e5b2abada3b61950e06e6312512e2e7c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 ICS-FORTH FOUNDATION FOR RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY-HELLAS INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER SCIENCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY http: //www. forth. gr/ics/isl/ Head: Prof. Panos Constantopoulos 1
ICS-FORTH FOUNDATION FOR RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY-HELLAS INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER SCIENCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY http: //www. forth. gr/ics/isl/ Head: Prof. Panos Constantopoulos 1
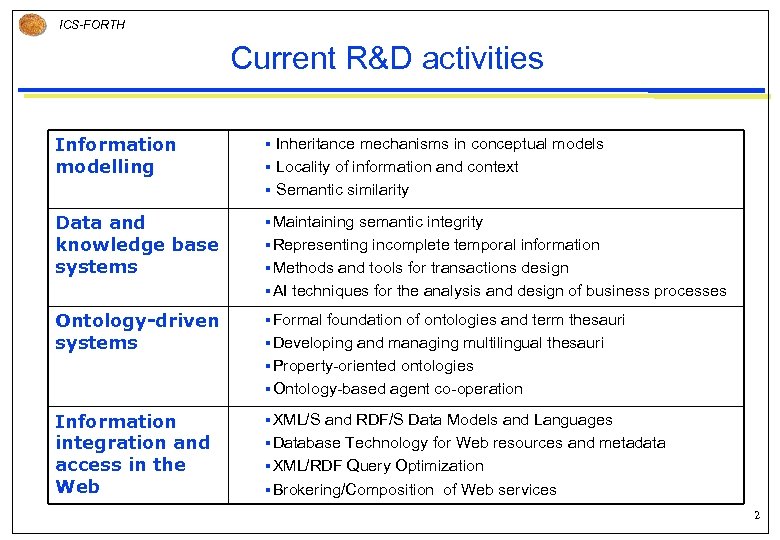 ICS-FORTH Current R&D activities Information modelling § Data and knowledge base systems § Maintaining Ontology-driven systems § Formal Information integration and access in the Web § XML/S Inheritance mechanisms in conceptual models § Locality of information and context § Semantic similarity semantic integrity § Representing incomplete temporal information § Methods and tools for transactions design § AI techniques for the analysis and design of business processes foundation of ontologies and term thesauri § Developing and managing multilingual thesauri § Property-oriented ontologies § Ontology-based agent co-operation and RDF/S Data Models and Languages § Database Technology for Web resources and metadata § XML/RDF Query Optimization § Brokering/Composition of Web services 2
ICS-FORTH Current R&D activities Information modelling § Data and knowledge base systems § Maintaining Ontology-driven systems § Formal Information integration and access in the Web § XML/S Inheritance mechanisms in conceptual models § Locality of information and context § Semantic similarity semantic integrity § Representing incomplete temporal information § Methods and tools for transactions design § AI techniques for the analysis and design of business processes foundation of ontologies and term thesauri § Developing and managing multilingual thesauri § Property-oriented ontologies § Ontology-based agent co-operation and RDF/S Data Models and Languages § Database Technology for Web resources and metadata § XML/RDF Query Optimization § Brokering/Composition of Web services 2
 ICS-FORTH Application areas Scientific, technical and legal documentation and knowledge bases § Organizational memories, digital libraries Web data and service platforms § Portlets, Active Workflows E-business § product catalogues, service brokering Enterprise resource planning 3
ICS-FORTH Application areas Scientific, technical and legal documentation and knowledge bases § Organizational memories, digital libraries Web data and service platforms § Portlets, Active Workflows E-business § product catalogues, service brokering Enterprise resource planning 3
 ICS-FORTH Centre for Cultural Informatics A unit of ISL specializing in the analysis, design, development and application of IT systems in the cultural heritage sector § Follows a cross-disciplinary approach § Aims at covering the entire lifecycle of cultural information and of documentation processes Areas of activity § monument and museum information systems § source material management systems § models and standards for cultural data § terminology systems 4
ICS-FORTH Centre for Cultural Informatics A unit of ISL specializing in the analysis, design, development and application of IT systems in the cultural heritage sector § Follows a cross-disciplinary approach § Aims at covering the entire lifecycle of cultural information and of documentation processes Areas of activity § monument and museum information systems § source material management systems § models and standards for cultural data § terminology systems 4
 ICS-FORTH Technological results highlights Standards § The Conceptual Reference Model of the Documentation Committee, International Council of Museums now a candidate ISO standard. Enabling technologies § The Semantic Index System (SIS) A versatile, high performance tool for concept and semantic link management, especially suited for meta-modelling. Offered as product. § The RDF Suite Includes a parser supporting semantic validation, a database generator, and a declarative query language, all the first of their kind. Open source. Selected application systems § The SIS-TMS multilingual thesaurus management system. Offered as product. 35 installations to-date. § The POLEMON National Monuments Record system Approved by the Central Archaeological Council for application at all units and supervised organizations of the Ministry of Culture. Already deployed at 21 locations. § Integrated documentation and document management system for the Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Nuremberg. 5
ICS-FORTH Technological results highlights Standards § The Conceptual Reference Model of the Documentation Committee, International Council of Museums now a candidate ISO standard. Enabling technologies § The Semantic Index System (SIS) A versatile, high performance tool for concept and semantic link management, especially suited for meta-modelling. Offered as product. § The RDF Suite Includes a parser supporting semantic validation, a database generator, and a declarative query language, all the first of their kind. Open source. Selected application systems § The SIS-TMS multilingual thesaurus management system. Offered as product. 35 installations to-date. § The POLEMON National Monuments Record system Approved by the Central Archaeological Council for application at all units and supervised organizations of the Ministry of Culture. Already deployed at 21 locations. § Integrated documentation and document management system for the Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Nuremberg. 5
 ICS-FORTH Personnel (November 2002) Researchers: Univ. of Crete faculty: Affiliated researcher: R&D engineers: Doctoral research assistants: M. Sc. Research assistants: Graduate trainees: 2 5 1 12 3 12 6 6
ICS-FORTH Personnel (November 2002) Researchers: Univ. of Crete faculty: Affiliated researcher: R&D engineers: Doctoral research assistants: M. Sc. Research assistants: Graduate trainees: 2 5 1 12 3 12 6 6
 ICS-FORTH Collaborations National § National Technical University (NTUA), Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Institute for Language and Speech Processing (ILSP), Greek Ministry of Culture, Minoan Lines, . . . International § University Paris-Sud, Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et Automatique (INRIA), Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers (CNAM), Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Télécommunications – Bretagne (ENST), Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL), Getty Information Institute, Ministere de la Culture (France), Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie, Germanisches Nationalmuseum –Nuremberg, … Industrial § Intrasoft SA, Epsilon Software SA, Unixfor (UF), Bull, Valoris, Finsiel, System Simulation Limited (SSL), . . . 7
ICS-FORTH Collaborations National § National Technical University (NTUA), Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Institute for Language and Speech Processing (ILSP), Greek Ministry of Culture, Minoan Lines, . . . International § University Paris-Sud, Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et Automatique (INRIA), Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers (CNAM), Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Télécommunications – Bretagne (ENST), Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL), Getty Information Institute, Ministere de la Culture (France), Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie, Germanisches Nationalmuseum –Nuremberg, … Industrial § Intrasoft SA, Epsilon Software SA, Unixfor (UF), Bull, Valoris, Finsiel, System Simulation Limited (SSL), . . . 7
 ICS-FORTH The ICS-FORTH R&D Activities on the Semantic Web 8
ICS-FORTH The ICS-FORTH R&D Activities on the Semantic Web 8
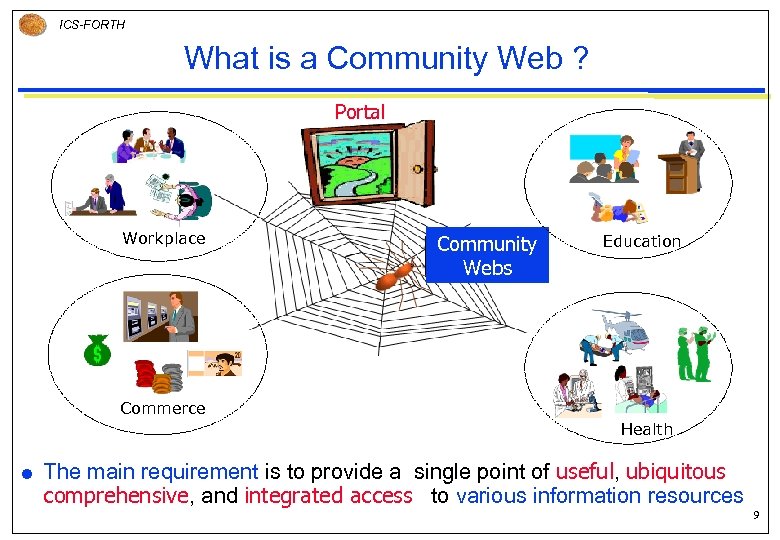 ICS-FORTH What is a Community Web ? Portal Workplace Community Webs Education Commerce Health The main requirement is to provide a single point of useful, ubiquitous comprehensive, and integrated access to various information resources 9
ICS-FORTH What is a Community Web ? Portal Workplace Community Webs Education Commerce Health The main requirement is to provide a single point of useful, ubiquitous comprehensive, and integrated access to various information resources 9
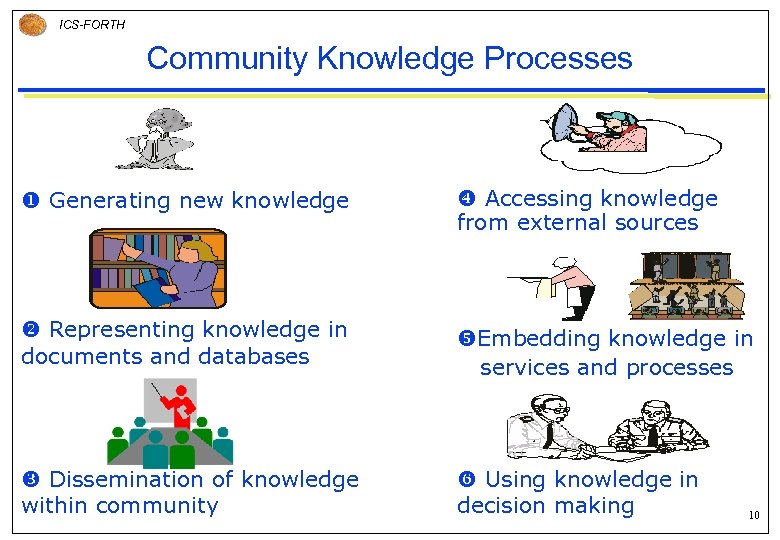 ICS-FORTH Community Knowledge Processes u Generating new knowledge x Accessing knowledge from external sources v Representing knowledge in documents and databases y. Embedding knowledge in services and processes w Dissemination of knowledge within community z Using knowledge in decision making 10
ICS-FORTH Community Knowledge Processes u Generating new knowledge x Accessing knowledge from external sources v Representing knowledge in documents and databases y. Embedding knowledge in services and processes w Dissemination of knowledge within community z Using knowledge in decision making 10
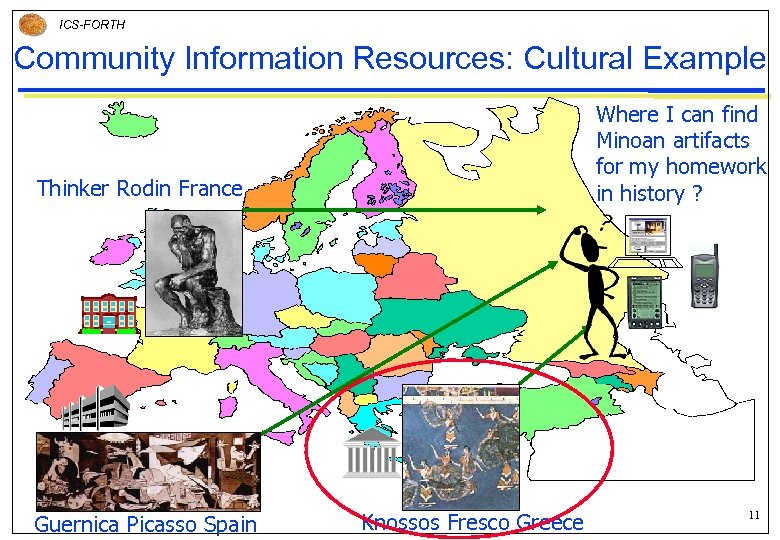 ICS-FORTH Community Information Resources: Cultural Example Where I can find Minoan artifacts for my homework in history ? Thinker Rodin France Guernica Picasso Spain Knossos Fresco Greece 11
ICS-FORTH Community Information Resources: Cultural Example Where I can find Minoan artifacts for my homework in history ? Thinker Rodin France Guernica Picasso Spain Knossos Fresco Greece 11
 ICS-FORTH Metadata exists for Almost Anything/Everywhere Physical Objects, Places, People, Devices, Networks, Infrastructure, Digital Documents, Data, Programs, User Profiles, Preferences,
ICS-FORTH Metadata exists for Almost Anything/Everywhere Physical Objects, Places, People, Devices, Networks, Infrastructure, Digital Documents, Data, Programs, User Profiles, Preferences,
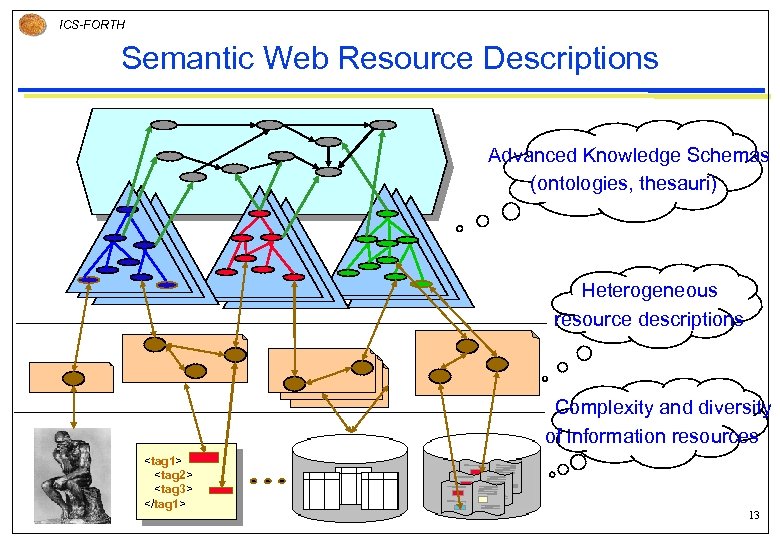 ICS-FORTH Semantic Web Resource Descriptions Advanced Knowledge Schemas (ontologies, thesauri) Heterogeneous resource descriptions Complexity and diversity of information resources
ICS-FORTH Semantic Web Resource Descriptions Advanced Knowledge Schemas (ontologies, thesauri) Heterogeneous resource descriptions Complexity and diversity of information resources
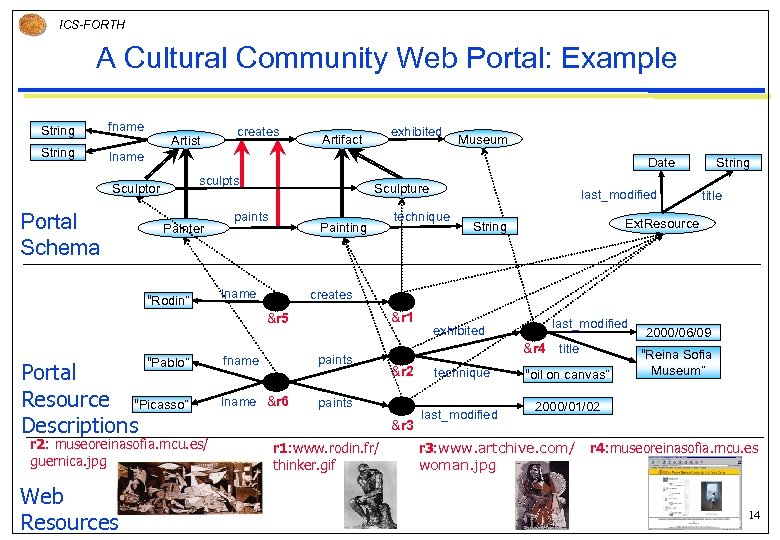 ICS-FORTH A Cultural Community Web Portal: Example String fname String lname Artist exhibited Artifact sculpts Painter “Rodin” Sculpture paints Painting lname “Pablo” Portal Resource “Picasso” Descriptions r 2: museoreinasofia. mcu. es/ guernica. jpg last_modified technique String title Ext. Resource String creates &r 1 &r 5 Web Resources Museum Date Sculptor Portal Schema creates fname paints lname &r 6 last_modified &r 4 title paints &r 2 &r 3 r 1: www. rodin. fr/ thinker. gif exhibited technique last_modified “oil on canvas” 2000/06/09 “Reina Sofia Museum” 2000/01/02 r 3: www. artchive. com/ woman. jpg r 4: museoreinasofia. mcu. es 14
ICS-FORTH A Cultural Community Web Portal: Example String fname String lname Artist exhibited Artifact sculpts Painter “Rodin” Sculpture paints Painting lname “Pablo” Portal Resource “Picasso” Descriptions r 2: museoreinasofia. mcu. es/ guernica. jpg last_modified technique String title Ext. Resource String creates &r 1 &r 5 Web Resources Museum Date Sculptor Portal Schema creates fname paints lname &r 6 last_modified &r 4 title paints &r 2 &r 3 r 1: www. rodin. fr/ thinker. gif exhibited technique last_modified “oil on canvas” 2000/06/09 “Reina Sofia Museum” 2000/01/02 r 3: www. artchive. com/ woman. jpg r 4: museoreinasofia. mcu. es 14
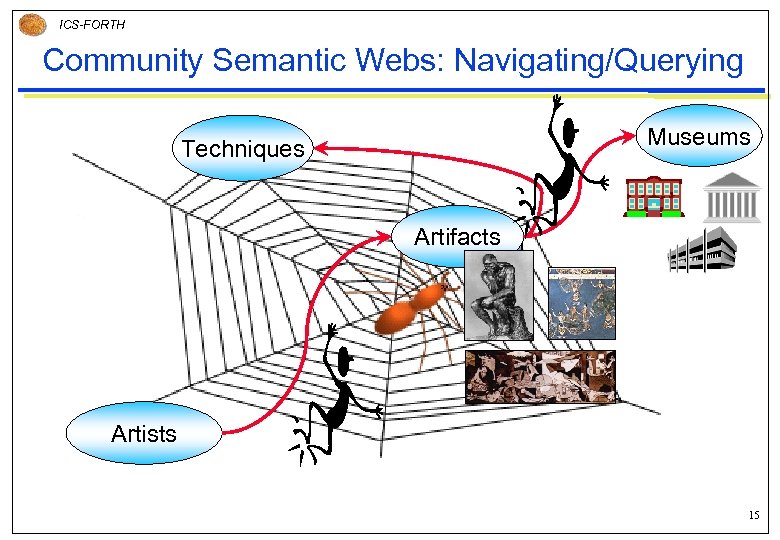 ICS-FORTH Community Semantic Webs: Navigating/Querying Museums Techniques Artifacts Artists 15
ICS-FORTH Community Semantic Webs: Navigating/Querying Museums Techniques Artifacts Artists 15
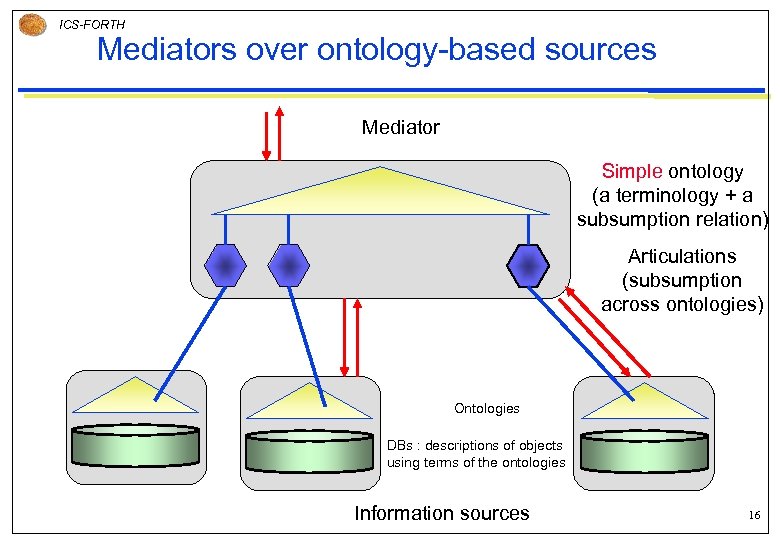 ICS-FORTH Mediators over ontology-based sources Mediator Simple ontology (a terminology + a subsumption relation) Articulations (subsumption across ontologies) Ontologies DBs : descriptions of objects using terms of the ontologies Information sources 16
ICS-FORTH Mediators over ontology-based sources Mediator Simple ontology (a terminology + a subsumption relation) Articulations (subsumption across ontologies) Ontologies DBs : descriptions of objects using terms of the ontologies Information sources 16
 ICS-FORTH Mediators over ontology-based sources, cont. Integration approach for providing unified access over ontology-based information sources of the kind of Web Catalogs (e. g. Yahoo!, ODP) § e. g. for defining user views over the catalogs of the web Sources and mediators can operate in a variety of modes according to specific application needs (recall or precision) § lower & upper approximation § sure & possible answer Articulation (instead of merging) enables a very natural, incremental evolution of a network of information sources. 17
ICS-FORTH Mediators over ontology-based sources, cont. Integration approach for providing unified access over ontology-based information sources of the kind of Web Catalogs (e. g. Yahoo!, ODP) § e. g. for defining user views over the catalogs of the web Sources and mediators can operate in a variety of modes according to specific application needs (recall or precision) § lower & upper approximation § sure & possible answer Articulation (instead of merging) enables a very natural, incremental evolution of a network of information sources. 17
 ICS-FORTH The ICS-FORTH RDFSuite Main Components Open Source Code (C-Web license): http: //139. 91. 183. 30: 9090/RDF/ The Validating RDF Parser (VRP): Karsten Tolle Diploma Thesis § The First RDF Parser supporting semantic validation of both resource descriptions and schemas The RDF Schema Specific Data. Base (RSSDB): Sophia Alexaki MSc. Thesis § The First RDF Store using schema knowledge to automatically generate an Object-Relational (SQL 3) representation of RDF metadata and load resource descriptions The RDF Query Language (RQL): Greg Karvournarakis MSc. Thesis § The First Declarative Language for uniformly querying RDF schemas and resource descriptions 18
ICS-FORTH The ICS-FORTH RDFSuite Main Components Open Source Code (C-Web license): http: //139. 91. 183. 30: 9090/RDF/ The Validating RDF Parser (VRP): Karsten Tolle Diploma Thesis § The First RDF Parser supporting semantic validation of both resource descriptions and schemas The RDF Schema Specific Data. Base (RSSDB): Sophia Alexaki MSc. Thesis § The First RDF Store using schema knowledge to automatically generate an Object-Relational (SQL 3) representation of RDF metadata and load resource descriptions The RDF Query Language (RQL): Greg Karvournarakis MSc. Thesis § The First Declarative Language for uniformly querying RDF schemas and resource descriptions 18
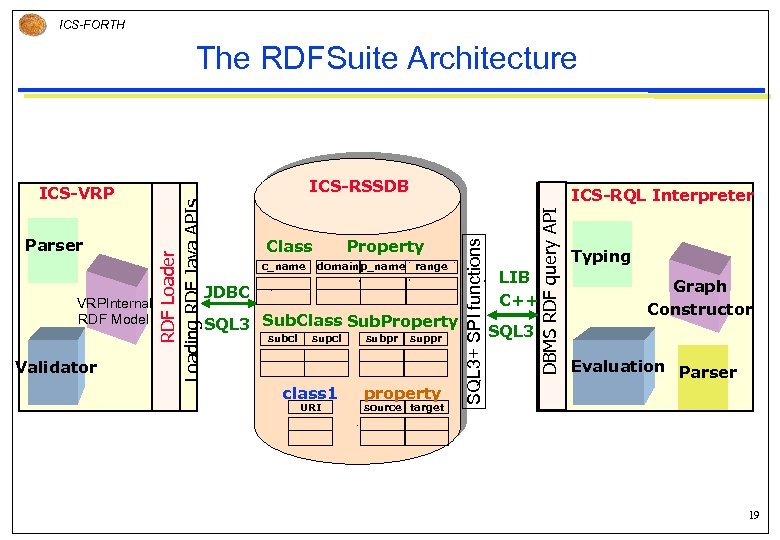 ICS-FORTH The RDFSuite Architecture Validator c_name Property domain p_name range JDBC SQL 3 Sub. Class Sub. Property subcl supcl class 1 URI creates subpr suppr property source target DBMS RDF query API VRPInternal RDF Model Class ICS-RQL Interpreter SQL 3+ SPI functions Parser ICS-RSSDB RDF Loader Loading RDF Java APIs ICS-VRP LIB C++ SQL 3 Typing Graph Constructor Evaluation Parser paints creates 19
ICS-FORTH The RDFSuite Architecture Validator c_name Property domain p_name range JDBC SQL 3 Sub. Class Sub. Property subcl supcl class 1 URI creates subpr suppr property source target DBMS RDF query API VRPInternal RDF Model Class ICS-RQL Interpreter SQL 3+ SPI functions Parser ICS-RSSDB RDF Loader Loading RDF Java APIs ICS-VRP LIB C++ SQL 3 Typing Graph Constructor Evaluation Parser paints creates 19
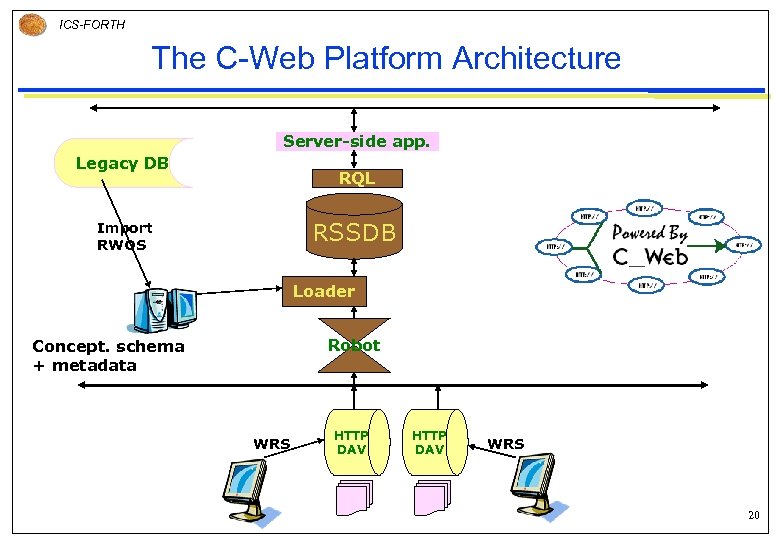 ICS-FORTH The C-Web Platform Architecture Server-side app. Legacy DB RQL RSSDB Import RWOS Loader Robot Concept. schema + metadata WRS HTTP DAV WRS 20
ICS-FORTH The C-Web Platform Architecture Server-side app. Legacy DB RQL RSSDB Import RWOS Loader Robot Concept. schema + metadata WRS HTTP DAV WRS 20
 ICS-FORTH The C-Web Project EC IST Project (13479) 1999 -2000 Overall Aim: Set-up methodologies and infrastructure for fast deployment and easy management of Web Portals for communities requiring § effective knowledge assimilation, elicitation § efficient semantic query answering Partners: INRIA(FR), FORTH(GR), EDW(IT) Application Scenarios: Learning Portals for intranets or the Internet § Corporate Knowledge Servers (e. g. , automobile, telecommunications) § Memory Organizations (e. g. , museums, libraries, archives) 21
ICS-FORTH The C-Web Project EC IST Project (13479) 1999 -2000 Overall Aim: Set-up methodologies and infrastructure for fast deployment and easy management of Web Portals for communities requiring § effective knowledge assimilation, elicitation § efficient semantic query answering Partners: INRIA(FR), FORTH(GR), EDW(IT) Application Scenarios: Learning Portals for intranets or the Internet § Corporate Knowledge Servers (e. g. , automobile, telecommunications) § Memory Organizations (e. g. , museums, libraries, archives) 21
 ICS-FORTH The Project “MESMUSES” EC IST Project (26074) 2001 – 2003 Overall Aim: design and experiment knowledge maps for organising, structuring and presenting scientific and technical knowledge § semantic portals: create and offer a cartography of connected or neighbouring knowledge domains § knowledge itineraries: navigate either on predefined routes, or on new routes that users define in a cooperative manner Partners: INRIA(FR), FINSIEL(IT) FORTH (GR), ENSTB (FR), VALORIS (FR), IMSS (IT), CSI (FR), EDW (IT), DET-UNIFI (IT) Application Scenario: scientific museums 22
ICS-FORTH The Project “MESMUSES” EC IST Project (26074) 2001 – 2003 Overall Aim: design and experiment knowledge maps for organising, structuring and presenting scientific and technical knowledge § semantic portals: create and offer a cartography of connected or neighbouring knowledge domains § knowledge itineraries: navigate either on predefined routes, or on new routes that users define in a cooperative manner Partners: INRIA(FR), FINSIEL(IT) FORTH (GR), ENSTB (FR), VALORIS (FR), IMSS (IT), CSI (FR), EDW (IT), DET-UNIFI (IT) Application Scenario: scientific museums 22
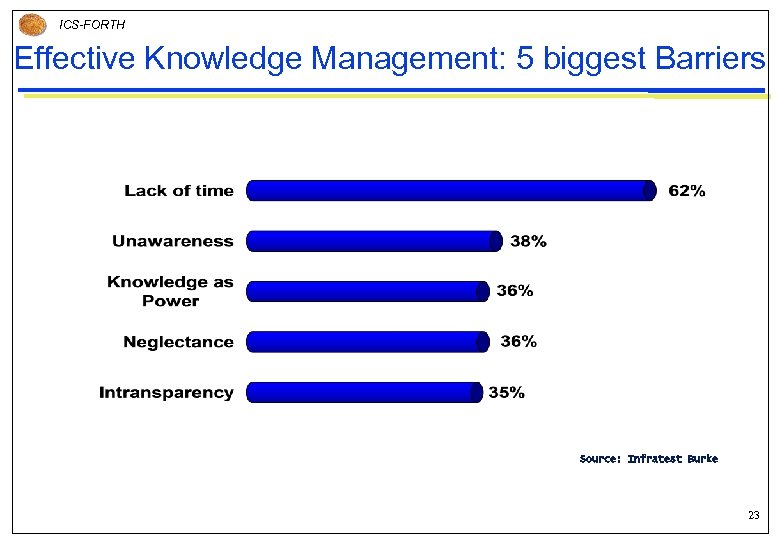 ICS-FORTH Effective Knowledge Management: 5 biggest Barriers Source: Infratest Burke 23
ICS-FORTH Effective Knowledge Management: 5 biggest Barriers Source: Infratest Burke 23
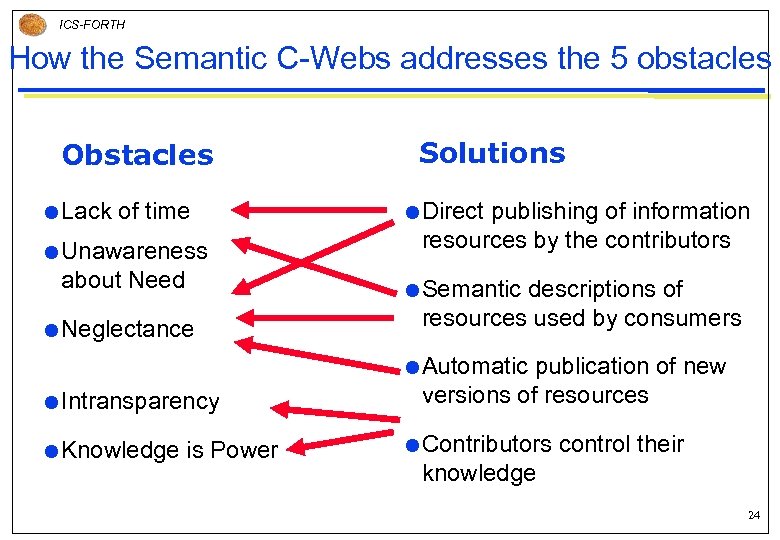 ICS-FORTH How the Semantic C-Webs addresses the 5 obstacles Obstacles Lack of time Unawareness about Need Solutions Direct publishing of information resources by the contributors Semantic Neglectance descriptions of resources used by consumers Automatic Intransparency Knowledge is Power publication of new versions of resources Contributors control their knowledge 24
ICS-FORTH How the Semantic C-Webs addresses the 5 obstacles Obstacles Lack of time Unawareness about Need Solutions Direct publishing of information resources by the contributors Semantic Neglectance descriptions of resources used by consumers Automatic Intransparency Knowledge is Power publication of new versions of resources Contributors control their knowledge 24
 ICS-FORTH A Wider Perspective for Se. Lene: Peer-to-Peer Knowledge Sharing 25
ICS-FORTH A Wider Perspective for Se. Lene: Peer-to-Peer Knowledge Sharing 25
 ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? 26
ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? 26
 ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? Server Client 27
ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? Server Client 27
 ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? Peer 28
ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? Peer 28
 ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? 29
ICS-FORTH What is P 2 P ? 29
 ICS-FORTH The P 2 P Paradigm for Knowledge Management Three examples: § Searching information resources in a research organization § On the fly Collaborations between People § Knowledge exchange without central cost center 30
ICS-FORTH The P 2 P Paradigm for Knowledge Management Three examples: § Searching information resources in a research organization § On the fly Collaborations between People § Knowledge exchange without central cost center 30
 ICS-FORTH Sharing Knowledge in Research Organization Vassilis searches tutorials on “P 2 P” Vassilis browses the KM server Dimitris has worked on “P 2 P” but forgot to publish the information to the KM server Vassilis “P 2 P” calls Dimitris to ask about searches desktops of her fellow researchers and downloads information Meta-information is transmitted on request Time-efficient Dimitris doesn’t have to think about publishing his information Dimitris could restrict access to Dimitris e-mails Vassilis relevant files meta data and “sell” the full tutorial 31
ICS-FORTH Sharing Knowledge in Research Organization Vassilis searches tutorials on “P 2 P” Vassilis browses the KM server Dimitris has worked on “P 2 P” but forgot to publish the information to the KM server Vassilis “P 2 P” calls Dimitris to ask about searches desktops of her fellow researchers and downloads information Meta-information is transmitted on request Time-efficient Dimitris doesn’t have to think about publishing his information Dimitris could restrict access to Dimitris e-mails Vassilis relevant files meta data and “sell” the full tutorial 31
 ICS-FORTH On the fly Collaborations between People Collaborative Commerce is the next wave of enterprise applications § Customer Relationship Management § Supply Chain (B 2 B) Management § Product Lifecycle Management Distributed collaborative networks of data, applications and knowledge § Spontaneous online collaboration with colleagues, suppliers, customers, . . . § Central administration can not provide the necessary flexibility to manipulate user data and applications on each other’s computers Many people resort to e-mail as communication tool: § Necessity for active (push) publication and distribution § New versions have to be resend § People get flooded by information 32
ICS-FORTH On the fly Collaborations between People Collaborative Commerce is the next wave of enterprise applications § Customer Relationship Management § Supply Chain (B 2 B) Management § Product Lifecycle Management Distributed collaborative networks of data, applications and knowledge § Spontaneous online collaboration with colleagues, suppliers, customers, . . . § Central administration can not provide the necessary flexibility to manipulate user data and applications on each other’s computers Many people resort to e-mail as communication tool: § Necessity for active (push) publication and distribution § New versions have to be resend § People get flooded by information 32
 ICS-FORTH On the fly Collaborations between People Product Lifecycle Management Supplier Management Extended relationship management (XRM) § requires truly decentralized administration to collaborate in an ever faster changing environment § peering management and connection technology on a scalable network architecture § semantic vs physical network oriented message routing 33
ICS-FORTH On the fly Collaborations between People Product Lifecycle Management Supplier Management Extended relationship management (XRM) § requires truly decentralized administration to collaborate in an ever faster changing environment § peering management and connection technology on a scalable network architecture § semantic vs physical network oriented message routing 33
 ICS-FORTH Knowledge Exchange without Central Cost Center Athens Nicosia Departments around the world want to share information. They decide to use the Internet (or VPN): ¿Allocate P 2 P platform allows exchange of information without upfront investments a budget for web server, administration, and content management Every ¿Structure Contributors the available information ¿Administrate Paris users on web server participant pays for his own platform keep control of their knowledge London 34
ICS-FORTH Knowledge Exchange without Central Cost Center Athens Nicosia Departments around the world want to share information. They decide to use the Internet (or VPN): ¿Allocate P 2 P platform allows exchange of information without upfront investments a budget for web server, administration, and content management Every ¿Structure Contributors the available information ¿Administrate Paris users on web server participant pays for his own platform keep control of their knowledge London 34
 ICS-FORTH KM and e-Learning: Four Scenarios Planet of Contenteous Nomadict Planet Instantia Planet of Cafélattia 35
ICS-FORTH KM and e-Learning: Four Scenarios Planet of Contenteous Nomadict Planet Instantia Planet of Cafélattia 35
 ICS-FORTH Planet of Contenteous Classical transmission model of knowledge § rich content & learning process § formal testing & feedback § assessment on reproduction & critique Technology as a content delivery system § content & learning management systems, § multi media, DVDs, digital & cable TV. a Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) § support different media § automatic testing & tracking § eye into reality, simulations, virtuality § mass viewing, individual assessment § asynchronous & synchronous scheduling 36
ICS-FORTH Planet of Contenteous Classical transmission model of knowledge § rich content & learning process § formal testing & feedback § assessment on reproduction & critique Technology as a content delivery system § content & learning management systems, § multi media, DVDs, digital & cable TV. a Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) § support different media § automatic testing & tracking § eye into reality, simulations, virtuality § mass viewing, individual assessment § asynchronous & synchronous scheduling 36
 ICS-FORTH Planet Instantia Continuous, autonomous, adaptive skill’s development § flexible & instant § just for me, just in time § just for now, just enough § assessment on authenticity & tracking Technology as a tool for in-house knowledge assimilation § from computer desk § learning objects rule the planet! Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) § high reliable, scalable as courses increase § individualisation, customisation 37
ICS-FORTH Planet Instantia Continuous, autonomous, adaptive skill’s development § flexible & instant § just for me, just in time § just for now, just enough § assessment on authenticity & tracking Technology as a tool for in-house knowledge assimilation § from computer desk § learning objects rule the planet! Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) § high reliable, scalable as courses increase § individualisation, customisation 37
 ICS-FORTH Nomadict Truly any time, any place learning § work with varying cultures & traditions § learner chooses style, focused learning § components interact with learners’ environments § student designed assessments (with helpers) Wearable, portable & embedded technologies promote student ownership of learning process § PDAs, Palms tops, 3 rd generation mobile phones § GPS, wireless & personal § national & international communication networks VLEs accessible anywhere without client software § support tiny chunks of learning activities (modularity) § ambient intelligence § personalized assessment 38
ICS-FORTH Nomadict Truly any time, any place learning § work with varying cultures & traditions § learner chooses style, focused learning § components interact with learners’ environments § student designed assessments (with helpers) Wearable, portable & embedded technologies promote student ownership of learning process § PDAs, Palms tops, 3 rd generation mobile phones § GPS, wireless & personal § national & international communication networks VLEs accessible anywhere without client software § support tiny chunks of learning activities (modularity) § ambient intelligence § personalized assessment 38
 ICS-FORTH Planet of Cafélattia Social context for learning: p 2 p information exchange & knowledge construction processes § acquisition, argument & application § find & interact with like-minded others § free expression, intellectual extension by dialogue § sharing of tacit knowledge (professional communities) § negotiated assessment: problem solving skills Developed Internet (beyond the browser!) technologies as § mediating devices § contexts & community space § asynchronous & synchronous groupware § distributed computing resources: P 2 P memory space sharing VLE support many standards and/or compatibility addressed § knowledge management tools § much improved group working tools § sophistication in collaborative environments 39
ICS-FORTH Planet of Cafélattia Social context for learning: p 2 p information exchange & knowledge construction processes § acquisition, argument & application § find & interact with like-minded others § free expression, intellectual extension by dialogue § sharing of tacit knowledge (professional communities) § negotiated assessment: problem solving skills Developed Internet (beyond the browser!) technologies as § mediating devices § contexts & community space § asynchronous & synchronous groupware § distributed computing resources: P 2 P memory space sharing VLE support many standards and/or compatibility addressed § knowledge management tools § much improved group working tools § sophistication in collaborative environments 39
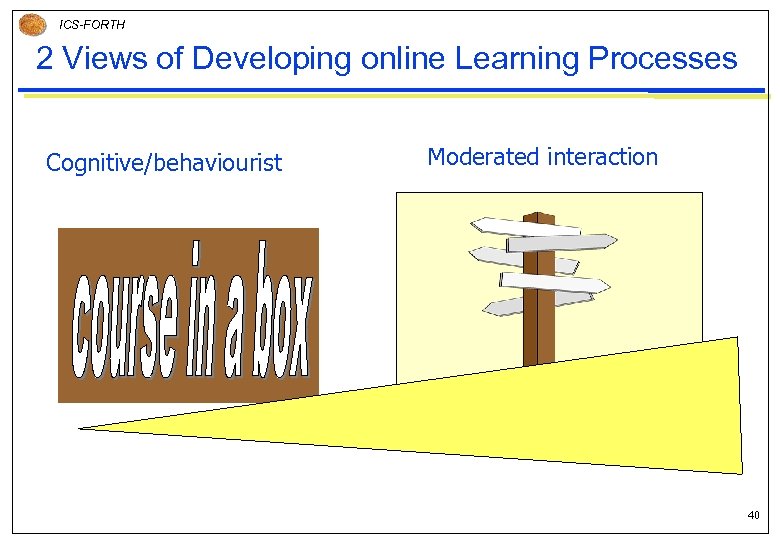 ICS-FORTH 2 Views of Developing online Learning Processes Cognitive/behaviourist Moderated interaction 40
ICS-FORTH 2 Views of Developing online Learning Processes Cognitive/behaviourist Moderated interaction 40
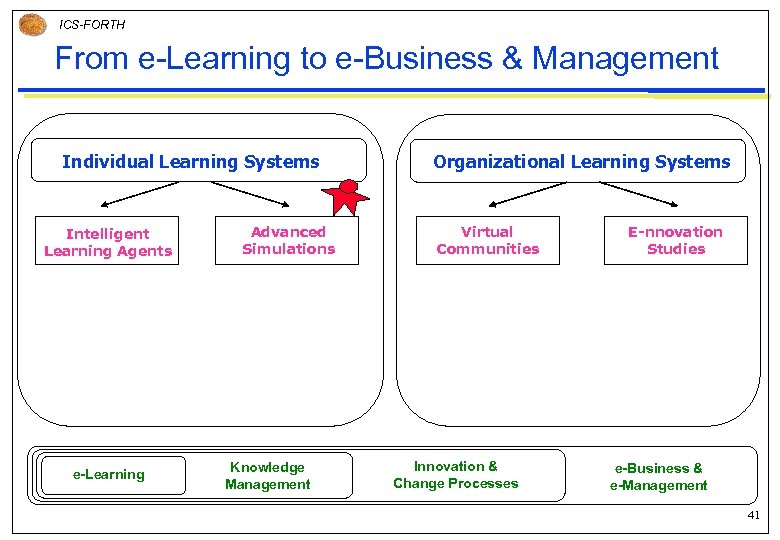 ICS-FORTH From e-Learning to e-Business & Management Individual Learning Systems Intelligent Learning Agents e-Learning Advanced Simulations Knowledge Management Organizational Learning Systems Virtual Communities Innovation & Change Processes E-nnovation Studies e-Business & e-Management 41
ICS-FORTH From e-Learning to e-Business & Management Individual Learning Systems Intelligent Learning Agents e-Learning Advanced Simulations Knowledge Management Organizational Learning Systems Virtual Communities Innovation & Change Processes E-nnovation Studies e-Business & e-Management 41
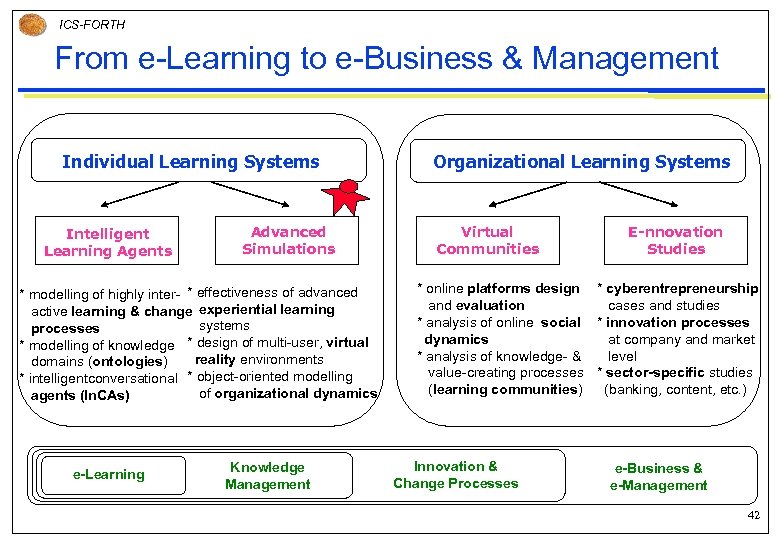 ICS-FORTH From e-Learning to e-Business & Management Individual Learning Systems Intelligent Learning Agents Advanced Simulations * modelling of highly inter- * effectiveness of advanced active learning & change experiential learning systems processes * modelling of knowledge * design of multi-user, virtual reality environments domains (ontologies) * intelligentconversational * object-oriented modelling of organizational dynamics agents (In. CAs) e-Learning Knowledge Management Organizational Learning Systems Virtual Communities E-nnovation Studies * online platforms design * cyberentrepreneurship and evaluation cases and studies * analysis of online social * innovation processes dynamics at company and market * analysis of knowledge- & level value-creating processes * sector-specific studies (learning communities) (banking, content, etc. ) Innovation & Change Processes e-Business & e-Management 42
ICS-FORTH From e-Learning to e-Business & Management Individual Learning Systems Intelligent Learning Agents Advanced Simulations * modelling of highly inter- * effectiveness of advanced active learning & change experiential learning systems processes * modelling of knowledge * design of multi-user, virtual reality environments domains (ontologies) * intelligentconversational * object-oriented modelling of organizational dynamics agents (In. CAs) e-Learning Knowledge Management Organizational Learning Systems Virtual Communities E-nnovation Studies * online platforms design * cyberentrepreneurship and evaluation cases and studies * analysis of online social * innovation processes dynamics at company and market * analysis of knowledge- & level value-creating processes * sector-specific studies (learning communities) (banking, content, etc. ) Innovation & Change Processes e-Business & e-Management 42


