0583cdab5303b112389a6c6b0d4f6d84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

ICLEAC Survey Presentation Instability Control of Low Emission Aero-Engine Combustors G 4 RD-CT-2000 -0215 R&T project within the 5 th Framework program of the European Union: Presented by: L. Hernandez Turbomeca 1 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation 4 year program started March 1 2000

ICLEAC Survey Presentation Instability Control of Low Emission Aero-Engine Combustors Partners Mission Organisation Experiments and Measurements Calculations Exploitation and Dissemination Questions 2 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Agenda
ICLEAC Partners 3 F D UK I F F UK D D I UK Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Turbomeca MTU D Rolls-Royce Deutschland Snecma F Rolls-Royce AVIO S. p. A. QINETIQ UK CERFACS CNRS/DR 5/EM 2 C Cranfield University Karlsruhe University - EBI Munich University - TDM Genova University - DIMSET UCAM-DENG

ICLEAC Mission Low Emissions Treatment of CI today: a posteriori – expensive and time consuming • re-design • tests • Objective: being able to deal with the problem a priori – Concept phase • Design Rules • Low Order Models – Development phase • Heavy CFD methods: URANS* and LES* * Unsteady Reynolds Averaged Navier Stokes * Large Eddy Simulation 4 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation • Combustion Instabilities

ICLEAC Mission • Injector Aerodynamics and spray databases (steady and unsteady) • Flame Transfer Functions (FTF) in simple and engine like sector rigs • Generic and real engine geometry thermo acoustics and mixing Calculations • FTF calculated by URANS and LES • URANS and LES development Tools • Design rules • Low Order Model (LOM) • URANS and LES 5 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Measurements

ICLEAC Organisation 5 Work Packages WP 1 Management and exploitation • WP 2 Unsteady behaviour of Fluid-dynamic LP*/LPP* injection systems • WP 3 Measurement of Transfer Functions • WP 4 Combustion Instabilities Prediction • WP 5 Advanced 2 and 3 D diagnostics on combustors 4 year program started March 1 2000 • Final report April 2004 * Lean Premixed * Lean Pre-vaporised Premixed 6 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation •
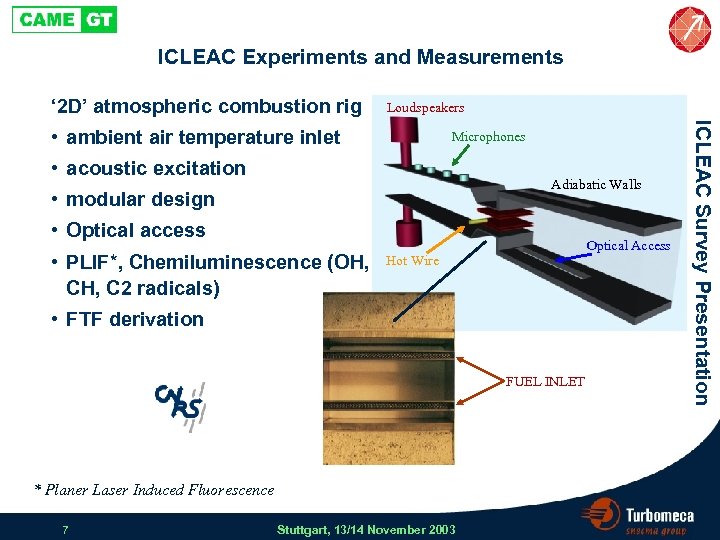
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements ‘ 2 D’ atmospheric combustion rig Loudspeakers Microphones • acoustic excitation Adiabatic Walls • modular design • Optical access • PLIF*, Chemiluminescence (OH, C 2 radicals) Optical Access Hot Wire • FTF derivation FUEL INLET * Planer Laser Induced Fluorescence 7 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation • ambient air temperature inlet

ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements • Optical access • Acoustic excitation • PDA* and LSD* for droplet size, velocity, and concentration measurement in dense sprays • Spray FTF derivation * Phase Doppler Anemometry * Laser Sheet Drop sizing 8 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Atmospheric Injector Spray Rig

ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements Injector spray test rig • 300 -500 K • Acoustic excitation • Optical access • PDA and LSD for droplet size, velocity, and concentration measurement in dense sprays • Spray FTF derivation 9 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation • 3 bar
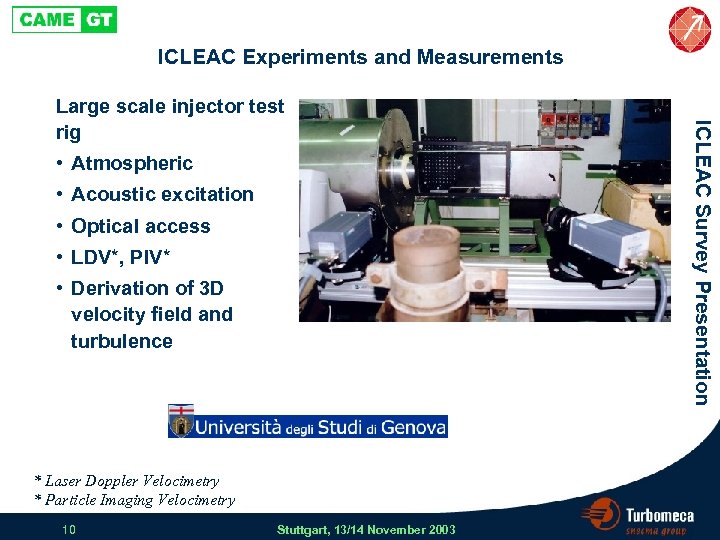
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements • Atmospheric • Acoustic excitation • Optical access • LDV*, PIV* • Derivation of 3 D velocity field and turbulence * Laser Doppler Velocimetry * Particle Imaging Velocimetry 10 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Large scale injector test rig
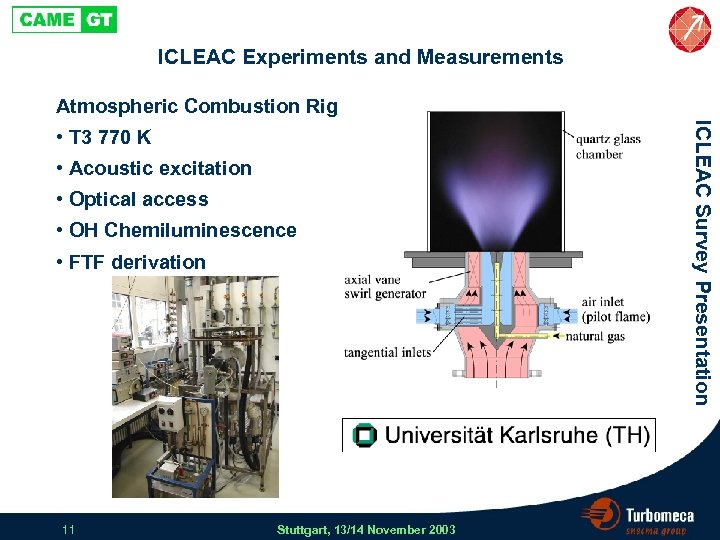
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements Atmospheric Combustion Rig • Acoustic excitation • Optical access • OH Chemiluminescence • FTF derivation 11 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation • T 3 770 K
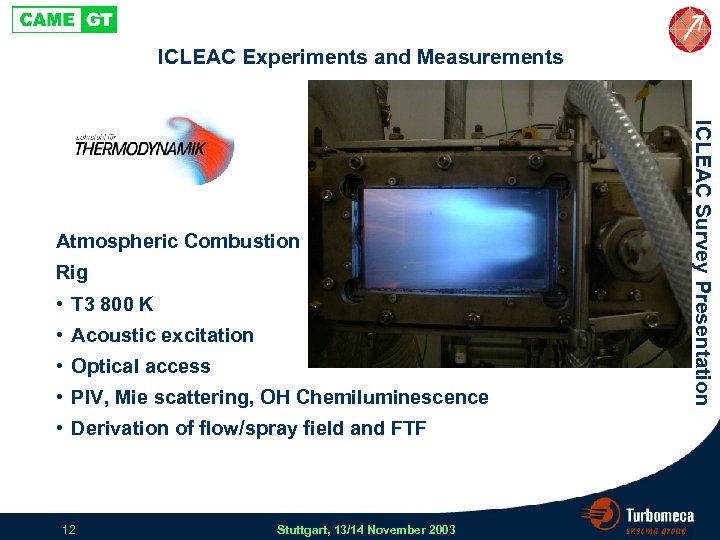
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements Rig • T 3 800 K • Acoustic excitation • Optical access • PIV, Mie scattering, OH Chemiluminescence • Derivation of flow/spray field and FTF 12 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Atmospheric Combustion

ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements • P 3 40 bar • T 3 800 K • Acoustic excitation • Optical access • PIV, OH Chemiluminescence 13 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation High Pressure Combustion Rig
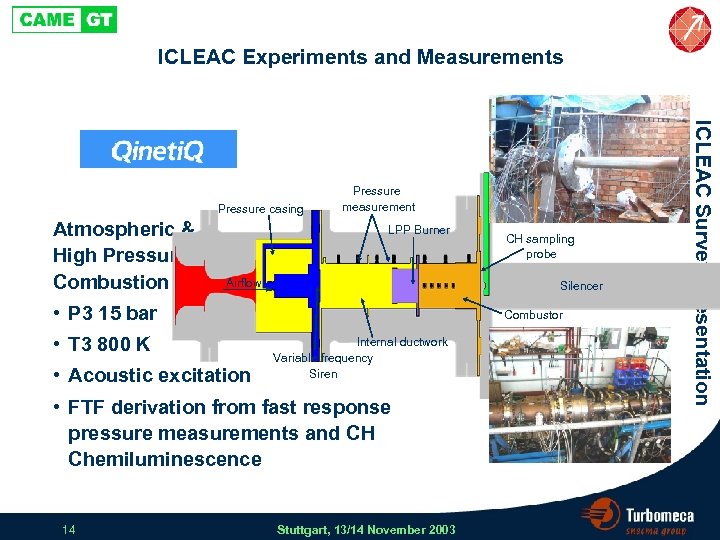
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements Atmospheric & High Pressure Combustion Rig LPP Burner Airflow Silencer • P 3 15 bar • T 3 800 K • Acoustic excitation Combustor Internal ductwork Variable frequency Siren • FTF derivation from fast response pressure measurements and CH Chemiluminescence 14 CH sampling probe Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Pressure casing Pressure measurement
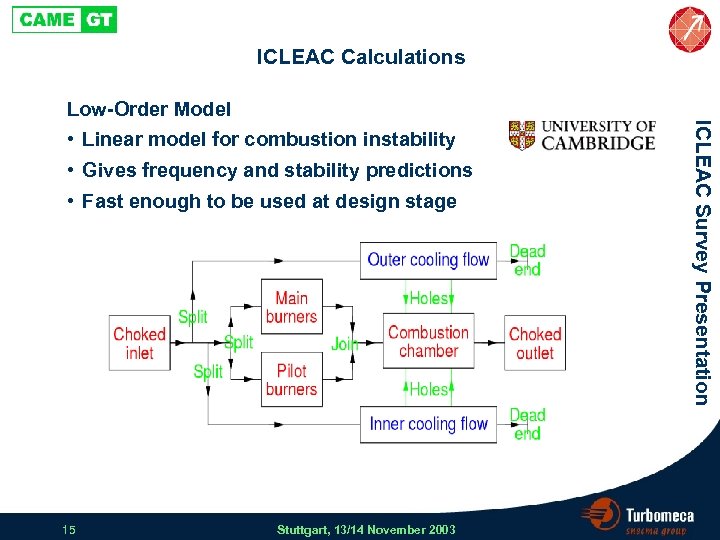
ICLEAC Calculations • Linear model for combustion instability • Gives frequency and stability predictions • Fast enough to be used at design stage 15 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Low-Order Model
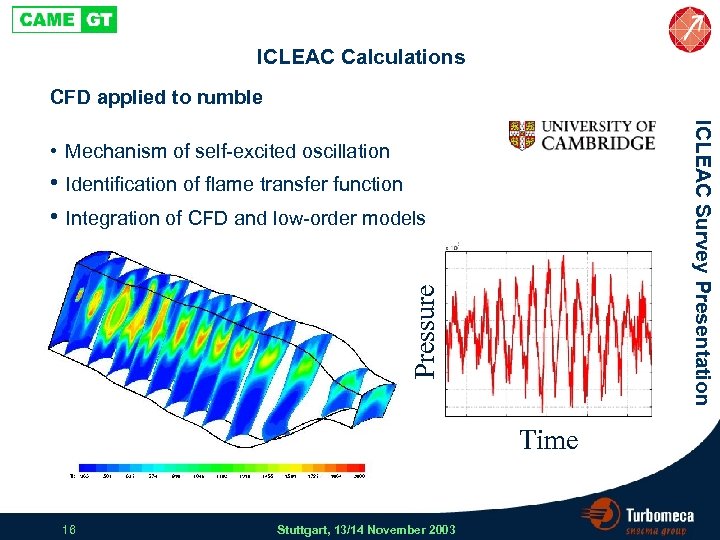
ICLEAC Calculations CFD applied to rumble ICLEAC Survey Presentation • Mechanism of self-excited oscillation Pressure • Identification of flame transfer function • Integration of CFD and low-order models Time 16 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003
Exploitation and Dissemination RR-UK & RRD LPP modules • delay time • effective area Air blast burners Flame characterization • Flame transfer functions • Spray transfer functions CRANFIELD / QINETIQ / TD-Munich ICLEAC UCAM RR-UK large engines RRD medium engines 17 CFD simulations • 2 D & 3 D geometries • numerical FTF • self-excitation LOM • 1 D geometry • implementation of FTF • validation CFD simulations • in-house application • best practice • validation Multi-Link Flow Network • in-house application • integration of LOM • validation Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Single sector test rigs • atmospheric • low pressure < 3 bar • intermediate pressure < 15 bar
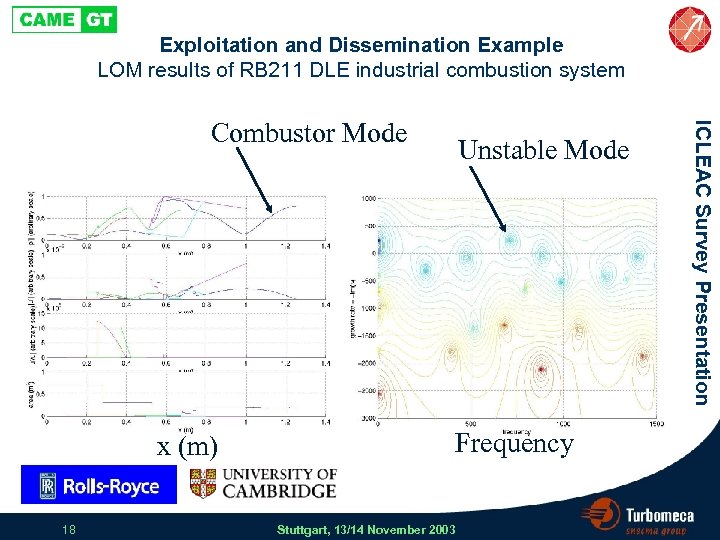
Exploitation and Dissemination Example LOM results of RB 211 DLE industrial combustion system x (m) 18 Unstable Mode Frequency Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Combustor Mode
Exploitation and Dissemination AVIO S. p. A ICLEAC Measurement techniques • 3 D LDV • hot-wire anemometry • PIV Unsteady aerodynamic investigation • Time averaged and ensemble averaged flow field • Reynolds stress distributions • unsteady phenomena detection • data sets for time-dependent N. S. and RANS code assessment UNIGE-DIMSET: Experimental activities UNIGE-DIMSET: Numerical activities Unsteady CFD Solver Nast. Comb: • in-house development & validation • advanced turbulence model • reactive prediction (detailed) • radiation modelling Analysis mode (large scale premixer): • comparison of flow fields and unstable behaviour • critical modes detection • parametric optimisation AVIO S. p. A URANS Transient Performance Method (TPM) applied to gas turbine combustor development 19 Design mode (Real LPP prototype): • preheated 2 -phase behaviour • fully reactive conditions • Transient Performance Method (CFD based) • LPP double swirler injector design • RANS code for design and analysis validation Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Laboratory • LPP double swirler injector of AVIO design • large scale model • same Re number • original and modified geometries
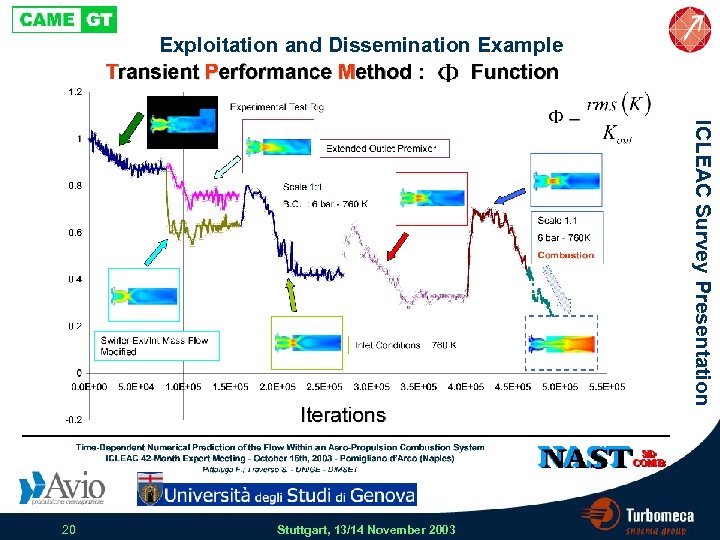
Exploitation and Dissemination Example ICLEAC Survey Presentation 20 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003
Exploitation and Dissemination Turbomeca & SNECMA Measurements • PIV • OH chem. • Hot wire anemometry Flame Characterisation • Transfer functions • velocity profiles • visualisation, . . . EM 2 C ICLEAC CERFACS SNECMA Turbomeca 21 LES modelling results LES model development LES modelling applied to gas turbine combustor development Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Laboratory rig • non-premixed • turbulent burner
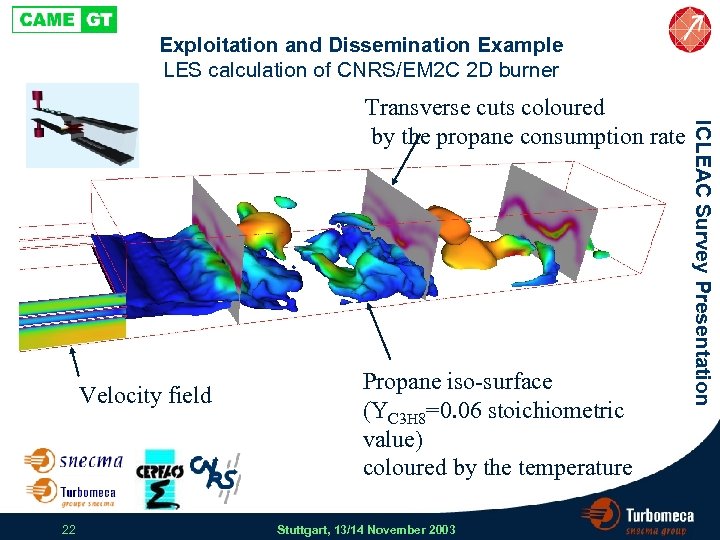
Exploitation and Dissemination Example LES calculation of CNRS/EM 2 C 2 D burner Velocity field 22 Propane iso-surface (YC 3 H 8=0. 06 stoichiometric value) coloured by the temperature Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Transverse cuts coloured by the propane consumption rate
Exploitation and Dissemination Example LES calculation of CNRS/EM 2 C 2 D burner Movie of forced case 23 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Simulation time 21 ms ( one flow-through time)

Questions ICLEAC Survey Presentation 24 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003
Acronyms ICLEAC Survey Presentation 25 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003

ICLEAC Organisation In each Work package we have two types of hardware that are investigated : • generic / academic hardware • real scale / Low Emission Aero Engine hardware. 26 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation WP 2 : isothermal experiments on injection systems WP 3 : transfer functions on combustors - effect of damping technologies WP 4 : development of simulation methods WP 5 : detailed measurements on combustors
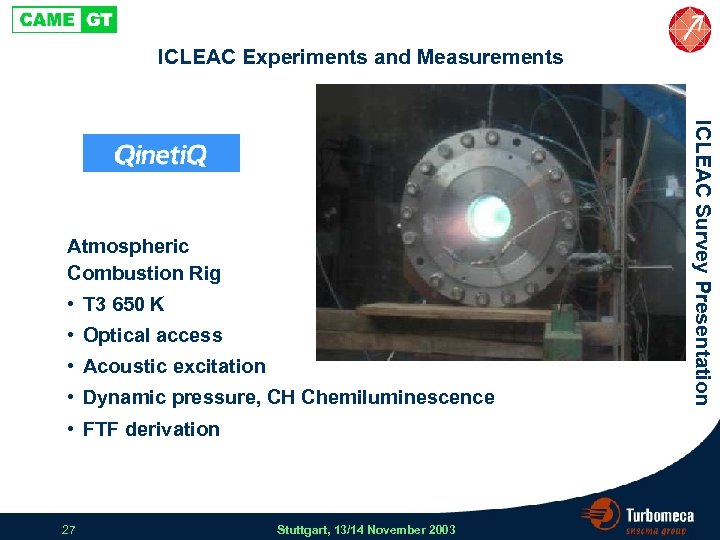
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements • T 3 650 K • Optical access • Acoustic excitation • Dynamic pressure, CH Chemiluminescence • FTF derivation 27 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation Atmospheric Combustion Rig
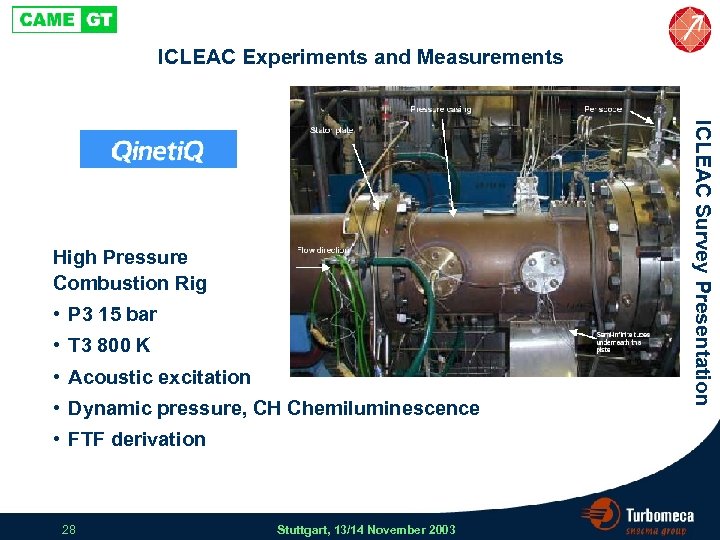
ICLEAC Experiments and Measurements • P 3 15 bar • T 3 800 K • Acoustic excitation • Dynamic pressure, CH Chemiluminescence • FTF derivation 28 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation High Pressure Combustion Rig

ICLEAC Mission 29 Stuttgart, 13/14 November 2003 ICLEAC Survey Presentation To understand fundamental mechanisms leading to Combustion Instabilities in Aero Engine Low Emission Combustors. This includes the elaboration of comprehensive databases on academic flames and real combustor flames used both for analysis and code validation To develop and validate predictive tools on generic and real Low Emission combustors also used in other programmes. This includes RANS and LES methods as well as a low order model (TALON) that is delivered to the partners during the last year of the programme To define and validate design rules for Low Emission Combustors for Aero Engines to avoid/reduce combustion instabilities. Includes correlations between combustor geometries, and oscillation frequencies / amplitudes.
0583cdab5303b112389a6c6b0d4f6d84.ppt