c289a41c116a8a7b97b4eee382217385.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
IBM User Technology A Short Introduction to Darwin Information Typing Architecture: DITA Michael Priestley IBM® | November 2005 | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies What’s ahead? History of DITA – Why was DITA developed? Introduction to DITA – What is DITA? Benefits of DITA – Why should you care? 2 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies Background: Why DITA? 3 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies Identify the need – Customer issues Solutions, not products • Integration of information Information glut • More meaningful information (role & task based) Out-of-date information in books • Updating and maintaining information Reduce cost of deployment of information • Provide information on-line Reduce support costs • Customize and update information 4 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
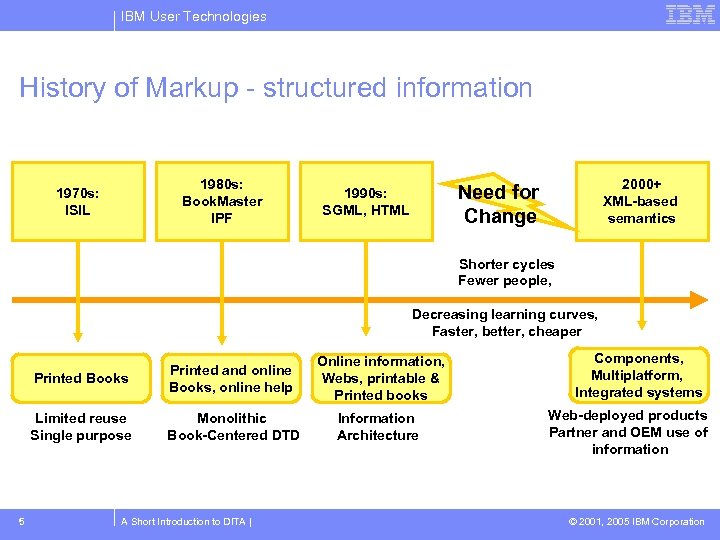
IBM User Technologies History of Markup - structured information 1980 s: Book. Master IPF 1970 s: ISIL 2000+ XML-based semantics Need for Change 1990 s: SGML, HTML Shorter cycles Fewer people, Decreasing learning curves, Faster, better, cheaper Printed Books Online information, Webs, printable & Printed books Limited reuse Single purpose 5 Printed and online Books, online help Monolithic Book-Centered DTD Information Architecture A Short Introduction to DITA | Components, Multiplatform, Integrated systems Web-deployed products Partner and OEM use of information © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies The Vision (1998/1999) 6 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies DITA at IBM In use across IBM 100 s of projects 100, 000 s of topics Both new and converted from SGML or HTML Translate DITA content into over 50 languages 7 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies “Open” DITA 1. 0 specification is an OASIS standard • XML tool vendors (Arbortext, Blast Radius, Idiom, Rascal, Syntext) • Consultants (Comtech, Innodata, Mulberrytech) • Companies (BMC, Boeing, IBM, Intel, Lucent, Nokia, Sun) • Organizations (National Library of Medicine, US Department of Defense) • DITA Technical Committee working now on 1. 1 requirements. DITA-OT as Open Source on Source. Forge • http: //dita-ot. sourceforge. net • Reference implementation - Will continue to be enhanced as a production system • Developing vendor/contributor relations for known build-out niches (FO, indexing, style interface, new outputs, etc. ) Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards 8 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies What is DITA? 9 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies DITA defined Darwin: DITA utilizes principles of inheritance for specialization Information Typing: DITA was designed for technical information based on an information architecture of Concept, Task and Reference Architecture: DITA is a model for extension both of design and of processes 10 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Core design principles of DITA Topic orientation • Discrete units of information covering a specific subject with a specific intent Topic granularity • Self-contained topics combine with other topics into information sets Strong typing • DTDs and schemas guarantee that DITA types follow identical information structures Specialization • Architecture for extending basic types to new types adapted for a particular use within an information set Common base class • Top-level "generic" base type provides “fallback” for all types 11 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
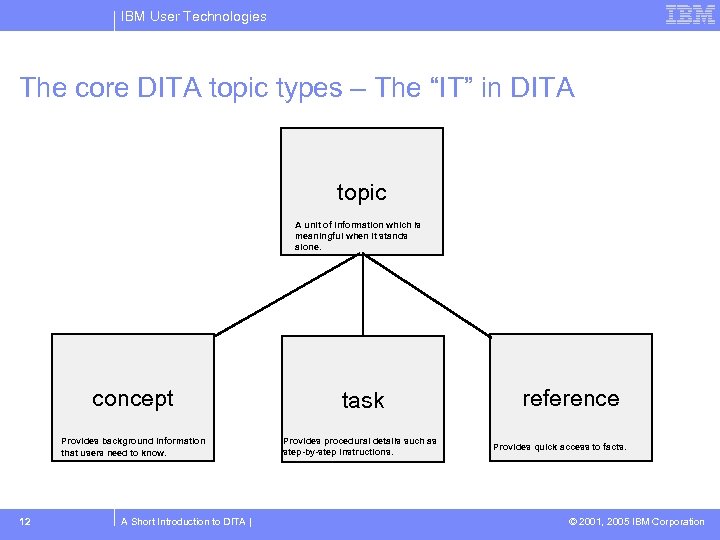
IBM User Technologies The core DITA topic types – The “IT” in DITA topic A unit of information which is meaningful when it stands alone. concept Provides background information that users need to know. 12 A Short Introduction to DITA | task Provides procedural details such as step-by-step instructions. reference Provides quick access to facts. © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies DITA and reuse 13 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Promise and Reality of XML Promise • Separate content from form: reuse content in different presentation media • Use specific markup to describe your content • Use standard solution to enable easy exchange of information Reality – Generic XML • Generic XML provides an SGML with simpler syntax but similar problems • Generic solutions - not specific to needs • Knowledge representation is strongly related to current corporate culture Tradeoff • The more useful your markup is to you, the more it will cost you and the fewer people will share the costs 14 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Resolve tradeoffs through more efficient reuse Reuse of content Reuse of design Reuse of processing 15 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

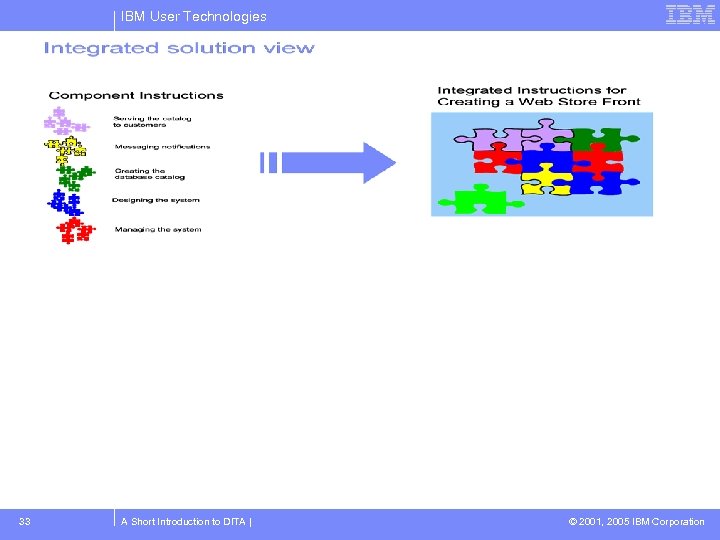
IBM User Technologies Reuse of content Reuse flows from the topic-based paradigm If content is authored as standalone topics • Topics can be reused in different contexts • Topics from multiple components can be integrated as a solution Good writing enables reuse 16 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies Topics reused in deliverables Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 ƒ Deliverables select topics from a pool Deliverable 1 uses topics 1 and 4 ƒ Deliverable 2 uses topics 2 and 4 ƒ Neither deliverable uses topic 3 ƒ 17 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
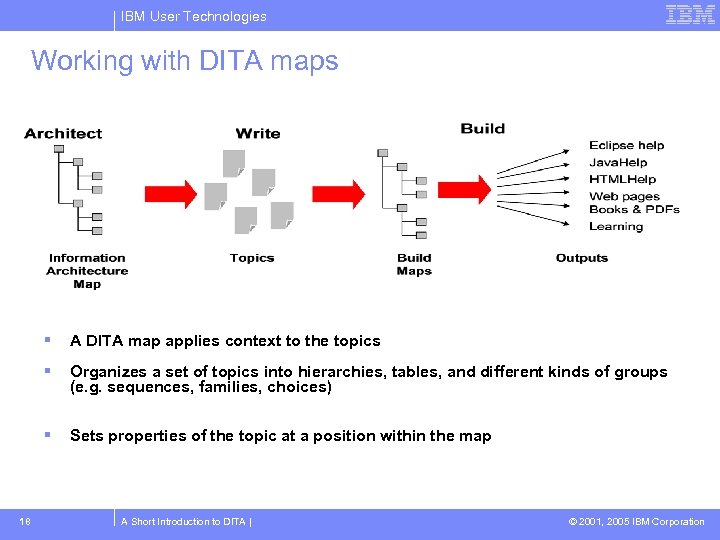
IBM User Technologies Working with DITA maps Eclipse help Java. Help HTMLHelp web pages books Organizes a set of topics into hierarchies, tables, and different kinds of groups (e. g. sequences, families, choices) 18 A DITA map applies context to the topics Sets properties of the topic at a position within the map A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Reuse of design General types are rarely enough • Requirements specific to organization or industry Meet requirements with new elements • New element specializes existing element • New content is a subset of base content Add only the deltas - still use the base Designs are modular • For instance, optional b and i highlighting 19 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
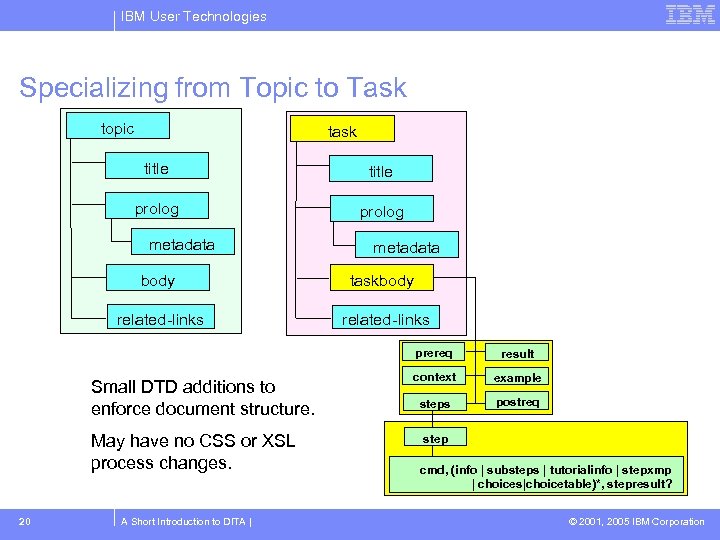
IBM User Technologies Specializing from Topic to Task topic task title prolog metadata body taskbody related-links prereq Small DTD additions to enforce document structure. May have no CSS or XSL process changes. 20 A Short Introduction to DITA | result context example taskxmp steps postreq step cmd, (info | substeps | tutorialinfo | stepxmp cmd, (info | substeps | tutorialinfo | | choices|choicetable)*, xmp | choices)*, result? stepresult? © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
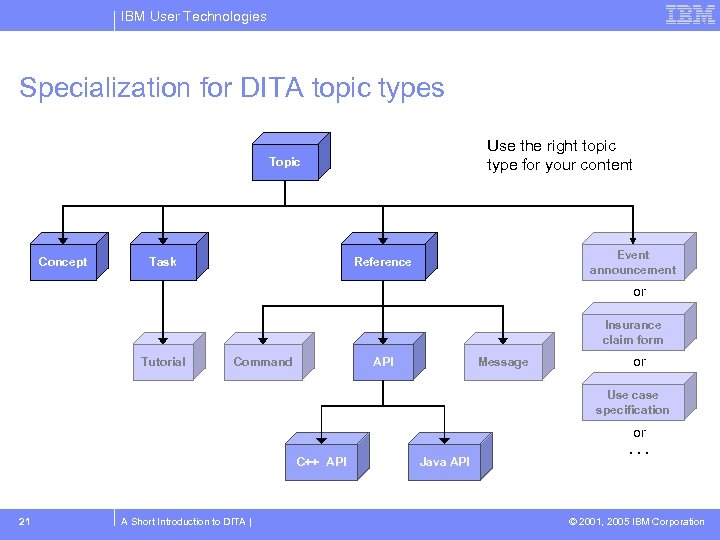
IBM User Technologies Specialization for DITA topic types Use the right topic type for your content Topic Concept Task Event announcement Reference or Insurance claim form Tutorial Command API Message or Use case specification C++ API 21 A Short Introduction to DITA | Java API or. . . © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
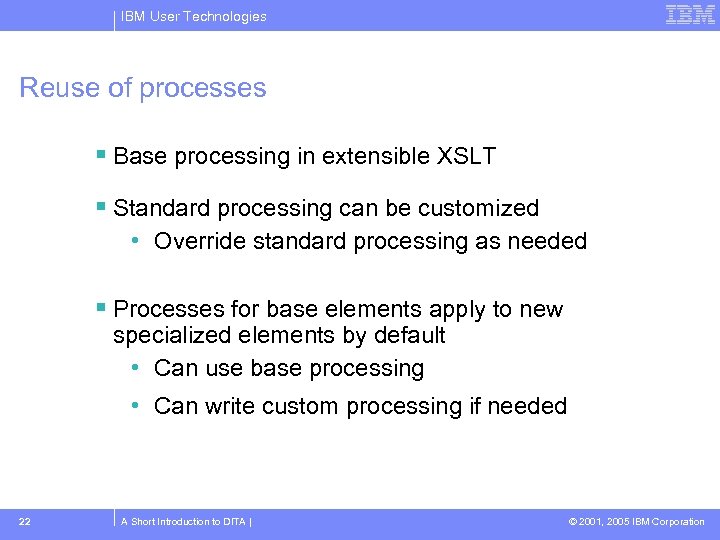
IBM User Technologies Reuse of processes Base processing in extensible XSLT Standard processing can be customized • Override standard processing as needed Processes for base elements apply to new specialized elements by default • Can use base processing • Can write custom processing if needed 22 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
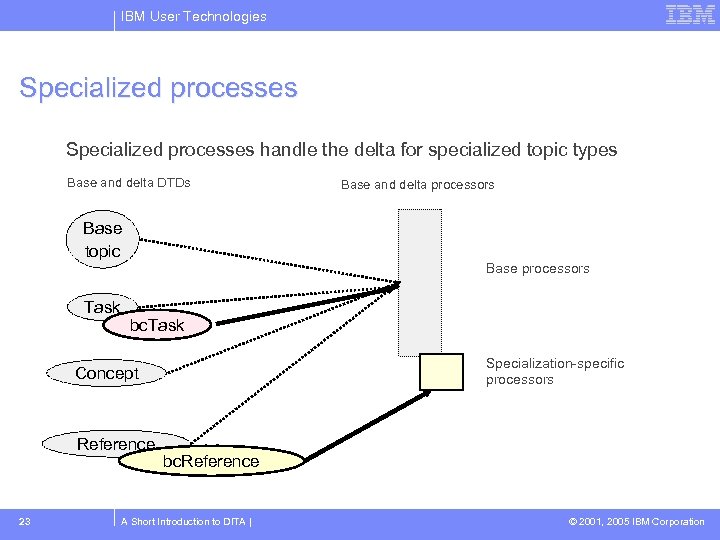
IBM User Technologies Specialized processes handle the delta for specialized topic types Base and delta DTDs Base topic Task Base processors bc. Task Specialization-specific processors Concept Reference 23 Base and delta processors bc. Reference A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies Summary of reuse Reuse content through topics • Author content as standalone information Reuse designs through specialization • Meet requirements specific to organization • Keep interoperability with others Reuse processing • Customize only as needed 24 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Summary of problems solved üDevelopment challenges met • Shorter development cycles • Eliminate variability in HTML outputs • Support componentization of products and need for reuse • Integration of information • More meaningful information (role & task based) • Updating and maintaining information • Provide information on-line • Customize and update information üDeliver solution information, not product information üInformation glut üOut-of-date information in books üReduce cost of deployment of information üReduce support costs 25 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Summary of business value Faster time to value – create solution offering across industry stacks or within your business with different components Increased reuse – of content by referencing topics in many map contexts – of designs by providing only the specialized delta on the general base – of processing by overriding the base only where needed Investment protection – because of automated fallback to more general markup 26 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
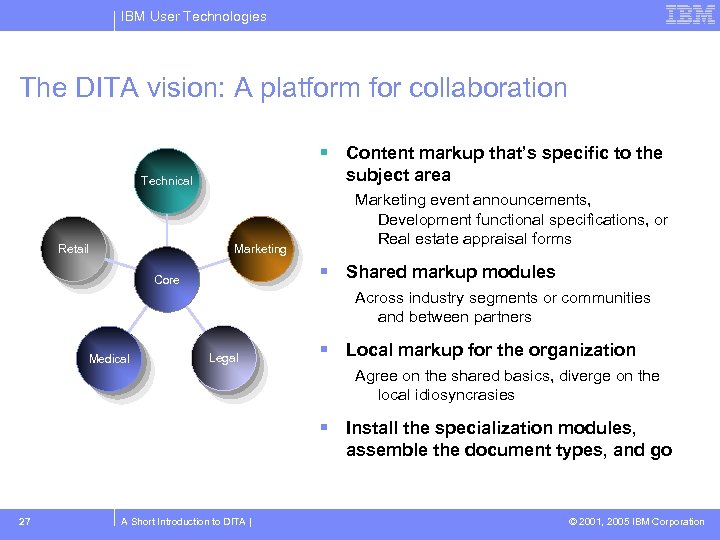
IBM User Technologies The DITA vision: A platform for collaboration Content markup that’s specific to the subject area Technical Retail Marketing event announcements, Development functional specifications, or Real estate appraisal forms Shared markup modules Core Across industry segments or communities and between partners Medical Legal Local markup for the organization Agree on the shared basics, diverge on the local idiosyncrasies Install the specialization modules, assemble the document types, and go 27 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies Where next? Learn more about DITA • OASIS – http: //www. oasis-open. org/committees/dita • Cover pages – http: //xml. coverpages. org/dita. html Where do we take DITA together? • Join the dialog on the DITA forum – http: //groups. yahoo. com/group/dita-users/ Download the DITA Open Toolkit • 28 http: //sourceforge. net/projects/dita-ot/ A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM User Technologies Backup Slides 29 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Value of DITA to content creators DITA is the foundation for collaboration for developing information. • DITA allows product / component families to easily share content. This allows us to build solutions much more than we have every done before and much more quickly. Teams can pull information from across diverse products into a single output. Teams can manage the integration of information by using DITA maps. • DITA maps pull together individual topics into an order. This allows different teams to pull the same topic into different maps and to build a solution map, pulling topics from across components or products. This allows flexibility in combining and recombining information with maps and does not require authors to touch the original topics. DITA provides authoring consistency. • Authoring consistency comes from strong information typing. Information typing also facilitates reuse and integration across product teams. DITA defines an architecture for extending and specializing its core information types, enabling rapid response to frequent industry changes. DITA enforces business process / architectures. • New information types are extended as delta changes from a core type, greatly reducing the time and resource needed for development, testing, and deployment. DITA supports personalization through a rich set of metadata. DITA’s tag set is based on a core set of familiar HTML tags, making it easy to teach others and allowing new authors to get up to speed quickly. 30 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Value of DITA to customers and users DITA organizes content into topic-based information units, with each topic describing a single task, concept, or reference item. Because of this focus on topics, customers can: • Update and replace single topics of information quickly as needed to support an ondemand environment. • Receive increased consistency - a task is a task, a concept is a concept, and so on, and all follow a consistent and agreed-upon structure. • Receive a quicker time to value -- the sharp focus on tasks that customers must do quickly brings the emphasis on specific core tasks, not requiring customers to wade through information. There is an improved quality when information is written in DITA. • Authors can use analytic techniques to ensure that the information about new features and functions is complete: each feature/function requires one or more tasks, one or more pieces of conceptual information, one or more pieces of reference information. Customers can use DITA as a foundation on which to build their information; to also integrate their information with other information. DITA easily supports topic -oriented content for their internal training and education courses. 31 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies Value of DITA to business partners & content integrators DITA enables a foundation both for interoperability with other DITA adopters and for extensibility to meet the requirements of their industry or organization. Focused – allows 3 rd parties to specialize with own information • Third-parties can easily customize or provide new content with standard tools. Vendors can quickly integrate information about their products with other vendors’ products. DITA allows additional leverage since the information can also be customized and extended in a consistent, standard, pre-determined data format. DITA metadata and domain vocabularies can be defined at an industry level, such as telecom, allowing other industries to leverage consistent vocabularies. Standards-based • Define platform for interchange - DITA topic is base with fallback for specialization Rapid development platform for extending base information • Rules for inheritance – allow others to add with small modifications, not rewrite DTD from scratch Reuse across functions • 32 Reuse topics in education / learning environments A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM User Technologies 33 A Short Introduction to DITA | © 2001, 2005 IBM Corporation
c289a41c116a8a7b97b4eee382217385.ppt