8b7bafa3afd3c16e22bfa9846985b5a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
IBM Total. Storage SAN File System • Overview • SAN FS for Grid & HPC Paul L. Bradshaw Breakthrough to On Demand with IBM Total. Storage IBM Almaden Research Center © 2004 IBM Corporation
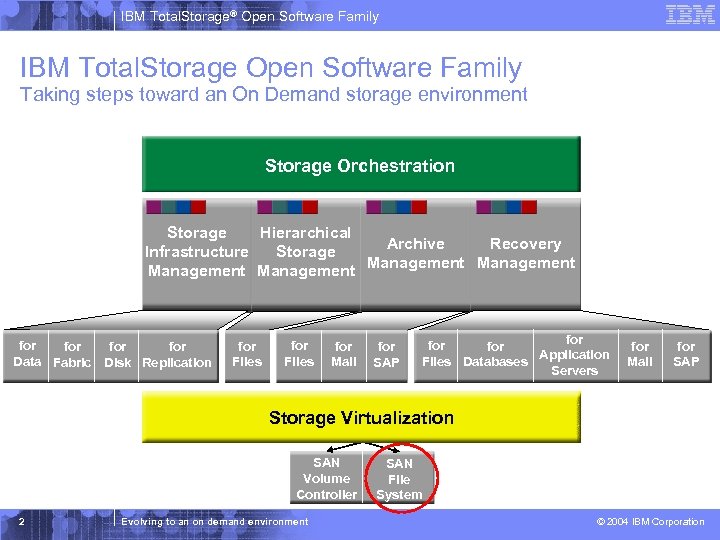
IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family Taking steps toward an On Demand storage environment Storage Orchestration Storage Hierarchical Archive Recovery Infrastructure Storage Management for for Data Fabric Disk Replication for Files for Mail for SAP for for Application Files Databases Servers for Mail for SAP Storage Virtualization SAN Volume Controller 2 Evolving to an on demand environment SAN File System © 2004 IBM Corporation
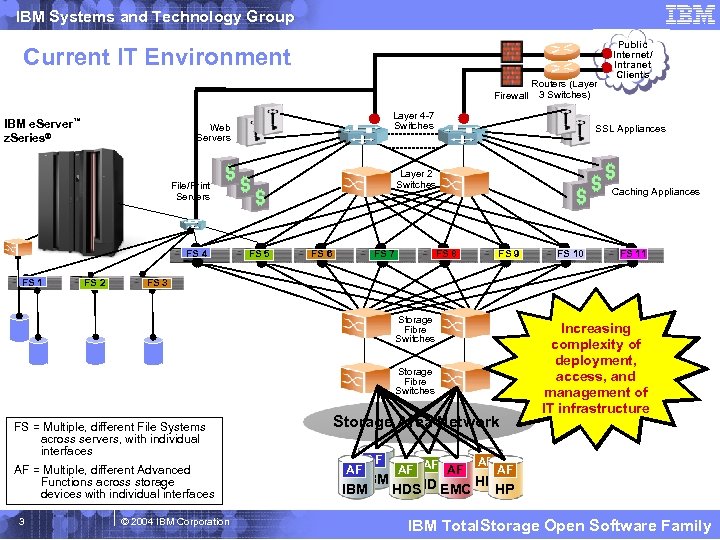
IBM Systems and Technology Group Current IT Environment Firewall IBM e. Server™ z. Series® Layer 4 -7 Switches Web Servers FS 1 FS 2 SSL Appliances Layer 2 Switches File/Print Servers FS 4 FS 5 FS 7 FS 6 Caching Appliances FS 8 FS 9 FS 10 FS 11 FS 3 Storage Fibre Switches FS = Multiple, different File Systems across servers, with individual interfaces AF = Multiple, different Advanced Functions across storage devices with individual interfaces 3 Routers (Layer 3 Switches) Public Internet/ Intranet Clients © 2004 IBM Corporation Storage Area Network AF AF AF Increasing complexity of deployment, access, and management of IT infrastructure AF IBM HP HDS IBM HDS EMC HP IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family
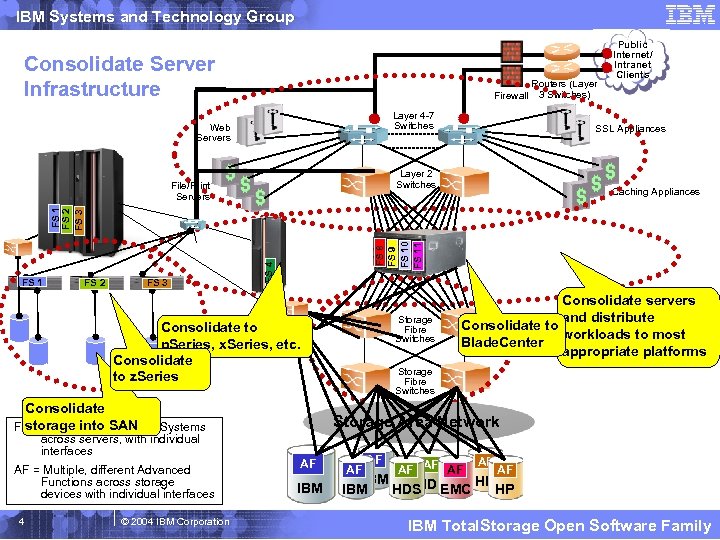
IBM Systems and Technology Group Consolidate Server Infrastructure Firewall Routers (Layer 3 Switches) Layer 4 -7 Switches Web Servers SSL Appliances Layer 2 Switches Caching Appliances FS 1 FS 2 FS 3 FS 5 FS 7 FS 6 FS 4 FS 8 FS 9 FS 10 FS 11 FS 2 FS 3 File/Print Servers Public Internet/ Intranet Clients Storage Fibre Switches Consolidate to p. Series, x. Series, etc. Consolidate to z. Series Consolidate storage into SAN FS = Multiple, different File Systems across servers, with individual interfaces AF = Multiple, different Advanced Functions across storage devices with individual interfaces 4 © 2004 IBM Corporation FS 8 FS 9 FS 10 FS 11 Consolidate servers and distribute Consolidate to workloads to most Blade. Center appropriate platforms Storage Fibre Switches Storage Area Network AF IBM AF AF IBM HP HDS IBM HDS EMC HP IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family
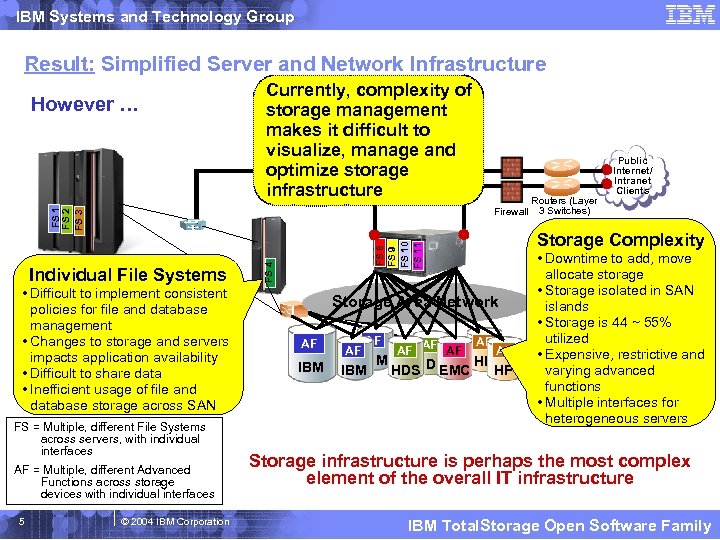
IBM Systems and Technology Group Result: Simplified Server and Network Infrastructure However … Currently, complexity of storage management makes it difficult to visualize, manage and optimize storage infrastructure FS 1 FS 2 FS 3 Firewall • Difficult to implement consistent policies for file and database management • Changes to storage and servers impacts application availability • Difficult to share data • Inefficient usage of file and database storage across SAN FS = Multiple, different File Systems across servers, with individual interfaces AF = Multiple, different Advanced Functions across storage devices with individual interfaces 5 © 2004 IBM Corporation Storage Complexity FS 8 FS 9 FS 10 FS 11 FS 4 Individual File Systems Storage Area Network AF IBM AF AF AF Routers (Layer 3 Switches) Public Internet/ Intranet Clients AF AF IBM HP HDS IBM HDS EMC HP • Downtime to add, move allocate storage • Storage isolated in SAN islands • Storage is 44 ~ 55% utilized • Expensive, restrictive and varying advanced functions • Multiple interfaces for heterogeneous servers Storage infrastructure is perhaps the most complex element of the overall IT infrastructure IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family
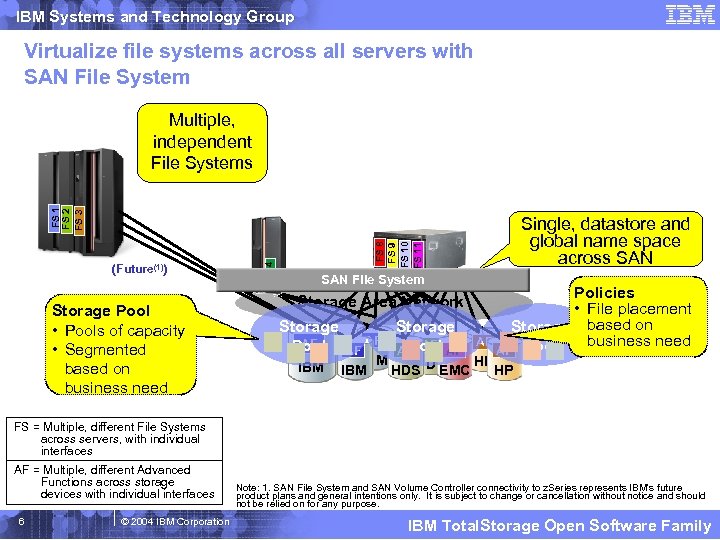
IBM Systems and Technology Group Virtualize file systems across all servers with SAN File System Storage Pool • Pools of capacity • Segmented based on business need Single, datastore and global name space across SAN FS 8 FS 9 FS 10 FS 11 (Future(1)) FS 4 FS 1 FS 2 FS 3 Multiple, independent File Systems SAN File System Storage Area Network Storage AF Pool IBM AF AF Storage Pool AF AF AF Policies • File placement Storage based on business need AF AF Pool IBM HP HDS IBM HDS EMC HP FS = Multiple, different File Systems across servers, with individual interfaces AF = Multiple, different Advanced Functions across storage devices with individual interfaces 6 © 2004 IBM Corporation Note: 1. SAN File System and SAN Volume Controller connectivity to z. Series represents IBM's future product plans and general intentions only. It is subject to change or cancellation without notice and should not be relied on for any purpose. IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family
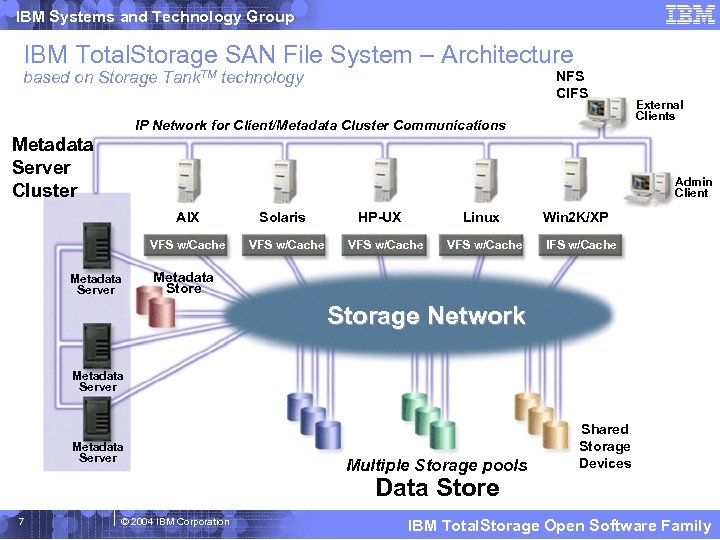
IBM Systems and Technology Group IBM Total. Storage SAN File System – Architecture based on Storage Tank. TM technology NFS CIFS IP Network for Client/Metadata Cluster Communications Metadata Server Cluster External Clients Admin Client AIX VFS w/Cache Metadata Server Solaris VFS w/Cache HP-UX Linux VFS w/Cache Win 2 K/XP IFS w/Cache Metadata Store Storage Network Metadata Server Multiple Storage pools Shared Storage Devices Data Store 7 © 2004 IBM Corporation IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family
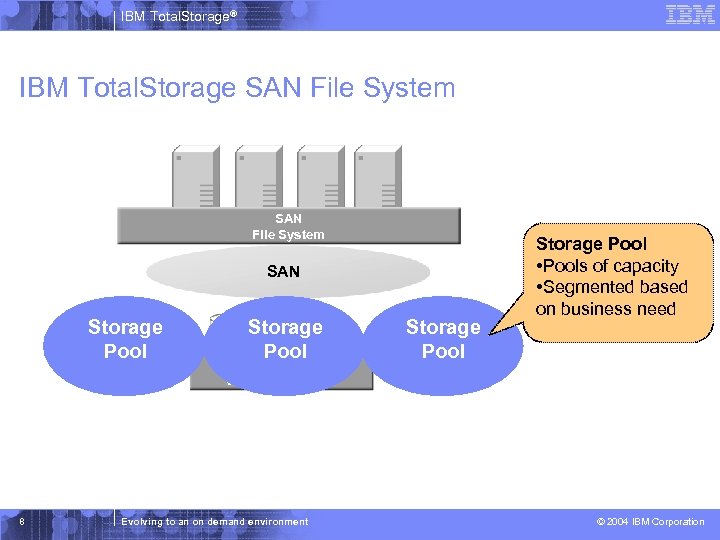
IBM Total. Storage® IBM Total. Storage SAN File System SAN Customer Project A Storage Good ESS Pool 1 8 Customer Project B Storage Better Virtual Disk Pool Disk 2 Virtual Disk SAN Volume Controller Evolving to an on demand environment Customer Project C Storage Best SATA Pool 3 Storage Pool • Pools of capacity • Segmented based on business need © 2004 IBM Corporation
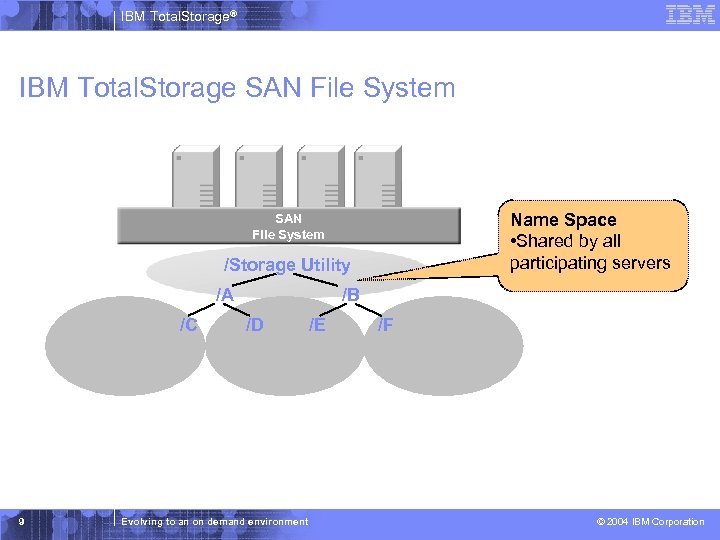
IBM Total. Storage® IBM Total. Storage SAN File System Name Space • Shared by all participating servers SAN File System /Storage Utility /A /C 9 /B /D Evolving to an on demand environment /E /F © 2004 IBM Corporation
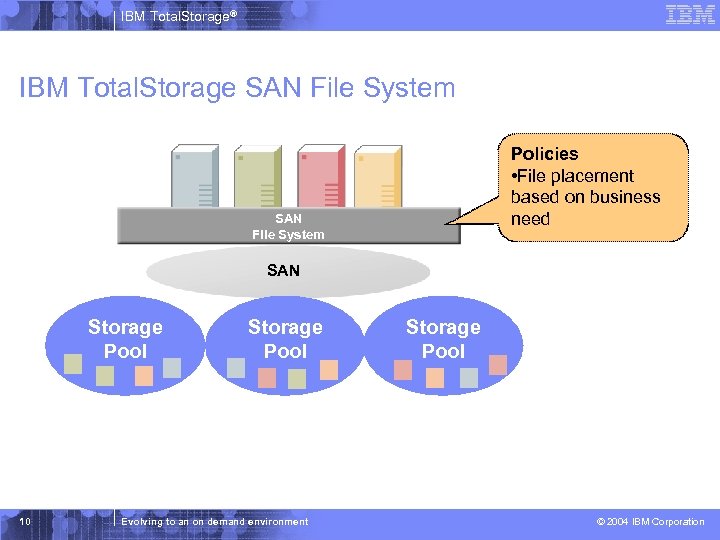
IBM Total. Storage® IBM Total. Storage SAN File System Policies • File placement based on business need SAN File System SAN Storage Pool 10 Storage Pool Evolving to an on demand environment Storage Pool © 2004 IBM Corporation
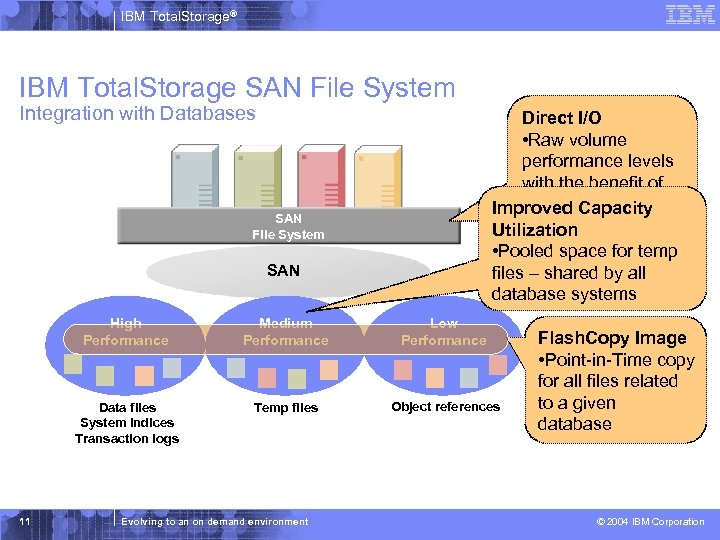
IBM Total. Storage® IBM Total. Storage SAN File System Integration with Databases Direct I/O • Raw volume performance levels with the benefit of SAN File System Improved Capacity file management Utilization • Pooled space for temp files – shared by all database systems SAN File System SAN High Performance Low Performance Data files System indices Transaction logs 11 Medium Performance Temp files Object references Evolving to an on demand environment Flash. Copy Image • Point-in-Time copy for all files related to a given database © 2004 IBM Corporation
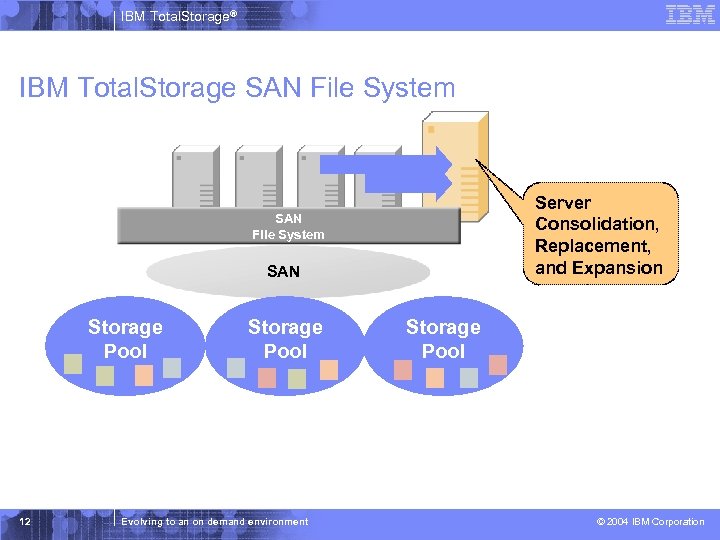
IBM Total. Storage® IBM Total. Storage SAN File System Server Consolidation, Replacement, and Expansion SAN File System SAN Storage Pool 12 Storage Pool Evolving to an on demand environment Storage Pool © 2004 IBM Corporation
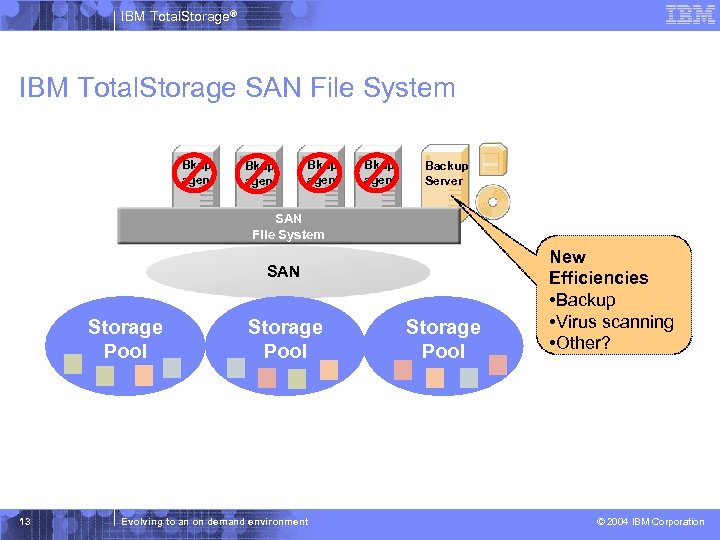
IBM Total. Storage® IBM Total. Storage SAN File System Bkup agent Backup Server SAN File System SAN Storage Pool 13 Storage Pool Evolving to an on demand environment Storage Pool New Efficiencies • Backup • Virus scanning • Other? © 2004 IBM Corporation
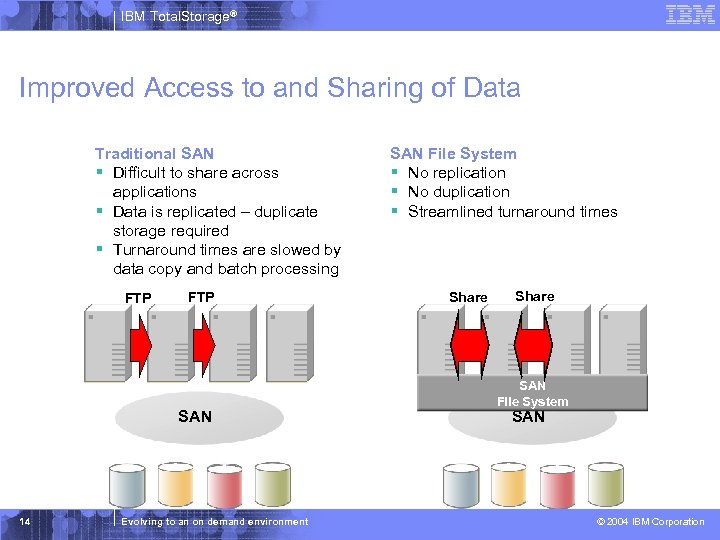
IBM Total. Storage® Improved Access to and Sharing of Data Traditional SAN § Difficult to share across applications § Data is replicated – duplicate storage required § Turnaround times are slowed by data copy and batch processing FTP SAN 14 Evolving to an on demand environment SAN File System § No replication § No duplication § Streamlined turnaround times Share SAN File System SAN © 2004 IBM Corporation
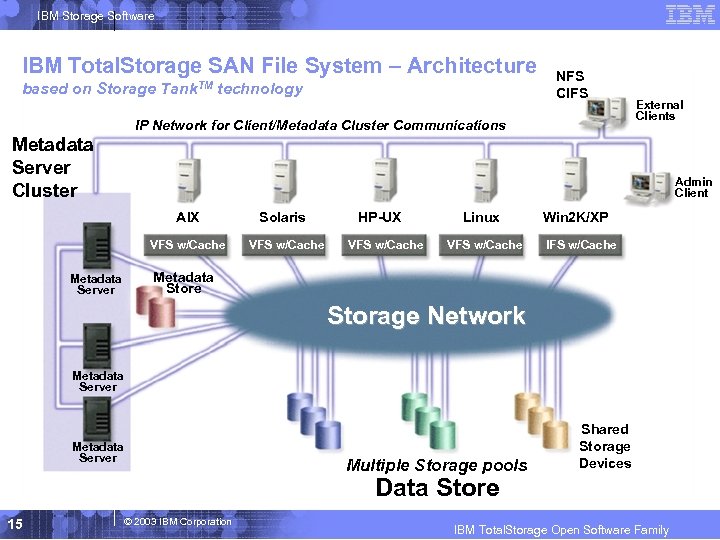
IBM Storage Software IBM Total. Storage SAN File System – Architecture based on Storage Tank. TM technology NFS CIFS IP Network for Client/Metadata Cluster Communications External Clients Metadata Server Cluster Admin Client AIX VFS w/Cache Metadata Server Solaris VFS w/Cache HP-UX VFS w/Cache Linux VFS w/Cache Win 2 K/XP IFS w/Cache Metadata Store Storage Network Metadata Server Multiple Storage pools Shared Storage Devices Data Store 15 © 2003 IBM Corporation IBM Total. Storage Open Software Family
IBM Total. Storage® Functions of the components § Functions of the Meta-Data Servers Heterogeneous file and byte range level locking Mandatory and advisory Lease based scheme so locks are renewed on a configurable interval When a lease expires then a lock can be revoked and the work transferred to another server Locks can non-disruptively move between meta-data servers on a meta -data server failure Space allocation Configurable block and partition sizes Allocation of blocks occurs in partitions, adjusted dynamically Striping of data across LUNs in a storage pool Configurable striping interval, round robin allocation Volume Drain Automated, non-disruptive movement of data LUN labeling Quota management Soft and hard quotas per fileset Volume management in storage pools Flash copy image 32 per fileset active Updates are written to new blocks 16 Evolving to an on demand environment © 2004 IBM Corporation
IBM Total. Storage® Functions of the components § Functions of the SAN file system clients Linux client reference implementation available via open source Caching of the meta-data Aggressive caching Pro-active cache invalidation Mapping of access control rights to local file system semantics Mapping of operating system file interface to common file system functions Direct I/O, parallel i/o, async i/o support Benchmarks show we are only limited by SAN bandwidth, linear scalability as we add clients § Install/Packaging Software Only Rolling Upgrade maintains service during upgrade N and n-1 supported simultaneously Services lined up Current hardware supported Servers can be upgraded independently of clients 17 Evolving to an on demand environment © 2004 IBM Corporation
IBM Total. Storage® RAS § High Availability Non-disruptive move of workload between meta-data servers Built-in clustering and failover § Serviceability Meta-data checker enhancements Master Console Performance improvements for diagnostic logging One button data collection for error handling § Manageability Consistent on-line help Log filtering Fileset transaction statistics Policy set statistics Storage Pool assignment verification 18 Evolving to an on demand environment © 2004 IBM Corporation
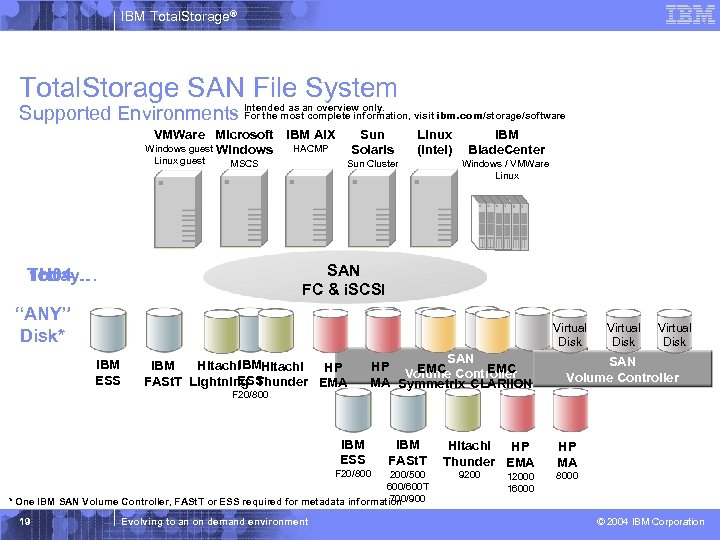
IBM Total. Storage® Total. Storage SAN File System For the most complete information, Supported Environments Intended as an overview only. visit ibm. com/storage/software VMWare Microsoft IBM AIX Windows guest Windows Linux guest MSCS Sun Solaris HACMP Linux (Intel) Sun Cluster IBM Blade. Center Windows / VMWare Linux SAN FC & i. SCSI Today… 1 H 04… “ANY” Disk* Virtual Disk IBM ESS IBM Hitachi. IBMHitachi HP ESS FASt. T Lightning Thunder EMA F 20/800 SAN HP EMC Controller EMC Volume MA Symmetrix CLARii. ON IBM ESS F 20/800 IBM FASt. T 200/500 600/600 T 700/900 * One IBM SAN Volume Controller, FASt. T or ESS required for metadata information 19 Evolving to an on demand environment Virtual Disk SAN Volume Controller Hitachi HP Thunder EMA HP MA 12000 16000 8000 9200 © 2004 IBM Corporation
IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family What are the characteristics of SAN file system? ü Scalable Heterogeneous Data Sharing High Performance Automation No architectural limits to file system size, size or number of files. Research tested 100’s of millions of files ü Resources are pooled across heterogeneous server and OS platforms. (heterogeneous storage support in 2 Q’ 04) Simultaneous access to same storage and data eliminates islands. ü Storage organized by class of service ü Automated provisioning of storage by class of service with customer defined soft and hard quotas Direct access to data volumes takes advantage of SAN technology Information Life Cycle Management leveraging Tivoli Centralized Management Data Protection Value Add ü Strong locking and security to enable centralized data management and on-demand clustering and availability solutions Fast storage efficient recovery points which can be leveraged to simplify data protection solutions ü ü Enabling layer for value add for other components through open standards SAN File System exploits the SAN to provide significantly enhanced file and data management for an on demand storage environment 20 Evolving to an on demand environment IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation

IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family 21 Evolving to an on demand environment IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation
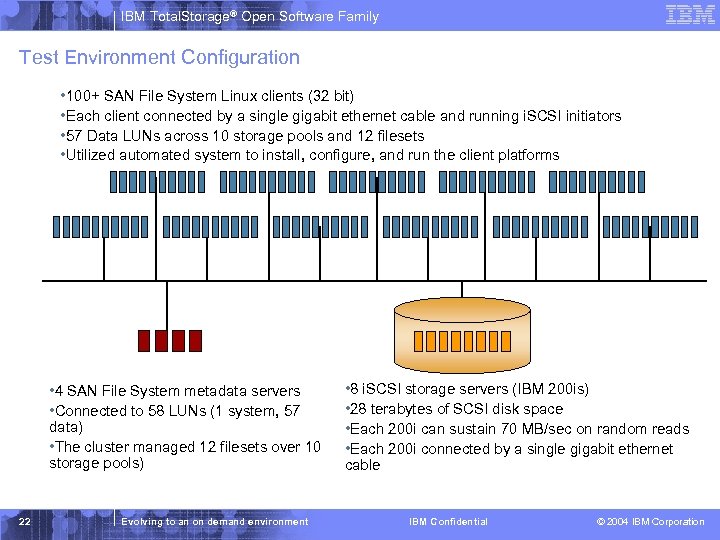
IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family Test Environment Configuration • 100+ SAN File System Linux clients (32 bit) • Each client connected by a single gigabit ethernet cable and running i. SCSI initiators • 57 Data LUNs across 10 storage pools and 12 filesets • Utilized automated system to install, configure, and run the client platforms • 4 SAN File System metadata servers • Connected to 58 LUNs (1 system, 57 data) • The cluster managed 12 filesets over 10 storage pools) 22 Evolving to an on demand environment • 8 i. SCSI storage servers (IBM 200 is) • 28 terabytes of SCSI disk space • Each 200 i can sustain 70 MB/sec on random reads • Each 200 i connected by a single gigabit ethernet cable IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation

IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family Ramp Up Test Notes § The storage controllers used were: 8 i. SCSI storage units Each unit was capable of 70 MB/sec for large random reads in optimum configuration (limited by older RAID card in the units) Storage LUNs were RAID-1 (mirrored) § Client ramp up: Clients started the test application one at a time Once all 100+ clients were running additional processes/threads were started sequentially 23 Evolving to an on demand environment IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation
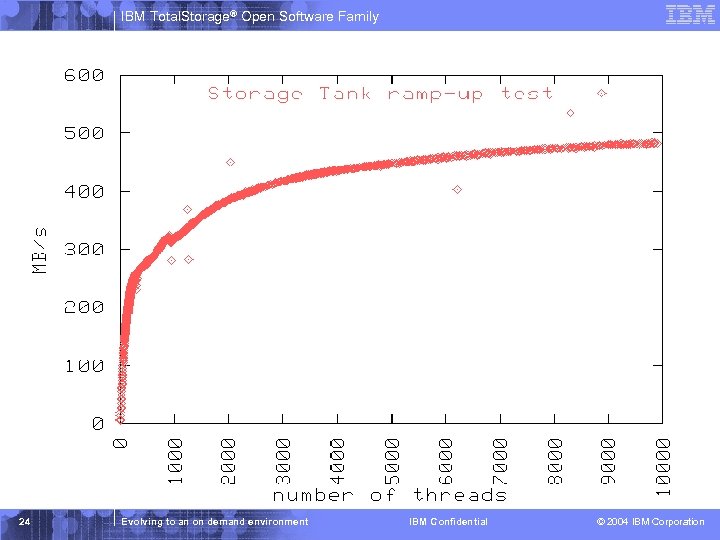
IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family 24 Evolving to an on demand environment IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation
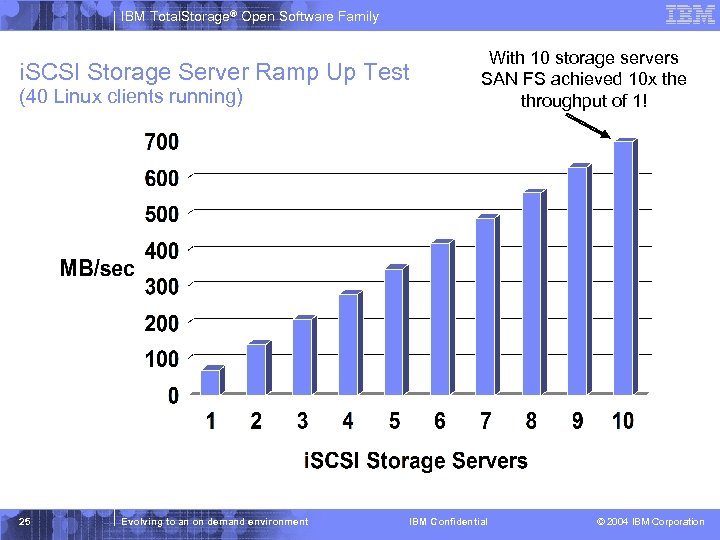
IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family i. SCSI Storage Server Ramp Up Test (40 Linux clients running) 25 Evolving to an on demand environment With 10 storage servers SAN FS achieved 10 x the throughput of 1! IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation
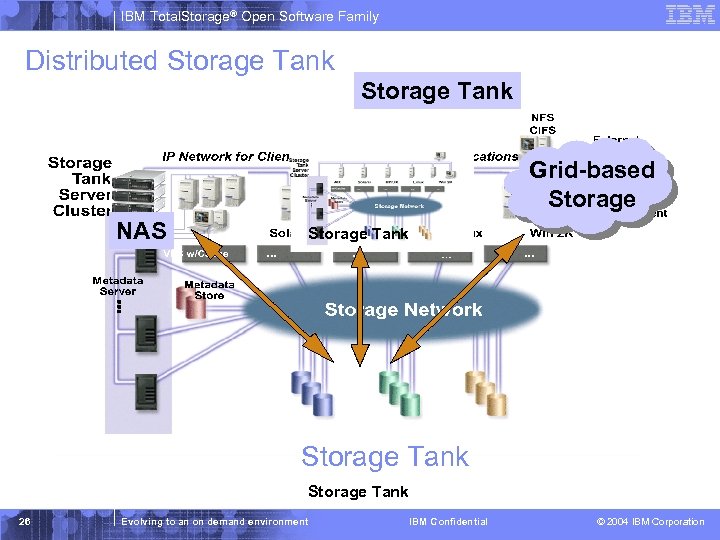
IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family Distributed Storage Tank Grid-based Storage NAS Storage Tank 26 Evolving to an on demand environment IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation

IBM Total. Storage® Open Software Family 27 Evolving to an on demand environment IBM Confidential © 2004 IBM Corporation
8b7bafa3afd3c16e22bfa9846985b5a6.ppt