b28c17355b75b3a1de56582636b04210.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

IBM Security Bitcoin : Technology Implications of a Digital Currency Technology & Innovation - the Future of Security in Financial Services Scott Ainslie Senior Security Consultant 1 © 2012 IBM Corporation
IBM Security What is Cryptocurrency? § It is a digital currency designed to provide peer-to-peer transactions – Not regulated – Decentralised system of management – Takes advantage of cryptography or mathematical approach to provide surety of transaction – Presently not regulated but closely monitored by regulatory authorities from both the financial and law enforcement sectors – The cryptocurrency is generally capped – limited release § Several types exist of which most notable is Bitcoin 2 © 2012 IBM Corporation
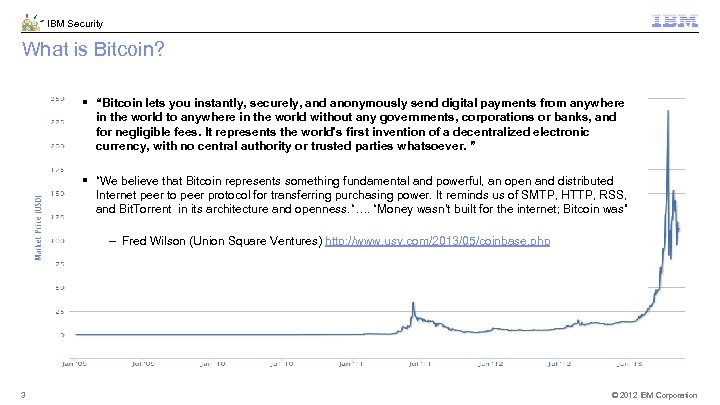
IBM Security What is Bitcoin? § “Bitcoin lets you instantly, securely, and anonymously send digital payments from anywhere in the world to anywhere in the world without any governments, corporations or banks, and for negligible fees. It represents the world's first invention of a decentralized electronic currency, with no central authority or trusted parties whatsoever. ” § “We believe that Bitcoin represents something fundamental and powerful, an open and distributed Internet peer to peer protocol for transferring purchasing power. It reminds us of SMTP, HTTP, RSS, and Bit. Torrent in its architecture and openness. “…. “Money wasn’t built for the internet; Bitcoin was” – Fred Wilson (Union Square Ventures) http: //www. usv. com/2013/05/coinbase. php 3 © 2012 IBM Corporation
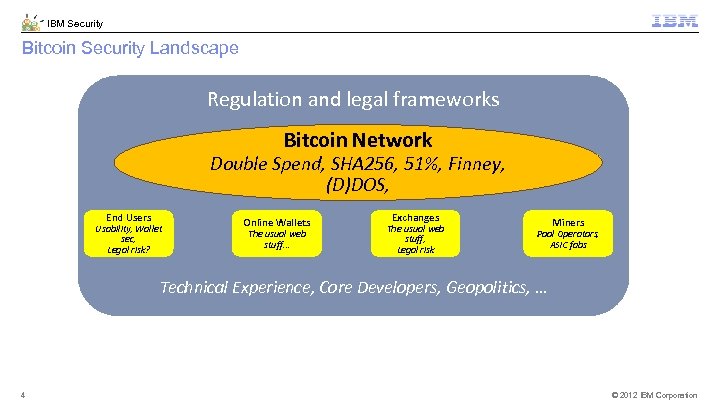
IBM Security Bitcoin Security Landscape Regulation and legal frameworks Bitcoin Network Double Spend, SHA 256, 51%, Finney, (D)DOS, End Users Usability, Wallet sec, Legal risk? Online Wallets The usual web stuff… Exchanges The usual web stuff, Legal risk Miners Pool Operators, ASIC fabs Technical Experience, Core Developers, Geopolitics, … 4 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security The regulators are very interested but still feeling their way… 5 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security 6 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Strategy So what went wrong? What is the threat landscape out there today…. ? 7 IBM Confidential © 2011 IBM Corporation
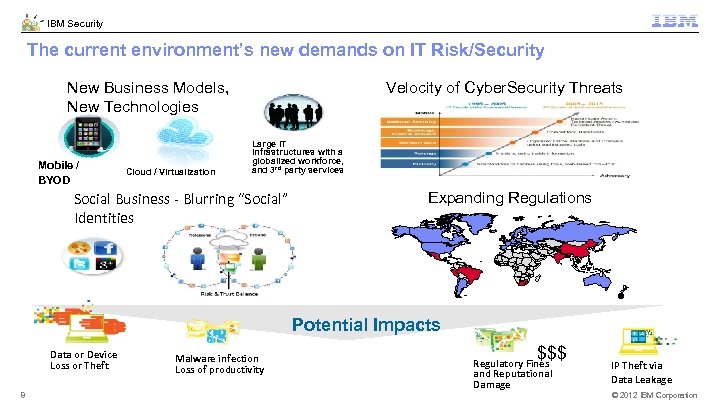
IBM Security The current environment’s new demands on IT Risk/Security New Business Models, New Technologies Mobile / BYOD Cloud / Virtualization Velocity of Cyber. Security Threats Large IT infrastructures with a globalized workforce, and 3 rd party services Social Business - Blurring “Social” Identities Expanding Regulations - • Potential Impacts Data or Device Loss or Theft 8 Malware infection Loss of productivity $$$ Regulatory Fines and Reputational Damage IP Theft via Data Leakage © 2012 IBM Corporation
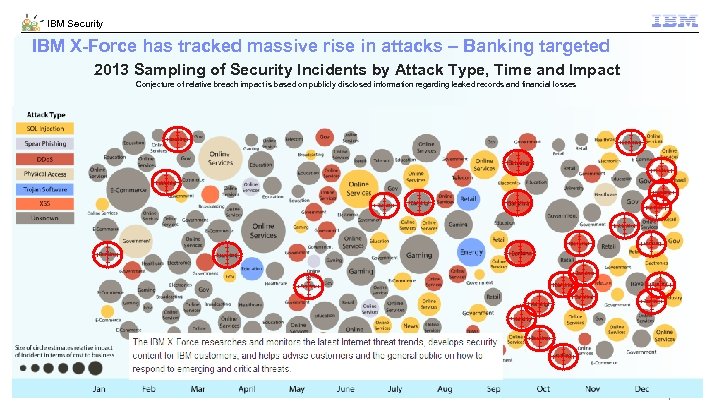
IBM Security IBM X-Force has tracked massive rise in attacks – Banking targeted 2013 Sampling of Security Incidents by Attack Type, Time and Impact Conjecture of relative breach impact is based on publicly disclosed information regarding leaked records and financial losses 9 © 2012 IBM Corporation
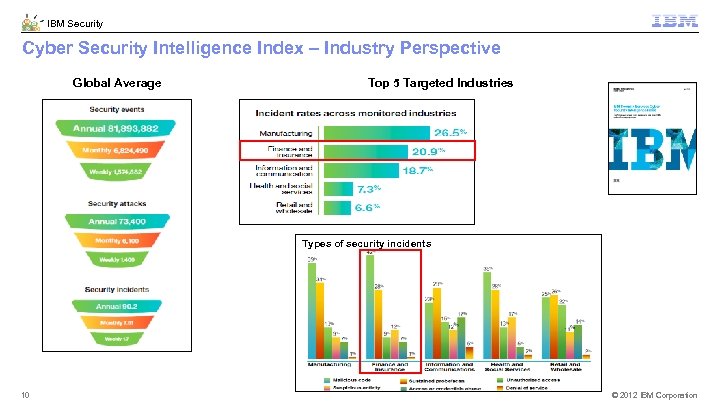
IBM Security Cyber Security Intelligence Index – Industry Perspective Global Average Top 5 Targeted Industries Types of security incidents 10 © 2012 IBM Corporation
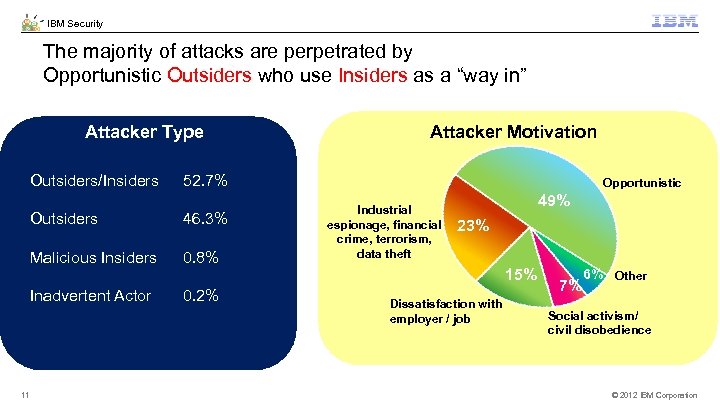
IBM Security The majority of attacks are perpetrated by Opportunistic Outsiders who use Insiders as a “way in” Attacker Type Attacker Motivation Outsiders/Insiders 52. 7% Outsiders 46. 3% Malicious Insiders 0. 8% Inadvertent Actor 11 0. 2% Opportunistic Industrial espionage, financial crime, terrorism, data theft 49% 23% 15% Dissatisfaction with employer / job 7% 6% Other Social activism/ civil disobedience © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security The Mobile Banking Security Challenge 400% increase in Android malware since summer 2010. Juniper Networks 1, 000 Almost 40, 000 new apps a month 48% apps in the official mobile app stores (Apple and Google) More than 40 rogue mobile banking apps were introduced to the android market of end users do not adopt mobile banking due to security concerns The Federal Reserve 12 Malicious Mobile Threats Report 2010/2011 Consumers & Mobile Financial Services March 2012 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Strategy IBM Security Intelligence …. . Less threat – more intelligence 13 IBM Confidential © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Strategy 14 IBM Confidential © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Criminals Attack the Weak Link With Malware Easy Retail/Business Customer Accounts Easy Cyber Criminals 15 Difficult © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Anatomy of Malware Attack User Target Social Engineering 16 System Exploit Web / OS Vulnerability Malware Infection Code Install Fraud Scheme Execution Web Injection, Capture Credentials Money Loss Mule Transfers, Real-time Fraud © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security IBM security strategy – target fraud & cybercrime - Acquisition strengthens the IBM portfolio of integrated solutions IBM Enters Web Fraud Protection leading web fraud capabilities assists IBM’s financial services and web commerce customers Strengthens Mobile Security Trusteer helps enable secure transactions from devices to the back office Extends Advanced Threat Protection provides a unique endpoint solution to help identify and prevent Advanced Persistent Threats Security-as-a-Service cloud-based deployment enables rapid adoption and real-time updates 17 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security IBM Leads Innovation in Security Intelligence – - QRadar expanding capability in Financial Sector Log Management Next. Gen SIEM Network Activity Monitoring Risk Management Vulnerability Management Network Forensics Offenses Dashboard 18 Assets Log Activity Investigation Network Activity Reports Administration © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Amplifying Security Intelligence with Big Data Analytics The Triggers That Motivate Big Data Analytics for Security Intelligence: 19 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security The People approach IBM’s ‘Chief Information Security Officer Study’ revealed the changing role of the CISO How they differ Influencers • Confident / prepared • Strategic focus Protectors • Less confident • Somewhat strategic • Lack necessary structural elements Responders • Least confident • Focus on protection and compliance have a dedicated CISO have a security/risk committee have information security as a board topic use a standard set of security metrics to track their progress focused on improving enterprise communication/ collaboration focused on providing education and awareness 20 Source: IBM Center for Applied Insights, Finding a Strategic Voice: Insights from the 2012 -13 IBM Chief Information Security Officer Assessment © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security The layered approach - technology Defence in Depth remains a solid cornerstone 1. Detecting threats • Arm yourself with comprehensive security intelligence 2. Consolidating data silos 3. Detecting insider fraud 4. 5. 21 • Collect, correlate and report on data in one integrated solution • Next-generation SIEM with identity correlation Better predicting risks to your business • Full life cycle of compliance and risk management for network and security infrastructures Addressing regulation mandates • Automated data collection and configuration audits © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Strategy It is all about trust 22 IBM Confidential © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Valuable Offerings, Recognised Leadership – WHY NOT? According to IDC, IBM has pushed into third place in According to IDC, IBM has pushed into worldwide enterprise security revenue, dominating in identity and access management as well as security and vulnerability management. IBM is considered to be in third place in “server security” and “network intrusion detection and prevention. ” Brendan Hannigan is general manager of the IBM Security Systems Division 23 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Top 10 essential practices for IT Risk and Security Leaders 10 Essential Practices 1. Build a risk aware culture and management system 2. Manage security incidents with intelligence 3. Defend the mobile and social workplace 6. Control network access and assure resilience 7. Address new complexity of cloud and virtualization 8. Manage third party security compliance 9. Secure data and protect privacy 4. Secure services, by design 10. Manage the identity lifecycle 5. Automate security “hygiene” 24 © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security GRC, IT Risk and Security Risk Management Convergence Business Analytics Open. Pages – Enterprise GRC Platform § IT GRC Platform GRC Stack Top down approach to requirements Security GRC Security Information and Event Management Vulnerability Management § Primarily driven by IT Security teams focusing on log collection, event analysis and compliance reporting Focus is on distilling vast amounts of data in an IT environment down to timely, relevant security intel § Bottom up approach to requirements Security portfolio, leading assets in: Infra App Data Security Foundation People QRadar Risk Manager and Security Intelligence § Log Management 25 Focus is on Finance, Legal and Operational requirements (e. g. Finance controls, business continuity, vertical regulations) § IT GRC Primarily driven by Enterprise Risk Management teams focusing on regulations such as ORM, FCM/S-OX, FFIEC § Enterprise GRC § § Identity management Data security Application security Network and endpoint security © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Valuable Offerings, Recognised Leadership – WHY NOT? Recent Wins Forrester Wave Security Consulting 26 Managed Security Services © 2012 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Strategy Security. Intelligence. Questions? Integration. Expertise. Thank You 27 IBM Confidential © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Strategy 28 IBM Confidential © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM Security Statement of Good Security Practices: IT system security involves protecting systems and information through prevention, detection and response to improper access from within and outside your enterprise. Improper access can result in information being altered, destroyed or misappropriated or can result in damage to or misuse of your systems, including to attack others. No IT system or product should be considered completely secure and no single product or security measure can be completely effective in preventing improper access. IBM systems and products are designed to be part of a comprehensive security approach, which will necessarily involve additional operational procedures, and may require other systems, products or services to be most effective. IBM DOES NOT WARRANT THAT SYSTEMS AND PRODUCTS ARE IMMUNE FROM THE MALICIOUS OR ILLEGAL CONDUCT OF ANY PARTY. ibm. com/security © Copyright IBM Corporation 2012. All rights reserved. The information contained in these materials is provided for informational purposes only, and is provided AS IS without warranty of any kind, express or implied. IBM shall not be responsible for any damages arising out of the use of, or otherwise related to, these materials. Nothing contained in these materials is intended to, nor shall have the effect of, creating any warranties or representations from IBM or its suppliers or licensors, or altering the terms and conditions of the applicable license agreement governing the use of IBM software. References in these materials to IBM products, programs, or services do not imply that they will be available in all countries in which IBM operates. Product release dates and/or capabilities referenced in these materials may change at any time at IBM’s sole discretion based on market opportunities or other factors, and are not intended to be a commitment to future product or feature availability in any way. IBM, the IBM logo, and other IBM products and services are trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation, in the United States, other countries or both. Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others. 29 © 2012 IBM Corporation
b28c17355b75b3a1de56582636b04210.ppt