b7fd41cc86c3a468de024b6924f8cb42.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

® IBM Software Group Rational Business Developer – Version 7. 1 Featuring, Enterprise Generation Language This is the first module in the learning Tutorials. It covers EGL/RBD overview – product and course setup and introduces you to “how to learn” from these slides and examples. © 2006 IBM Corporation

Course Contributing Authors § Thanks to the following individuals, for assisting with this course: 4 Jeri Petersen, Scott Pecnik, Mark Evans, Jim Buck, Sanjay Chandru , Timothy Mc. Mackin, Narinder Makin, Jing Qian, Claus Weiss, Paul Hoffman, Matthew Heitz, Yukihiro Minote, Jorge Serrano, Glenn Gundermann, Reginaldo Barosa, Jake Berberich, Brice Small, Chandra Krothapalli, Jon Shavor, Brian Svihovec, Thom Haynes, Joe Pluta, Peter Young, Jeff Cook, Jing Qian, Joe Vincens, Justin Spadea, John Riendeau, Kendall Coolidge, Amit Joglekar, Damian Madden, Mike Kohlndorfer, Alan Naylor, Mitch Davidson, 2

IBM Trademarks and Copyrights 4 © Copyright IBM Corporation 2007, 2008. All rights reserved. 4 The information contained in these materials is provided for informational purposes only, and is provided AS IS without warranty of any kind, express or implied. IBM shall not be responsible for any damages arising out of the use of, or otherwise related to, these materials. Nothing contained in these materials is intended to, nor shall have the effect of, creating any warranties or representations from IBM or its suppliers or licensors, or altering the terms and conditions of the applicable license agreement governing the use of IBM software. References in these materials to IBM products, programs, or services do not imply that they will be available in all countries in which IBM operates. 4 This information is based on current IBM product plans and strategy, which are subject to change by IBM without notice. Product release dates and/or capabilities referenced in these materials may change at any time at IBM’s sole discretion based on market opportunities or other factors, and are not intended to be a commitment to future product or feature availability in any way. 4 IBM, the IBM logo, the on-demand business logo, Rational, the Rational logo, and other IBM Rational products and services are trademarks or registered trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation, in the United States, other countries or both. Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others. 3

Course Details § Audience 4 This course is designed for application developers who have programmed in a 3 rd or 4 th generation language – and who need to build leading-edge applications using Rational Business Developer. § Prerequisites 4 This course assumes that the student has the basic knowledge of IS technologies, data processing, software and havs programmed for at least two or more years in a language such as: COBOL, RPG, PL/1, Pascal, or some 4 th Generation Language or tool. 4 Knowledge of SQL (Structured Query Language) for database access is assumed as well. 4 Basic PC and mouse-driven development skills is also assumed. 4 Finally, it is assumed that you know a little bit about IBM’s Rational Business Developer and EGL (Enterprise Generation Language) – at least from a highlevel “what is” perspective. 4

Course Objectives § At the end of this course, you will be able to: 4 Create EGL Programs, Libraries, Services and JSFHandlers that operate in a leading-edge application like a web app to deliver business functionality. 4 Code statements to define and declare EGL primitive data, Data. Items, Records and EGL properties 4 Code structured looping, conditional and assignment statements. 4 Code EGL SQL and data access statements to read and write from programs to external databases and files 4 Analyze whether an SQL statement is efficient and code it differently if it is not. 4 Create EGL business logic at or near the production requirements specification level in terms of: § Complexity § Breadth and Scope 5

Course Introduction – Unit Descriptions § The first unit, RBD Workbench, introduces the Eclipse IDE (Integrated Development Environment) and discusses EGL terms and concepts from a high-level perspective. § The EGL Quick. Start unit takes you through the process of building a small web application using EGL and JSF from scratch throughout the entire development lifecycle. § In the third unit, Programming In EGL, you learn how to translate what you know in System z and System i programming language parlance to EGL, and to write production-quality business applications using EGL statements. § In the fifth unit, Database and File Access Using EGL, you learn how to leverage the EGL language abstractions to simplify and expedite developing complex and efficient database access. You will also learn how to access external files from EGL programs. § In the sixth unit, EGL and Services you learn how to create, consume, deploy, test and use externally created Web Services, and you also learn about how EGL can be used in a Service Oriented Architecture. § The final unit, Calling External Programs in Other Languages, discusses how to call Java, COBOL, RPG and C++ programs from EGL. 6

Course RBD/EGL Development Units: § What is EGL (and what is RBD)? 7
What is Enterprise Generation Language (EGL)? § High-level programming language for developing leading-edge business applications § Independent of implementation 4 Hides technology complexities 4 Presentation and persistence layer API fully generated § Enables Rapid Application Development § Simplifies development of Services § Run-time code generated for appropriate platform 4 Java for Windows, Linux, and so forth 4 COBOL for System z and System i § Development and Generating Tools included with RBD § Migration path for CSP, Visual Age Generator, and Informix 4 GL customers § Integrates with leading-edge software technologies 4 Eclipse, JSF, Application Servers, etc. - See the Help topic: Introduction to EGL 8
What is Rational Business Developer (RBD)? § Commercial product, from IBM for the EGL language, targeted to business developers § Member of the Rational Software offerings suite § Support for wide range of platform, middleware, and technologies § Rich Eclipse-based tooling for productive development of leadingedge and legacy application functionality 9

EGL Principles § Decouples application specification from runtimes. § Useable by developers of any technical software background. § Hides technical complexity. § Supports emerging standards and technologies. § Allows optimal (native) deployment to any runtime (new and traditional) § Ensures easy inter-operability with legacy. § Delivers productivity without compromising flexibility: 4 Language simplicity. 4 Language robustness. 10

Declarations La ng ua ge 4 “Records” provide access to: § RBD SQL, Indexed, Relative, Serial, DL/I, Service data, Message Queues 4 Common Verbs for data access (Get, Add, Replace, Delete). 4 Allows complete access to SQL statement if needed. 4 Common Error Handling. § Remote Invocation 4 4 4 § User Interface: 4 EGL “handlers” hide complexities of § § Web (JSF) UI Reports (BIRT) Portlets Rich Web (Ajax) 11 Tools n tio era e en Ge § Data access: SOA s ns tio ct tra st Ab A EGL Language “Abstractions” Call COBOL, RPG, C, Java. Linkage information separated from code. Data mapping, protocol invocation all resolved at runtime, NO code necessary!
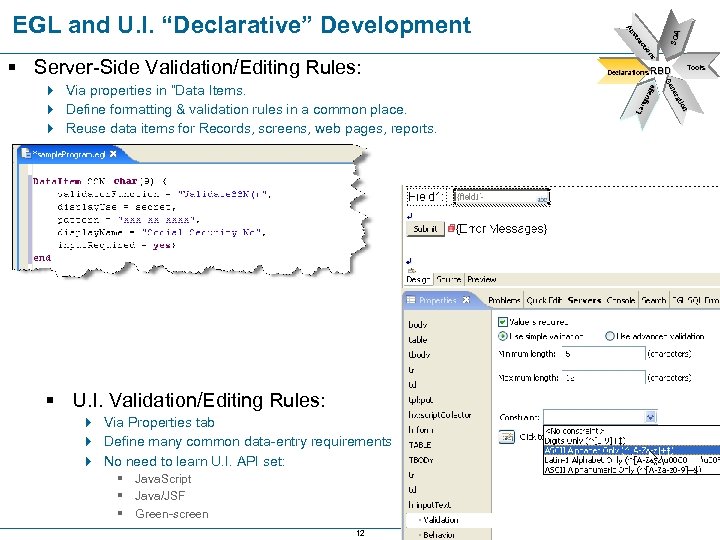
§ U. I. Validation/Editing Rules: 4 Via Properties tab 4 Define many common data-entry requirements 4 No need to learn U. I. API set: § Java. Script § Java/JSF § Green-screen 12 SOA Tools n tio t era ne Ge Ge 4 Via properties in “Data Items. 4 Define formatting & validation rules in a common place. 4 Reuse data items for Records, screens, web pages, reports. Declarations RBD La ng ua ge § Server-Side Validation/Editing Rules: s on tio ac tra bs Ab EGL and U. I. “Declarative” Development
4 Internet/Web – JSF 4 Internet/Web 2. 0 - Rich U. I. 4 COBOL Generation - Legacy § Rich data types 4 Simple, traditional, new, complex § Keywords 4 Case, if-then-else, while, for loop cycling through a database result set, etc. § High power language capabilities 4 Automated Casting (e. g. using AS operator) 4 Mixing data types in assignments and expressions 4 Exception handling § Rich libraries of built-in functions 4 Math, string, date/time, system, i 5/OS resources (Data Areas, Data Queues) access § Robust integration with existing investment or access to low level APIs 4 Call RPG, COBOL, C, etc. 4 Full Java interoperability § § RBD La ng ua ge Declarations Invoke Java from EGL (map Java classes with EGL External Types) Invoke EGL from Java 13 Tools n tio t era ne Ge Ge § Procedural, operationally and computationally complete, provides Server-side logic for: SOA Language s on tio ac tra bs Ab Enterprise Generation
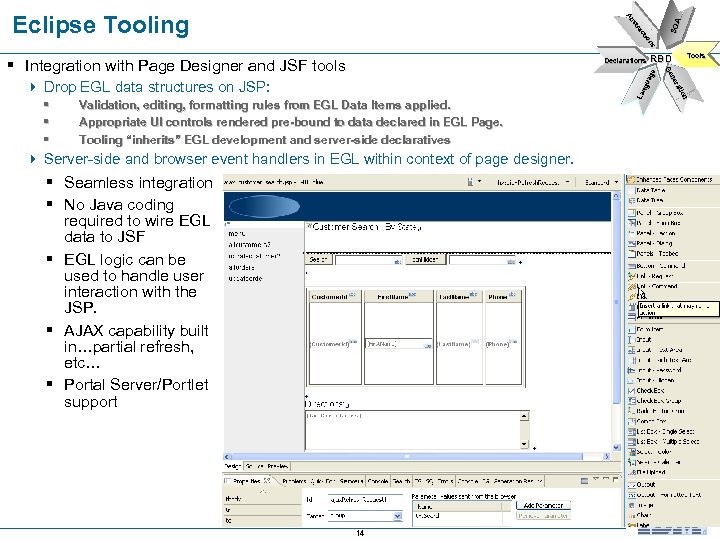
4 Drop EGL data structures on JSP: § § § Validation, editing, formatting rules from EGL Data Items applied. Appropriate UI controls rendered pre-bound to data declared in EGL Page. Tooling “inherits” EGL development and server-side declaratives 4 Server-side and browser event handlers in EGL within context of page designer. § Seamless integration § No Java coding required to wire EGL data to JSF § EGL logic can be used to handle user interaction with the JSP. § AJAX capability built in…partial refresh, etc… § Portal Server/Portlet support 14 RBD La ng ua ge Declarations Tools n tio era e en Ge § Integration with Page Designer and JSF tools SOA s on io ct tra bs Ab Eclipse Tooling
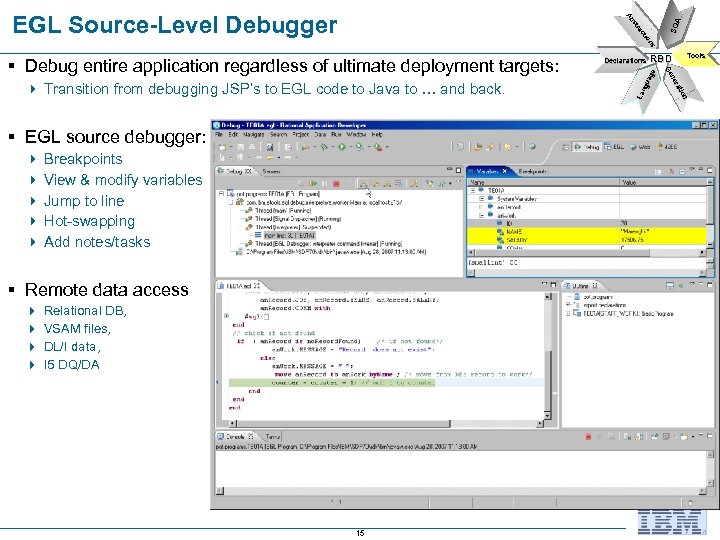
§ EGL source debugger: 4 Breakpoints 4 View & modify variables 4 Jump to line 4 Hot-swapping 4 Add notes/tasks § Remote data access 4 4 Relational DB, VSAM files, DL/I data, I 5 DQ/DA 15 La ng ua ge 4 Transition from debugging JSP’s to EGL code to Java to … and back. RBD Tools n tio era e en Ge § Debug entire application regardless of ultimate deployment targets: Declarations SOA s on io ct tra bs Ab EGL Source-Level Debugger

4 A built-in language part containing code that will be accessed: § § From EGL code by way of a local or TCP/IP connection ( EGL Service). From any code by way of an HTTP connection (EGL Web service). 16 RBD La ng ua ge Declarations Tools on tio era ea en Ge § Service part: SOA s on iio ct c ra r st s Ab EGL and Services
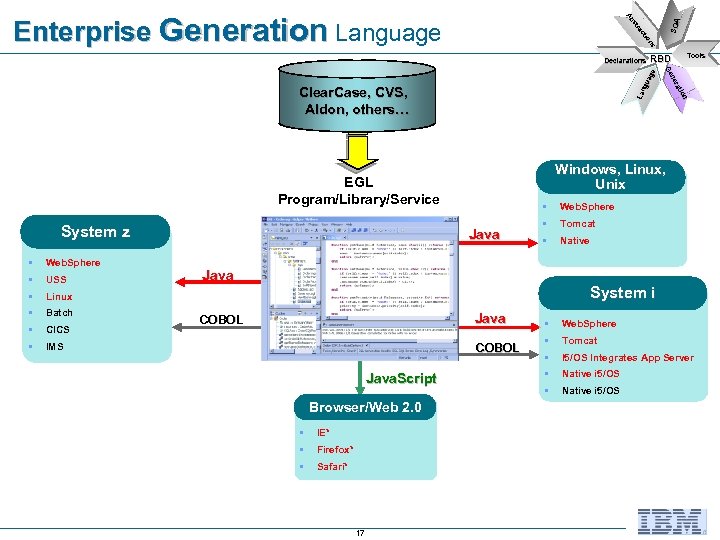
§ § Web. Sphere § USS § Batch § CICS § § Java Linux § Windows, Linux, z. Series Unix § EGL Program/Library/Service System z IMS Tools n tio t era ne Ge Ge Clear. Case, CVS, Aldon, others… z. Series RBD La ng ua ge Declarations SOA s on tio ac tra bs Ab Enterprise Generation Language Web. Sphere § Tomcat § Native Java COBOL Java. Script § Browser/Web 2. 0 § IE* § Firefox* § Safari* 17 § z. Series System i i. Series § Web. Sphere § Tomcat § I 5/OS Integrates App Server § Native i 5/OS
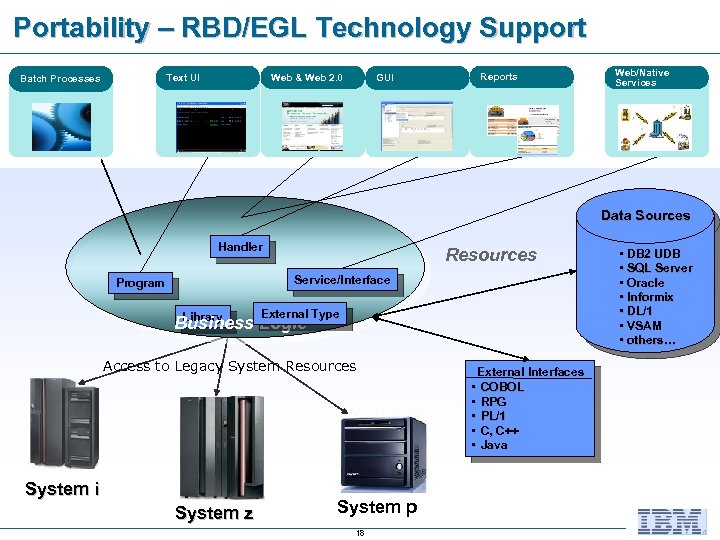
Portability – RBD/EGL Technology Support Web & Web 2. 0 Text UI Batch Processes GUI Reports Web/Native Services Data Sources Handler Resources Service/Interface Program External Type Library Business Logic Access to Legacy System Resources System i System z System p 18 External Interfaces • COBOL • RPG • PL/1 • C, C++ • Java • DB 2 UDB • SQL Server • Oracle • Informix • DL/1 • VSAM • others…
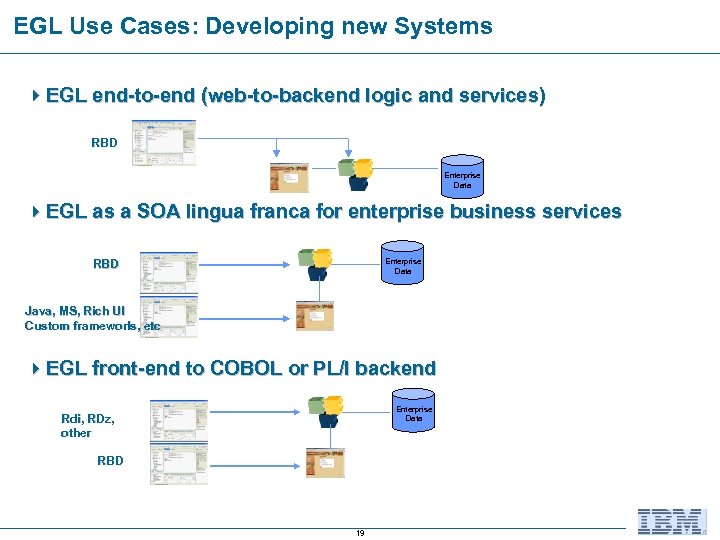
EGL Use Cases: Developing new Systems 4 EGL end-to-end (web-to-backend logic and services) RBD Enterprise Data 4 EGL as a SOA lingua franca for enterprise business services Enterprise Data RBD Java, MS, Rich UI Custom frameworls, etc frameworls, 4 EGL front-end to COBOL or PL/I backend Enterprise Data Rdi, RDz, Rdi, other RBD 19
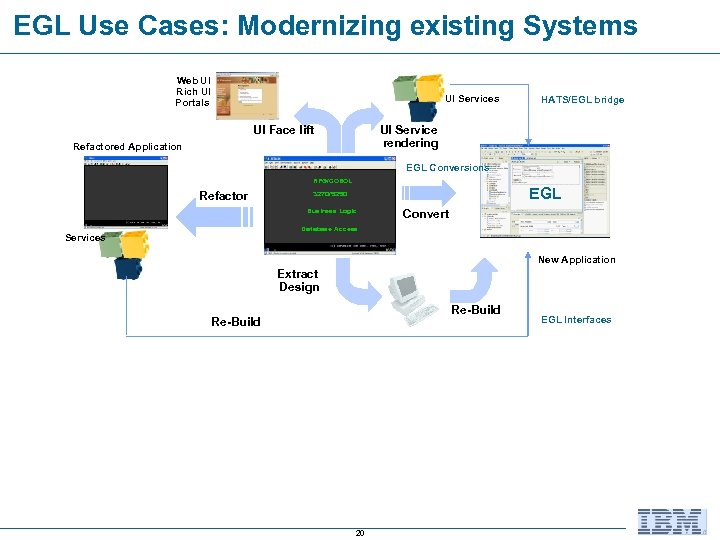
EGL Use Cases: Modernizing existing Systems Web UI Rich UI Portals UI Services UI Face lift HATS/EGL bridge UI Service rendering Refactored Application EGL Conversions RPG/COBOL Refactor EGL 3270/5250 Business Logic Convert Database Access Services New Application Extract Design Re-Build 20 EGL Interfaces
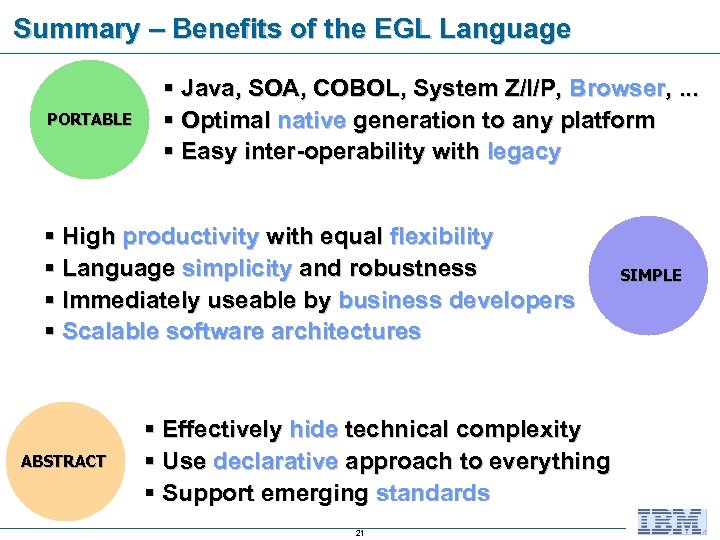
Summary – Benefits of the EGL Language PORTABLE § Java, SOA, COBOL, System Z/I/P, Browser, . . . § Optimal native generation to any platform § Easy inter-operability with legacy § High productivity with equal flexibility § Language simplicity and robustness § Immediately useable by business developers § Scalable software architectures ABSTRACT § Effectively hide technical complexity § Use declarative approach to everything § Support emerging standards 21 SIMPLE

UNIT RBD Product and Course Setup Topics: § How to take this course § Downloading RBD software (trial edition) § Installing and configuring Tomcat (application server) § Installing and configuring the course project and database 22

How to use this book § This course has two different modes of educational delivery – each based on both content matter, and on effective knowledge transfer: 4 Read and Learn: 4 Do and Acquire: 23

Read and Learn Read and learn is the most prevalent form of education presented in this course. 4 From the slides you are viewing, you can read and understand concepts about RBD and EGL. This is static information presented as traditional text and graphics. 4 The Notes (at the bottom of most slides) present additional information on each concept. The Notes also present (wherever relevant) System z and System i programmer analogies 4 There are numerous slides that allow you to test your knowledge and learning. These slides contain paper/pencil questions. The answers to most of these questions are at the end of the Power. Point slides. 24

How to use this book Do and Acquire 4 To make all of the pieces of information covered in this course yours – and to convince you that you’ve got the skills to match the knowledge you accumulate, you will need to use RBD and EGL to create software functionality. 4 There are lots of workshops and labs throughout this course, that will allow you to discover, practice and master the RBD functionality and development techniques used to create no-compromise, production-worthy applications. 4 All of the “do this” steps have a consistent icon to the left of them, the: 4 When you see this symbol either at the top of a page, or at the beginning of a step, it signifies that you are to “do” something with the product or language. 25

View the Slide Notes Using your mouse expand the Notes at the bottom of this slide and read them. Adjust the size of the slides or notes to suit your viewing Figure 1 – Power. Point Notes View 26
Learn More! There a large number of excellent sources for background information freely available online. Here a few we use a lot: Product Help § Help Contents § Search § Tutorials and examples – from the Sample Gallery § Programmer’s Guide § EGL Language Reference § Cheat Sheets IBM Systems Information Center http: //publib. boulder. ibm. com/infocenter/systems/index. jsp GOOGLE Search www. google. com Search on any topic Wikipedia Search http: //wikipedia. org/ Answers, for virtually any topic From the home page, click: 27
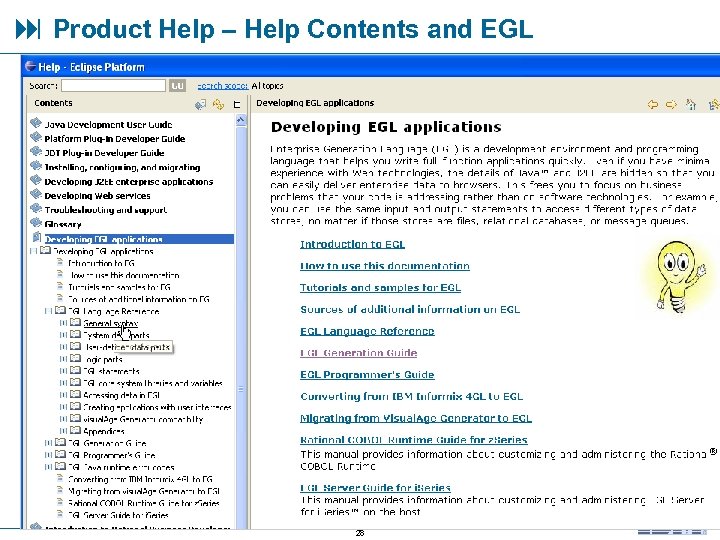
Product Help – Help Contents and EGL 28

UNIT RBD Product and Course Setup Topics: § How to take this course. § Downloading RBD software (trial edition) and installing and configuring your app-server, the sample project and your database - overview 29

RBD v 7. 1 Installation Process § RBD v 7. 1 can be installed standalone, or can be installed into (on top of): 4 RDz 4 RDi SOA 4 RAD § The RBD v 7. 1 installation process covered in the EGL-RBD-v 71. ppt In addition to the RBD v 7. 1 software, you will also need to download to your workstation: 4 EGLDerby. R 7. zip – the course database 4 And either 4 v 71 Project_Tomcat. zip – for doing this course using Tomcat …or… 4 v 71 Project_WAS. zip – for doing this course using WAS 4 Your course setup e-Mail will direct you as to where to get these resources 30
Course Application Server Considerations IMPORTANT NOTES 4 With RBD and EGL you have a choice of a number of application servers to run web applications with, including: Web. Sphere Application Server and Tomcat 4 In order to accommodate customers with limited access to application servers, we will use Tomcat in our examples. 4 Someone may have already installed and configured the Tomcat application server for you. 4 If you wish to use Tomcat, you might first read about the software from this link: § http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Apache_Tomcat 4 The RBD-EGL-v 71. ppt has detailed instructions on Tomcat installation. 31
Installing and configuring the course database § This course uses a pre-configured Project and an open-source (Derby) database, which you will need to install and configure. § You will unzip EGLDerby. R 7. zip To: C: databases § Your files should look like this after you have unzipped them Again the RBD-EGL-v 71. ppt will cover this step in detail 32

Installing and configuring the course project This course uses a pre-configured Project, which you will need to install and configure. Someone may already have installed and configured the project for you. If so, you may skip ahead to the next section. If not, please follow the steps below to install and configure the course project: From the Windows start menu, you will launch RBD …or…RAD with RBD (depending on what product you have installed on your PC) Again: 1. This step is covered in-depth, in the RBD-EGL-v 71. ppt 2. You will choose either a Tomcat or Web. Sphere project – depending on which application server you installed. 33

Unit Summary § Now that you have completed this topic, you should be able to: 4 Launch RBD – and select a workspace 4 View the Education Project in eclipse 4 Connect to the Derby database and view data rendered in a simple EGL/JSF web page § Note this verifies that all of the software components necessary for this course are: – Installed – Configured – Operational 34
b7fd41cc86c3a468de024b6924f8cb42.ppt