c7390cb732d57f90f4df5708f5b52e2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

IEEE BES / BMS ITSC Presentation August 11 th 2004 1

Agenda – Sally Waselik • Introduction • ICSS and BMS background • BES Vs. BMS 2
ICSS and BMS background • Current ICSS system – 10 year old, Coupled with Oracle financials AR, Custom developed, Limitations, De-supported • ICSS Upgrade – Decouple from AR, Upgrade to latest technology stack • IEEE BMS – Add efficiencies in old system, Support new features, Complete re-design / Buy 3
BES Vs. BMS • Distinct business needs – BES focus on Non member – Non Individual Entities – BMS focus on Individual entities • Different business / Technology drivers • Yet commonality and integration necessary 4

Agenda – William Cook • • Key drivers for successful IEEE business Key stake holders for BES / BMS Non member Business needs IEEE BES Phased implementation 5

Agenda – Nimish Shah • IEEE BMS Business needs • Keys to Efficient IT solutions • Business need / System limitations / Proposed solution mapping • IT Implementation plan – high level • BES Options / Investment / Staffing • BMS Options / Investment / Staffing • BES / BMS integration points • Enterprise Architecture 6

Keys Drivers for a Successful IEEE Business • Outstanding Products – Relevancy to Member and Non-Member markets – Best-in-Class • Customer and Market Driven Offerings – Targeted and flexible product offerings – Individualized Marketing • Exceptional Service – Building Member Retention and Loyalty – Higher than some for-profit organizations • Operational Efficiencies 7 – Transactional throughput – Volunteer productivity

IEEE “Lines of Operations” Key Stake Holders – Publications • Publications, Sales & Marketing, Customer Service, Information Technology – Membership & Public Imperatives • Regional Activities, Technical Activities, Publications, Corporate Communications, Corporate Activities, Member Service, Information Technology – Standards • Standards, Publications, Customer Service, Information Technology. – Conferences • Technical Activities, Information Technology – “Other” 8

IEEE BES Business Requirements • $92+ million dollar business – both print and electronic - Growing needs and complexity • BES System Requirements Include: – – – 9 Integrated System reporting. Hierarchical Customer structures. Automatic billing & commission calculations. Automatic renewals and invoicing. Integrated Xplore/e. Rights authentication setup.

IEEE BES Business Needs – Cont. • BES System Requirements (continued): – Automate Quotation, and customer correspondence – Integration between Marketing, Sales, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Fulfillment systems – Better reporting tools 10
Current System Implementation & Limitations • Customer contact detail information and hierarchy maintained separately in Maximizer CRM system by Contract Administration & Sales. • Customer billing detail maintained separately in Excel file by Customer Service. • Renewal bills generated and sent via Word & Excel by Customer Service. • Manual billing and commission calculations input to Oracle AR system to record revenue. • Customer access detail manually input into e. Rights by Customer Service. • Reporting generated via multiple sources depending on the requirement – often doesn’t reconcile. 11

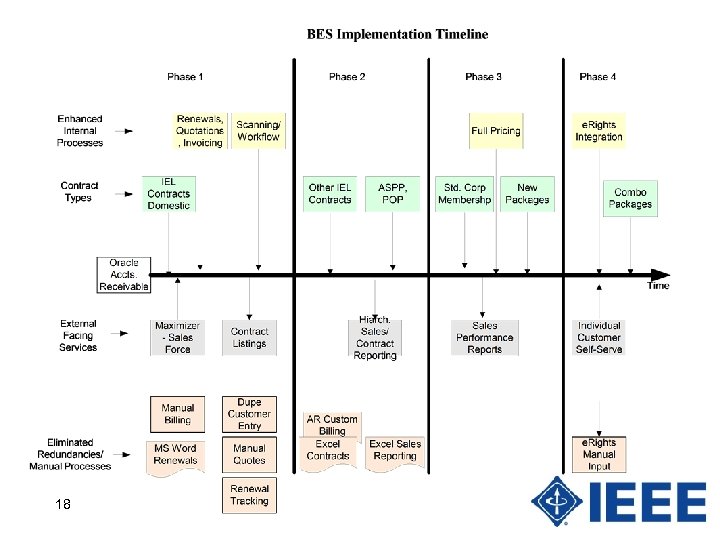
BES Phase 1 • Will include all US IEL customers • Will utilize existing non member customer base already in Oracle system. • Will be integrated with CRM* customer account information in Maximizer (changes in one system will feed the other – “circle of life”). * Customer relationship management 12

BES Phase 1 • Built in scanning and work flow using Feith software: – 90/60/30 day system driven renewal follow up. – “Contract” software will automatically generate appropriate notice (currently manual). – Notice can be emailed or printed and mailed directly to sales rep or customer. – Eliminates manual invoice tracking via Excel. 13

BES Phase 1 • On receipt of payment will automatically create an invoice and send to Oracle AR system. • Provides automatic feed into Oracle GL system based on defined revenue recognition rules. • Significant step in improving automation of back end business system – leads to improved customer service & processing efficiency. 14

BES Phase 2 • Expands deployment and accompanying Phase 1 benefits to non-US IEL product line, and all other electronic only packages such as ASPP and POP. 15

BES Phase 3 • Continues software integration with purchase of Advanced Pricing and Sales Reporting Modules. – Functional integration to be expanded to include new electronic offerings (eg. Enterprise, IEL “Lite”) and print subscription ordering & fulfillment. – Will provide integrated internal system to improve service and drive operational efficiencies. 16

BES Phase 4 – Possible enhancement to include customer facing self-service applications and integration into content delivery platform (Xplore). 17
18

Agenda – Nimish Shah • IEEE BMS Business needs • Keys to Efficient IT solutions • Business need / System limitations / Proposed solution mapping • IT Implementation plan – high level • BES Options / Investment / Staffing • BMS Options / Investment / Staffing • BES / BMS integration points • Enterprise Architecture 19

IEEE BMS Business needs • Member (Individual Entity) – Unified view of customer – Ability segment markets and preferences – Remove dependency on annual subscription based processes and system – Flexibility on Products and offerings – Self service and web technologies – Operational efficiencies. 20
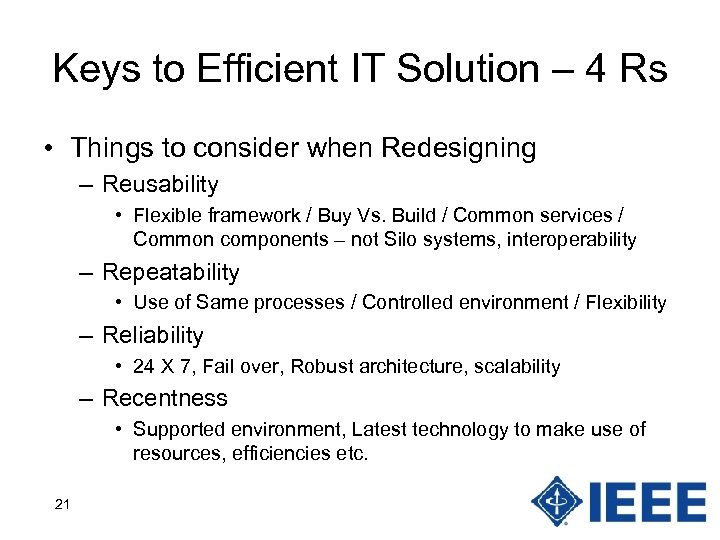
Keys to Efficient IT Solution – 4 Rs • Things to consider when Redesigning – Reusability • Flexible framework / Buy Vs. Build / Common services / Common components – not Silo systems, interoperability – Repeatability • Use of Same processes / Controlled environment / Flexibility – Reliability • 24 X 7, Fail over, Robust architecture, scalability – Recentness • Supported environment, Latest technology to make use of resources, efficiencies etc. 21
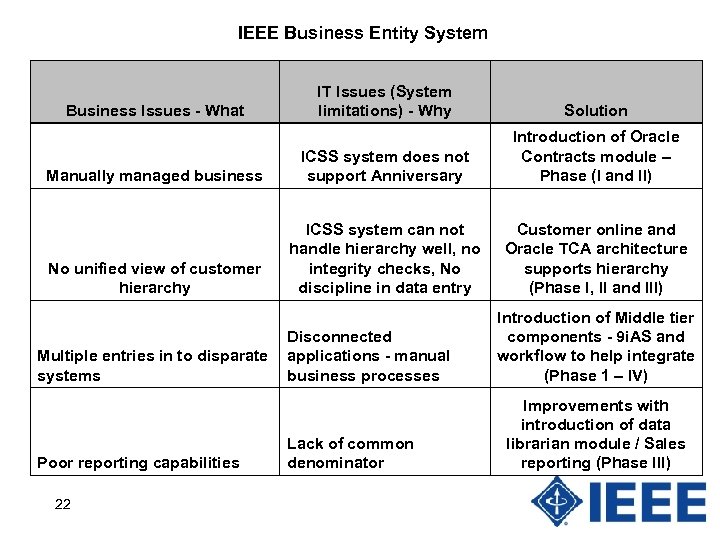
IEEE Business Entity System IT Issues (System limitations) - Why Solution Manually managed business ICSS system does not support Anniversary Introduction of Oracle Contracts module – Phase (I and II) No unified view of customer hierarchy ICSS system can not handle hierarchy well, no integrity checks, No discipline in data entry Customer online and Oracle TCA architecture supports hierarchy (Phase I, II and III) Business Issues - What Multiple entries in to disparate systems Poor reporting capabilities 22 Disconnected applications - manual business processes Lack of common denominator Introduction of Middle tier components - 9 i. AS and workflow to help integrate (Phase 1 – IV) Improvements with introduction of data librarian module / Sales reporting (Phase III)
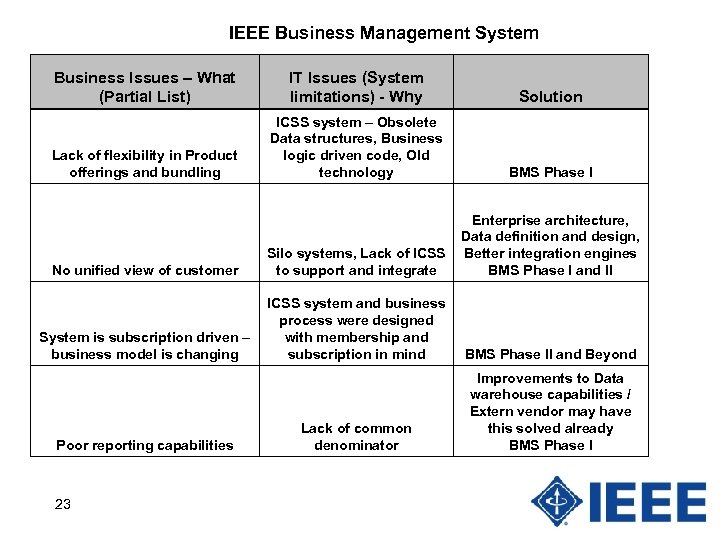
IEEE Business Management System Business Issues – What (Partial List) IT Issues (System limitations) - Why Solution Lack of flexibility in Product offerings and bundling ICSS system – Obsolete Data structures, Business logic driven code, Old technology BMS Phase I No unified view of customer Silo systems, Lack of ICSS to support and integrate Enterprise architecture, Data definition and design, Better integration engines BMS Phase I and II System is subscription driven – business model is changing ICSS system and business process were designed with membership and subscription in mind BMS Phase II and Beyond Lack of common denominator Improvements to Data warehouse capabilities / Extern vendor may have this solved already BMS Phase I Poor reporting capabilities 23
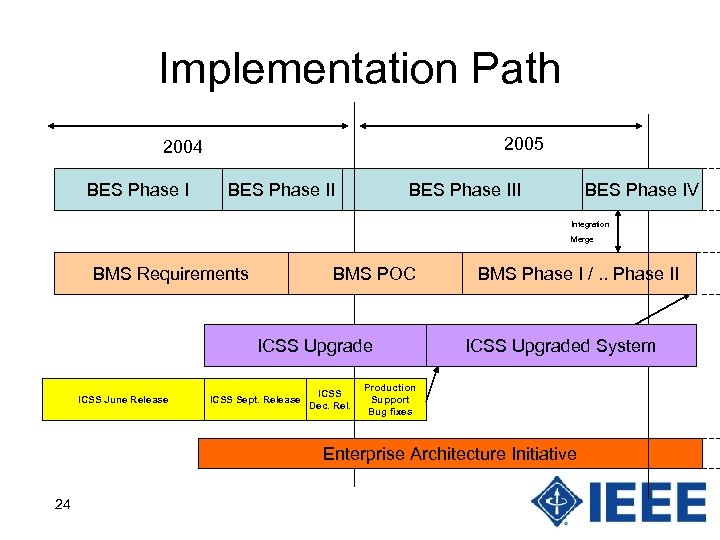
Implementation Path 2005 2004 BES Phase III BES Phase IV Integration Merge BMS Requirements BMS POC ICSS Upgrade ICSS June Release ICSS Sept. Release ICSS Dec. Rel. BMS Phase I /. . Phase II ICSS Upgraded System Production Support Bug fixes Enterprise Architecture Initiative 24

Project investment Phase 1 and 2 • 2003 / 2004 – Invested app. 350 K on capital for Oracle modules and 165 K on incremental head count – On target for cost and on schedule for project delivery dates! 25

Project Investment / needs – BES Phase 3 and 4 • 2005 (Projected) Covers Phase III deployed and Phase IV Requirements for the year 2005 – Capital – 560 K – Expense + Depreciation – 135 K (2005) (Includes incremental contractors and Oracle software investments) • Additional internal staff needs managed through work program prioritization Developers, DBAs, QA, Infrastructure, Users etc. 26
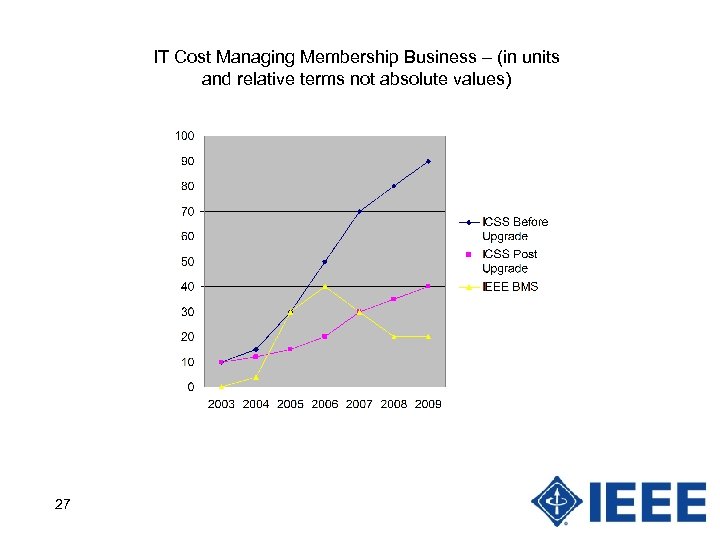
IT Cost Managing Membership Business – (in units and relative terms not absolute values) 27
Project Costs - BMS • Capital for 2005 – 2. 9 MM, Expense and depreciation – 465 K * – Assuming Oracle modules and depreciation for the part of the year (The development starts 2 Q 2005) • Timing, Expectations – Internal Buy-In on Range of Costs – Seek Contingency Funding from BOD – Specific target milestones for approvals and Project Initiation *Based on what we know today…. 28

Enterprise Architecture Focus for 2004 / 2005 • Baseline current capabilities • Build team and facilitate in defining Enterprise architecture • Identify key technology components to go after for 2004 and 2005 such as – – – 29 User experience / Portal Membership / customer / Subscription BES / BMS synergies and Integration Data warehouse / Reporting Infrastructure – OS / Database / Security

BES / BMS Issues Discussion Ben Johnson / Sally Waselik 30

Action Plan on BMS initiative • Get a buy in from ITSC to move forward on BES and BMS Projects – 8/2004 • Obtain agreement in principle on Requirements – 8/2004 • Send out RFP to vendors for their response – late August 2004 • Continue to narrow down the list of vendors and keep fine tuning cost projections – 8/2004 – 2/2005 • Follow-up ITSC prior to November Board series – 10/2004 • Finalize recommendation to the board • FINCOM presentation if possible • Present motion in November Board Series – 11/2004 31
c7390cb732d57f90f4df5708f5b52e2d.ppt