b4926db2198e5287f91ed70af5b7bd17.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 90
 ICPAK INTERNAL AUDIT CONFERENCE INTERNAL AUDIT & RISK ENVIRONMENTS Presentation by: KIMEU, Jones Musyoki Mombasa Continental Beach Resort th Wednesday 20 August, 2014
ICPAK INTERNAL AUDIT CONFERENCE INTERNAL AUDIT & RISK ENVIRONMENTS Presentation by: KIMEU, Jones Musyoki Mombasa Continental Beach Resort th Wednesday 20 August, 2014
 Introduction Background Ø MBA (For Executives) Ø BCom. (Hons) Ø CPAK Ø CISA Ø FCCA Ø Over 15 years experience in Risk Management, Audit, Consultancy in risk, internal controls, IT audits and Corporate Governance 2 KIMEU, Jones Musyoki +254 722 607157 Jones_kimeu@yahoo. com
Introduction Background Ø MBA (For Executives) Ø BCom. (Hons) Ø CPAK Ø CISA Ø FCCA Ø Over 15 years experience in Risk Management, Audit, Consultancy in risk, internal controls, IT audits and Corporate Governance 2 KIMEU, Jones Musyoki +254 722 607157 Jones_kimeu@yahoo. com
 CONTENT • • Introduction The Context Internal and external risks environments. Factors affecting a firms risk appetite and tolerance. • Integrated risk management. Slide 3
CONTENT • • Introduction The Context Internal and external risks environments. Factors affecting a firms risk appetite and tolerance. • Integrated risk management. Slide 3
 INTRODUCTION The possibility that an event will occur and adversely affect the achievement of objectives • Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) Enterprise Risk Management Framework The chance of something happening that will have an impact upon objectives • AS/NZS 4360: 1999, Risk Management Events that may have a positive impact represent opportunities Slide 4
INTRODUCTION The possibility that an event will occur and adversely affect the achievement of objectives • Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) Enterprise Risk Management Framework The chance of something happening that will have an impact upon objectives • AS/NZS 4360: 1999, Risk Management Events that may have a positive impact represent opportunities Slide 4
 INTRODUCTION • Risks can be defined as real or potential events which reduce the likelihood of achieving strategic and operational objectives • Risk identification is the process of determining risks that could potentially prevent the program, enterprise, or investment from achieving its objectives. It includes documenting and communicating the concern. Slide 5
INTRODUCTION • Risks can be defined as real or potential events which reduce the likelihood of achieving strategic and operational objectives • Risk identification is the process of determining risks that could potentially prevent the program, enterprise, or investment from achieving its objectives. It includes documenting and communicating the concern. Slide 5
 CONTEXT: In today's world, change and uncertainty are constants. . . Dynamic IT Industry Security of confidential Information Reputation All Risk types Transparency & Accountability Labour strikes Fire Bad press reports 17
CONTEXT: In today's world, change and uncertainty are constants. . . Dynamic IT Industry Security of confidential Information Reputation All Risk types Transparency & Accountability Labour strikes Fire Bad press reports 17
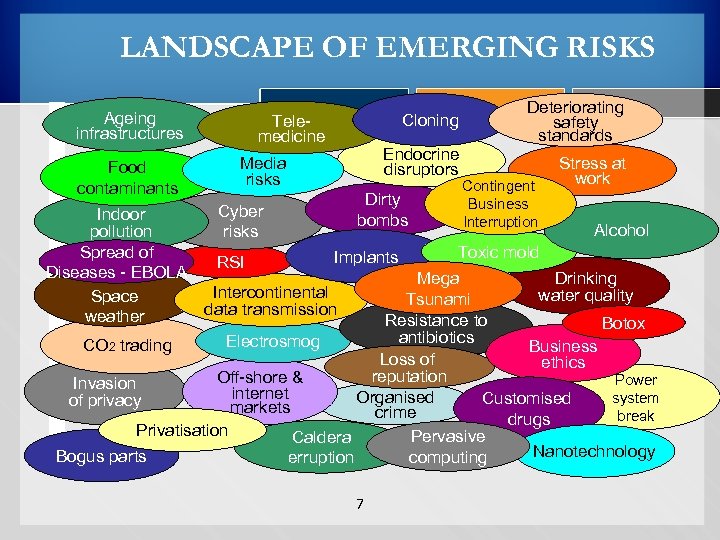 LANDSCAPE OF EMERGING RISKS Ageing infrastructures Food contaminants Indoor pollution Spread of Diseases - EBOLA Space weather Cloning Telemedicine Endocrine disruptors Media risks Dirty bombs Cyber risks RSI Implants Deteriorating safety standards Contingent Business Interruption Stress at work Alcohol Toxic mold Drinking Mega water quality Tsunami Resistance to Botox antibiotics Electrosmog CO 2 trading Business Loss of ethics reputation Off-shore & Power Invasion internet Organised system Customised of privacy markets crime break drugs Privatisation Pervasive Caldera Nanotechnology Bogus parts computing erruption Intercontinental data transmission 7
LANDSCAPE OF EMERGING RISKS Ageing infrastructures Food contaminants Indoor pollution Spread of Diseases - EBOLA Space weather Cloning Telemedicine Endocrine disruptors Media risks Dirty bombs Cyber risks RSI Implants Deteriorating safety standards Contingent Business Interruption Stress at work Alcohol Toxic mold Drinking Mega water quality Tsunami Resistance to Botox antibiotics Electrosmog CO 2 trading Business Loss of ethics reputation Off-shore & Power Invasion internet Organised system Customised of privacy markets crime break drugs Privatisation Pervasive Caldera Nanotechnology Bogus parts computing erruption Intercontinental data transmission 7
 CONTEXT § People – fraud, vandalism, human error, strikes, miscommunication, riots etc § Systems – machine breakdown, internal control deficiencies, obsolescence etc § External factors – suppliers, customers, natural perils (earthquakes, floods) etc Slide 8
CONTEXT § People – fraud, vandalism, human error, strikes, miscommunication, riots etc § Systems – machine breakdown, internal control deficiencies, obsolescence etc § External factors – suppliers, customers, natural perils (earthquakes, floods) etc Slide 8
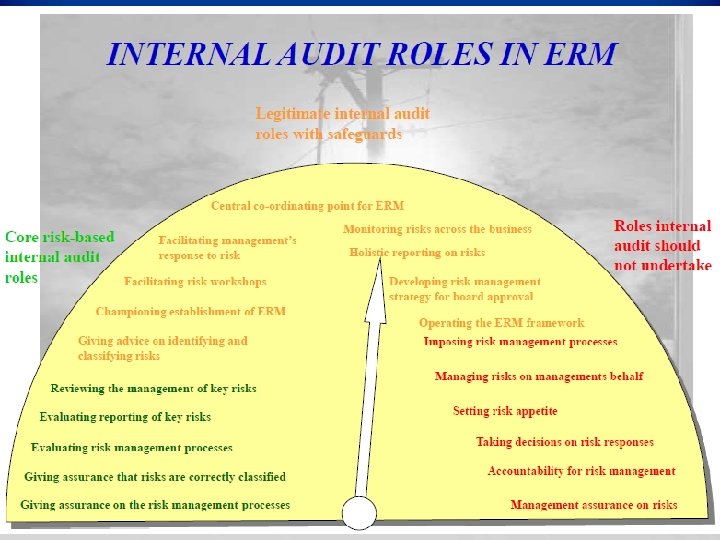
 ROLE OF INTERNAL AUDIT § Independent appraisal of the policies, processes, and controls relating to risk management framework and reporting to all levels of management § The Role of Internal Audit in Risk Management is important but one that can also present significant challenges- source IIA Slide 9
ROLE OF INTERNAL AUDIT § Independent appraisal of the policies, processes, and controls relating to risk management framework and reporting to all levels of management § The Role of Internal Audit in Risk Management is important but one that can also present significant challenges- source IIA Slide 9
 10 IIA
10 IIA
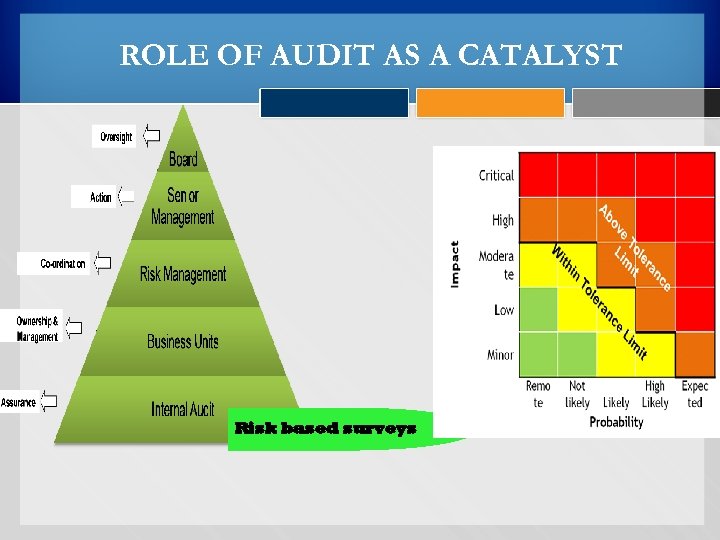 ROLE OF AUDIT AS A CATALYST Risk based surveys
ROLE OF AUDIT AS A CATALYST Risk based surveys
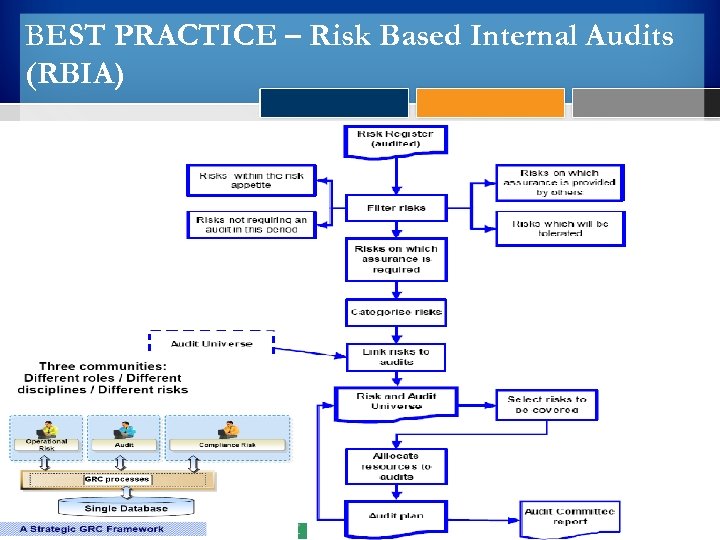 BEST PRACTICE – Risk Based Internal Audits (RBIA)
BEST PRACTICE – Risk Based Internal Audits (RBIA)
 RISK UNIVERSE INTERNAL AND EXERNAL RISKS
RISK UNIVERSE INTERNAL AND EXERNAL RISKS
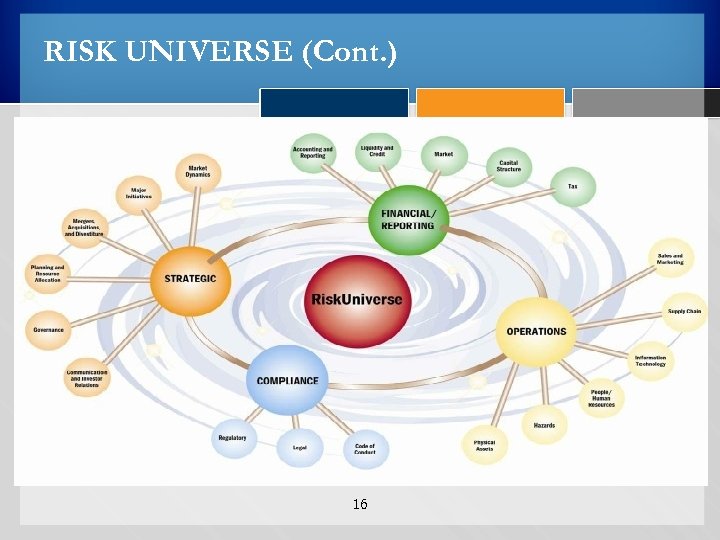
 RISK UNIVERSE Definition: All risk types and categories across all business lines, functions, geographical locations and legal entities that could affect an organization. 14
RISK UNIVERSE Definition: All risk types and categories across all business lines, functions, geographical locations and legal entities that could affect an organization. 14
 ESTABLISH THE CONTEXT Political Government Agenda Regulatory Legal External Environment Internal Environment Mandate Goals and Objectives Business Financial Culture Skills Brand Community Social accountability Vulnerability to fraud & corruption 15 Competition Market Trends Legislation Suppliers Contractors Trade Unions
ESTABLISH THE CONTEXT Political Government Agenda Regulatory Legal External Environment Internal Environment Mandate Goals and Objectives Business Financial Culture Skills Brand Community Social accountability Vulnerability to fraud & corruption 15 Competition Market Trends Legislation Suppliers Contractors Trade Unions
 RISK UNIVERSE (Cont. ) 16
RISK UNIVERSE (Cont. ) 16
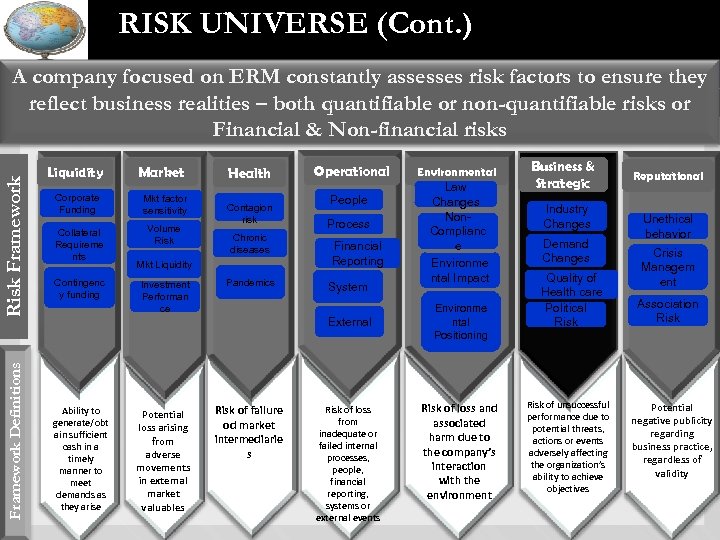 RISK UNIVERSE (Cont. ) Framework Definitions Risk Framework A company focused on ERM constantly assesses risk factors to ensure they reflect business realities – both quantifiable or non-quantifiable risks or Financial & Non-financial risks Liquidity Market Corporate Funding Mkt factor sensitivity Collateral Requireme nts Volume Risk Contingenc y funding Health Contagion risk Chronic diseases Mkt Liquidity Investment Performan ce Pandemics Operational People Process Financial Reporting System External Ability to generate/obt ain sufficient cash in a timely manner to meet demands as they arise Potential loss arising from adverse movements in external market valuables Risk of failure od market intermediarie s Risk of loss from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, financial reporting, systems or external events Environmental Law Changes Non. Complianc e Environme ntal Impact Environme ntal Positioning Risk of loss and associated harm due to the company’s interaction with the environment Business & Strategic Industry Changes Demand Changes Quality of Health care Political Risk of unsuccessful performance due to potential threats, actions or events adversely affecting the organization’s ability to achieve objectives Reputational Unethical behavior Crisis Managem ent Association Risk Potential negative publicity regarding business practice, regardless of validity
RISK UNIVERSE (Cont. ) Framework Definitions Risk Framework A company focused on ERM constantly assesses risk factors to ensure they reflect business realities – both quantifiable or non-quantifiable risks or Financial & Non-financial risks Liquidity Market Corporate Funding Mkt factor sensitivity Collateral Requireme nts Volume Risk Contingenc y funding Health Contagion risk Chronic diseases Mkt Liquidity Investment Performan ce Pandemics Operational People Process Financial Reporting System External Ability to generate/obt ain sufficient cash in a timely manner to meet demands as they arise Potential loss arising from adverse movements in external market valuables Risk of failure od market intermediarie s Risk of loss from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, financial reporting, systems or external events Environmental Law Changes Non. Complianc e Environme ntal Impact Environme ntal Positioning Risk of loss and associated harm due to the company’s interaction with the environment Business & Strategic Industry Changes Demand Changes Quality of Health care Political Risk of unsuccessful performance due to potential threats, actions or events adversely affecting the organization’s ability to achieve objectives Reputational Unethical behavior Crisis Managem ent Association Risk Potential negative publicity regarding business practice, regardless of validity
 RISKS AT 3 LEVELS 1. Strategic/Corporate Level Risk - Strategic alignment, Governance, Culture, Funding, etc. 2. Business Level - Organization (structure / Segregation of duties, Infrastructure, Competence, Staff attitudes, etc. 3. Transaction Level - P 2 P, Treasury Management, Financial Reporting, etc. 18
RISKS AT 3 LEVELS 1. Strategic/Corporate Level Risk - Strategic alignment, Governance, Culture, Funding, etc. 2. Business Level - Organization (structure / Segregation of duties, Infrastructure, Competence, Staff attitudes, etc. 3. Transaction Level - P 2 P, Treasury Management, Financial Reporting, etc. 18
 STRATEGIC /CORPORATE RISKS • • Organization structure Resource Allocation Governance Reputation 19
STRATEGIC /CORPORATE RISKS • • Organization structure Resource Allocation Governance Reputation 19
 STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Organization structure • Organization charts and reporting lines • Authority and Responsibility • Segregation of duties (SOD) 20
STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Organization structure • Organization charts and reporting lines • Authority and Responsibility • Segregation of duties (SOD) 20
 STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Resource Allocation • Budgeting and planning • Goal /Objective setting • Timelines • Metrics & Measurement 21
STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Resource Allocation • Budgeting and planning • Goal /Objective setting • Timelines • Metrics & Measurement 21
 STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Governance • Culture • Ethical behavior • Board effectiveness • Succession planning • Tone at the top 22
STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Governance • Culture • Ethical behavior • Board effectiveness • Succession planning • Tone at the top 22
 STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Reputation • Image and Branding • Stakeholder Relations 23
STRATEGIC RISKS (Cont. ) Reputation • Image and Branding • Stakeholder Relations 23
 FINANCE RISK • • Finance/Budget Management Financial Reporting Internal Controls Accounting 24
FINANCE RISK • • Finance/Budget Management Financial Reporting Internal Controls Accounting 24
 FINANCE RISK (Cont. ) Finance/Budget Management • Cash forecast • Liquidity • Cash flow Management • Analytics Financial Reporting • Financial Statement close process 25
FINANCE RISK (Cont. ) Finance/Budget Management • Cash forecast • Liquidity • Cash flow Management • Analytics Financial Reporting • Financial Statement close process 25
 FINANCE RISK (Cont. ) Internal Controls • Transaction management (Initiation, approval, recording and custody) Accounting • Application of accounting regulations, rules and procedures 26
FINANCE RISK (Cont. ) Internal Controls • Transaction management (Initiation, approval, recording and custody) Accounting • Application of accounting regulations, rules and procedures 26
 OPERATIONAL RISK • • Infrastructure People Process Technology 27
OPERATIONAL RISK • • Infrastructure People Process Technology 27
 OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) Infrastructure • Capability • Office Space • Assets • Tools • Physical Security • Business Continuity 28
OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) Infrastructure • Capability • Office Space • Assets • Tools • Physical Security • Business Continuity 28
 OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) People • Leadership – board /management expertise • HR – responsibility & accountability • Health & Safety • Risk-reward alignment • Performance Management • Empowerment 29 • Mindset • Buy-in--consensus • Balance between revenue driven and control driven • Competitor pressure • Communication • Sustaining vigilance
OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) People • Leadership – board /management expertise • HR – responsibility & accountability • Health & Safety • Risk-reward alignment • Performance Management • Empowerment 29 • Mindset • Buy-in--consensus • Balance between revenue driven and control driven • Competitor pressure • Communication • Sustaining vigilance
 OPERATIONAL RISKS - PEOPLE People Behavior People Risk Supports or undermines strategy Ø …. . alignment
OPERATIONAL RISKS - PEOPLE People Behavior People Risk Supports or undermines strategy Ø …. . alignment
 OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) Process • Fraud • Policies and Procedures • Outsourcing • Third Party Fraud • Business processes 31
OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) Process • Fraud • Policies and Procedures • Outsourcing • Third Party Fraud • Business processes 31
 OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) Technology • Integrity • Accuracy • Availability /Timeliness • Relevance • Restricted Access 32
OPERATIONAL RISK (Cont. ) Technology • Integrity • Accuracy • Availability /Timeliness • Relevance • Restricted Access 32
 COMPLIANCE RISKS • • Regulatory risks Contractual commitments (contract) Policies and procedures Code of Business Conduct 33
COMPLIANCE RISKS • • Regulatory risks Contractual commitments (contract) Policies and procedures Code of Business Conduct 33
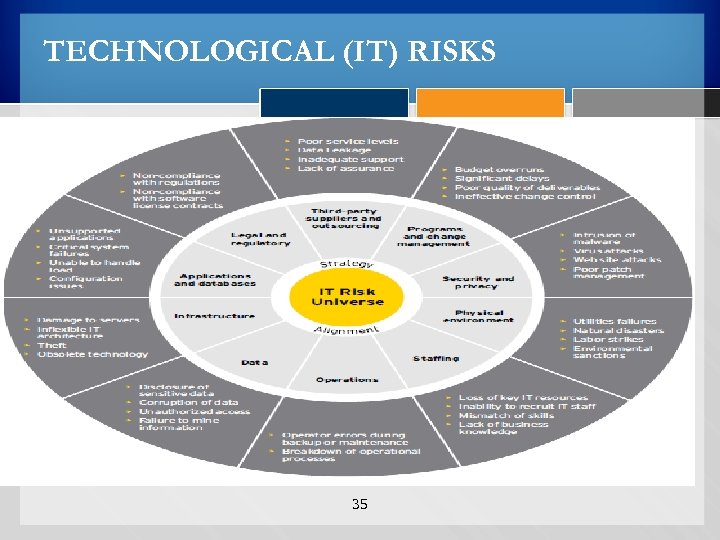
 ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS § Economic: Such as; Donor Support, Skilled Labor supply, Forex Fluctuations • Natural Environment: • Political: Will, priorities & political stability • Social: demographics, attitudes, tastes and preferences • Technological (IT Risk): Eg. Innovations 34
ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS § Economic: Such as; Donor Support, Skilled Labor supply, Forex Fluctuations • Natural Environment: • Political: Will, priorities & political stability • Social: demographics, attitudes, tastes and preferences • Technological (IT Risk): Eg. Innovations 34
 TECHNOLOGICAL (IT) RISKS 35
TECHNOLOGICAL (IT) RISKS 35
 TEAM EXERCISE Identify common risks affecting your organization and your industry Classify these risks - strategic, business, operational 36
TEAM EXERCISE Identify common risks affecting your organization and your industry Classify these risks - strategic, business, operational 36
 FACTORS AFFECTING A FIRMS RISK APPETITE AND TOLERANCE
FACTORS AFFECTING A FIRMS RISK APPETITE AND TOLERANCE
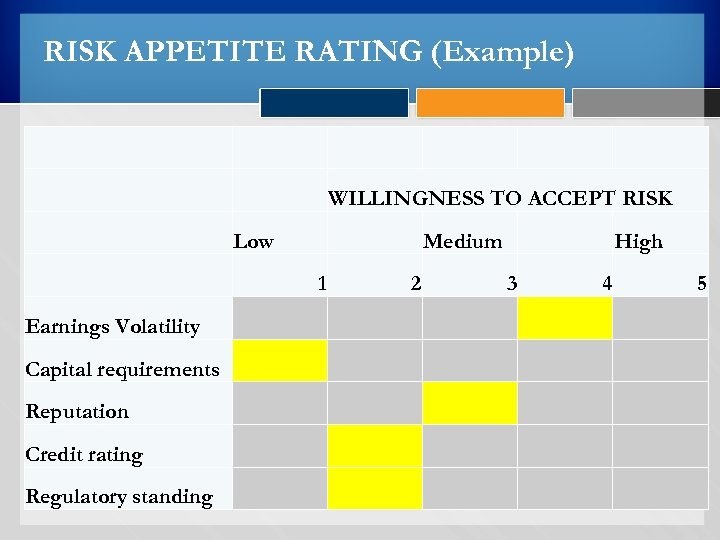
 RISK APPETITE Definition: Risk appetite can be defined as the amount of risk on a broad level, that an organization is willing to take on in pursuit of value. Or other words the total impact of risk an organization is prepared to accept in the pursuit of its strategic objectives. § It goes to the heart of an organization, how it does business, perception by stakeholders (employees, customers, regulators, rating agencies etc):
RISK APPETITE Definition: Risk appetite can be defined as the amount of risk on a broad level, that an organization is willing to take on in pursuit of value. Or other words the total impact of risk an organization is prepared to accept in the pursuit of its strategic objectives. § It goes to the heart of an organization, how it does business, perception by stakeholders (employees, customers, regulators, rating agencies etc):
 RISK APPETITE The following factors influence Risk Appetite of an organization; § The external environment § People § Business systems and policies NB/ Risk appetites vary from organization to organization, business units and risk types {For instance a banks lending to a mature market will differ with an emerging market}.
RISK APPETITE The following factors influence Risk Appetite of an organization; § The external environment § People § Business systems and policies NB/ Risk appetites vary from organization to organization, business units and risk types {For instance a banks lending to a mature market will differ with an emerging market}.
 RISK APPETITE § From another perspective, smaller losses incurred as a consequence of fraudulent activity (such as cybercrime) can have a more adverse impact on a bank reputation than much higher lending losses incurred in the normal course of business. § Consequently financial institutions set a much lower risk appetite for fraudulent or unethical practices which could damage reputation.
RISK APPETITE § From another perspective, smaller losses incurred as a consequence of fraudulent activity (such as cybercrime) can have a more adverse impact on a bank reputation than much higher lending losses incurred in the normal course of business. § Consequently financial institutions set a much lower risk appetite for fraudulent or unethical practices which could damage reputation.
 RISK APPETITE Ways to measure risk appetite; § Simple qualitative {reputational, management effort and regulatory compliance} measures (such as defining risk categories and setting target levels) § Based on the above, develop complex quantitative models of economic capital and earnings volatility {capital adequacy, target debt rating, earnings volatility, credit rating etc}. Conclusion: Provides a cornerstone for the organization’s Risk Management framework
RISK APPETITE Ways to measure risk appetite; § Simple qualitative {reputational, management effort and regulatory compliance} measures (such as defining risk categories and setting target levels) § Based on the above, develop complex quantitative models of economic capital and earnings volatility {capital adequacy, target debt rating, earnings volatility, credit rating etc}. Conclusion: Provides a cornerstone for the organization’s Risk Management framework
 RISK APPETITE - CHARACTERISTICS A well defined Risk Appetite should have the following characteristics; 1. Reflective of strategy, including objectives, business plans and stakeholder expectations; 2. Reflective of all aspects of the business 3. Acknowledge a willingness and capacity to take on risks 4. Is documented as a formal risk appetite statement
RISK APPETITE - CHARACTERISTICS A well defined Risk Appetite should have the following characteristics; 1. Reflective of strategy, including objectives, business plans and stakeholder expectations; 2. Reflective of all aspects of the business 3. Acknowledge a willingness and capacity to take on risks 4. Is documented as a formal risk appetite statement
 RISK APPETITE - CHARACTERISTICS 5. Considers the skills, resources and technology required to monitor and manage the risk exposure in the context if risk appetite. 6. Is inclusive of a tolerance for loss or negative events that can be reasonably quantified 7. Is periodically review and reconsidered with reference to evolving industry and market conditions 8. Has been approved by the board
RISK APPETITE - CHARACTERISTICS 5. Considers the skills, resources and technology required to monitor and manage the risk exposure in the context if risk appetite. 6. Is inclusive of a tolerance for loss or negative events that can be reasonably quantified 7. Is periodically review and reconsidered with reference to evolving industry and market conditions 8. Has been approved by the board
 RISK APPETITE RATING (Example) WILLINGNESS TO ACCEPT RISK Low 1 Earnings Volatility Medium 2 3 High 4 5 Capital requirements Reputation Credit rating Regulatory standing
RISK APPETITE RATING (Example) WILLINGNESS TO ACCEPT RISK Low 1 Earnings Volatility Medium 2 3 High 4 5 Capital requirements Reputation Credit rating Regulatory standing
 RISK TOLERANCE Definition: Risk Tolerance: § The degree of variability in investment returns that an individual is willing to withstand. § An important component in investing. § An individual should have a realistic understanding of his or her ability and willingness to stomach large swings in the value of his or her investments. § Investors who take on too much risk may panic and sell at the wrong time
RISK TOLERANCE Definition: Risk Tolerance: § The degree of variability in investment returns that an individual is willing to withstand. § An important component in investing. § An individual should have a realistic understanding of his or her ability and willingness to stomach large swings in the value of his or her investments. § Investors who take on too much risk may panic and sell at the wrong time
 RISK TOLERANCE - Cont. The factors affecting Risk Tolerance (assess using risk tolerance questionnaires) include; § Review worst-case returns for different asset classes historically in order to get an idea of how much money one would feel comfortable losing if his or her investments have a bad year or bad series of years. § The time horizon that one has to invest, future earning capacity, and § the presence of other assets such as a home, pension, social security or inheritance{In general, one can take greater risk with investable assets when there are other, more stable sources of funds available}.
RISK TOLERANCE - Cont. The factors affecting Risk Tolerance (assess using risk tolerance questionnaires) include; § Review worst-case returns for different asset classes historically in order to get an idea of how much money one would feel comfortable losing if his or her investments have a bad year or bad series of years. § The time horizon that one has to invest, future earning capacity, and § the presence of other assets such as a home, pension, social security or inheritance{In general, one can take greater risk with investable assets when there are other, more stable sources of funds available}.
 RISK TOLERANCE § Your investment time frame: cliché is what we'll refer to as ‘age-based’ investment risk tolerance. When will the capital be needed? If the time horizon is relatively short, risk tolerance should shift to be more conservative. § Your Risk capital: Money available to invest or trade that will not affect your lifestyle if lost (liquid capital). § Your Investment experience: Aim to get some experience under your belt before committing too much capital. Always remember the old cliché and strive for preservation of capital.
RISK TOLERANCE § Your investment time frame: cliché is what we'll refer to as ‘age-based’ investment risk tolerance. When will the capital be needed? If the time horizon is relatively short, risk tolerance should shift to be more conservative. § Your Risk capital: Money available to invest or trade that will not affect your lifestyle if lost (liquid capital). § Your Investment experience: Aim to get some experience under your belt before committing too much capital. Always remember the old cliché and strive for preservation of capital.
 RISK TOLERANCE § Your investment objectives: If you are saving for your retirement, how much risk do you really want to take with those funds? § The actual investment your are considering: Different investments carry different levels of risk. All investments involve a degree of risk and returns can never be guaranteed so it is important to choose investments that suit your circumstances
RISK TOLERANCE § Your investment objectives: If you are saving for your retirement, how much risk do you really want to take with those funds? § The actual investment your are considering: Different investments carry different levels of risk. All investments involve a degree of risk and returns can never be guaranteed so it is important to choose investments that suit your circumstances
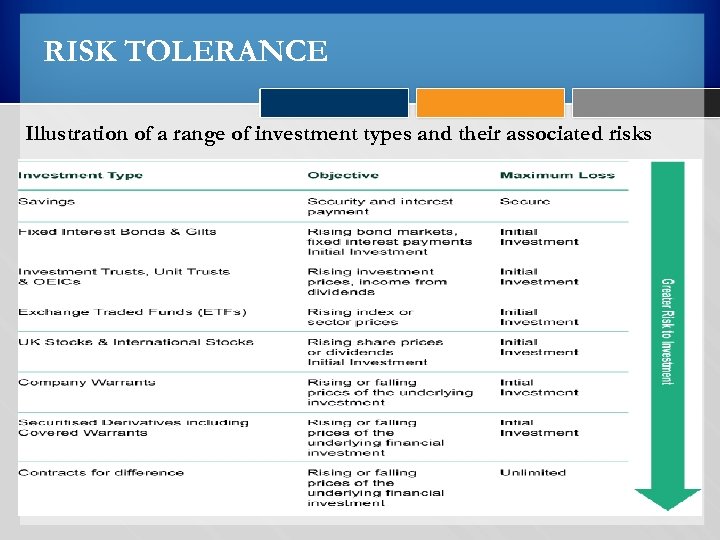 RISK TOLERANCE Illustration of a range of investment types and their associated risks
RISK TOLERANCE Illustration of a range of investment types and their associated risks
 INTEGRATION: RISK LANGUAGE & CULTURE 50
INTEGRATION: RISK LANGUAGE & CULTURE 50
 INTEGRATION – LANGUAGE & CULTURE Develop a Common Risk and Control Language: • Take an inventory of all current risk practices and taxonomies. • Determine which ones best meet our business needs. • Align remaining practices and taxonomies with the ones we determined are best. Train
INTEGRATION – LANGUAGE & CULTURE Develop a Common Risk and Control Language: • Take an inventory of all current risk practices and taxonomies. • Determine which ones best meet our business needs. • Align remaining practices and taxonomies with the ones we determined are best. Train
 INTEGRATED RISK MANAGEMENT {ENTEPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT & GOVERNANCE} 52
INTEGRATED RISK MANAGEMENT {ENTEPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT & GOVERNANCE} 52
 RISK MANAGEMENT GOVERNANCE Governance Board, Audit & Risk committee, Exec Risk Committee(s), Risk appetite, Risk universe 1. Governance Committees • • Audit committee – Expanded mandate to cover risk oversight Board Risk Management committee (new)– Executive committee chaired by CEO with representation by all HODs. Risk manager to be secretary (but can’t chair). Forum for risk discussions. Audit and Risk Committee 2. Risk appetite - The amount of risk that an organisation is willing to seek or accept in the pursuit of its mandate to be clearly defined through a delegation of authority matrix, policies, procedures 3. Tone at the Top – Board to set clear leadership (clarity of direction) and expectations for risk management (informed risk/reward) Risk Management Committee (Exec) HOD 1 HOD 2 HOD 3
RISK MANAGEMENT GOVERNANCE Governance Board, Audit & Risk committee, Exec Risk Committee(s), Risk appetite, Risk universe 1. Governance Committees • • Audit committee – Expanded mandate to cover risk oversight Board Risk Management committee (new)– Executive committee chaired by CEO with representation by all HODs. Risk manager to be secretary (but can’t chair). Forum for risk discussions. Audit and Risk Committee 2. Risk appetite - The amount of risk that an organisation is willing to seek or accept in the pursuit of its mandate to be clearly defined through a delegation of authority matrix, policies, procedures 3. Tone at the Top – Board to set clear leadership (clarity of direction) and expectations for risk management (informed risk/reward) Risk Management Committee (Exec) HOD 1 HOD 2 HOD 3
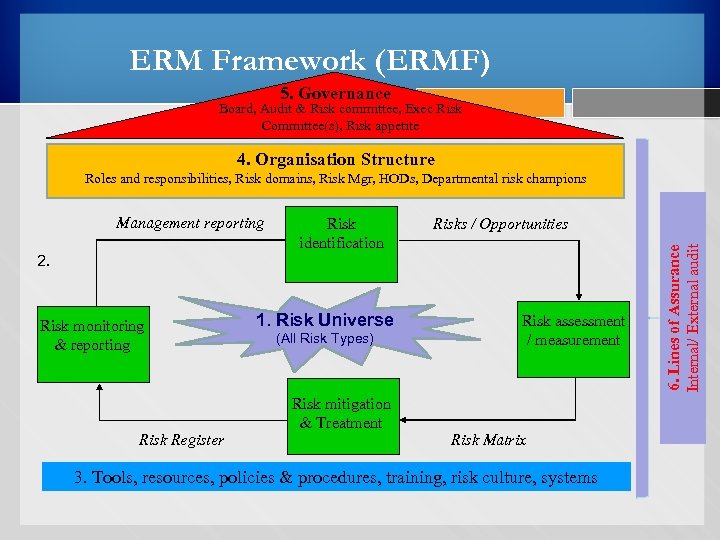 ERM Framework (ERMF) 5. Governance Board, Audit & Risk committee, Exec Risk Committee(s), Risk appetite 4. Organisation Structure Roles and responsibilities, Risk domains, Risk Mgr, HODs, Departmental risk champions 2. Risk monitoring & reporting Risk Register Risk identification 1. Risk Universe (All Risk Types) Risk mitigation & Treatment Risks / Opportunities Risk assessment / measurement Risk Matrix 3. Tools, resources, policies & procedures, training, risk culture, systems 6. Lines of Assurance Internal/ External audit Management reporting
ERM Framework (ERMF) 5. Governance Board, Audit & Risk committee, Exec Risk Committee(s), Risk appetite 4. Organisation Structure Roles and responsibilities, Risk domains, Risk Mgr, HODs, Departmental risk champions 2. Risk monitoring & reporting Risk Register Risk identification 1. Risk Universe (All Risk Types) Risk mitigation & Treatment Risks / Opportunities Risk assessment / measurement Risk Matrix 3. Tools, resources, policies & procedures, training, risk culture, systems 6. Lines of Assurance Internal/ External audit Management reporting
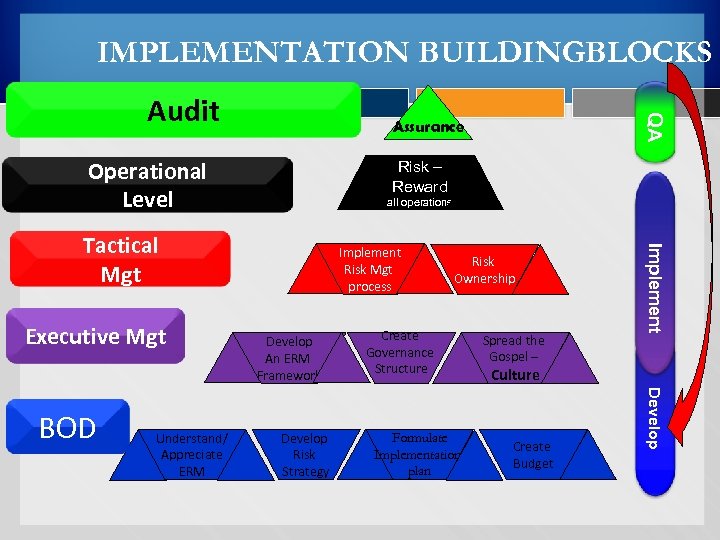 IMPLEMENTATION BUILDINGBLOCKS Assurance Operational Level Risk – Reward all operations Understand/ Appreciate ERM Develop An ERM Framework Develop Risk Strategy Risk Ownership Create Governance Structure Formulate Implementation plan Spread the Gospel – Culture Create Budget Develop BOD Implement Risk Mgt process Implement Tactical Mgt Executive Mgt QA Audit
IMPLEMENTATION BUILDINGBLOCKS Assurance Operational Level Risk – Reward all operations Understand/ Appreciate ERM Develop An ERM Framework Develop Risk Strategy Risk Ownership Create Governance Structure Formulate Implementation plan Spread the Gospel – Culture Create Budget Develop BOD Implement Risk Mgt process Implement Tactical Mgt Executive Mgt QA Audit
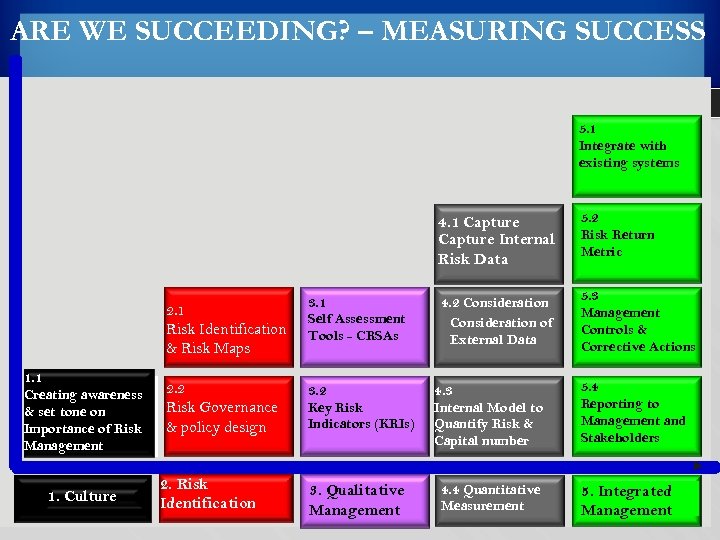 ARE WE SUCCEEDING? – MEASURING SUCCESS 5. 1 Integrate with existing systems 4. 1 Capture Internal Risk Data 2. 1 Risk Identification & Risk Maps 1. 1 Creating awareness & set tone on Importance of Risk Management 1. Culture 2. 2 Risk Governance & policy design 2. Risk Identification 3. 1 Self Assessment Tools - CRSAs 3. 2 Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) 3. Qualitative Management 5. 2 Risk Return Metric 4. 2 Consideration of External Data 5. 3 Management Controls & Corrective Actions 4. 3 Internal Model to Quantify Risk & Capital number 4. 4 Quantitative Measurement 5. 4 Reporting to Management and Stakeholders 5. Integrated Management
ARE WE SUCCEEDING? – MEASURING SUCCESS 5. 1 Integrate with existing systems 4. 1 Capture Internal Risk Data 2. 1 Risk Identification & Risk Maps 1. 1 Creating awareness & set tone on Importance of Risk Management 1. Culture 2. 2 Risk Governance & policy design 2. Risk Identification 3. 1 Self Assessment Tools - CRSAs 3. 2 Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) 3. Qualitative Management 5. 2 Risk Return Metric 4. 2 Consideration of External Data 5. 3 Management Controls & Corrective Actions 4. 3 Internal Model to Quantify Risk & Capital number 4. 4 Quantitative Measurement 5. 4 Reporting to Management and Stakeholders 5. Integrated Management
 MONITORING & EVALUATION Monitoring. Internal control systems need to be monitored, a process that assesses the quality of the system’s performance over time. This is accomplished through ongoing monitoring activities, separate evaluations or a combination of the two. 57
MONITORING & EVALUATION Monitoring. Internal control systems need to be monitored, a process that assesses the quality of the system’s performance over time. This is accomplished through ongoing monitoring activities, separate evaluations or a combination of the two. 57
 INSTITUTIONALISING RISK MANAGEMENT 1. Crucial to set the tone at the top - leadership and consistency 2. Promote Risk Management as a day-to-day management tool to, inter alia, ensure achieve of strategic objective/mandate and enhanced service delivery 3. Senior managers should establish clear risk management roles and responsibilities 58
INSTITUTIONALISING RISK MANAGEMENT 1. Crucial to set the tone at the top - leadership and consistency 2. Promote Risk Management as a day-to-day management tool to, inter alia, ensure achieve of strategic objective/mandate and enhanced service delivery 3. Senior managers should establish clear risk management roles and responsibilities 58
 INSTITUTIONALISING RISK MANAGEMENT (Cont. ) 4. Staff should have capacity (skill, training, knowledge, information and resources necessary) to perform risk management roles 5. Integration with strategic planning, new initiatives and projects 6. Every person has a role a play (performance management) 59
INSTITUTIONALISING RISK MANAGEMENT (Cont. ) 4. Staff should have capacity (skill, training, knowledge, information and resources necessary) to perform risk management roles 5. Integration with strategic planning, new initiatives and projects 6. Every person has a role a play (performance management) 59
 RISK MANAGEMENT The most important phases of risk management process include: the risk identification, risk analysis and risk response. a) The risk identification is achieved by completing checklists, organizing meetings for identifying risks and analysis of archived documents. 60
RISK MANAGEMENT The most important phases of risk management process include: the risk identification, risk analysis and risk response. a) The risk identification is achieved by completing checklists, organizing meetings for identifying risks and analysis of archived documents. 60
 RISK MANAGEMENT (Cont. ) b) The risk analysis methods such as: uses determining the expected value, Monte Carlo simulation and decision trees. c) The risk response includes measures and actions to reduce, eliminate or risk allocation. 61
RISK MANAGEMENT (Cont. ) b) The risk analysis methods such as: uses determining the expected value, Monte Carlo simulation and decision trees. c) The risk response includes measures and actions to reduce, eliminate or risk allocation. 61
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES 62
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES 62
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES • • • People Organization Process Systems Change Management 63
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES • • • People Organization Process Systems Change Management 63
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES (Cont. ) People • Lack of commitment buy-in from board/ senior management / staff • No in-house expertise or experience in performing risk management • Risk management culture not well established 64
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES (Cont. ) People • Lack of commitment buy-in from board/ senior management / staff • No in-house expertise or experience in performing risk management • Risk management culture not well established 64
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Organization • Inappropriate risk management organisation structure • Not aligned with institutions / departments objective 65
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Organization • Inappropriate risk management organisation structure • Not aligned with institutions / departments objective 65
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Processes • Inadequate project funding • No clear understanding of policies and procedures to establish the risk management architecture • Failure to prioritise implementation activities 66
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Processes • Inadequate project funding • No clear understanding of policies and procedures to establish the risk management architecture • Failure to prioritise implementation activities 66
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Systems • Inadequate technologies to collect and measure risks • Inadequate communications systems to capture and communicate risk information • Disintegrated systems/ old traditional applications 67
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Systems • Inadequate technologies to collect and measure risks • Inadequate communications systems to capture and communicate risk information • Disintegrated systems/ old traditional applications 67
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Change Management • Articulating and measuring the potential benefits of ERM • Integrating risk management into strategic planning processes 68
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Change Management • Articulating and measuring the potential benefits of ERM • Integrating risk management into strategic planning processes 68
 ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Change Management (Cont. ) • Understand industry specific risks and risk management standards/solutions • Risk management information not well communicated including risk appetite and risk tolerance 69
ERM IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES Change Management (Cont. ) • Understand industry specific risks and risk management standards/solutions • Risk management information not well communicated including risk appetite and risk tolerance 69
 RISK REPORTING
RISK REPORTING
 RISK REGISTER Central repository / log for all risks identified by the organisation 71
RISK REGISTER Central repository / log for all risks identified by the organisation 71
 CONTENTS OF A RISK REGISTER 1. The risk 2. Root cause 3. Mitigating controls / correction action plan 4. Responsible party 5. Target date 6. Impact/probability assessment 72
CONTENTS OF A RISK REGISTER 1. The risk 2. Root cause 3. Mitigating controls / correction action plan 4. Responsible party 5. Target date 6. Impact/probability assessment 72
 Risk Register Risk Event Description Inherent Impact Inherent Description of Likelihood Standard Controls Control Rating Residual Impact Residual Likelihood Action plan Responsibl e Person Due Date
Risk Register Risk Event Description Inherent Impact Inherent Description of Likelihood Standard Controls Control Rating Residual Impact Residual Likelihood Action plan Responsibl e Person Due Date
 RISK ASSESSMENT/MEASUREMENT 74
RISK ASSESSMENT/MEASUREMENT 74
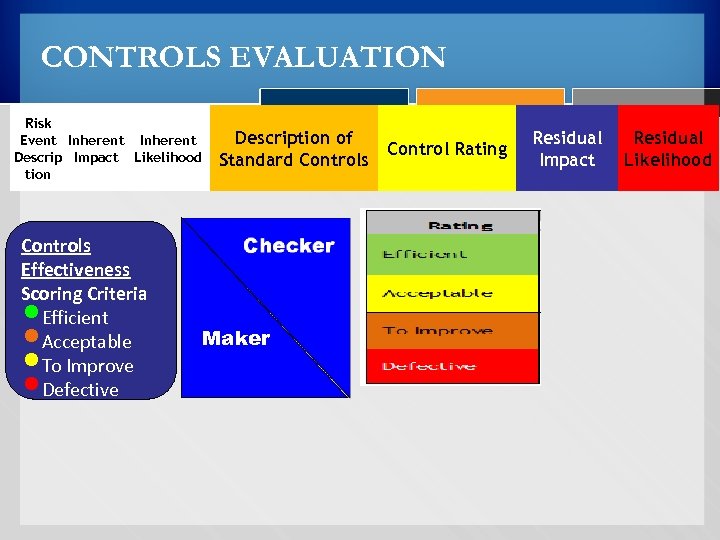 CONTROLS EVALUATION Risk Event Inherent Descrip Impact Likelihood tion Controls Effectiveness Scoring Criteria Efficient Acceptable To Improve Defective • • Description of Control Rating Standard Controls Maker Residual Impact Residual Likelihood
CONTROLS EVALUATION Risk Event Inherent Descrip Impact Likelihood tion Controls Effectiveness Scoring Criteria Efficient Acceptable To Improve Defective • • Description of Control Rating Standard Controls Maker Residual Impact Residual Likelihood
 CONTROLS EVALUATION Each Control or a set of controls effectiveness is /are rated on a four point scale; 1. Efficient - The internal control system is efficient and adequate 2. Acceptable - A few corrections should make the internal control system satisfactory 3. To Improve - The internal control system has to be enhanced and the process monitored more closely 4. Poor - The internal control system of the process has to be reorganized immediately
CONTROLS EVALUATION Each Control or a set of controls effectiveness is /are rated on a four point scale; 1. Efficient - The internal control system is efficient and adequate 2. Acceptable - A few corrections should make the internal control system satisfactory 3. To Improve - The internal control system has to be enhanced and the process monitored more closely 4. Poor - The internal control system of the process has to be reorganized immediately
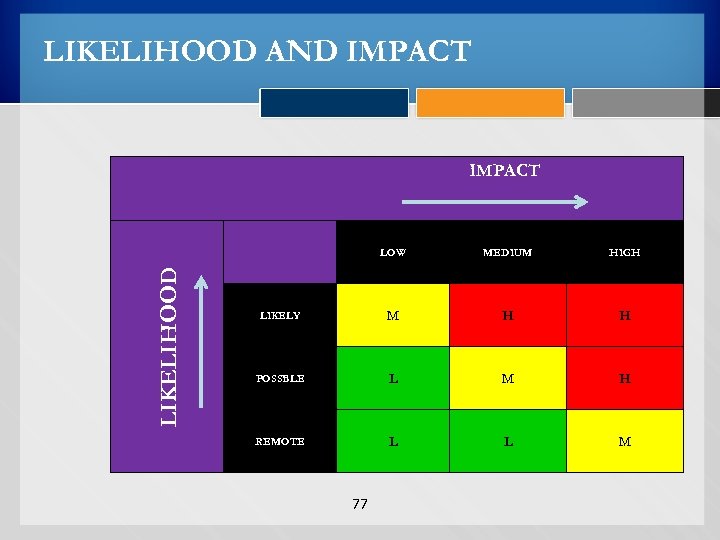 LIKELIHOOD AND IMPACT LIKELIHOOD LOW MEDIUM HIGH LIKELY M H H POSSBLE L M H REMOTE L L M 77
LIKELIHOOD AND IMPACT LIKELIHOOD LOW MEDIUM HIGH LIKELY M H H POSSBLE L M H REMOTE L L M 77
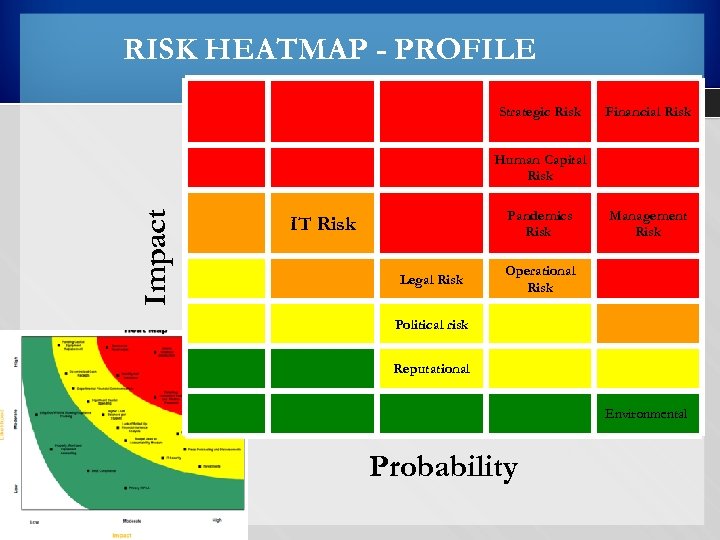 RISK HEATMAP - PROFILE Strategic Risk Financial Risk Impact Human Capital Risk IT Risk Pandemics Risk Legal Risk Management Risk Operational Risk Political risk Reputational Probability Environmental
RISK HEATMAP - PROFILE Strategic Risk Financial Risk Impact Human Capital Risk IT Risk Pandemics Risk Legal Risk Management Risk Operational Risk Political risk Reputational Probability Environmental
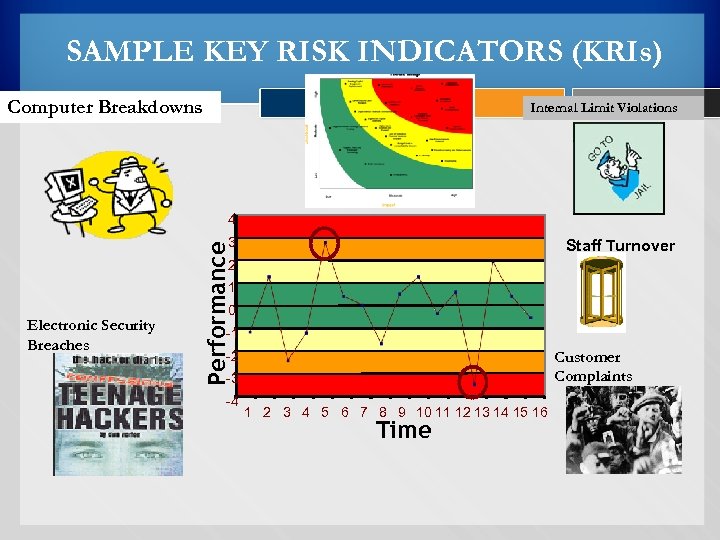 SAMPLE KEY RISK INDICATORS (KRIs) Computer Breakdowns Internal Limit Violations 4 3 Performance Staff Turnover 2 1 Electronic Security Breaches 0 -1 -2 Customer Complaints -3 -4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Time
SAMPLE KEY RISK INDICATORS (KRIs) Computer Breakdowns Internal Limit Violations 4 3 Performance Staff Turnover 2 1 Electronic Security Breaches 0 -1 -2 Customer Complaints -3 -4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Time
 GAINING RISK REPORTING
GAINING RISK REPORTING
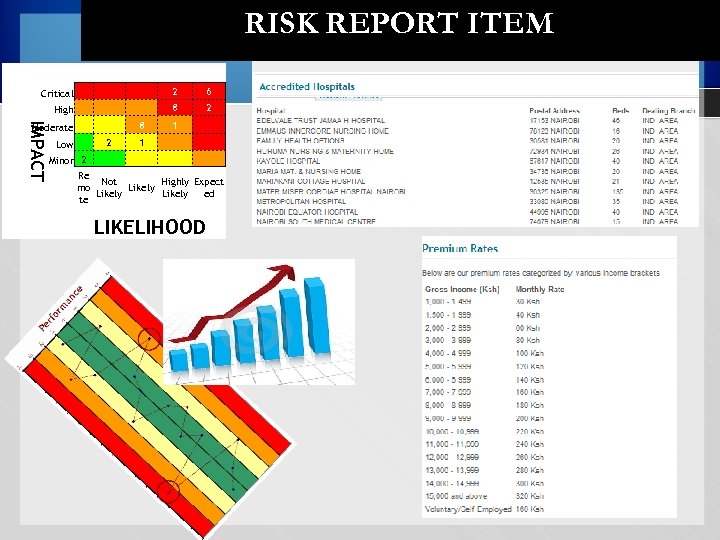 RISK REPORT ITEM 2 6 8 2 Moderate Low 8 1 2 1 IMPACT Critical High Minor 2 Re Not Highly Expect mo Likely ed te LIKELIHOOD 2
RISK REPORT ITEM 2 6 8 2 Moderate Low 8 1 2 1 IMPACT Critical High Minor 2 Re Not Highly Expect mo Likely ed te LIKELIHOOD 2

 k is R on ti ec ir D
k is R on ti ec ir D
 Management Action Plan Report Status
Management Action Plan Report Status
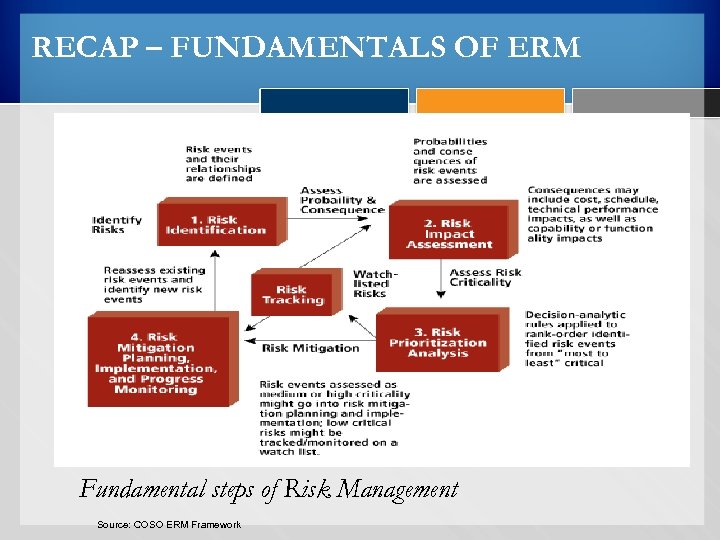 RECAP – FUNDAMENTALS OF ERM Objective Setting Event Identification Risk Assessment Risk Response Control Activities Information & Communication Monitoring Fundamental steps of Risk Management Source: COSO ERM Framework
RECAP – FUNDAMENTALS OF ERM Objective Setting Event Identification Risk Assessment Risk Response Control Activities Information & Communication Monitoring Fundamental steps of Risk Management Source: COSO ERM Framework
 RECAP - BEST PRACTICE IN ERM Slide 86
RECAP - BEST PRACTICE IN ERM Slide 86
 Quote of the day "…in all my experience, I have never been in an accident of any sort worth speaking about. I have seen but one vessel in distress in all my years at sea… I never saw a wreck and have never been wrecked, nor was I ever in any predicament that threatened to end in disaster of any sort. " Edward J. Smith interviewed by the New York press, 1907 Slide 87
Quote of the day "…in all my experience, I have never been in an accident of any sort worth speaking about. I have seen but one vessel in distress in all my years at sea… I never saw a wreck and have never been wrecked, nor was I ever in any predicament that threatened to end in disaster of any sort. " Edward J. Smith interviewed by the New York press, 1907 Slide 87
 Slide 88
Slide 88
 Think the unthinkable! Expect the unexpected! On April 15, 1912, RMS Titanic sank with the loss of more than 1500 lives-one of which was its Captain-E. J. Smith Slide 89
Think the unthinkable! Expect the unexpected! On April 15, 1912, RMS Titanic sank with the loss of more than 1500 lives-one of which was its Captain-E. J. Smith Slide 89
 I thank you KIMEU, JM. Email: jones_kimeu@yahoo. com # 0722 607157
I thank you KIMEU, JM. Email: jones_kimeu@yahoo. com # 0722 607157


