5f819c42203f4ef583599fbe66637697.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

® IBM Software Group Recommending Materialized Views and Indexes with the IBM DB 2 Design Advisor (Automating Physical Database Design) Jarek Gryz
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Agenda § § § Motivation Indexes in DB 2 Materialized query tables in DB 2 Problem definition How does the DB 2 Design Advisor tool work ? Experiments
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Motivation
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Why have an index? § Performance, Performance § Provides order 4 for example : Joins, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, DISTINCT § Limits I/O and data retrieved due to filtering with predicates 4 Range of values (start/stop keys) 4 Join predicates § Provides index-only access § Enforces uniqueness or other constraints § Provides statistics useful to the optimizer for cardinality estimation 4 for example: statistics on number of keys
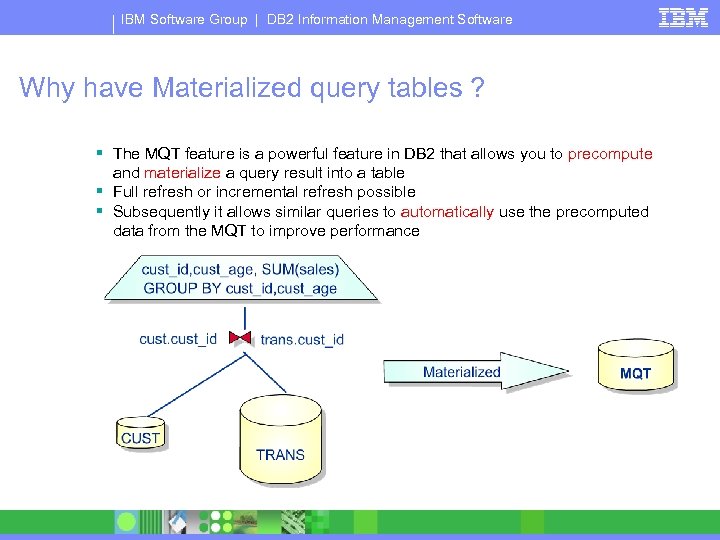
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Why have Materialized query tables ? § The MQT feature is a powerful feature in DB 2 that allows you to precompute and materialize a query result into a table § Full refresh or incremental refresh possible § Subsequently it allows similar queries to automatically use the precomputed data from the MQT to improve performance
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Problem Definition § Given: 4 Workload information 4 System configuration 4 Database characteristics § Determine: 4 An Index and MQT set that will • lead to good workload performance • in a reasonable or specified maximum time • considering disk space and maintenance constraints • and be easy to use
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software The DB 2 Design Advisor § Automatically capture : 4 A representative query workload (potentially compressing it to reduce its size) 4 The existing database characteristics and environment 4 System information § Determines: 4 An Index and MQT set that will lead to good ESTIMATED workload response time • • • Using DB 2's Query Rewriter/Optimizer to suggest candidates Using DB 2's Optimizer to provide cost / benefit information Using a combinatorial algorithm to perform a cost-benefit analysis observing constraints of (1) advisor execution time, (2) disk space and (3) anticipated DB 2 costs of creating the entities plus overhead during INSERT / UPDATE / DELETE activity. Using sampled or estimated statistics of new entities Providing both GUI and command line options for initiating
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Issues in automating physical DB design selection § When to initiate the design algorithm? 4 Health monitor with health indicators such as number of sort overflows to initiate the advisor § What data to use to make the decision? 4 Automatically capture workload, DB, and system information 4 Allow work on real data or just statistics § How to make the decision? 4 Method to be described § How are the recommendations implemented? 4 Little user interaction to ask if or when to initiate to gain DBA trust 4 Online methods to reduce implementation cost • E. g. , online index creation
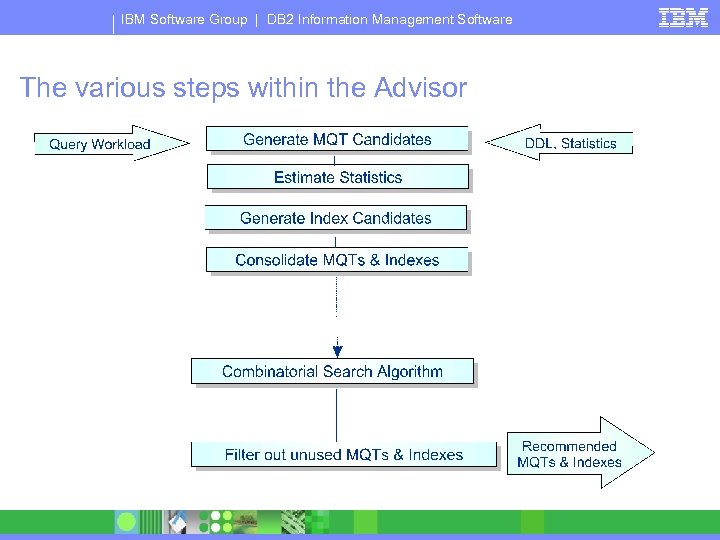
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software The various steps within the Advisor
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Index candidate generation § During optimization generate virtual candidates when: 4 Predicate exists but no index (e. g. , R. A > 5 or R. A=S. B) 4 Ordering required 4 Uniqueness required § Winning candidates are the virtuals in the final optimized query plan § Provides candidates we know the optimizer will use
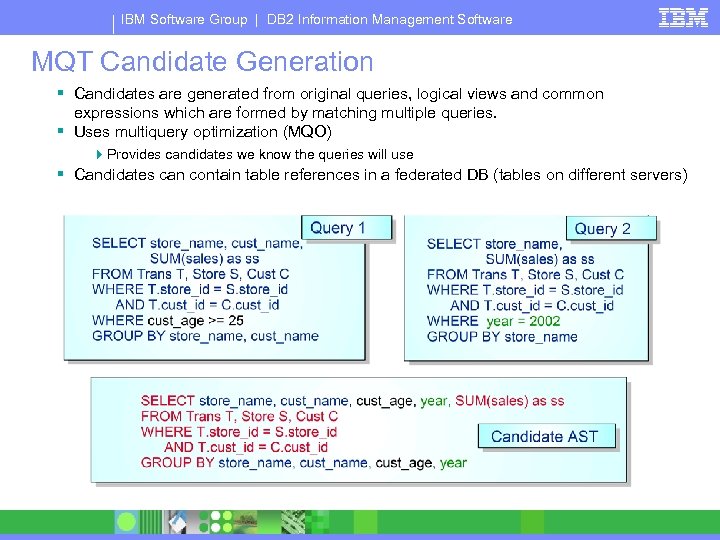
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software MQT Candidate Generation § Candidates are generated from original queries, logical views and common expressions which are formed by matching multiple queries. § Uses multiquery optimization (MQO) 4 Provides candidates we know the queries will use § Candidates can contain table references in a federated DB (tables on different servers)

IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Combinatorial search algorithm § The search phase uses a knapsack algorithm and random swap method to choose the recommended index and MQT set § Requires each candidate to have a cost-benefit ratio (cbratio) 4 Benefit based on estimated cost with and without MQT usage (updates have negative benefit) 4 Cost based on disk space usage § REFRESH DEFERRED or IMMEDIATE MQTs recommended. 4 Assumption (DEFERRED): • estimated time for population = full refresh cost • one refresh cost included in the calculation 4 IMMEDIATE changes added in plans for insert/update/deletes § If indexes on candidate MQT are selected, then the MQT must be selected as well
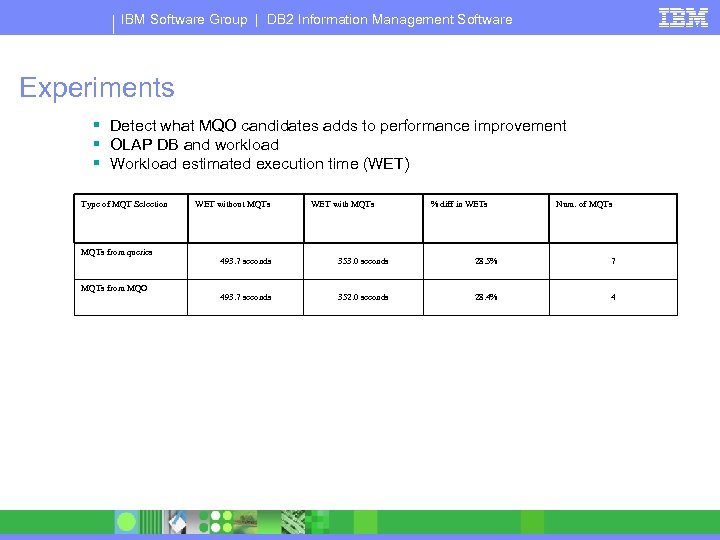
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Experiments § Detect what MQO candidates adds to performance improvement § OLAP DB and workload § Workload estimated execution time (WET) Type of MQT Selection MQTs from queries MQTs from MQO WET without MQTs WET with MQTs % diff in WETs Num. of MQTs 493. 7 seconds 353. 0 seconds 28. 5% 7 493. 7 seconds 352. 0 seconds 28. 4% 4
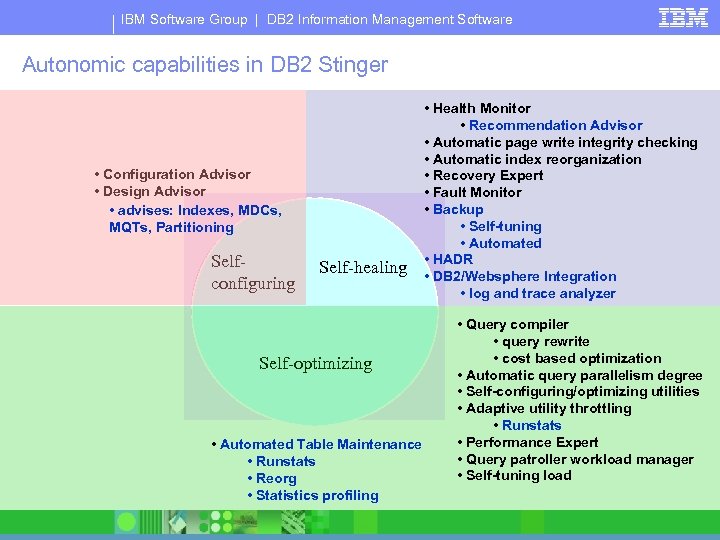
IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Autonomic capabilities in DB 2 Stinger • Configuration Advisor • Design Advisor • advises: Indexes, MDCs, MQTs, Partitioning Selfconfiguring Self-healing Self-optimizing • Automated Table Maintenance • Runstats • Reorg • Statistics profiling • Health Monitor • Recommendation Advisor • Automatic page write integrity checking • Automatic index reorganization • Recovery Expert • Fault Monitor • Backup • Self-tuning • Automated • HADR • DB 2/Websphere Integration • log and trace analyzer • Query compiler • query rewrite • cost based optimization • Automatic query parallelism degree • Self-configuring/optimizing utilities • Adaptive utility throttling • Runstats • Performance Expert • Query patroller workload manager • Self-tuning load

IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software
5f819c42203f4ef583599fbe66637697.ppt