ff4e812dec2c30ef452eeba27c3b9014.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 ICT for Development e-Governance and the peace agenda ICT 4 D Lecture 15 Tim Unwin
ICT for Development e-Governance and the peace agenda ICT 4 D Lecture 15 Tim Unwin
 “For millions of people across the world, war and violence are as much parts of daily life as are going to school, shopping in the supermarket, or surfing the Net for people in Western Europe or North America” (Unwin, 2002)
“For millions of people across the world, war and violence are as much parts of daily life as are going to school, shopping in the supermarket, or surfing the Net for people in Western Europe or North America” (Unwin, 2002)
 Outline • War and Peace • The Governance Agenda w MDGs w The UN and donor organisations • • UN e-Government A framework for ICT in governance Case Studies Picture me an enemy w The use of video Lecture 15
Outline • War and Peace • The Governance Agenda w MDGs w The UN and donor organisations • • UN e-Government A framework for ICT in governance Case Studies Picture me an enemy w The use of video Lecture 15
 War and peace • War and violence affect many aspects of poor people’s lives w International conflicts w Civil strife w Domestic violence • But what exactly is the relationship between poverty and violence? • Many conflicts caused by interests of global capital w US imperialism Lecture 15
War and peace • War and violence affect many aspects of poor people’s lives w International conflicts w Civil strife w Domestic violence • But what exactly is the relationship between poverty and violence? • Many conflicts caused by interests of global capital w US imperialism Lecture 15
 Governance and Government • Governance w The processes and systems by which a government or governor operates • Government w The institutions and people involved w The dominant decision making arm of the state • Also governance in the IT industry w The processes that need to be in place for a successful project w This coalescence of usages, may help explain why e. Governance is such a prominent concept Lecture 15
Governance and Government • Governance w The processes and systems by which a government or governor operates • Government w The institutions and people involved w The dominant decision making arm of the state • Also governance in the IT industry w The processes that need to be in place for a successful project w This coalescence of usages, may help explain why e. Governance is such a prominent concept Lecture 15
 The governance agenda • Peace and good governance vital to improving the lives of poor people • The Washington consensus (Williamson, 1990) w macroeconomic discipline w a market economy w openness to the world. • The twin pillars of modern capitalism w Free market w Liberal democracy § And thus the importance of good governance § Essential for enabling economic growth, and thus profit Lecture 15
The governance agenda • Peace and good governance vital to improving the lives of poor people • The Washington consensus (Williamson, 1990) w macroeconomic discipline w a market economy w openness to the world. • The twin pillars of modern capitalism w Free market w Liberal democracy § And thus the importance of good governance § Essential for enabling economic growth, and thus profit Lecture 15
 The governance agenda • The logics of growth and governance w If economic growth is essential to eliminate poverty w Then it is crucial to have good governance to enable growth • Governance is interestingly not one of the MDGs w But donors keen on delivering macro-economic policy instruments see good governance as an essential enabler w And it is in target 12 of Goal 8 (the catch-all) Lecture 15
The governance agenda • The logics of growth and governance w If economic growth is essential to eliminate poverty w Then it is crucial to have good governance to enable growth • Governance is interestingly not one of the MDGs w But donors keen on delivering macro-economic policy instruments see good governance as an essential enabler w And it is in target 12 of Goal 8 (the catch-all) Lecture 15
 The governance agenda • David Held has argued that there are many different kinds of democracy w Yet world’s powerful nations are determined to impose one particular vision w This is surely itself not ‘democratic’ w Democracy serves those in power • This is not to deny that creating conditions that reduce conflict and violence is desirable w But it is to argue that the motives for this need to be transparent w And that we need to focus on interests of the poor Lecture 15
The governance agenda • David Held has argued that there are many different kinds of democracy w Yet world’s powerful nations are determined to impose one particular vision w This is surely itself not ‘democratic’ w Democracy serves those in power • This is not to deny that creating conditions that reduce conflict and violence is desirable w But it is to argue that the motives for this need to be transparent w And that we need to focus on interests of the poor Lecture 15
 UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 “Economic and social empowerment today rests on the ability to access, gather, analyze and utilize information and knowledge to widen individual choices for political, economic, social, cultural and behavioral decisions. ICTs are the conduits which transmit information and knowledge. By integrating technology into development planning, more effective and speedy solutions can be found for economic growth and sustainable human development” (UN e-Government Readiness report, 2004 http: //www. unpan. org/egovernment 4. asp) Lecture 15
UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 “Economic and social empowerment today rests on the ability to access, gather, analyze and utilize information and knowledge to widen individual choices for political, economic, social, cultural and behavioral decisions. ICTs are the conduits which transmit information and knowledge. By integrating technology into development planning, more effective and speedy solutions can be found for economic growth and sustainable human development” (UN e-Government Readiness report, 2004 http: //www. unpan. org/egovernment 4. asp) Lecture 15
 UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 • e-Government readiness w Based on five stages § § § Emerging presence Enhanced presence Interactive presence Transactional presence Networked presence • E-Participation index w Assesses the quality, relevance, usefulness and willingness of government websites for providing online information and participatory tools and services to the people Lecture 15
UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 • e-Government readiness w Based on five stages § § § Emerging presence Enhanced presence Interactive presence Transactional presence Networked presence • E-Participation index w Assesses the quality, relevance, usefulness and willingness of government websites for providing online information and participatory tools and services to the people Lecture 15
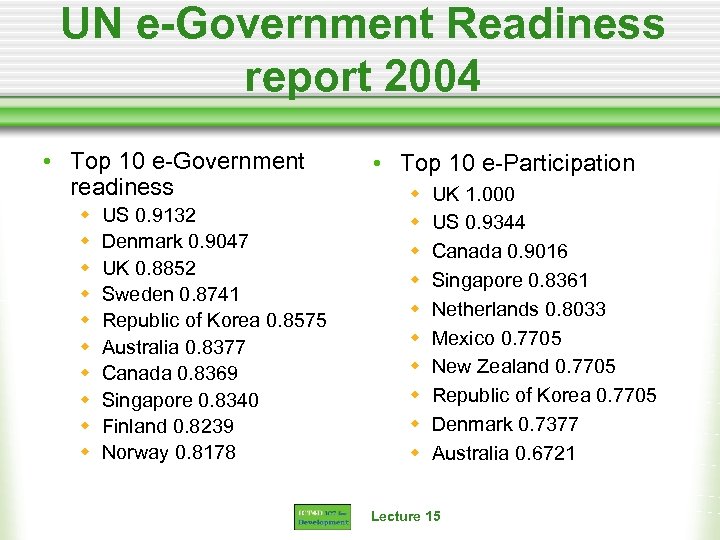 UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 • Top 10 e-Government readiness w w w w w US 0. 9132 Denmark 0. 9047 UK 0. 8852 Sweden 0. 8741 Republic of Korea 0. 8575 Australia 0. 8377 Canada 0. 8369 Singapore 0. 8340 Finland 0. 8239 Norway 0. 8178 • Top 10 e-Participation w w w w w UK 1. 000 US 0. 9344 Canada 0. 9016 Singapore 0. 8361 Netherlands 0. 8033 Mexico 0. 7705 New Zealand 0. 7705 Republic of Korea 0. 7705 Denmark 0. 7377 Australia 0. 6721 Lecture 15
UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 • Top 10 e-Government readiness w w w w w US 0. 9132 Denmark 0. 9047 UK 0. 8852 Sweden 0. 8741 Republic of Korea 0. 8575 Australia 0. 8377 Canada 0. 8369 Singapore 0. 8340 Finland 0. 8239 Norway 0. 8178 • Top 10 e-Participation w w w w w UK 1. 000 US 0. 9344 Canada 0. 9016 Singapore 0. 8361 Netherlands 0. 8033 Mexico 0. 7705 New Zealand 0. 7705 Republic of Korea 0. 7705 Denmark 0. 7377 Australia 0. 6721 Lecture 15
 UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 • Examples of e-Government readiness w w w w 55 th South Africa 0. 4902 67 th China 0. 4356 86 th India 0. 3879 114 th Uganda 0. 3290 130 th Zimbabwe 0. 2833 136 th Egypt 0. 2653 140 th Rwanda 0. 2511 World Average 0. 4127 Lecture 15
UN e-Government Readiness report 2004 • Examples of e-Government readiness w w w w 55 th South Africa 0. 4902 67 th China 0. 4356 86 th India 0. 3879 114 th Uganda 0. 3290 130 th Zimbabwe 0. 2833 136 th Egypt 0. 2653 140 th Rwanda 0. 2511 World Average 0. 4127 Lecture 15
 ICT in governance • UN Readiness Report: ICT can help w “Improve transparency and efficiency of the public sector” w “Create network links across service delivery agencies” w “Cut bureaucratic red tape” w “Realize vast savings” w “ICTs in the public sector can engage citizens as participants in the overall development of the future” Lecture 15
ICT in governance • UN Readiness Report: ICT can help w “Improve transparency and efficiency of the public sector” w “Create network links across service delivery agencies” w “Cut bureaucratic red tape” w “Realize vast savings” w “ICTs in the public sector can engage citizens as participants in the overall development of the future” Lecture 15
 ICT and ‘Good’ Governance • ‘Good’ governance: freedoms w w To access information about government To be represented To vote To meet collectively • Technologies w w Internet: enabling access to information Creating networks and communities Radio and TV: disseminating electoral messages Mechanisms for ‘being heard’ and commenting on services Lecture 15
ICT and ‘Good’ Governance • ‘Good’ governance: freedoms w w To access information about government To be represented To vote To meet collectively • Technologies w w Internet: enabling access to information Creating networks and communities Radio and TV: disseminating electoral messages Mechanisms for ‘being heard’ and commenting on services Lecture 15
 WSIS - WGIG 2003 -5 • Working Group on Internet Governance w One of the key agendas of WSIS Tunis 2005 § The terms ‘governance’ and ‘govern’ mean more than ‘government activities’ § the enabling dimension includes organized and cooperative activities between different stakeholders § Internet governance encompasses a wider range of conditions and mechanisms than IP numbering and domain name administration. § But at Tunis dominated by role of US in w Public policy issues around § § Equitable distribution of resources Access for all Stable and secure functioning of the Internet Lecture 15 Multilingualism
WSIS - WGIG 2003 -5 • Working Group on Internet Governance w One of the key agendas of WSIS Tunis 2005 § The terms ‘governance’ and ‘govern’ mean more than ‘government activities’ § the enabling dimension includes organized and cooperative activities between different stakeholders § Internet governance encompasses a wider range of conditions and mechanisms than IP numbering and domain name administration. § But at Tunis dominated by role of US in w Public policy issues around § § Equitable distribution of resources Access for all Stable and secure functioning of the Internet Lecture 15 Multilingualism
 WSIS Tunis 2005 • Considerable debate over the role of the US in ‘controlling’ the Internet • Internet Governance w ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) § To retain role as manager of domain names w But creation of a new Internet Governance Forum § To include government, business and civil society representation • Focus on governance, SPAM, cyber crime and privacy Lecture 15
WSIS Tunis 2005 • Considerable debate over the role of the US in ‘controlling’ the Internet • Internet Governance w ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) § To retain role as manager of domain names w But creation of a new Internet Governance Forum § To include government, business and civil society representation • Focus on governance, SPAM, cyber crime and privacy Lecture 15
 Case Studies • • Jamaica e-Governance programme Information Kerala Mission Lesotho 2002 elections UPEACE Lecture 15
Case Studies • • Jamaica e-Governance programme Information Kerala Mission Lesotho 2002 elections UPEACE Lecture 15
 Jamaica e-Governance programme • Facilitation of access to information and knowledge, which forms the basis of decision making eg by way government websites, other online sources of information • Automating tedious tasks such as filing tax forms, checking the status of applications etc. • Providing avenues for citizens to communicate with government officials • Providing a mechanism for advocacy on issues of public interest among disparate groups • But issues surrounding practical delivery Lecture 15
Jamaica e-Governance programme • Facilitation of access to information and knowledge, which forms the basis of decision making eg by way government websites, other online sources of information • Automating tedious tasks such as filing tax forms, checking the status of applications etc. • Providing avenues for citizens to communicate with government officials • Providing a mechanism for advocacy on issues of public interest among disparate groups • But issues surrounding practical delivery Lecture 15
 Information Kerala Mission • Aims w Innovative ICT-based knowledge societies at the grass roots level under the leadership of Local Self Governments • Activities w Samveditha web portal of 1215 local bodies in Kerala w Sanchitha repository of legislations, executive orders and promulgations w Swathantra information systems on 53 municipalities • http: //www. infokerala. org/new/ Lecture 15
Information Kerala Mission • Aims w Innovative ICT-based knowledge societies at the grass roots level under the leadership of Local Self Governments • Activities w Samveditha web portal of 1215 local bodies in Kerala w Sanchitha repository of legislations, executive orders and promulgations w Swathantra information systems on 53 municipalities • http: //www. infokerala. org/new/ Lecture 15
 Lesotho 2002 elections • History of contested elections w Key issue was voter registration • 2002 elections w South African company Arivia provided § Sites and software § Voter registration, including capturing of biological data and fingerprints • Photograph, signature and fingerprint of each voter w Encouraged widespread acceptance of results • But real wider issues over balance between government efficiency and citizen’s rights w A global issue! Lecture 15
Lesotho 2002 elections • History of contested elections w Key issue was voter registration • 2002 elections w South African company Arivia provided § Sites and software § Voter registration, including capturing of biological data and fingerprints • Photograph, signature and fingerprint of each voter w Encouraged widespread acceptance of results • But real wider issues over balance between government efficiency and citizen’s rights w A global issue! Lecture 15
 UPEACE (University for Peace) • UPEACE established in Costa Rica in 1980 w First country in modern world to abolish its army • Revitalized by Kofi Annan in late 1990 s w Worldwide programme w Africa Programme launched 2002 § Linking of African scholars into a knowledge network § Providing access to best international peace education § International, multicultural and multidisciplinary Lecture 15
UPEACE (University for Peace) • UPEACE established in Costa Rica in 1980 w First country in modern world to abolish its army • Revitalized by Kofi Annan in late 1990 s w Worldwide programme w Africa Programme launched 2002 § Linking of African scholars into a knowledge network § Providing access to best international peace education § International, multicultural and multidisciplinary Lecture 15
 Picture me an enemy • 1991 war in former Yugoslavia • Documentary film told through stories w Natasa, a Serbo-Croat from Croatia w Tahija, a Bosniak (Bosnian Muslim) • http: //www. visavisproductions. com/ Lecture 15
Picture me an enemy • 1991 war in former Yugoslavia • Documentary film told through stories w Natasa, a Serbo-Croat from Croatia w Tahija, a Bosniak (Bosnian Muslim) • http: //www. visavisproductions. com/ Lecture 15
 Conclusions • E-Governance as being highly contested w The rights of individuals and the rights of states w Considerable ethical debate • Role of G 8 and UN in promoting governance agendas w And links with WSIS second phase • ICT does have real potential to enhance transparency w But will this necessarily be in the interests of poor people? Lecture 15
Conclusions • E-Governance as being highly contested w The rights of individuals and the rights of states w Considerable ethical debate • Role of G 8 and UN in promoting governance agendas w And links with WSIS second phase • ICT does have real potential to enhance transparency w But will this necessarily be in the interests of poor people? Lecture 15


