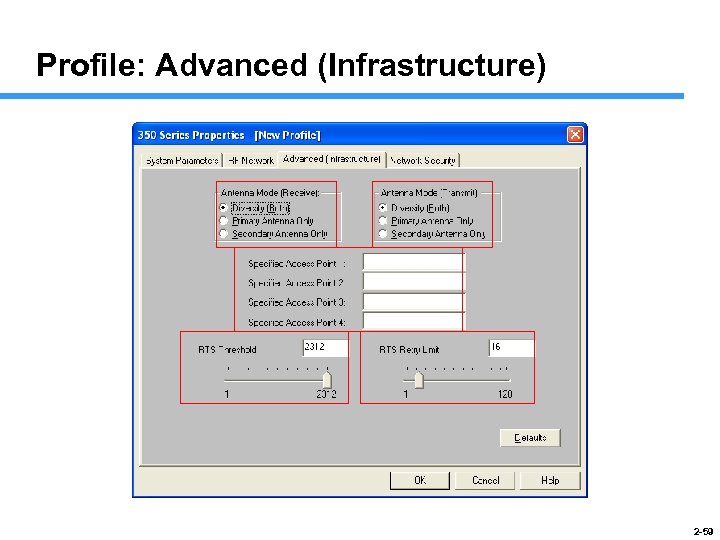 Profile: Advanced (Infrastructure) 2 -59
Profile: Advanced (Infrastructure) 2 -59
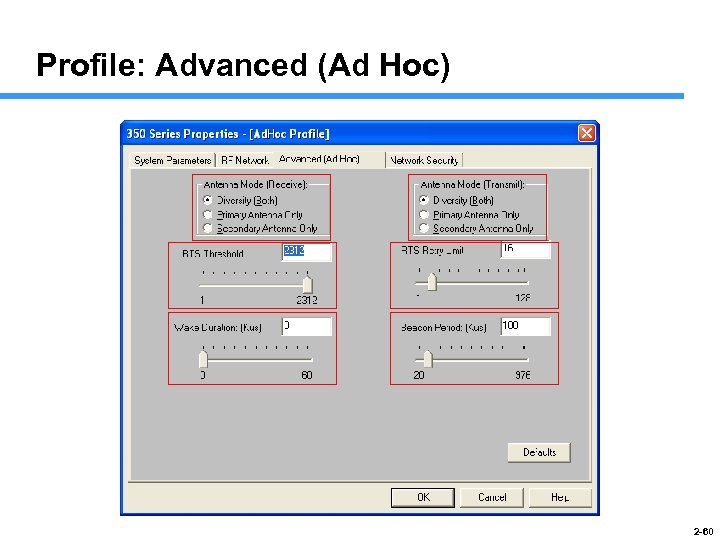 Profile: Advanced (Ad Hoc) 2 -60
Profile: Advanced (Ad Hoc) 2 -60
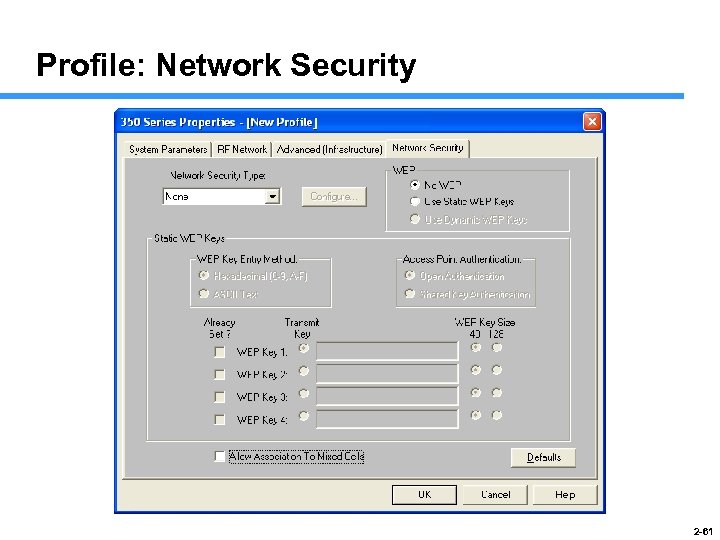 Profile: Network Security 2 -61
Profile: Network Security 2 -61
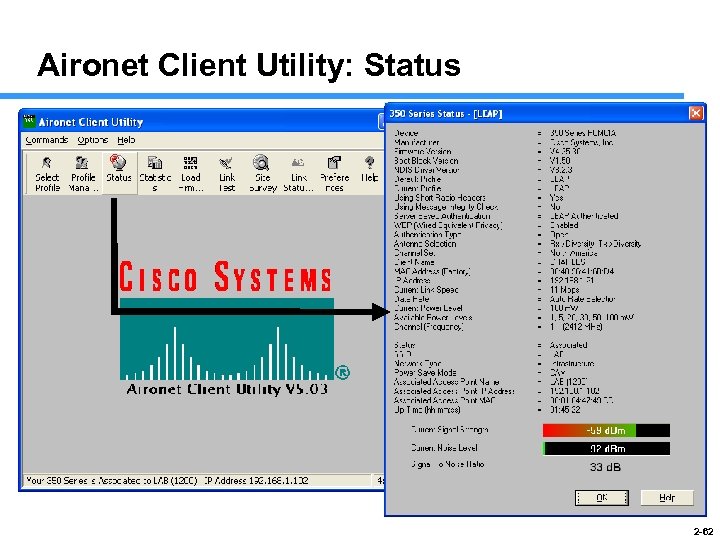 Aironet Client Utility: Status 2 -62
Aironet Client Utility: Status 2 -62
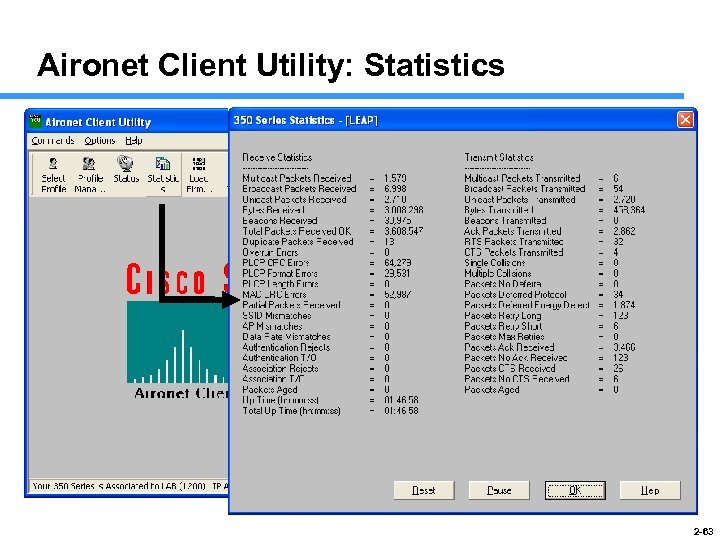 Aironet Client Utility: Statistics 2 -63
Aironet Client Utility: Statistics 2 -63
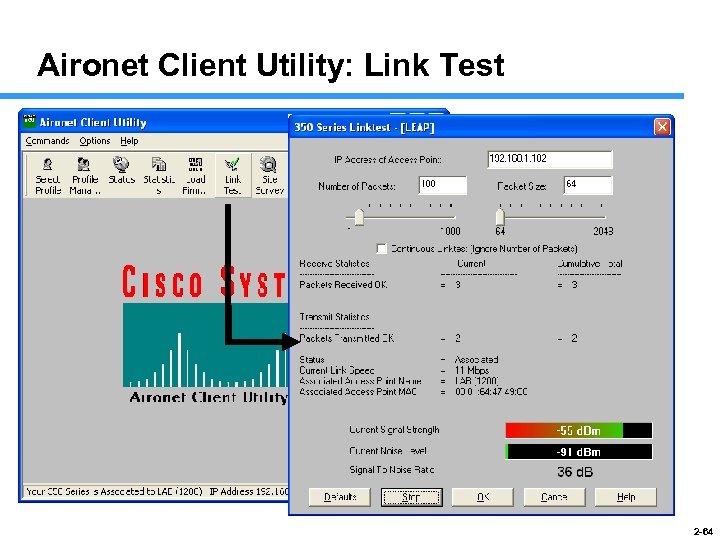 Aironet Client Utility: Link Test 2 -64
Aironet Client Utility: Link Test 2 -64
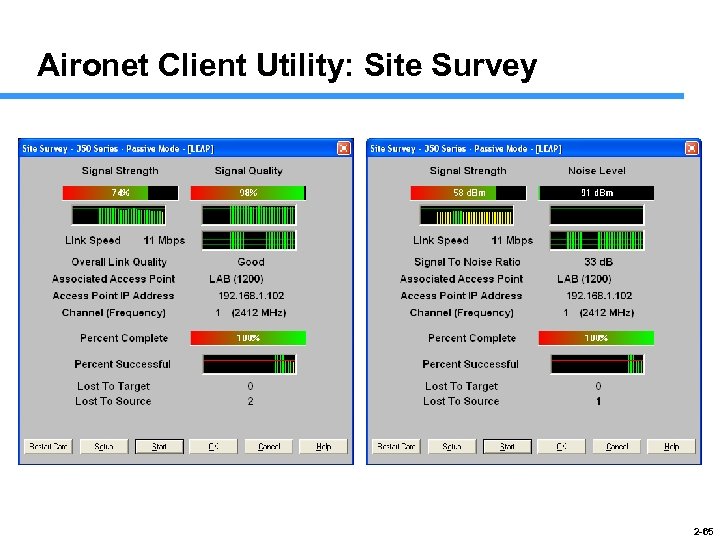 Aironet Client Utility: Site Survey 2 -65
Aironet Client Utility: Site Survey 2 -65
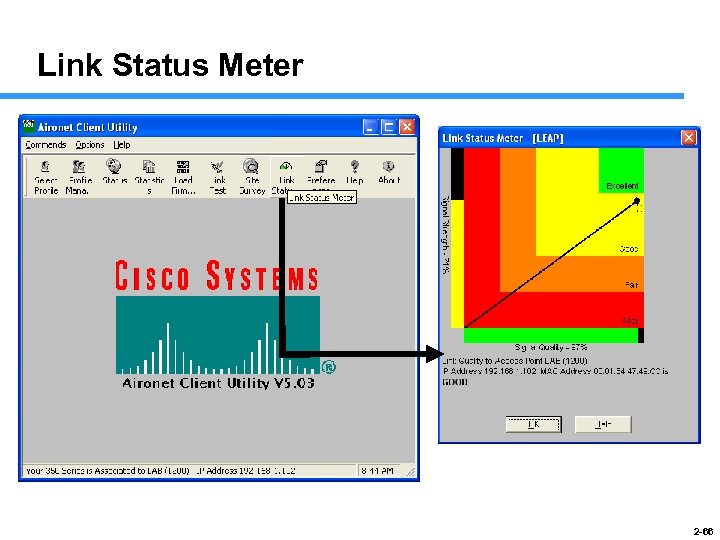 Link Status Meter 2 -66
Link Status Meter 2 -66
 Labs 2 -67
Labs 2 -67
 Labs of Section 2 Lab 2. 4. 3 Install a WLAN Adapter Card Lab 2. 5. 2 Install Aironet Client Utility (ACU) Lab 2. 5. 5 Configure Auto Profiles Lab 2. 6. 5. 1 ACU Utilities Lab 2. 6. 5. 2 Creating an Adhoc Network 2 -68
Labs of Section 2 Lab 2. 4. 3 Install a WLAN Adapter Card Lab 2. 5. 2 Install Aironet Client Utility (ACU) Lab 2. 5. 5 Configure Auto Profiles Lab 2. 6. 5. 1 ACU Utilities Lab 2. 6. 5. 2 Creating an Adhoc Network 2 -68


