4cd993108b4b00303cb525fca7eb9267.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 ICD HISTORY • 1853 FIRST INTERNATIONAL STATISTICAL CONGRESS – FIRST UNIFORM CLASSIFICATION OF CAUSES OF DEATH-INTERNATIONAL CAUSES OF DEATH (ICD) – TWO COMPETING APPROACHES • 1855 CONGRESS ENTERTAINED BOTH SETS – WILLIAM FARR USED ANATOMICAL SITES AS BASIS – MARC d’ESPINE USED NATURE OF DISEASE (GOUTY, HERPETIC, HEMATIC) – INITIAL COMPROMISE--186 RUBRICS – 20 YEARS TO RECONCILE THE DIFFERENCES—FARR WON – NOW ICD REVISED ABOUT EVERY DECADE—HENCE ICD-10 1
ICD HISTORY • 1853 FIRST INTERNATIONAL STATISTICAL CONGRESS – FIRST UNIFORM CLASSIFICATION OF CAUSES OF DEATH-INTERNATIONAL CAUSES OF DEATH (ICD) – TWO COMPETING APPROACHES • 1855 CONGRESS ENTERTAINED BOTH SETS – WILLIAM FARR USED ANATOMICAL SITES AS BASIS – MARC d’ESPINE USED NATURE OF DISEASE (GOUTY, HERPETIC, HEMATIC) – INITIAL COMPROMISE--186 RUBRICS – 20 YEARS TO RECONCILE THE DIFFERENCES—FARR WON – NOW ICD REVISED ABOUT EVERY DECADE—HENCE ICD-10 1
 ICD/ICF HISTORY • 1979 NINTH REVISION OF ICD/ICD-9 – RECOMMENDED “PROVISIONAL PROCEDURES CLASSIFICATIONS” BE PUBLISHED TO NINTH REVISION-CPT CODES BEGIN 1980 RECOMMENDED IMPAIRMENTS AND HANDICAPS CLASSIFICATIONS AS SUPPLEMENT Provisional acceptance--INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF IMPAIRMENTS, DISABILITIES, AND HANDICAPS (ICIDH) 1993 REVISION OF ICIDH BEGUN 2001 International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) APPROVED BY THE WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY 2
ICD/ICF HISTORY • 1979 NINTH REVISION OF ICD/ICD-9 – RECOMMENDED “PROVISIONAL PROCEDURES CLASSIFICATIONS” BE PUBLISHED TO NINTH REVISION-CPT CODES BEGIN 1980 RECOMMENDED IMPAIRMENTS AND HANDICAPS CLASSIFICATIONS AS SUPPLEMENT Provisional acceptance--INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF IMPAIRMENTS, DISABILITIES, AND HANDICAPS (ICIDH) 1993 REVISION OF ICIDH BEGUN 2001 International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) APPROVED BY THE WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY 2
 ICF AIM AND PRINCIPLES • AIM—PROVIDE A UNIFIED AND STANDARD LANGUAGE AND FRAMEWORK FOR THE DESCRIPTION OF HEALTH STATES • • » PRINCIPLES UNIVERSAL NATURE OF DISABILITY EXPERIENCE CROSSES THE LIFE SPAN— BIRTH TO DEATH ETIOLOGY NEUTRAL— PHYSICAL, EMOTIONAL, etc. NEUTRAL LANGUAGE— FUNCTION, ACTIVITY, PARTICIPATION, ENVIRONMENT 3
ICF AIM AND PRINCIPLES • AIM—PROVIDE A UNIFIED AND STANDARD LANGUAGE AND FRAMEWORK FOR THE DESCRIPTION OF HEALTH STATES • • » PRINCIPLES UNIVERSAL NATURE OF DISABILITY EXPERIENCE CROSSES THE LIFE SPAN— BIRTH TO DEATH ETIOLOGY NEUTRAL— PHYSICAL, EMOTIONAL, etc. NEUTRAL LANGUAGE— FUNCTION, ACTIVITY, PARTICIPATION, ENVIRONMENT 3
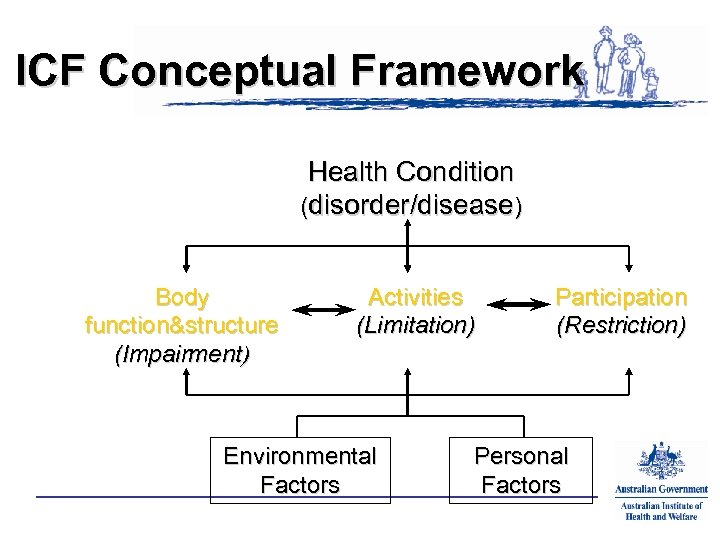 ICF Conceptual Framework Health Condition (disorder/disease) Body function&structure (Impairment) Activities (Limitation) Environmental Factors Participation (Restriction) Personal Factors
ICF Conceptual Framework Health Condition (disorder/disease) Body function&structure (Impairment) Activities (Limitation) Environmental Factors Participation (Restriction) Personal Factors
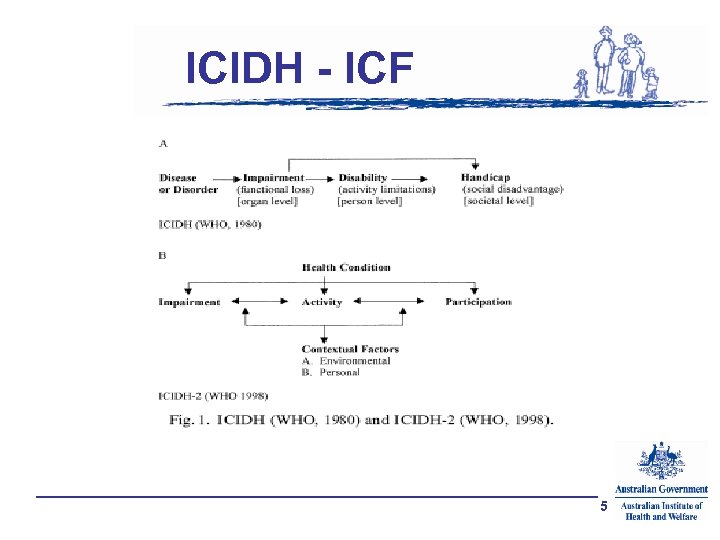 ICIDH - ICF 5
ICIDH - ICF 5
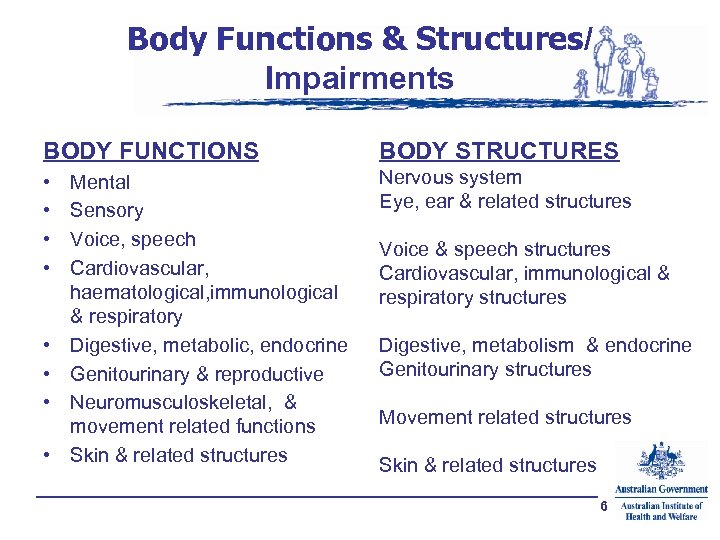 Body Functions & Structures/ Impairments BODY FUNCTIONS BODY STRUCTURES • • Nervous system Eye, ear & related structures • • Mental Sensory Voice, speech Cardiovascular, haematological, immunological & respiratory Digestive, metabolic, endocrine Genitourinary & reproductive Neuromusculoskeletal, & movement related functions Skin & related structures Voice & speech structures Cardiovascular, immunological & respiratory structures Digestive, metabolism & endocrine Genitourinary structures Movement related structures Skin & related structures 6
Body Functions & Structures/ Impairments BODY FUNCTIONS BODY STRUCTURES • • Nervous system Eye, ear & related structures • • Mental Sensory Voice, speech Cardiovascular, haematological, immunological & respiratory Digestive, metabolic, endocrine Genitourinary & reproductive Neuromusculoskeletal, & movement related functions Skin & related structures Voice & speech structures Cardiovascular, immunological & respiratory structures Digestive, metabolism & endocrine Genitourinary structures Movement related structures Skin & related structures 6
 Activities and Participation: Limitations/Restrictions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Learning & Applying Knowledge General Tasks and Demands Communication Movement Self Care Domestic Life Areas Interpersonal Interactions Major Life Areas Community, Social & Civic Life 7
Activities and Participation: Limitations/Restrictions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Learning & Applying Knowledge General Tasks and Demands Communication Movement Self Care Domestic Life Areas Interpersonal Interactions Major Life Areas Community, Social & Civic Life 7
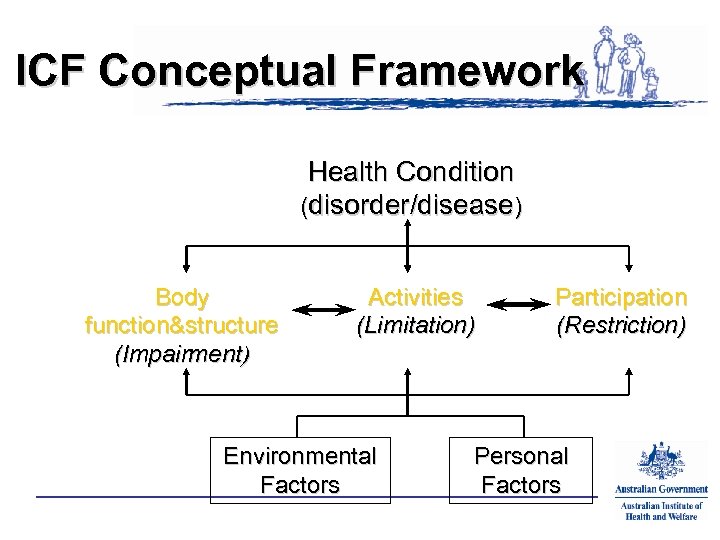 ICF Conceptual Framework Health Condition (disorder/disease) Body function&structure (Impairment) Activities (Limitation) Environmental Factors Participation (Restriction) Personal Factors
ICF Conceptual Framework Health Condition (disorder/disease) Body function&structure (Impairment) Activities (Limitation) Environmental Factors Participation (Restriction) Personal Factors
 Environmental Factors: Barriers/Facilitators 1. Products and technology 2. Natural environment and humanmade changes to the environment 3. Support and relationships 4. Attitudes 5. Services, systems and policies 9
Environmental Factors: Barriers/Facilitators 1. Products and technology 2. Natural environment and humanmade changes to the environment 3. Support and relationships 4. Attitudes 5. Services, systems and policies 9
 Example: Polio • May have caused paralysis of legs (Body Function) • Affects ability to walk or climb stairs (Activity) • Impedes ability to attend school or find employment within the current environment (Participation) BUT…. 10
Example: Polio • May have caused paralysis of legs (Body Function) • Affects ability to walk or climb stairs (Activity) • Impedes ability to attend school or find employment within the current environment (Participation) BUT…. 10
 Example, continued • Mobility related activities, such as getting around the house or community can be improved with accessible environment and assistive devices • Participation can be increased with reduced stigma, accessible environments and flexible job design • Disability is NOT independent of the environment, and therefore is not static 11
Example, continued • Mobility related activities, such as getting around the house or community can be improved with accessible environment and assistive devices • Participation can be increased with reduced stigma, accessible environments and flexible job design • Disability is NOT independent of the environment, and therefore is not static 11
 Need for version of ICF for children & youth • Nature and form of functioning in children different from that of adults—children are not small adults • Child is a “moving target” in classification of function—changes every 6 -12 months throughout developing years, esp. activities • Primary environments and participation areas differ for children • ICF version for children and youth facilitates continuity of documentation e. g. transitions from child to adult services and communication among professionals and with parents 12
Need for version of ICF for children & youth • Nature and form of functioning in children different from that of adults—children are not small adults • Child is a “moving target” in classification of function—changes every 6 -12 months throughout developing years, esp. activities • Primary environments and participation areas differ for children • ICF version for children and youth facilitates continuity of documentation e. g. transitions from child to adult services and communication among professionals and with parents 12
 Need for ICF-CY éDeveloping child as “moving target” 13
Need for ICF-CY éDeveloping child as “moving target” 13
 Need for ICF-CY é Activities differ from those of adults 14
Need for ICF-CY é Activities differ from those of adults 14
 Need for ICF-CY é Precursors of participation and life roles 15
Need for ICF-CY é Precursors of participation and life roles 15
 Need for ICF-CY é Emerging habitual, frequent and occasional environments 16
Need for ICF-CY é Emerging habitual, frequent and occasional environments 16
 Development of the ICF-CY • Structure ICF main volume maintained • Inclusion/exclusion criteria for codes were expanded • New content added to unused codes at 4, 5 and 6 character level to address needs outlined before • 2 nd draft prepared for review on WHO website fall of 2005 • Publication expected 2006 17
Development of the ICF-CY • Structure ICF main volume maintained • Inclusion/exclusion criteria for codes were expanded • New content added to unused codes at 4, 5 and 6 character level to address needs outlined before • 2 nd draft prepared for review on WHO website fall of 2005 • Publication expected 2006 17
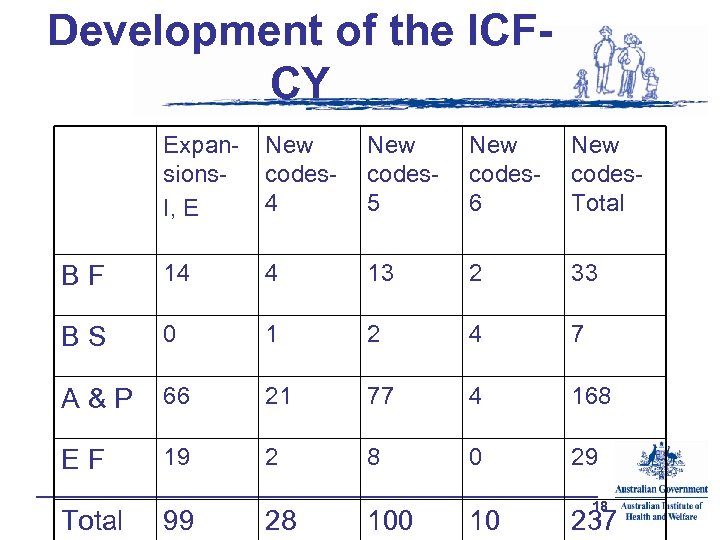 Development of the ICFCY Expansions. I, E New codes 4 New codes 5 New codes 6 New codes. Total BF 14 4 13 2 33 BS 0 1 2 4 7 A&P 66 21 77 4 168 EF 19 2 8 0 29 Total 99 28 100 10 18 237
Development of the ICFCY Expansions. I, E New codes 4 New codes 5 New codes 6 New codes. Total BF 14 4 13 2 33 BS 0 1 2 4 7 A&P 66 21 77 4 168 EF 19 2 8 0 29 Total 99 28 100 10 18 237
 ICF-CY: Example of new code for Body Functions • b 120 General cognitive functions • General mental functions required to represent, and constructively integrate knowledge of objects, events and experiences and apply that knowledge in tasks requiring mental rather than physical activity. • Exclusion: higher level cognitive functions (b 164) 19
ICF-CY: Example of new code for Body Functions • b 120 General cognitive functions • General mental functions required to represent, and constructively integrate knowledge of objects, events and experiences and apply that knowledge in tasks requiring mental rather than physical activity. • Exclusion: higher level cognitive functions (b 164) 19
 ICF-CY: representative new A/P codes • d 1200 -03 mouthing, touching, smelling, tasting • d 133 Acquiring language – d 1330 acquiring single words or meaningful symbols – d 1331 combining words into phrases – d 1332 acquiring syntax • • d 2300 Following routines d 2304 Adapting to changes in daily routine d 2305 Adapting to changes in time demands d 2306 Managing one’s time • d 5205 Caring for the nose • d 53000 -10/ Indicating need for urination, defecation • d 880 Engagement in play—solitary, onlooker, parallel, shared 20
ICF-CY: representative new A/P codes • d 1200 -03 mouthing, touching, smelling, tasting • d 133 Acquiring language – d 1330 acquiring single words or meaningful symbols – d 1331 combining words into phrases – d 1332 acquiring syntax • • d 2300 Following routines d 2304 Adapting to changes in daily routine d 2305 Adapting to changes in time demands d 2306 Managing one’s time • d 5205 Caring for the nose • d 53000 -10/ Indicating need for urination, defecation • d 880 Engagement in play—solitary, onlooker, parallel, shared 20
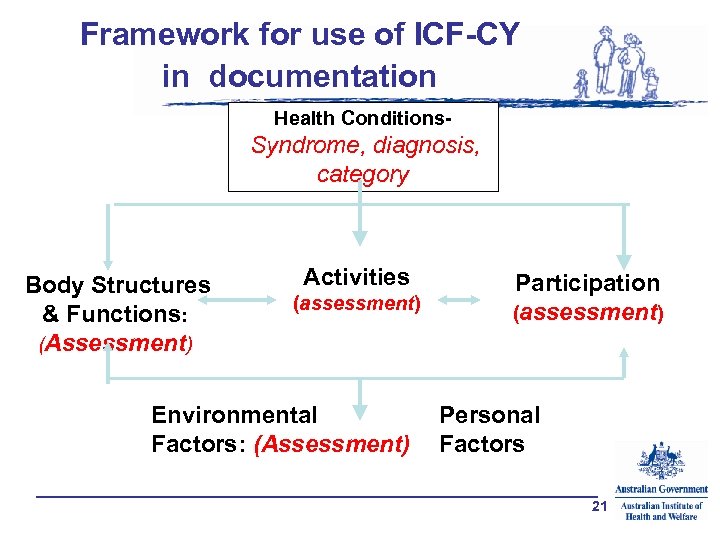 Framework for use of ICF-CY in documentation Health Conditions- Syndrome, diagnosis, category Body Structures & Functions: (Assessment) Activities (assessment) Environmental Factors: (Assessment) Participation (assessment) Personal Factors 21
Framework for use of ICF-CY in documentation Health Conditions- Syndrome, diagnosis, category Body Structures & Functions: (Assessment) Activities (assessment) Environmental Factors: (Assessment) Participation (assessment) Personal Factors 21
 ACTIVITIES and PARTICIPATION 1. Learning & applying knowledge 2. General tasks & demands 3. Communication 4. Mobility 5. Self-care 6. Domestic life 7. Interpersonal interactions & relationships 8. Major life areas 9. Community, social & civic life 22
ACTIVITIES and PARTICIPATION 1. Learning & applying knowledge 2. General tasks & demands 3. Communication 4. Mobility 5. Self-care 6. Domestic life 7. Interpersonal interactions & relationships 8. Major life areas 9. Community, social & civic life 22
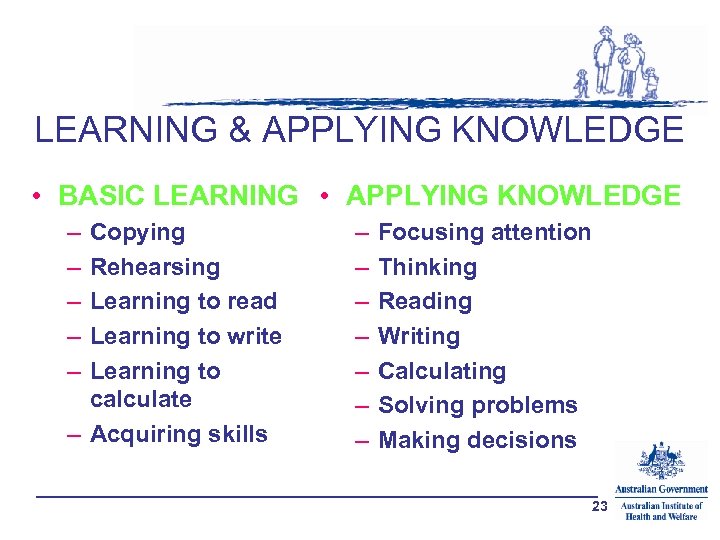 LEARNING & APPLYING KNOWLEDGE • BASIC LEARNING • APPLYING KNOWLEDGE – – – Copying Rehearsing Learning to read Learning to write Learning to calculate – Acquiring skills – – – – Focusing attention Thinking Reading Writing Calculating Solving problems Making decisions 23
LEARNING & APPLYING KNOWLEDGE • BASIC LEARNING • APPLYING KNOWLEDGE – – – Copying Rehearsing Learning to read Learning to write Learning to calculate – Acquiring skills – – – – Focusing attention Thinking Reading Writing Calculating Solving problems Making decisions 23
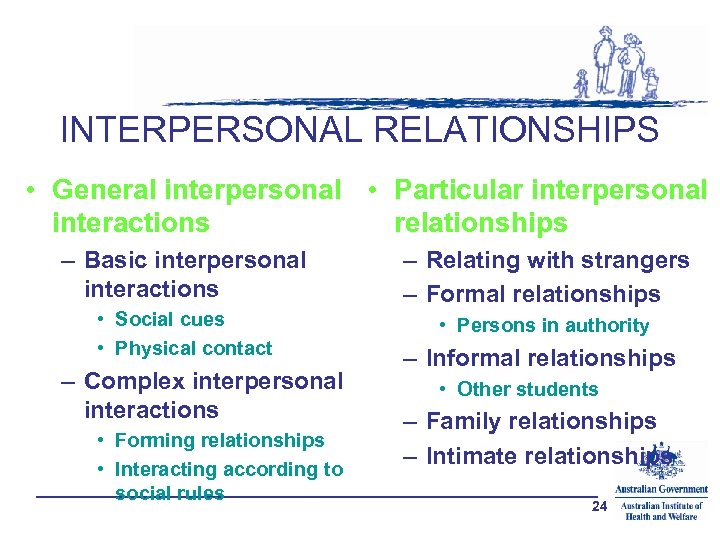 INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS • General interpersonal • Particular interpersonal interactions relationships – Basic interpersonal interactions – Relating with strangers – Formal relationships • Social cues • Physical contact • Persons in authority – Complex interpersonal interactions • Forming relationships • Interacting according to social rules – Informal relationships • Other students – Family relationships – Intimate relationships 24
INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS • General interpersonal • Particular interpersonal interactions relationships – Basic interpersonal interactions – Relating with strangers – Formal relationships • Social cues • Physical contact • Persons in authority – Complex interpersonal interactions • Forming relationships • Interacting according to social rules – Informal relationships • Other students – Family relationships – Intimate relationships 24
 Disabilities Associated with ADHD • d 160 Focusing attention – Intentionally focusing on specific stimuli, such as by filtering out distracting noises 25
Disabilities Associated with ADHD • d 160 Focusing attention – Intentionally focusing on specific stimuli, such as by filtering out distracting noises 25
 Disabilities Associated with ADHD • d 7202 Regulating behaviors within interactions – Regulating emotions and impulses, verbal aggression and physical aggression in interactions with others, in a contextually and socially appropriate manner 26
Disabilities Associated with ADHD • d 7202 Regulating behaviors within interactions – Regulating emotions and impulses, verbal aggression and physical aggression in interactions with others, in a contextually and socially appropriate manner 26
 Disabilities Associated with ADHD • d 820 School education – Gaining admission to school, engaging in all school-related responsibilities and privileges, and learning the course material, subjects and other curriculum requirements in a primary or secondary education program, including attending school regularly, working cooperatively with other students, taking direction from teachers, organizing, studying and completing assigned tasks and projects, and advancing to other stages of education 27
Disabilities Associated with ADHD • d 820 School education – Gaining admission to school, engaging in all school-related responsibilities and privileges, and learning the course material, subjects and other curriculum requirements in a primary or secondary education program, including attending school regularly, working cooperatively with other students, taking direction from teachers, organizing, studying and completing assigned tasks and projects, and advancing to other stages of education 27
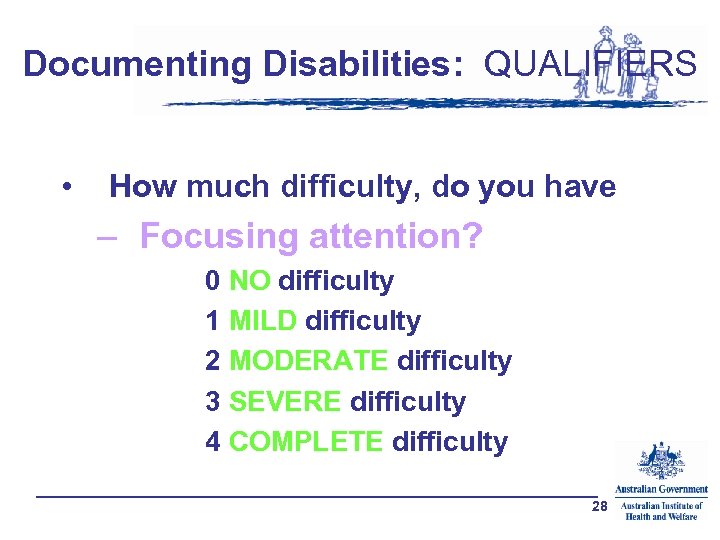 Documenting Disabilities: QUALIFIERS • How much difficulty, do you have – Focusing attention? 0 NO difficulty 1 MILD difficulty 2 MODERATE difficulty 3 SEVERE difficulty 4 COMPLETE difficulty 28
Documenting Disabilities: QUALIFIERS • How much difficulty, do you have – Focusing attention? 0 NO difficulty 1 MILD difficulty 2 MODERATE difficulty 3 SEVERE difficulty 4 COMPLETE difficulty 28
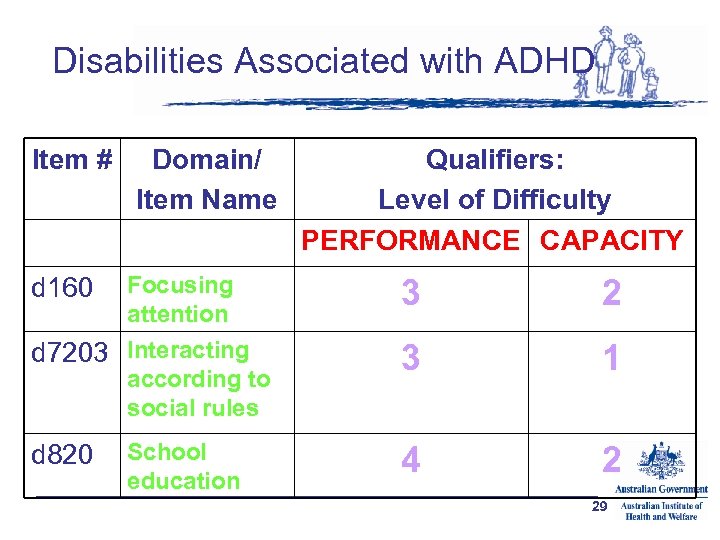 Disabilities Associated with ADHD Item # Domain/ Item Name Focusing attention d 7203 Interacting according to social rules d 160 d 820 School education Qualifiers: Level of Difficulty PERFORMANCE CAPACITY 3 2 3 1 4 2 29
Disabilities Associated with ADHD Item # Domain/ Item Name Focusing attention d 7203 Interacting according to social rules d 160 d 820 School education Qualifiers: Level of Difficulty PERFORMANCE CAPACITY 3 2 3 1 4 2 29
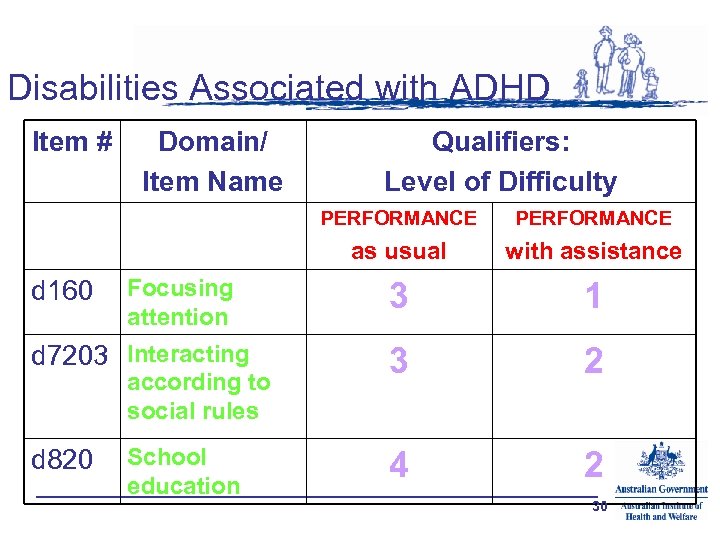 Disabilities Associated with ADHD Item # Domain/ Item Name Qualifiers: Level of Difficulty PERFORMANCE as usual d 160 Focusing attention d 7203 Interacting according to social rules d 820 School education PERFORMANCE with assistance 3 1 3 2 4 2 30
Disabilities Associated with ADHD Item # Domain/ Item Name Qualifiers: Level of Difficulty PERFORMANCE as usual d 160 Focusing attention d 7203 Interacting according to social rules d 820 School education PERFORMANCE with assistance 3 1 3 2 4 2 30
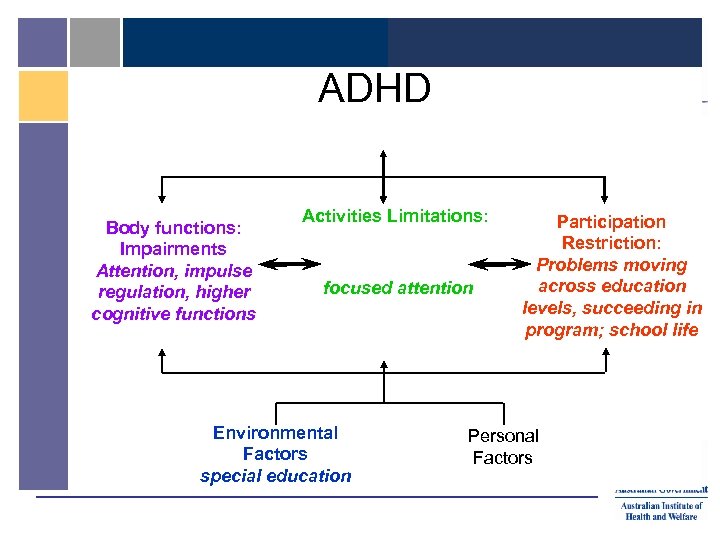 ADHD Body functions: Impairments Attention, impulse regulation, higher cognitive functions Activities Limitations: focused attention Environmental Factors special education Participation Restriction: Problems moving across education levels, succeeding in program; school life Personal Factors
ADHD Body functions: Impairments Attention, impulse regulation, higher cognitive functions Activities Limitations: focused attention Environmental Factors special education Participation Restriction: Problems moving across education levels, succeeding in program; school life Personal Factors
 • Activity limitations are not unique to any disorder, either physical or mental • Activity limitations can be characteristic of certain disorders • ICF is developed to encompass lifespan • ICF is dynamic, captures change • ICF includes effects of health condition and environment on functioning and disabilities 32
• Activity limitations are not unique to any disorder, either physical or mental • Activity limitations can be characteristic of certain disorders • ICF is developed to encompass lifespan • ICF is dynamic, captures change • ICF includes effects of health condition and environment on functioning and disabilities 32
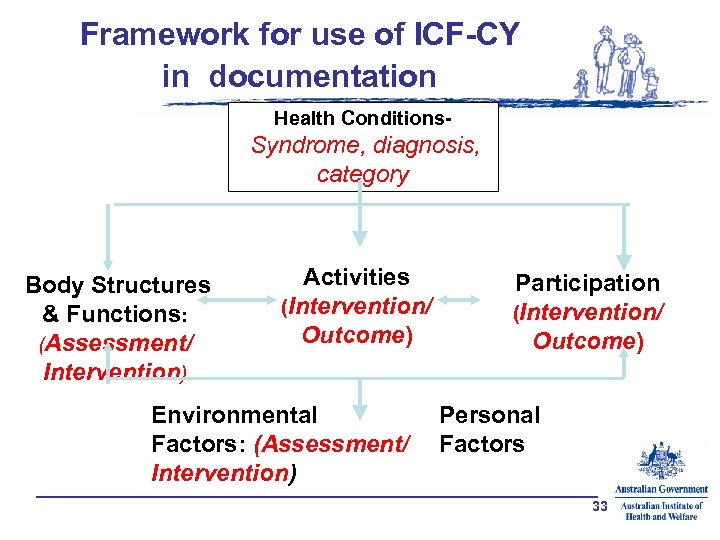 Framework for use of ICF-CY in documentation Health Conditions- Syndrome, diagnosis, category Body Structures & Functions: (Assessment/ Intervention) Activities (Intervention/ Outcome) Environmental Factors: (Assessment/ Intervention) Participation (Intervention/ Outcome) Personal Factors 33
Framework for use of ICF-CY in documentation Health Conditions- Syndrome, diagnosis, category Body Structures & Functions: (Assessment/ Intervention) Activities (Intervention/ Outcome) Environmental Factors: (Assessment/ Intervention) Participation (Intervention/ Outcome) Personal Factors 33
 34
34
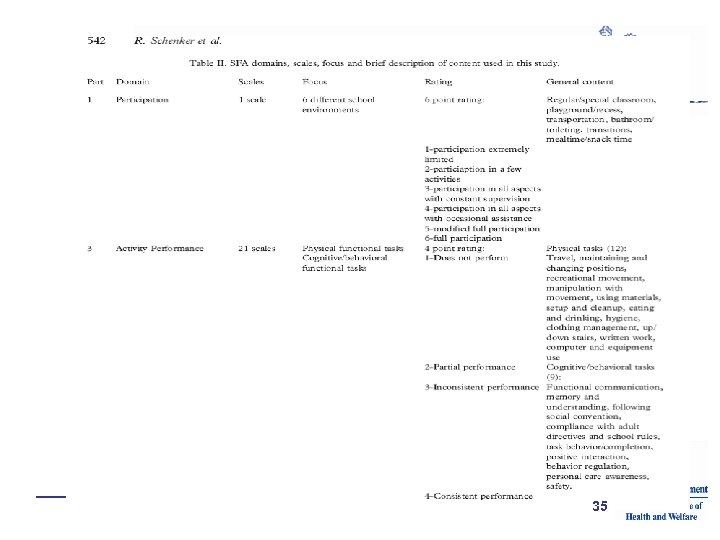 35
35
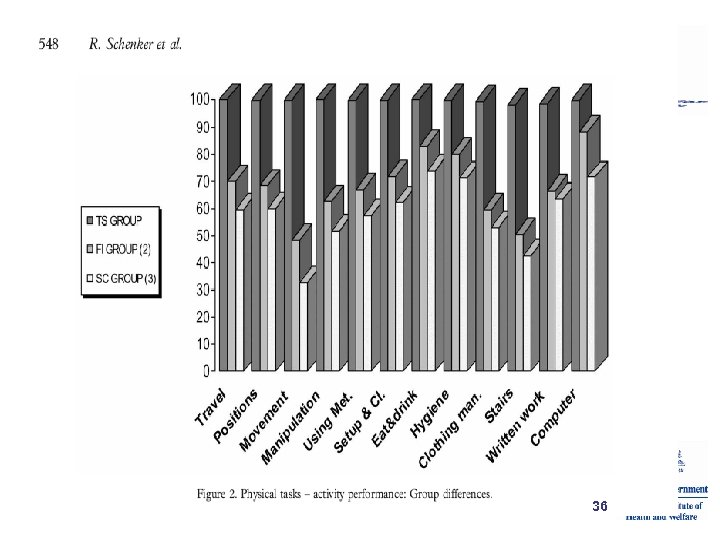 36
36
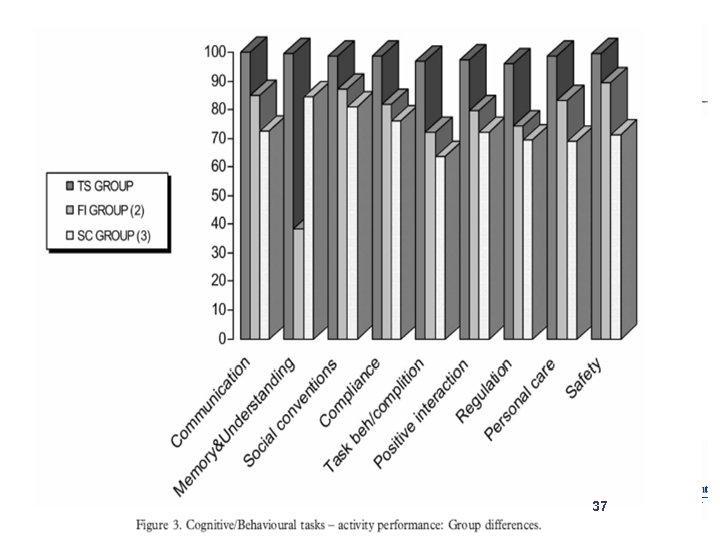 37
37
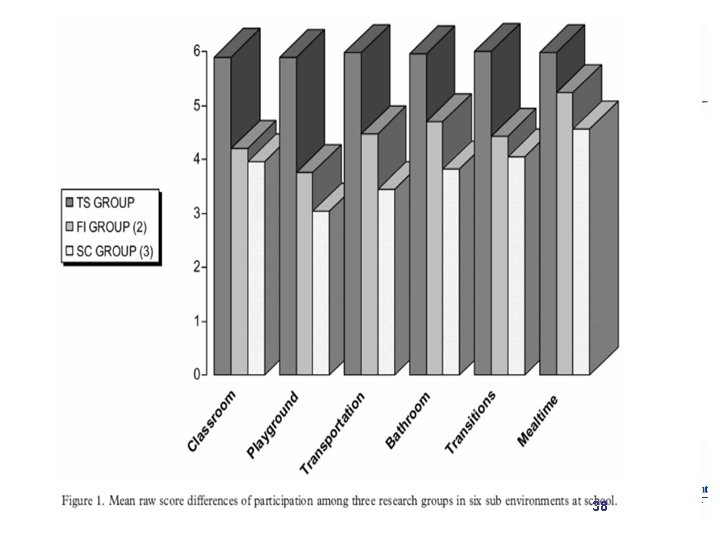 38
38
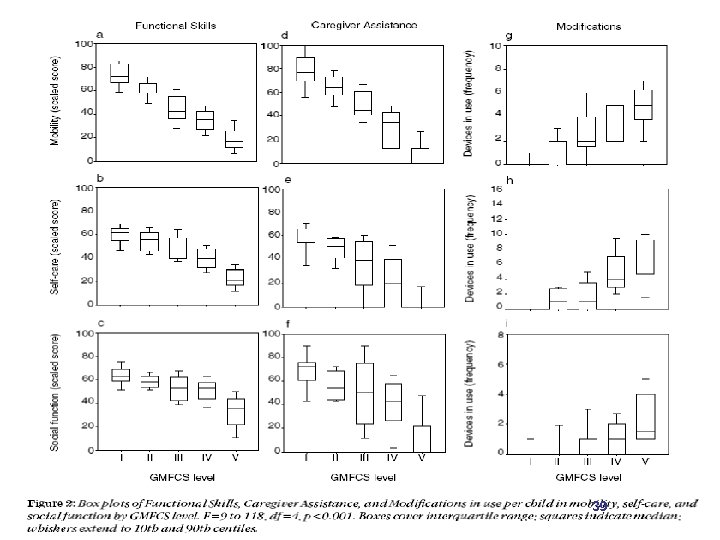 39
39
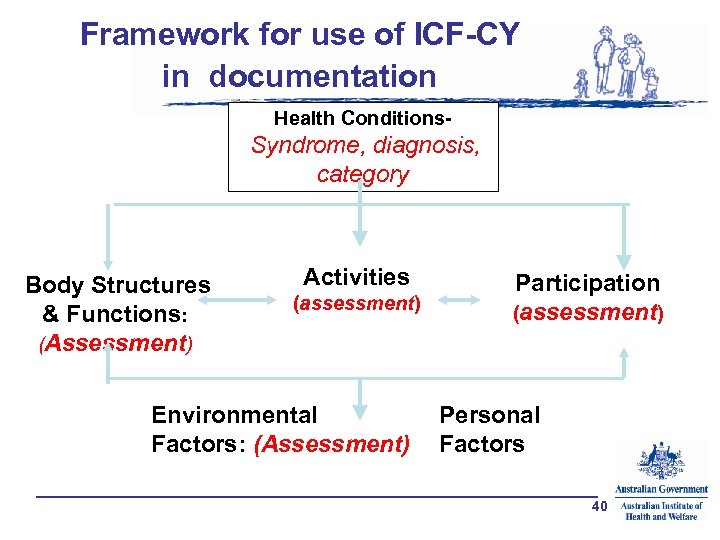 Framework for use of ICF-CY in documentation Health Conditions- Syndrome, diagnosis, category Body Structures & Functions: (Assessment) Activities (assessment) Environmental Factors: (Assessment) Participation (assessment) Personal Factors 40
Framework for use of ICF-CY in documentation Health Conditions- Syndrome, diagnosis, category Body Structures & Functions: (Assessment) Activities (assessment) Environmental Factors: (Assessment) Participation (assessment) Personal Factors 40


