66f32f481ab8aa3059bf97ec5929807c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 If progress is the advancement of society, what is congress? CONGRESS
If progress is the advancement of society, what is congress? CONGRESS
 CONGRESS US CAPITOL BUILDING Legislative Branch – “makes laws”
CONGRESS US CAPITOL BUILDING Legislative Branch – “makes laws”
 FOUNDERS’ INTENTIONS 1. 2. 3. Strongest branch Separation of lawmaking power from executive Bicameralism balances large/small states House – more connected to people (2 yr term) Senate – allows for independent thinking (6 yr term)
FOUNDERS’ INTENTIONS 1. 2. 3. Strongest branch Separation of lawmaking power from executive Bicameralism balances large/small states House – more connected to people (2 yr term) Senate – allows for independent thinking (6 yr term)
 IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES House 435 members 2 year term 7 year citizen Initiate impeachment Revenue bills Senate 100 members 6 year term 9 year citizen Strict debate rules Tries impeachment Approve presidential appointments Approve treaties’ Loose debate rules
IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES House 435 members 2 year term 7 year citizen Initiate impeachment Revenue bills Senate 100 members 6 year term 9 year citizen Strict debate rules Tries impeachment Approve presidential appointments Approve treaties’ Loose debate rules
 SHARED DUTIES Establish Federal courts: i. e. inferior courts Congressional oversight: exercise some control over executive agencies. Current issue—Obamacare and Mrs. Sebilius coming before Congress to answer questions.
SHARED DUTIES Establish Federal courts: i. e. inferior courts Congressional oversight: exercise some control over executive agencies. Current issue—Obamacare and Mrs. Sebilius coming before Congress to answer questions.
 CONSTITUTIONAL POWERS Article I, Section 8 To lay and collect taxes, duties, imports To borrow money To regulate commerce (states and foreign) To establish rules for naturalization To coin money To create courts (except Supreme Court) To declare war To raise and support an army and navy
CONSTITUTIONAL POWERS Article I, Section 8 To lay and collect taxes, duties, imports To borrow money To regulate commerce (states and foreign) To establish rules for naturalization To coin money To create courts (except Supreme Court) To declare war To raise and support an army and navy
 EVOLUTION OF POWERS Elastic clause has extended Congress powers Oversight of budget – can restrict the fed. budget prepared by executive branch Appropriations – set amount of money made available for various activity in a fiscal year Investigation – Congress can launch investigations (Watergate, Clinton-Lewinski hearings, Steroids in baseball)
EVOLUTION OF POWERS Elastic clause has extended Congress powers Oversight of budget – can restrict the fed. budget prepared by executive branch Appropriations – set amount of money made available for various activity in a fiscal year Investigation – Congress can launch investigations (Watergate, Clinton-Lewinski hearings, Steroids in baseball)
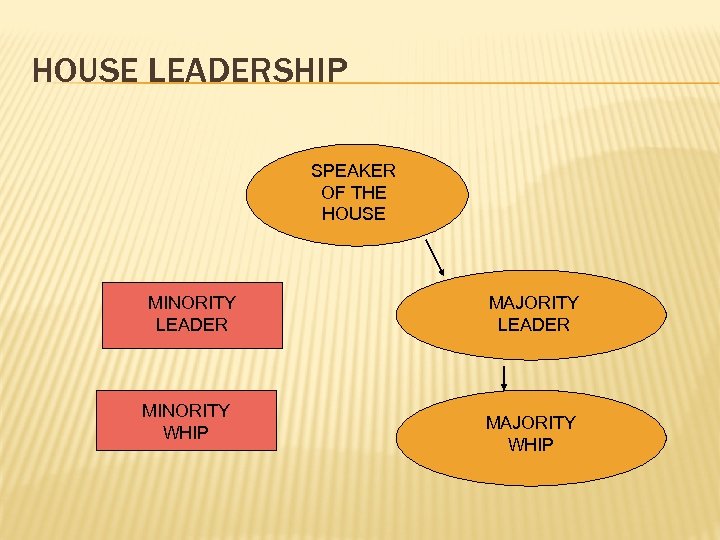 HOUSE LEADERSHIP SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE MINORITY LEADER MINORITY WHIP MAJORITY LEADER MAJORITY WHIP
HOUSE LEADERSHIP SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE MINORITY LEADER MINORITY WHIP MAJORITY LEADER MAJORITY WHIP
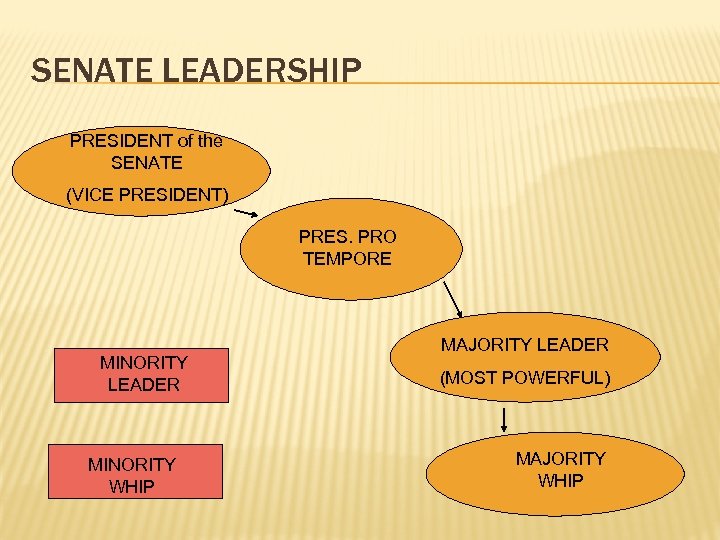 SENATE LEADERSHIP PRESIDENT of the SENATE (VICE PRESIDENT) PRES. PRO TEMPORE MINORITY LEADER MINORITY WHIP MAJORITY LEADER (MOST POWERFUL) MAJORITY WHIP
SENATE LEADERSHIP PRESIDENT of the SENATE (VICE PRESIDENT) PRES. PRO TEMPORE MINORITY LEADER MINORITY WHIP MAJORITY LEADER (MOST POWERFUL) MAJORITY WHIP
 LEADERSHIP Majority party controls the most significant leadership positions House - Speaker of the House Allows people to speak on floor Assigns bills to committees Influences which bills are brought to a vote Appoints members of special and select committees Senate – Majority Leader Schedules Senate business Prioritizes bills
LEADERSHIP Majority party controls the most significant leadership positions House - Speaker of the House Allows people to speak on floor Assigns bills to committees Influences which bills are brought to a vote Appoints members of special and select committees Senate – Majority Leader Schedules Senate business Prioritizes bills
 WHO’S IN CONGRESS? 110 th Congress (2007 -2008) 85% male 85% White 40% Lawyers 109 th Congress (2005 -2006) 29 accused of spousal abuse 7 have been arrested for fraud 19 arrested for writing bad checks 117 have bankrupted at least 2 businesses 8 have been arrested for shoplifting In 1998 alone, 84 were stopped for drunk driving
WHO’S IN CONGRESS? 110 th Congress (2007 -2008) 85% male 85% White 40% Lawyers 109 th Congress (2005 -2006) 29 accused of spousal abuse 7 have been arrested for fraud 19 arrested for writing bad checks 117 have bankrupted at least 2 businesses 8 have been arrested for shoplifting In 1998 alone, 84 were stopped for drunk driving
 ELECTIONS House members directly elected Senators directly elected after 17 th Amend House Incumbent advantage – Why? Name recognition Proven track record Franking privileges – free mailing
ELECTIONS House members directly elected Senators directly elected after 17 th Amend House Incumbent advantage – Why? Name recognition Proven track record Franking privileges – free mailing
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=yx 47 Njaj 1 h g&feature=endscreen&NR=1 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=LES 2 Fn. Ix. Og&feature=endscreen&NR=1
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=yx 47 Njaj 1 h g&feature=endscreen&NR=1 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=LES 2 Fn. Ix. Og&feature=endscreen&NR=1
 REPRESENTATION Malapportionment – unequal population in districts Wesberry v. Sanders (1963) – found unequal district pop. unconstitutional – 14 th amend Gerrymandering – district boundaries are redrawn in strange ways to make it easy for candidate of one party to win Easley v. Cromartie (2001) – redistricting for political ideology was constitutional, led to increase in minority reps
REPRESENTATION Malapportionment – unequal population in districts Wesberry v. Sanders (1963) – found unequal district pop. unconstitutional – 14 th amend Gerrymandering – district boundaries are redrawn in strange ways to make it easy for candidate of one party to win Easley v. Cromartie (2001) – redistricting for political ideology was constitutional, led to increase in minority reps
 HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • Create legislation, make laws • Founders believed in a SLOW process • Founders believed efficiency was a trait of an oppressive government • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=KKv. Y 0 Q 3 t. I 6 I&feature=relmfu
HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • Create legislation, make laws • Founders believed in a SLOW process • Founders believed efficiency was a trait of an oppressive government • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=KKv. Y 0 Q 3 t. I 6 I&feature=relmfu
 STEP 1 – INTRODUCE BILL Introduced in Senate or House (except tax) Single or multiple reps can introduce bill
STEP 1 – INTRODUCE BILL Introduced in Senate or House (except tax) Single or multiple reps can introduce bill
 STEP 2 - COMMITTEE 1. 2. 3. 4. Bill is assigned to a particular committee in its category (Ex. Tax bill – Ways and Means Committee, Farm bill – Agriculture Committee) Bill is then placed in sub-committee Bills are debated and “marked up” Most bills die in committee, committee can vote to “report out” a bill
STEP 2 - COMMITTEE 1. 2. 3. 4. Bill is assigned to a particular committee in its category (Ex. Tax bill – Ways and Means Committee, Farm bill – Agriculture Committee) Bill is then placed in sub-committee Bills are debated and “marked up” Most bills die in committee, committee can vote to “report out” a bill
 STEP 3–RULES COMMITTEE Before bill can go to floor in House, it must first set time limits and amendment regulations. Closed rule – sets time limits, restricts amendments Open rule – permits amendments Restrictive rule – permits some amendments
STEP 3–RULES COMMITTEE Before bill can go to floor in House, it must first set time limits and amendment regulations. Closed rule – sets time limits, restricts amendments Open rule – permits amendments Restrictive rule – permits some amendments
 STEP 4 – FLOOR DEBATE Senate Debate Less formal, no speaking limit Filibuster – practice of stalling a bill w/ debate Cloture – 3/5 of the Senate vote to stop debate House Debate More formal, no filibuster, strict rules
STEP 4 – FLOOR DEBATE Senate Debate Less formal, no speaking limit Filibuster – practice of stalling a bill w/ debate Cloture – 3/5 of the Senate vote to stop debate House Debate More formal, no filibuster, strict rules
 STEP 5 - VOTING Majority passes If the bill passes, it must go through the same process in the opposite chamber with a sponsor If the bill passes one house and fails the other, it must start over If the Senate and House cannot come to agreement over two versions, it goes to Conference Committee to fix it and resubmit the bill
STEP 5 - VOTING Majority passes If the bill passes, it must go through the same process in the opposite chamber with a sponsor If the bill passes one house and fails the other, it must start over If the Senate and House cannot come to agreement over two versions, it goes to Conference Committee to fix it and resubmit the bill
 PRESIDENTIAL ACTION Sign – bill becomes law Veto – bill returns to origin Override – 2/3 vote in both houses can override veto Pocket Veto – President has 10 days to act on a piece of legislation. If he receives the bill within 10 days of the end of the Congressional session, and doesn’t sign, it dies
PRESIDENTIAL ACTION Sign – bill becomes law Veto – bill returns to origin Override – 2/3 vote in both houses can override veto Pocket Veto – President has 10 days to act on a piece of legislation. If he receives the bill within 10 days of the end of the Congressional session, and doesn’t sign, it dies
 OVERRIDE
OVERRIDE
 COMMITTEES AND SUBCOMMITTEES Most real work happens here Bills are passed, changed, ignored, or killed http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EI 8 Ib. BHWe Xo
COMMITTEES AND SUBCOMMITTEES Most real work happens here Bills are passed, changed, ignored, or killed http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EI 8 Ib. BHWe Xo
 TYPES OF COMMITTEES Standing committee – handle bills in different policy areas (ex. Appropriations, Agriculture, Armed Services, Science, etc. ) – most important and have been “standing” (existing) for a long time Select committee – formed for specific purposes and usually temporary – run investigations (ex. Aging, Intelligence)
TYPES OF COMMITTEES Standing committee – handle bills in different policy areas (ex. Appropriations, Agriculture, Armed Services, Science, etc. ) – most important and have been “standing” (existing) for a long time Select committee – formed for specific purposes and usually temporary – run investigations (ex. Aging, Intelligence)
 TYPES OF COMMITTEES Joint committee – consist of both House and Senate members similar in purpose to Select committee Meant to draw attention to issues Conference committee – consist of both House reps and Senators formed to hammer out differences between House and Senate versions of similar bills Congressional Committees and Subcommittees
TYPES OF COMMITTEES Joint committee – consist of both House and Senate members similar in purpose to Select committee Meant to draw attention to issues Conference committee – consist of both House reps and Senators formed to hammer out differences between House and Senate versions of similar bills Congressional Committees and Subcommittees
 COMMITTEE MEMBERSHIP Controlled by majority party, committee membership divided proportionally Committee Chairman Senior member of committee Controls membership and debate
COMMITTEE MEMBERSHIP Controlled by majority party, committee membership divided proportionally Committee Chairman Senior member of committee Controls membership and debate
 WORK OF COMMITTEES 11, 000 bills introduced yearly, most die Committees can… Report out favorably/unfavorably Pigeonholed/table (do not discuss) Amend / “mark up” (change or rewrite)
WORK OF COMMITTEES 11, 000 bills introduced yearly, most die Committees can… Report out favorably/unfavorably Pigeonholed/table (do not discuss) Amend / “mark up” (change or rewrite)
 CONGRESSIONAL CAUCUSES Groupings of members pushing for similar interests Ex. – Sunbelt, Northeast-Midwest, Congressional Black, Women’s, Democratic Study Group, Boll Weevils, Steel
CONGRESSIONAL CAUCUSES Groupings of members pushing for similar interests Ex. – Sunbelt, Northeast-Midwest, Congressional Black, Women’s, Democratic Study Group, Boll Weevils, Steel
 CRITICISMS OF CONGRESS “Pork” – aka “pork-barrel legislation” – bills to benefit constituents in hope of gaining their votes Logrolling – Congress members exchange votes, bills might pass for frivolous reasons Christmas-tree bill –bill with many riders (pork) in Senate, no limit exists on amendments, so Senators try to attach riders that will benefit their home state
CRITICISMS OF CONGRESS “Pork” – aka “pork-barrel legislation” – bills to benefit constituents in hope of gaining their votes Logrolling – Congress members exchange votes, bills might pass for frivolous reasons Christmas-tree bill –bill with many riders (pork) in Senate, no limit exists on amendments, so Senators try to attach riders that will benefit their home state
 TERM-LIMITS DEBATE 1. 2. No current limit on how many terms members of Congress can serve Some argue this has weakened popular control of Congress, reps might be unresponsive to their constituents Some argue most experienced reps have the expertise to bring home more benefits (pork, riders, etc. )
TERM-LIMITS DEBATE 1. 2. No current limit on how many terms members of Congress can serve Some argue this has weakened popular control of Congress, reps might be unresponsive to their constituents Some argue most experienced reps have the expertise to bring home more benefits (pork, riders, etc. )


