df1411ff3b468b1c566ba9142d4af6a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

IBM z. Series Scholars Program WAS for z/OS V 5: Web Container © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 Course materials may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written permission of IBM. 3. 3. 1

Unit Objectives IBM z. Series After completing this unit, you should be able to: § Describe the components needed to run a Web. Sphere V 5 web application § Configure the administration objects that are needed to activate web client access to a Web. Sphere application § Describe how the request URL is processed so that the required servlet class file is loaded for a request § Define the configuration elements needed to support the IBM HTTP server plug-in for Web. Sphere V 5 © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 2
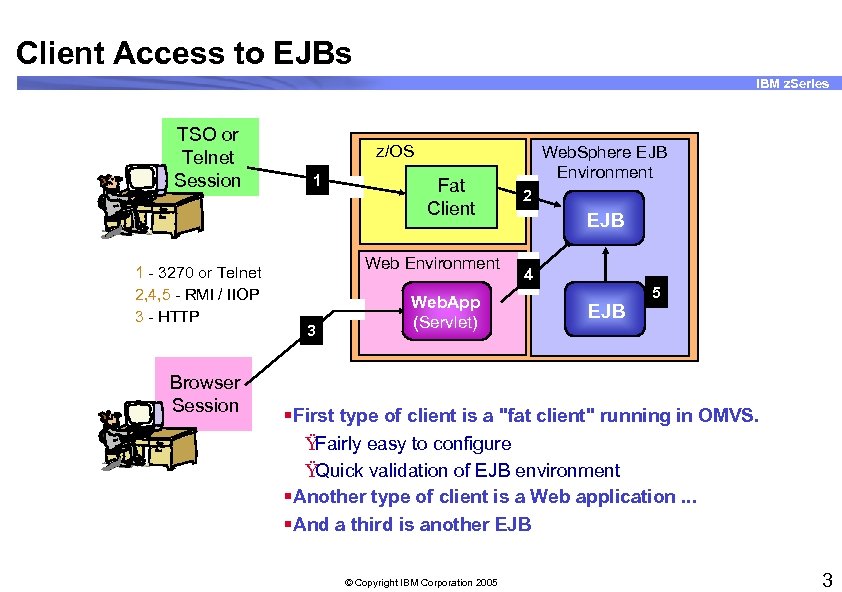
Client Access to EJBs IBM z. Series TSO or Telnet Session 1 - 3270 or Telnet 2, 4, 5 - RMI / IIOP 3 - HTTP Browser Session z/OS 1 Fat Client Web Environment 3 Web. App (Servlet) Web. Sphere EJB Environment 2 EJB 4 EJB 5 §First type of client is a "fat client" running in OMVS. Ÿ Fairly easy to configure Ÿ Quick validation of EJB environment §Another type of client is a Web application. . . §And a third is another EJB © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 3
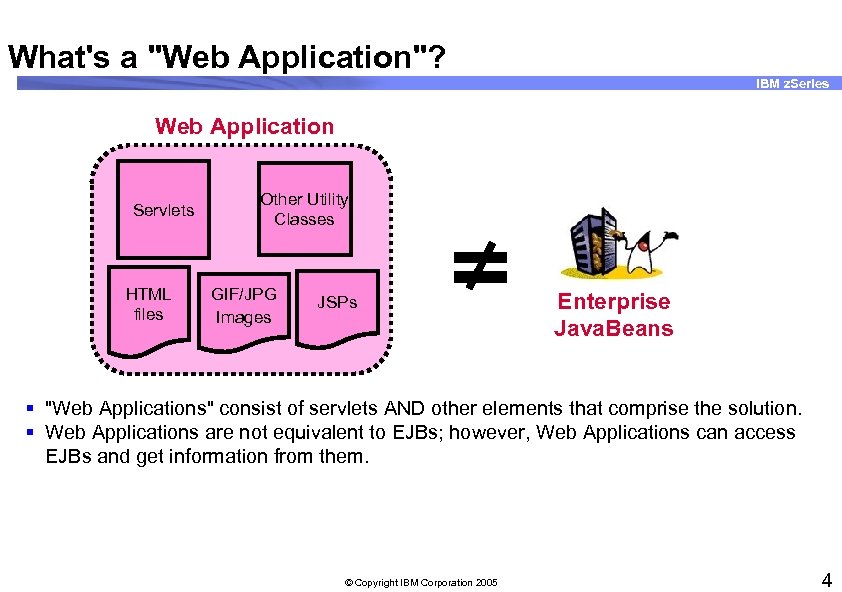
What's a "Web Application"? IBM z. Series Web Application Servlets HTML files Other Utility Classes GIF/JPG Images JSPs Enterprise Java. Beans § "Web Applications" consist of servlets AND other elements that comprise the solution. § Web Applications are not equivalent to EJBs; however, Web Applications can access EJBs and get information from them. © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 4
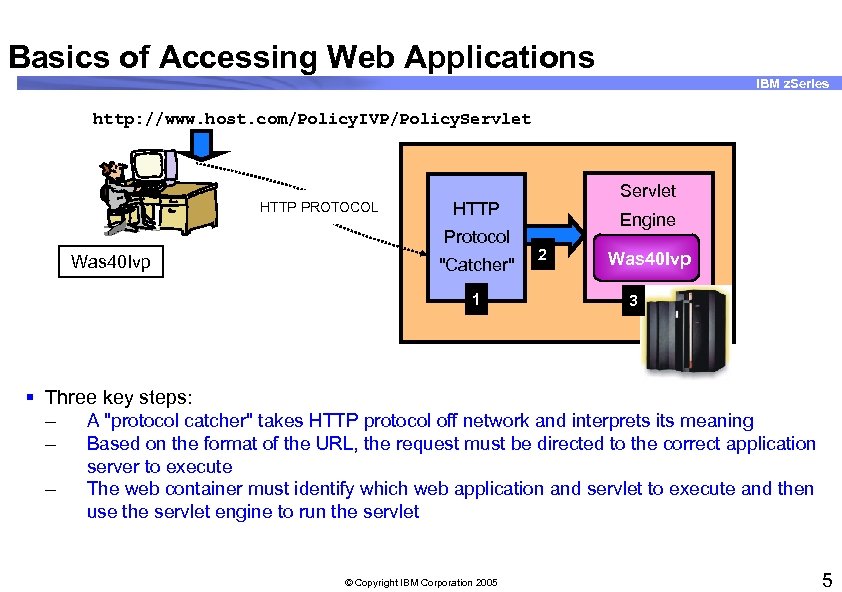
Basics of Accessing Web Applications IBM z. Series http: //www. host. com/Policy. IVP/Policy. Servlet HTTP PROTOCOL HTTP Protocol Was 40 Ivp Servlet "Catcher" 1 Engine 2 Was 40 Ivp 3 § Three key steps: – A "protocol catcher" takes HTTP protocol off network and interprets its meaning – Based on the format of the URL, the request must be directed to the correct application – server to execute The web container must identify which web application and servlet to execute and then use the servlet engine to run the servlet © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 5
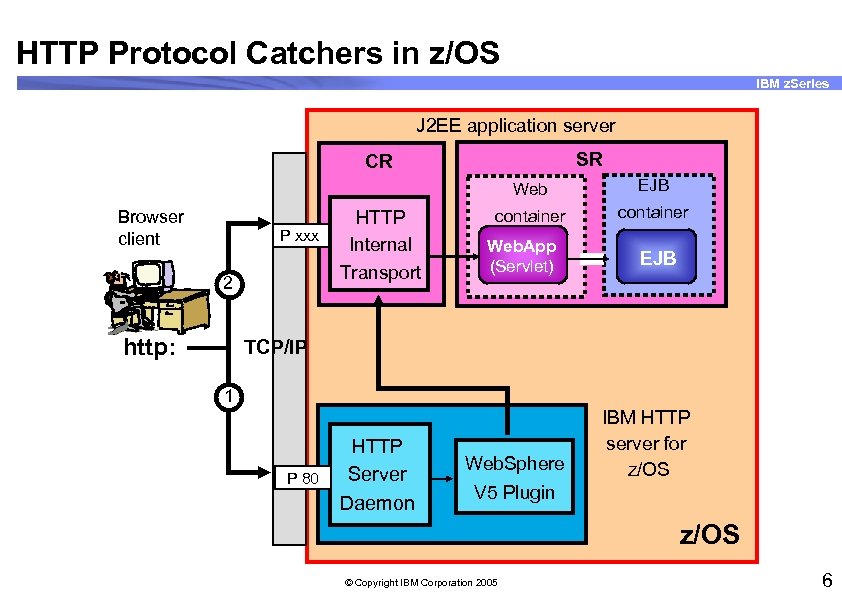
HTTP Protocol Catchers in z/OS IBM z. Series J 2 EE application server SR CR Web Browser client P xxx 2 http: HTTP Internal Transport EJB container Web. App (Servlet) EJB TCP/IP 1 P 80 HTTP Server Daemon Web. Sphere IBM HTTP server for z/OS V 5 Plugin z/OS © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 6
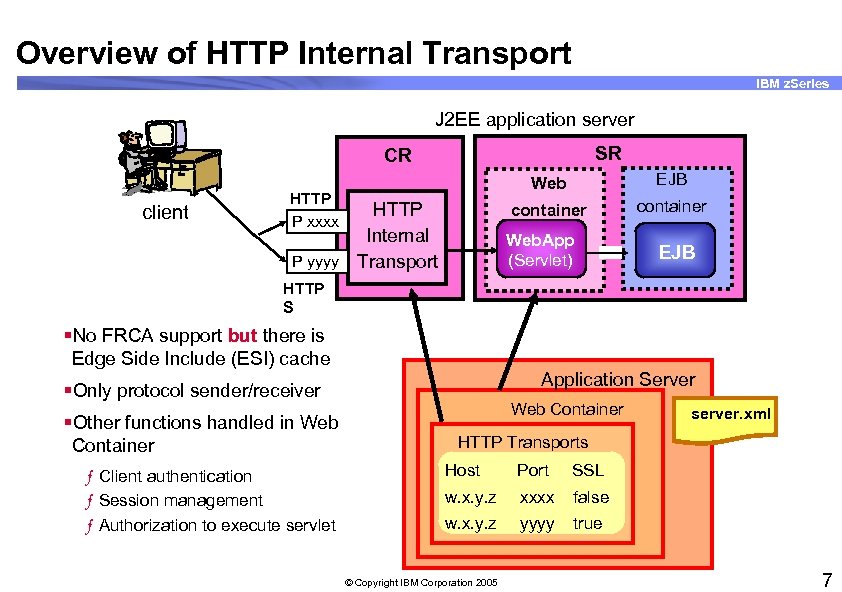
Overview of HTTP Internal Transport IBM z. Series J 2 EE application server SR CR client Web container HTTP P xxxx HTTP Internal P yyyy Transport EJB container Web. App (Servlet) EJB HTTP S §No FRCA support but there is Edge Side Include (ESI) cache Application Server §Only protocol sender/receiver §Other functions handled in Web Container ƒ Client authentication ƒ Session management ƒ Authorization to execute servlet Web Container server. xml HTTP Transports Host Port SSL w. x. y. z xxxx false w. x. y. z yyyy true © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 7
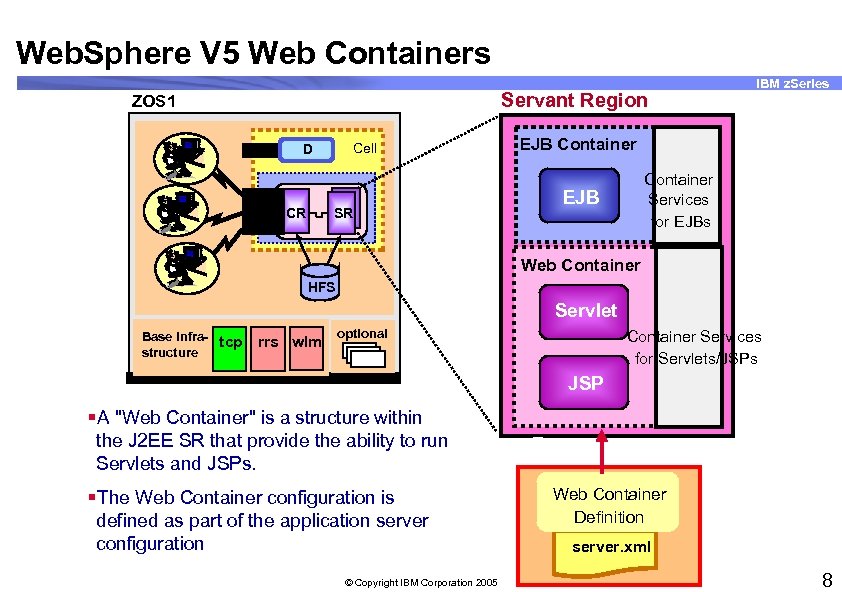
Web. Sphere V 5 Web Containers Servant Region ZOS 1 Cell D CR SR IBM z. Series EJB Container Services for EJBs EJB Web Container HFS Servlet Base infrastructure tcp rrs wlm optional Container Services for Servlets/JSPs JSP §A "Web Container" is a structure within the J 2 EE SR that provide the ability to run Servlets and JSPs. §The Web Container configuration is defined as part of the application server configuration © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 Web Container Definition server. xml 8
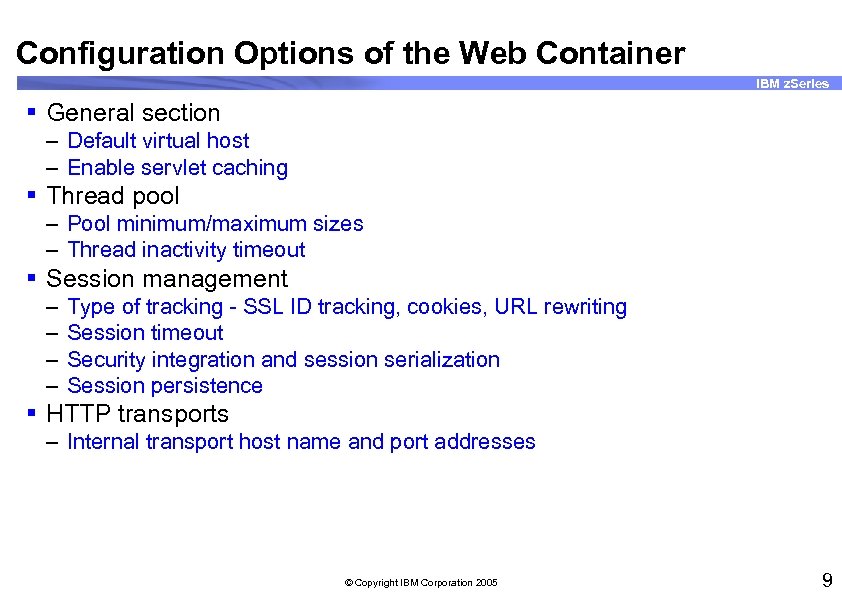
Configuration Options of the Web Container IBM z. Series § General section – Default virtual host – Enable servlet caching § Thread pool – Pool minimum/maximum sizes – Thread inactivity timeout § Session management – – Type of tracking - SSL ID tracking, cookies, URL rewriting Session timeout Security integration and session serialization Session persistence § HTTP transports – Internal transport host name and port addresses © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 9
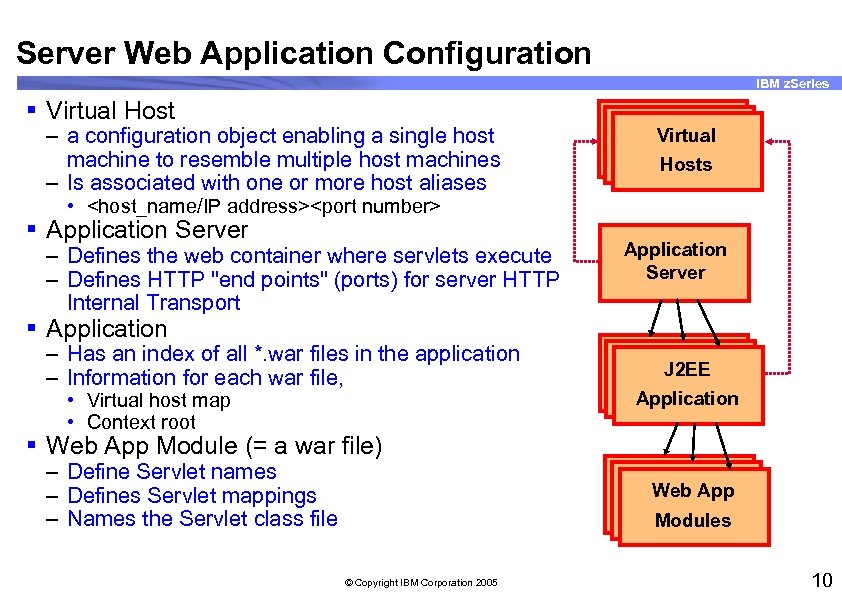
Server Web Application Configuration IBM z. Series § Virtual Host – a configuration object enabling a single host machine to resemble multiple host machines – Is associated with one or more host aliases Virtual Hosts • <host_name/IP address><port number> § Application Server – Defines the web container where servlets execute – Defines HTTP "end points" (ports) for server HTTP Internal Transport Application Server § Application – Has an index of all *. war files in the application – Information for each war file, • Virtual host map • Context root J 2 EE Application § Web App Module (= a war file) – Define Servlet names – Defines Servlet mappings – Names the Servlet class file Web App Modules © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 10
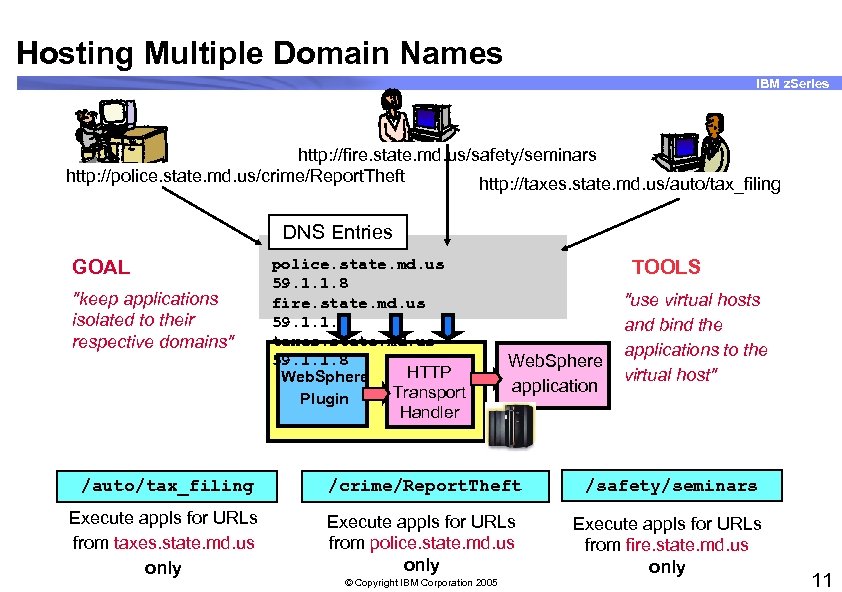
Hosting Multiple Domain Names IBM z. Series http: //fire. state. md. us/safety/seminars http: //police. state. md. us/crime/Report. Theft http: //taxes. state. md. us/auto/tax_filing DNS Entries GOAL "keep applications isolated to their respective domains" police. state. md. us 59. 1. 1. 8 fire. state. md. us 59. 1. 1. 8 taxes. state. md. us 59. 1. 1. 8 HTTP Web. Sphere Transport Plugin TOOLS Web. Sphere application "use virtual hosts and bind the applications to the virtual host" Handler /auto/tax_filing /crime/Report. Theft /safety/seminars Execute appls for URLs from taxes. state. md. us only Execute appls for URLs from police. state. md. us only Execute appls for URLs from fire. state. md. us only © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 11
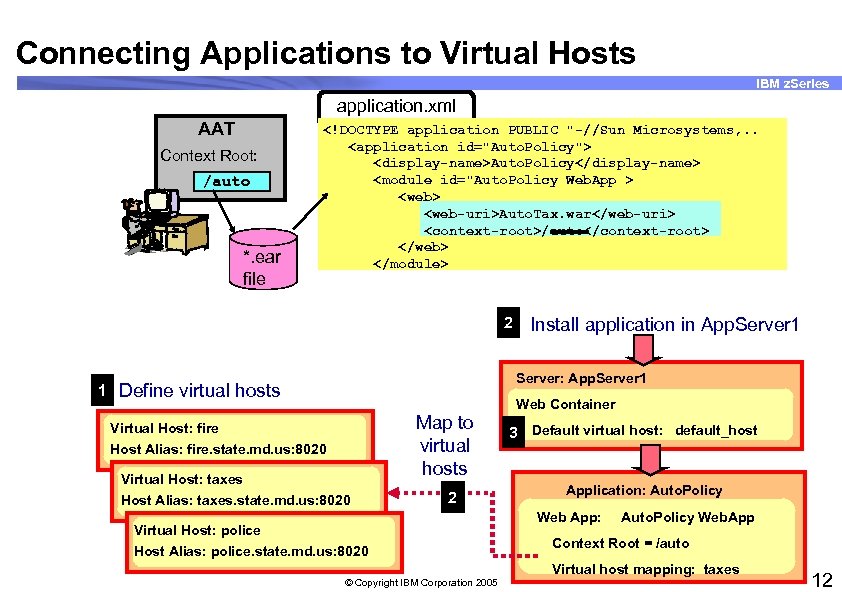
Connecting Applications to Virtual Hosts IBM z. Series application. xml AAT Context Root: /auto *. ear file <!DOCTYPE application PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, . . <application id="Auto. Policy"> <display-name>Auto. Policy</display-name> <module id="Auto. Policy Web. App > <web-uri>Auto. Tax. war</web-uri> <context-root>/auto</context-root> </web> </module> 2 Install application in App. Server 1 Server: App. Server 1 1 Define virtual hosts Web Container Virtual Host: fire Host Alias: fire. state. md. us: 8020 Virtual Host: taxes Host Alias: taxes. state. md. us: 8020 Map to virtual hosts 2 Virtual Host: police Host Alias: police. state. md. us: 8020 3 Default virtual host: default_host Application: Auto. Policy Web App: Auto. Policy Web. App Context Root = /auto Virtual host mapping: taxes © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 12
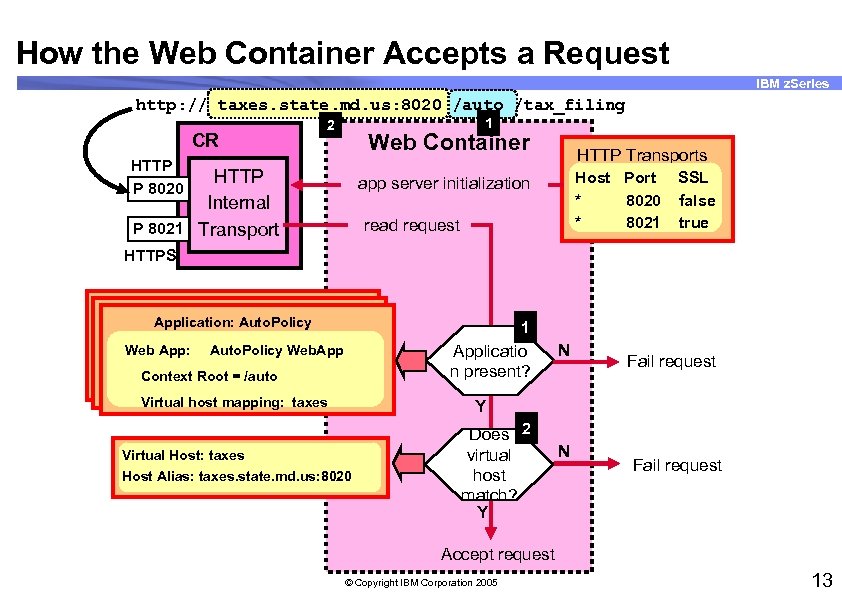
How the Web Container Accepts a Request IBM z. Series http: // taxes. state. md. us: 8020 /auto /tax_filing CR 1 2 Web Container HTTP P 8020 HTTP Internal P 8021 Transport HTTP Transports Host Port * 8020 * 8021 app server initialization read request SSL false true HTTPS Application: Auto. Policy Web App: 1 Applicatio n present? Auto. Policy Web. App Context Root = /auto Virtual host mapping: taxes N Fail request Y Virtual Host: taxes Host Alias: taxes. state. md. us: 8020 Does 2 virtual host match? Y N Fail request Accept request © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 13
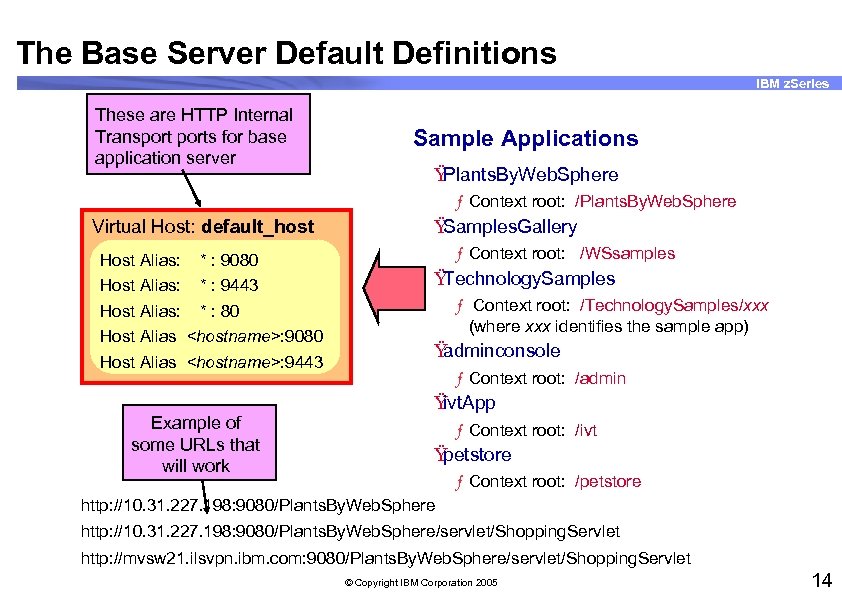
The Base Server Default Definitions IBM z. Series These are HTTP Internal Transports for base application server Sample Applications Ÿ Plants. By. Web. Sphere ƒ Context root: /Plants. By. Web. Sphere Virtual Host: default_host Host Alias: * : 9080 Host Alias: * : 9443 Host Alias: * : 80 Host Alias <hostname>: 9080 Host Alias <hostname>: 9443 Example of some URLs that will work Ÿ Samples. Gallery ƒ Context root: /WSsamples Ÿ Technology. Samples ƒ Context root: /Technology. Samples/xxx (where xxx identifies the sample app) Ÿ adminconsole ƒ Context root: /admin Ÿ ivt. App ƒ Context root: /ivt Ÿ petstore ƒ Context root: /petstore http: //10. 31. 227. 198: 9080/Plants. By. Web. Sphere/servlet/Shopping. Servlet http: //mvsw 21. ilsvpn. ibm. com: 9080/Plants. By. Web. Sphere/servlet/Shopping. Servlet © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 14
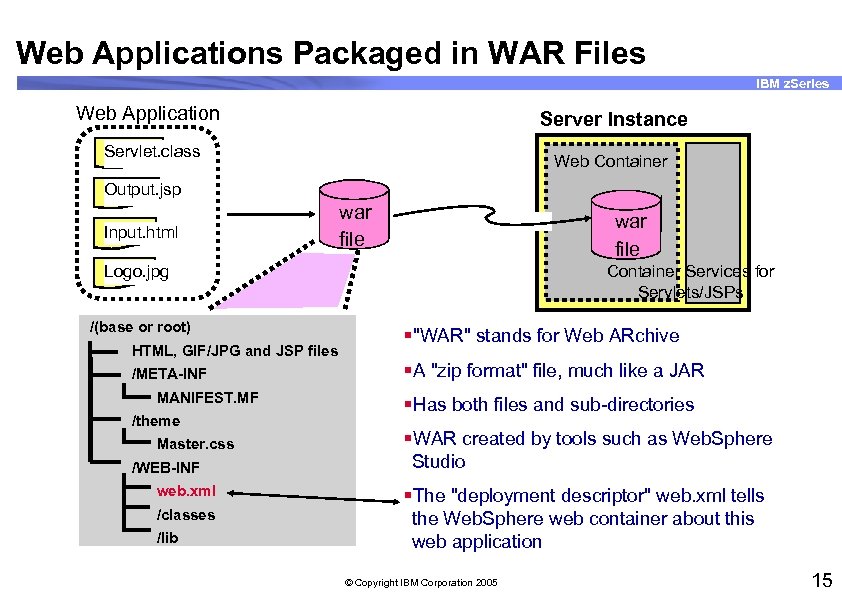
Web Applications Packaged in WAR Files IBM z. Series Web Application Server Instance Servlet. class Web Container Output. jsp Input. html war file Logo. jpg /(base or root) HTML, GIF/JPG and JSP files /META-INF MANIFEST. MF /theme Master. css /WEB-INF web. xml /classes /lib Container Services for Servlets/JSPs §"WAR" stands for Web ARchive §A "zip format" file, much like a JAR §Has both files and sub-directories §WAR created by tools such as Web. Sphere Studio §The "deployment descriptor" web. xml tells the Web. Sphere web container about this web application © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 15
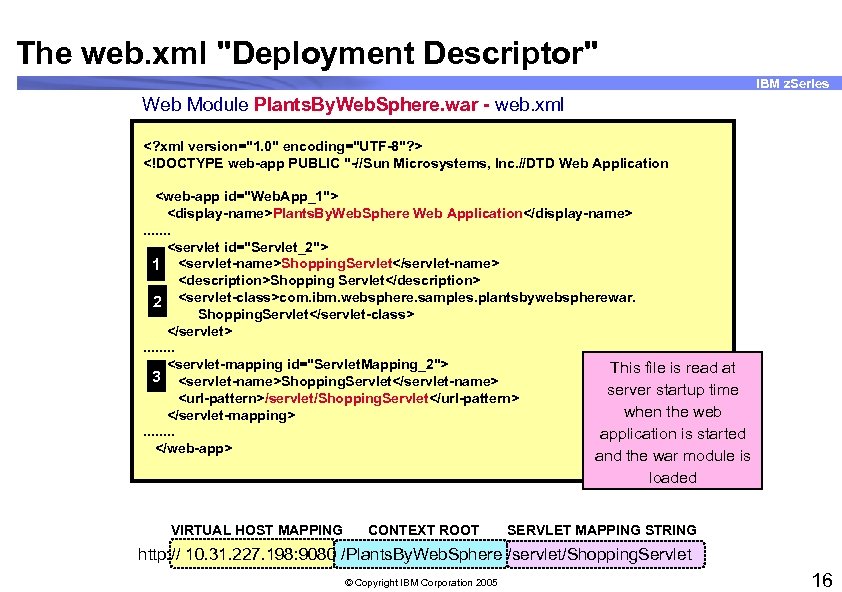
The web. xml "Deployment Descriptor" IBM z. Series Web Module Plants. By. Web. Sphere. war - web. xml <? xml version="1. 0" encoding="UTF-8"? > <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc. //DTD Web Application <web-app id="Web. App_1"> <display-name>Plants. By. Web. Sphere Web Application</display-name>. . . . <servlet id="Servlet_2"> 1 <servlet-name>Shopping. Servlet</servlet-name> <description>Shopping Servlet</description> 2 <servlet-class>com. ibm. websphere. samples. plantsbywebspherewar. Shopping. Servlet</servlet-class> </servlet>. . . . <servlet-mapping id="Servlet. Mapping_2"> This file is read at 3 <servlet-name>Shopping. Servlet</servlet-name> server startup time <url-pattern>/servlet/Shopping. Servlet</url-pattern> when the web </servlet-mapping>. . . . application is started </web-app> and the war module is loaded VIRTUAL HOST MAPPING CONTEXT ROOT SERVLET MAPPING STRING http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 9080 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere /servlet/Shopping. Servlet © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 16
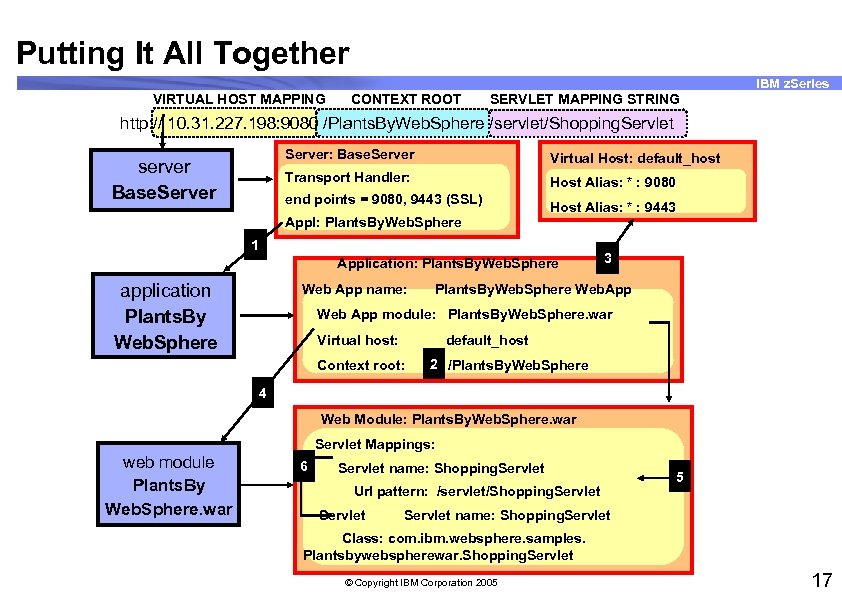
Putting It All Together IBM z. Series VIRTUAL HOST MAPPING CONTEXT ROOT SERVLET MAPPING STRING http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 9080 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere /servlet/Shopping. Servlet Server: Base. Server Virtual Host: default_host Transport Handler: server Base. Server Host Alias: * : 9080 end points = 9080, 9443 (SSL) Appl: Plants. By. Web. Sphere Host Alias: * : 9443 1 Application: Plants. By. Web. Sphere application Plants. By Web. Sphere Web App name: 3 Plants. By. Web. Sphere Web. App Web App module: Plants. By. Web. Sphere. war Virtual host: default_host Context root: 2 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere 4 Web Module: Plants. By. Web. Sphere. war Servlet Mappings: web module Plants. By Web. Sphere. war 6 Servlet name: Shopping. Servlet Url pattern: /servlet/Shopping. Servlet 5 Servlet name: Shopping. Servlet Class: com. ibm. websphere. samples. Plantsbywebspherewar. Shopping. Servlet © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 17
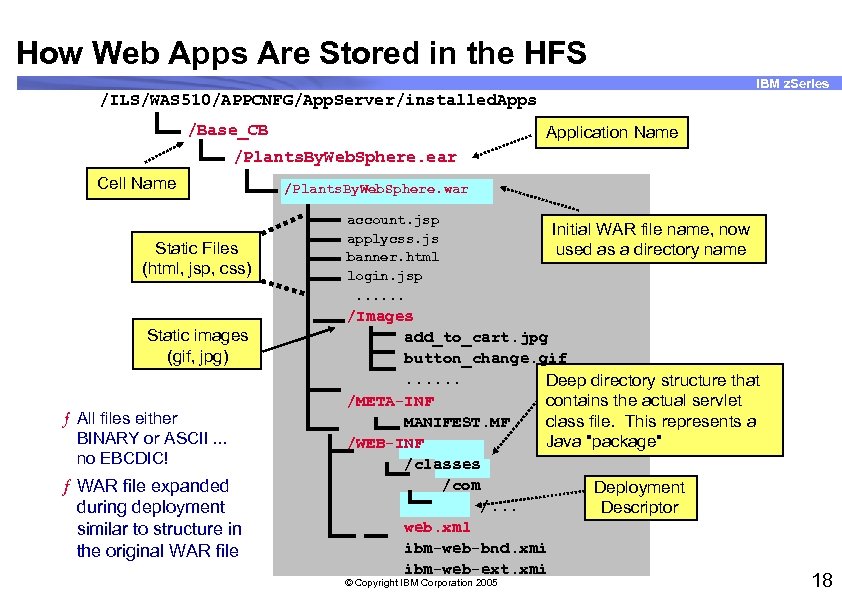
How Web Apps Are Stored in the HFS IBM z. Series /ILS/WAS 510/APPCNFG/App. Server/installed. Apps /Base_CB Application Name /Plants. By. Web. Sphere. ear Cell Name Static Files (html, jsp, css) Static images (gif, jpg) ƒ All files either BINARY or ASCII. . . no EBCDIC! ƒ WAR file expanded during deployment similar to structure in the original WAR file /Plants. By. Web. Sphere. war account. jsp applycss. js banner. html login. jsp. . . Initial WAR file name, now used as a directory name /Images add_to_cart. jpg button_change. gif. . . Deep directory structure that /META-INF contains the actual servlet MANIFEST. MF class file. This represents a Java "package" /WEB-INF /classes /com Deployment /. . . Descriptor web. xml ibm-web-bnd. xmi ibm-web-ext. xmi © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 18
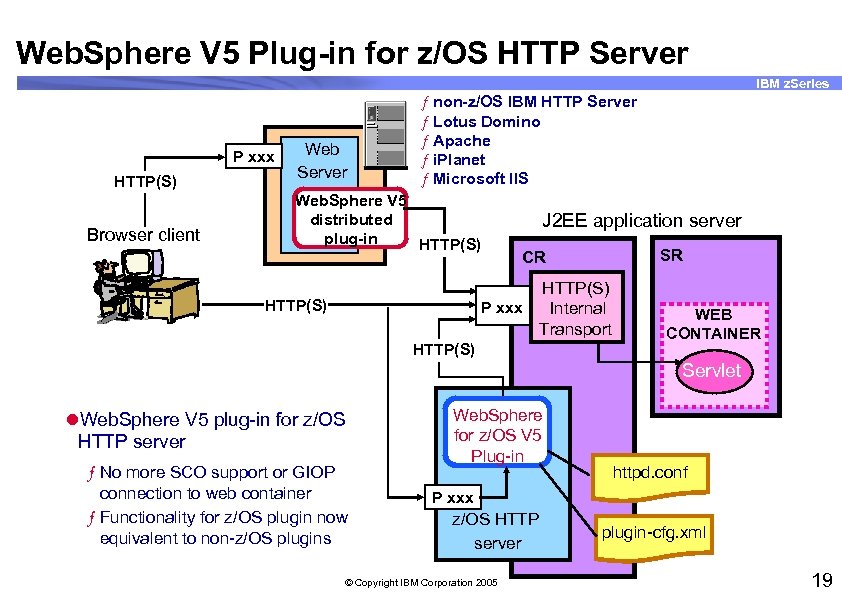
Web. Sphere V 5 Plug-in for z/OS HTTP Server IBM z. Series P xxx HTTP(S) Browser client Web Server ƒ non-z/OS IBM HTTP Server ƒ Lotus Domino ƒ Apache ƒ i. Planet ƒ Microsoft IIS Web. Sphere V 5 distributed plug-in HTTP(S) J 2 EE application server SR CR HTTP(S) P xxx Internal Transport HTTP(S) WEB CONTAINER Servlet l. Web. Sphere V 5 plug-in for z/OS HTTP server ƒ No more SCO support or GIOP connection to web container ƒ Functionality for z/OS plugin now equivalent to non-z/OS plugins Web. Sphere for z/OS V 5 Plug-in httpd. conf P xxx z/OS HTTP server © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 plugin-cfg. xml 19
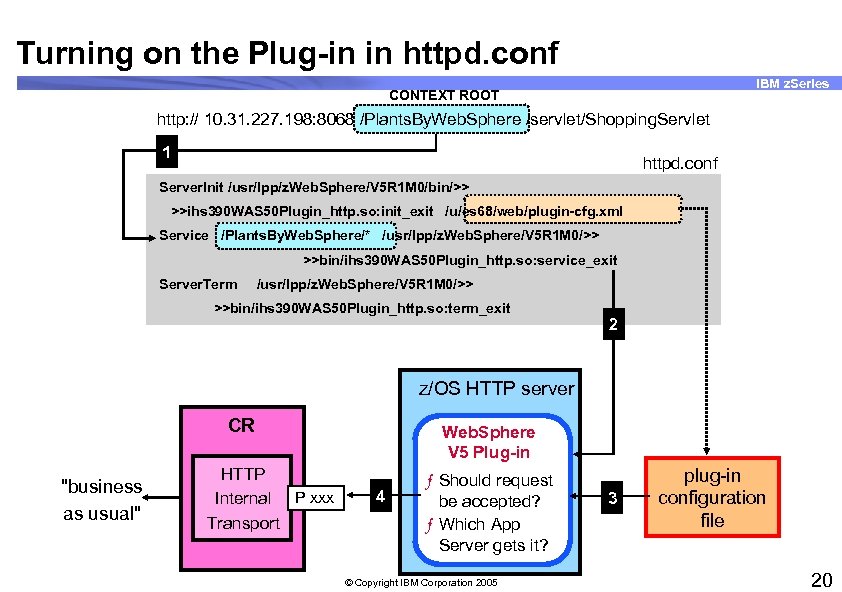
Turning on the Plug-in in httpd. conf IBM z. Series CONTEXT ROOT http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 8068 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere /servlet/Shopping. Servlet 1 httpd. conf Server. Init /usr/lpp/z. Web. Sphere/V 5 R 1 M 0/bin/>> >>ihs 390 WAS 50 Plugin_http. so: init_exit /u/es 68/web/plugin-cfg. xml Service /Plants. By. Web. Sphere/* /usr/lpp/z. Web. Sphere/V 5 R 1 M 0/>> >>bin/ihs 390 WAS 50 Plugin_http. so: service_exit Server. Term /usr/lpp/z. Web. Sphere/V 5 R 1 M 0/>> >>bin/ihs 390 WAS 50 Plugin_http. so: term_exit 2 z/OS HTTP server CR "business as usual" HTTP Internal P xxx Transport Web. Sphere V 5 Plug-in 4 ƒ Should request be accepted? ƒ Which App Server gets it? © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 3 plug-in configuration file 20
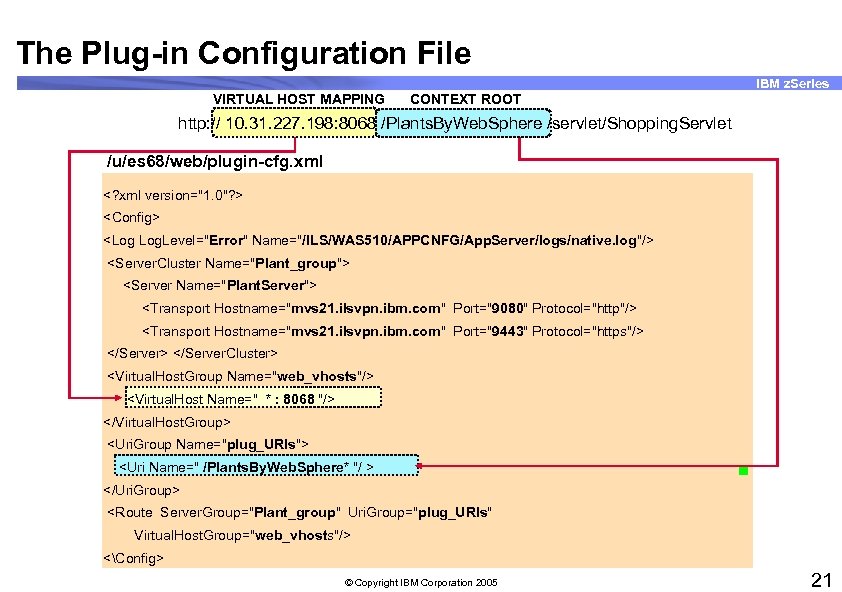
The Plug-in Configuration File IBM z. Series VIRTUAL HOST MAPPING CONTEXT ROOT http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 8068 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere /servlet/Shopping. Servlet /u/es 68/web/plugin-cfg. xml <? xml version="1. 0"? > <Config> <Log Log. Level="Error" Name="/ILS/WAS 510/APPCNFG/App. Server/logs/native. log"/> <Server. Cluster Name="Plant_group"> <Server Name="Plant. Server"> <Transport Hostname="mvs 21. ilsvpn. ibm. com" Port="9080" Protocol="http"/> <Transport Hostname="mvs 21. ilsvpn. ibm. com" Port="9443" Protocol="https"/> </Server. Cluster> <Virtual. Host. Group Name="web_vhosts"/> <Virtual. Host Name=" * : 8068 "/> </Virtual. Host. Group> <Uri. Group Name="plug_URIs"> <Uri Name=" /Plants. By. Web. Sphere* "/ > </Uri. Group> <Route Server. Group="Plant_group" Uri. Group="plug_URIs" Virtual. Host. Group="web_vhosts"/> <Config> © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 21
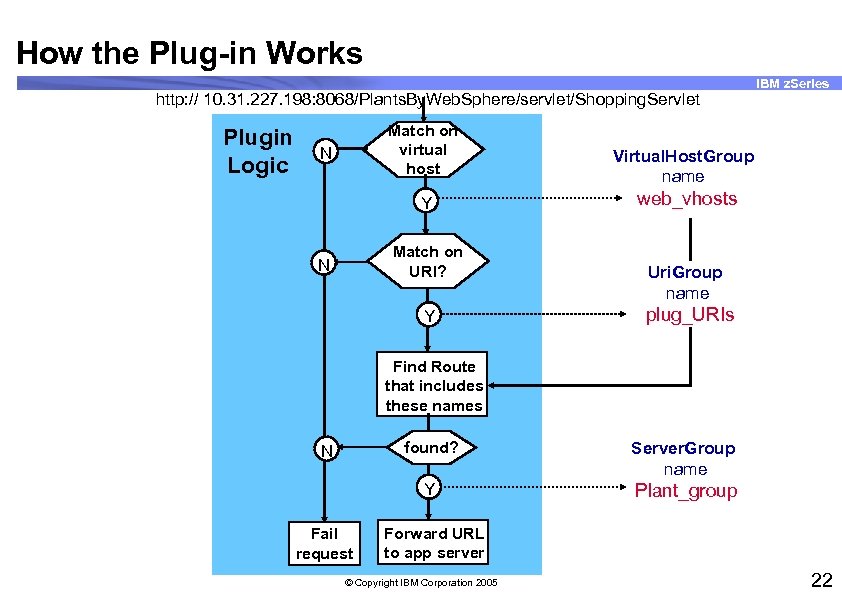
How the Plug-in Works http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 8068/Plants. By. Web. Sphere/servlet/Shopping. Servlet Plugin Logic Match on virtual host N Y Match on URI? N Y IBM z. Series Virtual. Host. Group name web_vhosts Uri. Group name plug_URIs Find Route that includes these names found? Fail request Server. Group name Y N Plant_group Forward URL to app server © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 22
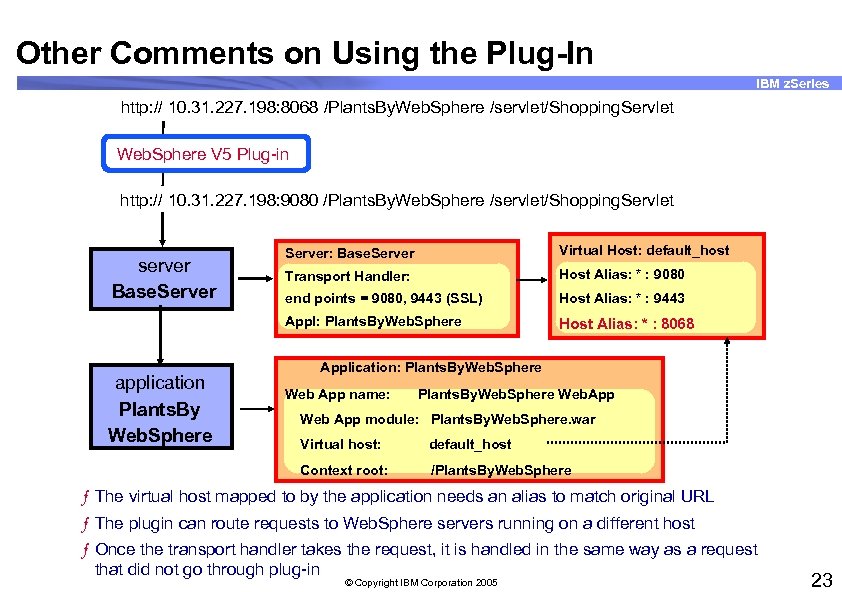
Other Comments on Using the Plug-In IBM z. Series http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 8068 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere /servlet/Shopping. Servlet Web. Sphere V 5 Plug-in http: // 10. 31. 227. 198: 9080 /Plants. By. Web. Sphere /servlet/Shopping. Servlet application Plants. By Web. Sphere Virtual Host: default_host Transport Handler: Host Alias: * : 9080 end points = 9080, 9443 (SSL) Host Alias: * : 9443 Appl: Plants. By. Web. Sphere server Base. Server: Base. Server Host Alias: * : 8068 Application: Plants. By. Web. Sphere Web App name: Plants. By. Web. Sphere Web. App Web App module: Plants. By. Web. Sphere. war Virtual host: default_host Context root: /Plants. By. Web. Sphere ƒ The virtual host mapped to by the application needs an alias to match original URL ƒ The plugin can route requests to Web. Sphere servers running on a different host ƒ Once the transport handler takes the request, it is handled in the same way as a request that did not go through plug-in © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 23
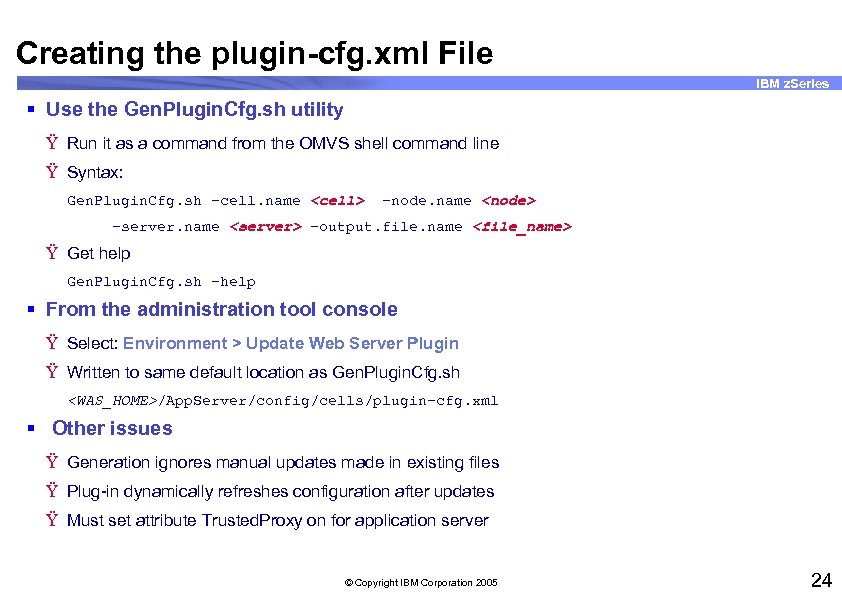
Creating the plugin-cfg. xml File IBM z. Series § Use the Gen. Plugin. Cfg. sh utility Ÿ Run it as a command from the OMVS shell command line Ÿ Syntax: Gen. Plugin. Cfg. sh -cell. name <cell> -node. name <node> -server. name <server> -output. file. name <file_name> Ÿ Get help Gen. Plugin. Cfg. sh -help § From the administration tool console Ÿ Select: Environment > Update Web Server Plugin Ÿ Written to same default location as Gen. Plugin. Cfg. sh <WAS_HOME>/App. Server/config/cells/plugin-cfg. xml § Other issues Ÿ Generation ignores manual updates made in existing files Ÿ Plug-in dynamically refreshes configuration after updates Ÿ Must set attribute Trusted. Proxy on for application server © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 24
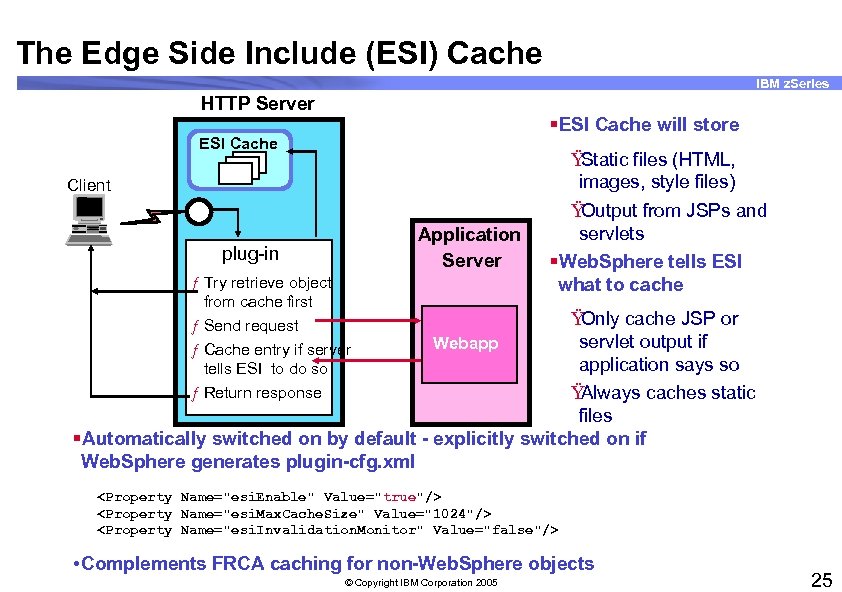
The Edge Side Include (ESI) Cache IBM z. Series HTTP Server §ESI Cache will store ESI Cache Client Application Server plug-in ƒ Try retrieve object from cache first ƒ Send request ƒ Cache entry if server tells ESI to do so ƒ Return response Ÿ Static files (HTML, images, style files) Ÿ Output from JSPs and servlets §Web. Sphere tells ESI what to cache Ÿ Only cache JSP or servlet output if Webapp application says so Ÿ Always caches static files §Automatically switched on by default - explicitly switched on if Web. Sphere generates plugin-cfg. xml <Property Name="esi. Enable" Value="true"/> <Property Name="esi. Max. Cache. Size" Value="1024"/> <Property Name="esi. Invalidation. Monitor" Value="false"/> • Complements FRCA caching for non-Web. Sphere objects © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 25

Unit Summary IBM z. Series Having completed this unit, you should be able to: § Describe the components needed to run a Web. Sphere V 5 web application § Configure the administration objects that are needed to activate web client access to a Web. Sphere application § Describe how the request URL is processed so that the required servlet class file is loaded for a request § Define the configuration elements needed to support the IBM HTTP server plug-in for Web. Sphere V 5 © Copyright IBM Corporation 2005 26
df1411ff3b468b1c566ba9142d4af6a6.ppt