9fdac41a2ca39813fc774aea2474bf4a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 ICAO language proficiency requirements Dr Jeremy Mell Head of Language Studies ENAC, Toulouse, France jeremy. mell@enac. fr ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 1
ICAO language proficiency requirements Dr Jeremy Mell Head of Language Studies ENAC, Toulouse, France jeremy. mell@enac. fr ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 1
 Language proficiency: general concepts • single complex skill OR many sub-skills • knowledge/competence • competence/performance • receptive/productive • spoken/written • accuracy/fluency • general/special purpose (LSP) • AND for aviation… phraseology/plain language ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 2
Language proficiency: general concepts • single complex skill OR many sub-skills • knowledge/competence • competence/performance • receptive/productive • spoken/written • accuracy/fluency • general/special purpose (LSP) • AND for aviation… phraseology/plain language ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 2
 Communicative language competence • linguistic competence – lexical range, control • single words, fixed expressions – grammatical accuracy • syntax, morphology – phonological control • phonemes, syllable structure, prosody – interaction/fluency • pragmatic competence – relevance, rules for interpretation – appropriateness of tone/register/dialect – scripts, interaction schemata, – appropriateness of response – evaluation of outcomes • impacts on safety • impacts on efficiency ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 3
Communicative language competence • linguistic competence – lexical range, control • single words, fixed expressions – grammatical accuracy • syntax, morphology – phonological control • phonemes, syllable structure, prosody – interaction/fluency • pragmatic competence – relevance, rules for interpretation – appropriateness of tone/register/dialect – scripts, interaction schemata, – appropriateness of response – evaluation of outcomes • impacts on safety • impacts on efficiency ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 3
 ICAO language proficiency : who is concerned? • ALL partners in aeronautical communications (English and local language) • – « There are no native speakers of English as an International language » – foreign language speakers (FL) • training and testing – first language speakers (L 1) and second language speakers (L 2) • • accommodation and monitoring Smith (1992) - a study of intelligibility using speakers of 9 national varieties of English: Yoshida (2004) - ICAO seminar Tokyo • English as an International language (EIL) arises from a mutual need for comprehensible input: – refrain from using idioms/jargon – modulate delivery – be specific, explicit, direct – « native speakers … were not found to be the most easily understood, nor were they, as subjects, found to be best able to understand the different varieties of English » ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 4
ICAO language proficiency : who is concerned? • ALL partners in aeronautical communications (English and local language) • – « There are no native speakers of English as an International language » – foreign language speakers (FL) • training and testing – first language speakers (L 1) and second language speakers (L 2) • • accommodation and monitoring Smith (1992) - a study of intelligibility using speakers of 9 national varieties of English: Yoshida (2004) - ICAO seminar Tokyo • English as an International language (EIL) arises from a mutual need for comprehensible input: – refrain from using idioms/jargon – modulate delivery – be specific, explicit, direct – « native speakers … were not found to be the most easily understood, nor were they, as subjects, found to be best able to understand the different varieties of English » ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 4
 The rating scale: FAQ • Why a rating scale? – Not applied in other fields of aviation competency, but. . . – … well-established in the language training/testing profession • What are the benefits? – lower levels for recruitment/training – higher levels to predict future language loss – top level brings native-speakers within the purview of LPRs • Why an ICAO rating scale? – many general rating scales world-wide, but. . . – …. associated with particular tests (often commercial) or individual state, and. . . –. . . do not address specific requirements of aeronautical communications within a single level band – ICAO scale ensures • acceptability to stakeholders • efficiency in training/testing ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 5
The rating scale: FAQ • Why a rating scale? – Not applied in other fields of aviation competency, but. . . – … well-established in the language training/testing profession • What are the benefits? – lower levels for recruitment/training – higher levels to predict future language loss – top level brings native-speakers within the purview of LPRs • Why an ICAO rating scale? – many general rating scales world-wide, but. . . – …. associated with particular tests (often commercial) or individual state, and. . . –. . . do not address specific requirements of aeronautical communications within a single level band – ICAO scale ensures • acceptability to stakeholders • efficiency in training/testing ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 5
 ICAO language proficiency : foundations • PRICE SG: operational and academic • subject-matter experts + language experts • Evaluation of existing language proficiency scales • DLI/Council of Europe/…. • Findings of several job-specific linguistic needs analyses (cf. Appendix to Doc 9835): • FAA • Eurocontrol (PELA) • DGAC/ENAC (F) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 6
ICAO language proficiency : foundations • PRICE SG: operational and academic • subject-matter experts + language experts • Evaluation of existing language proficiency scales • DLI/Council of Europe/…. • Findings of several job-specific linguistic needs analyses (cf. Appendix to Doc 9835): • FAA • Eurocontrol (PELA) • DGAC/ENAC (F) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 6
 Language proficiency in aviation: what ICAO tells us (1) • Concerns only • Holistic descriptors – PIL/CTL radiotelephony communications (Annex 1) – communications between ATC units (Annex 11) • Excludes other professional tasks: – PIL: intra-cockpit, cabin announcements, ground staff… – CTL: intra-unit, external services, . . . – – – Proficient speakers shall: communicate effectively in voice only and in face to face situations. communicate on common, concrete, and work-related topics with accuracy and clarity. use appropriate communicative strategies to exchange messages and to recognize and resolve misunderstandings (to check, confirm, or clarify information. ) handle successfully and with relative ease the linguistic challenges presented by a complication or unexpected turn of events that occurs within the context of a routine work situation or communicative task with which they are otherwise familiar. use a dialect or accent which is intelligible to the aeronautical community. ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 7
Language proficiency in aviation: what ICAO tells us (1) • Concerns only • Holistic descriptors – PIL/CTL radiotelephony communications (Annex 1) – communications between ATC units (Annex 11) • Excludes other professional tasks: – PIL: intra-cockpit, cabin announcements, ground staff… – CTL: intra-unit, external services, . . . – – – Proficient speakers shall: communicate effectively in voice only and in face to face situations. communicate on common, concrete, and work-related topics with accuracy and clarity. use appropriate communicative strategies to exchange messages and to recognize and resolve misunderstandings (to check, confirm, or clarify information. ) handle successfully and with relative ease the linguistic challenges presented by a complication or unexpected turn of events that occurs within the context of a routine work situation or communicative task with which they are otherwise familiar. use a dialect or accent which is intelligible to the aeronautical community. ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 7
 Language proficiency in aviation: what ICAO tells us (2) • – • « ICAO standardized phraseology shall be used in all situations for which it has been specified. Only when standardized phraseology cannot serve an intended transmission, plain language shall be used. » Words and phrases (vocabulary) – – • – minimum “operational level” = 4 Attachment to Appendix to Annex 1: ICAO Rating scale – – – 6 levels of proficiency 6 skill areas (pronunciation, structure, vocabulary, comprehension, fluency, interactions) “The language proficiency requirements are applicable to the use of both phraseologies and plain language. ” • « relevant grammatical structures and sentence patterns are determined by language functions appropriate to the task » Phonology (pronunciation) – • « common, concrete and work-related topics » “paraphrase successfully” Grammatical structures Annex 1 – • • Annex 10, 5. 1. 1. 1 « accent which is intelligible to the aeronautical community » Interactions – – «voice-only and face-to-face situations » «general or work-related context » « complication or unexpected turn of events » « apparent misunderstandings » ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 8
Language proficiency in aviation: what ICAO tells us (2) • – • « ICAO standardized phraseology shall be used in all situations for which it has been specified. Only when standardized phraseology cannot serve an intended transmission, plain language shall be used. » Words and phrases (vocabulary) – – • – minimum “operational level” = 4 Attachment to Appendix to Annex 1: ICAO Rating scale – – – 6 levels of proficiency 6 skill areas (pronunciation, structure, vocabulary, comprehension, fluency, interactions) “The language proficiency requirements are applicable to the use of both phraseologies and plain language. ” • « relevant grammatical structures and sentence patterns are determined by language functions appropriate to the task » Phonology (pronunciation) – • « common, concrete and work-related topics » “paraphrase successfully” Grammatical structures Annex 1 – • • Annex 10, 5. 1. 1. 1 « accent which is intelligible to the aeronautical community » Interactions – – «voice-only and face-to-face situations » «general or work-related context » « complication or unexpected turn of events » « apparent misunderstandings » ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 8
 Work related topics: aviation • Domains – accident investigation, aerial work, aerodrome, aeronautical information, air transport management, aircraft, approach, ATC automation, ATC staff, cartography, collision risk, en-route, fuel management, ground movements, in-flight incidents, landing, liaison, meteorology, navaids, organizations, position reporting, private flying, radar, radio communications, regulations, search and rescue, take-off and departure, telephone monitoring, traffic information (source AIRWORD ENAC/Eurocontrol, ) • Sub-domains – aerodrome • • • status management general terms amenities facilities services surface conditions runways/taxiways security problems water aerodrome ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 9
Work related topics: aviation • Domains – accident investigation, aerial work, aerodrome, aeronautical information, air transport management, aircraft, approach, ATC automation, ATC staff, cartography, collision risk, en-route, fuel management, ground movements, in-flight incidents, landing, liaison, meteorology, navaids, organizations, position reporting, private flying, radar, radio communications, regulations, search and rescue, take-off and departure, telephone monitoring, traffic information (source AIRWORD ENAC/Eurocontrol, ) • Sub-domains – aerodrome • • • status management general terms amenities facilities services surface conditions runways/taxiways security problems water aerodrome ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 9
 Work related topics: non-aviation • • • Abbreviations, acronyms Animals, birds, Behaviour, activities Cargo, merchandise, packaging Causes, conditions Geography, topographical features, Health, medecine Language, spoken communication Modality (obligation, probability, possibility) • Numbers • • Perception, senses Problems, errors, accidents, malfunctions Rules, enforcement, infringement, protocol Space, movement, position, distance, dimension Technology Time, duration, schedules Transport, travel, vehicles Weather, climate, natural disasters ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 10
Work related topics: non-aviation • • • Abbreviations, acronyms Animals, birds, Behaviour, activities Cargo, merchandise, packaging Causes, conditions Geography, topographical features, Health, medecine Language, spoken communication Modality (obligation, probability, possibility) • Numbers • • Perception, senses Problems, errors, accidents, malfunctions Rules, enforcement, infringement, protocol Space, movement, position, distance, dimension Technology Time, duration, schedules Transport, travel, vehicles Weather, climate, natural disasters ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 10
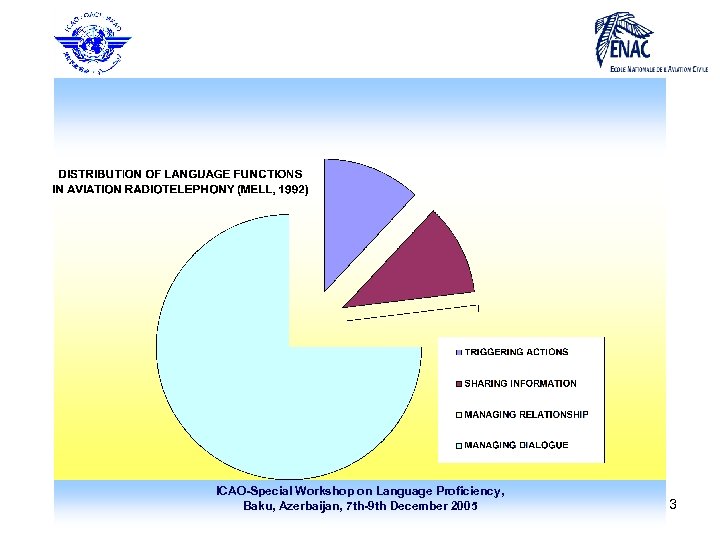
 Grammatical structures: overview • • “grammatical structures and sentence patterns are determined by language functions appropriate to the task ” communicative function – – • speaker’s intention in producing a given utterance (a “speech act”) e. g. … “request information”, “thank”, “deny approval”, … intentions are linked to activities being undertaken, so we can identify a limited predictable range of frequently occurring functions – – • same functions can be realised in professional OR non-professional contexts distinguish different functions for comprehension and production 4 major function groups in aeronautical R/T (Doc 9835, Appendix B) – – triggering actions (orders, requests/offers to act, advice, permission/approval, undertakings, . . . ) sharing information (states, actions, events in the past, present or future, necessity, feasibility, …) managing the relationship (satisfaction, complaint, reprimand, concern, reassurance, apologies, …) managing the dialogue (opening/closing, self-correction, readback, acknowledgement, checking, repetition, confirmation, clarification, relaying, …) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 11
Grammatical structures: overview • • “grammatical structures and sentence patterns are determined by language functions appropriate to the task ” communicative function – – • speaker’s intention in producing a given utterance (a “speech act”) e. g. … “request information”, “thank”, “deny approval”, … intentions are linked to activities being undertaken, so we can identify a limited predictable range of frequently occurring functions – – • same functions can be realised in professional OR non-professional contexts distinguish different functions for comprehension and production 4 major function groups in aeronautical R/T (Doc 9835, Appendix B) – – triggering actions (orders, requests/offers to act, advice, permission/approval, undertakings, . . . ) sharing information (states, actions, events in the past, present or future, necessity, feasibility, …) managing the relationship (satisfaction, complaint, reprimand, concern, reassurance, apologies, …) managing the dialogue (opening/closing, self-correction, readback, acknowledgement, checking, repetition, confirmation, clarification, relaying, …) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 11
 Individual functions (example) • Triggering actions: – orders - controller • • • give an order give an amended order give a negative order give alternative orders give a sequence of orders • cancel an order • « give an order » : – phraseology • TURN LEFT – plain language • NOW, I WANT YOU TO TURN LEFT ABEAM THE SHOPPING MALL AT YOUR 1 O ’CLOCK. DO YOU HAVE IT IN SIGHT? – orders - pilot • announce compliance • announce non-compliance ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 12
Individual functions (example) • Triggering actions: – orders - controller • • • give an order give an amended order give a negative order give alternative orders give a sequence of orders • cancel an order • « give an order » : – phraseology • TURN LEFT – plain language • NOW, I WANT YOU TO TURN LEFT ABEAM THE SHOPPING MALL AT YOUR 1 O ’CLOCK. DO YOU HAVE IT IN SIGHT? – orders - pilot • announce compliance • announce non-compliance ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 12
 ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 13
ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 13
 Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • • Complex move – I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 14
Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • • Complex move – I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 14
 Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • • Complex move – I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 15
Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • • Complex move – I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 15
 Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) • – – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • Complex move • Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Complex exchange – – – Are you direct BRC? Yes sir. Do we need to come right a little? I think you proceed initially to Abbeville, if you wish Abbeville by the right. Understand turn right. We could go to Abbeville VOR, BRC Negative. Proceed Abbeville, BRC or if you prefer BRC direct. Direct to the BRC ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 16
Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) • – – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • Complex move • Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Complex exchange – – – Are you direct BRC? Yes sir. Do we need to come right a little? I think you proceed initially to Abbeville, if you wish Abbeville by the right. Understand turn right. We could go to Abbeville VOR, BRC Negative. Proceed Abbeville, BRC or if you prefer BRC direct. Direct to the BRC ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 16
 Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) • – – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • Complex move • Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Complex exchange – – – Are you direct BRC? Yes sir. Do we need to come right a little? I think you proceed initially to Abbeville, if you wish Abbeville by the right. Understand turn right. We could go to Abbeville VOR, BRC Negative. Proceed Abbeville, BRC or if you prefer BRC direct. Direct to the BRC ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 17
Interaction schemata • Simple (2 moves) • – – Maintain flight level 2 7 0 – Maintain 270 • Simple (3 moves) CTL initiative: – Say heading – 1 7 3 roger • Complex move • Simple (3 moves) PIL initiative: – Requesting descent – Descend flight level 1 3 0 I ’ve got an emergency, short on fuel, and I ’m steering to the beacon on II 2. 3, and I ’ve been told to tune onto the IFR to get me into an airfield. I have less than 15 minutes fuel supply sir. Have you copied? Over. Complex exchange – – – Are you direct BRC? Yes sir. Do we need to come right a little? I think you proceed initially to Abbeville, if you wish Abbeville by the right. Understand turn right. We could go to Abbeville VOR, BRC Negative. Proceed Abbeville, BRC or if you prefer BRC direct. Direct to the BRC ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 17
 Phonology - the problem • phonology is a crucial parameter for intelligibility, – sound channel imperfections – absence of visual channel – non-native speaker (NNS) reliance on acoustic input • but phonological features are: – – least described by linguists strongly influenced by mother tongue most closely linked with personal identity least susceptible to conscious control ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 18
Phonology - the problem • phonology is a crucial parameter for intelligibility, – sound channel imperfections – absence of visual channel – non-native speaker (NNS) reliance on acoustic input • but phonological features are: – – least described by linguists strongly influenced by mother tongue most closely linked with personal identity least susceptible to conscious control ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 18
 Phonology - some solutions • All stakeholders follow ICAO recommendations • • standardised phraseology/standardised pronunciation of alphabet, numbers NNS renounce a pure native speaker (NS) target for pronunciation – linguists define core phonology e. g. Lingua Franca Core (Jenkins) combining crucial features of regional variants • • vowel length distinctions, correct placing of nuclear stress, marking of tone boundaries, avoid simplification of some consonant clusters – learners practise paired interactions (different first language backgrounds) • NS cultivate skills of accommodation in speaking • • perception of interlocutor’s possible linguistic difficulties replacement of ‘ high-risk ’ L 1 features to increase communicative efficiency – • a natural inclination if intelligibility is a salient feature of the interaction NS + NNS develop skills of “convergence” ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 19
Phonology - some solutions • All stakeholders follow ICAO recommendations • • standardised phraseology/standardised pronunciation of alphabet, numbers NNS renounce a pure native speaker (NS) target for pronunciation – linguists define core phonology e. g. Lingua Franca Core (Jenkins) combining crucial features of regional variants • • vowel length distinctions, correct placing of nuclear stress, marking of tone boundaries, avoid simplification of some consonant clusters – learners practise paired interactions (different first language backgrounds) • NS cultivate skills of accommodation in speaking • • perception of interlocutor’s possible linguistic difficulties replacement of ‘ high-risk ’ L 1 features to increase communicative efficiency – • a natural inclination if intelligibility is a salient feature of the interaction NS + NNS develop skills of “convergence” ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 19
 Spontaneous convergence, if. . . - Productive convergence: - • intelligibility is most salient aspect of interaction (eg Information transfer) speaker appreciates listener's difficulties in using extra-linguistic context target LFC item is within speaker's repertoire and can be produced effortlessly no processing overload to prevent focus on pronunciation Receptive convergence: - motivated to understand (eg. Information transfer) prior exposure to speaker's accent prior exposure to a range of L 2 accents and tolerance of difference no fear of acquiring speaker's transfer errors linguistically and affectively able to signal non-comprehension ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 20
Spontaneous convergence, if. . . - Productive convergence: - • intelligibility is most salient aspect of interaction (eg Information transfer) speaker appreciates listener's difficulties in using extra-linguistic context target LFC item is within speaker's repertoire and can be produced effortlessly no processing overload to prevent focus on pronunciation Receptive convergence: - motivated to understand (eg. Information transfer) prior exposure to speaker's accent prior exposure to a range of L 2 accents and tolerance of difference no fear of acquiring speaker's transfer errors linguistically and affectively able to signal non-comprehension ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 20
 Level 4: implementation issues • A licensing requirement: – level 4 = operational (the safety standard) – levels 4 -6: re-test intervals – supplementary descriptors for ICAO phraseology? • A training objective: – intermediate levels (3. 5…) – aim higher to: • • increase safety margins? facilitate maintenance – unstable vs. consolidated levels • • • variability of performance (mood, stress, …) one or more skills are borderline A potential benchmark for: – monitoring performance in aeronautical commmunications – analysing occurrences, incidents, . . . ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 21
Level 4: implementation issues • A licensing requirement: – level 4 = operational (the safety standard) – levels 4 -6: re-test intervals – supplementary descriptors for ICAO phraseology? • A training objective: – intermediate levels (3. 5…) – aim higher to: • • increase safety margins? facilitate maintenance – unstable vs. consolidated levels • • • variability of performance (mood, stress, …) one or more skills are borderline A potential benchmark for: – monitoring performance in aeronautical commmunications – analysing occurrences, incidents, . . . ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 21
 Level 4: application to phraseology • Possible descriptors: – Uses standard ICAO phraseology accurately and appropriately, even when switching between phraseology and appropriate plain language. – Pronunciation of phraseology conforms to ICAO recommended pronunciations when available, or otherwise to a natural model of pronunciation which is intelligible to the aeronautical community. – Speech transmitting technique (enunciation, rate of speech, pausing, and speaking volume) is adequate to fulfil ICAO recommendations for intelligibility. • Definition of accuracy: – Accurate use of phraseology implies that terminology, syntax and sentence frames conform to prescribed models whenever these are required by the situation or intended message – Accurate utterances contain: - - no unjustified deletions (eg. “Climb 350”) no unjustified additions (eg. “You can climb now to flight level 350”) no substitutions by plain language lexis or structures (eg. “OK” for “Roger”) no re-sequencing of elements (eg. Traffic information) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 22
Level 4: application to phraseology • Possible descriptors: – Uses standard ICAO phraseology accurately and appropriately, even when switching between phraseology and appropriate plain language. – Pronunciation of phraseology conforms to ICAO recommended pronunciations when available, or otherwise to a natural model of pronunciation which is intelligible to the aeronautical community. – Speech transmitting technique (enunciation, rate of speech, pausing, and speaking volume) is adequate to fulfil ICAO recommendations for intelligibility. • Definition of accuracy: – Accurate use of phraseology implies that terminology, syntax and sentence frames conform to prescribed models whenever these are required by the situation or intended message – Accurate utterances contain: - - no unjustified deletions (eg. “Climb 350”) no unjustified additions (eg. “You can climb now to flight level 350”) no substitutions by plain language lexis or structures (eg. “OK” for “Roger”) no re-sequencing of elements (eg. Traffic information) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 22
 Further reading • • ICAO (2004), Doc 9835 AN/453, Manual on the Implementation of ICAO Language Proficiency Requirements. Jenkins, J (2000), The Phonology of English as an International Language, Oxford University Press. Mell, J (1992), Etude des communications verbales entre pilote et contrôleur en situation standard et non-standard, Editions de l’ENAC. Websites – www. icaea. pata. pl (International Civil Aviation English Association) – http: //culture. coe. fr (Common European Framework for Modern Languages) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 23
Further reading • • ICAO (2004), Doc 9835 AN/453, Manual on the Implementation of ICAO Language Proficiency Requirements. Jenkins, J (2000), The Phonology of English as an International Language, Oxford University Press. Mell, J (1992), Etude des communications verbales entre pilote et contrôleur en situation standard et non-standard, Editions de l’ENAC. Websites – www. icaea. pata. pl (International Civil Aviation English Association) – http: //culture. coe. fr (Common European Framework for Modern Languages) ICAO-Special Workshop on Language Proficiency, Baku, Azerbaijan, 7 th-9 th December 2005 23


