36c86050f3c8452f9936ec11e5d108d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79
 ICD-10 Changes Everything in the Revenue Cycle Presented by: Day Egusquiza, President AR Systems, Inc. (W/ Karen Kvarfordt, RHIA, AHIMA ICD-10 Certified Trainer) President, Diagnosis. Plus, Inc.
ICD-10 Changes Everything in the Revenue Cycle Presented by: Day Egusquiza, President AR Systems, Inc. (W/ Karen Kvarfordt, RHIA, AHIMA ICD-10 Certified Trainer) President, Diagnosis. Plus, Inc.
 ICD-10 Implementation WHO ? What ? When ? Why ? How ? 2
ICD-10 Implementation WHO ? What ? When ? Why ? How ? 2
 It’s on your doorstep! The biggest change to happen in Health Information Management and Revenue Cycle in more than 30 years. Preparation is the KEY! Will you be ready? 3
It’s on your doorstep! The biggest change to happen in Health Information Management and Revenue Cycle in more than 30 years. Preparation is the KEY! Will you be ready? 3
 ICD-10 WHO (World Health Organization) owns & publishes ICD (International Classification of Diseases). WHO endorsed ICD-10 in 1990; members began using ICD-10 or modifications in 1994. U. S. is only industrialized country not using ICD 10, for morbidity reporting (coding diseases, illnesses, injuries in a healthcare setting). The U. S. has used ICD-10 for mortality reporting (coding of death certificates by Vital Statistics offices) since 1999. 4
ICD-10 WHO (World Health Organization) owns & publishes ICD (International Classification of Diseases). WHO endorsed ICD-10 in 1990; members began using ICD-10 or modifications in 1994. U. S. is only industrialized country not using ICD 10, for morbidity reporting (coding diseases, illnesses, injuries in a healthcare setting). The U. S. has used ICD-10 for mortality reporting (coding of death certificates by Vital Statistics offices) since 1999. 4
 Countries Using ICD-10 For Case Mix United Kingdom (1995) Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden (1994 – 1997) France (1997) Australia (1998) Belgium (1999) Germany (2000) Canada (2001) U. S. (2015) (Reimbursement + Case Mix + HIPAA Standard Transaction, 2003) That’s why! 5
Countries Using ICD-10 For Case Mix United Kingdom (1995) Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden (1994 – 1997) France (1997) Australia (1998) Belgium (1999) Germany (2000) Canada (2001) U. S. (2015) (Reimbursement + Case Mix + HIPAA Standard Transaction, 2003) That’s why! 5
 Coordination & Maintenance Committee ICD-9 -CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee is made of 4 parties: ◦ National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) – responsible for diagnoses (Volumes 1 & 2) ◦ Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) – responsible for procedures (Volume 3) ◦ American Hospital Association (AHA) ◦ American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) 6
Coordination & Maintenance Committee ICD-9 -CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee is made of 4 parties: ◦ National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) – responsible for diagnoses (Volumes 1 & 2) ◦ Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) – responsible for procedures (Volume 3) ◦ American Hospital Association (AHA) ◦ American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) 6
 Why Should We Do ICD-10? What is the benefit to the provider? ◦ Dramatic improvement in the assignment of costs to procedures performed. ICD-10 will allow us to develop meaningful estimates about what a disease state or a procedure costs us, while ICD-9 is limited in what it can do in this regard. ◦ Identify opportunities to avoid cost & improve lives. Additional information in an ICD-10 diagnosis code includes severity and specific comorbidity, but it can also include information about demographics and some of the underlying reasons for the diagnosis. 7
Why Should We Do ICD-10? What is the benefit to the provider? ◦ Dramatic improvement in the assignment of costs to procedures performed. ICD-10 will allow us to develop meaningful estimates about what a disease state or a procedure costs us, while ICD-9 is limited in what it can do in this regard. ◦ Identify opportunities to avoid cost & improve lives. Additional information in an ICD-10 diagnosis code includes severity and specific comorbidity, but it can also include information about demographics and some of the underlying reasons for the diagnosis. 7
 Additional Benefits… Share higher-quality data with other health care providers. ◦ ICD-10 increases the amount of “specific” specific information in every diagnosis code and makes this more valuable to other providers. For example, ICD-9 has a code for laceration of an artery. ICD-10 lets you know if that artery was in someone’s finger or in their heart. 8
Additional Benefits… Share higher-quality data with other health care providers. ◦ ICD-10 increases the amount of “specific” specific information in every diagnosis code and makes this more valuable to other providers. For example, ICD-9 has a code for laceration of an artery. ICD-10 lets you know if that artery was in someone’s finger or in their heart. 8
 Reimbursements will better align with activity & cost. ◦ Payers will reimburse severe & complex cases better and simple cases at lower rates. How? By the diagnosis codes! codes 9
Reimbursements will better align with activity & cost. ◦ Payers will reimburse severe & complex cases better and simple cases at lower rates. How? By the diagnosis codes! codes 9
 Here’s an Example Imagine you had a patient who was noncompliant with their medical therapy. In ICD-9, the only code we have available is V 15. 81 (personal history of noncompliance with medical treatment). Is the patient noncompliant because of their own personal reason? Or something else? 10
Here’s an Example Imagine you had a patient who was noncompliant with their medical therapy. In ICD-9, the only code we have available is V 15. 81 (personal history of noncompliance with medical treatment). Is the patient noncompliant because of their own personal reason? Or something else? 10
 How Will it Look in ICD-10? Z 9111 (Patient’s noncompliance with dietary regimen) Z 91120 (Patient's intentional underdosing of medication regimen due to financial hardship) Z 91128 (Patient’s intentional underdosing of medication regimen for other reason) Z 91130 (Patient’s unintentional underdosing of medication regimen due to age-related debility) Z 91138 (Patient’s unintentional underdosing of medication regimen for other reason) Shows whether or not the patient’s noncompliance was intentional, but also identifies if the patient needs some form of assistance from social services, etc. 11
How Will it Look in ICD-10? Z 9111 (Patient’s noncompliance with dietary regimen) Z 91120 (Patient's intentional underdosing of medication regimen due to financial hardship) Z 91128 (Patient’s intentional underdosing of medication regimen for other reason) Z 91130 (Patient’s unintentional underdosing of medication regimen due to age-related debility) Z 91138 (Patient’s unintentional underdosing of medication regimen for other reason) Shows whether or not the patient’s noncompliance was intentional, but also identifies if the patient needs some form of assistance from social services, etc. 11
 What is ICD-10 -CM and ICD-10 -PCS? 12
What is ICD-10 -CM and ICD-10 -PCS? 12
 What is ICD-9 -CM? International Classification of Diseases, 9 th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9 -CM) is based on the WHO ICD-9 standard diagnostic classification system. Volumes 1 & 2 (diagnosis codes) applies to ALL settings. Volume 3 (procedure codes) applies to inpatient hospital only. ICD-9 -CM diagnosis codes are required under HIPAA for uniform claim submission (2003). 13
What is ICD-9 -CM? International Classification of Diseases, 9 th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9 -CM) is based on the WHO ICD-9 standard diagnostic classification system. Volumes 1 & 2 (diagnosis codes) applies to ALL settings. Volume 3 (procedure codes) applies to inpatient hospital only. ICD-9 -CM diagnosis codes are required under HIPAA for uniform claim submission (2003). 13
 What is ICD-10 -CM/PCS? Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) mandated that HIPAA covered entities must update medical coding sets, effective October 1, 2015. sets 2015 Diagnosis code set changes from ICD-9 -CM to ICD-10 -CM Hospital inpatient procedure code set changes from ICD-9 -CM (Volume 3) to ICD-10 -PCS No impact on CPT and/or HCPCS codes. Yeah! We will still report CPT codes for all outpatient procedures/services & physician hospital visits to Observation and Inpatients (E&Ms). 14
What is ICD-10 -CM/PCS? Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) mandated that HIPAA covered entities must update medical coding sets, effective October 1, 2015. sets 2015 Diagnosis code set changes from ICD-9 -CM to ICD-10 -CM Hospital inpatient procedure code set changes from ICD-9 -CM (Volume 3) to ICD-10 -PCS No impact on CPT and/or HCPCS codes. Yeah! We will still report CPT codes for all outpatient procedures/services & physician hospital visits to Observation and Inpatients (E&Ms). 14
 The ICD-10 Impact! ICD-10 -CM (Diagnoses) ◦ Will be used by all hospitals, providers, clinics, lab, radiology, psych, rehab, nursing homes, etc. ICD-10 -PCS (Procedures) ◦ Will be used only for hospital claims for inpatient hospital procedures CPT/HCPCS – No change! ◦ Procedures for Hospital Outpatients, Physician Visits, Lab and Radiology Outpatients, etc. 15
The ICD-10 Impact! ICD-10 -CM (Diagnoses) ◦ Will be used by all hospitals, providers, clinics, lab, radiology, psych, rehab, nursing homes, etc. ICD-10 -PCS (Procedures) ◦ Will be used only for hospital claims for inpatient hospital procedures CPT/HCPCS – No change! ◦ Procedures for Hospital Outpatients, Physician Visits, Lab and Radiology Outpatients, etc. 15
 When is Implementation? Another year delay October 1, 2015 – Compliance date for implementation of ICD-10 -CM (diagnoses) and ICD-10 -PCS (inpatient procedures). CMS initially stated that there would be no grace period. Then why the 1 year delay? 16
When is Implementation? Another year delay October 1, 2015 – Compliance date for implementation of ICD-10 -CM (diagnoses) and ICD-10 -PCS (inpatient procedures). CMS initially stated that there would be no grace period. Then why the 1 year delay? 16
 ICD-10 Implementation Span Date CMS clarifies policy for processing split claims for hospital encounters that span the ICD-10 implementation date. ◦ MLN (Medical Learning Network) Matters Number: SE 1325 Split Claims ◦ Require providers split the claim so all ICD-9 codes remain on one claim with Date of Service (DOS) through September 30, 2015, and all ICD-10 codes placed on the other claim 2015 with DOS beginning October 1, 2015 and later ◦ CMS announces end to end testing, beginning Jan 2015. ◦ Same guidance for Inpatient and Outpatient encounters! 17
ICD-10 Implementation Span Date CMS clarifies policy for processing split claims for hospital encounters that span the ICD-10 implementation date. ◦ MLN (Medical Learning Network) Matters Number: SE 1325 Split Claims ◦ Require providers split the claim so all ICD-9 codes remain on one claim with Date of Service (DOS) through September 30, 2015, and all ICD-10 codes placed on the other claim 2015 with DOS beginning October 1, 2015 and later ◦ CMS announces end to end testing, beginning Jan 2015. ◦ Same guidance for Inpatient and Outpatient encounters! 17
 Non-HIM Uses For ICD-9 -CMPreparing for ICD-10 -CM – as we move from 15, 000 codes to over 70, 000 codes 18
Non-HIM Uses For ICD-9 -CMPreparing for ICD-10 -CM – as we move from 15, 000 codes to over 70, 000 codes 18
 ICD -10 Continues the Documentation Enhancement Story Along with focusing on enhanced documentation to support inpt level of care, the expanded narrative to support ICD 10 conversion continues the story. Support team to make this happen: Integrated CDI with feedback from coders PFS /denial ‘busters’ with feedback to CDI Payer new edits –PFS monitors and advises IT with ability to test, submit, and maintain both ICD 9 and ICD 10 post go live. Eyes in the record – nursing/24 -7. RAC 2014 19
ICD -10 Continues the Documentation Enhancement Story Along with focusing on enhanced documentation to support inpt level of care, the expanded narrative to support ICD 10 conversion continues the story. Support team to make this happen: Integrated CDI with feedback from coders PFS /denial ‘busters’ with feedback to CDI Payer new edits –PFS monitors and advises IT with ability to test, submit, and maintain both ICD 9 and ICD 10 post go live. Eyes in the record – nursing/24 -7. RAC 2014 19
 Ideas for Physician Engagement Rollout ‘monthly dedicated specialty specific’ audit and training. EX) May is ER month. Coders dual code an identified sample of ER claims. Identify ‘at risk’ documentation by provider. Turn into ‘easy to implement documentation. EX) If the facility has a CDI team, work cooperatively with the coding team to ‘coach/que’ the ER providers thru their month. EX) Do an month end dual coding – show improvement or challenges. 20
Ideas for Physician Engagement Rollout ‘monthly dedicated specialty specific’ audit and training. EX) May is ER month. Coders dual code an identified sample of ER claims. Identify ‘at risk’ documentation by provider. Turn into ‘easy to implement documentation. EX) If the facility has a CDI team, work cooperatively with the coding team to ‘coach/que’ the ER providers thru their month. EX) Do an month end dual coding – show improvement or challenges. 20
 Exploring new partnerships with provider offices Physician dictates, hospital coders code, UB is created. NEW: Why not share the codes with the providers who are attached to the account? Why repeat the same coding process in the office? NEW: Brown bag coding luncheons with the provider offices. Office brings samples to code, hospital coders code while teaching ICD 10 concepts. (TX: Lunch & Learn weekly) NEW: Hospital becomes the outsourcing company to assist small practices with coding. 21
Exploring new partnerships with provider offices Physician dictates, hospital coders code, UB is created. NEW: Why not share the codes with the providers who are attached to the account? Why repeat the same coding process in the office? NEW: Brown bag coding luncheons with the provider offices. Office brings samples to code, hospital coders code while teaching ICD 10 concepts. (TX: Lunch & Learn weekly) NEW: Hospital becomes the outsourcing company to assist small practices with coding. 21
 Non-HIM Impact Areas (HINT: Denial Busting) Scheduling –precerts, eligibility. Claims submission with scrubber – both ICD 9 and ICD 10 codes ( Min-1 yr ability to rebill, do duality with IT systems. ) Medical necessity CPT codes – software, manual processes, cheat sheets Recurring accounts – will need new precerts & recoded after 10 -1 -2015 Payer acceptance of new ICD 10 codes PLUS ICD 9 codes – 2 batches Payer contract language – Dx codes Payer remark codes/denial codes CDM – Hardcoded RT/LT needs to match with the soft coded RT/LT ICD 10 Trauma/Tumor registry - translated All IT systems within the organization 837/835 HIPAA transaction sets – new for ICD 10 locators Quality of care indicators – translated P 4 P indicators/Outcome Measures – translated Decision Support, utilization patterns, benchmarking – translated Medical care review – by provider, by dx, by LOS New business plan research/future healthcare trends – translated Monitoring and analyzing the incidence of disease & other health problems –translated & new Embedded dx attached to CPT codes Population Health History vs Current Revise forms to include new ICD 10 codes. 22
Non-HIM Impact Areas (HINT: Denial Busting) Scheduling –precerts, eligibility. Claims submission with scrubber – both ICD 9 and ICD 10 codes ( Min-1 yr ability to rebill, do duality with IT systems. ) Medical necessity CPT codes – software, manual processes, cheat sheets Recurring accounts – will need new precerts & recoded after 10 -1 -2015 Payer acceptance of new ICD 10 codes PLUS ICD 9 codes – 2 batches Payer contract language – Dx codes Payer remark codes/denial codes CDM – Hardcoded RT/LT needs to match with the soft coded RT/LT ICD 10 Trauma/Tumor registry - translated All IT systems within the organization 837/835 HIPAA transaction sets – new for ICD 10 locators Quality of care indicators – translated P 4 P indicators/Outcome Measures – translated Decision Support, utilization patterns, benchmarking – translated Medical care review – by provider, by dx, by LOS New business plan research/future healthcare trends – translated Monitoring and analyzing the incidence of disease & other health problems –translated & new Embedded dx attached to CPT codes Population Health History vs Current Revise forms to include new ICD 10 codes. 22
 Departments who are impacted by ICD -10 changes 1 st point of contact =provider offices/dx to get precertifications with payers. Pre-auth with payers = internal staff, UR Medically necessary edit = diagnosis to screen diagnosis against CPT tests to determine if Medicare or other payers will allow. ABN completed with Medicare pts prior to the test. Internal IT, scrubber company, payer’s IT systems = prior to go live and post go live. Concern: Worker’s Comp and Liability not covered entities/HIPAA Standard Transaction. Maintain both ICD 9 & ICD 10? ? RAC 2014 23
Departments who are impacted by ICD -10 changes 1 st point of contact =provider offices/dx to get precertifications with payers. Pre-auth with payers = internal staff, UR Medically necessary edit = diagnosis to screen diagnosis against CPT tests to determine if Medicare or other payers will allow. ABN completed with Medicare pts prior to the test. Internal IT, scrubber company, payer’s IT systems = prior to go live and post go live. Concern: Worker’s Comp and Liability not covered entities/HIPAA Standard Transaction. Maintain both ICD 9 & ICD 10? ? RAC 2014 23
 More areas impacted by ICD 10 Lab, Chemo, Imaging, Cardiology, Specialty services = all usually require “medically necessary payer screening” prior to the procedure. Cheat sheets = gone! Doctor offices = new encounter forms. Rehab = Work comp pre certs. (? ICD 9 & 10) PFS = new rejections, new return to provider edits, potential new denials HIM/the clean up crew = all payer rejections due to coding, internal issues, more? IT decision support = historical to current codes Others? = any area tracking by Dx code…more! RAC 2014 24
More areas impacted by ICD 10 Lab, Chemo, Imaging, Cardiology, Specialty services = all usually require “medically necessary payer screening” prior to the procedure. Cheat sheets = gone! Doctor offices = new encounter forms. Rehab = Work comp pre certs. (? ICD 9 & 10) PFS = new rejections, new return to provider edits, potential new denials HIM/the clean up crew = all payer rejections due to coding, internal issues, more? IT decision support = historical to current codes Others? = any area tracking by Dx code…more! RAC 2014 24
 Who Needs to Understand ICD-10? Beyond the coders… PFS leadership as payers may reject based on ICD -10 coding and medical necessary codes & denial software. PFS leadership and contracting to ensure contracts can accept both ICD-9 and ICD-10 on the UBs post go live. UR and all care mgt as payers will need to be able to do pre-certifications and concurrent review with ICD-10. Decision support and all areas using ICD-9/10 coding for tracking, reporting, etc. (Trauma registry, Tumor registry, outcome comparisons, contracting, etc. ). IT leadership must be involved to ensure all impacted areas are ready. A team leader or leaders are identified. 25
Who Needs to Understand ICD-10? Beyond the coders… PFS leadership as payers may reject based on ICD -10 coding and medical necessary codes & denial software. PFS leadership and contracting to ensure contracts can accept both ICD-9 and ICD-10 on the UBs post go live. UR and all care mgt as payers will need to be able to do pre-certifications and concurrent review with ICD-10. Decision support and all areas using ICD-9/10 coding for tracking, reporting, etc. (Trauma registry, Tumor registry, outcome comparisons, contracting, etc. ). IT leadership must be involved to ensure all impacted areas are ready. A team leader or leaders are identified. 25
 Payer Readiness - Letters with timelines to get started, test, dialogue UB submissions with ICD-9 and ICD-10 conversion dates Denials with new reasons –as ICD-10 is far more specific Contract language that addresses ICD-10 inclusions/exclusions Claim scrubbers/payer scrubbers – ABN issues (LCD/NDC dx codes), ‘if ‘ rules, edits Pre-authorization process/coverage WC and Liability are not subject to HIPAA standard transactions. Will they convert? 26
Payer Readiness - Letters with timelines to get started, test, dialogue UB submissions with ICD-9 and ICD-10 conversion dates Denials with new reasons –as ICD-10 is far more specific Contract language that addresses ICD-10 inclusions/exclusions Claim scrubbers/payer scrubbers – ABN issues (LCD/NDC dx codes), ‘if ‘ rules, edits Pre-authorization process/coverage WC and Liability are not subject to HIPAA standard transactions. Will they convert? 26
 More Payer Issues Will they deny ‘unspecified” dx? How many digits will they require to have a ‘pre authorization ‘ match? Testing – test pt type, create claim, thru scrubber, to payer to payment. When start? Post go live? Accept DOS with ICD 9 after go live? If delayed, notify CMS/HIPAA Standard Transaction 2003. Track and trend all payer issues – report to hospital association. 27
More Payer Issues Will they deny ‘unspecified” dx? How many digits will they require to have a ‘pre authorization ‘ match? Testing – test pt type, create claim, thru scrubber, to payer to payment. When start? Post go live? Accept DOS with ICD 9 after go live? If delayed, notify CMS/HIPAA Standard Transaction 2003. Track and trend all payer issues – report to hospital association. 27
 More On LCD/NCD Diagnosis Codes Under ICD-10 The Challenges… What? For each Lab NCD, the ICD-9 -CM codes and descriptions will have to be translated to ICD-10 -CM versions. When? ◦ Prepare ICD-10 -CM versions for full ICD-10 -CM implementation in 2015 ◦ HEY – look at MLN Matters MM 8197 3 -15 -13 ◦ “ICD conversion from ICD 9 to related code infrastructure of the Medicare shared systems as they relate to CMS’ NCDs. ” (Watch for more on this!) 28
More On LCD/NCD Diagnosis Codes Under ICD-10 The Challenges… What? For each Lab NCD, the ICD-9 -CM codes and descriptions will have to be translated to ICD-10 -CM versions. When? ◦ Prepare ICD-10 -CM versions for full ICD-10 -CM implementation in 2015 ◦ HEY – look at MLN Matters MM 8197 3 -15 -13 ◦ “ICD conversion from ICD 9 to related code infrastructure of the Medicare shared systems as they relate to CMS’ NCDs. ” (Watch for more on this!) 28
 LCD/NCD Objectives and Goal Translate all ICD-9 -CM codes and descriptors in each Lab NCD’s table of covered codes to the ICD -10 -CM equivalent(s). Provide these translated tables to the CMS contractor, so that the tables can be incorporated into the ‘codelist spreadsheet’ which will be processed for use by the shared systems for claims processing. (update 2/13 -NCDs available) TESTING UPDATE: Watch for updates! (CMS announced end to begin in Jan 2015) Other payers? 29
LCD/NCD Objectives and Goal Translate all ICD-9 -CM codes and descriptors in each Lab NCD’s table of covered codes to the ICD -10 -CM equivalent(s). Provide these translated tables to the CMS contractor, so that the tables can be incorporated into the ‘codelist spreadsheet’ which will be processed for use by the shared systems for claims processing. (update 2/13 -NCDs available) TESTING UPDATE: Watch for updates! (CMS announced end to begin in Jan 2015) Other payers? 29
 Results of Nov ICD-10 Acknowledgement Testing week Each MAC reported their success with testing. CMS reported a 7687% acceptance rate during the week of testing. CMS reported more than 500 providers, suppliers, billing companies, and clearinghouses participated in the Nov round of testing. While providers are welcome to submit acknowledgement test claims anytime, during the Nov testing week, testers submitted almost 13, 700 claims. Tested with a valid ICD-10 dx that matched the DOS, National Provider Identifier/NPI and an ICD-10 companion qualifier code to allow for processing of claims. Majority of physician/professional claims rejections were related to an invalid NPI. Testers intentionally included errors in their claims to make sure the claim rejected, a process referred to as ‘negative testing. ” 30
Results of Nov ICD-10 Acknowledgement Testing week Each MAC reported their success with testing. CMS reported a 7687% acceptance rate during the week of testing. CMS reported more than 500 providers, suppliers, billing companies, and clearinghouses participated in the Nov round of testing. While providers are welcome to submit acknowledgement test claims anytime, during the Nov testing week, testers submitted almost 13, 700 claims. Tested with a valid ICD-10 dx that matched the DOS, National Provider Identifier/NPI and an ICD-10 companion qualifier code to allow for processing of claims. Majority of physician/professional claims rejections were related to an invalid NPI. Testers intentionally included errors in their claims to make sure the claim rejected, a process referred to as ‘negative testing. ” 30
 Duality of Systems Will payers, vendors (claim submission and scrubber) and other IT systems be able to handle ICD-9 -CM as well as ICD-10 -CM and ICD-10 PCS at the same time? Rebills of pre-conversion, medical necessity software, scrubbers, ensuring all payers are ready to convert AND test with each payer = critical to the successful conversion. P. S. Don’t forget all payers (Medicaid too! Funded to keep both ICD 9 and ICD 10 live? ) 31
Duality of Systems Will payers, vendors (claim submission and scrubber) and other IT systems be able to handle ICD-9 -CM as well as ICD-10 -CM and ICD-10 PCS at the same time? Rebills of pre-conversion, medical necessity software, scrubbers, ensuring all payers are ready to convert AND test with each payer = critical to the successful conversion. P. S. Don’t forget all payers (Medicaid too! Funded to keep both ICD 9 and ICD 10 live? ) 31
 Hot Spots Make a master list of all vendors who currently support any ICD-9 activity. (Think Y 2 K) Look at all items /ordering tools where ICD-9 codes are present. Need reviewed and revised ◦ Lab requisitions ◦ Online ordering of services that also requests ICD-9 codes ◦ Physician super bills/encounter forms with pre-printed ICD-9 codes ◦ Dept specific ‘cheat sheets’ for covered dx. (Yep we know you have them!) 32
Hot Spots Make a master list of all vendors who currently support any ICD-9 activity. (Think Y 2 K) Look at all items /ordering tools where ICD-9 codes are present. Need reviewed and revised ◦ Lab requisitions ◦ Online ordering of services that also requests ICD-9 codes ◦ Physician super bills/encounter forms with pre-printed ICD-9 codes ◦ Dept specific ‘cheat sheets’ for covered dx. (Yep we know you have them!) 32
 Example of 200 Bed Hospital IT list 3 M or other encoder Main frame /main IT system Radiology-doc billing, radiology’s own system Clearing house/claims Hospital employed doctor’s software for billing SNF/RUG software for grouper HH/HHRG software for grouper Lab – pathology doc billing, lab’s own system Internal electronic medical record used for coding Software used for Trauma & Tumor registry Decision support Scheduling software All tied Medical Necessity software in different areas – main frame, bolt on software, individual areas screening Infection Control software Cardiology – EKG system Itemized statements with dx as needed by the payer/pt Clinical quality reporting software Cheat sheets in each dept! OR software Occupational Med software 33
Example of 200 Bed Hospital IT list 3 M or other encoder Main frame /main IT system Radiology-doc billing, radiology’s own system Clearing house/claims Hospital employed doctor’s software for billing SNF/RUG software for grouper HH/HHRG software for grouper Lab – pathology doc billing, lab’s own system Internal electronic medical record used for coding Software used for Trauma & Tumor registry Decision support Scheduling software All tied Medical Necessity software in different areas – main frame, bolt on software, individual areas screening Infection Control software Cardiology – EKG system Itemized statements with dx as needed by the payer/pt Clinical quality reporting software Cheat sheets in each dept! OR software Occupational Med software 33
 Diagnosis Coding (ICD-10 -CM) Building a code 34
Diagnosis Coding (ICD-10 -CM) Building a code 34
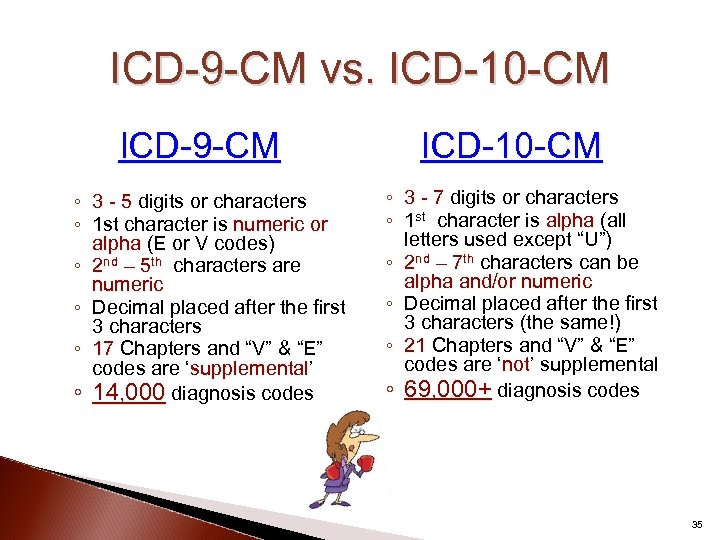 ICD-9 -CM vs. ICD-10 -CM ICD-9 -CM ◦ 3 - 5 digits or characters ◦ 1 st character is numeric or alpha (E or V codes) ◦ 2 nd – 5 th characters are numeric ◦ Decimal placed after the first 3 characters ◦ 17 Chapters and “V” & “E” codes are ‘supplemental’ supplemental ◦ 14, 000 diagnosis codes ICD-10 -CM ◦ 3 - 7 digits or characters ◦ 1 st character is alpha (all letters used except “U”) ◦ 2 nd – 7 th characters can be alpha and/or numeric ◦ Decimal placed after the first 3 characters (the same!) ◦ 21 Chapters and “V” & “E” codes are ‘not’ supplemental ◦ 69, 000+ diagnosis codes 35
ICD-9 -CM vs. ICD-10 -CM ICD-9 -CM ◦ 3 - 5 digits or characters ◦ 1 st character is numeric or alpha (E or V codes) ◦ 2 nd – 5 th characters are numeric ◦ Decimal placed after the first 3 characters ◦ 17 Chapters and “V” & “E” codes are ‘supplemental’ supplemental ◦ 14, 000 diagnosis codes ICD-10 -CM ◦ 3 - 7 digits or characters ◦ 1 st character is alpha (all letters used except “U”) ◦ 2 nd – 7 th characters can be alpha and/or numeric ◦ Decimal placed after the first 3 characters (the same!) ◦ 21 Chapters and “V” & “E” codes are ‘not’ supplemental ◦ 69, 000+ diagnosis codes 35
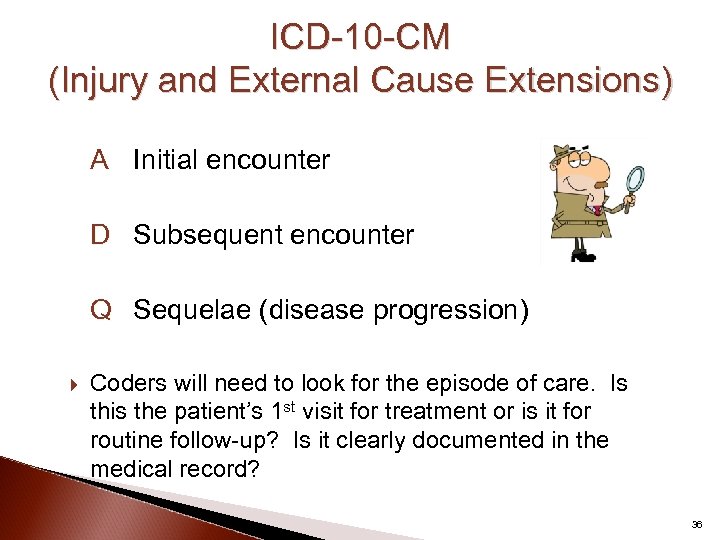 ICD-10 -CM (Injury and External Cause Extensions) A Initial encounter D Subsequent encounter Q Sequelae (disease progression) Coders will need to look for the episode of care. Is this the patient’s 1 st visit for treatment or is it for routine follow-up? Is it clearly documented in the medical record? 36
ICD-10 -CM (Injury and External Cause Extensions) A Initial encounter D Subsequent encounter Q Sequelae (disease progression) Coders will need to look for the episode of care. Is this the patient’s 1 st visit for treatment or is it for routine follow-up? Is it clearly documented in the medical record? 36
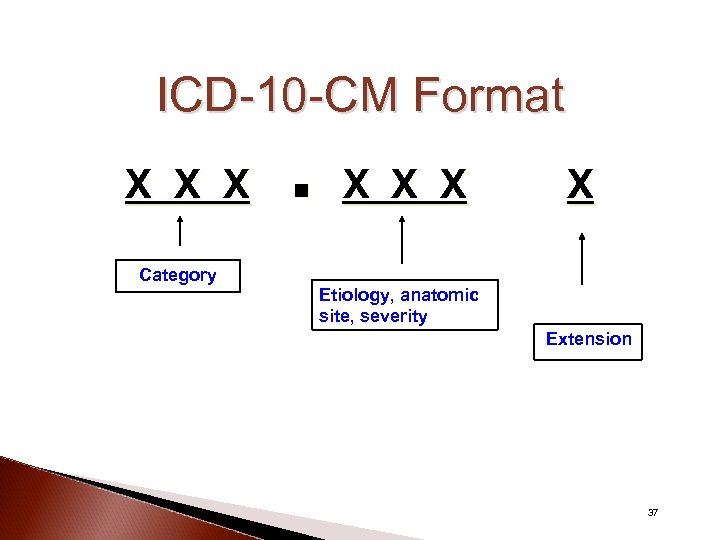 ICD-10 -CM Format X X X X Category Etiology, anatomic site, severity Extension 37
ICD-10 -CM Format X X X X Category Etiology, anatomic site, severity Extension 37
 Examples of ICD-10 -CM *Emergency Room* I 10 Essential (primary) hypertension S 01. 02 x. A Laceration with foreign body of scalp, initial encounter S 01. 02 x. D Laceration with foreign body of scalp, subsequent encounter S 02. 2 xx. A Fracture of nasal bones, initial encounter for closed fracture H 65. 01 Acute serous otitis media, right ear (CDM too) H 65. 02 Acute serous otitis media, left ear H 65. 03 Acute serous otitis media, bilateral 38
Examples of ICD-10 -CM *Emergency Room* I 10 Essential (primary) hypertension S 01. 02 x. A Laceration with foreign body of scalp, initial encounter S 01. 02 x. D Laceration with foreign body of scalp, subsequent encounter S 02. 2 xx. A Fracture of nasal bones, initial encounter for closed fracture H 65. 01 Acute serous otitis media, right ear (CDM too) H 65. 02 Acute serous otitis media, left ear H 65. 03 Acute serous otitis media, bilateral 38
 Quirky ICD-10 -CM Codes On any given day, anything can happen! W 17. 82 x. A Fall from (out of) grocery cart, initial encounter V 94. 4 xx. A Injury to barefoot water-skier, initial encounter W 61. 43 x. A Pecked by turkey, initial encounter Y 93. C 2 Activity, handheld interactive electronic device, i. e. , cellular phone Are we querying providers? Who wants it -payers? Have internal discussions, payer research, and make final decision. 39
Quirky ICD-10 -CM Codes On any given day, anything can happen! W 17. 82 x. A Fall from (out of) grocery cart, initial encounter V 94. 4 xx. A Injury to barefoot water-skier, initial encounter W 61. 43 x. A Pecked by turkey, initial encounter Y 93. C 2 Activity, handheld interactive electronic device, i. e. , cellular phone Are we querying providers? Who wants it -payers? Have internal discussions, payer research, and make final decision. 39
 Why Are There So Many Diagnosis Codes? Greater “specificity and detail” in all diagnosis codes! ◦ But…is there supporting physician documentation in the medical record? 34, 250 (50%) of all ICD-10 -CM codes are related to the musculoskeletal system 17, 045 (25%) of all ICD-10 -CM codes are related to fractures ◦ 10, 582 fracture codes will distinguish ‘right’ vs. ‘left’ 25, 000 (36%) of all ICD-10 -CM diagnosis codes will now distinguish right vs. left 40
Why Are There So Many Diagnosis Codes? Greater “specificity and detail” in all diagnosis codes! ◦ But…is there supporting physician documentation in the medical record? 34, 250 (50%) of all ICD-10 -CM codes are related to the musculoskeletal system 17, 045 (25%) of all ICD-10 -CM codes are related to fractures ◦ 10, 582 fracture codes will distinguish ‘right’ vs. ‘left’ 25, 000 (36%) of all ICD-10 -CM diagnosis codes will now distinguish right vs. left 40
 Cross Walking - GEMs CMS has created GEMs (General Equivalence Mappings) to assist hospitals with cross walking ICD-9 -CM ►ICD-10 -CM/PCS “forward mapping” & ICD-10 -CM/PCS ◄ ICD-9 -CM “backward mapping”. The correlation between the 2 code sets for some codes is fairly close, but not a straight correlation for others, i. e. OB, etc. Not always 1 to 1 crosswalk from ICD-9 -CM to ICD-10 -CM (www. cms. gov/ICD 10/11 b 15_2013_ICD 10 PCS. asp) Available on CMS’s website 41
Cross Walking - GEMs CMS has created GEMs (General Equivalence Mappings) to assist hospitals with cross walking ICD-9 -CM ►ICD-10 -CM/PCS “forward mapping” & ICD-10 -CM/PCS ◄ ICD-9 -CM “backward mapping”. The correlation between the 2 code sets for some codes is fairly close, but not a straight correlation for others, i. e. OB, etc. Not always 1 to 1 crosswalk from ICD-9 -CM to ICD-10 -CM (www. cms. gov/ICD 10/11 b 15_2013_ICD 10 PCS. asp) Available on CMS’s website 41
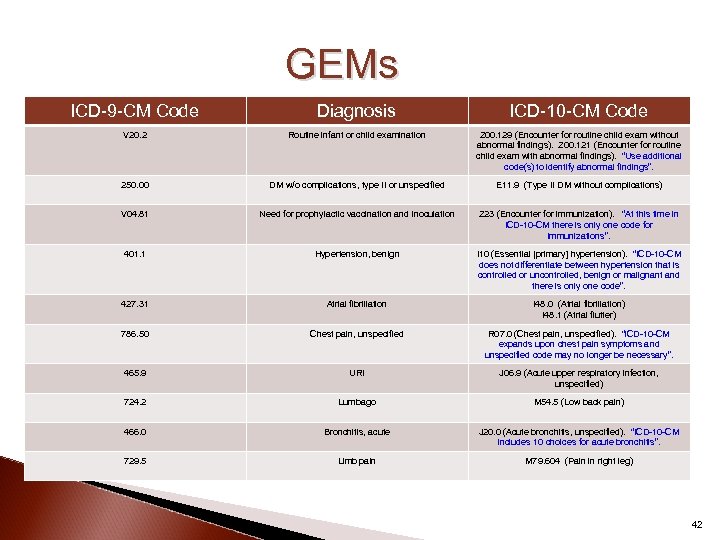 GEMs ICD-9 -CM Code Diagnosis ICD-10 -CM Code V 20. 2 Routine infant or child examination Z 00. 129 (Encounter for routine child exam without abnormal findings). Z 00. 121 (Encounter for routine child exam with abnormal findings). “Use additional code(s) to identify abnormal findings”. 250. 00 DM w/o complications, type II or unspecified E 11. 9 (Type II DM without complications) V 04. 81 Need for prophylactic vaccination and inoculation Z 23 (Encounter for immunization). “At this time in ICD-10 -CM there is only one code for immunizations”. 401. 1 Hypertension, benign I 10 (Essential [primary] hypertension). “ICD-10 -CM does not differentiate between hypertension that is controlled or uncontrolled, benign or malignant and there is only one code”. 427. 31 Atrial fibrillation I 48. 0 (Atrial fibrillation) I 48. 1 (Atrial flutter) 786. 50 Chest pain, unspecified R 07. 0 (Chest pain, unspecified). “ICD-10 -CM expands upon chest pain symptoms and unspecified code may no longer be necessary”. 465. 9 URI J 06. 9 (Acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified) 724. 2 Lumbago M 54. 5 (Low back pain) 466. 0 Bronchitis, acute J 20. 0 (Acute bronchitis, unspecified). “ICD-10 -CM includes 10 choices for acute bronchitis”. 729. 5 Limb pain M 79. 604 (Pain in right leg) 42
GEMs ICD-9 -CM Code Diagnosis ICD-10 -CM Code V 20. 2 Routine infant or child examination Z 00. 129 (Encounter for routine child exam without abnormal findings). Z 00. 121 (Encounter for routine child exam with abnormal findings). “Use additional code(s) to identify abnormal findings”. 250. 00 DM w/o complications, type II or unspecified E 11. 9 (Type II DM without complications) V 04. 81 Need for prophylactic vaccination and inoculation Z 23 (Encounter for immunization). “At this time in ICD-10 -CM there is only one code for immunizations”. 401. 1 Hypertension, benign I 10 (Essential [primary] hypertension). “ICD-10 -CM does not differentiate between hypertension that is controlled or uncontrolled, benign or malignant and there is only one code”. 427. 31 Atrial fibrillation I 48. 0 (Atrial fibrillation) I 48. 1 (Atrial flutter) 786. 50 Chest pain, unspecified R 07. 0 (Chest pain, unspecified). “ICD-10 -CM expands upon chest pain symptoms and unspecified code may no longer be necessary”. 465. 9 URI J 06. 9 (Acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified) 724. 2 Lumbago M 54. 5 (Low back pain) 466. 0 Bronchitis, acute J 20. 0 (Acute bronchitis, unspecified). “ICD-10 -CM includes 10 choices for acute bronchitis”. 729. 5 Limb pain M 79. 604 (Pain in right leg) 42
 Now Let’s Take a Look At ICD-10 -PCS! 43
Now Let’s Take a Look At ICD-10 -PCS! 43
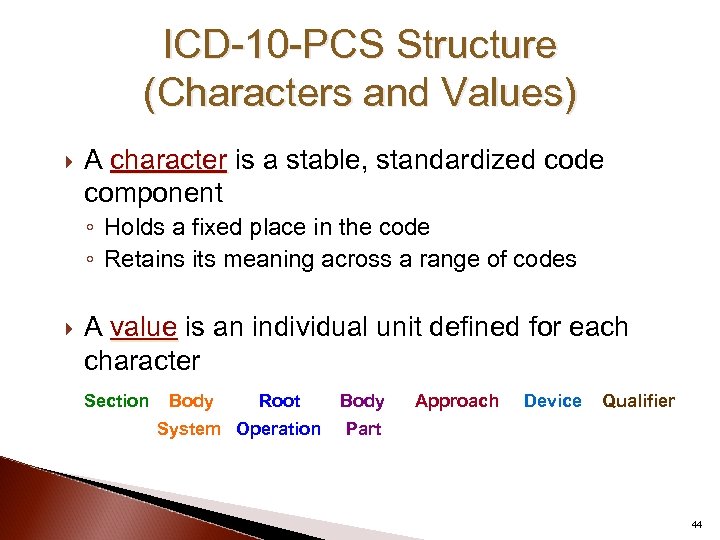 ICD-10 -PCS Structure (Characters and Values) A character is a stable, standardized code component ◦ Holds a fixed place in the code ◦ Retains its meaning across a range of codes A value is an individual unit defined for each character Section Body Root System Operation Body Approach Device Qualifier Part 44
ICD-10 -PCS Structure (Characters and Values) A character is a stable, standardized code component ◦ Holds a fixed place in the code ◦ Retains its meaning across a range of codes A value is an individual unit defined for each character Section Body Root System Operation Body Approach Device Qualifier Part 44
 Case # 1 Diagnostic Colonoscopy This 44 -year-old male patient is known to have diverticulitis of the colon. He has noticed melena occasionally for the past week. The initial impression was that this is acute bleeding from diverticulitis. Patient was scheduled for colonoscopy. Colonoscopy identified the cause of the bleeding to be angiodysplasia of the ascending colon. 45
Case # 1 Diagnostic Colonoscopy This 44 -year-old male patient is known to have diverticulitis of the colon. He has noticed melena occasionally for the past week. The initial impression was that this is acute bleeding from diverticulitis. Patient was scheduled for colonoscopy. Colonoscopy identified the cause of the bleeding to be angiodysplasia of the ascending colon. 45
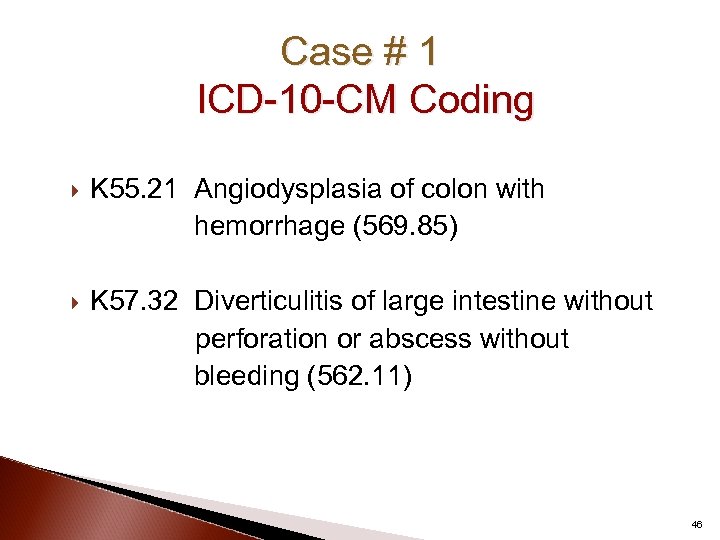 Case # 1 ICD-10 -CM Coding K 55. 21 Angiodysplasia of colon with hemorrhage (569. 85) K 57. 32 Diverticulitis of large intestine without perforation or abscess without bleeding (562. 11) 46
Case # 1 ICD-10 -CM Coding K 55. 21 Angiodysplasia of colon with hemorrhage (569. 85) K 57. 32 Diverticulitis of large intestine without perforation or abscess without bleeding (562. 11) 46
 Case # 1 ICD-10 -PCS Coding 0 DJD 8 ZZ Inspection of Lower Intestinal Tract, via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic (45. 23) 47
Case # 1 ICD-10 -PCS Coding 0 DJD 8 ZZ Inspection of Lower Intestinal Tract, via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic (45. 23) 47
 What Will ICD-10 Cost? 48
What Will ICD-10 Cost? 48
 Estimated Costs CMS estimates cost to the private sector for implementation of ICD-10 will exceed $130 million. Hay Group White Paper in 2006 estimated cost for hospitals ranged from $35 K - $150 K for < 100 beds, to $500 K to $2 million for 400+ beds. AAPC indicates current documentation = 50% could be coded. AHIMA indicates after ICD 10 - coders will be 50% slower for up to 3 months ++ 50% more physician queries. 49
Estimated Costs CMS estimates cost to the private sector for implementation of ICD-10 will exceed $130 million. Hay Group White Paper in 2006 estimated cost for hospitals ranged from $35 K - $150 K for < 100 beds, to $500 K to $2 million for 400+ beds. AAPC indicates current documentation = 50% could be coded. AHIMA indicates after ICD 10 - coders will be 50% slower for up to 3 months ++ 50% more physician queries. 49
 Potential Hidden Costs 50
Potential Hidden Costs 50
 Potential Hidden Costs Back log of uncoded claims with ICD-9 while trying to get coders ready for ICD-10. Remote/outsourced coding may need to occur as well as OT. Rejected claims from payers who are not ready to accept UB-04 with ICD -10 PLUS ICD-9 as necessary. Vendor software rejecting ICD-10 or edits not working correctly thus slowing claim submission. Manual intervention to ensure claims are submitted and accepted. New software if existing software for related ICD-10 work is not compatible. 51
Potential Hidden Costs Back log of uncoded claims with ICD-9 while trying to get coders ready for ICD-10. Remote/outsourced coding may need to occur as well as OT. Rejected claims from payers who are not ready to accept UB-04 with ICD -10 PLUS ICD-9 as necessary. Vendor software rejecting ICD-10 or edits not working correctly thus slowing claim submission. Manual intervention to ensure claims are submitted and accepted. New software if existing software for related ICD-10 work is not compatible. 51
 More Hidden Costs Cost to conduct a ‘risk assessment’ to assess current documentation patterns for providers and care givers. Potential salary adjustments for the coders. Cost to conduct training for providers and care givers on enhanced documentation. Cost to review EMR or other software to adapt to enhanced documentation requirements. Cost to conduct a ‘readiness assessment ‘ pre go live to determine readiness of coders, documentation and vendors. Cost of moving ‘related’ work from the coders during training period. (EX: Drug administration/charge capture) 52
More Hidden Costs Cost to conduct a ‘risk assessment’ to assess current documentation patterns for providers and care givers. Potential salary adjustments for the coders. Cost to conduct training for providers and care givers on enhanced documentation. Cost to review EMR or other software to adapt to enhanced documentation requirements. Cost to conduct a ‘readiness assessment ‘ pre go live to determine readiness of coders, documentation and vendors. Cost of moving ‘related’ work from the coders during training period. (EX: Drug administration/charge capture) 52
 And More …. Loss of productivity – rebills, denials, rejections, EOB work, medical necessity rejections/follow up (PFS+) Loss of productivity – excessive physician queries, coder slow down with new coding process (HIM) Growth in the discharged not final billed… Potential impact to the Case Mix Index Cost of a project manager (1 yr contract staff to coordinate all the IT, testing, training, documentation assessments) Cost of implementing a clinical documentation improvement program Cost of EMR changes and training of all impacted staff Cost of any changes to the functionality of the any software and training costs 53
And More …. Loss of productivity – rebills, denials, rejections, EOB work, medical necessity rejections/follow up (PFS+) Loss of productivity – excessive physician queries, coder slow down with new coding process (HIM) Growth in the discharged not final billed… Potential impact to the Case Mix Index Cost of a project manager (1 yr contract staff to coordinate all the IT, testing, training, documentation assessments) Cost of implementing a clinical documentation improvement program Cost of EMR changes and training of all impacted staff Cost of any changes to the functionality of the any software and training costs 53
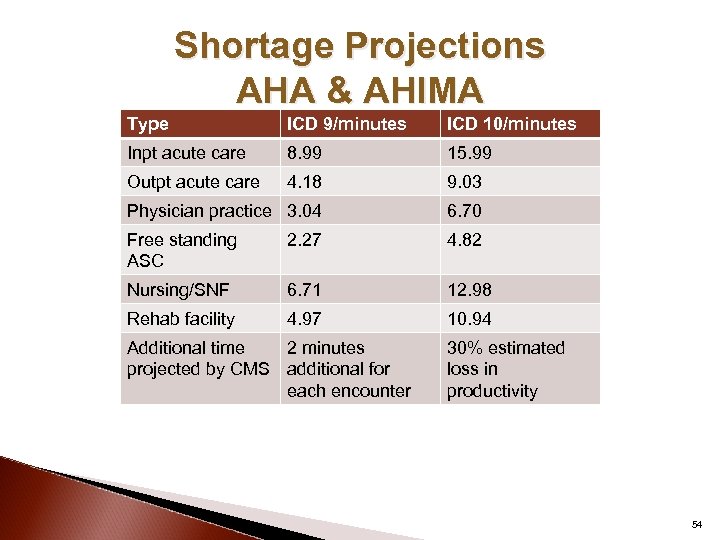 Shortage Projections AHA & AHIMA Type ICD 9/minutes ICD 10/minutes Inpt acute care 8. 99 15. 99 Outpt acute care 4. 18 9. 03 Physician practice 3. 04 6. 70 Free standing ASC 2. 27 4. 82 Nursing/SNF 6. 71 12. 98 Rehab facility 4. 97 10. 94 Additional time 2 minutes projected by CMS additional for each encounter 30% estimated loss in productivity 54
Shortage Projections AHA & AHIMA Type ICD 9/minutes ICD 10/minutes Inpt acute care 8. 99 15. 99 Outpt acute care 4. 18 9. 03 Physician practice 3. 04 6. 70 Free standing ASC 2. 27 4. 82 Nursing/SNF 6. 71 12. 98 Rehab facility 4. 97 10. 94 Additional time 2 minutes projected by CMS additional for each encounter 30% estimated loss in productivity 54
 Shortage Strategies Mentorship program /formal 30% less productive – alternatives? Back fill with remote coding Explore Computer Assisted Coding –uses natural language processing, cost analysis ◦ Outpt ancillary –high potential usage. (MN screening) ◦ Other outpt areas – depending on how well the provider is documenting new elements of ICD 10. (Queries) 55
Shortage Strategies Mentorship program /formal 30% less productive – alternatives? Back fill with remote coding Explore Computer Assisted Coding –uses natural language processing, cost analysis ◦ Outpt ancillary –high potential usage. (MN screening) ◦ Other outpt areas – depending on how well the provider is documenting new elements of ICD 10. (Queries) 55
 Education AHIMA estimates approximately 16 hours of coding training is needed for outpatient coders and 50 hours for inpatient coders. Additional time may be needed to refresh anatomy & physiology fundamentals. Learn foundational knowledge before more intensive training. Allow time for practice, practice (key!) Down time during training and practice time. And don’t forget the NON-HIM training needs 56
Education AHIMA estimates approximately 16 hours of coding training is needed for outpatient coders and 50 hours for inpatient coders. Additional time may be needed to refresh anatomy & physiology fundamentals. Learn foundational knowledge before more intensive training. Allow time for practice, practice (key!) Down time during training and practice time. And don’t forget the NON-HIM training needs 56
 What’s Next? 57
What’s Next? 57
 Developing an ICD-10 Implementation Team When ? By late 2014 (Already done, right? ) Who? Key leaders in the revenue cycle/IT and HIM. Will a designated project leader need identified? What? Create master list of all revenue cycle areas, IT, HIM and physician issues How? Identify timelines for when components will be done, who does it, results reviewed, testing, with ownership and timelines for completion Key benchmarks for completion done beginning 1 st Q 2015 or once final go live date is established After go live, complete a 2 nd set of benchmark assessments with barriers, delays, more education, etc. 58
Developing an ICD-10 Implementation Team When ? By late 2014 (Already done, right? ) Who? Key leaders in the revenue cycle/IT and HIM. Will a designated project leader need identified? What? Create master list of all revenue cycle areas, IT, HIM and physician issues How? Identify timelines for when components will be done, who does it, results reviewed, testing, with ownership and timelines for completion Key benchmarks for completion done beginning 1 st Q 2015 or once final go live date is established After go live, complete a 2 nd set of benchmark assessments with barriers, delays, more education, etc. 58
 Develop Phase 1 and Phase 2 Attack Plan Phase 1: Goal: 3 rd Q 2014 (if not already done) Phase 2: 1 st Q of 2015 and after go live. Awareness training of leadership Awareness training of coders – inpt/all others/providers Conduct a risk assessment of current documentation patterns Track and trend ALL queries for a defined period of time. Using the query, develop provider education –with structured rollout time frames Develop master list of impact areas – coders, PFS, IT, providers, etc. Develop structured coder education –based on type of pt. Conduct a readiness assessment –audit of documentation, testing of coders/per pt type, review of all IT functions, new forms, software testing, payer, contracting, etc. Coding comparison for case mix impact, MS-DRG. . Aggressively code all pending ICD -9 prior to Oct, 2015. Remote/outsourced coding before/during transition and training needed Contract coding company should have a ‘preparedness plan” Contract ICD-10 program manager or dedicated staff (Think 59
Develop Phase 1 and Phase 2 Attack Plan Phase 1: Goal: 3 rd Q 2014 (if not already done) Phase 2: 1 st Q of 2015 and after go live. Awareness training of leadership Awareness training of coders – inpt/all others/providers Conduct a risk assessment of current documentation patterns Track and trend ALL queries for a defined period of time. Using the query, develop provider education –with structured rollout time frames Develop master list of impact areas – coders, PFS, IT, providers, etc. Develop structured coder education –based on type of pt. Conduct a readiness assessment –audit of documentation, testing of coders/per pt type, review of all IT functions, new forms, software testing, payer, contracting, etc. Coding comparison for case mix impact, MS-DRG. . Aggressively code all pending ICD -9 prior to Oct, 2015. Remote/outsourced coding before/during transition and training needed Contract coding company should have a ‘preparedness plan” Contract ICD-10 program manager or dedicated staff (Think 59
 Steps to Implementation Communication Make a master list of all software where ICD-9 is being used. This will be essential to the seamless implementation of ICD-10 (or less anguish). Contact each vendor NOW to identify their roll out plan for compliance and when they will be ready to test. Test with each vendor early in 2015 or as soon as they are available for testing. HUGE CONCERN! Keep Sr. Leadership well aware of the status of ALL software testing and compliance. Be prepared to make changes if compliance is not achieved with testing 9 months prior to go live. 60
Steps to Implementation Communication Make a master list of all software where ICD-9 is being used. This will be essential to the seamless implementation of ICD-10 (or less anguish). Contact each vendor NOW to identify their roll out plan for compliance and when they will be ready to test. Test with each vendor early in 2015 or as soon as they are available for testing. HUGE CONCERN! Keep Sr. Leadership well aware of the status of ALL software testing and compliance. Be prepared to make changes if compliance is not achieved with testing 9 months prior to go live. 60
 Audits of Course! Documentation Audits ◦ Your CDI (Clinical Documentation Improvement) department can start now conducting ICD-10 documentation audits this year – risk assessments of current documentation practices. ◦ Audit top 25 ICD-9 -CM principal diagnosis codes and map to ICD-10 -CM codes and begin auditing to determine whether the records contain the necessary clinical information to support the ICD-10 -CM principal diagnosis code. Coding Audits ◦ Target certain inpatient cases for review based on the MSDRG assignment or the CC’s because both of these IP PPS components will undergo changes when reconfigured with the ICD-10 -CM codes. 61
Audits of Course! Documentation Audits ◦ Your CDI (Clinical Documentation Improvement) department can start now conducting ICD-10 documentation audits this year – risk assessments of current documentation practices. ◦ Audit top 25 ICD-9 -CM principal diagnosis codes and map to ICD-10 -CM codes and begin auditing to determine whether the records contain the necessary clinical information to support the ICD-10 -CM principal diagnosis code. Coding Audits ◦ Target certain inpatient cases for review based on the MSDRG assignment or the CC’s because both of these IP PPS components will undergo changes when reconfigured with the ICD-10 -CM codes. 61
 October 2013 & Beyond Possible decrease in cash flow due to: ◦ ◦ ◦ Increase in time to code medical records Learning curves, potential increase in errors Decreased coder productivity, when, or will it recover System, vendor or software issues Potential reimbursement impact due to payer systems, claim edits or processing issues ◦ Expect denials and underpayments ◦ Lower DRGs or IP lack of ‘severity of illness’ due to nonspecific documentation and unspecified diagnosis codes 62
October 2013 & Beyond Possible decrease in cash flow due to: ◦ ◦ ◦ Increase in time to code medical records Learning curves, potential increase in errors Decreased coder productivity, when, or will it recover System, vendor or software issues Potential reimbursement impact due to payer systems, claim edits or processing issues ◦ Expect denials and underpayments ◦ Lower DRGs or IP lack of ‘severity of illness’ due to nonspecific documentation and unspecified diagnosis codes 62
 Defense for 2015 63
Defense for 2015 63
 Defense for 2015 Never too late to start!! Provide adequate system and coding resources for ‘go live’ ◦ Will you need additional coding support? Contracted coders? Who will handle the coding of ‘prior to’ accounts vs. ‘go live’ accounts? Possible concurrent coding? Post ‘go live’ auditing & monitoring of: ◦ Coding & Documentation coding queries! ◦ Systems, data, reports ◦ Claims (UB & 1500), payments, denials Audit and then more auditing from a RISK to a READINESS environment… Remember, we are ALL in this together!! 64
Defense for 2015 Never too late to start!! Provide adequate system and coding resources for ‘go live’ ◦ Will you need additional coding support? Contracted coders? Who will handle the coding of ‘prior to’ accounts vs. ‘go live’ accounts? Possible concurrent coding? Post ‘go live’ auditing & monitoring of: ◦ Coding & Documentation coding queries! ◦ Systems, data, reports ◦ Claims (UB & 1500), payments, denials Audit and then more auditing from a RISK to a READINESS environment… Remember, we are ALL in this together!! 64
 Accreditation for Coders AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders) AHIMA (American Health Information Mgmt. Association) ◦ Certified coders will have opportunity to take the ICD-10 proficiency exam starting in October 2012 and must successfully complete the test by September 30, 2014. ◦ AAPC will require its certified coders to pass this test to retain their certification. ◦ Continuing education hours with ICD-10 -CM/PCS content will be required based on the specific AHIMA credential(s). RHIA - required to have at least 6 CEUs dedicated to ICD-10 -CM/PCS 12 for the CCS-P credential 18 for the CCS credential, etc. 65
Accreditation for Coders AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders) AHIMA (American Health Information Mgmt. Association) ◦ Certified coders will have opportunity to take the ICD-10 proficiency exam starting in October 2012 and must successfully complete the test by September 30, 2014. ◦ AAPC will require its certified coders to pass this test to retain their certification. ◦ Continuing education hours with ICD-10 -CM/PCS content will be required based on the specific AHIMA credential(s). RHIA - required to have at least 6 CEUs dedicated to ICD-10 -CM/PCS 12 for the CCS-P credential 18 for the CCS credential, etc. 65
 Resources www. ahima. org/icd 10 www. cdc. gov/nchs/about/otheract/icd 9/abticd 10. htm www. cms. hhs. gov/ICD 9 Provider. Diagnostic. Codes/08_ICD 10. asp www. cms. gov/ICD 10 www. who. int/classifications/icd/en www. cms. gov/ICD 10/Te 110/itemdetail. asp? filter. Type=none&filter. By. DID=99&sort. B y. DID=1&sort. Order=descending&item. ID=cms 1246998&int. Num. Per. Page=10 • CMS Sponsored Teleconference “Case Study in Translating Lab NCD” (5 -18 -11) Power. Point slides #23 & #24 66
Resources www. ahima. org/icd 10 www. cdc. gov/nchs/about/otheract/icd 9/abticd 10. htm www. cms. hhs. gov/ICD 9 Provider. Diagnostic. Codes/08_ICD 10. asp www. cms. gov/ICD 10 www. who. int/classifications/icd/en www. cms. gov/ICD 10/Te 110/itemdetail. asp? filter. Type=none&filter. By. DID=99&sort. B y. DID=1&sort. Order=descending&item. ID=cms 1246998&int. Num. Per. Page=10 • CMS Sponsored Teleconference “Case Study in Translating Lab NCD” (5 -18 -11) Power. Point slides #23 & #24 66
 AR Systems’ Contact Info Day Egusquiza, President AR Systems, Inc Box 2521 Twin Falls, Id 83303 208 423 9036 daylee 1@mindspring. com Thanks for joining us! Free info line available. NEW WEBPAGE: www. arsystemsdayegusquiza. com JOIN US FOR UR/PA Bootcamp in San Antonio July 2015 RAC 2014 67
AR Systems’ Contact Info Day Egusquiza, President AR Systems, Inc Box 2521 Twin Falls, Id 83303 208 423 9036 daylee 1@mindspring. com Thanks for joining us! Free info line available. NEW WEBPAGE: www. arsystemsdayegusquiza. com JOIN US FOR UR/PA Bootcamp in San Antonio July 2015 RAC 2014 67
 Physician Documentation 68
Physician Documentation 68
 Biggest Challenge? Documentation = Physicians! Begin providing them education now so that they are fully prepared on what will be required for appropriate documentation for correct ICD-10 code assignment and MS-DRG assignment. Customize the training for physicians based on their medical specialty. Do not just focus on inpatient diagnoses and/or procedures but also on outpatient diagnoses as this will require ‘beefed’ up documentation from your docs as well to support the codes. 69
Biggest Challenge? Documentation = Physicians! Begin providing them education now so that they are fully prepared on what will be required for appropriate documentation for correct ICD-10 code assignment and MS-DRG assignment. Customize the training for physicians based on their medical specialty. Do not just focus on inpatient diagnoses and/or procedures but also on outpatient diagnoses as this will require ‘beefed’ up documentation from your docs as well to support the codes. 69
 Coder’s Role As a “basic awareness”: ◦ Coders are required to code to the highest degree of specificity, but the quality of the physician documentation HAS to be there in the medical record. ◦ Coders are bound by many rules/guidelines for application of the translation process of narratives to numerical codes, which generates the bill/claim. ◦ Coders are not licensed to make the diagnoses, so if it is not stated, it cannot be coded! 70
Coder’s Role As a “basic awareness”: ◦ Coders are required to code to the highest degree of specificity, but the quality of the physician documentation HAS to be there in the medical record. ◦ Coders are bound by many rules/guidelines for application of the translation process of narratives to numerical codes, which generates the bill/claim. ◦ Coders are not licensed to make the diagnoses, so if it is not stated, it cannot be coded! 70
 Top 10 Documentation Tips 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Laterality (side) i. e. , left or right – 25, 000+ codes! Stage of Care, i. e. , initial, subsequent, sequelae Specific Diagnosis Specific Anatomy Associated and/or Related Conditions Cause of Injury Documentation of Additional Symptoms or Conditions Dominant vs. Non-dominant Side Tobacco Exposure or Use Gustilo-Anderson scale 71
Top 10 Documentation Tips 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Laterality (side) i. e. , left or right – 25, 000+ codes! Stage of Care, i. e. , initial, subsequent, sequelae Specific Diagnosis Specific Anatomy Associated and/or Related Conditions Cause of Injury Documentation of Additional Symptoms or Conditions Dominant vs. Non-dominant Side Tobacco Exposure or Use Gustilo-Anderson scale 71
 Fracture Coding… A 35 -year-old man suffered open displaced tibia and fibula fractures of the right leg as the result of an automobile accident. In addition, he lost a lot of blood, also from the right leg. To assign the correct ICD-10 -CM codes, coders will need to know: Which leg and which specific bone(s) the patient injured (in this example, it’s the right tibia and fibula) Whether the fracture is open or closed (in this case, open) Whether the fracture is displaced (in this case, displaced) For open fractures, coders will also need to know what type of trauma the patient suffered to choose the appropriate character based on the Gustilo-Anderson classification system. The 7 th character identifies open fractures using the Gustilo-Anderson classifications, which are the most commonly used classifications for open fractures. The Gustilo-Anderson classification identifies the severity of the soft tissue damage. 72
Fracture Coding… A 35 -year-old man suffered open displaced tibia and fibula fractures of the right leg as the result of an automobile accident. In addition, he lost a lot of blood, also from the right leg. To assign the correct ICD-10 -CM codes, coders will need to know: Which leg and which specific bone(s) the patient injured (in this example, it’s the right tibia and fibula) Whether the fracture is open or closed (in this case, open) Whether the fracture is displaced (in this case, displaced) For open fractures, coders will also need to know what type of trauma the patient suffered to choose the appropriate character based on the Gustilo-Anderson classification system. The 7 th character identifies open fractures using the Gustilo-Anderson classifications, which are the most commonly used classifications for open fractures. The Gustilo-Anderson classification identifies the severity of the soft tissue damage. 72
 What is Gustilo-Anderson scale? “Classification of fractures” – may be new to your coders and physicians ◦ Type I: Wound is smaller than 1 cm, clean, and generally I caused by a fracture fragment that pierces the skin (low energy injury). ◦ Type II: Wound is longer than 1 cm, not contaminated, II and w/o major soft tissue damage or defect (low energy injury). ◦ Type III: Wound is longer than 1 cm, with significant soft III tissue disruption. The mechanism often involves highenergy trauma, resulting in a severely unstable fracture with varying degrees of fragmentation. 73
What is Gustilo-Anderson scale? “Classification of fractures” – may be new to your coders and physicians ◦ Type I: Wound is smaller than 1 cm, clean, and generally I caused by a fracture fragment that pierces the skin (low energy injury). ◦ Type II: Wound is longer than 1 cm, not contaminated, II and w/o major soft tissue damage or defect (low energy injury). ◦ Type III: Wound is longer than 1 cm, with significant soft III tissue disruption. The mechanism often involves highenergy trauma, resulting in a severely unstable fracture with varying degrees of fragmentation. 73
 Physician & Documentation Challenges Weaknesses ◦ Lack of understanding of what will be required for “specificity” of documentation. ◦ Need to ensure detailed documentation is present in the medical record. ◦ Will see a significant increase in the # of coding queries coming their way for further clarification and/or specificity of diagnoses as documented in the medical record. ◦ Need to be part of the “TEAM” as they will ‘drive’ the coding process. ◦ Docs will now be affected in their own offices and must change how they document, i. e. superbill, lab requisitions 74
Physician & Documentation Challenges Weaknesses ◦ Lack of understanding of what will be required for “specificity” of documentation. ◦ Need to ensure detailed documentation is present in the medical record. ◦ Will see a significant increase in the # of coding queries coming their way for further clarification and/or specificity of diagnoses as documented in the medical record. ◦ Need to be part of the “TEAM” as they will ‘drive’ the coding process. ◦ Docs will now be affected in their own offices and must change how they document, i. e. superbill, lab requisitions 74
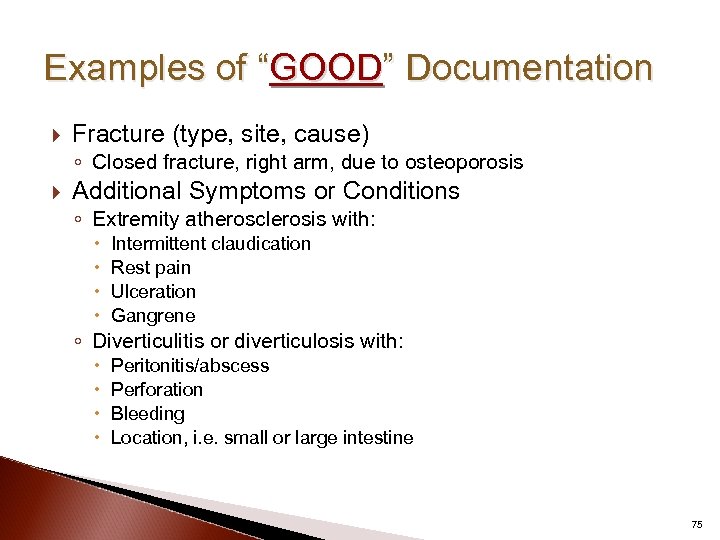 Examples of “GOOD” Documentation Fracture (type, site, cause) ◦ Closed fracture, right arm, due to osteoporosis Additional Symptoms or Conditions ◦ Extremity atherosclerosis with: Intermittent claudication Rest pain Ulceration Gangrene Peritonitis/abscess Perforation Bleeding Location, i. e. small or large intestine ◦ Diverticulitis or diverticulosis with: 75
Examples of “GOOD” Documentation Fracture (type, site, cause) ◦ Closed fracture, right arm, due to osteoporosis Additional Symptoms or Conditions ◦ Extremity atherosclerosis with: Intermittent claudication Rest pain Ulceration Gangrene Peritonitis/abscess Perforation Bleeding Location, i. e. small or large intestine ◦ Diverticulitis or diverticulosis with: 75
 And A Few More… Bucket, handle tear of lateral meniscus, current injury, right knee Internal bleeding hemorrhoids Barrett’s esophagus with low grade dysplasia Pressure ulcer of right ankle, stage II Mild persistent asthma with status asthmaticus Alzheimer’s disease, early onset Benign neoplasm of right ovary Strain of right Achilles tendon, subsequent encounter 76
And A Few More… Bucket, handle tear of lateral meniscus, current injury, right knee Internal bleeding hemorrhoids Barrett’s esophagus with low grade dysplasia Pressure ulcer of right ankle, stage II Mild persistent asthma with status asthmaticus Alzheimer’s disease, early onset Benign neoplasm of right ovary Strain of right Achilles tendon, subsequent encounter 76
 Coding Queries Expect a significant increase in the # of queries that will be generated from ICD-10. Existing coding queries will most likely have to be updated as you will be asking for different documentation to capture “specificity”. Make sure they are not ‘leading’ the physician to document one way or another. Consider making the query part of the permanent medical record – physician addendum. Track and trend for patterns. Then do more Ed! 77
Coding Queries Expect a significant increase in the # of queries that will be generated from ICD-10. Existing coding queries will most likely have to be updated as you will be asking for different documentation to capture “specificity”. Make sure they are not ‘leading’ the physician to document one way or another. Consider making the query part of the permanent medical record – physician addendum. Track and trend for patterns. Then do more Ed! 77
 Reduce Rework, Engage At Time Of Coding, Think Outside The Box! Think concurrent inpt coding. Immediate interaction with the provider and other caregivers on weak or incomplete documentation. Have coders on the floor with the care team. Back office coding results in ‘chasing’ the provider = delay in coding = delay in cash. Expand the CDI team…to include both UR needs/severity of illness & intensity of service PLUS specificity/laterality/ and other unique ICD-10 needs as identified thru queries and risk audits. 78
Reduce Rework, Engage At Time Of Coding, Think Outside The Box! Think concurrent inpt coding. Immediate interaction with the provider and other caregivers on weak or incomplete documentation. Have coders on the floor with the care team. Back office coding results in ‘chasing’ the provider = delay in coding = delay in cash. Expand the CDI team…to include both UR needs/severity of illness & intensity of service PLUS specificity/laterality/ and other unique ICD-10 needs as identified thru queries and risk audits. 78
 What Impact Will ICD-10 Have On MS-DRG Payments? Lack of ‘specificity’ for a certain diagnosis as documented in the record, could have the potential of not capturing the CC/MCC which could result in a lower paying MS-DRG shifts could occur due to improper training of the coding staff. ◦ Example: Coder selects the improper root operation for a code, i. e. excision vs. resection. ◦ This incorrect code assignment could also potentially cause changes within the MS-DRGs resulting in payment increases or decreases. 79
What Impact Will ICD-10 Have On MS-DRG Payments? Lack of ‘specificity’ for a certain diagnosis as documented in the record, could have the potential of not capturing the CC/MCC which could result in a lower paying MS-DRG shifts could occur due to improper training of the coding staff. ◦ Example: Coder selects the improper root operation for a code, i. e. excision vs. resection. ◦ This incorrect code assignment could also potentially cause changes within the MS-DRGs resulting in payment increases or decreases. 79


