ICG Angiography: A Complementary Technique to Identify







digital_icg_angiography.ppt
- Размер: 10.2 Мб
- Автор:
- Количество слайдов: 32
Описание презентации ICG Angiography: A Complementary Technique to Identify по слайдам
 ICG Angiography: A Complementary Technique to Identify CNV These slides are provided by kind permission from Dr Jason Slakter (Focus on digital camera ICG angiography)
ICG Angiography: A Complementary Technique to Identify CNV These slides are provided by kind permission from Dr Jason Slakter (Focus on digital camera ICG angiography)
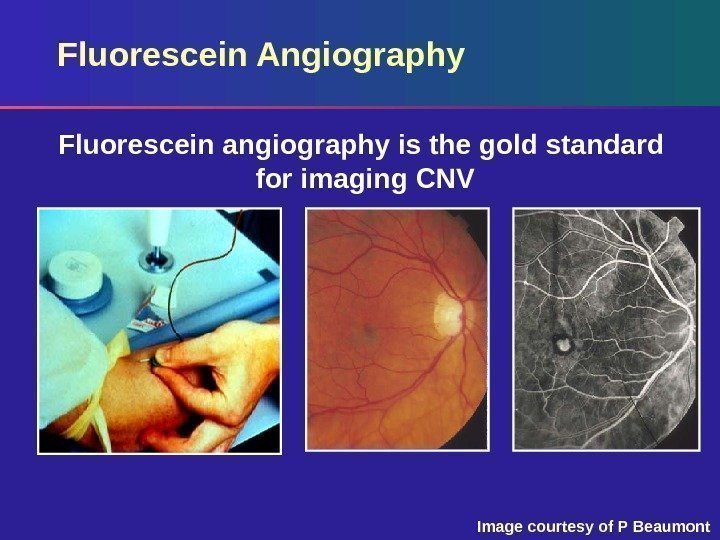
 Fluorescein Angiography Fluorescein angiography is the gold standard for imaging CNV Image courtesy of P Beaumont
Fluorescein Angiography Fluorescein angiography is the gold standard for imaging CNV Image courtesy of P Beaumont
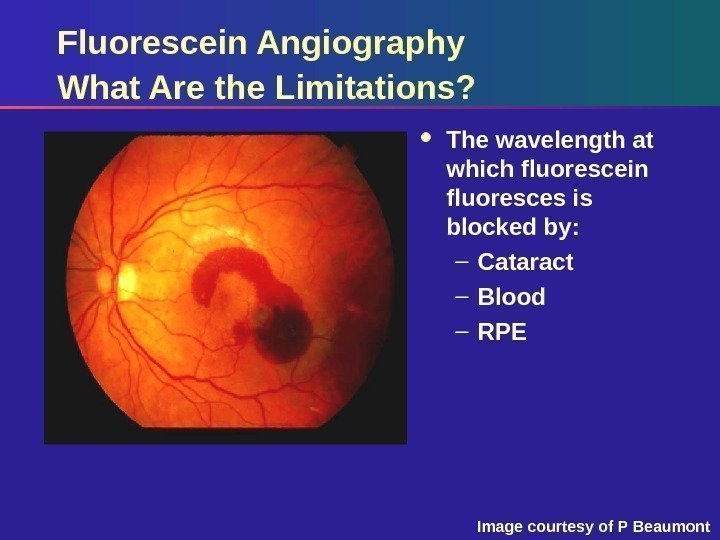
 Fluorescein Angiography What Are the Limitations? The wavelength at which fluorescein fluoresces is blocked by: – Cataract – Blood – RPE Image courtesy of P Beaumont
Fluorescein Angiography What Are the Limitations? The wavelength at which fluorescein fluoresces is blocked by: – Cataract – Blood – RPE Image courtesy of P Beaumont
 Need for Another Imaging Modality ICG Angiography
Need for Another Imaging Modality ICG Angiography
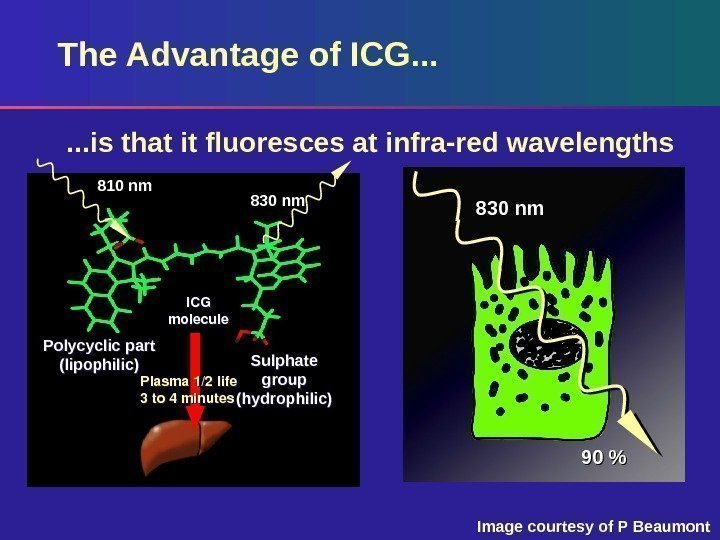
 The Advantage of ICG. . . Plasma 1/2 life 3 to 4 minutes ICG molecule 830 nm 90 %100%Plasma 1/2 life 3 to 4 minutes. Polycyclic part (lipophilic) ICG molecule Sulphate group (hydrophilic) 830 nm 810 nm. . . is that it fluoresces at infra-red wavelengths Image courtesy of P Beaumont
The Advantage of ICG. . . Plasma 1/2 life 3 to 4 minutes ICG molecule 830 nm 90 %100%Plasma 1/2 life 3 to 4 minutes. Polycyclic part (lipophilic) ICG molecule Sulphate group (hydrophilic) 830 nm 810 nm. . . is that it fluoresces at infra-red wavelengths Image courtesy of P Beaumont
 Another Advantage of ICG High plasma protein binding – Up to 98% bound in plasma – Slow leakage from choriocapillaris and CNV
Another Advantage of ICG High plasma protein binding – Up to 98% bound in plasma – Slow leakage from choriocapillaris and CNV
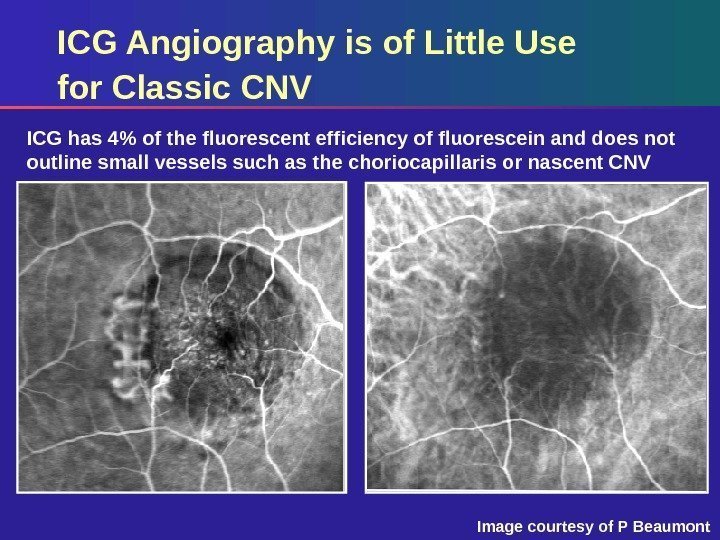
 ICG has 4% of the fluorescent efficiency of fluorescein and does not outline small vessels such as the choriocapillaris or nascent CNV ICG Angiography is of Little Use for Classic CNV Image courtesy of P Beaumont
ICG has 4% of the fluorescent efficiency of fluorescein and does not outline small vessels such as the choriocapillaris or nascent CNV ICG Angiography is of Little Use for Classic CNV Image courtesy of P Beaumont
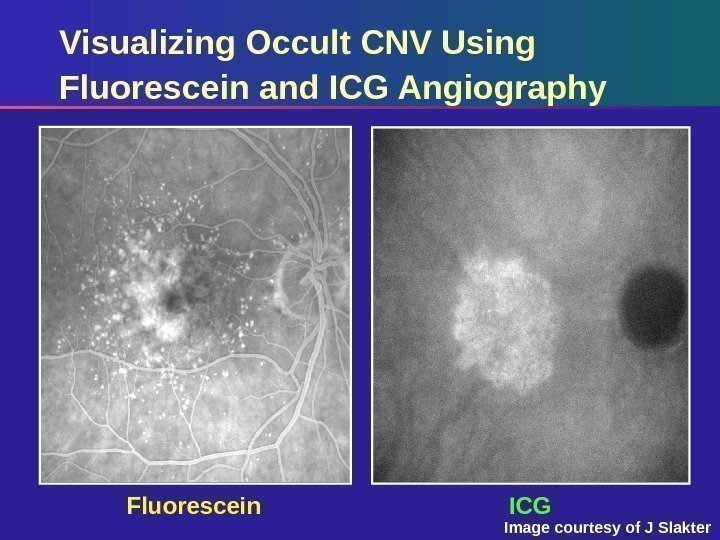
 Fluorescein ICGVisualizing Occult CNV Using Fluorescein and ICG Angiography Image courtesy of J Slakter
Fluorescein ICGVisualizing Occult CNV Using Fluorescein and ICG Angiography Image courtesy of J Slakter
 Types of Occult CNV Visualized Using ICG Angiography Focal occult CNV/hot spots – Well-delineated areas of hyperfluorescence – No larger than 1 disc diameter on ICG angiography Plaques – Usually subfoveal hyperfluorescent areas – Any area of occult CNV larger than 1 disc diameter – May or may not be well defined Combination lesions (plaques and hotspots in the same area)
Types of Occult CNV Visualized Using ICG Angiography Focal occult CNV/hot spots – Well-delineated areas of hyperfluorescence – No larger than 1 disc diameter on ICG angiography Plaques – Usually subfoveal hyperfluorescent areas – Any area of occult CNV larger than 1 disc diameter – May or may not be well defined Combination lesions (plaques and hotspots in the same area)
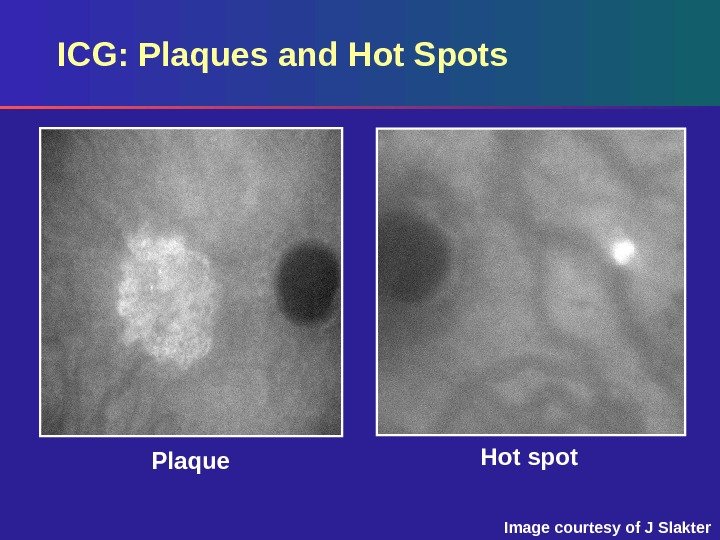
 Hot spot Plaque. ICG: Plaques and Hot Spots Image courtesy of J Slakter
Hot spot Plaque. ICG: Plaques and Hot Spots Image courtesy of J Slakter
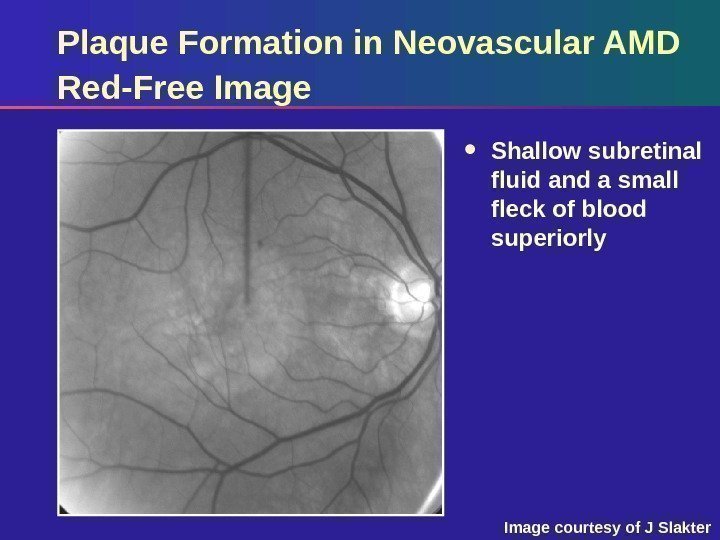
 Plaque Formation in Neovascular AMD Red-Free Image Shallow subretinal fluid and a small fleck of blood superiorly Image courtesy of J Slakter
Plaque Formation in Neovascular AMD Red-Free Image Shallow subretinal fluid and a small fleck of blood superiorly Image courtesy of J Slakter
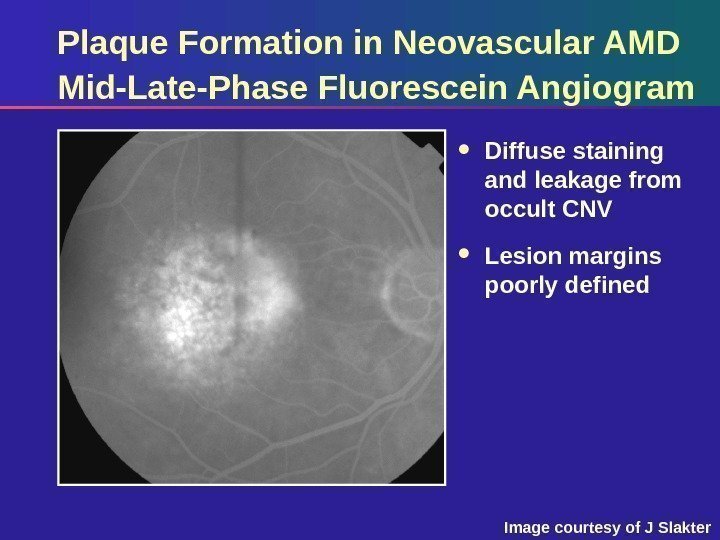
 Plaque Formation in Neovascular AMD Mid-Late-Phase Fluorescein Angiogram Diffuse staining and leakage from occult CNV Lesion margins poorly defined Image courtesy of J Slakter
Plaque Formation in Neovascular AMD Mid-Late-Phase Fluorescein Angiogram Diffuse staining and leakage from occult CNV Lesion margins poorly defined Image courtesy of J Slakter
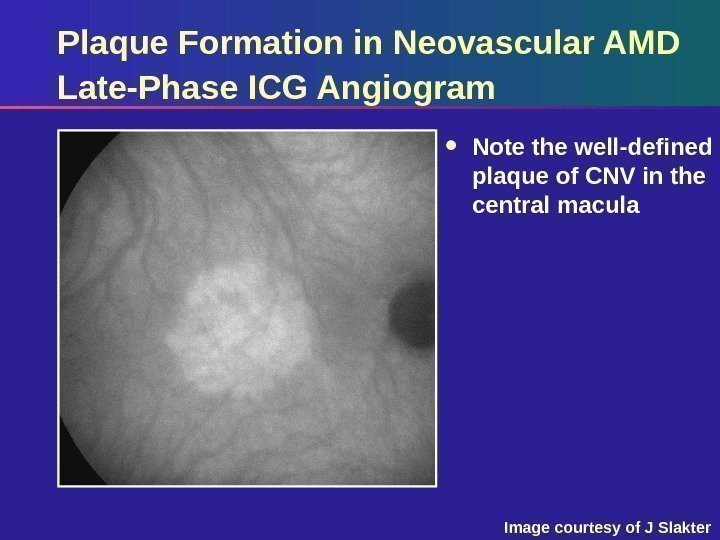
 Plaque Formation in Neovascular AMD Late-Phase ICG Angiogram Note the well-defined plaque of CNV in the central macula Image courtesy of J Slakter
Plaque Formation in Neovascular AMD Late-Phase ICG Angiogram Note the well-defined plaque of CNV in the central macula Image courtesy of J Slakter
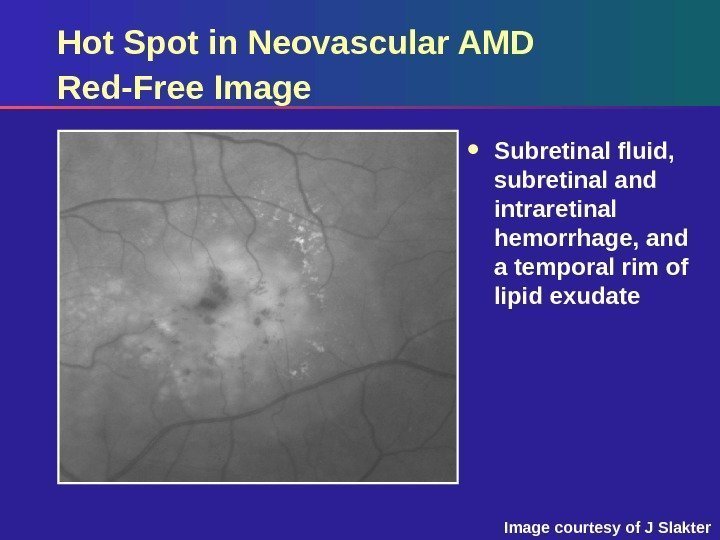
 Hot Spot in Neovascular AMD Red-Free Image Subretinal fluid, subretinal and intraretinal hemorrhage, and a temporal rim of lipid exudate Image courtesy of J Slakter
Hot Spot in Neovascular AMD Red-Free Image Subretinal fluid, subretinal and intraretinal hemorrhage, and a temporal rim of lipid exudate Image courtesy of J Slakter
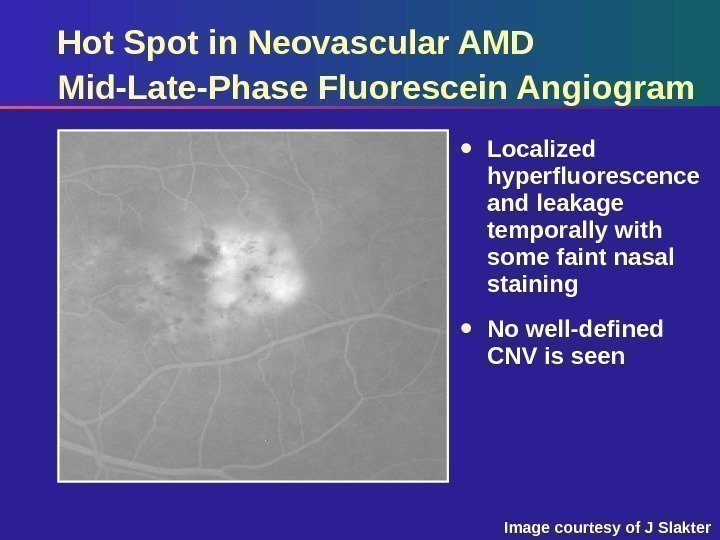
 Hot Spot in Neovascular AMD Mid-Late-Phase Fluorescein Angiogram Localized hyperfluorescence and leakage temporally with some faint nasal staining No well-defined CNV is seen Image courtesy of J Slakter
Hot Spot in Neovascular AMD Mid-Late-Phase Fluorescein Angiogram Localized hyperfluorescence and leakage temporally with some faint nasal staining No well-defined CNV is seen Image courtesy of J Slakter
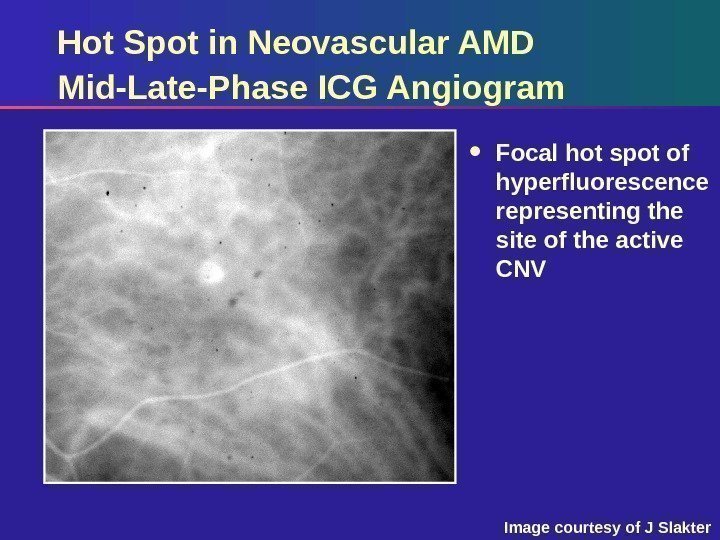
 Hot Spot in Neovascular AMD Mid-Late-Phase ICG Angiogram Focal hot spot of hyperfluorescence representing the site of the active CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
Hot Spot in Neovascular AMD Mid-Late-Phase ICG Angiogram Focal hot spot of hyperfluorescence representing the site of the active CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
 CNV-Related Abnormal Vessels Visualized Using ICG Angiography Choroidal-retinal anastomosis Feeder vessel Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
CNV-Related Abnormal Vessels Visualized Using ICG Angiography Choroidal-retinal anastomosis Feeder vessel Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
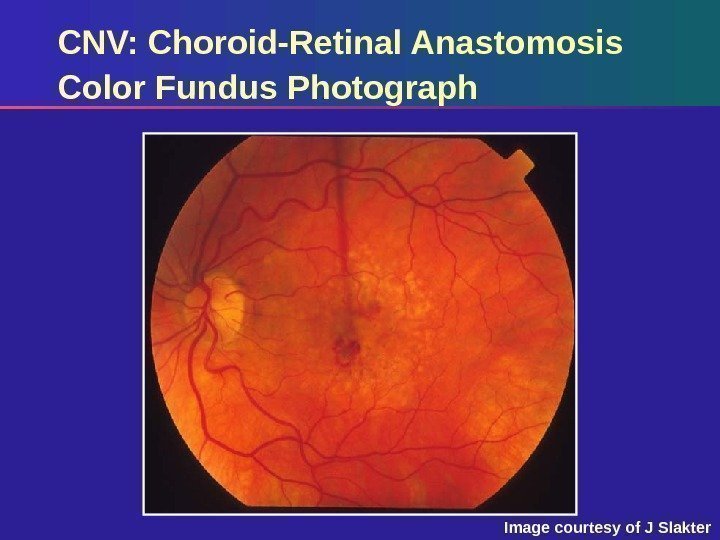
 CNV: Choroid-Retinal Anastomosis Color Fundus Photograph Image courtesy of J Slakter
CNV: Choroid-Retinal Anastomosis Color Fundus Photograph Image courtesy of J Slakter
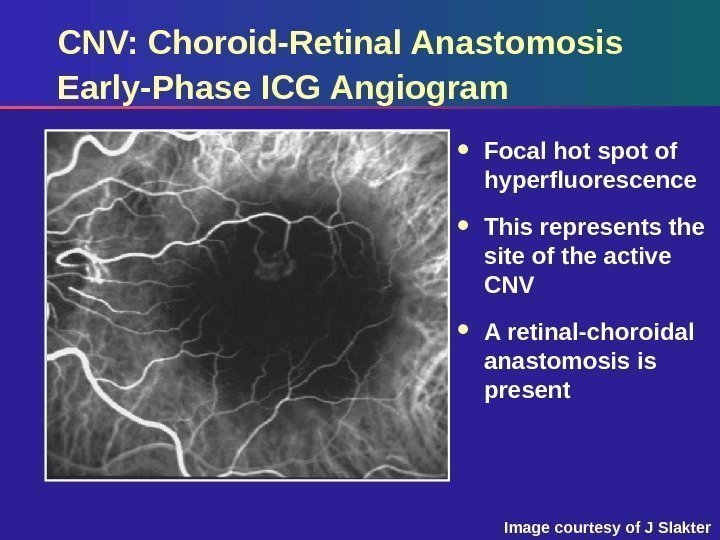
 CNV: Choroid-Retinal Anastomosis Early-Phase ICG Angiogram Focal hot spot of hyperfluorescence This represents the site of the active CNV A retinal-choroidal anastomosis is present Image courtesy of J Slakter
CNV: Choroid-Retinal Anastomosis Early-Phase ICG Angiogram Focal hot spot of hyperfluorescence This represents the site of the active CNV A retinal-choroidal anastomosis is present Image courtesy of J Slakter
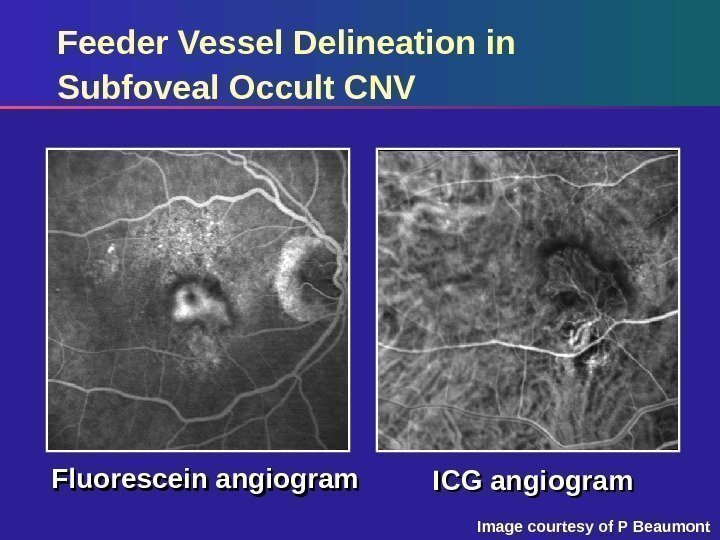
 Feeder Vessel Delineation in Subfoveal Occult CNV Fluorescein angiogram ICG angiogram Image courtesy of P Beaumont
Feeder Vessel Delineation in Subfoveal Occult CNV Fluorescein angiogram ICG angiogram Image courtesy of P Beaumont
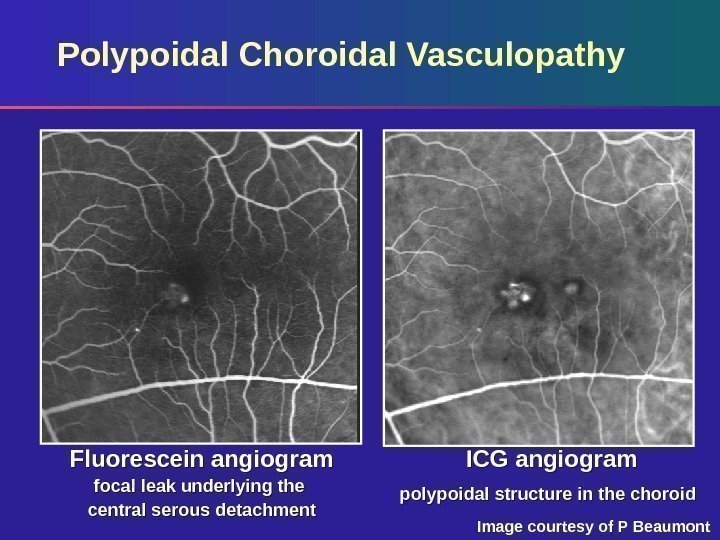
 Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Fluorescein angiogram focal leak underlying the central serous detachment ICG angiogram polypoidal structure in the choroid Image courtesy of P Beaumont
Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Fluorescein angiogram focal leak underlying the central serous detachment ICG angiogram polypoidal structure in the choroid Image courtesy of P Beaumont
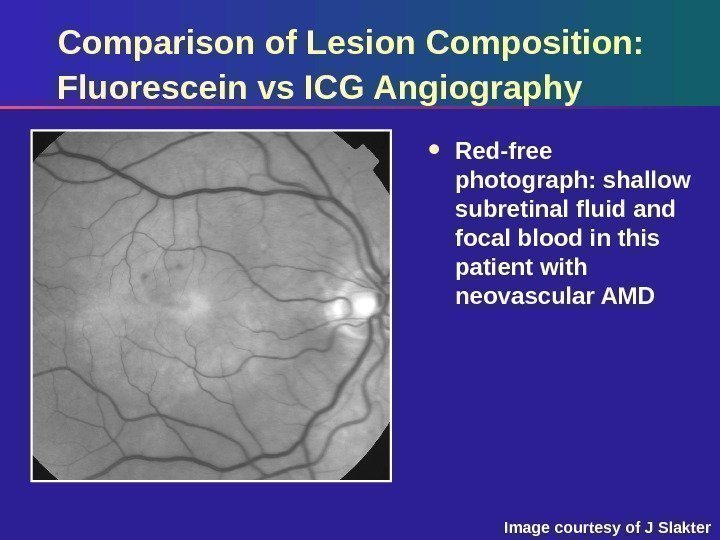
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Red-free photograph: shallow subretinal fluid and focal blood in this patient with neovascular AMD Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Red-free photograph: shallow subretinal fluid and focal blood in this patient with neovascular AMD Image courtesy of J Slakter
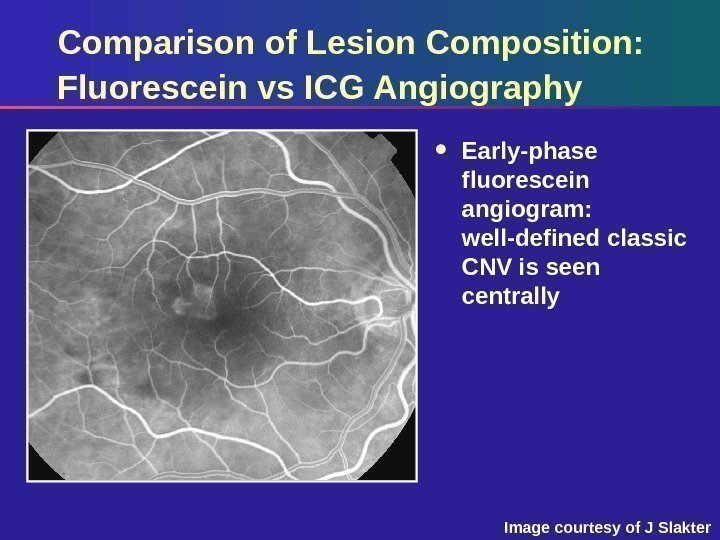
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Early-phase fluorescein angiogram: well-defined classic CNV is seen centrally Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Early-phase fluorescein angiogram: well-defined classic CNV is seen centrally Image courtesy of J Slakter
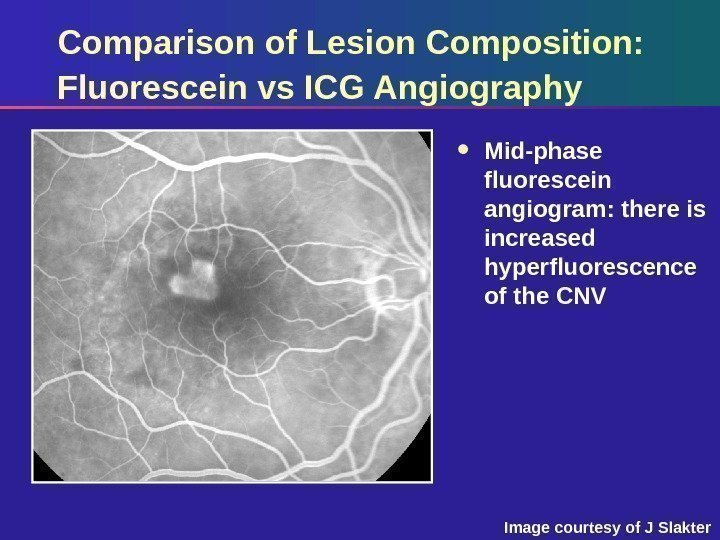
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Mid-phase fluorescein angiogram: there is increased hyperfluorescence of the CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Mid-phase fluorescein angiogram: there is increased hyperfluorescence of the CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
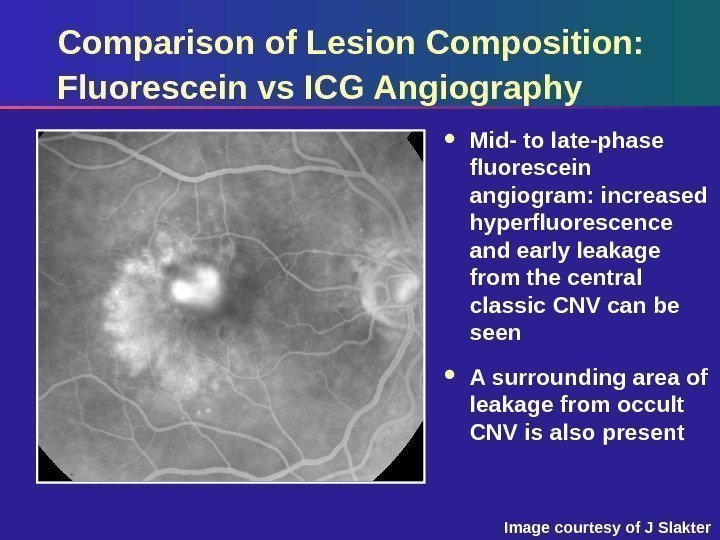
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Mid- to late-phase fluorescein angiogram: increased hyperfluorescence and early leakage from the central classic CNV can be seen A surrounding area of leakage from occult CNV is also present Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Mid- to late-phase fluorescein angiogram: increased hyperfluorescence and early leakage from the central classic CNV can be seen A surrounding area of leakage from occult CNV is also present Image courtesy of J Slakter
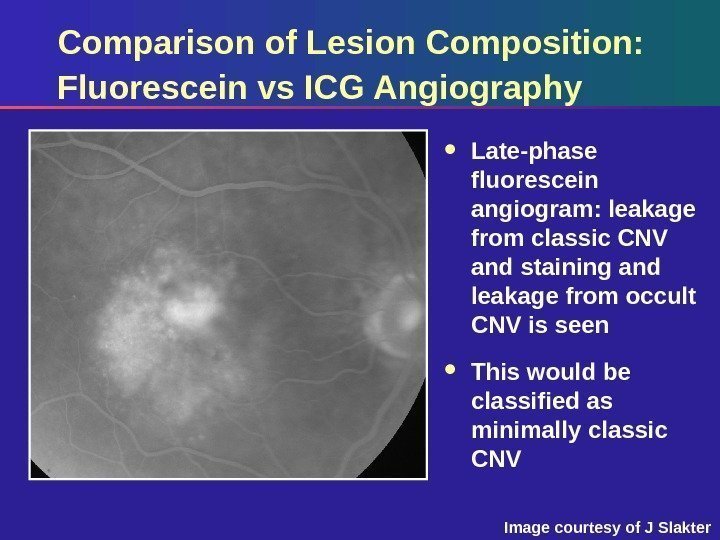
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Late-phase fluorescein angiogram: leakage from classic CNV and staining and leakage from occult CNV is seen This would be classified as minimally classic CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Late-phase fluorescein angiogram: leakage from classic CNV and staining and leakage from occult CNV is seen This would be classified as minimally classic CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
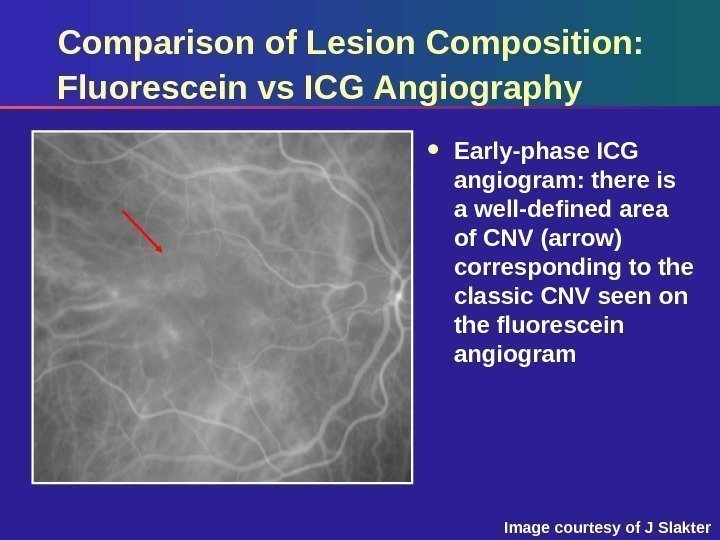
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Early-phase ICG angiogram: there is a well-defined area of CNV (arrow) corresponding to the classic CNV seen on the fluorescein angiogram Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Early-phase ICG angiogram: there is a well-defined area of CNV (arrow) corresponding to the classic CNV seen on the fluorescein angiogram Image courtesy of J Slakter
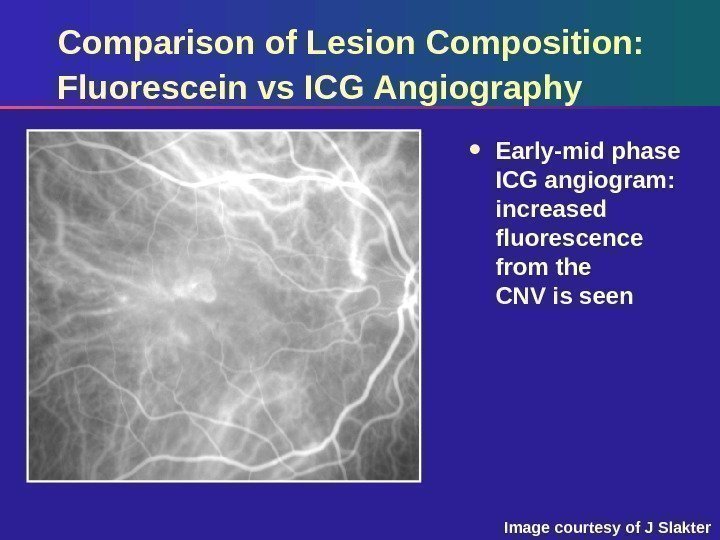
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Early-mid phase ICG angiogram: increased fluorescence from the CNV is seen Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Early-mid phase ICG angiogram: increased fluorescence from the CNV is seen Image courtesy of J Slakter
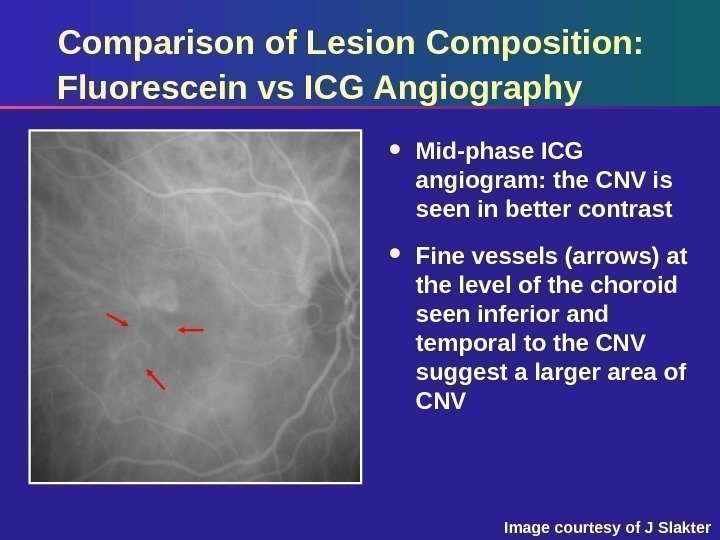
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Mid-phase ICG angiogram: the CNV is seen in better contrast Fine vessels (arrows) at the level of the choroid seen inferior and temporal to the CNV suggest a larger area of CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Mid-phase ICG angiogram: the CNV is seen in better contrast Fine vessels (arrows) at the level of the choroid seen inferior and temporal to the CNV suggest a larger area of CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
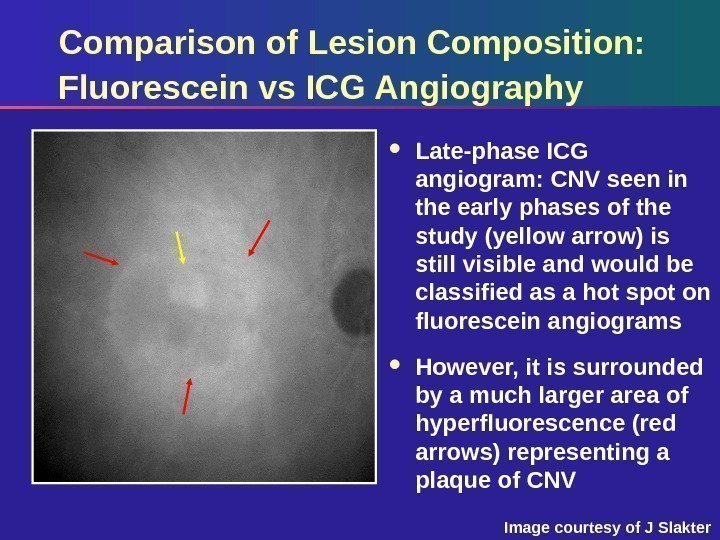
 Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Late-phase ICG angiogram: CNV seen in the early phases of the study (yellow arrow) is still visible and would be classified as a hot spot on fluorescein angiograms However, it is surrounded by a much larger area of hyperfluorescence (red arrows) representing a plaque of CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
Comparison of Lesion Composition: Fluorescein vs ICG Angiography Late-phase ICG angiogram: CNV seen in the early phases of the study (yellow arrow) is still visible and would be classified as a hot spot on fluorescein angiograms However, it is surrounded by a much larger area of hyperfluorescence (red arrows) representing a plaque of CNV Image courtesy of J Slakter
 ICG Angiography Summary Important adjunct in imaging occult CNV Identifies subtypes of occult disease – Hot spots – Plaque – Retinal choroidal anastomosis – Polypoidal lesions – Feeder vessels Clinical significance not yet known
ICG Angiography Summary Important adjunct in imaging occult CNV Identifies subtypes of occult disease – Hot spots – Plaque – Retinal choroidal anastomosis – Polypoidal lesions – Feeder vessels Clinical significance not yet known
 ICG Angiography Summary ICG angiography is included in newly initiated clinical trials for use of Visudyne therapy in minimally classic and occult CNV
ICG Angiography Summary ICG angiography is included in newly initiated clinical trials for use of Visudyne therapy in minimally classic and occult CNV

