91fa7dab758e9b2ae9c4e3b26f31244c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 IEEE 802. 16 m Fast and Efficiently Identifying Femtocells Subscriber Groups Document Number: IEEE C 80216 m-09_1232 r 1 Date Submitted: 2009 -07 -10 Source: Ying Li, Zhouyue Pi, Baowei Ji, Farooq Khan, Jaehee Cho, Jung Je Son, Anshuman Nigam, Kaushik Josiam, Sudhir Ramakrishna Email: yli 2@sta. samsung. com Phone: +1 -972 -761 -7903 Samsung Electronics Venue: IEEE Session #62 Base Contributions: Re: Change Request for IEEE 802. 16 m SDD, Section 15 Purpose: Notice: Discussion and Approval This document does not represent the agreed views of the IEEE 802. 16 Working Group or any of its subgroups. It represents only the views of the participants listed in the “Source(s)” field above. It is offered as a basis for discussion. It is not binding on the contributor(s), who reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. Release: The contributor grants a free, irrevocable license to the IEEE to incorporate material contained in this contribution, and any modifications thereof, in the creation of an IEEE Standards publication; to copyright in the IEEE’s name any IEEE Standards publication even though it may include portions of this contribution; and at the IEEE’s sole discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part the resulting IEEE Standards publication. The contributor also acknowledges and accepts that this contribution may be made public by IEEE 802. 16. Patent Policy: The contributor is familiar with the IEEE-SA Patent Policy and Procedures:
IEEE 802. 16 m Fast and Efficiently Identifying Femtocells Subscriber Groups Document Number: IEEE C 80216 m-09_1232 r 1 Date Submitted: 2009 -07 -10 Source: Ying Li, Zhouyue Pi, Baowei Ji, Farooq Khan, Jaehee Cho, Jung Je Son, Anshuman Nigam, Kaushik Josiam, Sudhir Ramakrishna Email: yli 2@sta. samsung. com Phone: +1 -972 -761 -7903 Samsung Electronics Venue: IEEE Session #62 Base Contributions: Re: Change Request for IEEE 802. 16 m SDD, Section 15 Purpose: Notice: Discussion and Approval This document does not represent the agreed views of the IEEE 802. 16 Working Group or any of its subgroups. It represents only the views of the participants listed in the “Source(s)” field above. It is offered as a basis for discussion. It is not binding on the contributor(s), who reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. Release: The contributor grants a free, irrevocable license to the IEEE to incorporate material contained in this contribution, and any modifications thereof, in the creation of an IEEE Standards publication; to copyright in the IEEE’s name any IEEE Standards publication even though it may include portions of this contribution; and at the IEEE’s sole discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part the resulting IEEE Standards publication. The contributor also acknowledges and accepts that this contribution may be made public by IEEE 802. 16. Patent Policy: The contributor is familiar with the IEEE-SA Patent Policy and Procedures:
 Use cases to support • Use cases will direct and shape our specific design • The possibilities of use cases could be, for example, – 1. Home • E. g. , a home owner can buy a femto and open it up only to family members and friends – 2. Enterprise • E. g. , a company can buy tens/hundreds femtocells to enhance the connectivity, then such femtos can be open only to the company employees – 3. Membership • E. g. , a use can buy a membership of Starbucks, which means all the femtocells owned by Starbucks should be open to the user – 4. Operator • E. g. , the operator uses femtocells to fix coverage holes, then such femtocells should be open to subscribers of this operator – And so on. 2
Use cases to support • Use cases will direct and shape our specific design • The possibilities of use cases could be, for example, – 1. Home • E. g. , a home owner can buy a femto and open it up only to family members and friends – 2. Enterprise • E. g. , a company can buy tens/hundreds femtocells to enhance the connectivity, then such femtos can be open only to the company employees – 3. Membership • E. g. , a use can buy a membership of Starbucks, which means all the femtocells owned by Starbucks should be open to the user – 4. Operator • E. g. , the operator uses femtocells to fix coverage holes, then such femtocells should be open to subscribers of this operator – And so on. 2
 Motivation (1/3) • IEEE 802. 16 m System Requirements – Shall support CSG (Closed Subscriber Group) – Shall allow dense deployment of large number of Femtocells – Shall support preferred access and handover of MS’s to their designated Femtocell BSs • Some operations (such as Cell Selection, Network RE-/Entry) could be different for Femtocells and macro cells, and for CSG and OSG (Open Subscriber Group) Femtocells. • Therefore, an MS may need to differentiate Femtocells from macro cells, CSG from OSG, or one CSG from the other CSG. 3
Motivation (1/3) • IEEE 802. 16 m System Requirements – Shall support CSG (Closed Subscriber Group) – Shall allow dense deployment of large number of Femtocells – Shall support preferred access and handover of MS’s to their designated Femtocell BSs • Some operations (such as Cell Selection, Network RE-/Entry) could be different for Femtocells and macro cells, and for CSG and OSG (Open Subscriber Group) Femtocells. • Therefore, an MS may need to differentiate Femtocells from macro cells, CSG from OSG, or one CSG from the other CSG. 3
 Motivation (2/3) • Accessibility of a BS – Macro BS: accessible to all MSs – OSG Femtocell BS: accessible to all MSs – CSG Femtocell BS: only accessible to its authorized MSs, though open to all MSs for emergency access. • An MS needs to determine whether it is allowed to access a CSG Femtocell – CSG BS may not be accessible to many MSs, the chance that an MS cannot access to a CSG BS is large, so the accessibility should be checked early. – The number of SCH symbols for cell IDs may not be large enough to differentiate a potential large number of CSG Femtocells. – PBCH can be a good place to offer information for MS to check accessibility. – Consider methods avoiding using expensive PBCH payload. 4
Motivation (2/3) • Accessibility of a BS – Macro BS: accessible to all MSs – OSG Femtocell BS: accessible to all MSs – CSG Femtocell BS: only accessible to its authorized MSs, though open to all MSs for emergency access. • An MS needs to determine whether it is allowed to access a CSG Femtocell – CSG BS may not be accessible to many MSs, the chance that an MS cannot access to a CSG BS is large, so the accessibility should be checked early. – The number of SCH symbols for cell IDs may not be large enough to differentiate a potential large number of CSG Femtocells. – PBCH can be a good place to offer information for MS to check accessibility. – Consider methods avoiding using expensive PBCH payload. 4
 Motivation (3/3) • CSG ID – to ease the management – Several Femtocell BSs could belong to a same CSG entity, which have the same group of authorized MSs. – Benefits of using a common CSG ID for this set of BSs Ø Shorten the list of allowable femtocells stored in MS Ø To ease the management at the paging controller, and avoid location update when the MS is moving inside the CSG. Ø To ease the management of subscriber groups. E. g. , an MS subscribes a membership of Starbucks, which has stores throughout country. Consider Starbucks installs a new femto BS, Ø Without CSG ID, Starbucks has to ask the operator to update it by adding this new femtocell to the white list of all its membership subscribers Ø With CSG ID, such update is not needed. 5
Motivation (3/3) • CSG ID – to ease the management – Several Femtocell BSs could belong to a same CSG entity, which have the same group of authorized MSs. – Benefits of using a common CSG ID for this set of BSs Ø Shorten the list of allowable femtocells stored in MS Ø To ease the management at the paging controller, and avoid location update when the MS is moving inside the CSG. Ø To ease the management of subscriber groups. E. g. , an MS subscribes a membership of Starbucks, which has stores throughout country. Consider Starbucks installs a new femto BS, Ø Without CSG ID, Starbucks has to ask the operator to update it by adding this new femtocell to the white list of all its membership subscribers Ø With CSG ID, such update is not needed. 5
 Challenges • Given potential large number of subscriber groups, CSG ID may need quite a few bits. • CSG ID needs to be broadcast by femtocells. • The additional bits in SFH to identify femtocells may consume the expensive SFH payload. – Consider approaches to avoid/reduce the payload consumption, such as by using the CRC scrambling with different masks on SFH. 6
Challenges • Given potential large number of subscriber groups, CSG ID may need quite a few bits. • CSG ID needs to be broadcast by femtocells. • The additional bits in SFH to identify femtocells may consume the expensive SFH payload. – Consider approaches to avoid/reduce the payload consumption, such as by using the CRC scrambling with different masks on SFH. 6
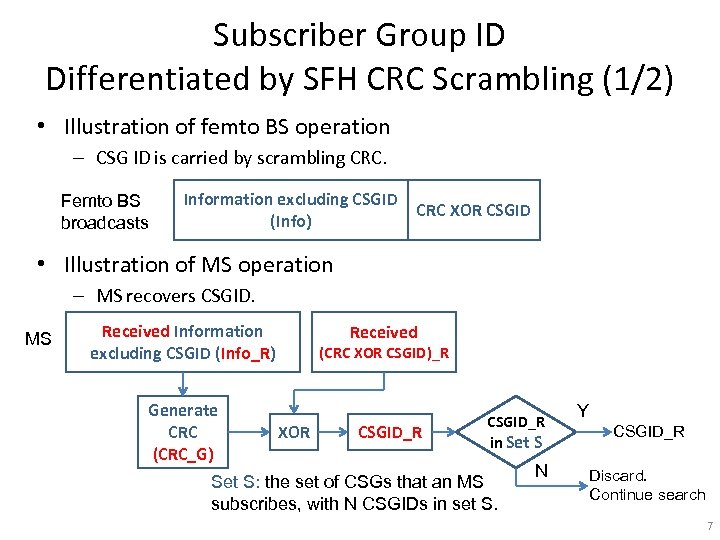 Subscriber Group ID Differentiated by SFH CRC Scrambling (1/2) • Illustration of femto BS operation – CSG ID is carried by scrambling CRC. Femto BS broadcasts Information excluding CSGID (Info) CRC XOR CSGID • Illustration of MS operation – MS recovers CSGID. MS Received Information excluding CSGID (Info_R) Generate CRC (CRC_G) Received (CRC XOR CSGID)_R XOR CSGID_R in Set S: the set of CSGs that an MS subscribes, with N CSGIDs in set S. N Y CSGID_R Discard. Continue search 7
Subscriber Group ID Differentiated by SFH CRC Scrambling (1/2) • Illustration of femto BS operation – CSG ID is carried by scrambling CRC. Femto BS broadcasts Information excluding CSGID (Info) CRC XOR CSGID • Illustration of MS operation – MS recovers CSGID. MS Received Information excluding CSGID (Info_R) Generate CRC (CRC_G) Received (CRC XOR CSGID)_R XOR CSGID_R in Set S: the set of CSGs that an MS subscribes, with N CSGIDs in set S. N Y CSGID_R Discard. Continue search 7
 Subscriber Group ID Differentiated by SFH CRC Scrambling (3/3) • Rationale: – An MS may only subscribe a few CSGs among the entire CSGID space. In information theory prospective, this gives the chance of compressing, e. g. , reducing the overhead by scrambling CRC. 8
Subscriber Group ID Differentiated by SFH CRC Scrambling (3/3) • Rationale: – An MS may only subscribe a few CSGs among the entire CSGID space. In information theory prospective, this gives the chance of compressing, e. g. , reducing the overhead by scrambling CRC. 8
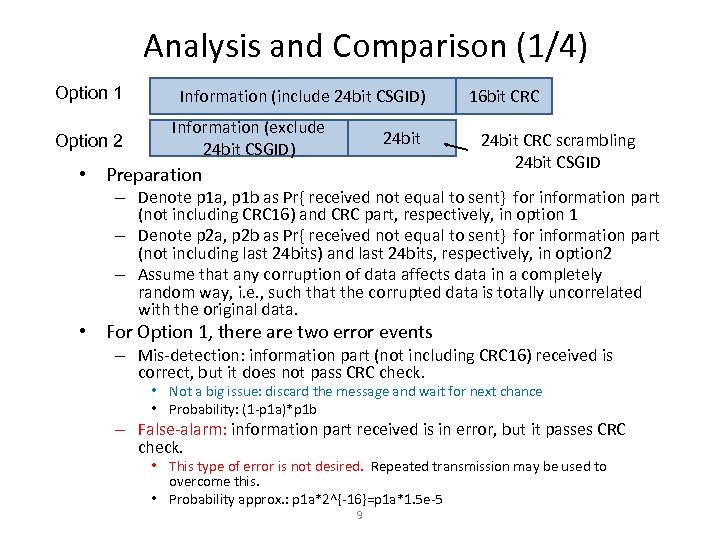 Analysis and Comparison (1/4) Option 1 Option 2 Information (include 24 bit CSGID) Information (exclude 24 bit CSGID) 24 bit • Preparation 16 bit CRC 24 bit CRC scrambling 24 bit CSGID – Denote p 1 a, p 1 b as Pr{ received not equal to sent} for information part (not including CRC 16) and CRC part, respectively, in option 1 – Denote p 2 a, p 2 b as Pr{ received not equal to sent} for information part (not including last 24 bits) and last 24 bits, respectively, in option 2 – Assume that any corruption of data affects data in a completely random way, i. e. , such that the corrupted data is totally uncorrelated with the original data. • For Option 1, there are two error events – Mis-detection: information part (not including CRC 16) received is correct, but it does not pass CRC check. • Not a big issue: discard the message and wait for next chance • Probability: (1 -p 1 a)*p 1 b – False-alarm: information part received is in error, but it passes CRC check. • This type of error is not desired. Repeated transmission may be used to overcome this. • Probability approx. : p 1 a*2^{-16}=p 1 a*1. 5 e-5 9
Analysis and Comparison (1/4) Option 1 Option 2 Information (include 24 bit CSGID) Information (exclude 24 bit CSGID) 24 bit • Preparation 16 bit CRC 24 bit CRC scrambling 24 bit CSGID – Denote p 1 a, p 1 b as Pr{ received not equal to sent} for information part (not including CRC 16) and CRC part, respectively, in option 1 – Denote p 2 a, p 2 b as Pr{ received not equal to sent} for information part (not including last 24 bits) and last 24 bits, respectively, in option 2 – Assume that any corruption of data affects data in a completely random way, i. e. , such that the corrupted data is totally uncorrelated with the original data. • For Option 1, there are two error events – Mis-detection: information part (not including CRC 16) received is correct, but it does not pass CRC check. • Not a big issue: discard the message and wait for next chance • Probability: (1 -p 1 a)*p 1 b – False-alarm: information part received is in error, but it passes CRC check. • This type of error is not desired. Repeated transmission may be used to overcome this. • Probability approx. : p 1 a*2^{-16}=p 1 a*1. 5 e-5 9
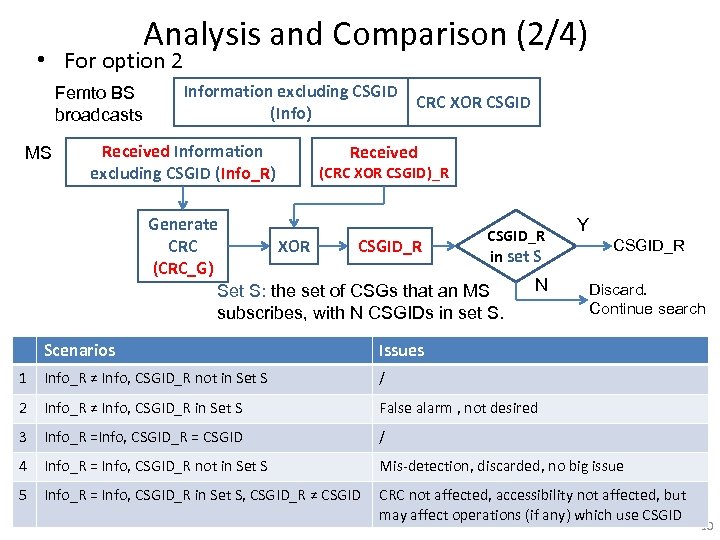 Analysis and Comparison (2/4) • For option 2 Femto BS broadcasts MS Information excluding CSGID (Info) Received Information excluding CSGID (Info_R) CRC XOR CSGID Received (CRC XOR CSGID)_R Generate CSGID_R XOR CSGID_R CRC in set S (CRC_G) N Set S: the set of CSGs that an MS subscribes, with N CSGIDs in set S. Y CSGID_R Discard. Continue search Scenarios Issues 1 Info_R ≠ Info, CSGID_R not in Set S / 2 Info_R ≠ Info, CSGID_R in Set S False alarm , not desired 3 Info_R =Info, CSGID_R = CSGID / 4 Info_R = Info, CSGID_R not in Set S Mis-detection, discarded, no big issue 5 Info_R = Info, CSGID_R in Set S, CSGID_R ≠ CSGID CRC not affected, accessibility not affected, but may affect operations (if any) which use CSGID 10
Analysis and Comparison (2/4) • For option 2 Femto BS broadcasts MS Information excluding CSGID (Info) Received Information excluding CSGID (Info_R) CRC XOR CSGID Received (CRC XOR CSGID)_R Generate CSGID_R XOR CSGID_R CRC in set S (CRC_G) N Set S: the set of CSGs that an MS subscribes, with N CSGIDs in set S. Y CSGID_R Discard. Continue search Scenarios Issues 1 Info_R ≠ Info, CSGID_R not in Set S / 2 Info_R ≠ Info, CSGID_R in Set S False alarm , not desired 3 Info_R =Info, CSGID_R = CSGID / 4 Info_R = Info, CSGID_R not in Set S Mis-detection, discarded, no big issue 5 Info_R = Info, CSGID_R in Set S, CSGID_R ≠ CSGID CRC not affected, accessibility not affected, but may affect operations (if any) which use CSGID 10
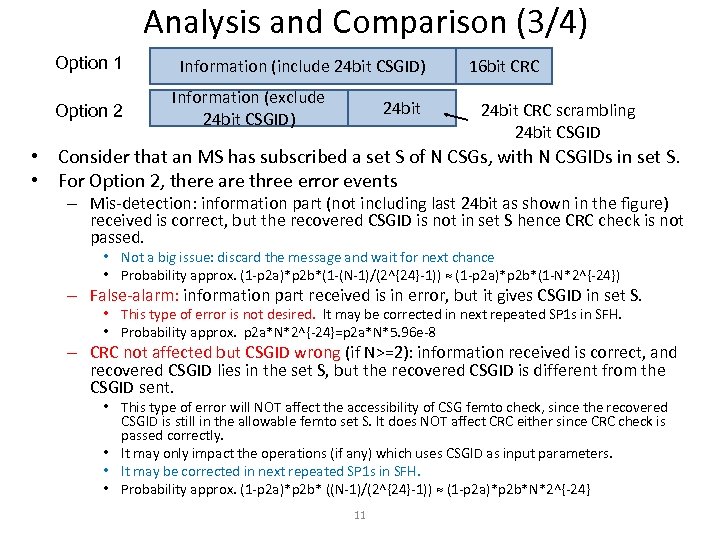 Analysis and Comparison (3/4) Option 1 Option 2 Information (include 24 bit CSGID) Information (exclude 24 bit CSGID) 24 bit 16 bit CRC 24 bit CRC scrambling 24 bit CSGID • Consider that an MS has subscribed a set S of N CSGs, with N CSGIDs in set S. • For Option 2, there are three error events – Mis-detection: information part (not including last 24 bit as shown in the figure) received is correct, but the recovered CSGID is not in set S hence CRC check is not passed. • Not a big issue: discard the message and wait for next chance • Probability approx. (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*(1 -(N-1)/(2^{24}-1)) ≈ (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*(1 -N*2^{-24}) – False-alarm: information part received is in error, but it gives CSGID in set S. • This type of error is not desired. It may be corrected in next repeated SP 1 s in SFH. • Probability approx. p 2 a*N*2^{-24}=p 2 a*N*5. 96 e-8 – CRC not affected but CSGID wrong (if N>=2): information received is correct, and recovered CSGID lies in the set S, but the recovered CSGID is different from the CSGID sent. • This type of error will NOT affect the accessibility of CSG femto check, since the recovered CSGID is still in the allowable femto set S. It does NOT affect CRC either since CRC check is passed correctly. • It may only impact the operations (if any) which uses CSGID as input parameters. • It may be corrected in next repeated SP 1 s in SFH. • Probability approx. (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b* ((N-1)/(2^{24}-1)) ≈ (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*N*2^{-24} 11
Analysis and Comparison (3/4) Option 1 Option 2 Information (include 24 bit CSGID) Information (exclude 24 bit CSGID) 24 bit 16 bit CRC 24 bit CRC scrambling 24 bit CSGID • Consider that an MS has subscribed a set S of N CSGs, with N CSGIDs in set S. • For Option 2, there are three error events – Mis-detection: information part (not including last 24 bit as shown in the figure) received is correct, but the recovered CSGID is not in set S hence CRC check is not passed. • Not a big issue: discard the message and wait for next chance • Probability approx. (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*(1 -(N-1)/(2^{24}-1)) ≈ (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*(1 -N*2^{-24}) – False-alarm: information part received is in error, but it gives CSGID in set S. • This type of error is not desired. It may be corrected in next repeated SP 1 s in SFH. • Probability approx. p 2 a*N*2^{-24}=p 2 a*N*5. 96 e-8 – CRC not affected but CSGID wrong (if N>=2): information received is correct, and recovered CSGID lies in the set S, but the recovered CSGID is different from the CSGID sent. • This type of error will NOT affect the accessibility of CSG femto check, since the recovered CSGID is still in the allowable femto set S. It does NOT affect CRC either since CRC check is passed correctly. • It may only impact the operations (if any) which uses CSGID as input parameters. • It may be corrected in next repeated SP 1 s in SFH. • Probability approx. (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b* ((N-1)/(2^{24}-1)) ≈ (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*N*2^{-24} 11
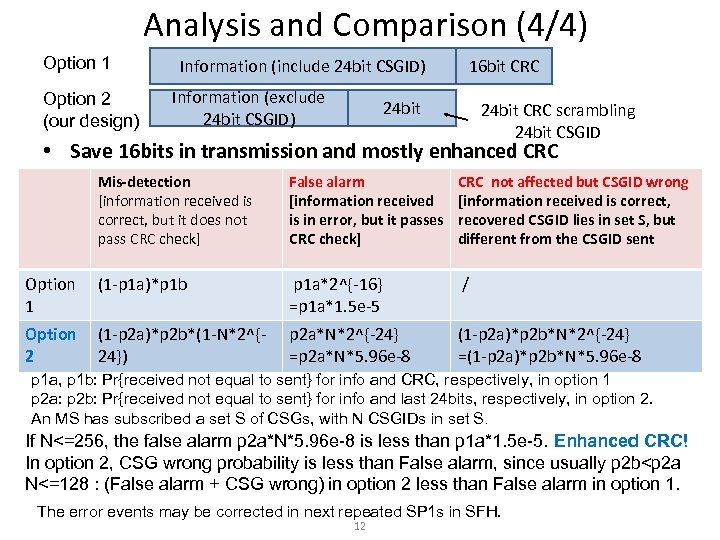 Analysis and Comparison (4/4) Option 1 Option 2 (our design) Information (include 24 bit CSGID) Information (exclude 24 bit CSGID) 16 bit CRC 24 bit CRC scrambling 24 bit CSGID • Save 16 bits in transmission and mostly enhanced CRC Mis-detection [information received is correct, but it does not pass CRC check] False alarm [information received is in error, but it passes CRC check] CRC not affected but CSGID wrong [information received is correct, recovered CSGID lies in set S, but different from the CSGID sent Option 1 (1 -p 1 a)*p 1 b p 1 a*2^{-16} =p 1 a*1. 5 e-5 / Option 2 (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*(1 -N*2^{24}) p 2 a*N*2^{-24} =p 2 a*N*5. 96 e-8 (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*N*2^{-24} =(1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*N*5. 96 e-8 p 1 a, p 1 b: Pr{received not equal to sent} for info and CRC, respectively, in option 1 p 2 a: p 2 b: Pr{received not equal to sent} for info and last 24 bits, respectively, in option 2. An MS has subscribed a set S of CSGs, with N CSGIDs in set S. If N<=256, the false alarm p 2 a*N*5. 96 e-8 is less than p 1 a*1. 5 e-5. Enhanced CRC! In option 2, CSG wrong probability is less than False alarm, since usually p 2 b
Analysis and Comparison (4/4) Option 1 Option 2 (our design) Information (include 24 bit CSGID) Information (exclude 24 bit CSGID) 16 bit CRC 24 bit CRC scrambling 24 bit CSGID • Save 16 bits in transmission and mostly enhanced CRC Mis-detection [information received is correct, but it does not pass CRC check] False alarm [information received is in error, but it passes CRC check] CRC not affected but CSGID wrong [information received is correct, recovered CSGID lies in set S, but different from the CSGID sent Option 1 (1 -p 1 a)*p 1 b p 1 a*2^{-16} =p 1 a*1. 5 e-5 / Option 2 (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*(1 -N*2^{24}) p 2 a*N*2^{-24} =p 2 a*N*5. 96 e-8 (1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*N*2^{-24} =(1 -p 2 a)*p 2 b*N*5. 96 e-8 p 1 a, p 1 b: Pr{received not equal to sent} for info and CRC, respectively, in option 1 p 2 a: p 2 b: Pr{received not equal to sent} for info and last 24 bits, respectively, in option 2. An MS has subscribed a set S of CSGs, with N CSGIDs in set S. If N<=256, the false alarm p 2 a*N*5. 96 e-8 is less than p 1 a*1. 5 e-5. Enhanced CRC! In option 2, CSG wrong probability is less than False alarm, since usually p 2 b
 Proposed Detailed Solution Based on SFH Design in AWD 80216 m-09_0010 r 2 • In current AWD 80216 m-09_0010 r 2, – S-SFH SPs have fixed size. – 16 -bit CRC is used for S-SFH. – In S-SFH SP 1, there is a 16 bit field for BS_EIRP • What we propose is – Femtocell uses 8 bit for BS_EIRP, instead of 16 bit, in SP 1 – Femtocell uses 24 bit CRC, instead of 16 bit – Femtocell 24 bit CSGID scrambles 24 bit CRC • Rationale: – SP 1 for femtocells different from macrocells, which is logically possible since femto and macro are differentiated by preamble partitions. 13
Proposed Detailed Solution Based on SFH Design in AWD 80216 m-09_0010 r 2 • In current AWD 80216 m-09_0010 r 2, – S-SFH SPs have fixed size. – 16 -bit CRC is used for S-SFH. – In S-SFH SP 1, there is a 16 bit field for BS_EIRP • What we propose is – Femtocell uses 8 bit for BS_EIRP, instead of 16 bit, in SP 1 – Femtocell uses 24 bit CRC, instead of 16 bit – Femtocell 24 bit CSGID scrambles 24 bit CRC • Rationale: – SP 1 for femtocells different from macrocells, which is logically possible since femto and macro are differentiated by preamble partitions. 13
 Advantages of Our Proposal • Advantages – Fast: Both femto BSID and CSGID (separately) can be carried in SP 1. – Reliable: If an MS subscribes less than 2^8=256 groups (which may be in most cases), the CRC is enhanced compared to 16 bit CRC. – Efficient: 24 bit femto CSGID is carried within a fixed size SFH SP. No need to enlarge the size of the current SP 1 for macro/femto. 14
Advantages of Our Proposal • Advantages – Fast: Both femto BSID and CSGID (separately) can be carried in SP 1. – Reliable: If an MS subscribes less than 2^8=256 groups (which may be in most cases), the CRC is enhanced compared to 16 bit CRC. – Efficient: 24 bit femto CSGID is carried within a fixed size SFH SP. No need to enlarge the size of the current SP 1 for macro/femto. 14
 Summary • CSG ID of femtocells is carried by using CSG ID as the mask to scramble CRC • The operation is for femtocell only. No change for macrocell. • The approach reduces overhead, and enhances CRC capability. 15
Summary • CSG ID of femtocells is carried by using CSG ID as the mask to scramble CRC • The operation is for femtocell only. No change for macrocell. • The approach reduces overhead, and enhances CRC capability. 15
 Proposed text Insert the following text to the end of 15. 3. 2. Subscriber groups of femtocells may be differentiated by scrambling the CRC of an SFH burst with different masks. Each CSG femtocell BS uses the mask corresponding to the CSG ID. 16
Proposed text Insert the following text to the end of 15. 3. 2. Subscriber groups of femtocells may be differentiated by scrambling the CRC of an SFH burst with different masks. Each CSG femtocell BS uses the mask corresponding to the CSG ID. 16


