3b8fa77874f8c56101876a9d3a61614a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers Learning Technologies Division HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT GROUP Commission on Information and Communications Technology
ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers Learning Technologies Division HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT GROUP Commission on Information and Communications Technology
 film
film
 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 3
i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 3
 Process Questions ● ● Any immediate reactions to the film and the comic strips? Describe the world and the people of the 21 st Century. – – – ● How different is today's society from that of your youth? What are considered important? What skills are considered necessary? What are the implications on today's education? – Describe the school/classroom, students, and teachers of today. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 4
Process Questions ● ● Any immediate reactions to the film and the comic strips? Describe the world and the people of the 21 st Century. – – – ● How different is today's society from that of your youth? What are considered important? What skills are considered necessary? What are the implications on today's education? – Describe the school/classroom, students, and teachers of today. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 4
 AGE OF INFORMATION REVOLUTION i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 5
AGE OF INFORMATION REVOLUTION i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 5
 Digital Economy We are living in a new economy… ● powered by technology ● fueled by information ● driven by knowledge. - Secretary’s Commission on Achieving Necessary Skills (SCANS), US Dept of Labor, 1991 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 6
Digital Economy We are living in a new economy… ● powered by technology ● fueled by information ● driven by knowledge. - Secretary’s Commission on Achieving Necessary Skills (SCANS), US Dept of Labor, 1991 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 6
 ● ● ● “instant” universal access to information, people, ideas real-time inter-operation/ interactivity through networked devices and databases active participation/involvement rather than passive observation i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 7
● ● ● “instant” universal access to information, people, ideas real-time inter-operation/ interactivity through networked devices and databases active participation/involvement rather than passive observation i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 7
 DIGITAL AGE READINESS INFORMATION AGE st 21 DIGITAL WORLD CENTURY SKILLS “Without 21 st century skills, students are being prepared to succeed in yesterday’s world – not tomorrow’s. ” – en. Gauge: 21 st Century Skills i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 8
DIGITAL AGE READINESS INFORMATION AGE st 21 DIGITAL WORLD CENTURY SKILLS “Without 21 st century skills, students are being prepared to succeed in yesterday’s world – not tomorrow’s. ” – en. Gauge: 21 st Century Skills i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 8
 Learning can, of course, take place in the classroom, but most of it doesn’t. Today’s learners are not just students; learning has suddenly become everybody’s business. In fact, learning “how to learn” may now be your most critical survival skill. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers from Jensen, E. Super Teaching. 1995. 9
Learning can, of course, take place in the classroom, but most of it doesn’t. Today’s learners are not just students; learning has suddenly become everybody’s business. In fact, learning “how to learn” may now be your most critical survival skill. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers from Jensen, E. Super Teaching. 1995. 9
 21 st Century Skills ● ● Innovation is the key! lifelong learning, learning how to learn, continuous development from “content-absorbers” to “information navigators” i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 10
21 st Century Skills ● ● Innovation is the key! lifelong learning, learning how to learn, continuous development from “content-absorbers” to “information navigators” i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 10
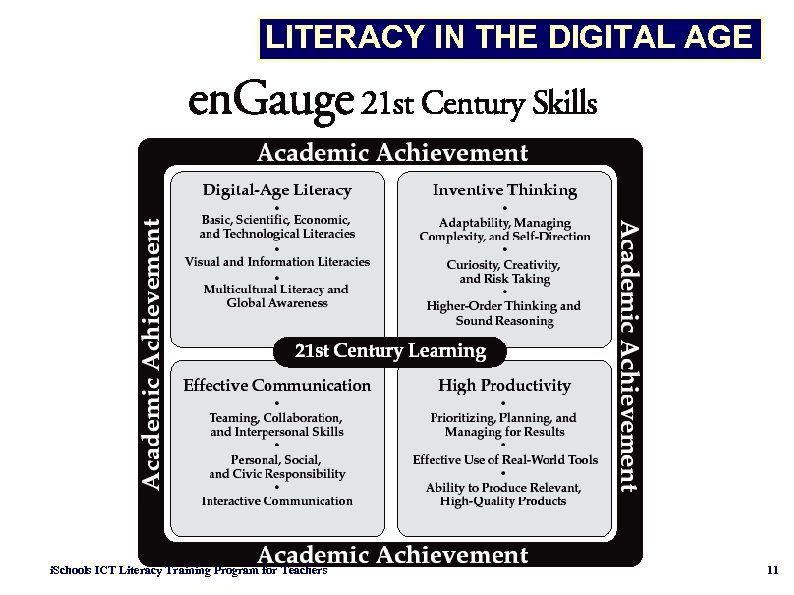 LITERACY IN THE DIGITAL AGE i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 11
LITERACY IN THE DIGITAL AGE i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 11
 21 st Century Skills ● desired competencies: – – – ● sift through loads of information and manage, integrate, evaluate, and create information act autonomously and reflectively join and function collaboratively in socially heterogeneous groups must be provided the necessary tools for life – use ICT to leverage knowledge & skills and match to current needs and opportunities Information literacy = e-literacy i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 12
21 st Century Skills ● desired competencies: – – – ● sift through loads of information and manage, integrate, evaluate, and create information act autonomously and reflectively join and function collaboratively in socially heterogeneous groups must be provided the necessary tools for life – use ICT to leverage knowledge & skills and match to current needs and opportunities Information literacy = e-literacy i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 12
 Bridging the Digital Divide ● ● ● Phase 1: access to technology (infrastructure) Phase 2: Internet access (connectivity) Phase 3: capability/readiness of individuals to use technology, networks, and information efficiently, effectively, productively (meaningful & innovative) – training and support i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 13
Bridging the Digital Divide ● ● ● Phase 1: access to technology (infrastructure) Phase 2: Internet access (connectivity) Phase 3: capability/readiness of individuals to use technology, networks, and information efficiently, effectively, productively (meaningful & innovative) – training and support i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 13
 REFLECTION ● “education” ● what is your vision of an ideal class – – students – community – strategies, assessment – ● role of a teacher setup and materials what is vs. what could be – hindrances to what could be – what can be done i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 14
REFLECTION ● “education” ● what is your vision of an ideal class – – students – community – strategies, assessment – ● role of a teacher setup and materials what is vs. what could be – hindrances to what could be – what can be done i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 14
 ICT 4 E Integrating technology into education in a meaningful way is key to making learning relevant to the generation of young learners for whom technology is an important part of their daily lives. from Educating for the Future by BSA, June 2004 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 15
ICT 4 E Integrating technology into education in a meaningful way is key to making learning relevant to the generation of young learners for whom technology is an important part of their daily lives. from Educating for the Future by BSA, June 2004 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 15
 Growing up Digital: THE NET GENERATION ● techno-natives (kids) vs. techno-migrants (us) – – ● India: “hole in the wall” experiment – 8 -13 y old kids learn computers on their own “instant”/ “copy-paste” generation US figures: – 90% (5 -17 years old) use computers – 65% are online – 2 million new Internet users per month (2002) ● ● children and teens: fastest-growing (41% increase from 2000) interactive Internet use: winning over passive TV-watching i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 16
Growing up Digital: THE NET GENERATION ● techno-natives (kids) vs. techno-migrants (us) – – ● India: “hole in the wall” experiment – 8 -13 y old kids learn computers on their own “instant”/ “copy-paste” generation US figures: – 90% (5 -17 years old) use computers – 65% are online – 2 million new Internet users per month (2002) ● ● children and teens: fastest-growing (41% increase from 2000) interactive Internet use: winning over passive TV-watching i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 16
 Digital Age Learning ● look at WHAT students learn and HOW & WHEN they learn – ● educate for opportunity! potential of technology: – – in society-at-large: driver for change, door to opportunities in education: to tap experts, visualize and analyze data, link to real-world contexts, timely feedback, reflection, and analysis (Bransford et al, 1999 in en. Gauge 21 st Century Skills) when used appropriately enhanced teaching and learning i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 17
Digital Age Learning ● look at WHAT students learn and HOW & WHEN they learn – ● educate for opportunity! potential of technology: – – in society-at-large: driver for change, door to opportunities in education: to tap experts, visualize and analyze data, link to real-world contexts, timely feedback, reflection, and analysis (Bransford et al, 1999 in en. Gauge 21 st Century Skills) when used appropriately enhanced teaching and learning i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 17
 EDUCATION vis-à-vis 21 st C Skills ● significant implications for – – – – pedagogy (evaluate standards vis-à-vis 21 st C skills) teacher and student roles curriculum strategies and tools assessment standards infrastructure (equipment, materials/supplies, layout) role of community i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 18
EDUCATION vis-à-vis 21 st C Skills ● significant implications for – – – – pedagogy (evaluate standards vis-à-vis 21 st C skills) teacher and student roles curriculum strategies and tools assessment standards infrastructure (equipment, materials/supplies, layout) role of community i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 18
 ICT 4 E ● advocates’ claims: (Kozma in Monitoring and Evaluation of ICT in Education Projects. Info. Dev, 2005) – – can positively impact student knowledge, skills, and attitudes can benefit both girls and boys, as well as students with special needs can contribute to changes in teaching practices, school innovation, and community services need for national policies and programs on ICT and related changes in curriculum pedagogy, assessment, and teacher training for widespread impact i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 19
ICT 4 E ● advocates’ claims: (Kozma in Monitoring and Evaluation of ICT in Education Projects. Info. Dev, 2005) – – can positively impact student knowledge, skills, and attitudes can benefit both girls and boys, as well as students with special needs can contribute to changes in teaching practices, school innovation, and community services need for national policies and programs on ICT and related changes in curriculum pedagogy, assessment, and teacher training for widespread impact i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 19
 How does a teacher become a catalyst for transforming a plagiarist into the artist? How do we reach for Picasso, when we are entrenched in a “paint by number” ideology? 75% of teachers: sequential, analytical presenters BUT 70% of students do not learn best this way The lesson plan is like a restaurant menu – it’s a useful planning tool, but it’s not the meal. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers from Jensen, E. Super Teaching. 1995. 20
How does a teacher become a catalyst for transforming a plagiarist into the artist? How do we reach for Picasso, when we are entrenched in a “paint by number” ideology? 75% of teachers: sequential, analytical presenters BUT 70% of students do not learn best this way The lesson plan is like a restaurant menu – it’s a useful planning tool, but it’s not the meal. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers from Jensen, E. Super Teaching. 1995. 20
 ICT 4 E Underlying Educational Philosophy: Constructivism ● ● learning = meaning is constructed from prior knowledge + experience with the environment learning is an active, personal inquiry and interpretation of the world collaborative learning for multiple perspectives learning = situated in realistic settings; testing = integrated with the task and not a separate activity; teacher assists create, develop, apply, analyze, assimilate, synthesize knowledge + collaborative learning (Merrill, 1991) i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 21
ICT 4 E Underlying Educational Philosophy: Constructivism ● ● learning = meaning is constructed from prior knowledge + experience with the environment learning is an active, personal inquiry and interpretation of the world collaborative learning for multiple perspectives learning = situated in realistic settings; testing = integrated with the task and not a separate activity; teacher assists create, develop, apply, analyze, assimilate, synthesize knowledge + collaborative learning (Merrill, 1991) i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 21
 Traditional vs. st 21 Century learning From: Tech. Know. Logia, Jan-March 2003, p. 78. www. Tech. Know. Logia. org i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 22
Traditional vs. st 21 Century learning From: Tech. Know. Logia, Jan-March 2003, p. 78. www. Tech. Know. Logia. org i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 22
 Traditional vs. st 21 From: Tech. Know. Logia, i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers Century learning Jan-March 2003, p. 78. www. Tech. Know. Logia. org 23
Traditional vs. st 21 From: Tech. Know. Logia, i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers Century learning Jan-March 2003, p. 78. www. Tech. Know. Logia. org 23
 Authentic Learning • Inquiry-based, relevant • Student Exhibit “Essential Question” rooted – share with others one’s constructed on real life applications – focus: process vs. output – collaborative, multidisciplinary • Scaffolding meaning/knowledge • Reflection – on the learning process and the new meaning gained • Resources – Guide questions, regular communication and timely – other students, parents, feedback external experts, school, books, Internet, community – Process worksheet, templates, rubrics, checklists i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 24
Authentic Learning • Inquiry-based, relevant • Student Exhibit “Essential Question” rooted – share with others one’s constructed on real life applications – focus: process vs. output – collaborative, multidisciplinary • Scaffolding meaning/knowledge • Reflection – on the learning process and the new meaning gained • Resources – Guide questions, regular communication and timely – other students, parents, feedback external experts, school, books, Internet, community – Process worksheet, templates, rubrics, checklists i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 24
 Assessment ● ● incorporated into the process rather than just an ending activity to check student’s learning + teacher’s understanding of student’s current understanding multiple skills measured: cognitive, creativity, collaboration, communication skills i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 25
Assessment ● ● incorporated into the process rather than just an ending activity to check student’s learning + teacher’s understanding of student’s current understanding multiple skills measured: cognitive, creativity, collaboration, communication skills i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 25
 Assessment ● use of clearly defined standards and expectations – – – mix of formative tests, rubrics, checklists performances (i. e. writing, revising, debate) products (e. g. concept maps, analysis of experiment, newsletter) portfolios (e. g. journal, peer reviews, diagrams, group reports, rough drafts & polished writing) self-assessment of learning process, accomplishment, and “next steps” i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 26
Assessment ● use of clearly defined standards and expectations – – – mix of formative tests, rubrics, checklists performances (i. e. writing, revising, debate) products (e. g. concept maps, analysis of experiment, newsletter) portfolios (e. g. journal, peer reviews, diagrams, group reports, rough drafts & polished writing) self-assessment of learning process, accomplishment, and “next steps” i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 26
 Summary of Implications ● ● ● schools: change or become obsolete multiple opportunities & channels to learn ICTs regular assessment and feedback to see if learning is indeed taking place and 21 st C skills are being developed “Look beyond the schoolhouse to the roles students will play when they leave to become workers, parents, and citizens. ” - (SCANS), US Dept of Labor, 1991 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 27
Summary of Implications ● ● ● schools: change or become obsolete multiple opportunities & channels to learn ICTs regular assessment and feedback to see if learning is indeed taking place and 21 st C skills are being developed “Look beyond the schoolhouse to the roles students will play when they leave to become workers, parents, and citizens. ” - (SCANS), US Dept of Labor, 1991 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 27
 From the Business Software Alliance from Educating for (how the business sector views 21 st Century Learning)the Future by BSA, June 2004 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 28
From the Business Software Alliance from Educating for (how the business sector views 21 st Century Learning)the Future by BSA, June 2004 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 28
 General Math, Science, and Engineering Skills: marrying cutting-edge technology with current problems and opportunities – facilitate analysis, evaluating information, making sound decisions, assessing and understanding results and implications, recommending improvements, etc. General Workforce Skills: use ICT to collaborate and practice teamwork on projects for shared credit; to enhance selfdirection, adaptability, accountability; critical thinking and creative problem solving; social responsibility and ethical behavior Global and Civic Awareness: interact with/ participate in gov’t, economic, and social institutions globally and locally, includes: finding multiple and best sources through ICT for accurate and unbiased information to gain multicultural literacy, and make sound decisions about various matters, taking advantage of egovernment services, etc. ICT Literacy: use of ICT tools to communicate and express ideas effectively, to facilitate analysis and problem solving, to sort through resources for research and information synthesis, to manage time and tasks effectively – includes technological literacy and information literacy Basic Literacy: functional proficiency in language and numeracy i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers adapted from Educating for the Future by BSA, June 2004 29
General Math, Science, and Engineering Skills: marrying cutting-edge technology with current problems and opportunities – facilitate analysis, evaluating information, making sound decisions, assessing and understanding results and implications, recommending improvements, etc. General Workforce Skills: use ICT to collaborate and practice teamwork on projects for shared credit; to enhance selfdirection, adaptability, accountability; critical thinking and creative problem solving; social responsibility and ethical behavior Global and Civic Awareness: interact with/ participate in gov’t, economic, and social institutions globally and locally, includes: finding multiple and best sources through ICT for accurate and unbiased information to gain multicultural literacy, and make sound decisions about various matters, taking advantage of egovernment services, etc. ICT Literacy: use of ICT tools to communicate and express ideas effectively, to facilitate analysis and problem solving, to sort through resources for research and information synthesis, to manage time and tasks effectively – includes technological literacy and information literacy Basic Literacy: functional proficiency in language and numeracy i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers adapted from Educating for the Future by BSA, June 2004 29
 ICT in Education ● ● ICT not as end in itself but as a tool to make learning more efficient, effective, and relevant 3 areas of application: 1. 2. 3. teach ABOUT technology technological literacy teach WITH computers to help perform administrative functions more efficiently use computer technology DIRECTLY to TEACH our classes information literacy, global awareness, collaboration, etc. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 30
ICT in Education ● ● ICT not as end in itself but as a tool to make learning more efficient, effective, and relevant 3 areas of application: 1. 2. 3. teach ABOUT technology technological literacy teach WITH computers to help perform administrative functions more efficiently use computer technology DIRECTLY to TEACH our classes information literacy, global awareness, collaboration, etc. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 30
 ICT 4 E Findings ● “simply putting computers into schols is not enough to impact student learning” but well-utilized ICTs enhance learning – – – allow multi-channel learning (different learning styles, tailored to individual needs and pacing) are motivating and engaging (authentic, multi-disciplinary, multisensorial, enjoyable) bring abstract concepts to life (via images, sounds movements, animations, simulations) foster inquiry and exploration in cost-effective & safe ways (bringing the world into the classroom) provide efficiency i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 31
ICT 4 E Findings ● “simply putting computers into schols is not enough to impact student learning” but well-utilized ICTs enhance learning – – – allow multi-channel learning (different learning styles, tailored to individual needs and pacing) are motivating and engaging (authentic, multi-disciplinary, multisensorial, enjoyable) bring abstract concepts to life (via images, sounds movements, animations, simulations) foster inquiry and exploration in cost-effective & safe ways (bringing the world into the classroom) provide efficiency i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 31
 Effective ICT 4 E infrastructure and connectivity ample and appropriate training (pre- / inservice) on ICT and corresponding student-centered pedagogy reliable tech support & continued ICT 4 E training appropriate policy framework (system changes, incentives, and sustainability), curriculum changes i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 32
Effective ICT 4 E infrastructure and connectivity ample and appropriate training (pre- / inservice) on ICT and corresponding student-centered pedagogy reliable tech support & continued ICT 4 E training appropriate policy framework (system changes, incentives, and sustainability), curriculum changes i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 32
 Teacher Training Standards ● ● ● Teachers understand technology operations and concepts. Teachers plan and design effective learning environments supported by technology. Teachers can implement plans that include methods for applying technology to maximize student learning. Teachers can apply technology to facilitate assessment. Teachers can use technology to enhance their own productivity. Teachers understand the social, ethical, legal, and human issues related to the use of technology. - from the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 33
Teacher Training Standards ● ● ● Teachers understand technology operations and concepts. Teachers plan and design effective learning environments supported by technology. Teachers can implement plans that include methods for applying technology to maximize student learning. Teachers can apply technology to facilitate assessment. Teachers can use technology to enhance their own productivity. Teachers understand the social, ethical, legal, and human issues related to the use of technology. - from the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 33
 Emerging Pedagogical Practices of Teachers supported by ICT ● students developing abilities to undertake independent learning ● providing weaker students with additional instruction ● ● ● organizing teaching and learning so that differences in entrance level, learning pace, and learning route are taken into account students learning to search for information, process data, and present information students being largely responsible for controlling their own learning progress ● students learning and/or working during lessons at their own pace ● students involved in cooperative and / or project-based learning ● combining parts of school projects with one another (multidisciplinary approach) Adapted from Pelgrum and Anderson, 1999. Appearing in M&E for ICT in Education, Info. Dev, 2005 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 34
Emerging Pedagogical Practices of Teachers supported by ICT ● students developing abilities to undertake independent learning ● providing weaker students with additional instruction ● ● ● organizing teaching and learning so that differences in entrance level, learning pace, and learning route are taken into account students learning to search for information, process data, and present information students being largely responsible for controlling their own learning progress ● students learning and/or working during lessons at their own pace ● students involved in cooperative and / or project-based learning ● combining parts of school projects with one another (multidisciplinary approach) Adapted from Pelgrum and Anderson, 1999. Appearing in M&E for ICT in Education, Info. Dev, 2005 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 34
 Indicators of student practices in the ICT-supported classrooms ● collaborate on a project with other students in the same class, from another school in own country, or from another country ● exchange information with students from another country ● gather and analyze resource materials on a problem or topic ● gather evidence to argue a position about an issue ● use graphics in a report ● collect information about another country or culture ● ● draw conclusions or make predictions using data gathered or obtained from resource materials communicate with parents or other members of the community about what you do in school Adapted from Kozma et al, 2004. Appearing in M&E for ICT in Education, Info. Dev, 2005 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 35
Indicators of student practices in the ICT-supported classrooms ● collaborate on a project with other students in the same class, from another school in own country, or from another country ● exchange information with students from another country ● gather and analyze resource materials on a problem or topic ● gather evidence to argue a position about an issue ● use graphics in a report ● collect information about another country or culture ● ● draw conclusions or make predictions using data gathered or obtained from resource materials communicate with parents or other members of the community about what you do in school Adapted from Kozma et al, 2004. Appearing in M&E for ICT in Education, Info. Dev, 2005 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 35
 Sample Positive ICT 4 E Impact ● ● use of computer tutorials in math, science, social science, reading: score significantly higher on tests + more positive attitudes toward instruction and the subject matters (US, Kenya) use of word processors: scored higher on measures on writing skill (US) use of networked computers: enhanced communication skills, knowledge of other cultures, reasoning skills, collaboration skills, Internet skills (Kenya, Uganda, Chile) teacher training on ICT 4 E: innovative pedagogical approaches and classroom practices, more positive attitudes about technology and teaching (Costa Rica) Studies mentioned in M&E in ICT in Education Projects, Info. Dev 2005. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 36
Sample Positive ICT 4 E Impact ● ● use of computer tutorials in math, science, social science, reading: score significantly higher on tests + more positive attitudes toward instruction and the subject matters (US, Kenya) use of word processors: scored higher on measures on writing skill (US) use of networked computers: enhanced communication skills, knowledge of other cultures, reasoning skills, collaboration skills, Internet skills (Kenya, Uganda, Chile) teacher training on ICT 4 E: innovative pedagogical approaches and classroom practices, more positive attitudes about technology and teaching (Costa Rica) Studies mentioned in M&E in ICT in Education Projects, Info. Dev 2005. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 36
 Findings in TIMSS (1999, 2003) ● ● Students who used computers and Internet performed better in science and mathematics Students who had other opportunities for learning outside the classrooms (ICT included) performed better in science and mathematics i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 37
Findings in TIMSS (1999, 2003) ● ● Students who used computers and Internet performed better in science and mathematics Students who had other opportunities for learning outside the classrooms (ICT included) performed better in science and mathematics i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 37
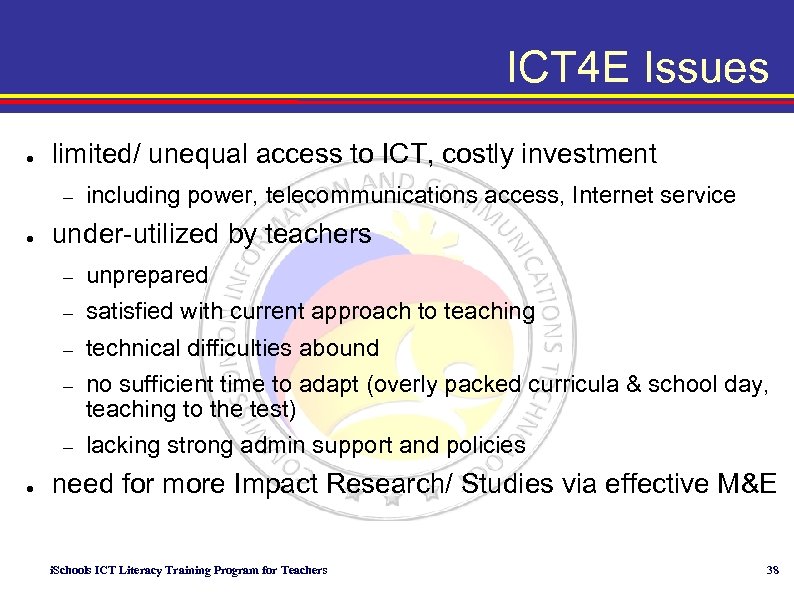 ICT 4 E Issues ● limited/ unequal access to ICT, costly investment – ● including power, telecommunications access, Internet service under-utilized by teachers – – satisfied with current approach to teaching – technical difficulties abound – no sufficient time to adapt (overly packed curricula & school day, teaching to the test) – ● unprepared lacking strong admin support and policies need for more Impact Research/ Studies via effective M&E i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 38
ICT 4 E Issues ● limited/ unequal access to ICT, costly investment – ● including power, telecommunications access, Internet service under-utilized by teachers – – satisfied with current approach to teaching – technical difficulties abound – no sufficient time to adapt (overly packed curricula & school day, teaching to the test) – ● unprepared lacking strong admin support and policies need for more Impact Research/ Studies via effective M&E i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 38
 ICT 4 E Philippines: Guiding Policies ● ● ● UN Millennium Development Goals PGMA’s 10 -point Agenda: EFA (Education for All) MTPDP 2004 -2010: Building on the Country's Strengths in Information and Communication Technology (to leapfrog into the new economy) BEC 2002: Information and Communication Technology shall be used in every learning area, wherever hardware and software available National Framework Plan for ICT in Basic Education, 2005 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 39
ICT 4 E Philippines: Guiding Policies ● ● ● UN Millennium Development Goals PGMA’s 10 -point Agenda: EFA (Education for All) MTPDP 2004 -2010: Building on the Country's Strengths in Information and Communication Technology (to leapfrog into the new economy) BEC 2002: Information and Communication Technology shall be used in every learning area, wherever hardware and software available National Framework Plan for ICT in Basic Education, 2005 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 39
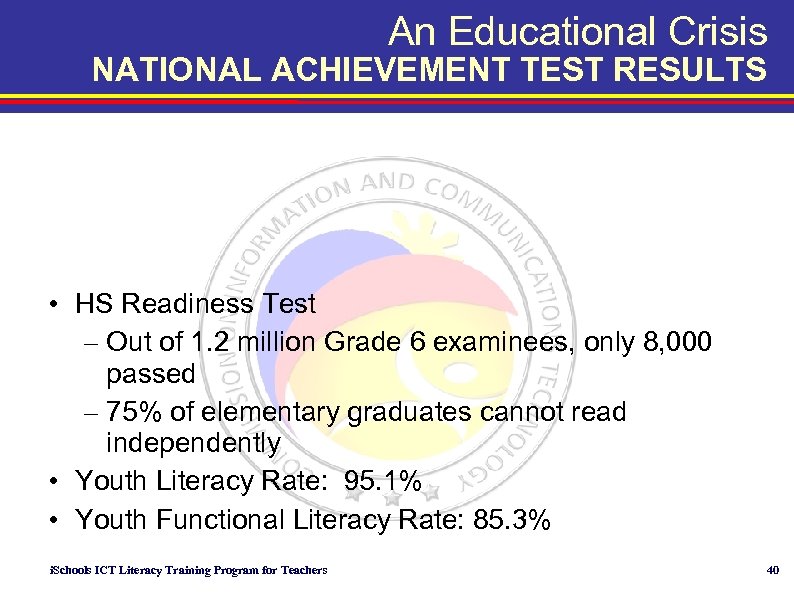 An Educational Crisis NATIONAL ACHIEVEMENT TEST RESULTS • HS Readiness Test – Out of 1. 2 million Grade 6 examinees, only 8, 000 passed – 75% of elementary graduates cannot read independently • Youth Literacy Rate: 95. 1% • Youth Functional Literacy Rate: 85. 3% i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 40
An Educational Crisis NATIONAL ACHIEVEMENT TEST RESULTS • HS Readiness Test – Out of 1. 2 million Grade 6 examinees, only 8, 000 passed – 75% of elementary graduates cannot read independently • Youth Literacy Rate: 95. 1% • Youth Functional Literacy Rate: 85. 3% i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 40
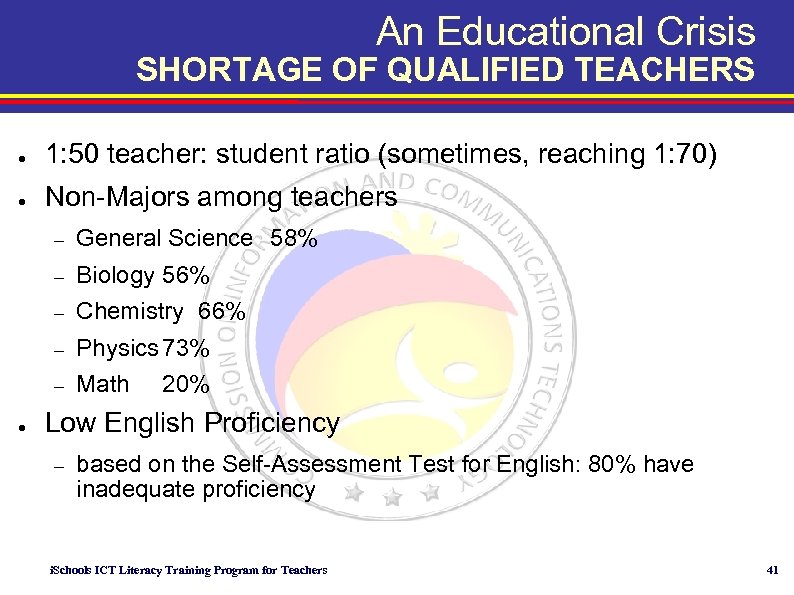 An Educational Crisis SHORTAGE OF QUALIFIED TEACHERS ● 1: 50 teacher: student ratio (sometimes, reaching 1: 70) ● Non-Majors among teachers – – Biology 56% – Chemistry 66% – Physics 73% – ● General Science 58% Math 20% Low English Proficiency – based on the Self-Assessment Test for English: 80% have inadequate proficiency i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 41
An Educational Crisis SHORTAGE OF QUALIFIED TEACHERS ● 1: 50 teacher: student ratio (sometimes, reaching 1: 70) ● Non-Majors among teachers – – Biology 56% – Chemistry 66% – Physics 73% – ● General Science 58% Math 20% Low English Proficiency – based on the Self-Assessment Test for English: 80% have inadequate proficiency i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 41
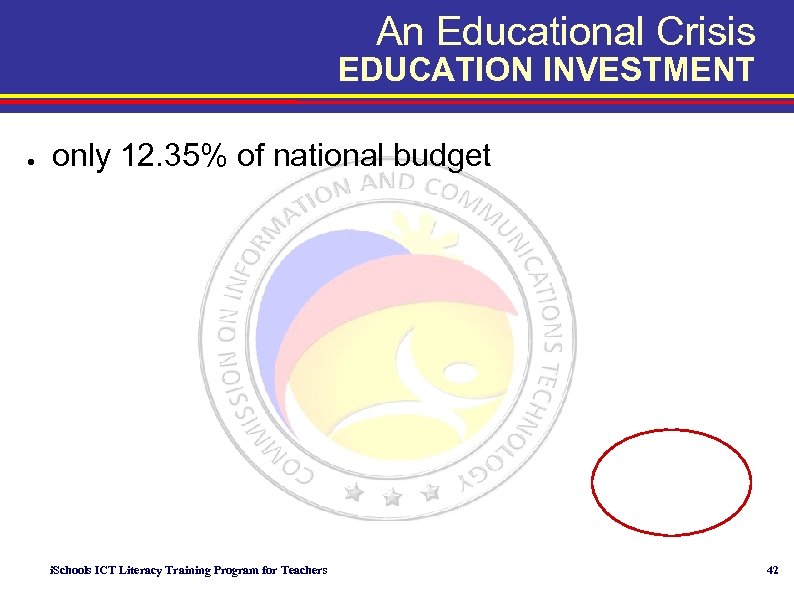 An Educational Crisis EDUCATION INVESTMENT ● only 12. 35% of national budget i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 42
An Educational Crisis EDUCATION INVESTMENT ● only 12. 35% of national budget i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 42
 An Educational Crisis COHORT SURVIVAL TREND ● dropout rate for HS: 9% in SY 1998 -1999 to 13. 10% in SY 2002 -2003 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 43
An Educational Crisis COHORT SURVIVAL TREND ● dropout rate for HS: 9% in SY 1998 -1999 to 13. 10% in SY 2002 -2003 i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 43
 2003 Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 44
2003 Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 44
 ICT 4 E – Philippine Experience • various initiatives: – – – – DTI PCPS GILAS DOST-SEI ELSA text 2 teach SEAMEO INNOTECH FIT-ED Intel Teach to the Future Microsoft’s Partners in Learning/ Learn. ph – Coke ed. Venture – Knowledge Channel i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers • primary level: 1: 25, 000 computer: student ratio • secondary level: 1: 300 computer: student ratio – 67% penetration – DTI-Dep. Ed initiative: by 2006, full penetration at 10 PCs per school 45
ICT 4 E – Philippine Experience • various initiatives: – – – – DTI PCPS GILAS DOST-SEI ELSA text 2 teach SEAMEO INNOTECH FIT-ED Intel Teach to the Future Microsoft’s Partners in Learning/ Learn. ph – Coke ed. Venture – Knowledge Channel i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers • primary level: 1: 25, 000 computer: student ratio • secondary level: 1: 300 computer: student ratio – 67% penetration – DTI-Dep. Ed initiative: by 2006, full penetration at 10 PCs per school 45
 CICT-HCDG ICT 4 E Program ● ● vision: A nation competent in the use of ICT as a tool for sustainable human development KRAs: 1. A Culture of Creative ICT Use 2. An Educational System that Maximizes the Use of ICT in Learning 3. World Class Knowledge Worker i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 46
CICT-HCDG ICT 4 E Program ● ● vision: A nation competent in the use of ICT as a tool for sustainable human development KRAs: 1. A Culture of Creative ICT Use 2. An Educational System that Maximizes the Use of ICT in Learning 3. World Class Knowledge Worker i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 46
 Table of Activities in ICT in Education i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 47
Table of Activities in ICT in Education i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 47
 ICT 4 E Initiatives –High School • Educators’ Training • Infrastructure Deployment – ICT Literacy using FOSS – Lab Management – Sustainability Training – M&E – i. School Web Board – Intel Teach to the Future (FOSS version? ) i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers – Computer Labs with Internet • PCs for Teachers and Principals – Phil Education Network (Ph. Ed. Net) • a “walled garden” that hosts educational, learning and teaching materials for use by Filipino students, their teachers and parents 48
ICT 4 E Initiatives –High School • Educators’ Training • Infrastructure Deployment – ICT Literacy using FOSS – Lab Management – Sustainability Training – M&E – i. School Web Board – Intel Teach to the Future (FOSS version? ) i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers – Computer Labs with Internet • PCs for Teachers and Principals – Phil Education Network (Ph. Ed. Net) • a “walled garden” that hosts educational, learning and teaching materials for use by Filipino students, their teachers and parents 48
 ICT 4 E Initiatives –High School • Applications Development: common and integrated systems – Adopting existing system: Ubuntu developed systems – ‘ground up development’ via the Open Source in Education Initiative (OSEI) • Content Development – Developing skoool. ph – Transforming existing Dep. Ed materials into multimedia (OSEI) – HS Student-developed materials via contest: Science, Math, English, Social Studies – Faculty-developed Material • Contest: Science, Math, English, Social Studies • i. School Web. Board i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 49
ICT 4 E Initiatives –High School • Applications Development: common and integrated systems – Adopting existing system: Ubuntu developed systems – ‘ground up development’ via the Open Source in Education Initiative (OSEI) • Content Development – Developing skoool. ph – Transforming existing Dep. Ed materials into multimedia (OSEI) – HS Student-developed materials via contest: Science, Math, English, Social Studies – Faculty-developed Material • Contest: Science, Math, English, Social Studies • i. School Web. Board i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 49
 Related ICT 4 E Projects ● National ICT Competency Standards (vendor-neutral) – – – NICS-Basic NICS-Advanced NICS-Teachers ● ● focus on effective integration of ICT in teaching & learning ICT Literacy Project – FOSS CD KIT – FOSS Applications and CBTs i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 50
Related ICT 4 E Projects ● National ICT Competency Standards (vendor-neutral) – – – NICS-Basic NICS-Advanced NICS-Teachers ● ● focus on effective integration of ICT in teaching & learning ICT Literacy Project – FOSS CD KIT – FOSS Applications and CBTs i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 50
 i. Schools Internet in Public High Schools ● ● ● Community Mobilization Infrastructure Deployment Educators’ Training (Teachers, Lab Mgt, Sustainability, M&E) Content Development: competitions (student web contest, teachers’ Web. Quest contest) Applications Development: common and integrated systems ICT 4 E M&E i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 51
i. Schools Internet in Public High Schools ● ● ● Community Mobilization Infrastructure Deployment Educators’ Training (Teachers, Lab Mgt, Sustainability, M&E) Content Development: competitions (student web contest, teachers’ Web. Quest contest) Applications Development: common and integrated systems ICT 4 E M&E i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 51
 i. Schools ICT 4 E Training Program for Teachers ● based on NICS-Teachers ● ICT Skills of Teachers: – – Preparation, Delivery, Classroom Management/Admin hard skills + soft skills i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 52
i. Schools ICT 4 E Training Program for Teachers ● based on NICS-Teachers ● ICT Skills of Teachers: – – Preparation, Delivery, Classroom Management/Admin hard skills + soft skills i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 52
 i. Schools ICT 4 E Training Program for Teachers ● Phase 1: ICT Literacy Training (NICS-Basic) – – – – Module 1: intro to ICT 4 E Module 2: ICT Basics and File Management Module 3: Internet Module 4: Cyber Security, and Cyber Ethics Module 5: Word Processing Module 6: Electronic Spreadsheet Module 7: Multimedia Presentation i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 53
i. Schools ICT 4 E Training Program for Teachers ● Phase 1: ICT Literacy Training (NICS-Basic) – – – – Module 1: intro to ICT 4 E Module 2: ICT Basics and File Management Module 3: Internet Module 4: Cyber Security, and Cyber Ethics Module 5: Word Processing Module 6: Electronic Spreadsheet Module 7: Multimedia Presentation i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 53
 i. Schools ICT 4 E Training Program for Teachers ● Phase 2: i. Schools Web. Board ● empowering teachers to build online self-learning materials Phase 3 onwards: more advanced ICT 4 E skills – – including producing own Web. Quests, conducting online collaborative projects, designing integrated multidisciplinary student projects, etc. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 54
i. Schools ICT 4 E Training Program for Teachers ● Phase 2: i. Schools Web. Board ● empowering teachers to build online self-learning materials Phase 3 onwards: more advanced ICT 4 E skills – – including producing own Web. Quests, conducting online collaborative projects, designing integrated multidisciplinary student projects, etc. i. Schools ICT Literacy Training Program for Teachers 54
 END OF PRESENTATION Thank you Commission on Information and Communications Technology
END OF PRESENTATION Thank you Commission on Information and Communications Technology


