574dfb620b8016adffacea0c48cd5137.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Informix 4 GL and EGL § Jerry Keesee, Director of the Informix lab § S. Venkatesh Gopal, Development, Informix R&D February 2, 2005 © 2005 IBM Corporation

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Disclosure Information § PLANS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE OR CANCELLATION WITHOUT NOTICE 2 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Agenda § Informix 4 GL Today § Why EGL? § Overview of some EGL capabilities § 4 GL / EGL Syntax Comparison § JSF & EGL – Web Application Development Overview § Conversion of 4 GL to EGL 3 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
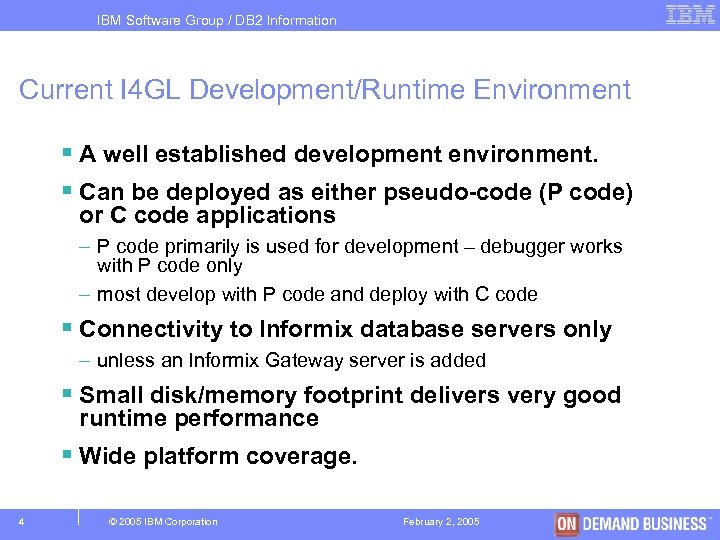
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Current I 4 GL Development/Runtime Environment § A well established development environment. § Can be deployed as either pseudo-code (P code) or C code applications – P code primarily is used for development – debugger works with P code only – most develop with P code and deploy with C code § Connectivity to Informix database servers only – unless an Informix Gateway server is added § Small disk/memory footprint delivers very good runtime performance § Wide platform coverage. 4 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
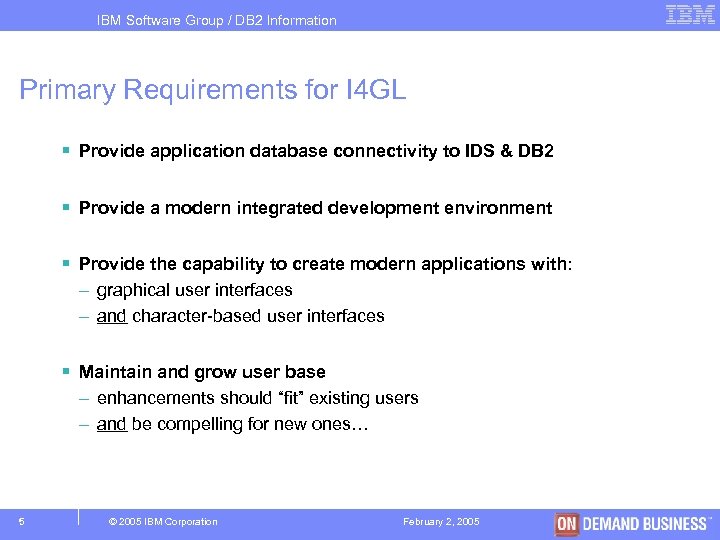
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Primary Requirements for I 4 GL § Provide application database connectivity to IDS & DB 2 § Provide a modern integrated development environment § Provide the capability to create modern applications with: – graphical user interfaces – and character-based user interfaces § Maintain and grow user base – enhancements should “fit” existing users – and be compelling for new ones… 5 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management EGL § A language as easy as I 4 GL to use and develop with. § Provides an industry standard IDE (Rational Application developer) for developing EGL, Java, Web and COBOL applications. § Provides an enriched set of the same capabilities. – Text user interface (Curses based). – Calls to “C” functions. – SQL (embedded, dynamic and more). – Interactive debugging capability. – Powerful reporting capability. – Command line based application development. – Data types (all of I 4 GL and some more in addition). 6 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management EGL. . . § In addition to the I 4 GL feature set provides – Development and runtime capabilities for Windows platforms. – More general programming capabilities. – Web Application development and deployment. • Same business logic can be shared in both deployments. – Multiple Database connectivity. • Uses JDBC and allows to connect to any DB. – – Service Oriented Architecture (Web Services). MQ Access. File I/O Provides for COBOL generation options (deployable in i-Series and z. Series). – Calling out Java code from EGL. – and more… 7 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management EGL (similarities to I 4 GL). § Lots of similarities. – Basic statements and looping constructs are similar. – SQL statements are similar to 4 GL (prepare, execute, open, get (fetch), close and for each). – Text user interface similar (with a more general programming model) to I 4 GL with extended capabilities. – Reporting framework provides for a wider set of output formats (PDF, Text, XML, CSV, HTML). – A highly interactive and visual debugging environment based on the Eclipse framework. 8 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Examples (Comparing I 4 GL to EGL). DEFINE INTVAL INTEGER INTVAL INT; DEFINE my. Record RECORD Record my. Record. Type intval INTEGER, intval int; floatval FLOAT, floatval float; decimalval DECIMAL decimalval decimal; END RECORD End my. Record. Type; myother. Record my. Record. Type; LET intval = 10 LET myrecord. intval = 10 my. Record. intval = 10; CALL func. Name(param 1, param 2) 9 intval = 10; func. Name(param 1, param 2); © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Examples (Comparing I 4 GL to EGL). while(i < 10) let i = i + 1 while(i < 10) i = i+1; end while End case (i) case(i) when 10 when (10) … when 20 … when (20) … … otherwise … … End case 10 © 2005 IBM Corporation end February 2, 2005
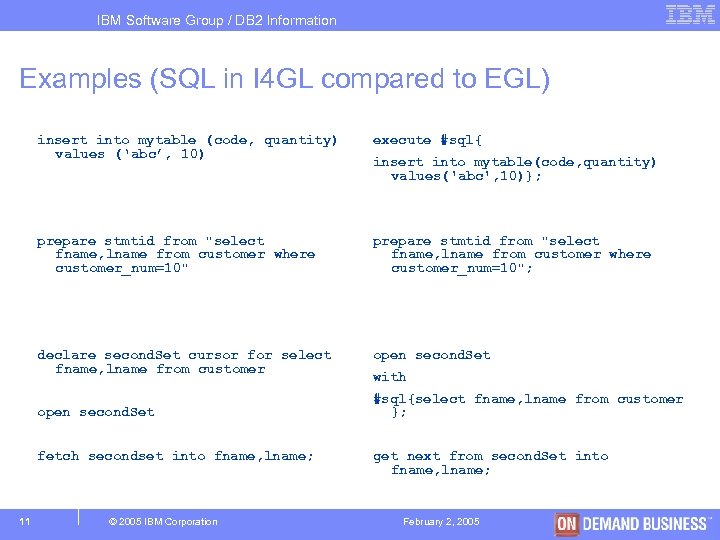
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Examples (SQL in I 4 GL compared to EGL) insert into mytable (code, quantity) values (‘abc’, 10) prepare stmtid from "select fname, lname from customer where customer_num=10"; declare second. Set cursor for select fname, lname from customer open second. Set #sql{select fname, lname from customer }; fetch secondset into fname, lname; 11 execute #sql{ get next from second. Set into fname, lname; © 2005 IBM Corporation insert into mytable(code, quantity) values('abc', 10)}; with February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Some Infrastructure differences… § EGL being IDE based requires knowledge of Eclipse Workspace paradigms. § Everything exists in a workspace – Workspace has projects. • Projects have packages. – Packages have files. – Files can be either EGL source files, EGL programs or EGL libraries. § A program is equivalent to a I 4 GL file having the main function. § A library is equivalent to any I 4 GL modules that provides functions for use by other I 4 GL modules or I 4 GL globals file. 12 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Informix 4 GL Today EGL Today PACKAGE Player. Stats. Application; DATABASE stats GLOBALS DEFINE player_bats RECORD LIKE informix. atbats. * DEFINE batting_ave RECORD LIKE informix. battingaverage. * END GLOBALS ---------------------MAIN ---------------------DEFINE BA DECIMAL (4, 3) DECLARE curs_at_bats cursor for select * from informix. atbats OPEN curs_at_bats WHILE (SQLCA. SQLCODE = 0) FETCH curs_at_bats into player_bats. * IF (SQLCA. SQLCODE = 100) THEN EXIT WHILE END IF CALL compute_BA(player_bats. atbats, player_bats. hits) RETURNING BA INSERT INTO informix. battingaverage VALUES (player_bats. lname, BA); END WHILE COMMIT WORK CLOSE curs_at_bats END MAIN import Infx. Db. Schema. sports. stats. *; PROGRAM player_main use player_ba; player_bats rec_like_informix_atbats; batting_ave rec_like_informix_battingaverage; FUNCTION main() BA DECIMAL (4, 3); PREPARE $_STMT_curs_at_bats FROM "select * from informix. atbats"; open curs_at_bats with $_STMT_curs_at_bats; WHILE (SQLCODE = 0) get next from curs_at_bats into player_bats. lname, player_bats. atbats, player_bats. hits, player_bats. walks; IF (SQLCODE = 100) EXIT WHILE; END BA = compute_BA(player_bats. atbats , player_bats. hits); execute #sql{INSERT INTO informix. battingaverage VALUES (: player_bats. lname, : BA) }; END //WHILE commit() ; CLOSE curs_at_bats; END // FUNCTION END // PROGRAM FUNCTION compute_BA(at_bats, hits) DEFINE at_bats INTEGER DEFINE hits INTEGER DEFINE BA DECIMAL (4, 3) LET BA = hits/at_bats RETURN BA END FUNCTION PACKAGE Player. Stats. Application; LIBRARY player_ba FUNCTION compute_BA(at_bats INT IN, hits INT IN) returns (DECIMAL (4, 3)) IDS BA DECIMAL (4, 3); BA = hits/at_bats; RETURN( BA); END // FUNCTION END // LIBRARY 13 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Compiling and running applications. § Set up the compilation options in the build descriptor. § Generate to Java § Run the application. § Take the generate Java and deploy it to any other machine with the runtime libraries. § If you have created a web application, deploy the web archives to the test server or any J 2 EE server from within the IDE. 14 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Some extended capabilities… 15 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Integrated development environment § An industry standard IDE § Based on the Eclipse framework § Provides for different development perspectives – EGL/Web – Java and more. § Context Sensitive editor § Debugging capability (Interpretive debugger). § Page designer for JSPs and page handlers. § Code Assist (using Ctrl + Space) 16 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Records § Different types… – Basic Records – SQL Records – Serial Records – Indexed Records – MQ Records. § Record type identifies the I/O that can be done § Same statements are used for different Record types § No I/O with Basic records. 17 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
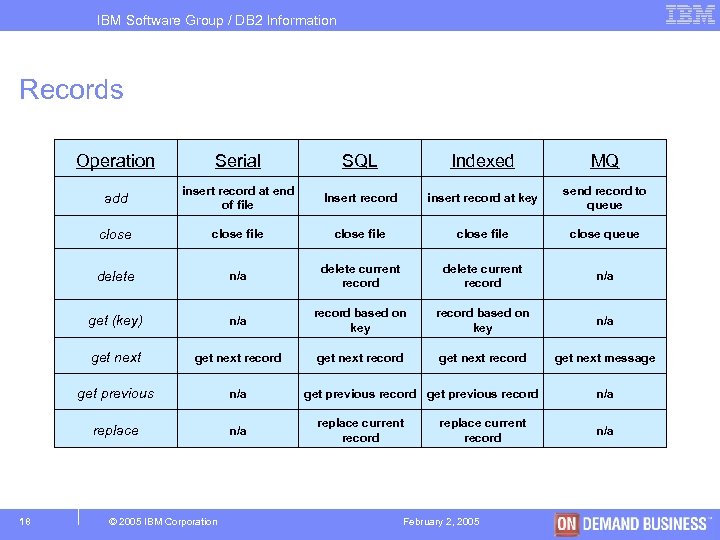
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Records Operation SQL Indexed MQ add insert record at end of file Insert record insert record at key send record to queue close file close queue delete n/a delete current record n/a get (key) n/a record based on key n/a get next record get next message get previous n/a replace 18 Serial n/a © 2005 IBM Corporation get previous record replace current record February 2, 2005 n/a

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Records (SQL Records) § Record definition Record Customer. Record type SQLRecord {table. Names=("customer") } customer_num int {column=customer_num}; fname char(15) {column = fname}; lname char(15) {column = lname}; company char(20) {column = company}; address 1 char(20) {column = address 1}; address 2 char(20) {column = address 2}; city char(15) {column = city}; state char(2) {column = state}; zipcode char(5) {column = zipcode}; phone char(18) {column = phone}; end § A default SQL statement is generated for every SQLRecord § The SQL column information can be extracted using the IDE. 19 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management SQL Records (example) mycustomer Customer. Record; my. Customer. Array customer. Record[]; open result. Set for mycustomer; try while(sqlcode = 0) get next from result. Set; //mycustomer_num has the value. if(sqlcode = 100) exit while; end on. Exception End get my. Customer. Array; 20 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management File I/O using Records § Create a serial. Record File. Record type serial. Record {filename="customer"} customer_num num(10); fname char(15); lname char(15); End § Create a Resource Association. § Write your code. myfilerecord File. Record; myfilerecord. customer_num = 100; myfilerecord. fname = “John”; myfilerecord. lname = “Doe”; add myfilerecord; 21 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Message Queue Access § Easy MQ handling. – Create Record definitions. Record my. MQRecord type MQRecord { queue. Name = "mq. RA" } fname char(10); lname char(10); End – Create a Resource Association between the queue. Name attribute and the MQ system. – Write your code. mqr my. MQRecord; mqr. fname="Venkatesh"; mqr. lname="Gopal"; add mqr; get mqr; – Take full advantage using a package called “MQReusable. Parts”, a part of your standard distribution. 22 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
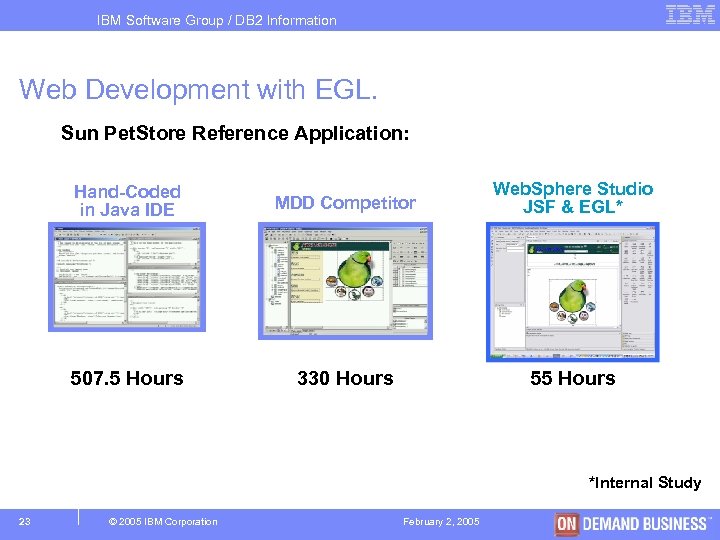
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Web Development with EGL. Sun Pet. Store Reference Application: Hand-Coded in Java IDE MDD Competitor Web. Sphere Studio JSF & EGL* 507. 5 Hours 330 Hours 55 Hours *Internal Study 23 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Web Development using JSF § JSF is a J 2 EE Web UI / programming framework § User interface component model - Set of standard widgets § Specification allows creation of custom UI components § Event handlers to process client-driven events § Actions to call business logic § Validation framework to allow server side validation § Internationalization/Localization 24 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
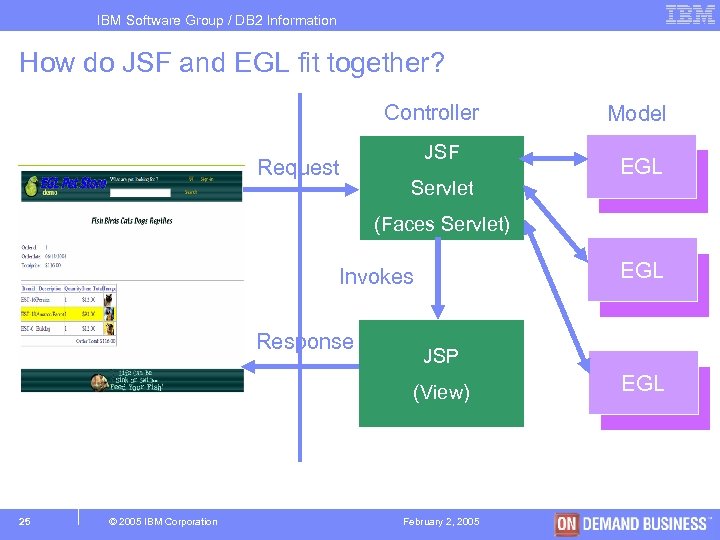
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management How do JSF and EGL fit together? Controller Request JSF Servlet Model EGL (Faces Servlet) EGL Invokes Response JSP (View) 25 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005 EGL

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management How do JSF and EGL fit together? § A perspective (EGL Web) that allows users to create a view (JSP) containing standard controls and widgets. § Easy Drag and Drop to bind the data components to presentation items in the view. § Automatic creation of a page handler that implements the controller – Has an on. Page. Load function, which is invoked the first time the web page is rendered. – A set of event handlers, each of which is invoked in response to a specific user action (like clicking on a button or a link). – Validation functions to validate web-page input fields. § Page handler can call other EGL library functions that implement the actual business logic. § Data can be passed between pages using simple EGL statements. 26 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Taking your applications from 4 GL to EGL 27 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management What is the Conversion Strategy? § Goal is to convert an I 4 GL application to the equivalent EGL application that uses: – the same display device – the same database server – I 4 GL TUI applications will be converted to EGL TUI applications § Convert, on a program-by-program basis, using the conversion utilities: – provided as part of the IDE – also available from the command line § Separate conversion passes required for: – database metadata extraction – shared libraries (C code or combination of C and I 4 GL code) – I 4 GL source code § Automated conversion should convert most 4 GL source code – but, some 4 GL programs may require manual intervention 28 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion Assumptions § I 4 GL code is “legal” – it will compile with I 4 GL 7. 32 compiler – conversion will not “fix” invalid I 4 GL code § Multiple passes are required § Functions that can not be resolved during conversion are assumed to be C code functions – if function is later found to be an I 4 GL function, re-conversion would be required § C code functions do not use undocumented I 4 GL internal functions 29 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management How is this Going to be Done? § Web. Sphere Studio conversion plug-in – runs within the EGL development environment (Windows or Linux) • I 4 GL source directories can be mounted from current environments • or copied to the EGL development environment – GUI wizard collects information about I 4 GL source environment: • • I 4 GL source and EGL destination directories I 4 GL source files (. 4 gl, . per, . c, . so, message files, etc) database connection information locale information – generates configuration XML files – invokes the conversion utility • displays conversion log upon completion 30 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management How is this Going to be Done? § Command line conversion utility – Java program can be run in current I 4 GL build environments • perhaps via current makefiles – requires XML configuration file describing current 4 GL environment: • could be generated using the IDE plugin • or generated via shell script – generates EGL conversion “projects” containing • • 31 database meta data makefiles to re-link C code with new EGL stack library EGL source files report designs and other reporting artifacts © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion Artifacts § Configuration file – XML file generated from interaction with conversion wizard – contains required conversion project information § Manifest file – XML file generated during conversion of shared libraries – contains declaration and usage information about each of the functions (C and I 4 GL) used in the shared library – used to resolve function declarations in dependent I 4 GL shared libraries – required for subsequent I 4 GL source code conversions § Log file – contains warnings and errors – status of each source file – summary of conversion 32 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Order of Conversion is Important! § Database metadata – conversion creates EGL packages for each database used in the project – schema metadata will become a separate EGL project which can be referenced by other EGL projects § Shared libraries – conversion generates Manifest file and makefile § I 4 GL source files –. 4 gl files –. per (form) files – message files 33 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Pre-Conversion Tasks § Identify & locate all the components of the 4 GL application to be converted – (. 4 gl, . per, message files, shared libraries) § Identify connection information for each database used § Start Informix database instances § Mount/copy source code to EGL development machine, if required § Determine destination directory for converted EGL source code & conversion artifacts § Identify “Client” locale – used to convert message files 34 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion Utility Processing § Map all I 4 GL constructs into equivalent EGL constructs § Convert existing “. 4 gl” source files into “. egl” source files § Convert existing “. per” form specification files into “. egl” TUI specification files – No special file extensions for EGL form definitions § Migrate existing I 4 GL error message files into EGL error messages § Convert existing I 4 GL reporting logic into equivalent EGL reporting logic § Generate a “makefile” that will be used to link the C shared libraries to the converted EGL project – makefile will have targets for different operating systems § Report all warnings and errors § Generate log file to indicate the status of conversion § Create default EGL build descriptor file for the project 35 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
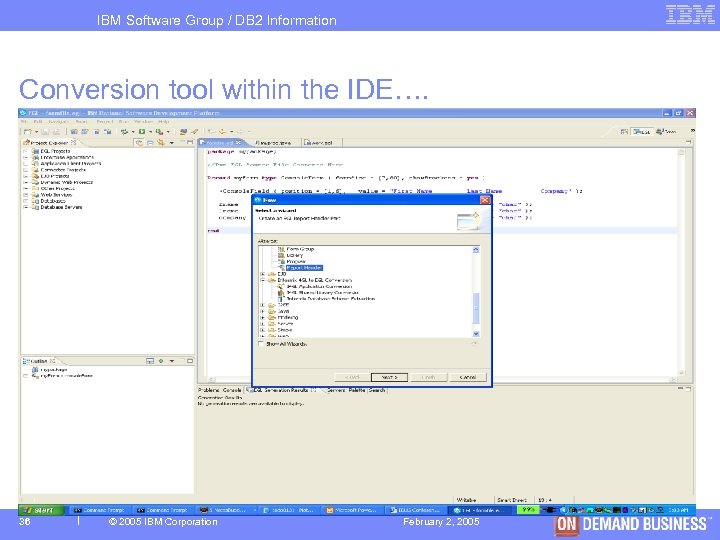
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion tool within the IDE…. 36 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion tool… 37 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion tool…. 38 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion tool (artifacts)… 39 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
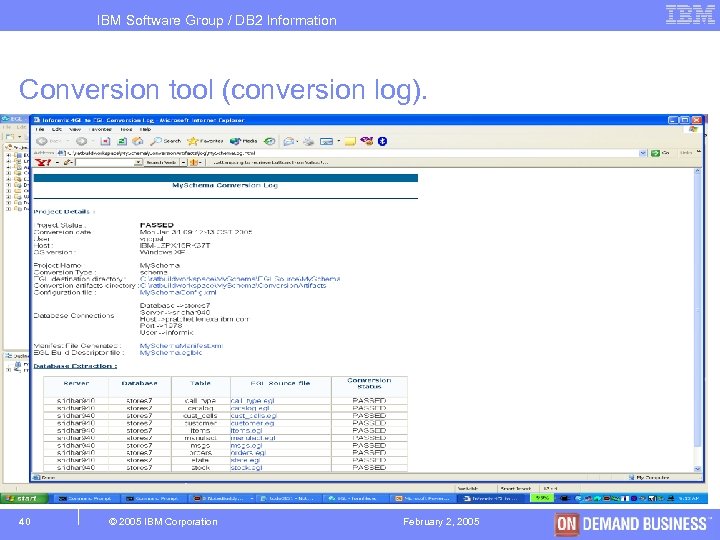
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion tool (conversion log). 40 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Post-Conversion Tasks § Review log file § Fix identified problems – on the 4 GL side and re-convert or – in the new EGL file – shared libraries may have to be re-converted if functions cannot be resolved § § Open the project in the IDE Verify EGL packages and source files View/update EGL build descriptor file “Generate” Java code for the project – fix problems in the EGL code § Set runtime properties from existing environment variables § Launch new EGL project 41 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Conversion Limitations § Database connections cannot be shared between EGL and C code § C code cannot call EGL functions § Default values set in syscolval table are not accessed § I 4 GL Dynamic Arrays (7. 32 release) will not be converted in initial release 42 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
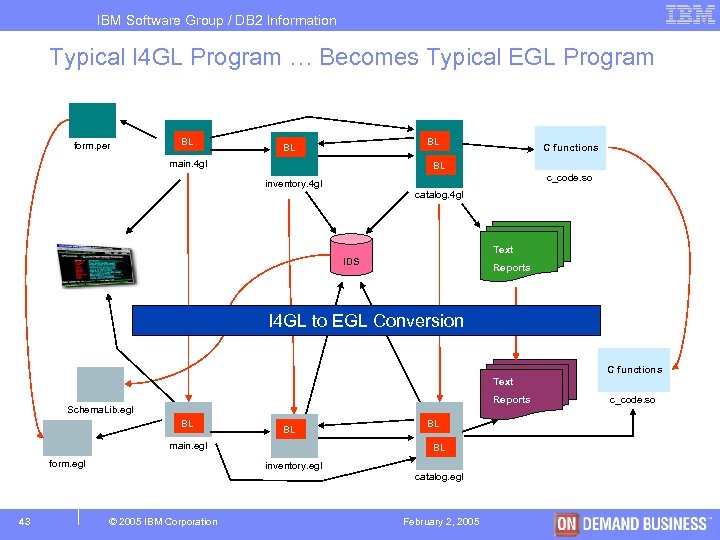
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Typical I 4 GL Program … Becomes Typical EGL Program form. per BL BL BL main. 4 gl C functions BL c_code. so inventory. 4 gl catalog. 4 gl Text IDS Reports I 4 GL to EGL Conversion C functions Text Reports Schema. Lib. egl BL BL main. egl form. egl 43 BL inventory. egl © 2005 IBM Corporation BL catalog. egl February 2, 2005 c_code. so
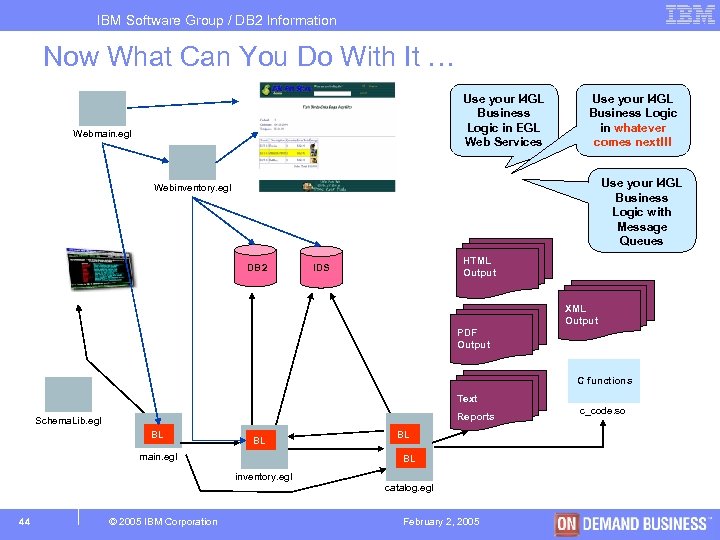
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management Now What Can You Do With It … Use your I 4 GL Business Logic in EGL Web Services Webmain. egl Use your I 4 GL Business Logic in whatever comes next!!! Use your I 4 GL Business Logic with Message Queues Webinventory. egl DB 2 HTML Output IDS XML Output PDF Output C functions Text Reports Schema. Lib. egl BL BL main. egl BL inventory. egl 44 © 2005 IBM Corporation BL catalog. egl February 2, 2005 c_code. so

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management EGL Releases… § 6. 0 ega 12/3/2004, GA 1/7 § fix 001 ega 12/20/2004 (first release for Informix) § ifix 003 ega 2/28/2005 (Release with conversion tool available through Rational updater). § 6. 0. 0. 1 ega 4/8/2005 (Conversion tool available through Rational updater) 45 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management EGL information § EGL site http: //www-128. ibm. com/developerworks/rational/products/egl/ § EGL downloads http: //www-106. ibm. com/developerworks/rational/library/egldoc. html 46 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management http: //www. ibm. com/software/data/informix 47 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005

IBM Software Group / DB 2 Information Management 48 © 2005 IBM Corporation February 2, 2005
574dfb620b8016adffacea0c48cd5137.ppt