f5f1511c971928b53373915413070e5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 IEEE 11073 Inter-LAN Work Group Status in association with HL 7 DEV SIG & ISO TC 215 @ HL 7 Working Group Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008 Jan 18 Mark Schnell, mschnell@cisco. com 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 1
IEEE 11073 Inter-LAN Work Group Status in association with HL 7 DEV SIG & ISO TC 215 @ HL 7 Working Group Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008 Jan 18 Mark Schnell, mschnell@cisco. com 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 1
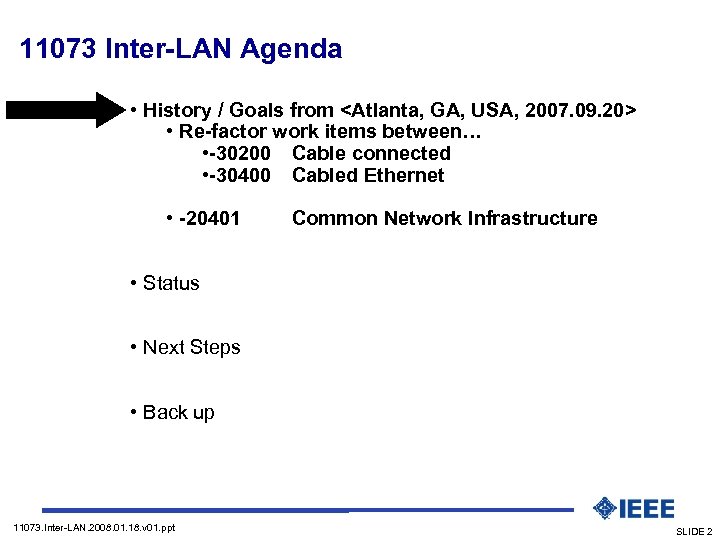 11073 Inter-LAN Agenda • History / Goals from
11073 Inter-LAN Agenda • History / Goals from
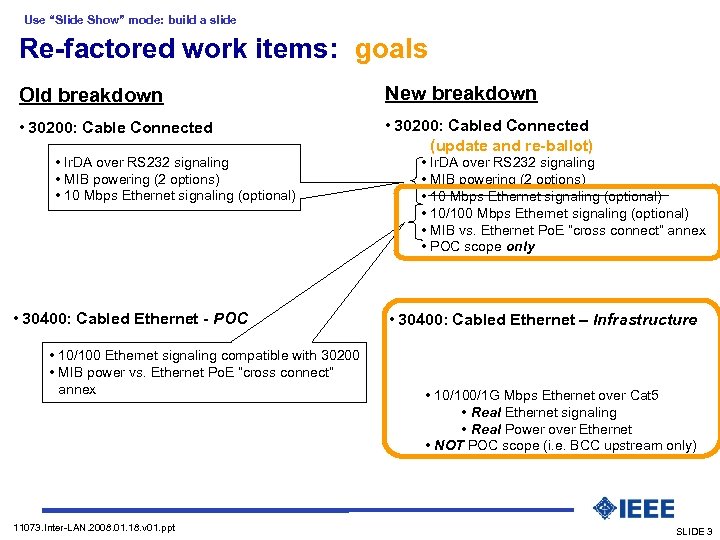 Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide Re-factored work items: goals Old breakdown New breakdown • 30200: Cable Connected • 30200: Cabled Connected (update and re-ballot) • Ir. DA over RS 232 signaling • MIB powering (2 options) • 10 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) • 30400: Cabled Ethernet - POC • 10/100 Ethernet signaling compatible with 30200 • MIB power vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” annex 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt • Ir. DA over RS 232 signaling • MIB powering (2 options) • 10 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) • 10/100 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) • MIB vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” annex • POC scope only • 30400: Cabled Ethernet – Infrastructure • 10/100/1 G Mbps Ethernet over Cat 5 • Real Ethernet signaling • Real Power over Ethernet • NOT POC scope (i. e. BCC upstream only) SLIDE 3
Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide Re-factored work items: goals Old breakdown New breakdown • 30200: Cable Connected • 30200: Cabled Connected (update and re-ballot) • Ir. DA over RS 232 signaling • MIB powering (2 options) • 10 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) • 30400: Cabled Ethernet - POC • 10/100 Ethernet signaling compatible with 30200 • MIB power vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” annex 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt • Ir. DA over RS 232 signaling • MIB powering (2 options) • 10 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) • 10/100 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) • MIB vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” annex • POC scope only • 30400: Cabled Ethernet – Infrastructure • 10/100/1 G Mbps Ethernet over Cat 5 • Real Ethernet signaling • Real Power over Ethernet • NOT POC scope (i. e. BCC upstream only) SLIDE 3
 Clinical Point of Care deployment diagram Point of Care area “A” reference point DCC DCC : “B” “C” MIB : Aggregation Device BCC “Curtain” “F” Non-Po. C area Infrastructure Ethernet “G” “E” : BCC “D” “H” “I” “J” Network Connected Medical Device
Clinical Point of Care deployment diagram Point of Care area “A” reference point DCC DCC : “B” “C” MIB : Aggregation Device BCC “Curtain” “F” Non-Po. C area Infrastructure Ethernet “G” “E” : BCC “D” “H” “I” “J” Network Connected Medical Device
 Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -20401 Work Item List: goals Ö 1. Device communications characteristics Ö 2. Application & Transport data types & characteristics 3. • Application typical use: continuous, episodic, control, alarm, document • Transport: streaming, transaction, batch IP address assignment mechanism Service discovery (w/ service attribute matching) Service definition mechanism Control (aka command/response) mechanism Notification (aka async event reporting) mechanism Data transport 1. 2. 3. • Revisit Discovery Analysis due to Microsoft not putting WS-Discovery into an SDO. • 11073 “Upper Layers” support this directly. Continuous (via streaming) data type Episodic, Control, Alarm (via transaction) data types Document (via batch) data type Inter-LAN test cases A. B. C. 5. Latency/reliability “ 12 -box” IP Interoperability Framework Analysis A. B. Ö C. Ö D. Ö E. F. 4. Device list, data rates, event intervals, …. Functionality defined Control Specifics defined Data transport Specifics defined Test case system “Extended Services” Defined A. In service fault detection mechanism 1. 2. 3. dropped packets latency measure … 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt B. Logging/audit mechanism 1. 2. 3. 4. alarms alerts interesting events misc. notes/messages SLIDE 5
Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -20401 Work Item List: goals Ö 1. Device communications characteristics Ö 2. Application & Transport data types & characteristics 3. • Application typical use: continuous, episodic, control, alarm, document • Transport: streaming, transaction, batch IP address assignment mechanism Service discovery (w/ service attribute matching) Service definition mechanism Control (aka command/response) mechanism Notification (aka async event reporting) mechanism Data transport 1. 2. 3. • Revisit Discovery Analysis due to Microsoft not putting WS-Discovery into an SDO. • 11073 “Upper Layers” support this directly. Continuous (via streaming) data type Episodic, Control, Alarm (via transaction) data types Document (via batch) data type Inter-LAN test cases A. B. C. 5. Latency/reliability “ 12 -box” IP Interoperability Framework Analysis A. B. Ö C. Ö D. Ö E. F. 4. Device list, data rates, event intervals, …. Functionality defined Control Specifics defined Data transport Specifics defined Test case system “Extended Services” Defined A. In service fault detection mechanism 1. 2. 3. dropped packets latency measure … 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt B. Logging/audit mechanism 1. 2. 3. 4. alarms alerts interesting events misc. notes/messages SLIDE 5
 11073 Inter-LAN Agenda • History / Goals from
11073 Inter-LAN Agenda • History / Goals from
 Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -30400 Work Item List: goals & status (Presentation mode: build-a-slide) Ö 1. 11073 -30400 Cabled Ethernet Infrastructure “Intent” Ö 2. Documentation strategy • High level goals. (i. e. Cat 5 cabling; 10/1000 base. T; special features) • NOT POC scope (aka BCC upstream only) • Start with 802. 3 -2005 (the latest monolithic 802. 3 spec) • Clause by clause (1 thru 67) and annex by annex: record thumbs up or thumbs down with an explanation/rationale as to the choice. Ö 3. Turn the crank • Technical content is complete 4. Balloting logistics Ö • Ballot group invitation started Ö • IEEE editorial review complete & comments folded in • • Ballot group invitation closes Ballot started Disposition comments Ballot complete 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt – 2008 Jan 25, Fri SLIDE 7
Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -30400 Work Item List: goals & status (Presentation mode: build-a-slide) Ö 1. 11073 -30400 Cabled Ethernet Infrastructure “Intent” Ö 2. Documentation strategy • High level goals. (i. e. Cat 5 cabling; 10/1000 base. T; special features) • NOT POC scope (aka BCC upstream only) • Start with 802. 3 -2005 (the latest monolithic 802. 3 spec) • Clause by clause (1 thru 67) and annex by annex: record thumbs up or thumbs down with an explanation/rationale as to the choice. Ö 3. Turn the crank • Technical content is complete 4. Balloting logistics Ö • Ballot group invitation started Ö • IEEE editorial review complete & comments folded in • • Ballot group invitation closes Ballot started Disposition comments Ballot complete 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt – 2008 Jan 25, Fri SLIDE 7
 Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -30200 Work Item List: goals & status Ö 1. Document strategy • • Thanks Todd, for this suggestion! No Word version of existing doc Only generate/review deltas to existing -30200 spec Have IEEE editors merge changes into a new, full -30200 spec Ballot resulting spec 2. Start with existing -30200 Cable Connected spec • Add current errata Yet to do. Ö 3. Change existing -30200 Annex F • • From: 10 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) To: 10/100 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) 4. Add new (informative) -30200 Annex O Ö • • From: MIB power vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” -30400 annex A To: MIB power vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” -30200 annex O Update “cross connect” details with latest “termination” information 75% complete 5. Ballot logistics 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 8
Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -30200 Work Item List: goals & status Ö 1. Document strategy • • Thanks Todd, for this suggestion! No Word version of existing doc Only generate/review deltas to existing -30200 spec Have IEEE editors merge changes into a new, full -30200 spec Ballot resulting spec 2. Start with existing -30200 Cable Connected spec • Add current errata Yet to do. Ö 3. Change existing -30200 Annex F • • From: 10 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) To: 10/100 Mbps Ethernet signaling (optional) 4. Add new (informative) -30200 Annex O Ö • • From: MIB power vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” -30400 annex A To: MIB power vs. Ethernet Po. E “cross connect” -30200 annex O Update “cross connect” details with latest “termination” information 75% complete 5. Ballot logistics 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 8
 Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -20401 Work Item List: goals & status Common Network Infrastructure Ö 1. Device communications characteristics Ö 2. Application & Transport data types & characteristics 3. alarm, document • Transport: streaming, transaction, batch No progress • Revisit Discovery Analysis due to Microsoft not putting WS-Discovery into an SDO. : ( 6. • Application typical use: continuous, episodic, control, IP address assignment mechanism Service discovery (w/ service attribute matching) Service definition mechanism Control (aka command/response) mechanism Notification (aka async event reporting) mechanism Data transport 1. 2. 3. 5. 5. Latency/reliability “ 12 -box” IP Interoperability Framework Analysis A. B. Ö C. Ö D. Ö E. F. 4. Device list, data rates, event intervals, …. • 11073 “Upper Layers” support this directly. Continuous (via streaming) data type Episodic, Control, Alarm (via transaction) data types Document (via batch) data type Macro usetest cases Inter-LAN scenarios A. B. C. 11073 -20601 (PHD) over IP. (i. e. 1 -agent to 1 -manager) Functionality defined Classic 11073 upper layers over IP. (i. e. 1 -agent to 1 Control Specifics defined manager and 1 -agent to n-managers) Data transport Specifics defined 1. 2. 3. Profile outline Test case system “Extended Services” Defined 1. A. 2. 3. Data plane: 1. channel use In service fault detection mechanism models Control plane: 1. dropped packets 2.
Use “Slide Show” mode: build a slide -20401 Work Item List: goals & status Common Network Infrastructure Ö 1. Device communications characteristics Ö 2. Application & Transport data types & characteristics 3. alarm, document • Transport: streaming, transaction, batch No progress • Revisit Discovery Analysis due to Microsoft not putting WS-Discovery into an SDO. : ( 6. • Application typical use: continuous, episodic, control, IP address assignment mechanism Service discovery (w/ service attribute matching) Service definition mechanism Control (aka command/response) mechanism Notification (aka async event reporting) mechanism Data transport 1. 2. 3. 5. 5. Latency/reliability “ 12 -box” IP Interoperability Framework Analysis A. B. Ö C. Ö D. Ö E. F. 4. Device list, data rates, event intervals, …. • 11073 “Upper Layers” support this directly. Continuous (via streaming) data type Episodic, Control, Alarm (via transaction) data types Document (via batch) data type Macro usetest cases Inter-LAN scenarios A. B. C. 11073 -20601 (PHD) over IP. (i. e. 1 -agent to 1 -manager) Functionality defined Classic 11073 upper layers over IP. (i. e. 1 -agent to 1 Control Specifics defined manager and 1 -agent to n-managers) Data transport Specifics defined 1. 2. 3. Profile outline Test case system “Extended Services” Defined 1. A. 2. 3. Data plane: 1. channel use In service fault detection mechanism models Control plane: 1. dropped packets 2.
 Data plane: Possible channel use models TCP socket • Role A: start up path • Initial contact • Negotiate for ‘transport control channel” • Note: temporary role TCP socket TCP or UDP or SCTP or
Data plane: Possible channel use models TCP socket • Role A: start up path • Initial contact • Negotiate for ‘transport control channel” • Note: temporary role TCP socket TCP or UDP or SCTP or
 Macro use scenarios Mgr POCTA-1 over IP -30200/30300 Mgr Classic 11073 over IP -30200/30300 PHD over USB BT IP Mgr : Dev/Network mgt tools? ? Classic’ 11073 or PHD over IP Agt Agt 1 to 1 1 to n “upper layer” options “lower layers” options 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt -90101 POCT 1 -A -20601 PHD -20101 Classic 11073 -30200 Cable connected -30300 Infrared wireless USB PHDC Blue Tooth MDP IP centric SLIDE 11
Macro use scenarios Mgr POCTA-1 over IP -30200/30300 Mgr Classic 11073 over IP -30200/30300 PHD over USB BT IP Mgr : Dev/Network mgt tools? ? Classic’ 11073 or PHD over IP Agt Agt 1 to 1 1 to n “upper layer” options “lower layers” options 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt -90101 POCT 1 -A -20601 PHD -20101 Classic 11073 -30200 Cable connected -30300 Infrared wireless USB PHDC Blue Tooth MDP IP centric SLIDE 11
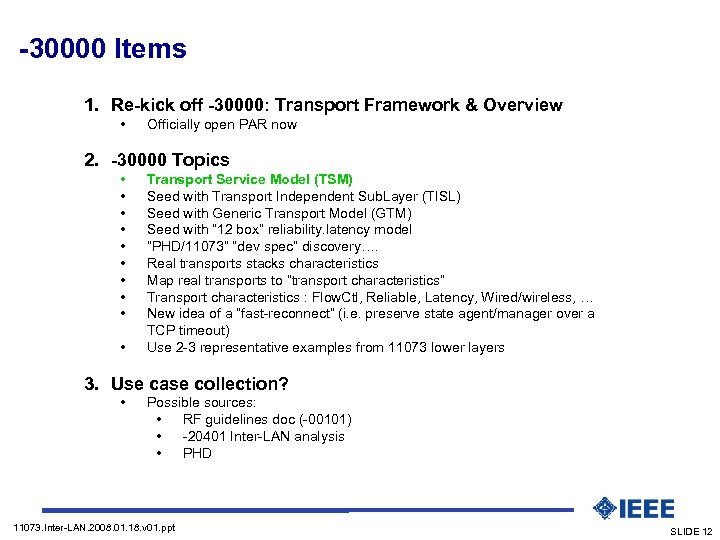 -30000 Items 1. Re-kick off -30000: Transport Framework & Overview • Officially open PAR now 2. -30000 Topics • • • Transport Service Model (TSM) Seed with Transport Independent Sub. Layer (TISL) Seed with Generic Transport Model (GTM) Seed with “ 12 box” reliability. latency model “PHD/11073” “dev spec” discovery…. Real transports stacks characteristics Map real transports to “transport characteristics” Transport characteristics : Flow. Ctl, Reliable, Latency, Wired/wireless, … New idea of a “fast-reconnect” (i. e. preserve state agent/manager over a TCP timeout) Use 2 -3 representative examples from 11073 lower layers 3. Use case collection? • Possible sources: • RF guidelines doc (-00101) • -20401 Inter-LAN analysis • PHD 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 12
-30000 Items 1. Re-kick off -30000: Transport Framework & Overview • Officially open PAR now 2. -30000 Topics • • • Transport Service Model (TSM) Seed with Transport Independent Sub. Layer (TISL) Seed with Generic Transport Model (GTM) Seed with “ 12 box” reliability. latency model “PHD/11073” “dev spec” discovery…. Real transports stacks characteristics Map real transports to “transport characteristics” Transport characteristics : Flow. Ctl, Reliable, Latency, Wired/wireless, … New idea of a “fast-reconnect” (i. e. preserve state agent/manager over a TCP timeout) Use 2 -3 representative examples from 11073 lower layers 3. Use case collection? • Possible sources: • RF guidelines doc (-00101) • -20401 Inter-LAN analysis • PHD 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 12
 11073 Inter-LAN Agenda • History / Goals from
11073 Inter-LAN Agenda • History / Goals from
 Next steps 1. -30400 Cabled Ethernet • Finish ballot process 2. -30200 Cable connected • • Finish ‘delta’ document Start and finish ballot process 3. -20401 Common Network Infrastructure • • Develop transport architecture Overlay supporting network services 4. -30000 Transport Framework & Overview • ? ? work as back ground to -20401 activities? ? 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 14
Next steps 1. -30400 Cabled Ethernet • Finish ballot process 2. -30200 Cable connected • • Finish ‘delta’ document Start and finish ballot process 3. -20401 Common Network Infrastructure • • Develop transport architecture Overlay supporting network services 4. -30000 Transport Framework & Overview • ? ? work as back ground to -20401 activities? ? 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 14
 Logistics/contacts Emails: list: chair: x 73 -30400@ieee. org x 73 -30400 -chair@ieee. org Weekly calls: • Date: Weekly on Tuesday • Time: 12: 00 PM (noon) USA/Eastern Time 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 15
Logistics/contacts Emails: list: chair: x 73 -30400@ieee. org x 73 -30400 -chair@ieee. org Weekly calls: • Date: Weekly on Tuesday • Time: 12: 00 PM (noon) USA/Eastern Time 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 15
 Back up / details 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 16
Back up / details 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 16
 (Item 1 from -20401 Work List) Device communications characteristics 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 17
(Item 1 from -20401 Work List) Device communications characteristics 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 17
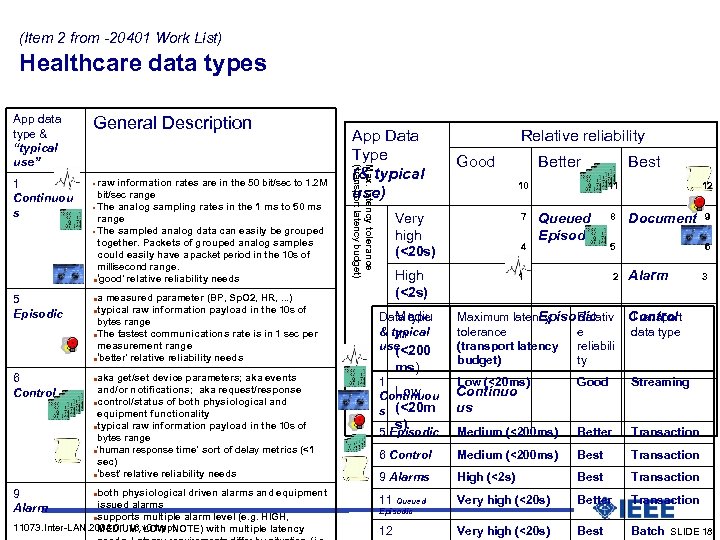 (Item 2 from -20401 Work List) Healthcare data types Presentation mode: build a slide 1 Continuou s 5 Episodic 6 Control General Description raw information rates are in the 50 bit/sec to 1. 2 M bit/sec range The analog sampling rates in the 1 ms to 50 ms range The sampled analog data can easily be grouped together. Packets of grouped analog samples could easily have a packet period in the 10 s of millisecond range. l ‘good’ relative reliability needs a measured parameter (BP, Sp. O 2, HR, . . . ) typical raw information payload in the 10 s of bytes range l The fastest communications rate is in 1 sec per measurement range l ‘better’ relative reliability needs App Data Type (& typical use) Max. latency tolerance (transport latency budget) App data type & “typical use” aka get/set device parameters; aka events and/or notifications; aka request/response l control/status of both physiological and equipment functionality l typical raw information payload in the 10 s of bytes range l 'human response time' sort of delay metrics (<1 sec) l ‘best’ relative reliability needs l both physiological driven alarms and equipment 9 issued alarms Alarm l supports multiple alarm level (e. g. HIGH, 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt MEDIUM, LOW, NOTE) with multiple latency l Good 7 4 High (<2 s) Mediu Data type & typical m use (<200 ms) Better 10 Very high (<20 s) l l Relative reliability Best 11 Queued Episodic 8 12 Document 5 1 2 9 6 Alarm Episodic Maximum latency Relativ tolerance e (transport latency reliabili budget) ty 3 Control Transport data type 1 Low Continuou s (<20 m Continuo us Low (<20 ms) Good Streaming 5 Episodic Medium (<200 ms) Better Transaction 6 Control Medium (<200 ms) Best Transaction 9 Alarms High (<2 s) Best Transaction 11 Queued Very high (<20 s) Better Transaction Very high (<20 s) Best Batch SLIDE 18 s) Episodic 12
(Item 2 from -20401 Work List) Healthcare data types Presentation mode: build a slide 1 Continuou s 5 Episodic 6 Control General Description raw information rates are in the 50 bit/sec to 1. 2 M bit/sec range The analog sampling rates in the 1 ms to 50 ms range The sampled analog data can easily be grouped together. Packets of grouped analog samples could easily have a packet period in the 10 s of millisecond range. l ‘good’ relative reliability needs a measured parameter (BP, Sp. O 2, HR, . . . ) typical raw information payload in the 10 s of bytes range l The fastest communications rate is in 1 sec per measurement range l ‘better’ relative reliability needs App Data Type (& typical use) Max. latency tolerance (transport latency budget) App data type & “typical use” aka get/set device parameters; aka events and/or notifications; aka request/response l control/status of both physiological and equipment functionality l typical raw information payload in the 10 s of bytes range l 'human response time' sort of delay metrics (<1 sec) l ‘best’ relative reliability needs l both physiological driven alarms and equipment 9 issued alarms Alarm l supports multiple alarm level (e. g. HIGH, 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt MEDIUM, LOW, NOTE) with multiple latency l Good 7 4 High (<2 s) Mediu Data type & typical m use (<200 ms) Better 10 Very high (<20 s) l l Relative reliability Best 11 Queued Episodic 8 12 Document 5 1 2 9 6 Alarm Episodic Maximum latency Relativ tolerance e (transport latency reliabili budget) ty 3 Control Transport data type 1 Low Continuou s (<20 m Continuo us Low (<20 ms) Good Streaming 5 Episodic Medium (<200 ms) Better Transaction 6 Control Medium (<200 ms) Best Transaction 9 Alarms High (<2 s) Best Transaction 11 Queued Very high (<20 s) Better Transaction Very high (<20 s) Best Batch SLIDE 18 s) Episodic 12
 A Day In The Life Of A Networked Medical Device (Presentation mode: build-a-slide) Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Set up in hospital IT? ? Find a network Get on the IP network Get the “clinical framework” Associate Med. end pts Disassociate Med. End pts • Encryption keys? ? • Home “domain”? ? (enables HLR/ VLR from cellular) • L 2 activity • AAA (Authentication, Authorization, & Accounting)? • 802. 1 x, Bluetooth “pairing”, other out-of -band pairing, … ? • • • Network services • Pri/sec association server • NTP • “Home” POC (for HLR/VLR for POC roaming? ) • … Clinical “services” • Which VS Mon • Which Nurse station • Which printer • Which plotter • … Dimensions • Static part • Dynamic part (esp. w/ wireless access) (use a “touch” association? ) • Association negotiation (esp. Med SLA check) (SIP w/ SDP ? ) • RTP/RCTP (w/ new profiles? ) (use a ‘test stream’ to measure the net at set up? ) (like a telephony ‘continuity tone’? ) • RSVP? ? • Transfer data • Release association (aka release end point & network resources) IP addr Sub-net Local domain Gateway Pri/sec “Clinical Framework” server (aka config server) • NAC (Network Access Control)? • Med SLA check? Service Ö Discovery Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Data Path Establishment Note: The 11073 Inter-LAN working group is using the above working diagram to assist in keeping focus on the appropriate scope for each step of our work 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 19
A Day In The Life Of A Networked Medical Device (Presentation mode: build-a-slide) Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Set up in hospital IT? ? Find a network Get on the IP network Get the “clinical framework” Associate Med. end pts Disassociate Med. End pts • Encryption keys? ? • Home “domain”? ? (enables HLR/ VLR from cellular) • L 2 activity • AAA (Authentication, Authorization, & Accounting)? • 802. 1 x, Bluetooth “pairing”, other out-of -band pairing, … ? • • • Network services • Pri/sec association server • NTP • “Home” POC (for HLR/VLR for POC roaming? ) • … Clinical “services” • Which VS Mon • Which Nurse station • Which printer • Which plotter • … Dimensions • Static part • Dynamic part (esp. w/ wireless access) (use a “touch” association? ) • Association negotiation (esp. Med SLA check) (SIP w/ SDP ? ) • RTP/RCTP (w/ new profiles? ) (use a ‘test stream’ to measure the net at set up? ) (like a telephony ‘continuity tone’? ) • RSVP? ? • Transfer data • Release association (aka release end point & network resources) IP addr Sub-net Local domain Gateway Pri/sec “Clinical Framework” server (aka config server) • NAC (Network Access Control)? • Med SLA check? Service Ö Discovery Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Data Path Establishment Note: The 11073 Inter-LAN working group is using the above working diagram to assist in keeping focus on the appropriate scope for each step of our work 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 19
 (Item 3 from -20401 Work List) IP Interoperability Framework: definitions (Presentation mode: build-a-slide) 3. IP Interoperability Framework feature areas: A. IP address assignment mechanism • How are IP addresses assigned to all the devices in an 11073 MDC system? B. Service discovery (w/ service attribute matching) • How are the various “services” of a given device advertised and discovered by other devices in the 11073 MDC system? C. Service definition mechanism • How are the various “services” of a given device actually described and defined such that the “service” is usable & understandable by other devices in the 11073 MDC system? D. Control mechanism • aka command/response mechanism • How is a generic “command” sent to a device and how is a response (if any) returned to the caller? E. Notification mechanism • aka subscribe/notify mechanism • aka receive specific/interesting async events • How does an “interested party” register with a device such that it will be notified when a particular event occurs? F. Data transport • How are the specific medical data transported over the IP network… • Document/batch data types • Episodic/transaction data types • Continuous/streaming data types …such that their specific latency & reliability requirements are met? 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 20
(Item 3 from -20401 Work List) IP Interoperability Framework: definitions (Presentation mode: build-a-slide) 3. IP Interoperability Framework feature areas: A. IP address assignment mechanism • How are IP addresses assigned to all the devices in an 11073 MDC system? B. Service discovery (w/ service attribute matching) • How are the various “services” of a given device advertised and discovered by other devices in the 11073 MDC system? C. Service definition mechanism • How are the various “services” of a given device actually described and defined such that the “service” is usable & understandable by other devices in the 11073 MDC system? D. Control mechanism • aka command/response mechanism • How is a generic “command” sent to a device and how is a response (if any) returned to the caller? E. Notification mechanism • aka subscribe/notify mechanism • aka receive specific/interesting async events • How does an “interested party” register with a device such that it will be notified when a particular event occurs? F. Data transport • How are the specific medical data transported over the IP network… • Document/batch data types • Episodic/transaction data types • Continuous/streaming data types …such that their specific latency & reliability requirements are met? 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 20
 (Item 3 A & 3 B from -20401 Work List) Service Discovery Analysis: Short list • Revisit Discovery Analysis due to Microsoft not putting WS-Discovery into an SDO. Risks/Issues 1. WS-Discovery Web Services Discovery • No Discovery Proxy • No standards body home 2. SLP Service Location Protocol • No Interoperable Directory Agent • “Service description framework” is out of scope 3. Zero. Conf Zero Configuration Preferred • “Service description framework” and… • Discovery “query matching” are out of scope 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 21
(Item 3 A & 3 B from -20401 Work List) Service Discovery Analysis: Short list • Revisit Discovery Analysis due to Microsoft not putting WS-Discovery into an SDO. Risks/Issues 1. WS-Discovery Web Services Discovery • No Discovery Proxy • No standards body home 2. SLP Service Location Protocol • No Interoperable Directory Agent • “Service description framework” is out of scope 3. Zero. Conf Zero Configuration Preferred • “Service description framework” and… • Discovery “query matching” are out of scope 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 21
 (Item 3 A & 3 B from -20401 Work List) Service Discovery Analysis: Summary WSSLP+ Discove DHCP+ ry Link. Loc al Zero. Conf (e. g. Bonjour) DICOM JXTA+ discovery DHCP+ Link. Loc al UPn. P Jini + DHCP Ala + carte 1 Link Local Addr Network topology: - ad hoc: - managed: Ö Ö Ö X Ö Ö Discovery mechanism - ad hoc: - managed: distrib central distrib. central X Central distrib central distrib X distrib Central Incremental code size (assume TCP stack & tasking OS) 45 KB -- 40 -60 KB -- 2. 9 MB -- JVM: 4. 5 MB Jini: -- -- Open source client available? 1 2 3 many 3 1 JVM: several; Jini: 1 -- Licensing costs no no no JVM: sometimes Jini: no no Implied SW language no no no Java no Target/classic uses ad hoc & mng net Networked devices Locally networked devices Med image eqpt Peer to peer Home networks Locally networked devices Medical devices Usable for ‘general’ service discovery yes yes NO Required network services (ad hoc & managed) none & (DHCP+ DP) none & (DHCP + DA) none & (DHCP + DNS) DHCP LDAP none & (DHCP + RP) none & (DHCP+ DNS) DHCP DNS DHCP LDAP DHCP DNS Selection Criteria Usable network services DHCP DNS 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 22
(Item 3 A & 3 B from -20401 Work List) Service Discovery Analysis: Summary WSSLP+ Discove DHCP+ ry Link. Loc al Zero. Conf (e. g. Bonjour) DICOM JXTA+ discovery DHCP+ Link. Loc al UPn. P Jini + DHCP Ala + carte 1 Link Local Addr Network topology: - ad hoc: - managed: Ö Ö Ö X Ö Ö Discovery mechanism - ad hoc: - managed: distrib central distrib. central X Central distrib central distrib X distrib Central Incremental code size (assume TCP stack & tasking OS) 45 KB -- 40 -60 KB -- 2. 9 MB -- JVM: 4. 5 MB Jini: -- -- Open source client available? 1 2 3 many 3 1 JVM: several; Jini: 1 -- Licensing costs no no no JVM: sometimes Jini: no no Implied SW language no no no Java no Target/classic uses ad hoc & mng net Networked devices Locally networked devices Med image eqpt Peer to peer Home networks Locally networked devices Medical devices Usable for ‘general’ service discovery yes yes NO Required network services (ad hoc & managed) none & (DHCP+ DP) none & (DHCP + DA) none & (DHCP + DNS) DHCP LDAP none & (DHCP + RP) none & (DHCP+ DNS) DHCP DNS DHCP LDAP DHCP DNS Selection Criteria Usable network services DHCP DNS 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 22
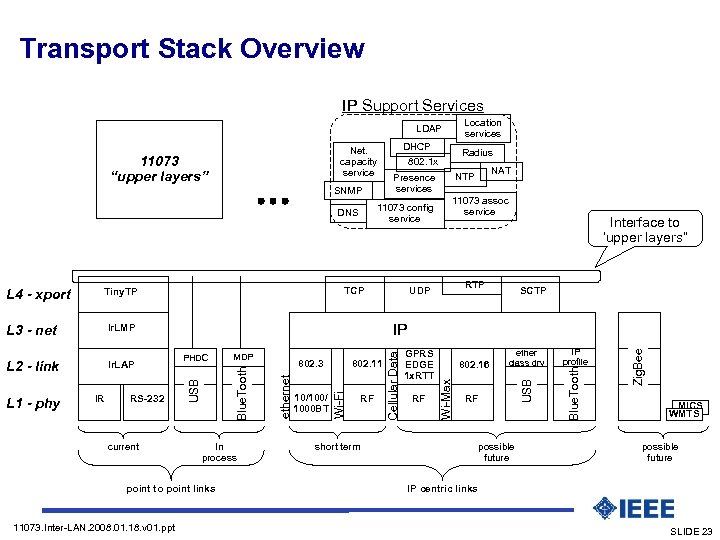 Transport Stack Overview IP Support Services Location services LDAP Net. capacity service 11073 “upper layers” SNMP current In process point to point links 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt Interface to ‘upper layers” RTP UDP SCTP RF short term possible future IP profile Zig. Bee ether class drv Blue. Tooth RF 802. 16 USB RF GPRS EDGE 1 x. RTT Wi-Max 10/100/ 1000 BT 802. 11 Cellular Data RS-232 802. 3 Wi-Fi IR MDP ethernet L 1 - phy PHDC Blue. Tooth L 2 - link Ir. LAP 11073 assoc service IP Ir. LMP USB L 3 - net NAT NTP Presence services TCP Tiny. TP Radius 802. 1 x 11073 config service DNS L 4 - xport DHCP MICS WMTS possible future IP centric links SLIDE 23
Transport Stack Overview IP Support Services Location services LDAP Net. capacity service 11073 “upper layers” SNMP current In process point to point links 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt Interface to ‘upper layers” RTP UDP SCTP RF short term possible future IP profile Zig. Bee ether class drv Blue. Tooth RF 802. 16 USB RF GPRS EDGE 1 x. RTT Wi-Max 10/100/ 1000 BT 802. 11 Cellular Data RS-232 802. 3 Wi-Fi IR MDP ethernet L 1 - phy PHDC Blue. Tooth L 2 - link Ir. LAP 11073 assoc service IP Ir. LMP USB L 3 - net NAT NTP Presence services TCP Tiny. TP Radius 802. 1 x 11073 config service DNS L 4 - xport DHCP MICS WMTS possible future IP centric links SLIDE 23
 The Eight Fallacies of Distributed Computing “Essentially everyone, when they first build a distributed application, makes the following eight assumptions. All prove to be false in the long run and all cause big trouble and painful learning experiences. “ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The network is reliable Latency is zero Bandwidth is infinite The network is secure Topology doesn't change There is one administrator Transport cost is zero The network is homogeneous Attribution: The true origins of this list are somewhat mythic, being largely based on the collective experience of many hackers in the early days of building distributed systems. Peter Deutsch is the one who first enumerated them as a clear way to frame thinking about why distributed systems are fundamentally different. He says the following on his home page: “I first published the "8 Fallacies of Networking" internally while working at Sun Microsystems Labs in 1991 -92. (The first 4 were originally described by either Bill or Dick Lyon; I added the other 4. ) 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 24
The Eight Fallacies of Distributed Computing “Essentially everyone, when they first build a distributed application, makes the following eight assumptions. All prove to be false in the long run and all cause big trouble and painful learning experiences. “ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The network is reliable Latency is zero Bandwidth is infinite The network is secure Topology doesn't change There is one administrator Transport cost is zero The network is homogeneous Attribution: The true origins of this list are somewhat mythic, being largely based on the collective experience of many hackers in the early days of building distributed systems. Peter Deutsch is the one who first enumerated them as a clear way to frame thinking about why distributed systems are fundamentally different. He says the following on his home page: “I first published the "8 Fallacies of Networking" internally while working at Sun Microsystems Labs in 1991 -92. (The first 4 were originally described by either Bill or Dick Lyon; I added the other 4. ) 11073. Inter-LAN. 2008. 01. 18. v 01. ppt SLIDE 24


