31403b71cb44c2a87a8daefa809f395d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

IDs at ALBA synchrotron: Some notes on strategy, design, Manufacturing, testing and future 1/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Summary • Strategy planned for IDs atat ALBA Strategy planned for IDs ALBA • Design • Manufacturing • Testing • Operation • Developments and future 2/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
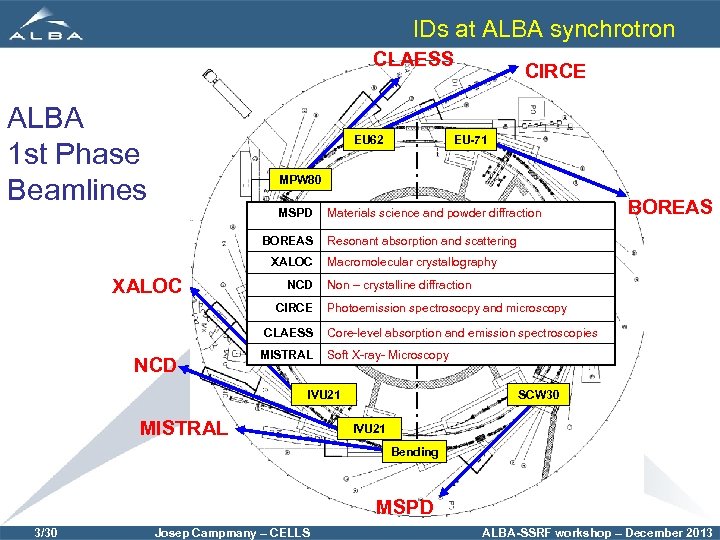
IDs at ALBA synchrotron CLAESS ALBA 1 st Phase Beamlines EU 62 CIRCE EU-71 MPW 80 MSPD BOREAS XALOC NCD CIRCE CLAESS NCD MISTRAL Materials science and powder diffraction Resonant absorption and scattering Macromolecular crystallography Non – crystalline diffraction Photoemission spectrosocpy and microscopy Core-level absorption and emission spectroscopies Soft X-ray- Microscopy IVU 21 MISTRAL BOREAS SCW 30 IVU 21 Bending MSPD 3/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
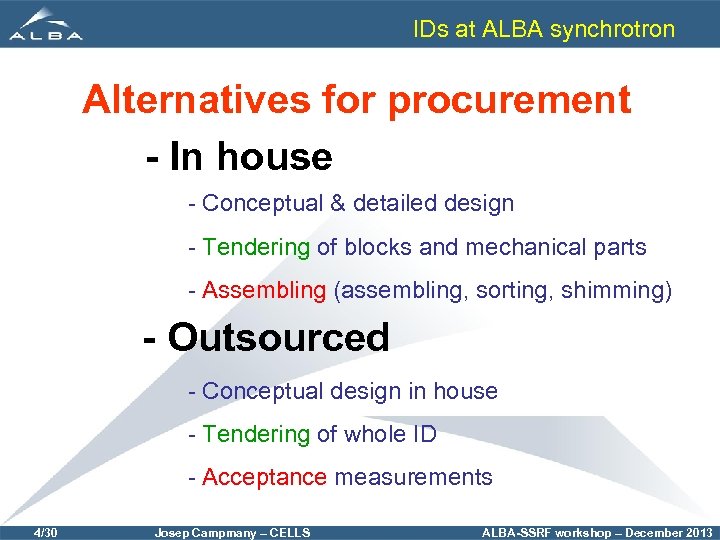
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Alternatives for procurement - In house - Conceptual & detailed design - Tendering of blocks and mechanical parts - Assembling (assembling, sorting, shimming) - Outsourced - Conceptual design in house - Tendering of whole ID - Acceptance measurements 4/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
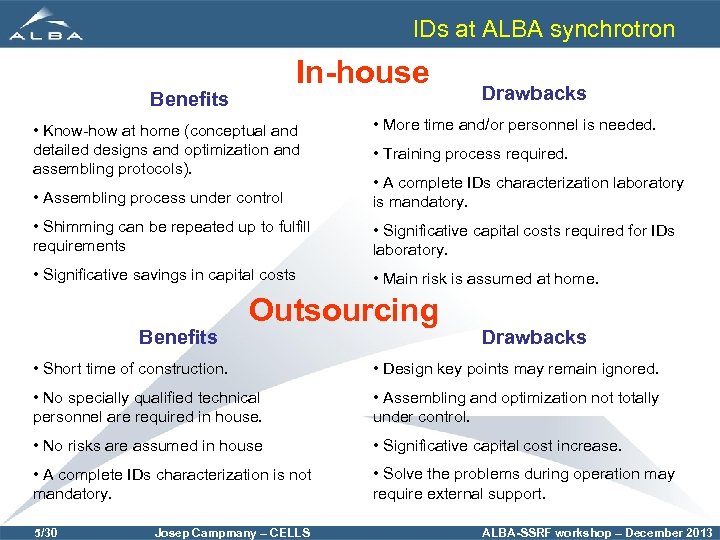
IDs at ALBA synchrotron In-house Benefits • Know-how at home (conceptual and detailed designs and optimization and assembling protocols). Drawbacks • More time and/or personnel is needed. • Training process required. • Assembling process under control • A complete IDs characterization laboratory is mandatory. • Shimming can be repeated up to fulfill requirements • Significative capital costs required for IDs laboratory. • Significative savings in capital costs • Main risk is assumed at home. Benefits Outsourcing Drawbacks • Short time of construction. • Design key points may remain ignored. • No specially qualified technical personnel are required in house. • Assembling and optimization not totally under control. • No risks are assumed in house • Significative capital cost increase. • A complete IDs characterization is not mandatory. • Solve the problems during operation may require external support. 5/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Decisions taken IDs a) Outsource all IDs but collaborative clauses referred to control system b) Build a magnetic laboratory allowing site acceptance tests and future activity inhouse c) Train engineers and technicians during follow up of the contracts Laboratory a) Upgrade in house the existing Hall probe bench and built a stretched wire bench b) Buy turn-key flipping coil and Helmholtz benches d) Create a group of 2 physicists in charge of IDlab ID definition Conceptual design of IDs was done according Experiments specifications 6/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Summary • Strategy planned for IDs at ALBA • Design • Manufacturing • Testing • Operation • Developments and future 7/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
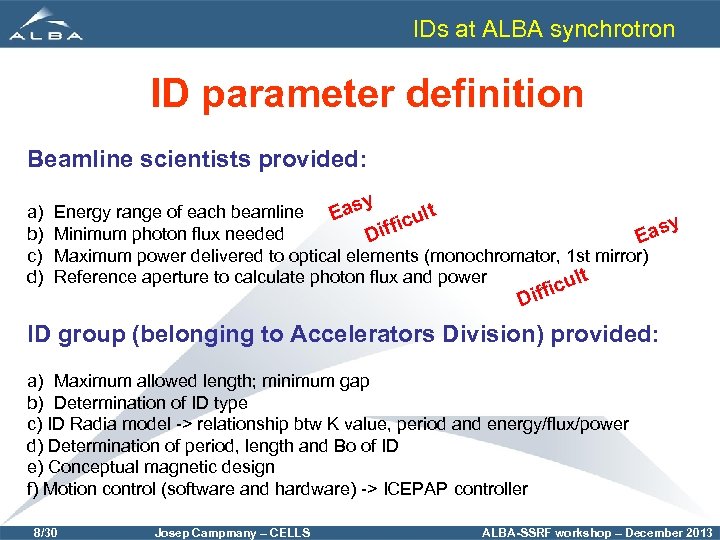
IDs at ALBA synchrotron ID parameter definition Beamline scientists provided: a) b) c) d) y Energy range of each beamline lt Eas y icu Minimum photon flux needed Diff Eas Maximum power delivered to optical elements (monochromator, 1 st mirror) Reference aperture to calculate photon flux and power ult ic Diff ID group (belonging to Accelerators Division) provided: a) Maximum allowed length; minimum gap b) Determination of ID type c) ID Radia model -> relationship btw K value, period and energy/flux/power d) Determination of period, length and Bo of ID e) Conceptual magnetic design f) Motion control (software and hardware) -> ICEPAP controller 8/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
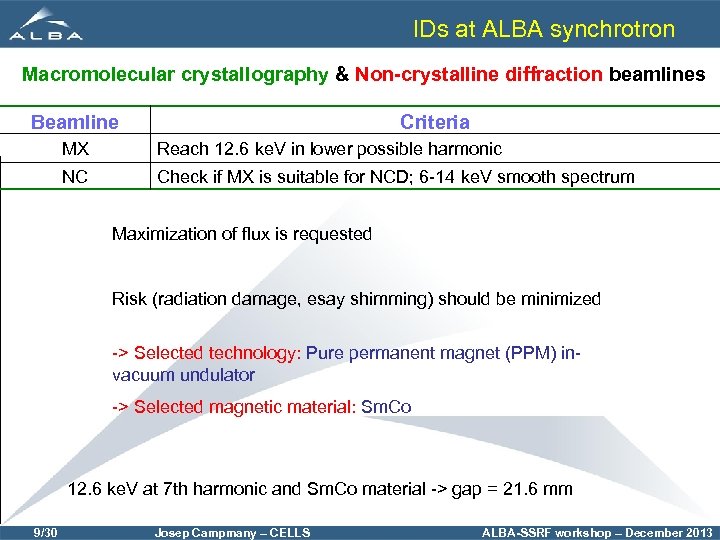
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Macromolecular crystallography & Non-crystalline diffraction beamlines Beamline Criteria MX Reach 12. 6 ke. V in lower possible harmonic NC Check if MX is suitable for NCD; 6 -14 ke. V smooth spectrum Maximization of flux is requested Risk (radiation damage, esay shimming) should be minimized -> Selected technology: Pure permanent magnet (PPM) invacuum undulator -> Selected magnetic material: Sm. Co 12. 6 ke. V at 7 th harmonic and Sm. Co material -> gap = 21. 6 mm 9/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
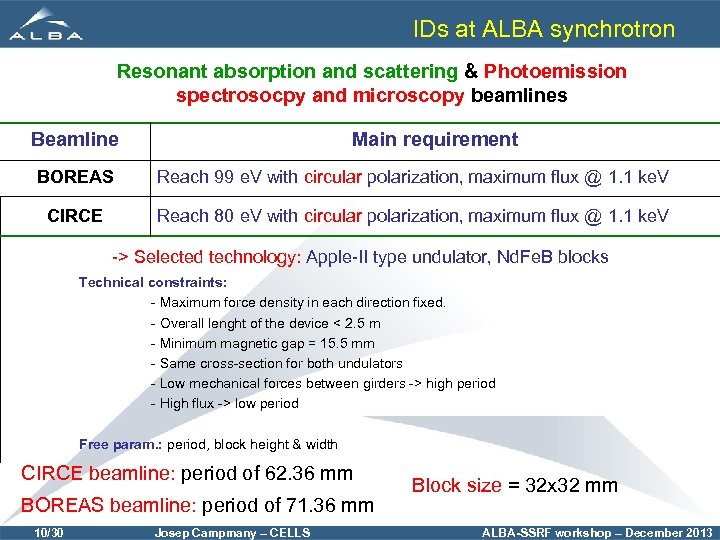
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Resonant absorption and scattering & Photoemission spectrosocpy and microscopy beamlines Beamline Main requirement BOREAS Reach 99 e. V with circular polarization, maximum flux @ 1. 1 ke. V CIRCE Reach 80 e. V with circular polarization, maximum flux @ 1. 1 ke. V -> Selected technology: Apple-II type undulator, Nd. Fe. B blocks Technical constraints: - Maximum force density in each direction fixed. - Overall lenght of the device < 2. 5 m - Minimum magnetic gap = 15. 5 mm - Same cross-section for both undulators - Low mechanical forces between girders -> high period - High flux -> low period Free param. : period, block height & width CIRCE beamline: period of 62. 36 mm BOREAS beamline: period of 71. 36 mm 10/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS Block size = 32 x 32 mm ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Core-level absorption and emission spectroscopies beamline Beamline CLAESS Main requirement Maximum flux, Energy range 2. 4 to 34 ke. V, smooth spectrum -> Selected technology: Conventional multipole wiggler, hybrid design, taper option Technical constraints: - Maximum power to monochromator, 700 W. - Maximum power to 1 st mirror, 1 k. W - Minimum magnetic gap = 12. 5 mm - H aperture =, v aperture = 0. 25 mrad, H aperture = 1. 5 un¡m Free param. : period, block height & width Balance: - Max. flux through aperture @ given E -> high field -> high period, high length - Min. power to optical elements -> limitation on length, limitation on field CLAESS beamline: period 80 mm, magnetic length 1 m 11/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
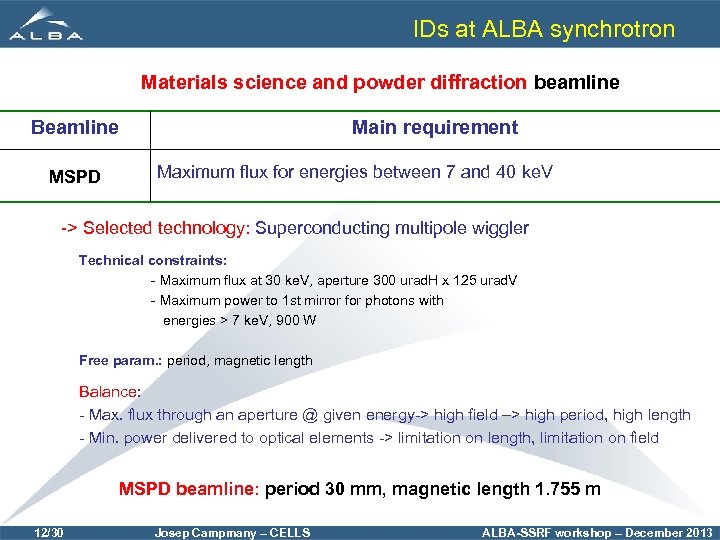
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Materials science and powder diffraction beamline Beamline MSPD Main requirement Maximum flux for energies between 7 and 40 ke. V -> Selected technology: Superconducting multipole wiggler Technical constraints: - Maximum flux at 30 ke. V, aperture 300 urad. H x 125 urad. V - Maximum power to 1 st mirror for photons with energies > 7 ke. V, 900 W Free param. : period, magnetic length Balance: - Max. flux through an aperture @ given energy-> high field –> high period, high length - Min. power delivered to optical elements -> limitation on length, limitation on field MSPD beamline: period 30 mm, magnetic length 1. 755 m 12/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Summary • Strategy planned for IDs at ALBA • Design • Manufacturing • Testing • Operation • Developments and future 13/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Procedure • ALBA produced conceptual design • ALBA prepared a test bench for motion control development – ICEPAP controller Manufacturing • Cooperation: (Elettra, BINP): Apple-II, SCW • Outsourcing: MPW, IVU (Tendering process) 14/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Manufacturing: some evaluation • Smooth manufacturing process • Successful and fruitful collaboration with institutions (Elettra, BINP) • Smooth relation with industry. Fruitful discussions. Easy follow up. • When problems appear, very open discussions and cooperation • CELLS personnel acquired practical knowledge on IDs. 15/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
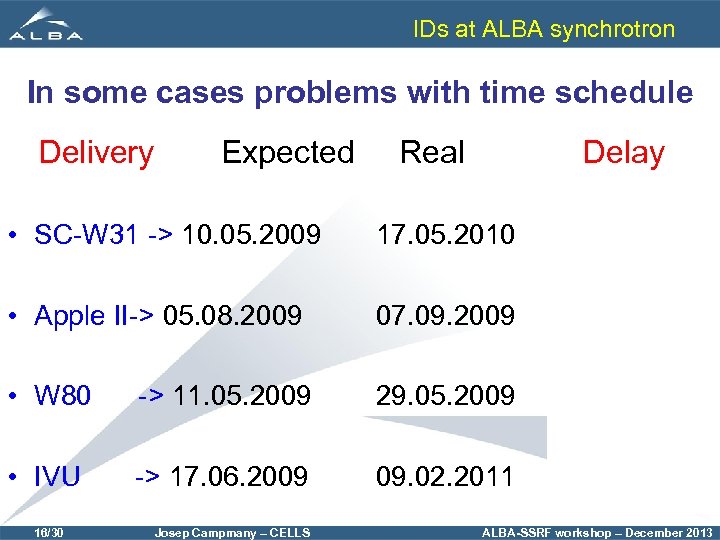
IDs at ALBA synchrotron In some cases problems with time schedule Delivery Expected Delay Real • SC-W 31 -> 10. 05. 2009 17. 05. 2010 12 months • Apple II-> 05. 08. 2009 07. 09. 2009 1 month • W 80 -> 11. 05. 2009 29. 05. 2009 0. 5 month • IVU -> 17. 06. 2009 09. 02. 2011 20 months 16/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Summary • Strategy planned for IDs at ALBA • Design • Manufacturing • Testing • Operation • Developments and future 17/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
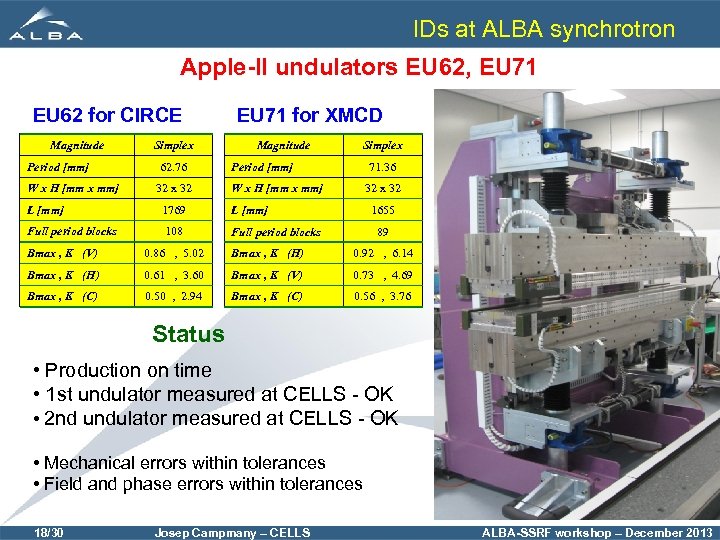
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Apple-II undulators EU 62, EU 71 EU 62 for CIRCE Magnitude Period [mm] W x H [mm x mm] Simplex 62. 76 32 x 32 EU 71 for XMCD Magnitude Simplex Period [mm] 71. 36 W x H [mm x mm] L [mm] 1769 L [mm] Full period blocks 108 32 x 32 Full period blocks 1655 89 Bmax , K (V) 0. 86 , 5. 02 Bmax , K (H) 0. 92 , 6. 14 Bmax , K (H) 0. 61 , 3. 60 Bmax , K (V) 0. 73 , 4. 69 Bmax , K (C) 0. 50 , 2. 94 Bmax , K (C) 0. 56 , 3. 76 Status • Production on time • 1 st undulator measured at CELLS - OK • 2 nd undulator measured at CELLS - OK • Mechanical errors within tolerances • Field and phase errors within tolerances 18/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
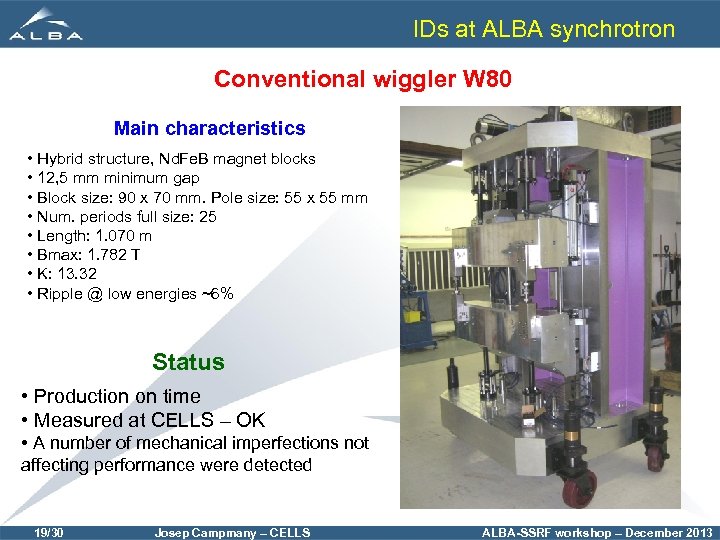
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Conventional wiggler W 80 Main characteristics • Hybrid structure, Nd. Fe. B magnet blocks • 12, 5 mm minimum gap • Block size: 90 x 70 mm. Pole size: 55 x 55 mm • Num. periods full size: 25 • Length: 1. 070 m • Bmax: 1. 782 T • K: 13. 32 • Ripple @ low energies ~6% Status • Production on time • Measured at CELLS – OK • A number of mechanical imperfections not affecting performance were detected 19/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Superconducting wiggler SC-W 31 Main characteristics • Superconducting wiggler • 12, 6 mm magnetic gap • Period: 30, 01 mm • Num. poles full field: 117 • Length: 1. 764 m • Bmax: 2. 16 T • K: 6. 08 Status • Innovation in the wire radius, cryostat design and liner manufacturing • Some manufacturing problems solved in good agreement • Measured al ALBA - OK 20/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
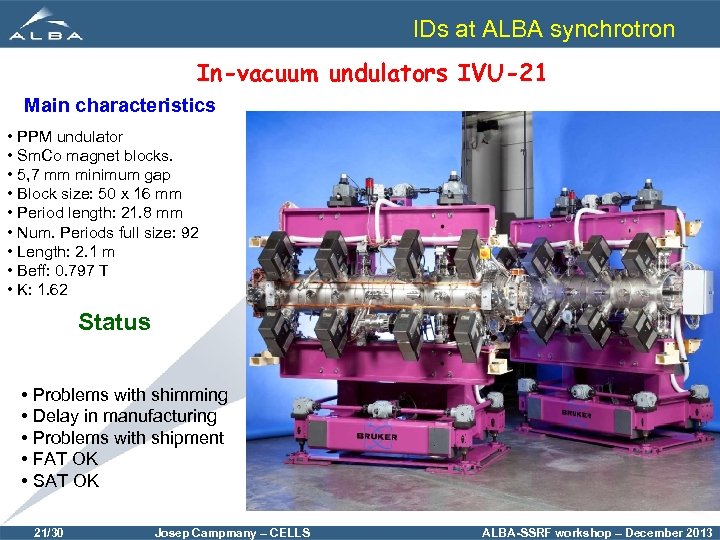
IDs at ALBA synchrotron In-vacuum undulators IVU-21 Main characteristics • PPM undulator • Sm. Co magnet blocks. • 5, 7 mm minimum gap • Block size: 50 x 16 mm • Period length: 21. 8 mm • Num. Periods full size: 92 • Length: 2. 1 m • Beff: 0. 797 T • K: 1. 62 Status • Problems with shimming • Delay in manufacturing • Problems with shipment • FAT OK • SAT OK 21/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
IDs at ALBA synchrotron ALBA Insertion Devices – Dec 2013 ID Characteristics IVU 21 Beamlines: Macromol. Christallography, Non-crystalline diff. Features: lu=21. 6 mm, L=2 m, Be=0. 7954 T, K=1. 60 EU 71 EU 62 Beamlines: Magnetic Dichroism, Low energy spectrosc. + PEEM Features: lu=71. 36 mm, L=1. 650 m, Be=0. 9460 T, K=6. 31 (H pol) Features: lu=62. 36 mm, L=1. 761 m, Be=0. 8843 T, K=5. 15 (H pol) SC-W 31 W 80 22/30 Beamline: High resolution powder diffraction Features: lu=30. 01 mm, L=1. 755 m, Bo=2. 15 T, K=6. 03 Beamline: X-ray absorption spectroscopies Features: lu=79. 93 mm, L=0. 999 m, Bo=1. 7374 T, K=12. 97 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Summary • Strategy planned for IDs at ALBA • Design • Manufacturing • Testing • Operation • Developments and future 23/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Generalities • «plug and play» for all IDs • No claims from BLs about light quality • No degradation of light detected so far • Good operation of critical devices: – Injection with IVUs at small gap (5. 7 mm) – Injection with SCW at maximum field (2. 1 T) • Few quenches happened, mainly induced by beam losses 24/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Operation in detail ID Operation main comments IVU 21 Excellent performance – no correction coils activation needed EU 71 EU 62 Correction coils are needed – big perturbations for antiphase Sometimes problems with tilt (6 motors each device) SC-W 31 W 80 25/30 Correction coils needed – big perturbation in orbit not foreseen Excellent cryogenic behaviour – zero losses Correction coils needed: manufactured coils not adequate - replaced Many problems: replacement of limit switches and general recabling Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Summary • Strategy planned for IDs at ALBA • Design • Manufacturing • Testing • Operation • Developments and future 26/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Developments • Magnetic measurement laboratory prepared (including hardware and methods) for building IDs in-house • Building a new magnetic measurement system for «closed» IDs to measure fieldmaps inside in-vacuum or similar • Prototype has been designed and will be ready on April 2014 • Final bench can be build according CELLS needs in 9 months 27/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
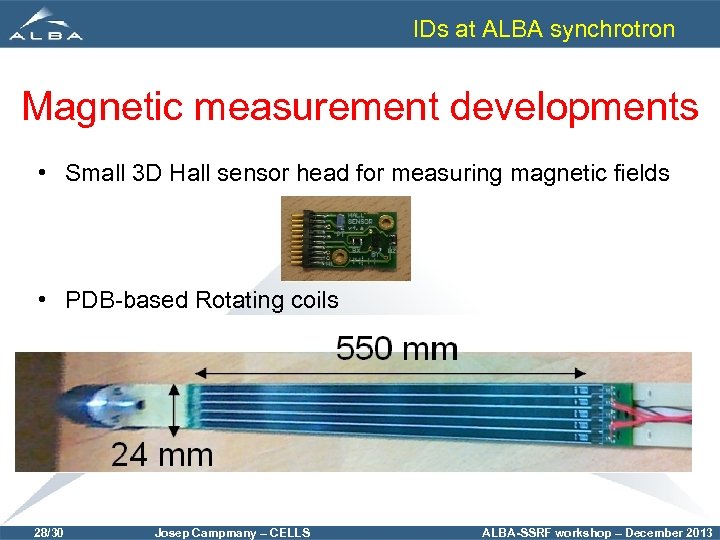
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Magnetic measurement developments • Small 3 D Hall sensor head for measuring magnetic fields • PDB-based Rotating coils 28/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
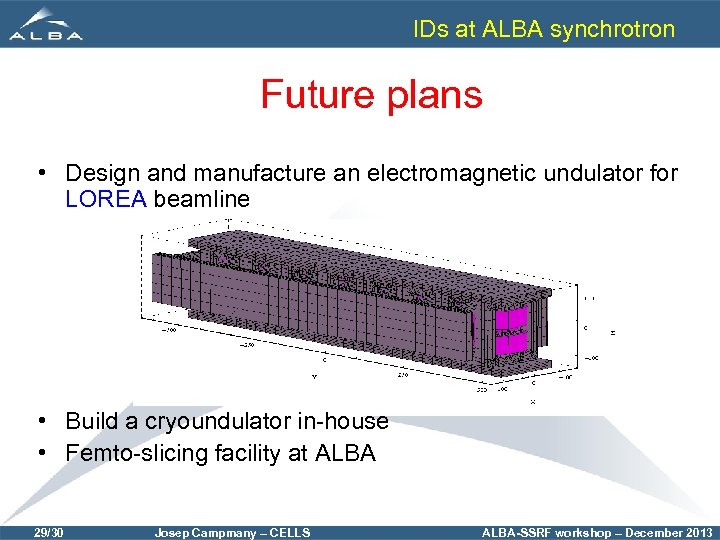
IDs at ALBA synchrotron Future plans • Design and manufacture an electromagnetic undulator for LOREA beamline • Build a cryoundulator in-house • Femto-slicing facility at ALBA 29/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013

IDs at ALBA synchrotron Thanks for your attention 30/30 Josep Campmany – CELLS ALBA-SSRF workshop – December 2013
31403b71cb44c2a87a8daefa809f395d.ppt