d29e6c49e62a05cc79cd593daf34427b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 ICD-10 -CM Diagnosis Coding and Documentation Teresa Stallman, MBA, RHIT AHIMA Approved ICD-10 Trainer
ICD-10 -CM Diagnosis Coding and Documentation Teresa Stallman, MBA, RHIT AHIMA Approved ICD-10 Trainer
 Agenda • Overview of ICD-10 -CM • Challenges • Keys to engaging clinicians • Coding examples • Resources
Agenda • Overview of ICD-10 -CM • Challenges • Keys to engaging clinicians • Coding examples • Resources
 Overview of ICD-10 -CM
Overview of ICD-10 -CM
 Overview: ICD-10 -CM • International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification • Effective date: Oct. 1, 2015 • Dates of service: Office visits: Oct. 1, 2015 Inpatient spanning before/after Oct. 1, 2015 Do not split bill • Usage: Improve health outcomes Improve clinical pathways
Overview: ICD-10 -CM • International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification • Effective date: Oct. 1, 2015 • Dates of service: Office visits: Oct. 1, 2015 Inpatient spanning before/after Oct. 1, 2015 Do not split bill • Usage: Improve health outcomes Improve clinical pathways
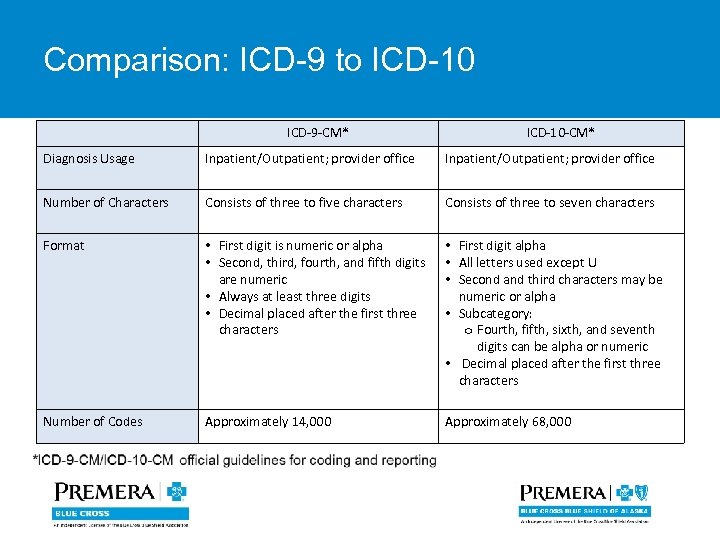 Comparison: ICD-9 to ICD-10 ICD-9 -CM* ICD-10 -CM* Diagnosis Usage Inpatient/Outpatient; provider office Number of Characters Consists of three to five characters Consists of three to seven characters Format • First digit is numeric or alpha • Second, third, fourth, and fifth digits are numeric • Always at least three digits • Decimal placed after the first three characters • First digit alpha • All letters used except U • Second and third characters may be numeric or alpha • Subcategory: o Fourth, fifth, sixth, and seventh digits can be alpha or numeric • Decimal placed after the first three characters Number of Codes Approximately 14, 000 Approximately 68, 000
Comparison: ICD-9 to ICD-10 ICD-9 -CM* ICD-10 -CM* Diagnosis Usage Inpatient/Outpatient; provider office Number of Characters Consists of three to five characters Consists of three to seven characters Format • First digit is numeric or alpha • Second, third, fourth, and fifth digits are numeric • Always at least three digits • Decimal placed after the first three characters • First digit alpha • All letters used except U • Second and third characters may be numeric or alpha • Subcategory: o Fourth, fifth, sixth, and seventh digits can be alpha or numeric • Decimal placed after the first three characters Number of Codes Approximately 14, 000 Approximately 68, 000
 Challenges
Challenges
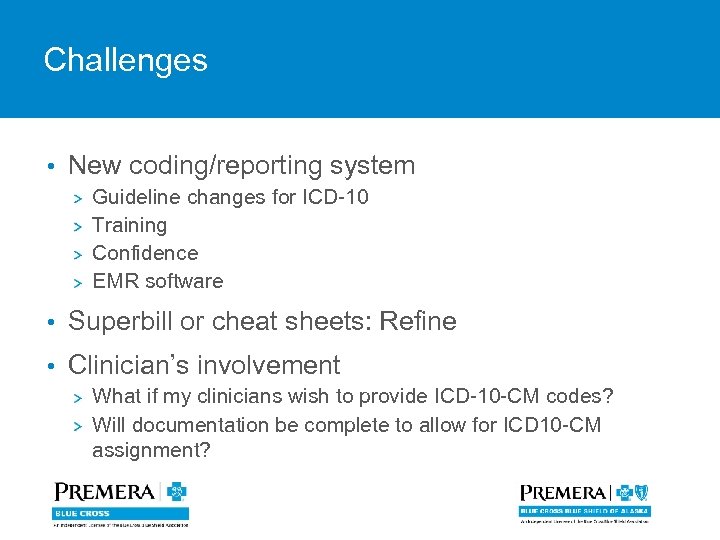 Challenges • New coding/reporting system Guideline changes for ICD-10 Training Confidence EMR software • Superbill or cheat sheets: Refine • Clinician’s involvement What if my clinicians wish to provide ICD-10 -CM codes? Will documentation be complete to allow for ICD 10 -CM assignment?
Challenges • New coding/reporting system Guideline changes for ICD-10 Training Confidence EMR software • Superbill or cheat sheets: Refine • Clinician’s involvement What if my clinicians wish to provide ICD-10 -CM codes? Will documentation be complete to allow for ICD 10 -CM assignment?
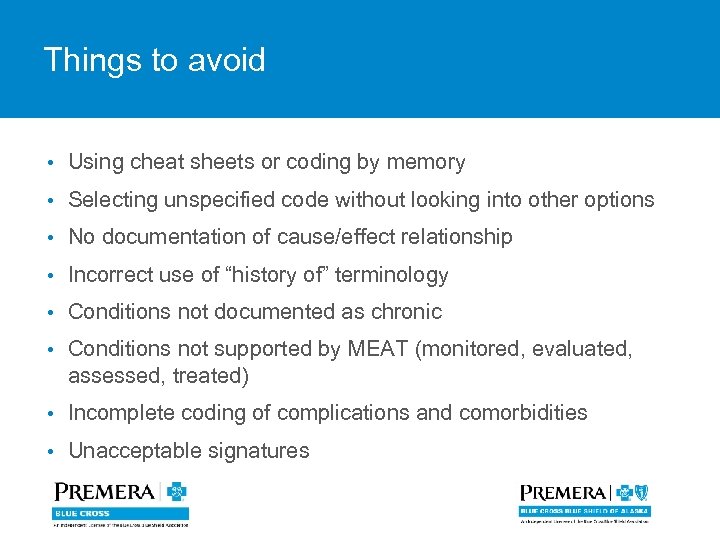 Things to avoid • Using cheat sheets or coding by memory • Selecting unspecified code without looking into other options • No documentation of cause/effect relationship • Incorrect use of “history of” terminology • Conditions not documented as chronic • Conditions not supported by MEAT (monitored, evaluated, assessed, treated) • Incomplete coding of complications and comorbidities • Unacceptable signatures
Things to avoid • Using cheat sheets or coding by memory • Selecting unspecified code without looking into other options • No documentation of cause/effect relationship • Incorrect use of “history of” terminology • Conditions not documented as chronic • Conditions not supported by MEAT (monitored, evaluated, assessed, treated) • Incomplete coding of complications and comorbidities • Unacceptable signatures
 Keys to Engaging with Clinicians
Keys to Engaging with Clinicians
 Before engaging with clinicians • Compare ICD-9 and ICD-10 coding guidelines • Identify the top services for the practice and/or by clinician • Review documentation of medical records • Code medical record ICD-10 scenarios • Identify gaps in documentation • Create templates by diagnosis, focusing on necessary elements: Incorporating identified changes in coding guidelines for ICD-10 • Identify the clinician(s) who consistently document fully: Liaison to clinician peers
Before engaging with clinicians • Compare ICD-9 and ICD-10 coding guidelines • Identify the top services for the practice and/or by clinician • Review documentation of medical records • Code medical record ICD-10 scenarios • Identify gaps in documentation • Create templates by diagnosis, focusing on necessary elements: Incorporating identified changes in coding guidelines for ICD-10 • Identify the clinician(s) who consistently document fully: Liaison to clinician peers
 Engaging your clinicians • Present findings By identified service De-identify provider name Include reimbursement • Develop action plan for improvement • Repeat audit
Engaging your clinicians • Present findings By identified service De-identify provider name Include reimbursement • Develop action plan for improvement • Repeat audit
 Documentation/Coding Examples
Documentation/Coding Examples
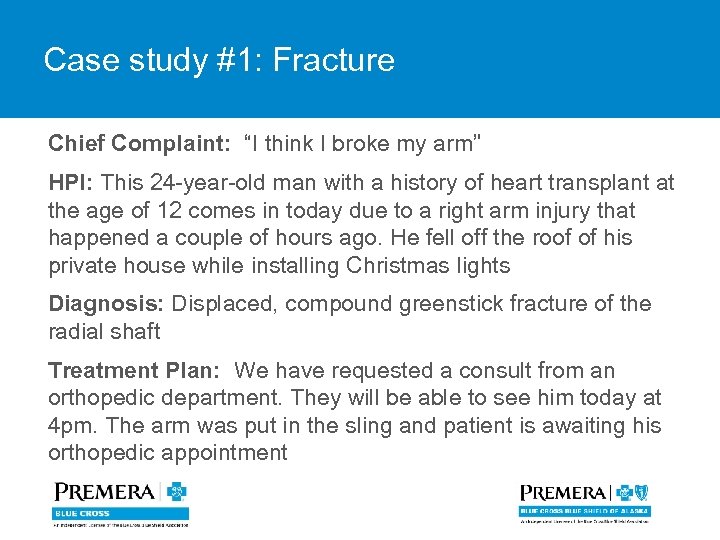 Case study #1: Fracture Chief Complaint: “I think I broke my arm” HPI: This 24 -year-old man with a history of heart transplant at the age of 12 comes in today due to a right arm injury that happened a couple of hours ago. He fell off the roof of his private house while installing Christmas lights Diagnosis: Displaced, compound greenstick fracture of the radial shaft Treatment Plan: We have requested a consult from an orthopedic department. They will be able to see him today at 4 pm. The arm was put in the sling and patient is awaiting his orthopedic appointment
Case study #1: Fracture Chief Complaint: “I think I broke my arm” HPI: This 24 -year-old man with a history of heart transplant at the age of 12 comes in today due to a right arm injury that happened a couple of hours ago. He fell off the roof of his private house while installing Christmas lights Diagnosis: Displaced, compound greenstick fracture of the radial shaft Treatment Plan: We have requested a consult from an orthopedic department. They will be able to see him today at 4 pm. The arm was put in the sling and patient is awaiting his orthopedic appointment
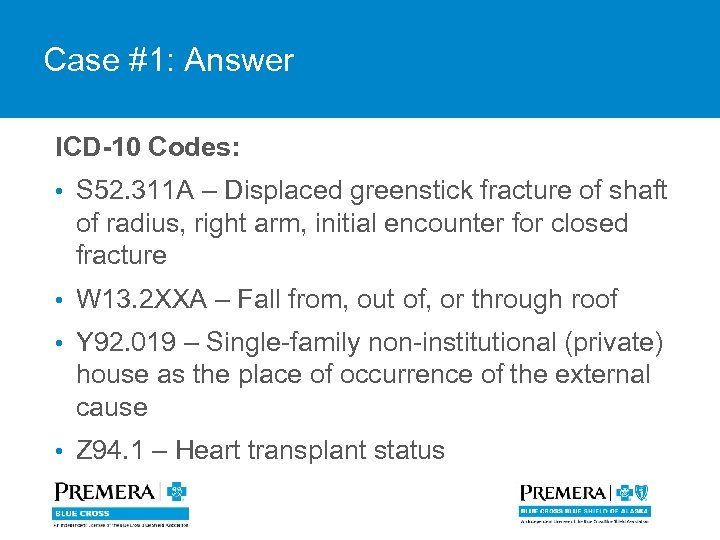 Case #1: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • S 52. 311 A – Displaced greenstick fracture of shaft of radius, right arm, initial encounter for closed fracture • W 13. 2 XXA – Fall from, out of, or through roof • Y 92. 019 – Single-family non-institutional (private) house as the place of occurrence of the external cause • Z 94. 1 – Heart transplant status
Case #1: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • S 52. 311 A – Displaced greenstick fracture of shaft of radius, right arm, initial encounter for closed fracture • W 13. 2 XXA – Fall from, out of, or through roof • Y 92. 019 – Single-family non-institutional (private) house as the place of occurrence of the external cause • Z 94. 1 – Heart transplant status
 Case study #2: Mental health Chief Complaint: “I have a lot of stress. ” HPI: Male patient had been seen for anxiety and depression since 2001. Currently patient has depressive symptoms of crying, insomnia, anorexia with recent weight loss, and psychomotor retardation. Patient has been taking Wellbutrin 150 mg daily, Lexapro 20 mg daily, and Xanax 1 mg 3 times a day. Patient also has asthma, which is well controlled with his Albuterol. It usually becomes an issue during his panic/anxiety attacks. Diagnosis: AXIS I 1. Major depressive disorder, recurrent, severe with psychotic symptoms. 2. Panic/anxiety disorder without agoraphobia. Treatment Plan: Because of severe psychotic symptoms, this patient will be transferred to the nearby hospital for inpatient admission to their psychiatric unit. Patient agrees with this plan
Case study #2: Mental health Chief Complaint: “I have a lot of stress. ” HPI: Male patient had been seen for anxiety and depression since 2001. Currently patient has depressive symptoms of crying, insomnia, anorexia with recent weight loss, and psychomotor retardation. Patient has been taking Wellbutrin 150 mg daily, Lexapro 20 mg daily, and Xanax 1 mg 3 times a day. Patient also has asthma, which is well controlled with his Albuterol. It usually becomes an issue during his panic/anxiety attacks. Diagnosis: AXIS I 1. Major depressive disorder, recurrent, severe with psychotic symptoms. 2. Panic/anxiety disorder without agoraphobia. Treatment Plan: Because of severe psychotic symptoms, this patient will be transferred to the nearby hospital for inpatient admission to their psychiatric unit. Patient agrees with this plan
 Case #2: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • F 33. 3 - Major depressive disorder, recurrent, severe with psychotic symptoms • F 41. 0 – Panic disorder without agoraphobia • J 45. 909 – Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated
Case #2: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • F 33. 3 - Major depressive disorder, recurrent, severe with psychotic symptoms • F 41. 0 – Panic disorder without agoraphobia • J 45. 909 – Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated
 Case study #3: Primary care Chief Complaint: Annual physical exam HPI: This 64 -year-old patient comes in for her annual physical exam. She is also being treated for DM, HTN, and CKD. Diagnosis: 1. Malignant Hypertension 2. Stage V Chronic Kidney Disease 3. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Plan: Her HTN and CKD are being monitored and treated by Dr. Smith. Continue the plan of treatment as prescribed. Her diabetes is well controlled with Lantus, diet, and exercise. Continue same medication dosage, monitor glucose level at home, and return in three months for recheck
Case study #3: Primary care Chief Complaint: Annual physical exam HPI: This 64 -year-old patient comes in for her annual physical exam. She is also being treated for DM, HTN, and CKD. Diagnosis: 1. Malignant Hypertension 2. Stage V Chronic Kidney Disease 3. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Plan: Her HTN and CKD are being monitored and treated by Dr. Smith. Continue the plan of treatment as prescribed. Her diabetes is well controlled with Lantus, diet, and exercise. Continue same medication dosage, monitor glucose level at home, and return in three months for recheck
 Case #3: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • Z 00. 00 – Encounter for general adult medical examination without abnormal findings • I 12. 0 - Hypertensive chronic kidney disease stage V chronic kidney disease or end stage renal disease • N 18. 5 - Chronic kidney disease, stage V • E 11. 9 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications • Z 79. 4 - Long-term (current) use of insulin
Case #3: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • Z 00. 00 – Encounter for general adult medical examination without abnormal findings • I 12. 0 - Hypertensive chronic kidney disease stage V chronic kidney disease or end stage renal disease • N 18. 5 - Chronic kidney disease, stage V • E 11. 9 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications • Z 79. 4 - Long-term (current) use of insulin
 Case study #4: Pregnancy Chief Complaint: OB/GYN routine follow-up visit HPI: This 22 -year-old pleasant lady with diabetes mellitus type 1 in her second trimester of pregnancy comes in for a follow-up visit. Diagnosis: 1. Pre-existing DM, Type 1, in pregnancy 2. 18 weeks gestation Treatment Plan: The patient’s blood sugar is well controlled and the patient tells us that she is doing well with her diet and exercise regimen. Patient should follow up in one month.
Case study #4: Pregnancy Chief Complaint: OB/GYN routine follow-up visit HPI: This 22 -year-old pleasant lady with diabetes mellitus type 1 in her second trimester of pregnancy comes in for a follow-up visit. Diagnosis: 1. Pre-existing DM, Type 1, in pregnancy 2. 18 weeks gestation Treatment Plan: The patient’s blood sugar is well controlled and the patient tells us that she is doing well with her diet and exercise regimen. Patient should follow up in one month.
 Case #4: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • O 24. 012 – Pre-existing diabetes mellitus, type 1, in pregnancy, second trimester • Z 3 A. 18 – 18 weeks gestation of pregnancy
Case #4: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • O 24. 012 – Pre-existing diabetes mellitus, type 1, in pregnancy, second trimester • Z 3 A. 18 – 18 weeks gestation of pregnancy
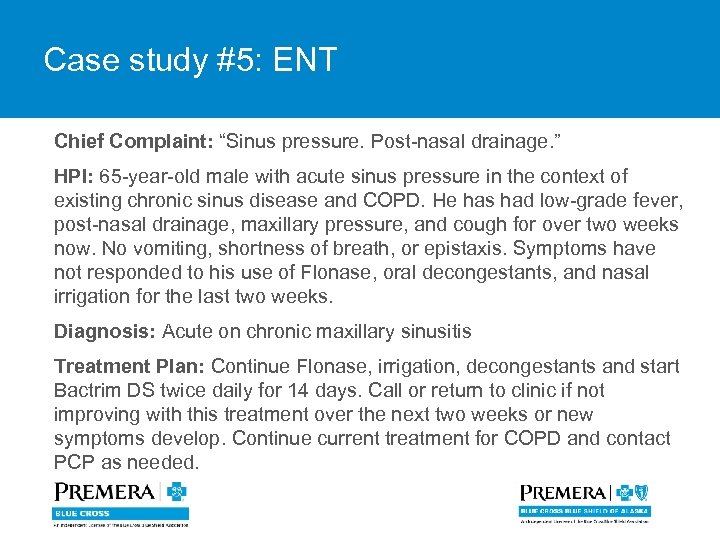 Case study #5: ENT Chief Complaint: “Sinus pressure. Post-nasal drainage. ” HPI: 65 -year-old male with acute sinus pressure in the context of existing chronic sinus disease and COPD. He has had low-grade fever, post-nasal drainage, maxillary pressure, and cough for over two weeks now. No vomiting, shortness of breath, or epistaxis. Symptoms have not responded to his use of Flonase, oral decongestants, and nasal irrigation for the last two weeks. Diagnosis: Acute on chronic maxillary sinusitis Treatment Plan: Continue Flonase, irrigation, decongestants and start Bactrim DS twice daily for 14 days. Call or return to clinic if not improving with this treatment over the next two weeks or new symptoms develop. Continue current treatment for COPD and contact PCP as needed.
Case study #5: ENT Chief Complaint: “Sinus pressure. Post-nasal drainage. ” HPI: 65 -year-old male with acute sinus pressure in the context of existing chronic sinus disease and COPD. He has had low-grade fever, post-nasal drainage, maxillary pressure, and cough for over two weeks now. No vomiting, shortness of breath, or epistaxis. Symptoms have not responded to his use of Flonase, oral decongestants, and nasal irrigation for the last two weeks. Diagnosis: Acute on chronic maxillary sinusitis Treatment Plan: Continue Flonase, irrigation, decongestants and start Bactrim DS twice daily for 14 days. Call or return to clinic if not improving with this treatment over the next two weeks or new symptoms develop. Continue current treatment for COPD and contact PCP as needed.
 Case #5: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • J 01. 00 Acute maxillary sinusitis, unspecified • J 32. 0 Chronic maxillary sinusitis • J 44. 9 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, unspecified
Case #5: Answer ICD-10 Codes: • J 01. 00 Acute maxillary sinusitis, unspecified • J 32. 0 Chronic maxillary sinusitis • J 44. 9 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, unspecified
 Resources
Resources
 Website links • AHIMA: www. ahima. org/education/onlineed/Programs/ICD 10 • AAPC: www. aapc. com/medical-coding • CMS: www. cms. gov/ICD 10 • CMS: www. roadto 10. org • ICD-9 to ICD-10: www. icd 10 data. com/convert • OHP: http: //www. ahima. org/education/onlineed/Program s/ICD 10
Website links • AHIMA: www. ahima. org/education/onlineed/Programs/ICD 10 • AAPC: www. aapc. com/medical-coding • CMS: www. cms. gov/ICD 10 • CMS: www. roadto 10. org • ICD-9 to ICD-10: www. icd 10 data. com/convert • OHP: http: //www. ahima. org/education/onlineed/Program s/ICD 10
 Next webinar • Go! ICD-10 Coding, Risk Adjustment, Audit Preparation presented by Tonya Owens, Coding Quality Educator. November 17, 12 -1 p. m. • Contact information Dedicated provider line at 1 -877 -342 -5258 (WA) 1800 -722 -4714 (AK), option 4 Email us at providerengagementteam@premera. com Fax: 425 -918 -6738; 855 -332 -4527
Next webinar • Go! ICD-10 Coding, Risk Adjustment, Audit Preparation presented by Tonya Owens, Coding Quality Educator. November 17, 12 -1 p. m. • Contact information Dedicated provider line at 1 -877 -342 -5258 (WA) 1800 -722 -4714 (AK), option 4 Email us at providerengagementteam@premera. com Fax: 425 -918 -6738; 855 -332 -4527
 Questions?
Questions?
 Thank You for Attending 034228 (08 -2015)
Thank You for Attending 034228 (08 -2015)


