615f8b35233180ded3c5c10f5b870a9b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
 IFIP-UNU ADVANCED COURSE ON NETWORKING AND SECURITY Module II-Wireless Communications Section 7 Antennas 7 -1
IFIP-UNU ADVANCED COURSE ON NETWORKING AND SECURITY Module II-Wireless Communications Section 7 Antennas 7 -1
 Overview This module will cover basic antenna theory, including directional and omni directional antenna selection. After discussing antenna theory and types of antennas, cables, connectors and accessories for antennas will be discussed. Additionally, important antenna design considerations, such as link engineering, path planning, and installation are also discussed. 7 -2
Overview This module will cover basic antenna theory, including directional and omni directional antenna selection. After discussing antenna theory and types of antennas, cables, connectors and accessories for antennas will be discussed. Additionally, important antenna design considerations, such as link engineering, path planning, and installation are also discussed. 7 -2
 Learning Objectives • Define how an antenna is used to propagate an RF signal. • Define basic facts of EIRP. • Define facts on FCC regulations for UNII-1, UNII 2 and UNII-3. • Identify what an isotropic antenna is and why it is used as a reference for other antennas. • Identify Cisco Aironet antennas, their coverage patterns, and the proper polarization of each antenna. 7 -3
Learning Objectives • Define how an antenna is used to propagate an RF signal. • Define basic facts of EIRP. • Define facts on FCC regulations for UNII-1, UNII 2 and UNII-3. • Identify what an isotropic antenna is and why it is used as a reference for other antennas. • Identify Cisco Aironet antennas, their coverage patterns, and the proper polarization of each antenna. 7 -3
 Key terms • • • Lobes Directional Omnidirectional Beamwidth and Bandwidth Polarization • Vertical • Horizontal • Diversity • Plane (H and E) • Fresnel Zone 7 -4
Key terms • • • Lobes Directional Omnidirectional Beamwidth and Bandwidth Polarization • Vertical • Horizontal • Diversity • Plane (H and E) • Fresnel Zone 7 -4
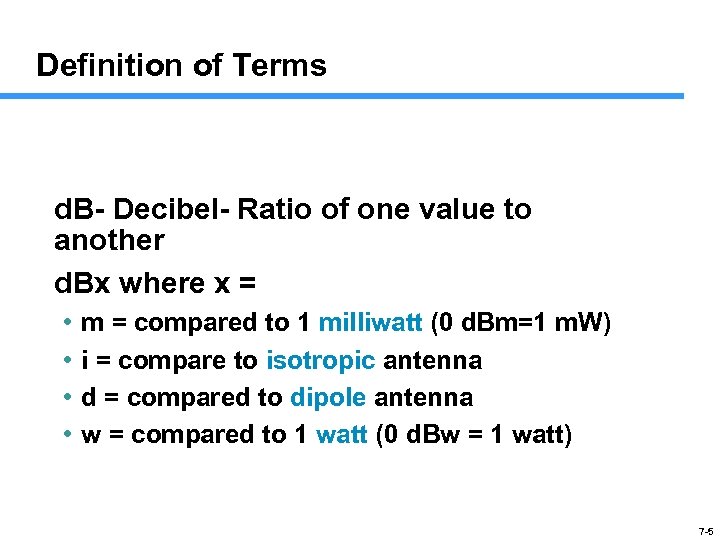 Definition of Terms d. B- Decibel- Ratio of one value to another d. Bx where x = • • m = compared to 1 milliwatt (0 d. Bm=1 m. W) i = compare to isotropic antenna d = compared to dipole antenna w = compared to 1 watt (0 d. Bw = 1 watt) 7 -5
Definition of Terms d. B- Decibel- Ratio of one value to another d. Bx where x = • • m = compared to 1 milliwatt (0 d. Bm=1 m. W) i = compare to isotropic antenna d = compared to dipole antenna w = compared to 1 watt (0 d. Bw = 1 watt) 7 -5
 Antennas 7 -6
Antennas 7 -6
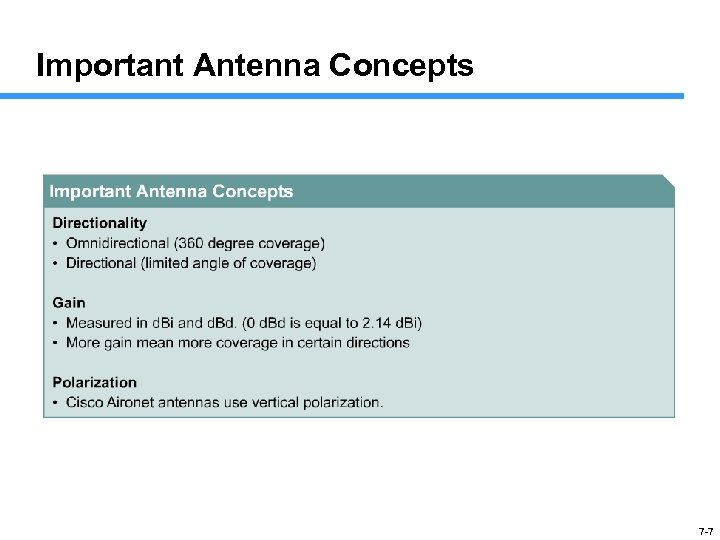 Important Antenna Concepts 7 -7
Important Antenna Concepts 7 -7
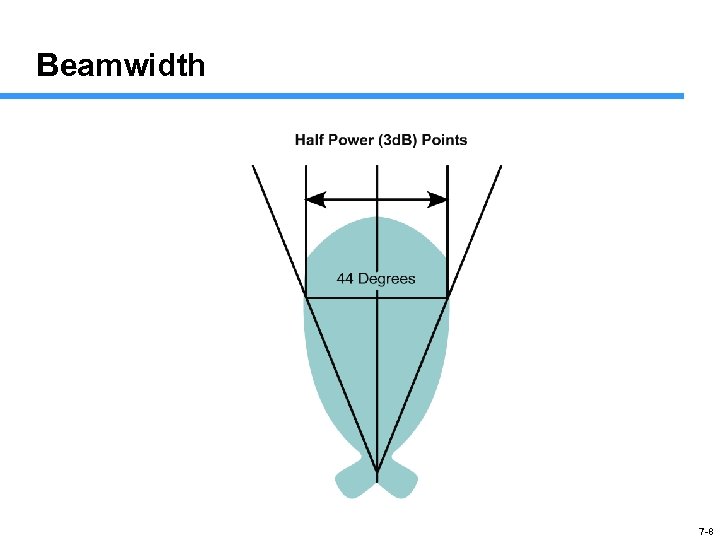 Beamwidth 7 -8
Beamwidth 7 -8
 Cisco Aironet 802. 11 b Antennas FCC requires that ALL antennas sold by a spread spectrum vendor be certified with the radio they are to be sold with All Cisco Aironet 802. 11 b supplied cables, RF devices and antennas have reverse polarity TNC (RP-TNC) connectors Cisco Aironet supplied antennas meet all FCC rules Wide variety of 802. 11 b antennas for most applications 7 -9
Cisco Aironet 802. 11 b Antennas FCC requires that ALL antennas sold by a spread spectrum vendor be certified with the radio they are to be sold with All Cisco Aironet 802. 11 b supplied cables, RF devices and antennas have reverse polarity TNC (RP-TNC) connectors Cisco Aironet supplied antennas meet all FCC rules Wide variety of 802. 11 b antennas for most applications 7 -9
 Cisco Aironet 802. 11 a Antennas FCC requires that all radios utilizing the UNII-1 Band (5. 15 GHz – 5. 25 GHz) must have nonremovable or integrated antennas FCC allows radios utilizing the UNII-2 Band (5. 25 GHz – 5. 35 GHz) to have external or removable antennas The Cisco Aironet 802. 11 a radios utilize both UNII-1 and UNII-2 bands, therefore cannot have external or removable antennas Cisco 802. 11 a antennas are integrated into the radio module Cisco 1400 radios utilize UNII-3 bands, therefore have external or removable antennas 7 -10
Cisco Aironet 802. 11 a Antennas FCC requires that all radios utilizing the UNII-1 Band (5. 15 GHz – 5. 25 GHz) must have nonremovable or integrated antennas FCC allows radios utilizing the UNII-2 Band (5. 25 GHz – 5. 35 GHz) to have external or removable antennas The Cisco Aironet 802. 11 a radios utilize both UNII-1 and UNII-2 bands, therefore cannot have external or removable antennas Cisco 802. 11 a antennas are integrated into the radio module Cisco 1400 radios utilize UNII-3 bands, therefore have external or removable antennas 7 -10
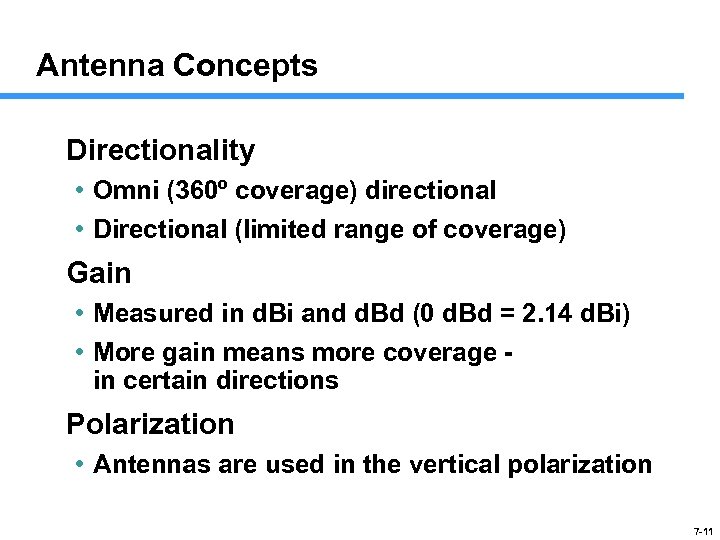 Antenna Concepts Directionality • Omni (360º coverage) directional • Directional (limited range of coverage) Gain • Measured in d. Bi and d. Bd (0 d. Bd = 2. 14 d. Bi) • More gain means more coverage in certain directions Polarization • Antennas are used in the vertical polarization 7 -11
Antenna Concepts Directionality • Omni (360º coverage) directional • Directional (limited range of coverage) Gain • Measured in d. Bi and d. Bd (0 d. Bd = 2. 14 d. Bi) • More gain means more coverage in certain directions Polarization • Antennas are used in the vertical polarization 7 -11
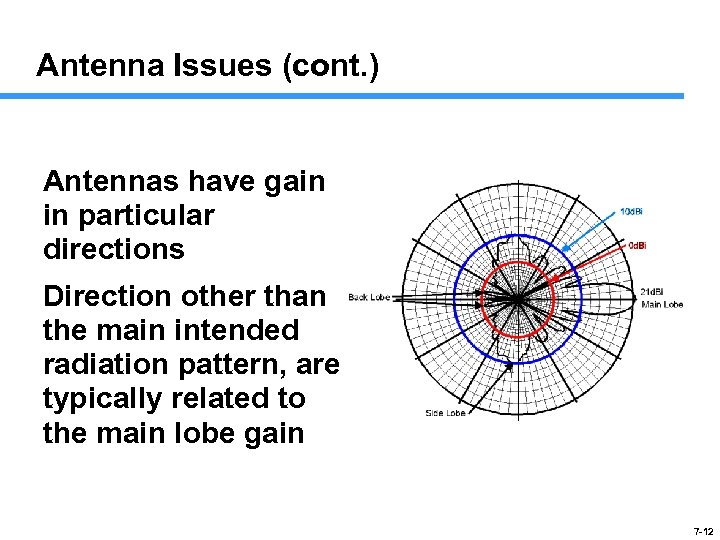 Antenna Issues (cont. ) Antennas have gain in particular directions Direction other than the main intended radiation pattern, are typically related to the main lobe gain 7 -12
Antenna Issues (cont. ) Antennas have gain in particular directions Direction other than the main intended radiation pattern, are typically related to the main lobe gain 7 -12
 Antenna Gain If the gain of an antenna goes up, the coverage area or angle goes down Coverage areas or radiation patterns are measured in degrees Angles are referred to as beamwidth • Horizontal measurement • Vertical measurement 7 -13
Antenna Gain If the gain of an antenna goes up, the coverage area or angle goes down Coverage areas or radiation patterns are measured in degrees Angles are referred to as beamwidth • Horizontal measurement • Vertical measurement 7 -13
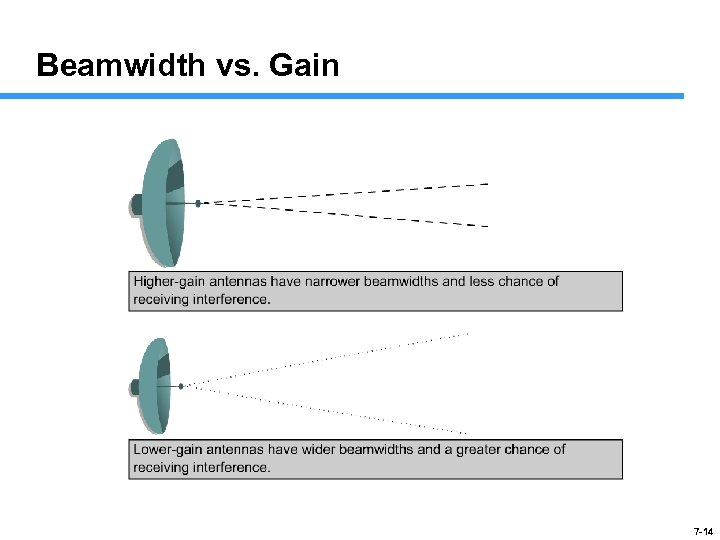 Beamwidth vs. Gain 7 -14
Beamwidth vs. Gain 7 -14
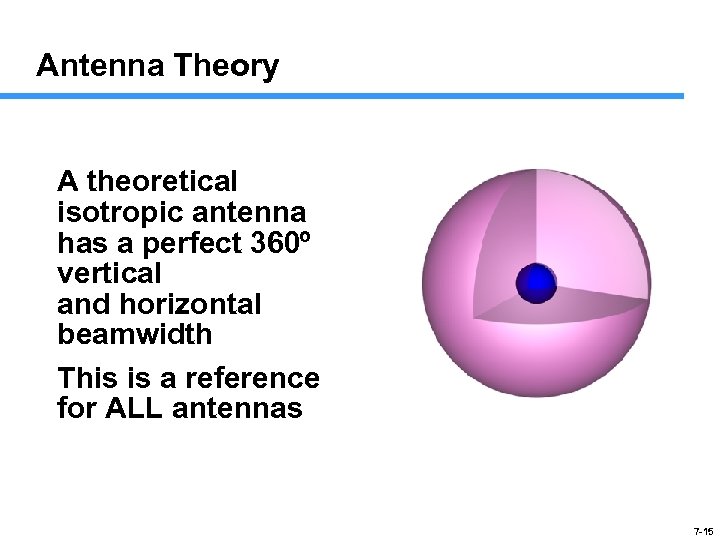 Antenna Theory A theoretical isotropic antenna has a perfect 360º vertical and horizontal beamwidth This is a reference for ALL antennas 7 -15
Antenna Theory A theoretical isotropic antenna has a perfect 360º vertical and horizontal beamwidth This is a reference for ALL antennas 7 -15
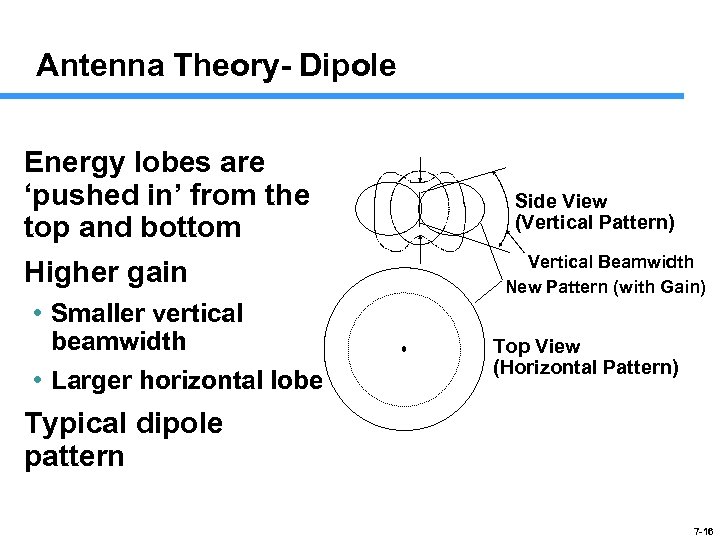 Antenna Theory- Dipole Energy lobes are ‘pushed in’ from the top and bottom Higher gain • Smaller vertical beamwidth • Larger horizontal lobe Side View (Vertical Pattern) Vertical Beamwidth New Pattern (with Gain) Top View (Horizontal Pattern) Typical dipole pattern 7 -16
Antenna Theory- Dipole Energy lobes are ‘pushed in’ from the top and bottom Higher gain • Smaller vertical beamwidth • Larger horizontal lobe Side View (Vertical Pattern) Vertical Beamwidth New Pattern (with Gain) Top View (Horizontal Pattern) Typical dipole pattern 7 -16
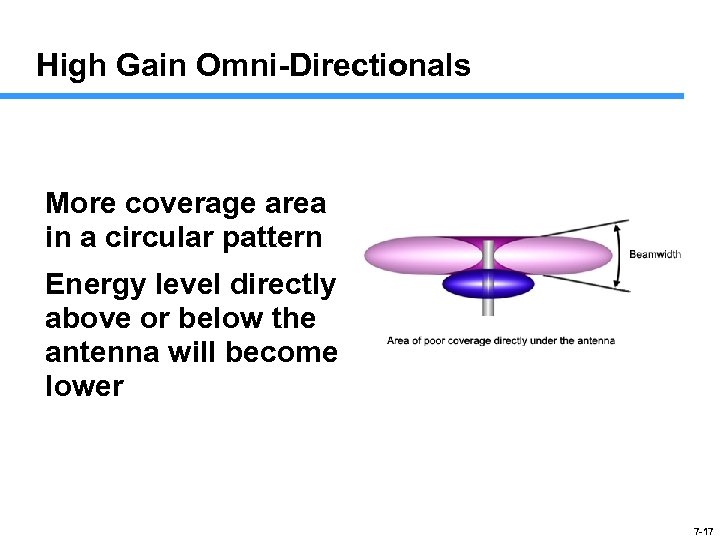 High Gain Omni-Directionals More coverage area in a circular pattern Energy level directly above or below the antenna will become lower 7 -17
High Gain Omni-Directionals More coverage area in a circular pattern Energy level directly above or below the antenna will become lower 7 -17
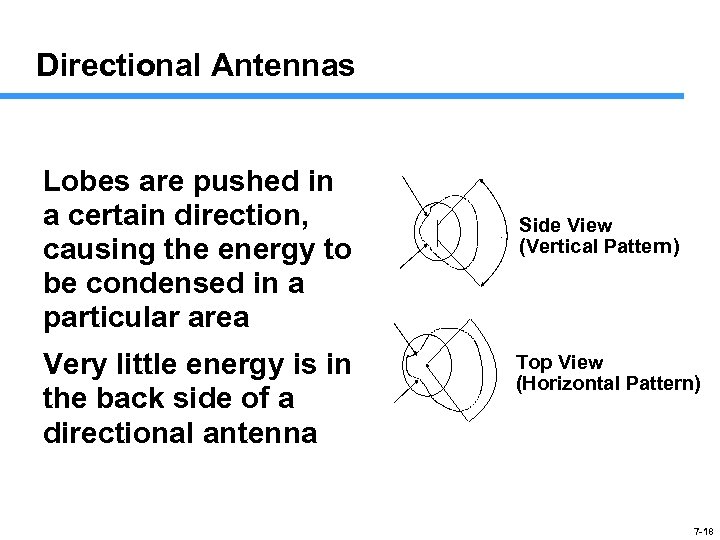 Directional Antennas Lobes are pushed in a certain direction, causing the energy to be condensed in a particular area Very little energy is in the back side of a directional antenna Side View (Vertical Pattern) Top View (Horizontal Pattern) 7 -18
Directional Antennas Lobes are pushed in a certain direction, causing the energy to be condensed in a particular area Very little energy is in the back side of a directional antenna Side View (Vertical Pattern) Top View (Horizontal Pattern) 7 -18
 FCC Part 15 Antenna Requirements 802. 11 b antenna • Must use a unique, or proprietary connector • Cisco Aironet products use RP-TNC connector Part 15 standards • Approved antenna may exceed • Exceeding may lead to interference problems • Penalties could result in fines • FCC standards apply to Part 15 users in the United States Different countries will have similar standards 7 -19
FCC Part 15 Antenna Requirements 802. 11 b antenna • Must use a unique, or proprietary connector • Cisco Aironet products use RP-TNC connector Part 15 standards • Approved antenna may exceed • Exceeding may lead to interference problems • Penalties could result in fines • FCC standards apply to Part 15 users in the United States Different countries will have similar standards 7 -19
 2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for FCC Governed Areas Point-to-Multipoint • FCC allows increasing the gain of an antenna/cable system if the transmitter power is reduced below 30 d. Bm in a 1: 1 ratio • Reduce Transmit Power below maximum of 30 d. Bm by 1 d. Bm and increase antenna/cable system gain by 1 d. Bi Point-to-Point • Maximum of 36 d. Bm EIRP • Installations – 30 d. Bm maximum transmitter power with 6 d. Bi in gain attributed to antenna and cable combination FCC allows exceeding the 36 d. Bm EIRP in Point-to. Point installations using the 3: 1 rule • Reduce Transmit Power below maximum of 30 d. Bm by 1 d. Bm and increase antenna/cable system gain by 3 d. Bi 7 -20
2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for FCC Governed Areas Point-to-Multipoint • FCC allows increasing the gain of an antenna/cable system if the transmitter power is reduced below 30 d. Bm in a 1: 1 ratio • Reduce Transmit Power below maximum of 30 d. Bm by 1 d. Bm and increase antenna/cable system gain by 1 d. Bi Point-to-Point • Maximum of 36 d. Bm EIRP • Installations – 30 d. Bm maximum transmitter power with 6 d. Bi in gain attributed to antenna and cable combination FCC allows exceeding the 36 d. Bm EIRP in Point-to. Point installations using the 3: 1 rule • Reduce Transmit Power below maximum of 30 d. Bm by 1 d. Bm and increase antenna/cable system gain by 3 d. Bi 7 -20
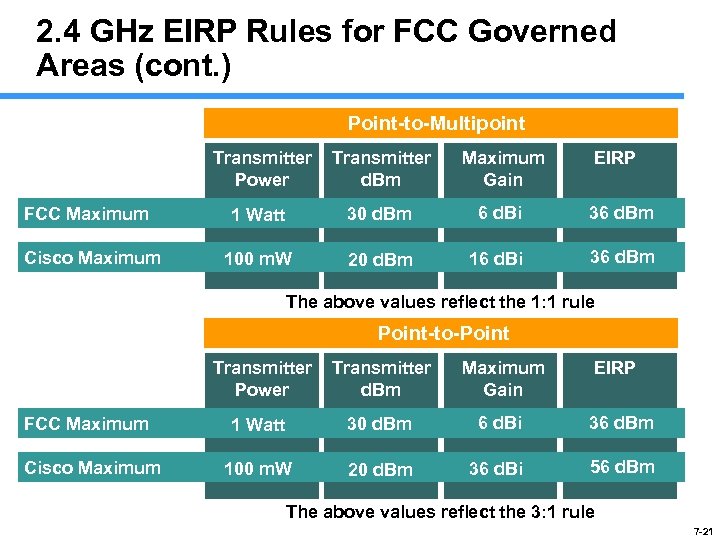 2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for FCC Governed Areas (cont. ) Point-to-Multipoint Transmitter Power FCC Maximum Cisco Maximum Transmitter d. Bm Maximum Gain EIRP 1 Watt 30 d. Bm 6 d. Bi 36 d. Bm 100 m. W 20 d. Bm 16 d. Bi 36 d. Bm The above values reflect the 1: 1 rule Point-to-Point Transmitter Power FCC Maximum Cisco Maximum Transmitter d. Bm Maximum Gain EIRP 1 Watt 30 d. Bm 6 d. Bi 36 d. Bm 100 m. W 20 d. Bm 36 d. Bi 56 d. Bm The above values reflect the 3: 1 rule 7 -21
2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for FCC Governed Areas (cont. ) Point-to-Multipoint Transmitter Power FCC Maximum Cisco Maximum Transmitter d. Bm Maximum Gain EIRP 1 Watt 30 d. Bm 6 d. Bi 36 d. Bm 100 m. W 20 d. Bm 16 d. Bi 36 d. Bm The above values reflect the 1: 1 rule Point-to-Point Transmitter Power FCC Maximum Cisco Maximum Transmitter d. Bm Maximum Gain EIRP 1 Watt 30 d. Bm 6 d. Bi 36 d. Bm 100 m. W 20 d. Bm 36 d. Bi 56 d. Bm The above values reflect the 3: 1 rule 7 -21
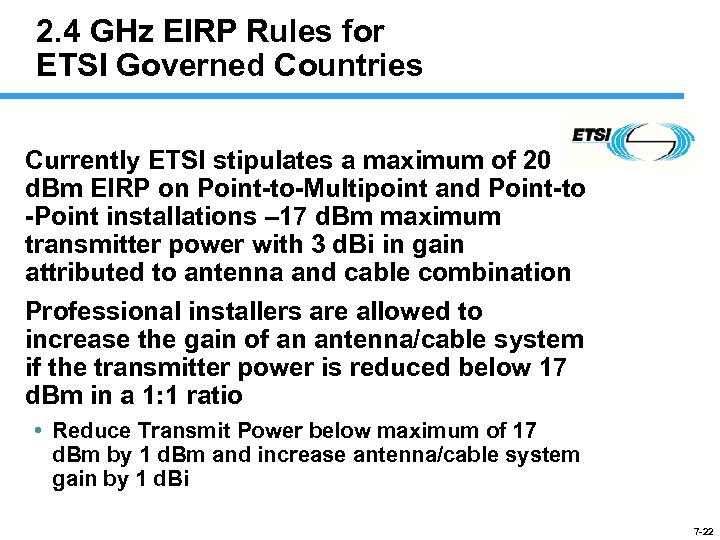 2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for ETSI Governed Countries Currently ETSI stipulates a maximum of 20 d. Bm EIRP on Point-to-Multipoint and Point-to -Point installations – 17 d. Bm maximum transmitter power with 3 d. Bi in gain attributed to antenna and cable combination Professional installers are allowed to increase the gain of an antenna/cable system if the transmitter power is reduced below 17 d. Bm in a 1: 1 ratio • Reduce Transmit Power below maximum of 17 d. Bm by 1 d. Bm and increase antenna/cable system gain by 1 d. Bi 7 -22
2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for ETSI Governed Countries Currently ETSI stipulates a maximum of 20 d. Bm EIRP on Point-to-Multipoint and Point-to -Point installations – 17 d. Bm maximum transmitter power with 3 d. Bi in gain attributed to antenna and cable combination Professional installers are allowed to increase the gain of an antenna/cable system if the transmitter power is reduced below 17 d. Bm in a 1: 1 ratio • Reduce Transmit Power below maximum of 17 d. Bm by 1 d. Bm and increase antenna/cable system gain by 1 d. Bi 7 -22
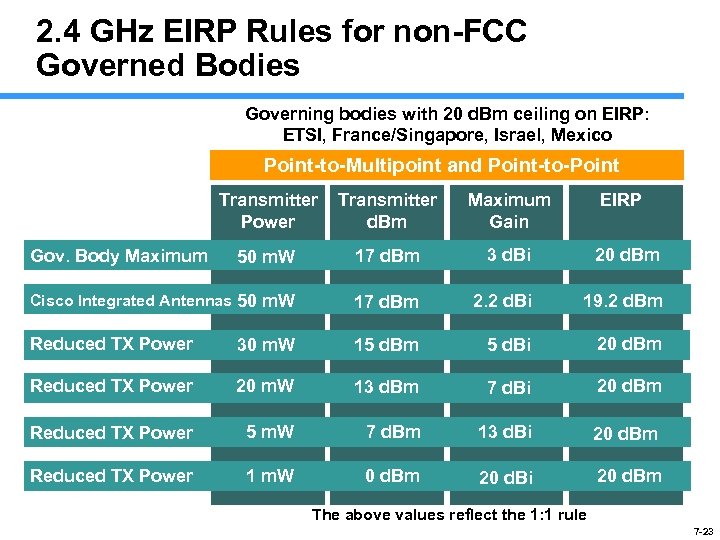 2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for non-FCC Governed Bodies Governing bodies with 20 d. Bm ceiling on EIRP: ETSI, France/Singapore, Israel, Mexico Point-to-Multipoint and Point-to-Point Transmitter Power Transmitter d. Bm Maximum Gain 50 m. W 17 d. Bm 3 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Cisco Integrated Antennas 50 m. W 17 d. Bm 2. 2 d. Bi 19. 2 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 30 m. W 15 d. Bm 5 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 20 m. W 13 d. Bm 7 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 5 m. W 7 d. Bm 13 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 1 m. W 0 d. Bm 20 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Gov. Body Maximum EIRP The above values reflect the 1: 1 rule 7 -23
2. 4 GHz EIRP Rules for non-FCC Governed Bodies Governing bodies with 20 d. Bm ceiling on EIRP: ETSI, France/Singapore, Israel, Mexico Point-to-Multipoint and Point-to-Point Transmitter Power Transmitter d. Bm Maximum Gain 50 m. W 17 d. Bm 3 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Cisco Integrated Antennas 50 m. W 17 d. Bm 2. 2 d. Bi 19. 2 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 30 m. W 15 d. Bm 5 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 20 m. W 13 d. Bm 7 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 5 m. W 7 d. Bm 13 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Reduced TX Power 1 m. W 0 d. Bm 20 d. Bi 20 d. Bm Gov. Body Maximum EIRP The above values reflect the 1: 1 rule 7 -23
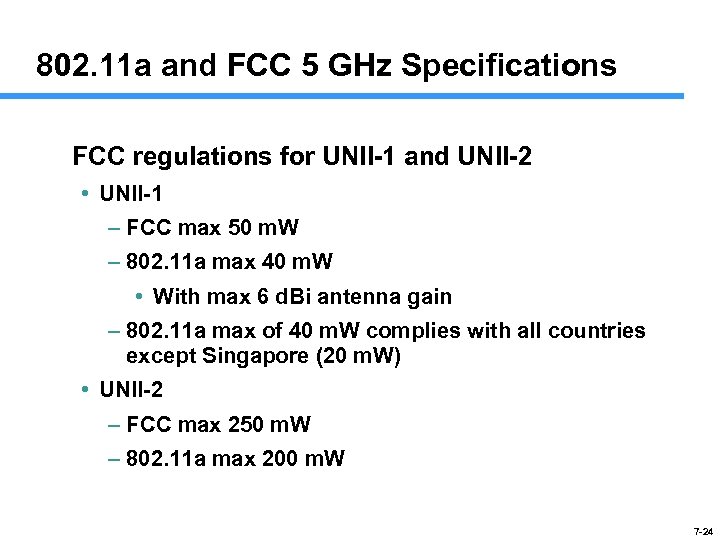 802. 11 a and FCC 5 GHz Specifications FCC regulations for UNII-1 and UNII-2 • UNII-1 – FCC max 50 m. W – 802. 11 a max 40 m. W • With max 6 d. Bi antenna gain – 802. 11 a max of 40 m. W complies with all countries except Singapore (20 m. W) • UNII-2 – FCC max 250 m. W – 802. 11 a max 200 m. W 7 -24
802. 11 a and FCC 5 GHz Specifications FCC regulations for UNII-1 and UNII-2 • UNII-1 – FCC max 50 m. W – 802. 11 a max 40 m. W • With max 6 d. Bi antenna gain – 802. 11 a max of 40 m. W complies with all countries except Singapore (20 m. W) • UNII-2 – FCC max 250 m. W – 802. 11 a max 200 m. W 7 -24
 FCC Rules for 802. 11 a - Antennas FCC requires that all radios utilizing the UNII-1 Band (5. 15 GHz – 5. 25 GHz) must have nonremovable or integrated antennas FCC allows radios utilizing the UNII-2 Band (5. 25 GHz – 5. 35 GHz) to have external or removable antennas FCC requires radios operating in both UNII-1 and UNII-2 bands must comply with antenna rules regulating UNII-1 band (including indoor use only) • The Cisco Aironet 802. 11 a radios utilize both UNII-1 and UNII-2 bands, therefore cannot have external or removable antennas and must be used indoors only • Cisco 802. 11 a antennas are integrated into the radio module 7 -25
FCC Rules for 802. 11 a - Antennas FCC requires that all radios utilizing the UNII-1 Band (5. 15 GHz – 5. 25 GHz) must have nonremovable or integrated antennas FCC allows radios utilizing the UNII-2 Band (5. 25 GHz – 5. 35 GHz) to have external or removable antennas FCC requires radios operating in both UNII-1 and UNII-2 bands must comply with antenna rules regulating UNII-1 band (including indoor use only) • The Cisco Aironet 802. 11 a radios utilize both UNII-1 and UNII-2 bands, therefore cannot have external or removable antennas and must be used indoors only • Cisco 802. 11 a antennas are integrated into the radio module 7 -25
 Omni directional Antennas 7 -26
Omni directional Antennas 7 -26
 2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 2 d. Bi Dipole "Standard Rubber Duck" 7 -27
2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 2 d. Bi Dipole "Standard Rubber Duck" 7 -27
 2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 5. 2 d. Bi Mast Mount Vertical 7 -28
2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 5. 2 d. Bi Mast Mount Vertical 7 -28
 2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 5. 2 d. Bi Ceiling Mount 7 -29
2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 5. 2 d. Bi Ceiling Mount 7 -29
 2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 5. 2 d. Bi Pillar Mount Diversity 7 -30
2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 5. 2 d. Bi Pillar Mount Diversity 7 -30
 2. 4 GHz Diversity Omni-Directional Antennas 2 d. Bi Diversity Omni-Directional Ceiling Mount 7 -31
2. 4 GHz Diversity Omni-Directional Antennas 2 d. Bi Diversity Omni-Directional Ceiling Mount 7 -31
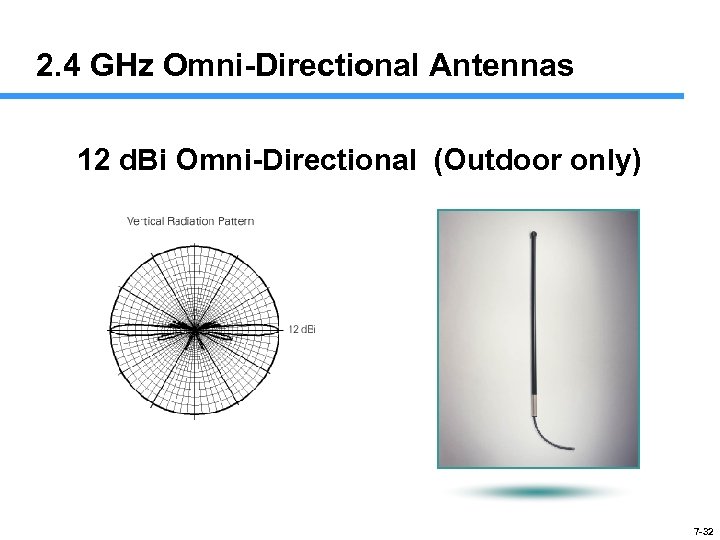 2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 12 d. Bi Omni-Directional (Outdoor only) 7 -32
2. 4 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 12 d. Bi Omni-Directional (Outdoor only) 7 -32
 5 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 9 d. Bi omni (Vertical polarization) 7 -33
5 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas 9 d. Bi omni (Vertical polarization) 7 -33
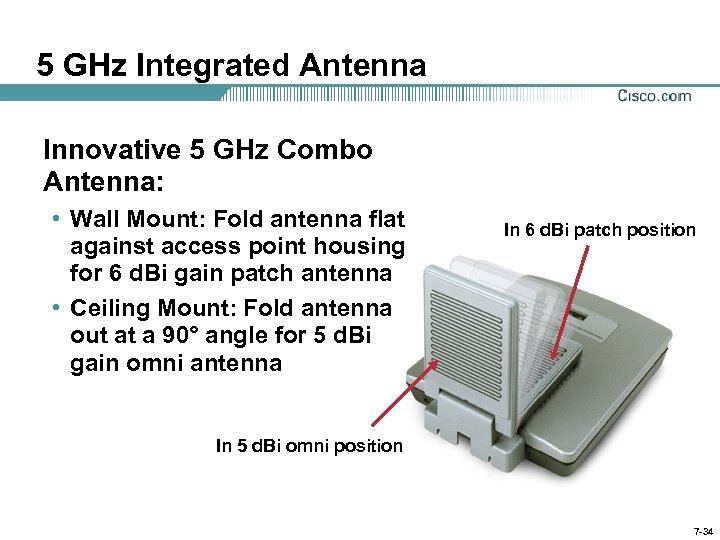 5 GHz Integrated Antenna Innovative 5 GHz Combo Antenna: • Wall Mount: Fold antenna flat against access point housing for 6 d. Bi gain patch antenna • Ceiling Mount: Fold antenna out at a 90° angle for 5 d. Bi gain omni antenna In 6 d. Bi patch position In 5 d. Bi omni position 7 -34
5 GHz Integrated Antenna Innovative 5 GHz Combo Antenna: • Wall Mount: Fold antenna flat against access point housing for 6 d. Bi gain patch antenna • Ceiling Mount: Fold antenna out at a 90° angle for 5 d. Bi gain omni antenna In 6 d. Bi patch position In 5 d. Bi omni position 7 -34
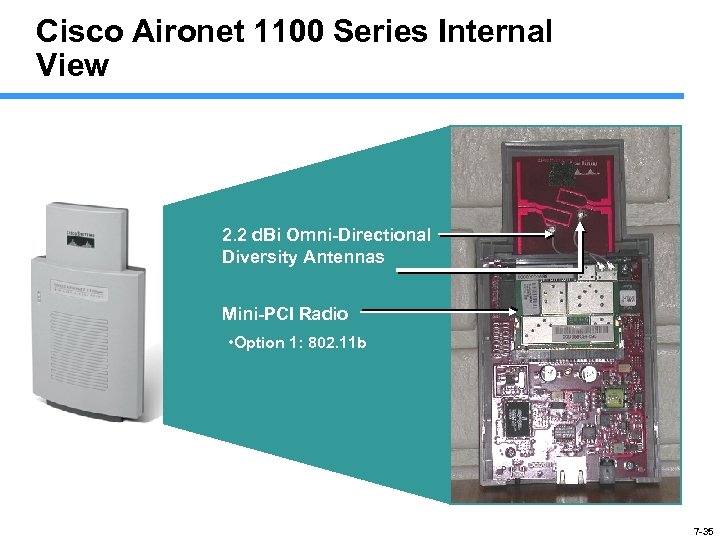 Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Internal View 2. 2 d. Bi Omni-Directional Diversity Antennas Mini-PCI Radio • Option 1: 802. 11 b 7 -35
Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Internal View 2. 2 d. Bi Omni-Directional Diversity Antennas Mini-PCI Radio • Option 1: 802. 11 b 7 -35
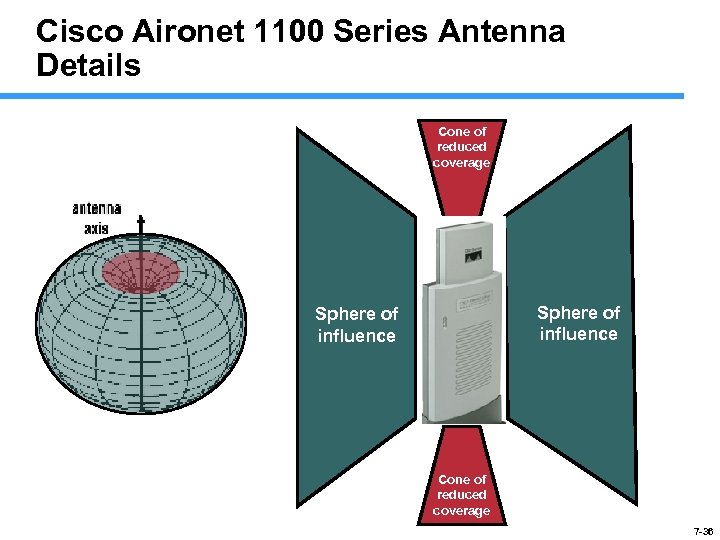 Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Antenna Details Cone of reduced coverage Sphere of influence Cone of reduced coverage 7 -36
Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Antenna Details Cone of reduced coverage Sphere of influence Cone of reduced coverage 7 -36
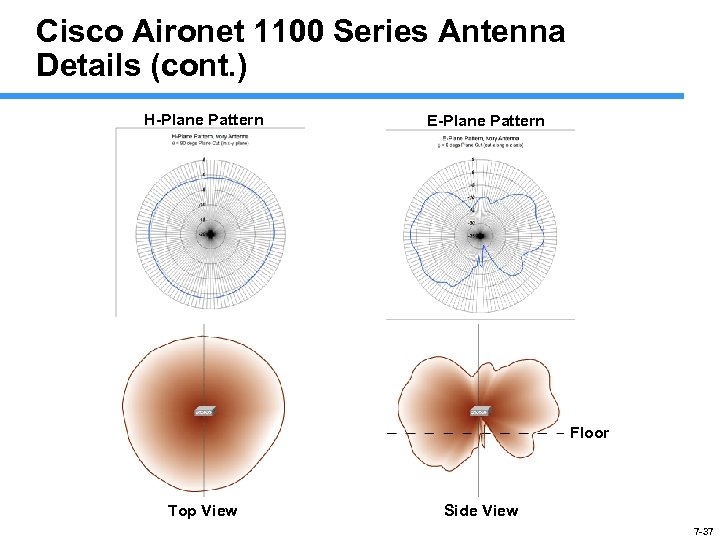 Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Antenna Details (cont. ) H-Plane Pattern E-Plane Pattern Floor Top View Side View 7 -37
Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Antenna Details (cont. ) H-Plane Pattern E-Plane Pattern Floor Top View Side View 7 -37
 Directional Antennas 7 -38
Directional Antennas 7 -38
 2. 4 GHz Diversity Antennas 6. 5 d. Bi Diversity Patch Wall Mount – 55 degree 7 -39
2. 4 GHz Diversity Antennas 6. 5 d. Bi Diversity Patch Wall Mount – 55 degree 7 -39
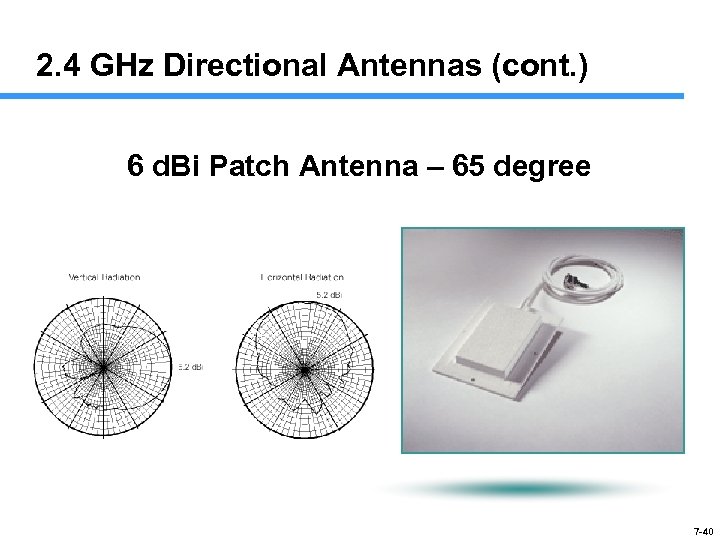 2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 6 d. Bi Patch Antenna – 65 degree 7 -40
2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 6 d. Bi Patch Antenna – 65 degree 7 -40
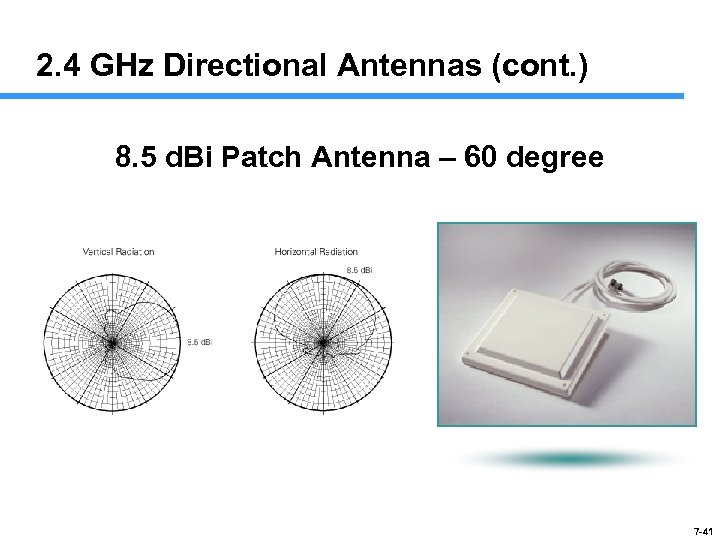 2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 8. 5 d. Bi Patch Antenna – 60 degree 7 -41
2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 8. 5 d. Bi Patch Antenna – 60 degree 7 -41
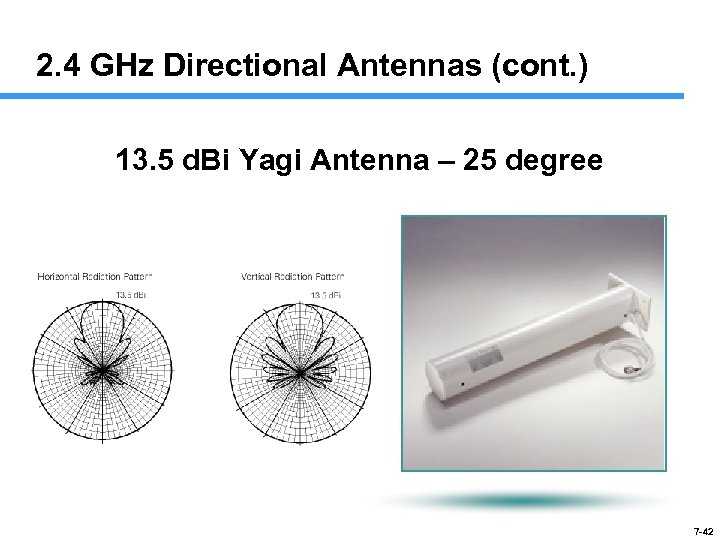 2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 13. 5 d. Bi Yagi Antenna – 25 degree 7 -42
2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 13. 5 d. Bi Yagi Antenna – 25 degree 7 -42
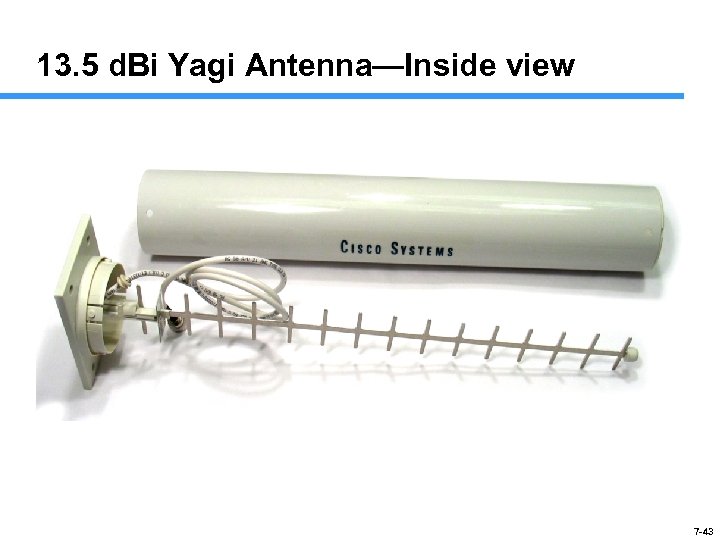 13. 5 d. Bi Yagi Antenna—Inside view 7 -43
13. 5 d. Bi Yagi Antenna—Inside view 7 -43
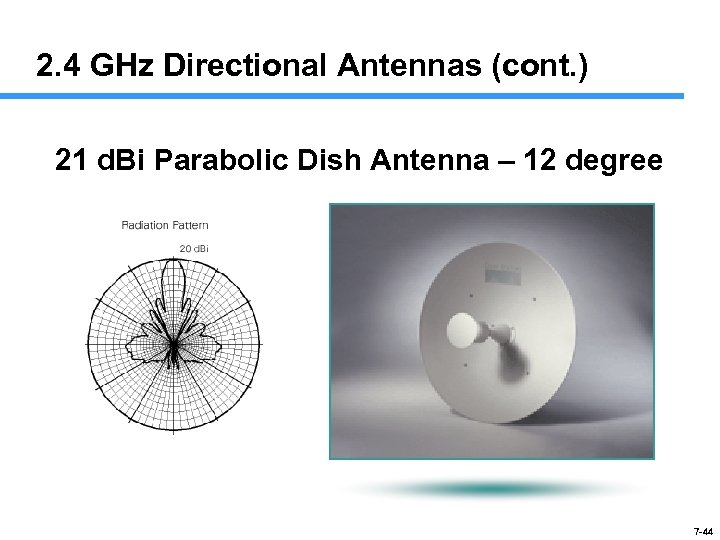 2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 21 d. Bi Parabolic Dish Antenna – 12 degree 7 -44
2. 4 GHz Directional Antennas (cont. ) 21 d. Bi Parabolic Dish Antenna – 12 degree 7 -44
 5 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas • 28 d. Bi dish (H or V polarization) 7 -45
5 GHz Omni-Directional Antennas • 28 d. Bi dish (H or V polarization) 7 -45
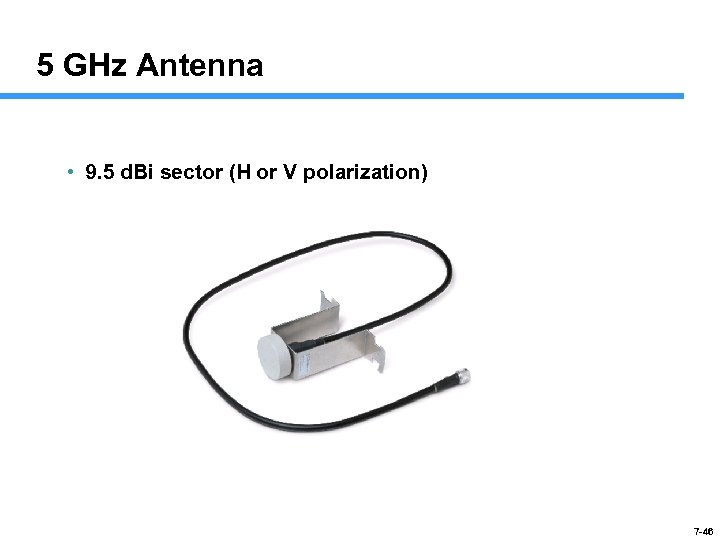 5 GHz Antenna • 9. 5 d. Bi sector (H or V polarization) 7 -46
5 GHz Antenna • 9. 5 d. Bi sector (H or V polarization) 7 -46
 Cable and Accessories 7 -47
Cable and Accessories 7 -47
 2. 4 GHz Accessories 7 -48
2. 4 GHz Accessories 7 -48
 RP-TNC Connectors 7 -49
RP-TNC Connectors 7 -49
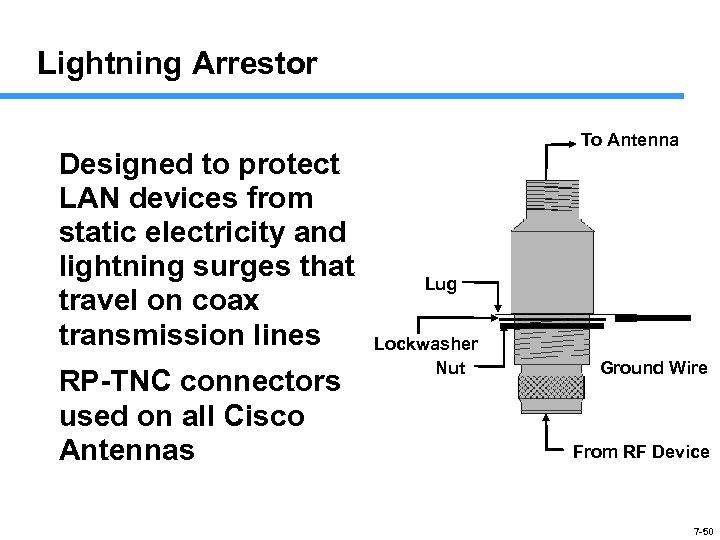 Lightning Arrestor Designed to protect LAN devices from static electricity and lightning surges that travel on coax transmission lines RP-TNC connectors used on all Cisco Antennas To Antenna Lug Lockwasher Nut Ground Wire From RF Device 7 -50
Lightning Arrestor Designed to protect LAN devices from static electricity and lightning surges that travel on coax transmission lines RP-TNC connectors used on all Cisco Antennas To Antenna Lug Lockwasher Nut Ground Wire From RF Device 7 -50
 Lightning Arrestor 7 -51
Lightning Arrestor 7 -51
 Coax Connection Sealing Number one problems with bridges - water in the connectors Proper sealing is important Coax Seal is one product that is inexpensive and works great 7 -52
Coax Connection Sealing Number one problems with bridges - water in the connectors Proper sealing is important Coax Seal is one product that is inexpensive and works great 7 -52
 1400 Accessories Antenna Alignment Assistance with status/alignment LEDs and RSSI port on outdoor unit Quick-hang mounting bracket supports weight of radio during installation process Complete solution provided with radio including: • Power Injector LR • Multi Function Mount • 20’ and 50’ length of dual RG-6 cable • Power supply and cord • Coaxial sealant for all exposed connectors • Corrosion proof gel for exposed metal surfaces Management via SNMP, Telnet CLI, HTTP Based upon 802. 11 a technology 7 -53
1400 Accessories Antenna Alignment Assistance with status/alignment LEDs and RSSI port on outdoor unit Quick-hang mounting bracket supports weight of radio during installation process Complete solution provided with radio including: • Power Injector LR • Multi Function Mount • 20’ and 50’ length of dual RG-6 cable • Power supply and cord • Coaxial sealant for all exposed connectors • Corrosion proof gel for exposed metal surfaces Management via SNMP, Telnet CLI, HTTP Based upon 802. 11 a technology 7 -53
 1400 Power Injector LR Converts standard 10/100 base. T Ethernet RJ-45 interface to F-Type connector dual coaxial cable Power provided over dual coaxial cable with power discovery to protect other appliances Support for longer cable runs by resetting the 100 meter, 100 base. T Ethernet timer, enabling total cable runs of 200 meters. Surge protection provided at the F-Type connectors to protect infrastructure devices 7 -54
1400 Power Injector LR Converts standard 10/100 base. T Ethernet RJ-45 interface to F-Type connector dual coaxial cable Power provided over dual coaxial cable with power discovery to protect other appliances Support for longer cable runs by resetting the 100 meter, 100 base. T Ethernet timer, enabling total cable runs of 200 meters. Surge protection provided at the F-Type connectors to protect infrastructure devices 7 -54
 Link Engineering and RF Path Planning 7 -55
Link Engineering and RF Path Planning 7 -55
 Path Considerations Radio line of sight Earth bulge Fresnel zone Antenna and cabling Data rate 7 -56
Path Considerations Radio line of sight Earth bulge Fresnel zone Antenna and cabling Data rate 7 -56
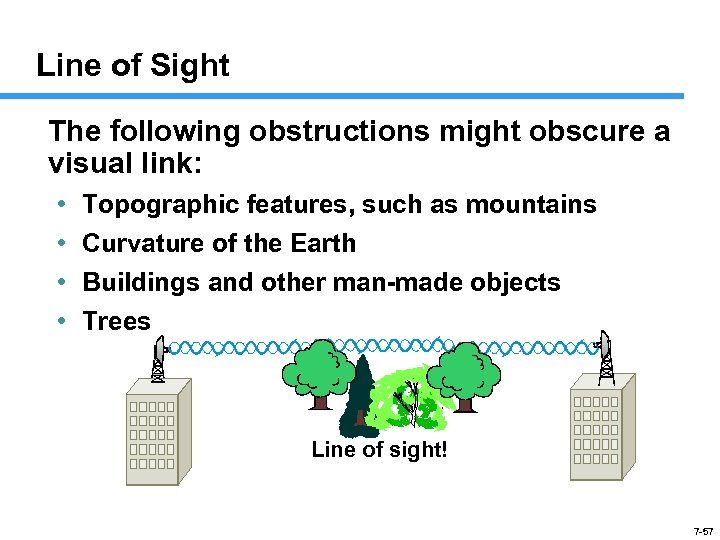 Line of Sight The following obstructions might obscure a visual link: • • Topographic features, such as mountains Curvature of the Earth Buildings and other man-made objects Trees Line of sight! 7 -57
Line of Sight The following obstructions might obscure a visual link: • • Topographic features, such as mountains Curvature of the Earth Buildings and other man-made objects Trees Line of sight! 7 -57
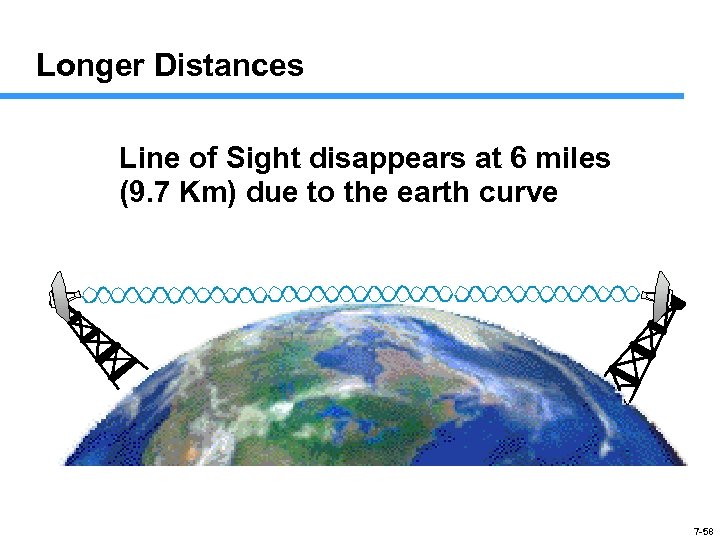 Longer Distances Line of Sight disappears at 6 miles (9. 7 Km) due to the earth curve 7 -58
Longer Distances Line of Sight disappears at 6 miles (9. 7 Km) due to the earth curve 7 -58
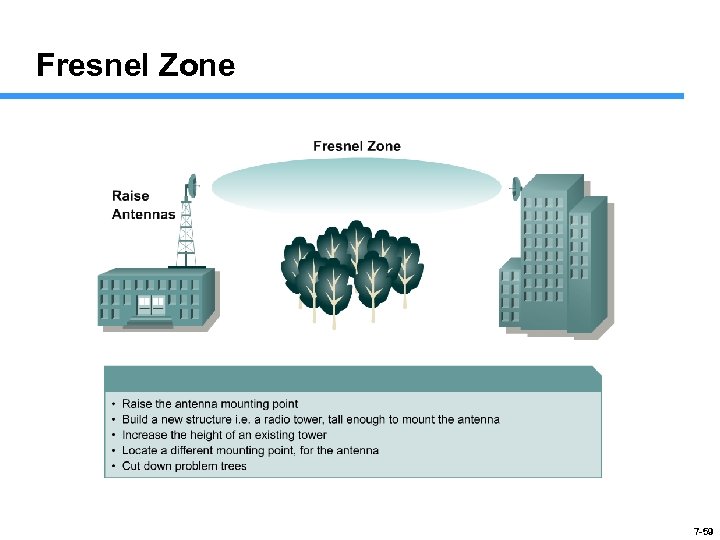 Fresnel Zone 7 -59
Fresnel Zone 7 -59
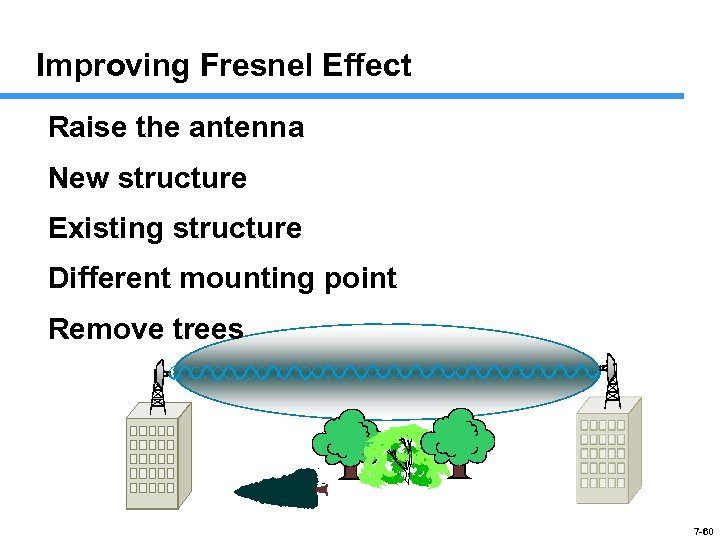 Improving Fresnel Effect Raise the antenna New structure Existing structure Different mounting point Remove trees 7 -60
Improving Fresnel Effect Raise the antenna New structure Existing structure Different mounting point Remove trees 7 -60
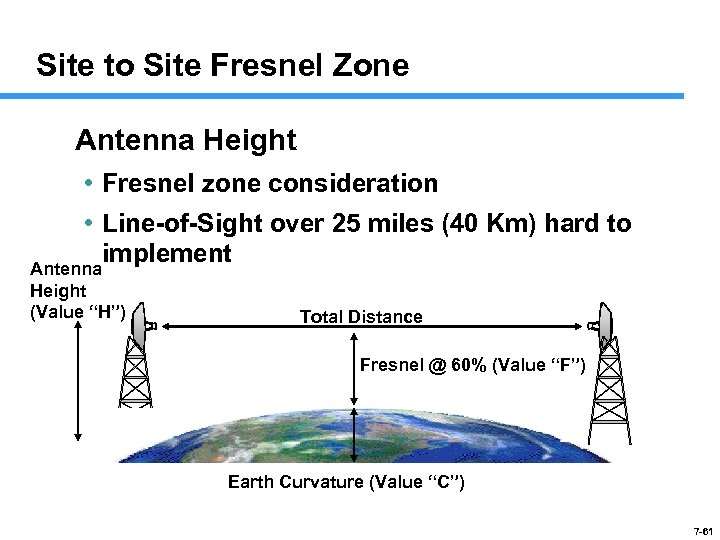 Site to Site Fresnel Zone Antenna Height • Fresnel zone consideration • Line-of-Sight over 25 miles (40 Km) hard to implement Antenna Height (Value “H”) Total Distance Fresnel @ 60% (Value “F”) Earth Curvature (Value “C”) 7 -61
Site to Site Fresnel Zone Antenna Height • Fresnel zone consideration • Line-of-Sight over 25 miles (40 Km) hard to implement Antenna Height (Value “H”) Total Distance Fresnel @ 60% (Value “F”) Earth Curvature (Value “C”) 7 -61
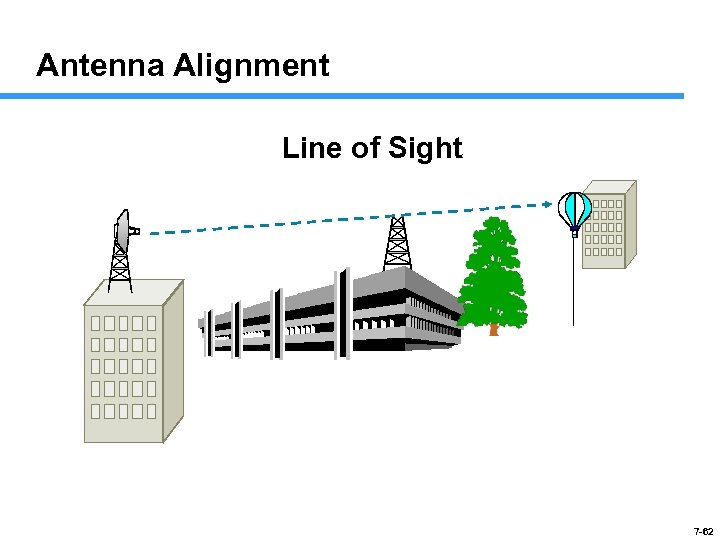 Antenna Alignment Line of Sight 7 -62
Antenna Alignment Line of Sight 7 -62
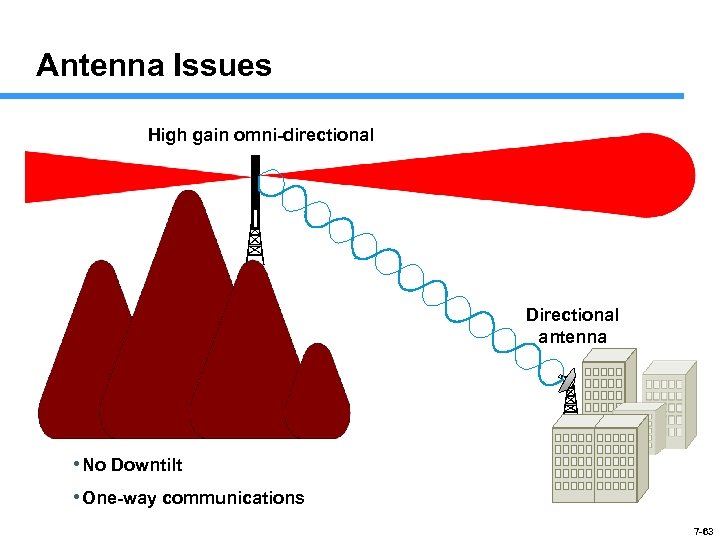 Antenna Issues High gain omni-directional Directional antenna • No Downtilt • One-way communications 7 -63
Antenna Issues High gain omni-directional Directional antenna • No Downtilt • One-way communications 7 -63
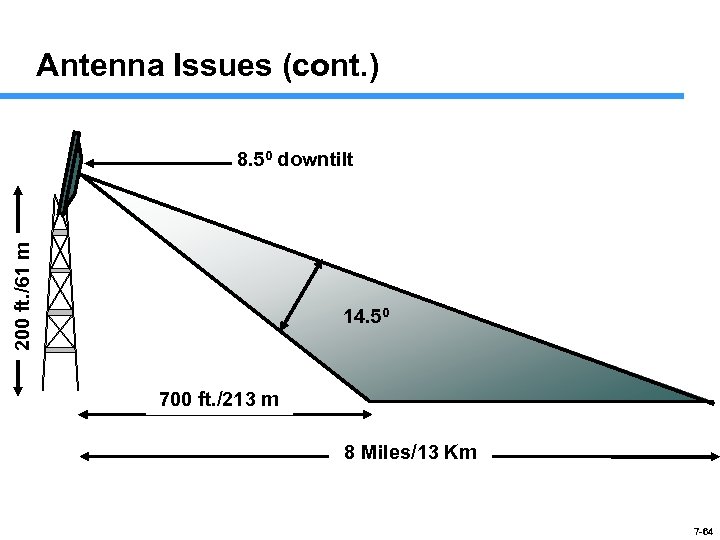 Antenna Issues (cont. ) 200 ft. /61 m 8. 50 downtilt 14. 50 700 ft. /213 m 8 Miles/13 Km 7 -64
Antenna Issues (cont. ) 200 ft. /61 m 8. 50 downtilt 14. 50 700 ft. /213 m 8 Miles/13 Km 7 -64
 Antenna Issues (cont. ) Omni-directional antennas provide 3600 coverage Also accepts interference from all directions 7 -65
Antenna Issues (cont. ) Omni-directional antennas provide 3600 coverage Also accepts interference from all directions 7 -65
 Antenna Installation 7 -66
Antenna Installation 7 -66
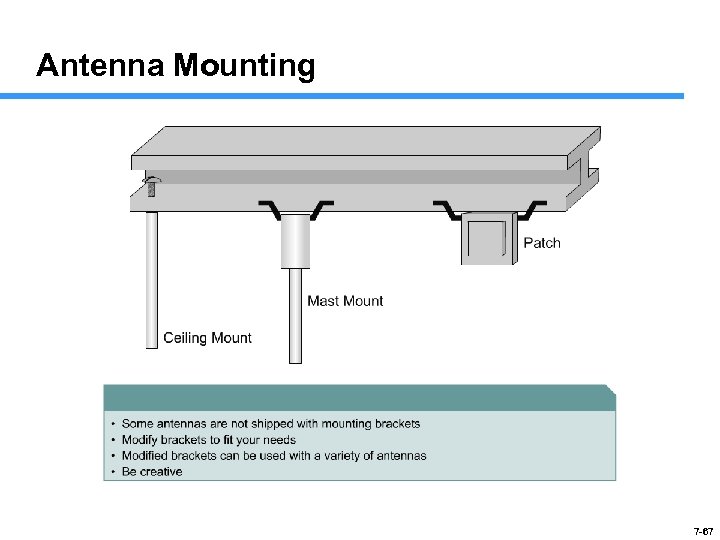 Antenna Mounting 7 -67
Antenna Mounting 7 -67
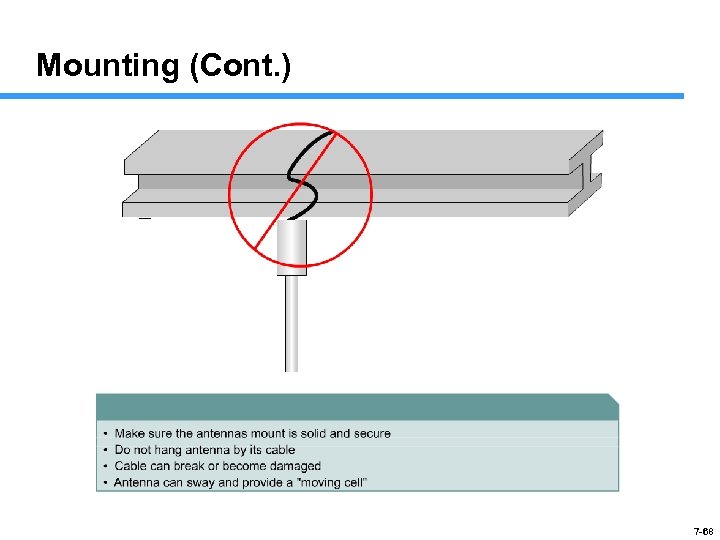 Mounting (Cont. ) 7 -68
Mounting (Cont. ) 7 -68
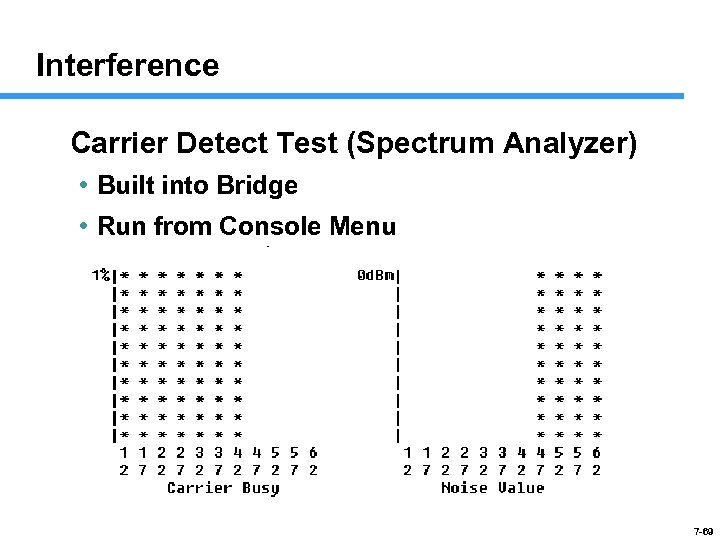 Interference Carrier Detect Test (Spectrum Analyzer) • Built into Bridge • Run from Console Menu 7 -69
Interference Carrier Detect Test (Spectrum Analyzer) • Built into Bridge • Run from Console Menu 7 -69
 Antenna Installation Towers and antennas may require permits and must meet local regulations 7 -70
Antenna Installation Towers and antennas may require permits and must meet local regulations 7 -70
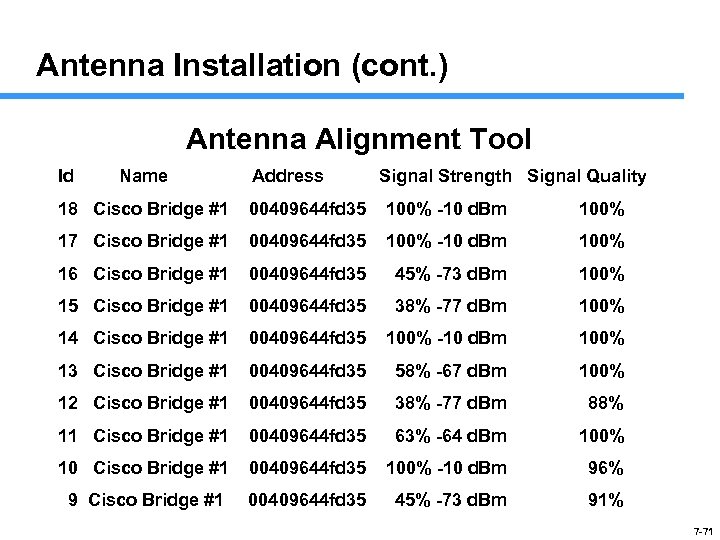 Antenna Installation (cont. ) Antenna Alignment Tool Id Name Address Signal Strength Signal Quality 18 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 100% 17 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 100% 16 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 45% -73 d. Bm 100% 15 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 38% -77 d. Bm 100% 14 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 100% 13 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 58% -67 d. Bm 100% 12 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 38% -77 d. Bm 88% 11 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 63% -64 d. Bm 100% 10 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 96% 9 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 45% -73 d. Bm 91% 7 -71
Antenna Installation (cont. ) Antenna Alignment Tool Id Name Address Signal Strength Signal Quality 18 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 100% 17 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 100% 16 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 45% -73 d. Bm 100% 15 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 38% -77 d. Bm 100% 14 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 100% 13 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 58% -67 d. Bm 100% 12 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 38% -77 d. Bm 88% 11 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 63% -64 d. Bm 100% 10 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 100% -10 d. Bm 96% 9 Cisco Bridge #1 00409644 fd 35 45% -73 d. Bm 91% 7 -71
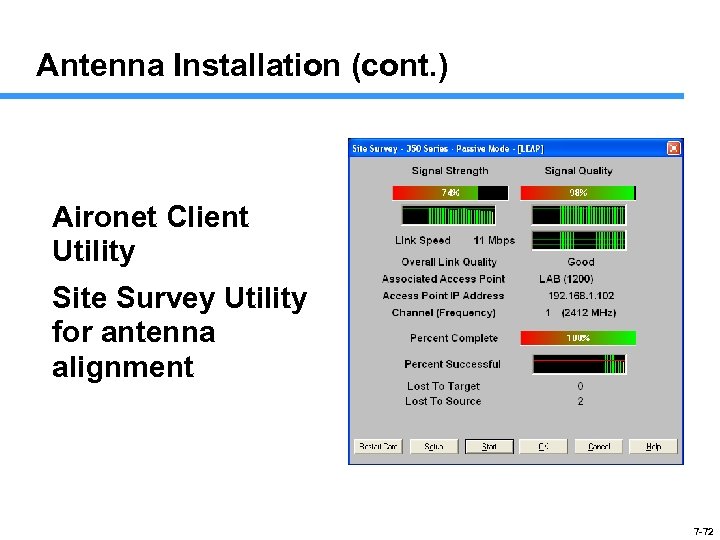 Antenna Installation (cont. ) Aironet Client Utility Site Survey Utility for antenna alignment 7 -72
Antenna Installation (cont. ) Aironet Client Utility Site Survey Utility for antenna alignment 7 -72
 Labs 7 -73
Labs 7 -73
 Labs of Section 7 Lab 7. 1. 4 Antenna Setup Lab 7. 1. 8. 1 Configure AP Diversity Settings Lab 7. 1. 8. 2 Configure Bridge Diversity Settings Lab 7. 2. 6 Omnidirectional Antennas Lab 7. 3. 4 Directional Antennas 7 -74
Labs of Section 7 Lab 7. 1. 4 Antenna Setup Lab 7. 1. 8. 1 Configure AP Diversity Settings Lab 7. 1. 8. 2 Configure Bridge Diversity Settings Lab 7. 2. 6 Omnidirectional Antennas Lab 7. 3. 4 Directional Antennas 7 -74


