3389eaa5035b6579bc57c01c20b0089c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

IBM Security Services Building a Security Operations Center Engin Özbay IBM Security, Turkey enginoz@tr. ibm. com © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Systems Security operations in a changing environment 2 © 2015 IBM Corporation © 2012 IBM Corporation
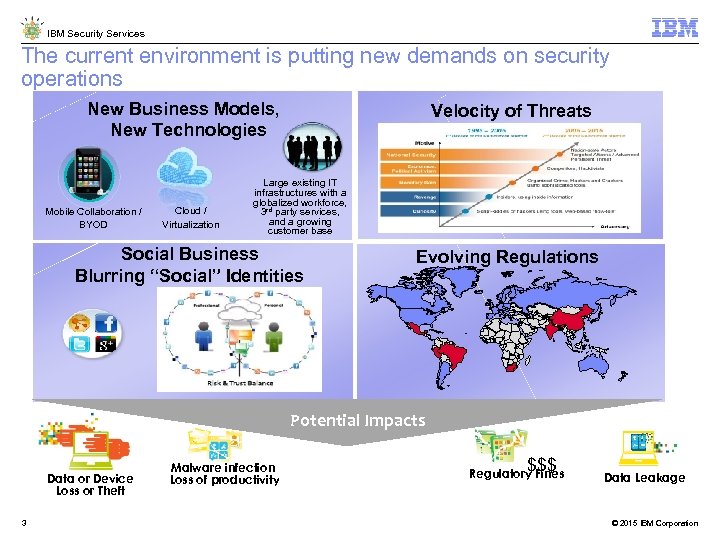
IBM Security Services The current environment is putting new demands on security operations New Business Models, New Technologies Mobile Collaboration / BYOD Cloud / Virtualization Velocity of Threats Large existing IT infrastructures with a globalized workforce, 3 rd party services, and a growing customer base Social Business Blurring “Social” Identities Evolving Regulations - • Potential Impacts Data or Device Loss or Theft 3 Malware infection Loss of productivity $$$ Regulatory Fines Data Leakage © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Why do we build operational security controls & capabilities? Reduce enterprise risk. Protect the business. Move from reactive response to proactive mitigation. Increase visibility over the environment. Meet compliance/regulatory requirements. © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services What is a Security Operations Center, or SOC? A Security Operations Center is a highly skilled team following defined definitions and processes to manage threats and reduce security risk Security Operations Centers (SOC) are designed to: – protect mission-critical data and assets – prepare for and respond to cyber emergencies – help provide continuity and efficient recovery – fortify the business infrastructure The SOC’s major responsibilities are: – Monitor, Analyze, Correlate & Escalate Intrusion Events – Develop Appropriate Responses; Protect, Detect, Respond – Conduct Incident Management and Forensic Investigation – Maintain Security Community Relationships – Assist in Crisis Operations 5 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Security operations centers must be responsive to the evolving threats and provide management the information and control that it needs The SOC …. Must demonstrate compliance with regulations Protect intellectual property and ensure privacy properly Manage security operations effectively and efficiently Provide real-time insight into the current security posture of your organization Provide security intelligence and the impact of threats on the organization Enable your organization to know who did what, when - and prove it (evidence) But it’s not that simple. . . 6 © 2015 IBM Corporation
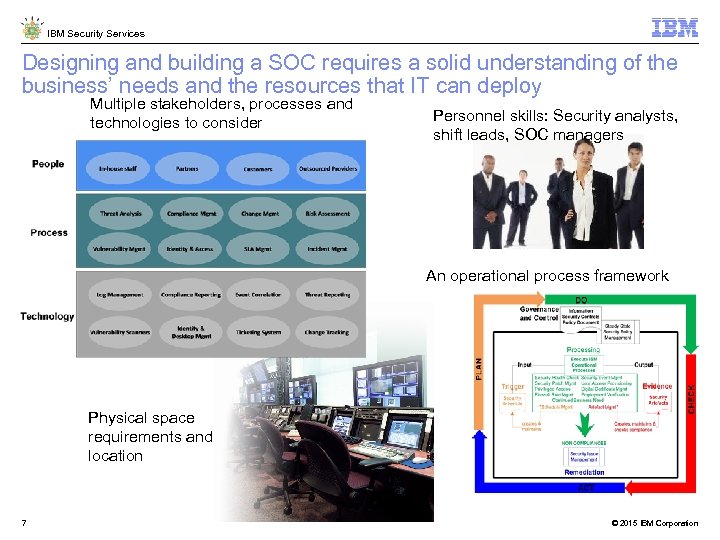
IBM Security Services Designing and building a SOC requires a solid understanding of the business’ needs and the resources that IT can deploy Multiple stakeholders, processes and technologies to consider Personnel skills: Security analysts, shift leads, SOC managers An operational process framework Physical space requirements and location 7 © 2015 IBM Corporation
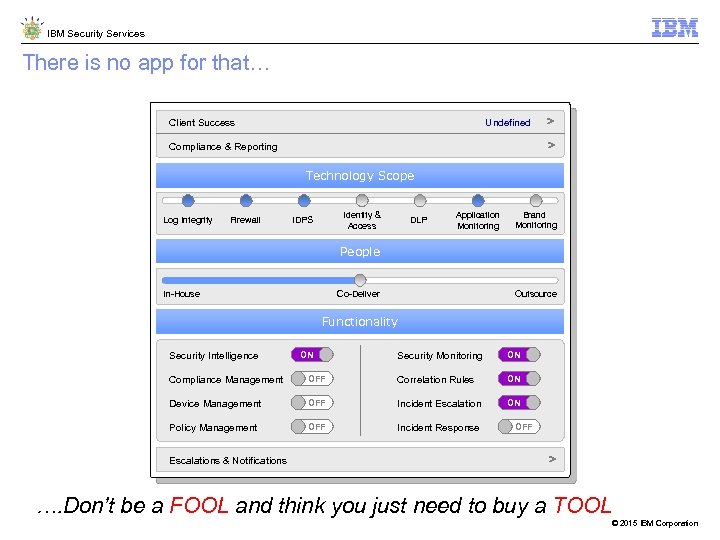
IBM Security Services There is no app for that… Client Success ndefined > U Compliance & Reporting > Technology Scope Log Integrity Firewall Identity & Access IDPS DLP Application Monitoring Brand Monitoring People In-House Co-Deliver Outsource Functionality Security Intelligence ON Security Monitoring ON Compliance Management OFF Correlation Rules ON Device Management OFF Incident Escalation ON Policy Management OFF Incident Response OFF Escalations & Notifications > …. Don’t be a FOOL and think you just need to buy a TOOL © 2015 IBM Corporation
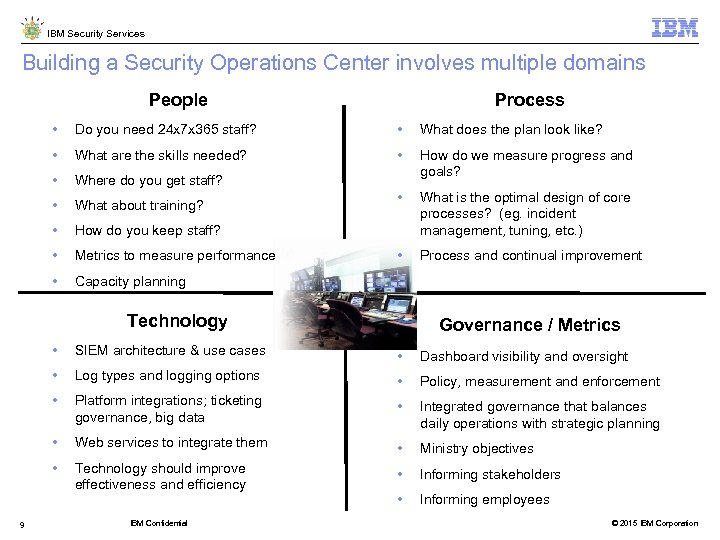
IBM Security Services Building a Security Operations Center involves multiple domains People Process • Do you need 24 x 7 x 365 staff? • What does the plan look like? • What are the skills needed? • • Where do you get staff? How do we measure progress and goals? • What about training? • • How do you keep staff? What is the optimal design of core processes? (eg. incident management, tuning, etc. ) • Metrics to measure performance • Process and continual improvement • Capacity planning Technology Governance / Metrics • • Dashboard visibility and oversight • Log types and logging options • Policy, measurement and enforcement • Platform integrations; ticketing governance, big data • Integrated governance that balances daily operations with strategic planning • Web services to integrate them • Ministry objectives • 9 SIEM architecture & use cases Technology should improve effectiveness and efficiency • Informing stakeholders • Informing employees IBM Confidential © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services SOC Models © 2012 IBM Corporation © 2015 IBM Corporation
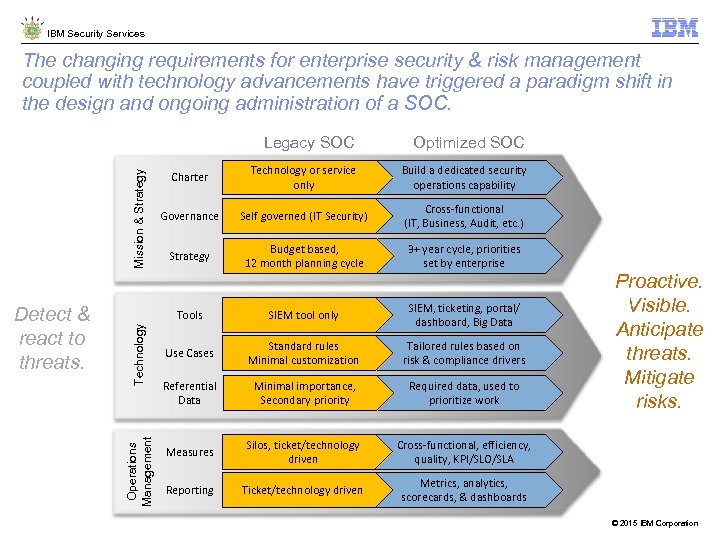
IBM Security Services The changing requirements for enterprise security & risk management coupled with technology advancements have triggered a paradigm shift in the design and ongoing administration of a SOC. Technology Operations Management Detect & react to threats. Optimized SOC Charter Technology or service only Build a dedicated security operations capability Governance Self governed (IT Security) Cross-functional (IT, Business, Audit, etc. ) Strategy Budget based, 12 month planning cycle 3+ year cycle, priorities set by enterprise Tools Mission & Strategy Legacy SOC SIEM tool only SIEM, ticketing, portal/ dashboard, Big Data Use Cases Standard rules Minimal customization Tailored rules based on risk & compliance drivers Referential Data Minimal importance, Secondary priority Required data, used to prioritize work Measures Silos, ticket/technology driven Cross-functional, efficiency, quality, KPI/SLO/SLA Reporting Ticket/technology driven Metrics, analytics, scorecards, & dashboards Proactive. Visible. Anticipate threats. Mitigate risks. © 2015 IBM Corporation
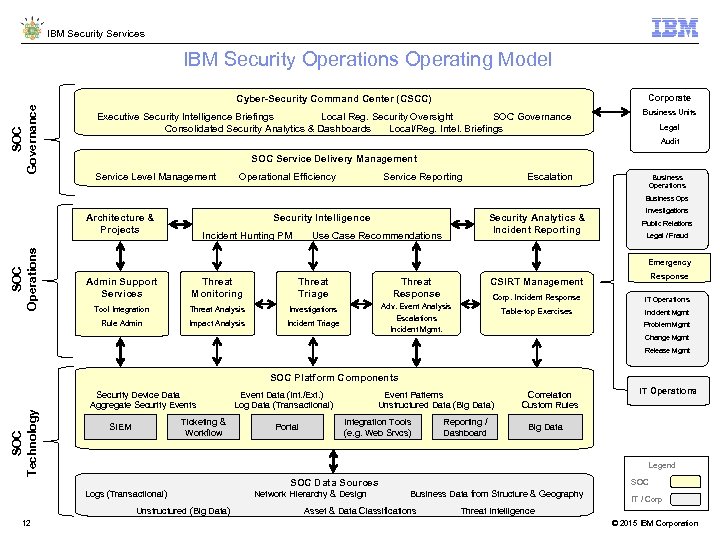
IBM Security Services IBM Security Operations Operating Model SOC Governance Cyber-Security Command Center (CSCC) Corporate Executive Security Intelligence Briefings Local Reg. Security Oversight SOC Governance Consolidated Security Analytics & Dashboards Local/Reg. Intel. Briefings Business Units Legal Audit SOC Service Delivery Management Service Level Management Operational Efficiency Service Reporting Escalation Business Operations Business Ops SOC Operations Architecture & Projects Security Intelligence Security Analytics & Incident Reporting Incident Hunting PM Use Case Recommendations Investigations Public Relations Legal / Fraud Emergency Admin Support Services Threat Monitoring Threat Triage Threat Response Tool Integration Threat Analysis Investigations Rule Admin Impact Analysis Incident Triage Adv. Event Analysis Escalations Incident Mgmt. Response CSIRT Management Corp. Incident Response Table-top Exercises IT Operations Incident Mgmt Problem Mgmt Change Mgmt Release Mgmt SOC Technology SOC Platform Components Security Device Data Aggregate Security Events Event Data (Int. /Ext. ) Log Data (Transactional) Ticketing & Workflow SIEM Portal Event Patterns Unstructured Data (Big Data) Integration Tools (e. g. Web Srvcs) Reporting / Dashboard Correlation Custom Rules Big Data Legend SOC Data Sources Logs (Transactional) Network Hierarchy & Design Business Data from Structure & Geography Unstructured (Big Data) 12 IT Operations SOC IT / Corp Asset & Data Classifications Threat Intelligence © 2015 IBM Corporation
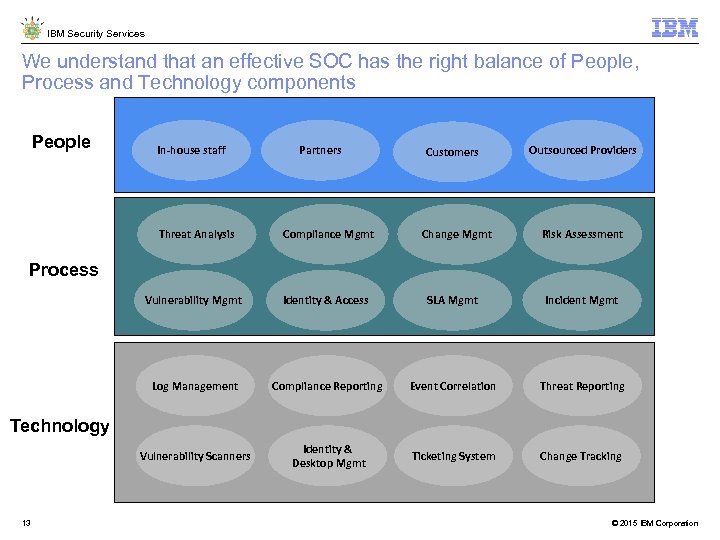
IBM Security Services We understand that an effective SOC has the right balance of People, Process and Technology components People In-house staff Partners Customers Change Mgmt Outsourced Providers Threat Analysis Compliance Mgmt Risk Assessment Vulnerability Mgmt Identity & Access SLA Mgmt Incident Mgmt Log Management Compliance Reporting Event Correlation Threat Reporting Vulnerability Scanners Identity & Desktop Mgmt Ticketing System Change Tracking Process Technology 13 © 2015 IBM Corporation
IBM Security Services It starts with the right people … People In-house staff Partners Customers Outsourced Providers The SOC is only as good as its people, and upfront planning for the unique people management aspects of a 24 x 7 security centric organization will provide significant long term returns. Points of Consideration: SOC staff have a specialized skill set and experienced staff are often difficult to find Training is expensive, time consuming, and improves marketability of staff. Compensation strategies must be evaluated accordingly. Retention of staff is difficult in a non-security centric organization due to continuous need for updated training, lack of expansive career path options, and burn-out. Beyond analysts for 24 x 7 coverage, other supporting functions must be considered: - System admins, Intelligence resources, Escalation resources, Compliance officers, Management / Supervision 14 © 2015 IBM Corporation
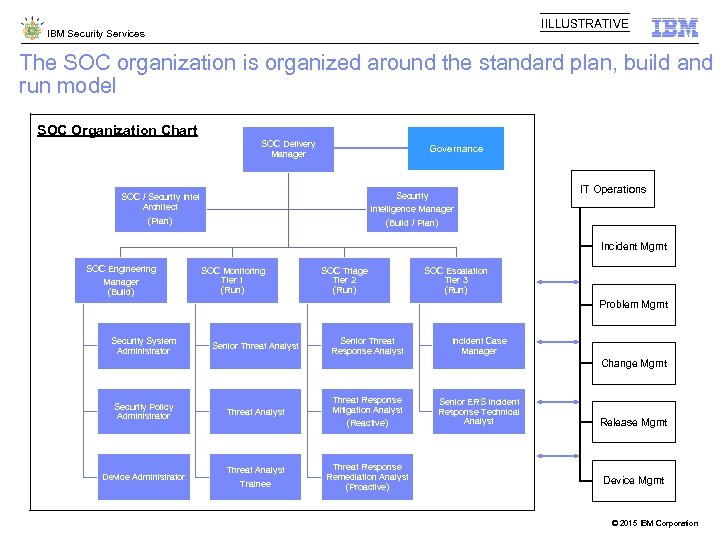
IILLUSTRATIVE IBM Security Services The SOC organization is organized around the standard plan, build and run model SOC Organization Chart SOC Delivery Manager Governance Security SOC / Security Intel Architect IT Op er ati on IT Operations s Intelligence Manager (Build / Plan) (Plan) Incident Mgmt SOC Engineering Manager (Build) SOC Monitoring Tier 1 (Run) SOC Triage Tier 2 (Run) SOC Escalation Tier 3 (Run) Problem Mgmt Security System Administrator Senior Threat Analyst Senior Threat Response Analyst Incident Case Manager Change Mgmt Security Policy Administrator Device Administrator Threat Analyst Trainee Threat Response Mitigation Analyst (Reactive) Threat Response Remediation Analyst (Proactive) Senior ERS Incident Response Technical Analyst Release Mgmt Device Mgmt © 2015 IBM Corporation
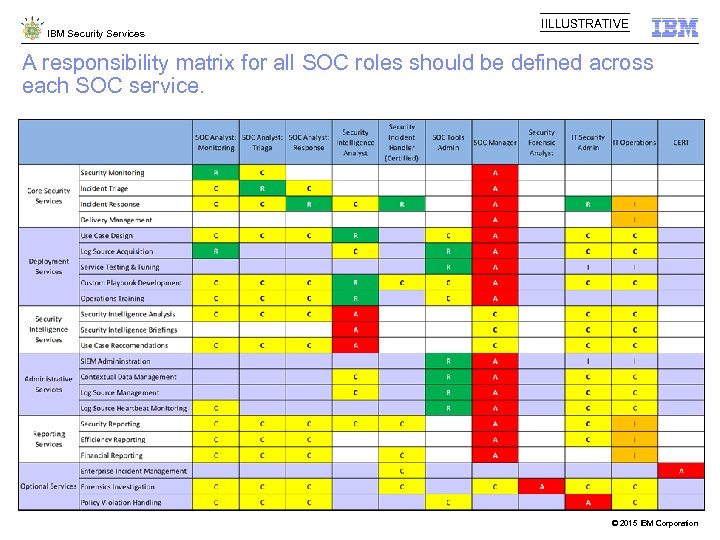
IBM Security Services IILLUSTRATIVE A responsibility matrix for all SOC roles should be defined across each SOC service. © 2015 IBM Corporation
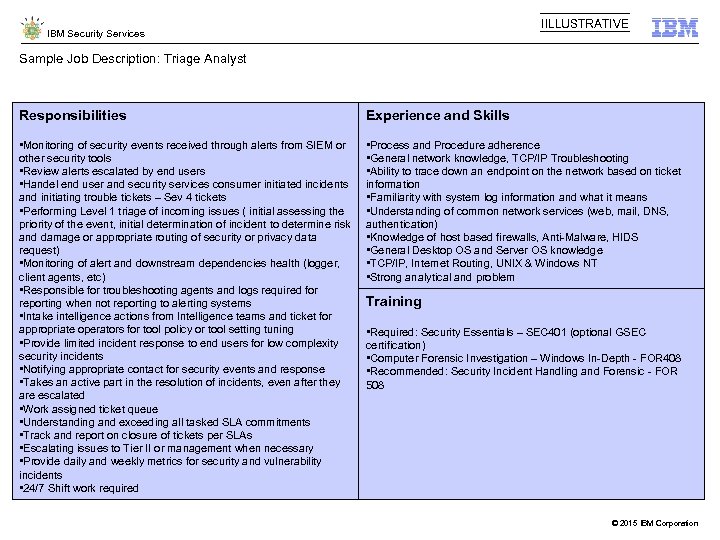
IILLUSTRATIVE IBM Security Services Sample Job Description: Triage Analyst Responsibilities Experience and Skills • Monitoring of security events received through alerts from SIEM or other security tools • Review alerts escalated by end users • Handel end user and security services consumer initiated incidents and initiating trouble tickets – Sev 4 tickets • Performing Level 1 triage of incoming issues ( initial assessing the priority of the event, initial determination of incident to determine risk and damage or appropriate routing of security or privacy data request) • Monitoring of alert and downstream dependencies health (logger, client agents, etc) • Responsible for troubleshooting agents and logs required for reporting when not reporting to alerting systems • Intake intelligence actions from Intelligence teams and ticket for appropriate operators for tool policy or tool setting tuning • Provide limited incident response to end users for low complexity security incidents • Notifying appropriate contact for security events and response • Takes an active part in the resolution of incidents, even after they are escalated • Work assigned ticket queue • Understanding and exceeding all tasked SLA commitments • Track and report on closure of tickets per SLAs • Escalating issues to Tier II or management when necessary • Provide daily and weekly metrics for security and vulnerability incidents • 24/7 Shift work required • Process and Procedure adherence • General network knowledge, TCP/IP Troubleshooting • Ability to trace down an endpoint on the network based on ticket information • Familiarity with system log information and what it means • Understanding of common network services (web, mail, DNS, authentication) • Knowledge of host based firewalls, Anti-Malware, HIDS • General Desktop OS and Server OS knowledge • TCP/IP, Internet Routing, UNIX & Windows NT • Strong analytical and problem Training • Required: Security Essentials – SEC 401 (optional GSEC certification) • Computer Forensic Investigation – Windows In-Depth - FOR 408 • Recommended: Security Incident Handling and Forensic - FOR 508 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Leveraging tested integrated processes …. Threat Analysis Compliance Mgmt Vulnerability Mgmt Identity & Access Change Mgmt Risk Assessment Process SLA Mgmt Incident Mgmt SOC processes must be documented, consistently implemented, and based upon existing standards / governance frameworks. Procedures must take into consideration corporate security policy, business controls, and relevant regulatory requirements. Points of Consideration: The SOC’s mission must be clearly defined – Incident discovery, CERT, etc. SOCs differ from NOCs, and an alarm does not always equate to action. Processes must take into consideration evaluation and incorporation of a constantly changing stream of potentially actionable threat intelligence. Best practices for incident investigation, response, and mitigation must be maintained and updated as technologies are added, change, or mature. 18 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Built on a solid technology platform Log Management Compliance Reporting Event Correlation Threat Reporting Vulnerability Scanners Identity & Desktop Mgmt Ticketing System Change Tracking Technology for a SOC build is the foundation on which the organization demonstrates the ability to provide security continuously, even under times of duress such as persistent attack, natural disaster, facilities failure, etc. Points of Consideration: SOC technologies (SIEM, trouble ticketing, incident management, etc. ) are often special purpose, costly, and challenging to maintain due to their overall complexity The number of disparate systems and volume of device / event data will typically require a dedicated IT staff for system administration Capacity management can be challenge due to the need to support peak loads which may include DDo. S, monthly batch processing, etc The management and reporting systems must be flexible enough to accommodate process and security policy as well as changes in the technology landscape 19 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services SOC Strategies & Approaches © 2015 IBM Corporation
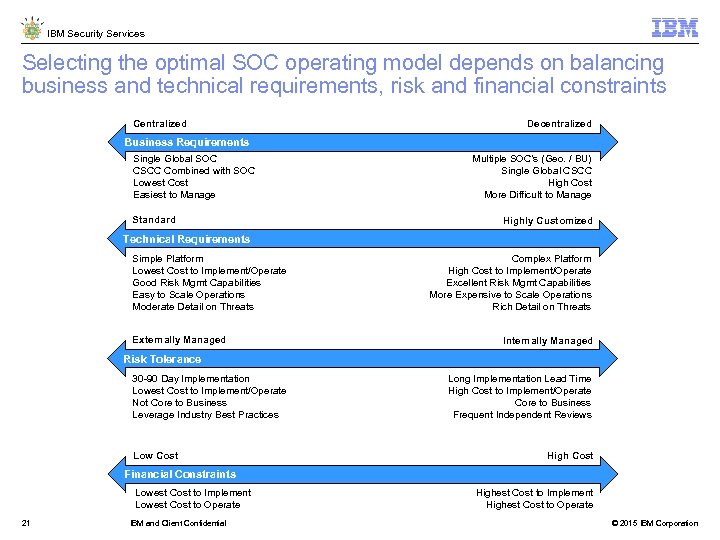
IBM Security Services Selecting the optimal SOC operating model depends on balancing business and technical requirements, risk and financial constraints Centralized Decentralized Business Requirements Single Global SOC CSCC Combined with SOC Lowest Cost Easiest to Manage Standard Multiple SOC’s (Geo. / BU) Single Global CSCC High Cost More Difficult to Manage Highly Customized Technical Requirements Simple Platform Lowest Cost to Implement/Operate Good Risk Mgmt Capabilities Easy to Scale Operations Moderate Detail on Threats Externally Managed Complex Platform High Cost to Implement/Operate Excellent Risk Mgmt Capabilities More Expensive to Scale Operations Rich Detail on Threats Internally Managed Risk Tolerance 30 -90 Day Implementation Lowest Cost to Implement/Operate Not Core to Business Leverage Industry Best Practices Low Cost Long Implementation Lead Time High Cost to Implement/Operate Core to Business Frequent Independent Reviews High Cost Financial Constraints Lowest Cost to Implement Lowest Cost to Operate 21 IBM and Client Confidential Highest Cost to Implement Highest Cost to Operate © 2015 IBM Corporation
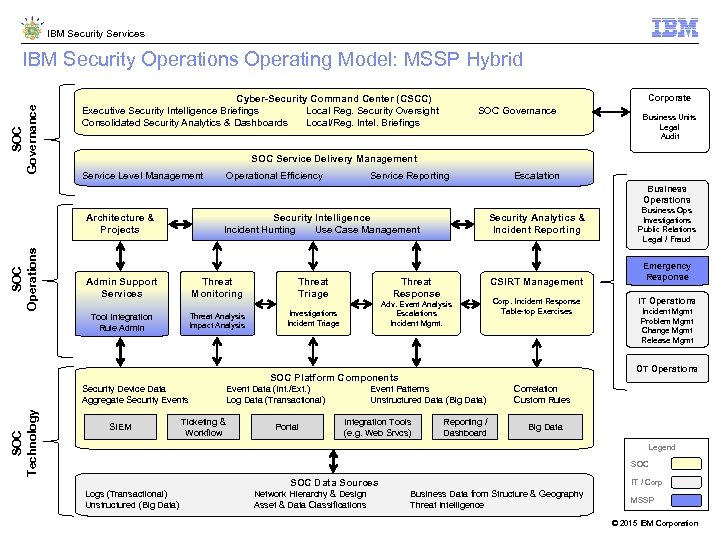
IBM Security Services SOC Governance IBM Security Operations Operating Model: MSSP Hybrid Cyber-Security Command Center (CSCC) Executive Security Intelligence Briefings Local Reg. Security Oversight SOC Governance Consolidated Security Analytics & Dashboards Local/Reg. Intel. Briefings Corporate Business Units Legal Audit SOC Service Delivery Management Service Level Management Operational Efficiency Service Reporting Escalation Business Operations SOC Operations Architecture & Projects Security Intelligence Incident Hunting Use Case Management Security Analytics & Incident Reporting Admin Support Services Threat Monitoring Threat Triage Threat Response CSIRT Management Tool Integration Rule Admin Threat Analysis Impact Analysis Investigations Incident Triage Adv. Event Analysis Escalations Incident Mgmt. Corp. Incident Response Table-top Exercises SOC Technology SIEM Event Data (Int. /Ext. ) Log Data (Transactional) Ticketing & Workflow Portal Event Patterns Unstructured Data (Big Data) Integration Tools (e. g. Web Srvcs) Emergency Response IT Operations Incident Mgmt Problem Mgmt Change Mgmt Release Mgmt OT Operations SOC Platform Components Security Device Data Aggregate Security Events Business Ops Investigations Public Relations Legal / Fraud Reporting / Dashboard Correlation Custom Rules Big Data Legend SOC Data Sources Logs (Transactional) Unstructured (Big Data) Network Hierarchy & Design Business Data from Structure & Geography Asset & Data Classifications Threat Intelligence IT / Corp MSSP © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Getting Started Develop a Strategy then a Plan © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services To get started, the organization should consider the following questions in establishing its objectives What is the primary purpose of the SOC? What are the specific tasks assigned to the SOC? (e. g. , threat intelligence, security device management, compliance management, detecting insider abuse on the financial systems, incident response and forensic analysis, vulnerability assessments, etc. ) Who are the consumers of the information collected analyzed by the SOC? What requirements do they have for the SOC? Who is the ultimate stakeholder for the SOC? Who will “sell” the SOC to the rest of the organization? What types of security events will eventually be fed into the SOC for monitoring? Will the organization seek an external partner to help manage the SOC? 24 © 2015 IBM Corporation
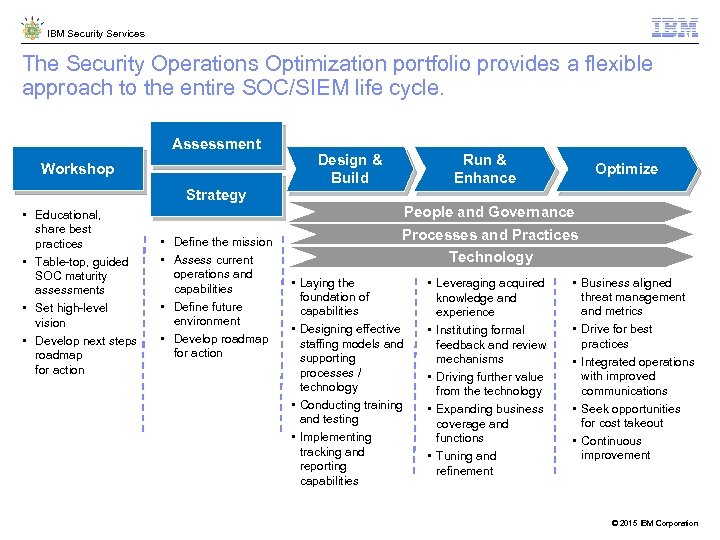
IBM Security Services The Security Operations Optimization portfolio provides a flexible approach to the entire SOC/SIEM life cycle. Assessment Workshop Strategy • Educational, share best practices • Table-top, guided SOC maturity assessments • Set high-level vision • Develop next steps roadmap for action • Define the mission • Assess current operations and capabilities • Define future environment • Develop roadmap for action Design & Build Run & Enhance Optimize People and Governance Processes and Practices Technology • Laying the foundation of capabilities • Designing effective staffing models and supporting processes / technology • Conducting training and testing • Implementing tracking and reporting capabilities • Leveraging acquired knowledge and experience • Instituting formal feedback and review mechanisms • Driving further value from the technology • Expanding business coverage and functions • Tuning and refinement • Business aligned threat management and metrics • Drive for best practices • Integrated operations with improved communications • Seek opportunities for cost takeout • Continuous improvement © 2015 IBM Corporation
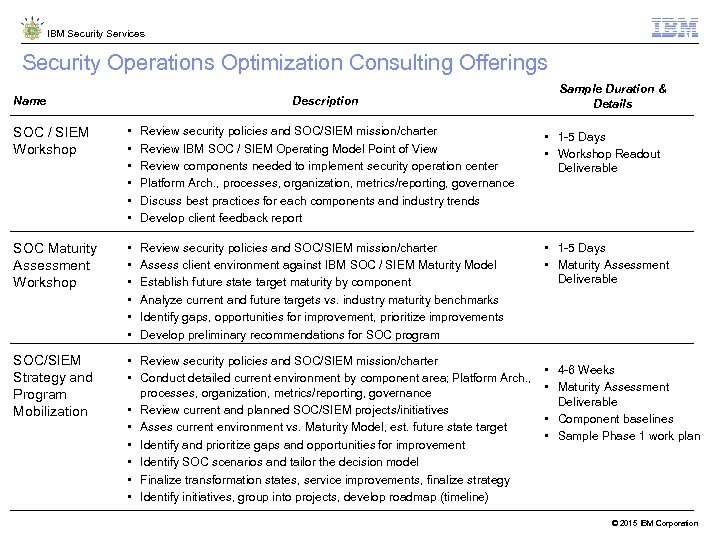
IBM Security Services Security Operations Optimization Consulting Offerings Name Description Sample Duration & Details SOC / SIEM Workshop • • • Review security policies and SOC/SIEM mission/charter Review IBM SOC / SIEM Operating Model Point of View Review components needed to implement security operation center Platform Arch. , processes, organization, metrics/reporting, governance Discuss best practices for each components and industry trends Develop client feedback report • 1 -5 Days • Workshop Readout Deliverable SOC Maturity Assessment Workshop • • • Review security policies and SOC/SIEM mission/charter Assess client environment against IBM SOC / SIEM Maturity Model Establish future state target maturity by component Analyze current and future targets vs. industry maturity benchmarks Identify gaps, opportunities for improvement, prioritize improvements Develop preliminary recommendations for SOC program • 1 -5 Days • Maturity Assessment Deliverable SOC/SIEM Strategy and Program Mobilization • Review security policies and SOC/SIEM mission/charter • Conduct detailed current environment by component area; Platform Arch. , processes, organization, metrics/reporting, governance • Review current and planned SOC/SIEM projects/initiatives • Asses current environment vs. Maturity Model, est. future state target • Identify and prioritize gaps and opportunities for improvement • Identify SOC scenarios and tailor the decision model • Finalize transformation states, service improvements, finalize strategy • Identify initiatives, group into projects, develop roadmap (timeline) • 4 -6 Weeks • Maturity Assessment Deliverable • Component baselines • Sample Phase 1 work plan © 2015 IBM Corporation
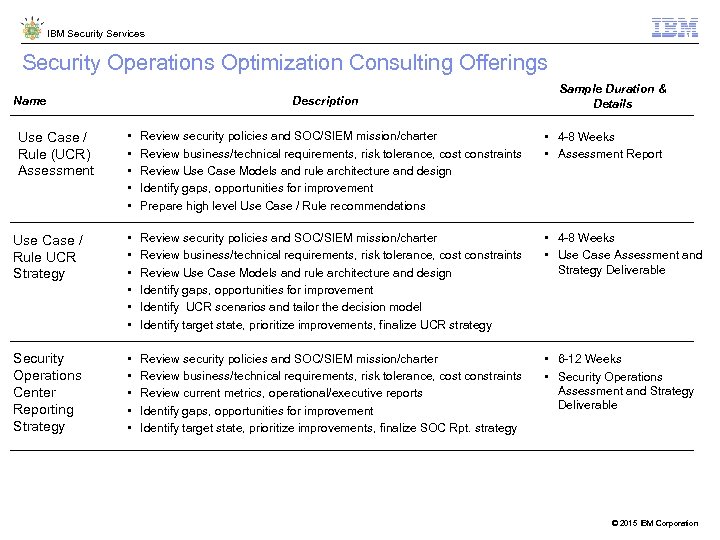
IBM Security Services Security Operations Optimization Consulting Offerings Name Description Sample Duration & Details • • • Review security policies and SOC/SIEM mission/charter Review business/technical requirements, risk tolerance, cost constraints Review Use Case Models and rule architecture and design Identify gaps, opportunities for improvement Prepare high level Use Case / Rule recommendations • 4 -8 Weeks • Assessment Report Use Case / Rule UCR Strategy • • • Review security policies and SOC/SIEM mission/charter Review business/technical requirements, risk tolerance, cost constraints Review Use Case Models and rule architecture and design Identify gaps, opportunities for improvement Identify UCR scenarios and tailor the decision model Identify target state, prioritize improvements, finalize UCR strategy • 4 -8 Weeks • Use Case Assessment and Strategy Deliverable Security Operations Center Reporting Strategy • • • Review security policies and SOC/SIEM mission/charter Review business/technical requirements, risk tolerance, cost constraints Review current metrics, operational/executive reports Identify gaps, opportunities for improvement Identify target state, prioritize improvements, finalize SOC Rpt. strategy • 6 -12 Weeks • Security Operations Assessment and Strategy Deliverable Use Case / Rule (UCR) Assessment © 2015 IBM Corporation
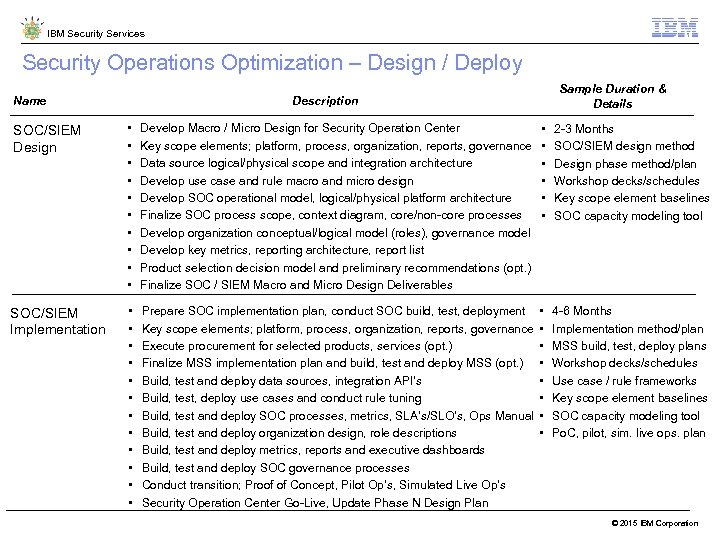
IBM Security Services Security Operations Optimization – Design / Deploy Name Sample Duration & Details Description SOC/SIEM Design • • • Develop Macro / Micro Design for Security Operation Center Key scope elements; platform, process, organization, reports, governance Data source logical/physical scope and integration architecture Develop use case and rule macro and micro design Develop SOC operational model, logical/physical platform architecture Finalize SOC process scope, context diagram, core/non-core processes Develop organization conceptual/logical model (roles), governance model Develop key metrics, reporting architecture, report list Product selection decision model and preliminary recommendations (opt. ) Finalize SOC / SIEM Macro and Micro Design Deliverables • • • 2 -3 Months SOC/SIEM design method Design phase method/plan Workshop decks/schedules Key scope element baselines SOC capacity modeling tool SOC/SIEM Implementation • • • Prepare SOC implementation plan, conduct SOC build, test, deployment Key scope elements; platform, process, organization, reports, governance Execute procurement for selected products, services (opt. ) Finalize MSS implementation plan and build, test and deploy MSS (opt. ) Build, test and deploy data sources, integration API’s Build, test, deploy use cases and conduct rule tuning Build, test and deploy SOC processes, metrics, SLA’s/SLO’s, Ops Manual Build, test and deploy organization design, role descriptions Build, test and deploy metrics, reports and executive dashboards Build, test and deploy SOC governance processes Conduct transition; Proof of Concept, Pilot Op’s, Simulated Live Op’s Security Operation Center Go-Live, Update Phase N Design Plan • • 4 -6 Months Implementation method/plan MSS build, test, deploy plans Workshop decks/schedules Use case / rule frameworks Key scope element baselines SOC capacity modeling tool Po. C, pilot, sim. live ops. plan © 2015 IBM Corporation
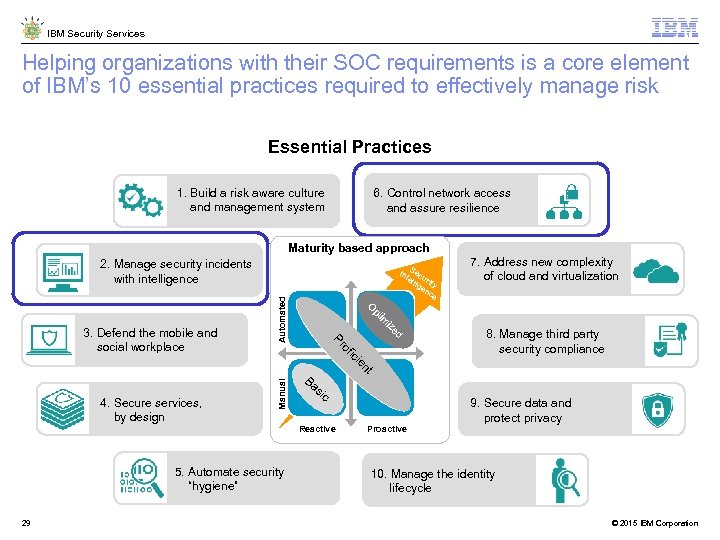
IBM Security Services Helping organizations with their SOC requirements is a core element of IBM’s 10 essential practices required to effectively manage risk Essential Practices 1. Build a risk aware culture and management system 6. Control network access and assure resilience Maturity based approach 2. Manage security incidents with intelligence Automated 7. Address new complexity of cloud and virtualization ed iz im pt O 8. Manage third party security compliance s Ba ic 4. Secure services, by design Manual nt ie ic of Pr 3. Defend the mobile and social workplace S in ecu te llig rity en ce Reactive 5. Automate security “hygiene” 29 Proactive 9. Secure data and protect privacy 10. Manage the identity lifecycle © 2015 IBM Corporation
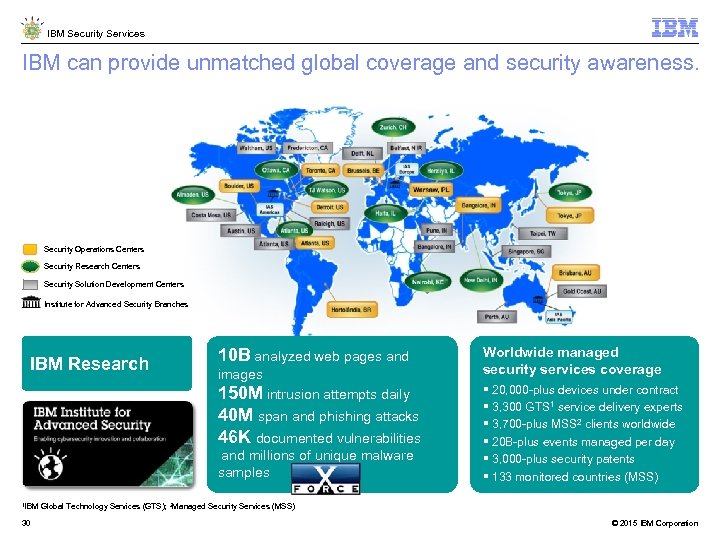
IBM Security Services IBM can provide unmatched global coverage and security awareness. Security Operations Centers Security Research Centers Security Solution Development Centers Institute for Advanced Security Branches IBM Research 10 B analyzed web pages and images 150 M intrusion attempts daily 40 M span and phishing attacks 46 K documented vulnerabilities and millions of unique malware samples Worldwide managed security services coverage 20, 000 -plus devices under contract 3, 300 GTS 1 service delivery experts 3, 700 -plus MSS 2 clients worldwide 20 B-plus events managed per day 3, 000 -plus security patents 133 monitored countries (MSS) 1 IBM Global Technology Services (GTS); 2 Managed Security Services (MSS) 30 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Largest Bank in Canada improves security by establishing SOC & implementing monitoring tools and processes Client Situation : The client had engaged IBM to help them map out their security needs, include SOC strategy, architecture, analyzing and querying log, threat, vulnerability data (SIEM) and ongoing management. A few high-level issues were: Lack of any SOC model and strategy roadmap There were no trained SOC Operations team or staff No Security monitoring tool or processes for security incidents Profile: Largest Bank in Canada, 3 rd largest in North America, top 10 globally. The bank serves 18 million clients and has 80, 100 employees worldwide. IBM Solution : IBM Security Services Team reviewed the client’s business and technical requirements, risk tolerance and cost constraints. After analyzing the requirements IBM developed a 3 year SOC Strategy and Roadmap with ongoing Phase implementations. Additionally the following high-level tasks were performed Global Installation of the QRadar monitoring tool Archer Ticketing System implementation (security tickets) Designed the SOC Organization, Process, People Model SOC Capacity Modeling Hired and Trained the client’s SOC Staff (~12 resources) Implemented SOC Operational Reporting and Executive Dashboards Client Benefits: Reduced risks & costs associated with security incidents and data breaches Addressed compliance issues by establishing clear audit trails for incident response Improved security posture with enterprise-wide security intelligence correlating events from IT & business critical systems/applications. IBM Confidential

IBM Security Services A global insurance company in United States improves security by establishing SOC & implementing monitoring tools and processes Client Situation : The client had made a board-level commitment to raise the visibility, effectiveness and efficiency of the global security program. A few high-level issues: Multiple day delays in identifying threats Extreme incident false positive ratios with current MSSP Labor intensive program, without clear lines of responsibility Minimal security analytics & dashboards IBM Solution : IBM Security Services Team began with a full day SOC optimization workshop to educate the client program team, review and validate the client’s vision and strategy. After the workshop and recommendations, the client requested IBM’s support to help them plan, design and build the SOC including the following: SOC Architecture development SIEM operationalization (Arc. Sight) Remedy Ticketing System implementation (security tickets) Designed the SOC organization including capacity models Developed best-practice core SOC process and created supporting documentation & artifacts & trained client staff Implemented Security Operational Reporting and Executive Dashboards Managed transition from previous MSSP to IBM Managed Services Client Benefits: Reduced incidentification time from hours to minutes and streamlined operations further reducing risks & associated costs & improved global security with end to end incident management Created an industry leading view into the overall security position allowing them to better manage their entire environment Profile: Global property and casualty insurer. Third largest insurer in the United States. Fortune 100 company. Operates in 900 location s distributed across 18 countries. The company has 50, 000+ employees worldwide. IBM Confidential

IBM Security Services A global financial services company in UK improves security by transforming SOC from compliance to cyber threat monitoring Client Situation : The client had invested into a SOC that was focused on policy violation and wanted to expand the capabilities of their existing investment: Compliance focused SOC Significant challenges with existing technology SOC manpower outsourced to 3 rd Party Minimal security analytics & dashboards, non-existent Security Intelligence IBM Solution : IBM Security Services Team began with a 2 week SOC maturity assessment to gauge the client’s current and future capabilities and to review and validate the client’s vision and strategy. After the assessment, recommendations were presented to the client and IBM lead the transformation programme including: Developed best-practice core SOC process and created supporting documentation & artifacts & trained client staff Establish a Security intelligence function Accelerate development and implementation of a Ticketing System Reviewed the SOC organisation and identified improvements Demonstrated the importance of capacity modelling Implemented Security Operational Reporting and Executive Dashboards Client Benefits: Increased efficiency from the existing SOC staff handling more events in a defined and repeatable way. Increased awareness of their own systems and future threats making use of Security Intelligence Better able to understand highlight the benefits of the SOC due to improved metrics and reporting 33 Profile: UK based financial services group. Retail, commercial, wealth and asset management, international and insurance arms. Operates in almost every community in the UK. Over 100, 000 employees (2014) IBM Confidential

IBM Security Services Tack Hindi ευχαριστώ Greek Swedish Спасибо Teşekkürler Gracias Thai Russian Spanish Thank You Arabic Portuguese Dankie Grazie Obrigado Merci German Afrikaans Italian French Hvala Slovenian Simplified Chinese Korean Köszönöm Hungarian Japanese © 2015 IBM Corporation
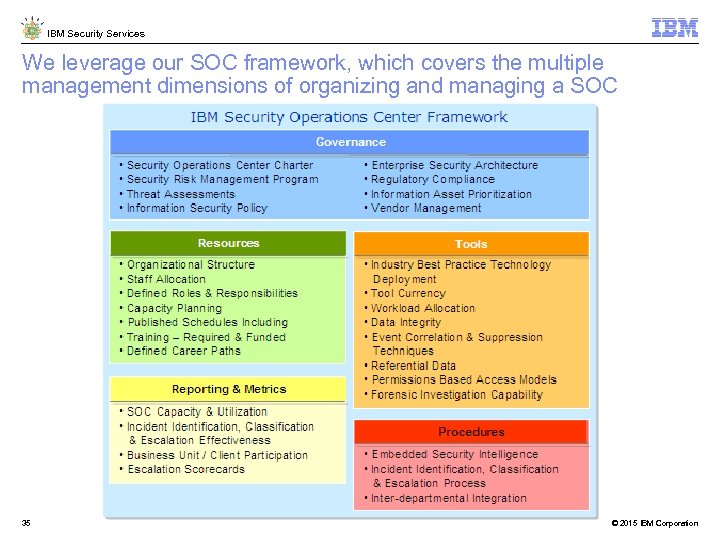
IBM Security Services We leverage our SOC framework, which covers the multiple management dimensions of organizing and managing a SOC 35 © 2015 IBM Corporation
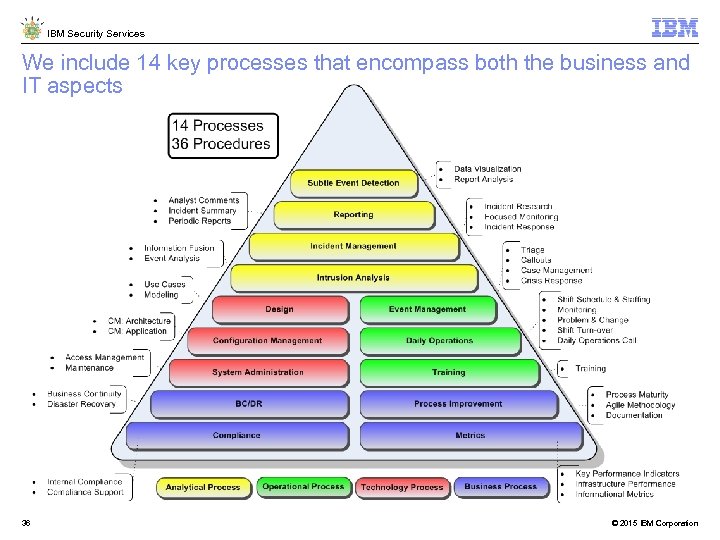
IBM Security Services We include 14 key processes that encompass both the business and IT aspects 36 © 2015 IBM Corporation
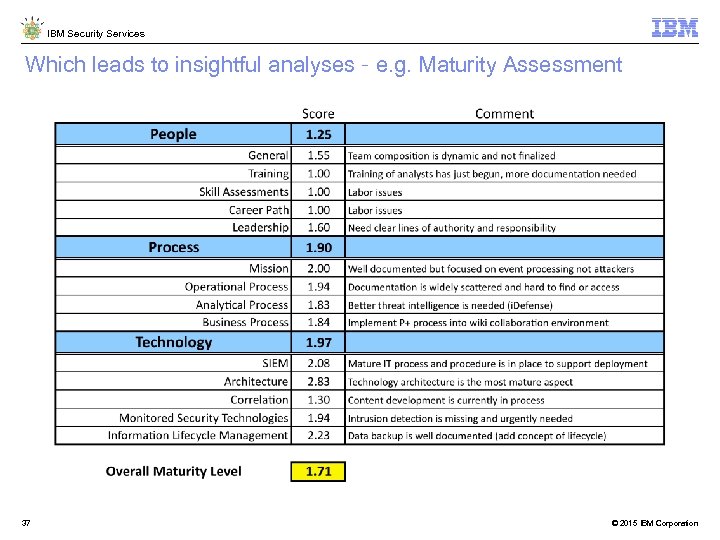
IBM Security Services Which leads to insightful analyses – e. g. Maturity Assessment 37 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services IBM offers multiple options in our consulting offerings Security Operations Center (SOC) Workshop – 1 day management workshop to establish goals and objectives for developing the SOC, identifying stakeholders, types of threats monitored, and the management model Security Operations Center (SOC) Assessment – Consulting assessment for clients that have en existing SOC but are looking for IBM to review their capabilities and process maturity and make recommendations for improvements Security Operations Center (SOC) Strategy Engagement – Consulting strategy engagement for clients who are seeking to develop a comprehensive strategy and plan to implement a SOC that addresses both IT and the business for managing security and mitigating threats Security Operations Center (SOC) Design / Build Project – – 38 Professional services to help clients design and build one or multiple SOC’s that meets the organization’s needs for improved security intelligence and risk management Components include. • Organization/People (Develop and implement staffing models, shift schedules, skills training etc. ) • Processes, Procedures, Guidelines (Define, develop and document, update existing) • Technology (Plan, design, deploy technology components, integrate feeds and other referential sources) © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services What you can expect as a result from a SOC implementation Better understanding of how your security program reduces risk in operations and therefore business risk Measurement of the real-time compliance of particular security controls in the organization Insight into the current state of your security posture Visibility of issues, hacks, infections and misuse that otherwise would require human discovery and correlation. Easier measurements of compliance and audit effort reduction 39 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Systems IBM knows security 40 © 2015 IBM Corporation © 2012 IBM Corporation
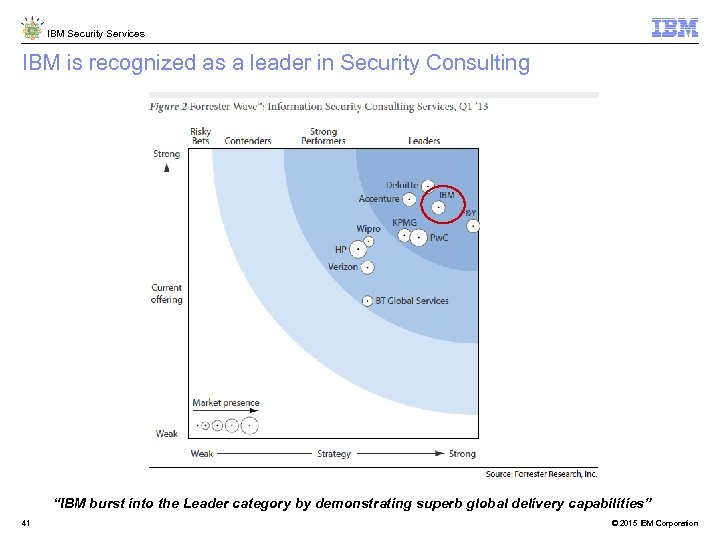
IBM Security Services IBM is recognized as a leader in Security Consulting “IBM burst into the Leader category by demonstrating superb global delivery capabilities” 41 © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Why IBM SIEM Security Technology? Breadth, deep expertise, integration Leadership Leader in “Magic Quadrant for Security Information and Event Management”, Gartner, May 12, 2011, May 13, 2010, May 29, 2009. #1 rated by Gartner for Compliance use cases ("Critical Capabilities for Security Information and Event Management Technology, " Gartner, 12 May 2011) Integration Integrated with 400+ products and vendor platforms SIEM, log management, network anomaly detection, and risk management combined in a single console People Endpoint Expertise Embedded 3 rd party security feeds including IBM X-Force Tight integration with Info. Sphere Guardium and IBM Identity Manager & Access Manager for optimized data & user security 42 Security Intelligence Data Network Applications © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Client example - a large financial services company Business Challenge: A large European financial institution with multiple global locations was searching for best practices and assistance in creating an in-house, compliant and effective Security Operations Center. Compounding the challenge of the sheer magnitude of their operations was the complications surrounding several recent acquisitions that have not been fully integrated. The current operation was largely driven by SOX compliance requirements and resulted in diluting the effectiveness of the SOC with “unimportant” log sources. Solution: A series of business and technical workshops were conducted to start the assessment as the client needed to refocus their operations on security, while retaining maintain regulatory compliance. These workshops then advanced to a full security operations design, integrating disparate business unit requirements, focusing analysis on important log sources, and reorganizing the department. Ultimately, the client chose to have IBM staff their new SOC, reducing the total number of hired staff and overall cost. Benefits: Overall SOC costs were reduced and the resulting organization is more focused and effective. 43 Solution components: IBM Q-Radar SIEM IBM Security Services SOC Workshop & Design IBM Security Services Professional Security Services © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Services Client example –global pharmaceutical company Business Challenge: A large global pharmaceutical company with research locations scattered around the world faces the ongoing threats of industrial espionage and is frequently a target of hactivitists. Their current security operations is decentralized allowing each unit to “fend for themselves”. After some minor faults but no major incidents, the company has decided to centralize their security operations and create a holistic view of security across the entire organization. Solution: A business and technical workshop was conducted to start the assessment and help the client envision the end-state should look like and how to initiate the centralization process. Leveraging a deployed IBM Q-Radar installation, the solution involves creating a two redundant SOC’s to centralize security intelligence and device management operations. These SOC’s will work cooperatively using the best-practice operational models derived from IBM MSS Global SOC’s providing a single, measurable view of security across their global operations. Benefits: A centralized operational model allows the economies of scale to drive costs down, while improving the effectiveness of the security operations and threat intelligence sharing. 44 Solution components: IBM Security Services SOC Workshop IBM Q-Radar IBM Security Services Managed SIEM © 2015 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Systems Thank you for your time! Questions and Answers 45 © 2015 IBM Corporation © 2012 IBM Corporation
IBM Security Services Backup Pages 46 © 2015 IBM Corporation
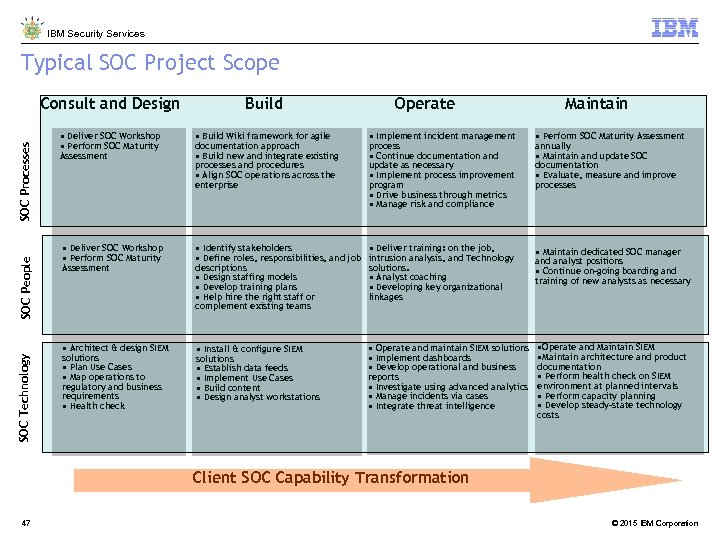
IBM Security Services Typical SOC Project Scope SOC People SOC Technology Build • Deliver SOC Workshop • Perform SOC Maturity • Build Wiki framework for agile • Deliver SOC Workshop • Perform SOC Maturity • Identify stakeholders • Deliver training: on the job, • Define roles, responsibilities, and job intrusion analysis, and Technology descriptions • Design staffing models • Develop training plans • Help hire the right staff or complement existing teams solutions. • Analyst coaching • Developing key organizational linkages • Architect & design SIEM SOC Processes Consult and Design • Install & configure SIEM • Operate and maintain SIEM solutions • Operate and Maintain SIEM • Maintain architecture and product • Implement dashboards documentation • Develop operational and business • Perform health check on SIEM reports • Investigate using advanced analytics environment at planned intervals • Perform capacity planning • Manage incidents via cases • Develop steady-state technology • Integrate threat intelligence Assessment solutions • Plan Use Cases • Map operations to regulatory and business requirements • Health check documentation approach • Build new and integrate existing processes and procedures • Align SOC operations across the enterprise solutions • Establish data feeds • Implement Use Cases • Build content • Design analyst workstations Operate • Implement incident management process • Continue documentation and update as necessary • Implement process improvement program • Drive business through metrics • Manage risk and compliance Maintain • Perform SOC Maturity Assessment annually • Maintain and update SOC documentation • Evaluate, measure and improve processes • Maintain dedicated SOC manager and analyst positions • Continue on-going boarding and training of new analysts as necessary costs Client SOC Capability Transformation 47 © 2015 IBM Corporation
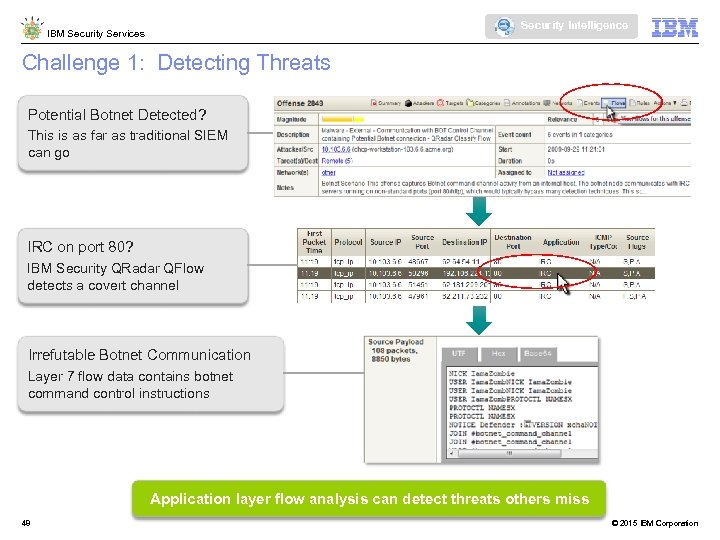
Security Intelligence IBM Security Services Challenge 1: Detecting Threats Potential Botnet Detected? This is as far as traditional SIEM can go IRC on port 80? IBM Security QRadar QFlow detects a covert channel Irrefutable Botnet Communication Layer 7 flow data contains botnet command control instructions Application layer flow analysis can detect threats others miss 48 © 2015 IBM Corporation
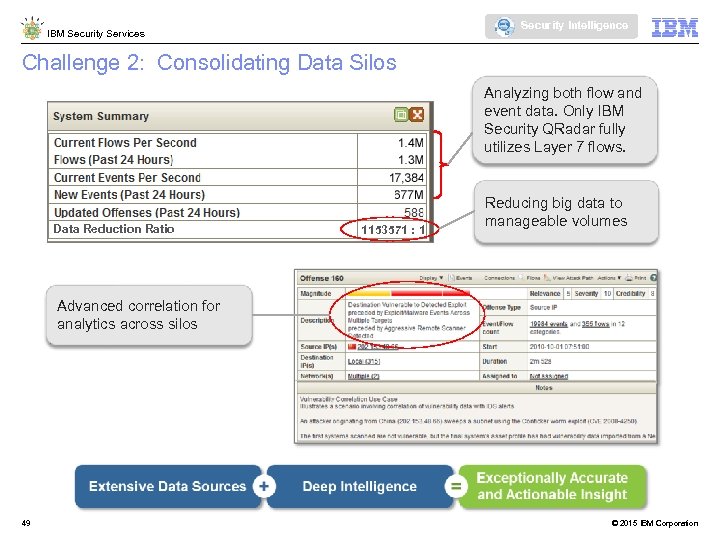
Security Intelligence IBM Security Services Challenge 2: Consolidating Data Silos Analyzing both flow and event data. Only IBM Security QRadar fully utilizes Layer 7 flows. Data Reduction Ratio 1153571 : 1 Reducing big data to manageable volumes Advanced correlation for analytics across silos 49 © 2015 IBM Corporation
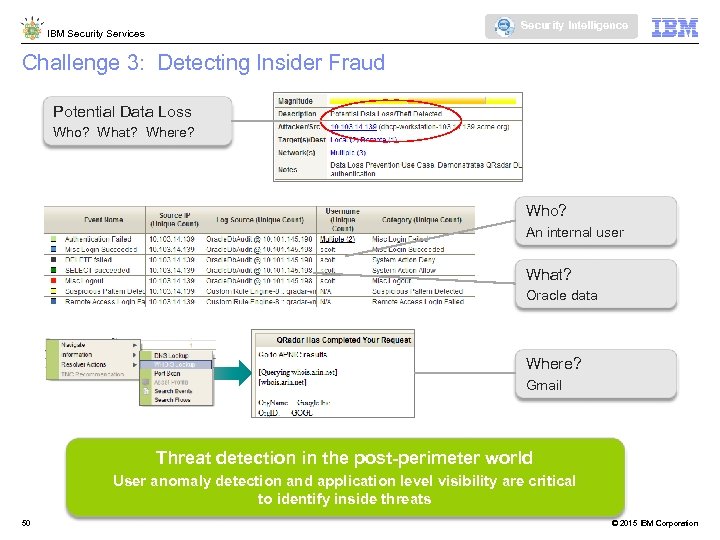
Security Intelligence IBM Security Services Challenge 3: Detecting Insider Fraud Potential Data Loss Who? What? Where? Who? An internal user What? Oracle data Where? Gmail Threat detection in the post-perimeter world User anomaly detection and application level visibility are critical to identify inside threats 50 © 2015 IBM Corporation
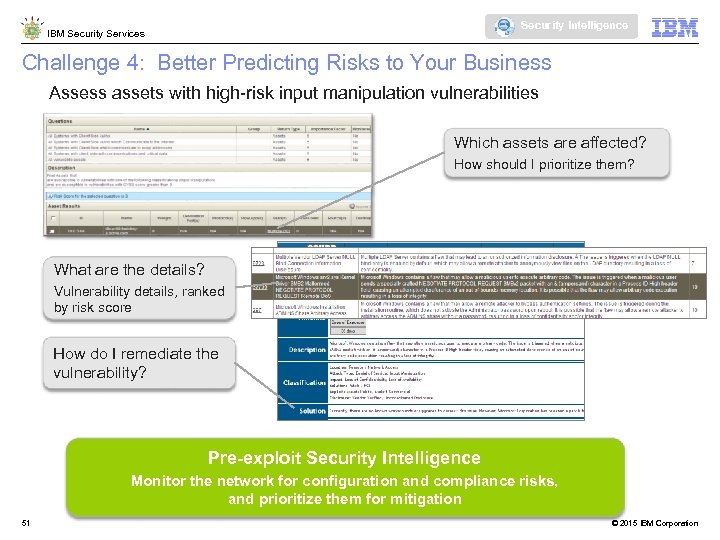
Security Intelligence IBM Security Services Challenge 4: Better Predicting Risks to Your Business Assess assets with high-risk input manipulation vulnerabilities Which assets are affected? How should I prioritize them? What are the details? Vulnerability details, ranked by risk score How do I remediate the vulnerability? Pre-exploit Security Intelligence Monitor the network for configuration and compliance risks, and prioritize them for mitigation 51 © 2015 IBM Corporation
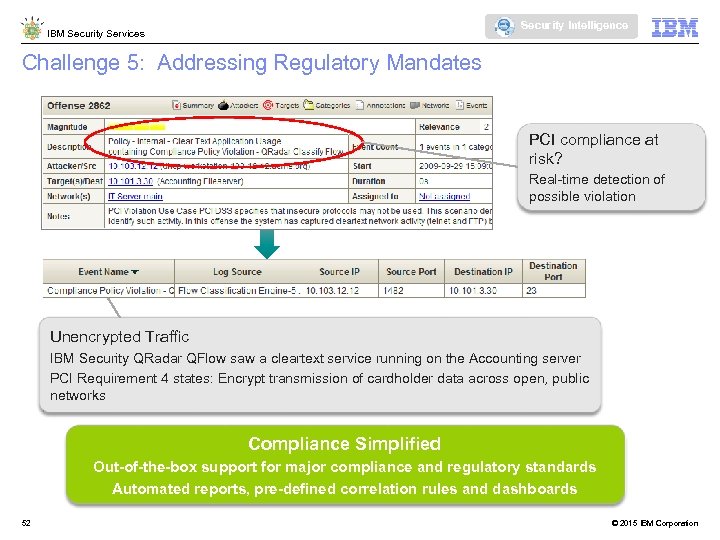
Security Intelligence IBM Security Services Challenge 5: Addressing Regulatory Mandates PCI compliance at risk? Real-time detection of possible violation Unencrypted Traffic IBM Security QRadar QFlow saw a cleartext service running on the Accounting server PCI Requirement 4 states: Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks Compliance Simplified Out-of-the-box support for major compliance and regulatory standards Automated reports, pre-defined correlation rules and dashboards 52 © 2015 IBM Corporation
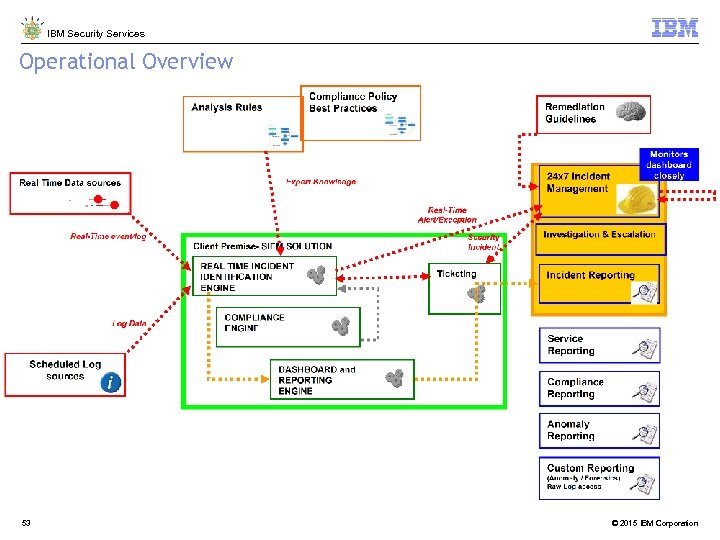
IBM Security Services Operational Overview 53 © 2015 IBM Corporation
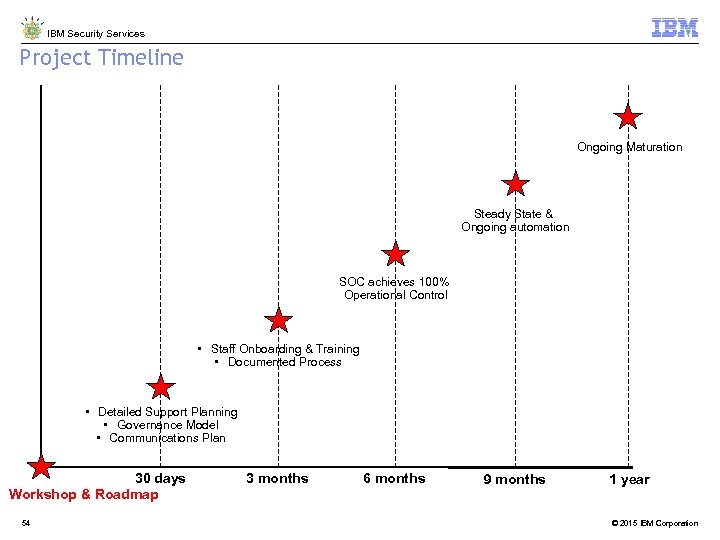
IBM Security Services Project Timeline Ongoing Maturation Steady State & Ongoing automation SOC achieves 100% Operational Control • Staff Onboarding & Training • Documented Process • Detailed Support Planning • Governance Model • Communications Plan 30 days Workshop & Roadmap 54 3 months 6 months 9 months 1 year © 2015 IBM Corporation
3389eaa5035b6579bc57c01c20b0089c.ppt