df2f1987184ea019da2322206b340165.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

IBM's Perspective on Cloud Computing Lauren States Vice President IBM Software Group October, 2008 Dave Lindquist IBM Fellow IBM Software Group

Agenda § Trends and Business Perspective § Architecture and Technology § Summary 2
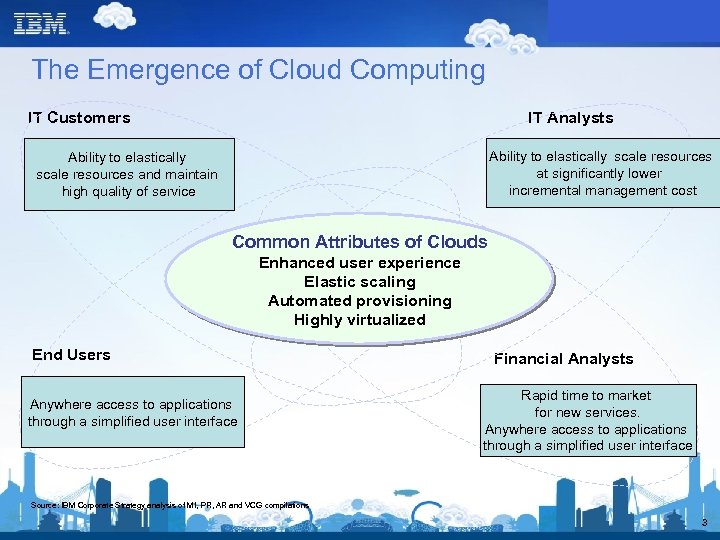
The Emergence of Cloud Computing IT Customers IT Analysts Ability to elastically scale resources at significantly lower incremental management cost Ability to elastically scale resources and maintain high quality of service Common Attributes of Clouds Enhanced user experience Elastic scaling Automated provisioning Highly virtualized End Users Anywhere access to applications through a simplified user interface Financial Analysts Rapid time to market for new services. Anywhere access to applications through a simplified user interface Source: IBM Corporate Strategy analysis of MI, PR, AR and VCG compilations 3
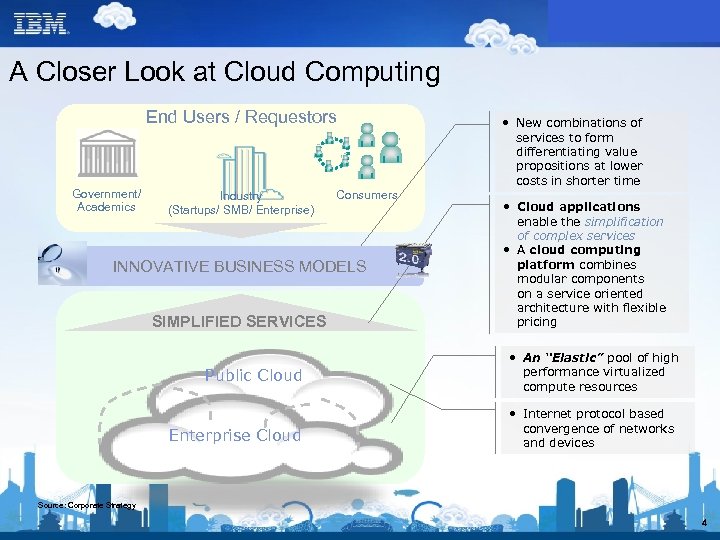
A Closer Look at Cloud Computing End Users / Requestors Government/ Academics Industry (Startups/ SMB/ Enterprise) Consumers INNOVATIVE BUSINESS MODELS SIMPLIFIED SERVICES Public Cloud Enterprise Cloud • New combinations of services to form differentiating value propositions at lower costs in shorter time • Cloud applications enable the simplification of complex services • A cloud computing platform combines modular components on a service oriented architecture with flexible pricing • An “Elastic” pool of high performance virtualized compute resources • Internet protocol based convergence of networks and devices Source: Corporate Strategy 4
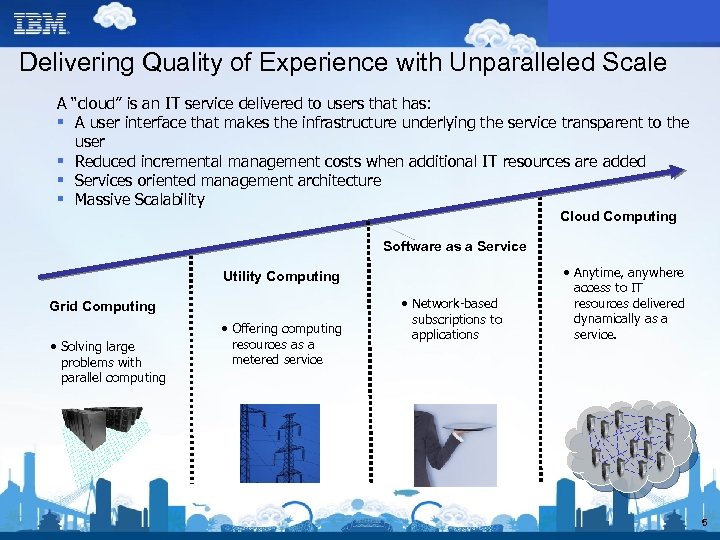
Delivering Quality of Experience with Unparalleled Scale A “cloud” is an IT service delivered to users that has: § A user interface that makes the infrastructure underlying the service transparent to the user § Reduced incremental management costs when additional IT resources are added § Services oriented management architecture § Massive Scalability Cloud Computing Software as a Service Utility Computing Grid Computing • Solving large problems with parallel computing • Offering computing resources as a metered service • Network-based subscriptions to applications • Anytime, anywhere access to IT resources delivered dynamically as a service. 5
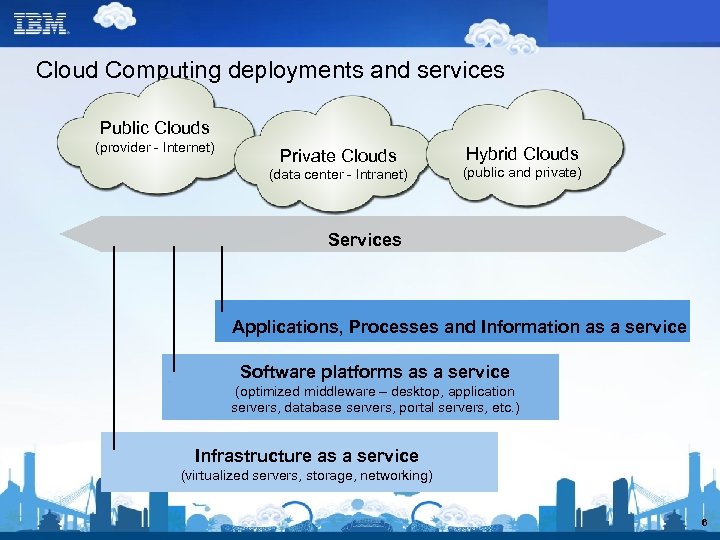
Cloud Computing deployments and services Public Clouds (provider - Internet) Private Clouds (data center - Intranet) Hybrid Clouds (public and private) Services Applications, Processes and Information as a service Software platforms as a service (optimized middleware – desktop, application servers, database servers, portal servers, etc. ) Infrastructure as a service (virtualized servers, storage, networking) 6

Architecture and Technology 7
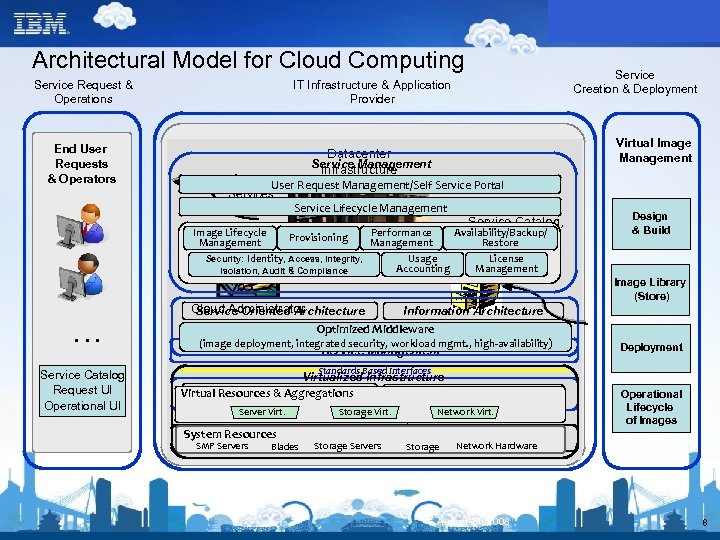
Architectural Model for Cloud Computing Service Request & Operations End User Requests & Operators Service Creation & Deployment IT Infrastructure & Application Provider Datacenter Service Management Infrastructure Virtual Image Management Access User Request Management/Self Service Portal Services Service Lifecycle Management Service Catalog, Image Lifecycle Performance Availability/Backup/ Provisioning Component Management Restore Library Usage License Security: Identity, Access, Integrity, Accounting Management Isolation, Audit & Compliance … Service Catalog Request UI Operational UI Design & Build Image Library (Store) Cloud Administrator Service Oriented Architecture Information Architecture Optimized Middleware (image deployment, integrated security, workload mgmt. , high-availability) Service Management Deployment Standards Based Interfaces Virtualized Infrastructure Service Oriented Architecture Information Architecture Virtual Resources & Aggregations Server Virt. System Resources SMP Servers Blades Storage Virt. Network Virt. Standards Based Interfaces Virtualized Infrastructure Storage Servers Storage Operational Lifecycle of Images Network Hardware August 24, 2008 8
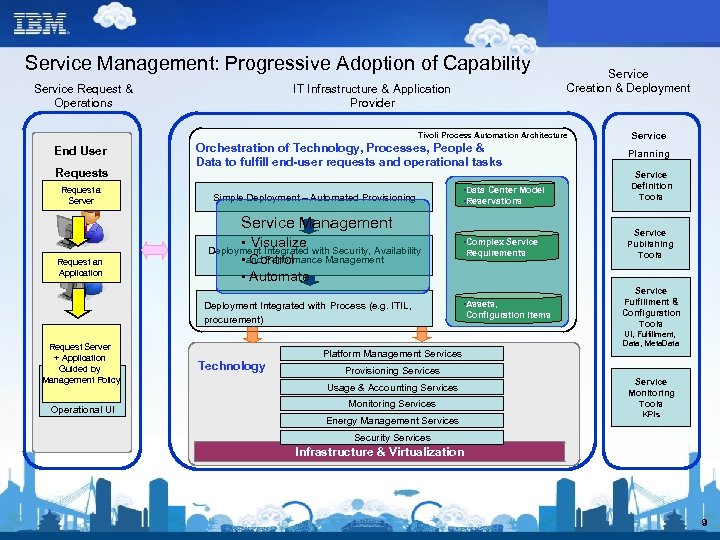
Service Management: Progressive Adoption of Capability Service Request & Operations IT Infrastructure & Application Provider Service Creation & Deployment Tivoli Process Automation Architecture End User Requests Request a & Operators Server Orchestration of Technology, Processes, People & Data to fulfill end-user requests and operational tasks Simple Deployment – Automated Provisioning • Data Center Model • Reservations Service Management Request an Application … Request Server + Application Guided by Service Catalog Management Policy Request UI Operational UI • Visualize Deployment Integrated with Security, Availability • and Performance Management Control • Automate Deployment Integrated with Process (e. g. ITIL, procurement) • Complex Service Requirements • Assets, Configuration Items Service Planning Service Definition Tools Service Publishing Tools Service Fulfillment & Configuration Tools UI, Fulfillment, Data, Meta. Data Technology Platform Management Services Provisioning Services Usage & Accounting Services Monitoring Services Energy Management Services Service Monitoring Tools KPIs Security Services Infrastructure & Virtualization 9
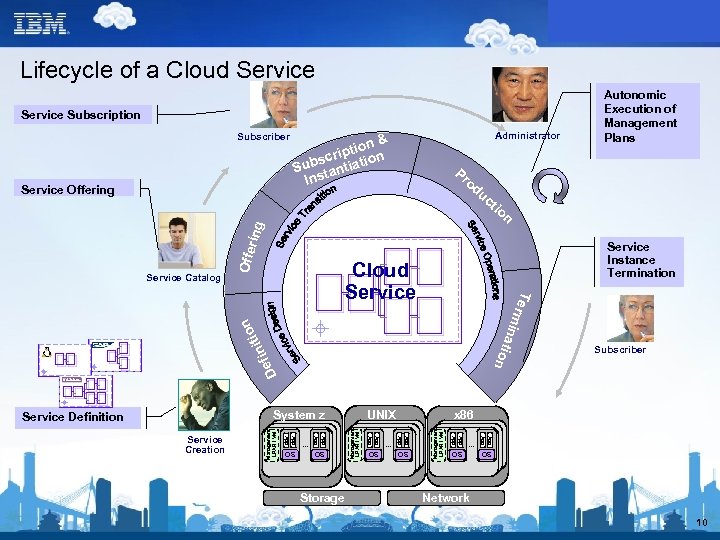
Lifecycle of a Cloud Service Subscription Subscriber Service Offering Administrator n& iptio on scr i Sub tantiat Ins Autonomic Execution of Management Plans Pr od uc tio Service Instance Termination r min at Te Cloud Service D efi ion n itio n Service Catalog Offe ring n OS Management LPAR / VM … … OS App Storage OS App OS x 86 App … UNIX App OS App App Service Creation Management LPAR / VM System z Service Definition Subscriber OS Network 10
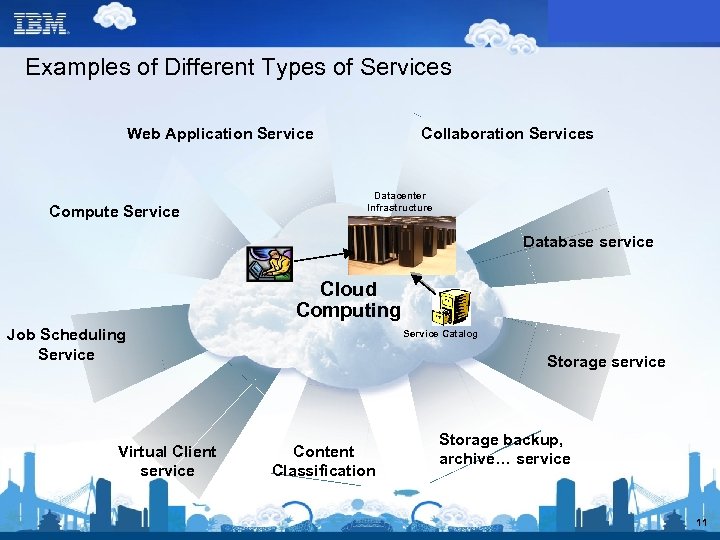
Examples of Different Types of Services Web Application Service Compute Service Collaboration Services Datacenter Infrastructure Database service Cloud Computing Job Scheduling Service Virtual Client service Service Catalog Storage service Content Classification Storage backup, archive… service 11
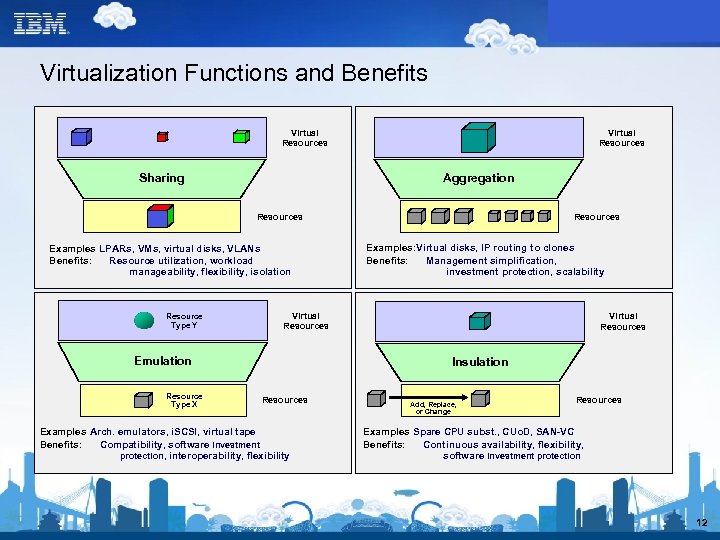
Virtualization Functions and Benefits Virtual Resources Aggregation Sharing Resources Examples: LPARs, VMs, virtual disks, VLANs Benefits: Resource utilization, workload manageability, flexibility, isolation Resource Type Y Examples: Virtual disks, IP routing to clones Benefits: Management simplification, investment protection, scalability Virtual Resources Emulation Resource Type X Resources Virtual Resources Insulation Resources Examples: Arch. emulators, i. SCSI, virtual tape Benefits: Compatibility, software investment protection, interoperability, flexibility Add, Replace, or Change Resources Examples: Spare CPU subst. , CUo. D, SAN-VC Benefits: Continuous availability, flexibility, software investment protection 12
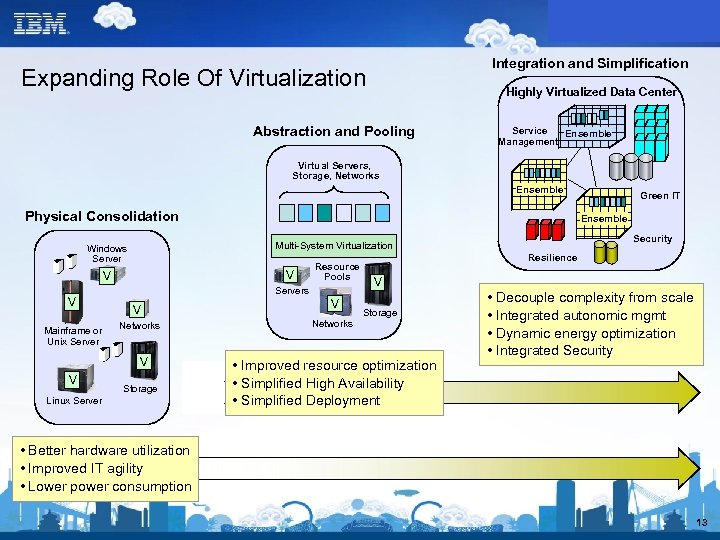
Integration and Simplification Expanding Role Of Virtualization Highly Virtualized Data Center Abstraction and Pooling Service Ensemble Management. Virtual Servers, Storage, Networks Ensemble Physical Consolidation V V V Mainframe or Unix Server Resource Pools Servers V Networks V V Ensemble Security Multi-System Virtualization Windows Server Storage Linux Server Green IT V Networks Resilience V Storage • Improved resource optimization • Simplified High Availability • Simplified Deployment • Decouple complexity from scale • Integrated autonomic mgmt • Dynamic energy optimization • Integrated Security • Better hardware utilization • Improved IT agility • Lower power consumption 13
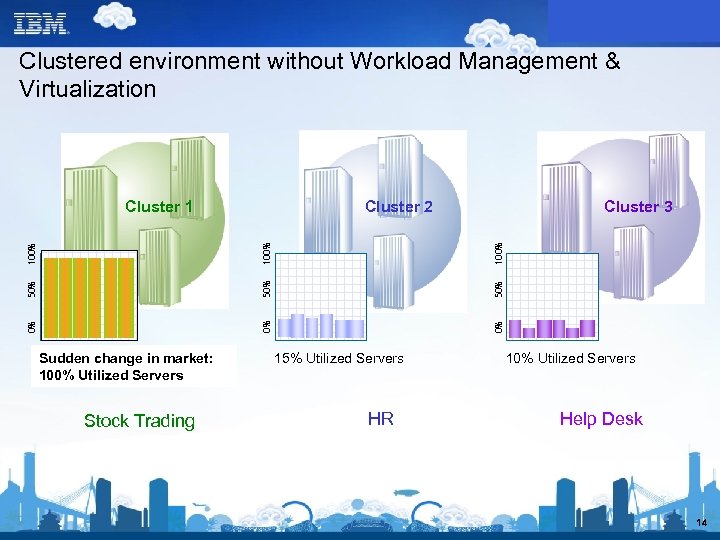
Clustered environment without Workload Management & Virtualization 0% 0% 50% 100% 50% 0% Sudden change in market: 55% 20% Utilized Servers 75% Cluster 3 100% Cluster 2 100% Cluster 1 15% Utilized Servers 100% Utilized Servers Stock Trading HR Help Desk 14
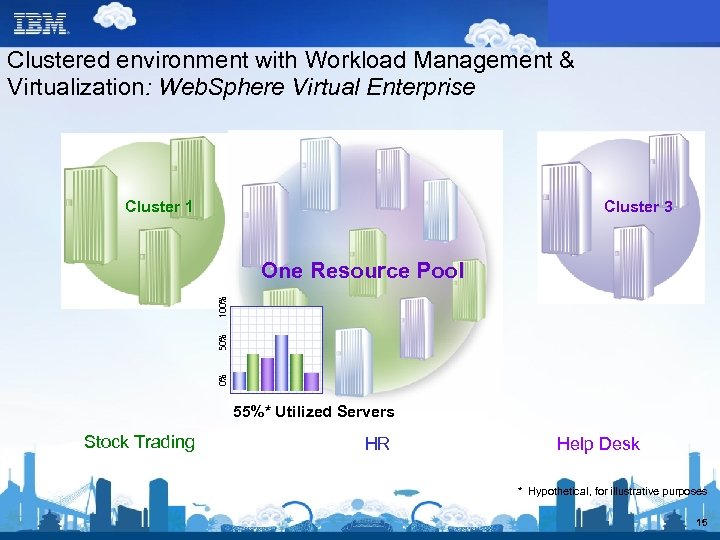
Clustered environment with Workload Management & Virtualization: Web. Sphere Virtual Enterprise Cluster 1 Cluster 2 Cluster 3 0% 50% 100% One Resource Pool 55%* Utilized Servers Stock Trading HR Help Desk * Hypothetical, for illustrative purposes 15

Introducing “Bluehouse” Store and Share File sharing service for uploading, storing and sharing of files § A set of integrated Web 2. 0 collaboration services that allows businesses to connect and work together easily § Enables collaboration beyond the boundaries of an organization § Provides the essential software to help teams of people work together § Connect from anywhere, anytime § Focus on business, rather than worry about IT Contacts Keep track of your contacts. Share Contact information Chat Instant messaging among “Bluehouse” users Meetings Your personal meeting room for Web meetings Activities Collaborate on projects, share files, Bookmarks and comments Business Forms Ability to create Business Forms Live Charts Visualize data through charts, graphs etc. IBM and Partner Confidential 16
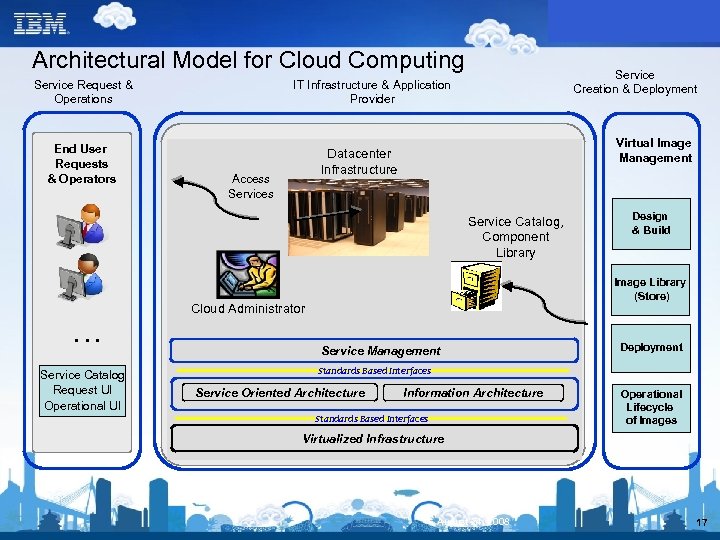
Architectural Model for Cloud Computing Service Request & Operations End User Requests & Operators Service Creation & Deployment IT Infrastructure & Application Provider Virtual Image Management Datacenter Infrastructure Access Service Catalog, Component Library … Service Catalog Request UI Operational UI Design & Build Image Library (Store) Cloud Administrator Service Management Deployment Standards Based Interfaces Service Oriented Architecture Information Architecture Standards Based Interfaces Operational Lifecycle of Images Virtualized Infrastructure August 24, 2008 17

Value Proposition 18
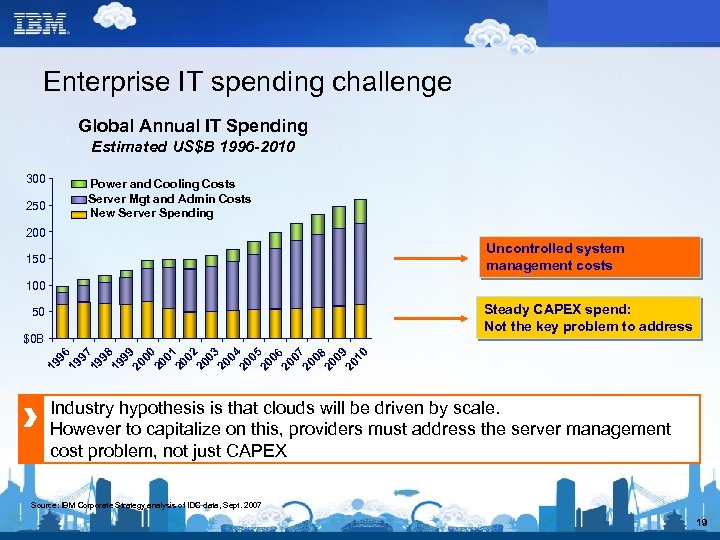
Enterprise IT spending challenge Global Annual IT Spending Estimated US$B 1996 -2010 300 250 Power and Cooling Costs Server Mgt and Admin Costs New Server Spending 200 Uncontrolled system management costs 150 100 Steady CAPEX spend: Not the key problem to address 50 19 96 19 97 19 98 19 99 20 00 20 01 20 02 20 03 20 04 20 05 20 06 20 07 20 08 20 09 20 10 $0 B Industry hypothesis is that clouds will be driven by scale. However to capitalize on this, providers must address the server management cost problem, not just CAPEX Source: IBM Corporate Strategy analysis of IDC data, Sept. 2007 19
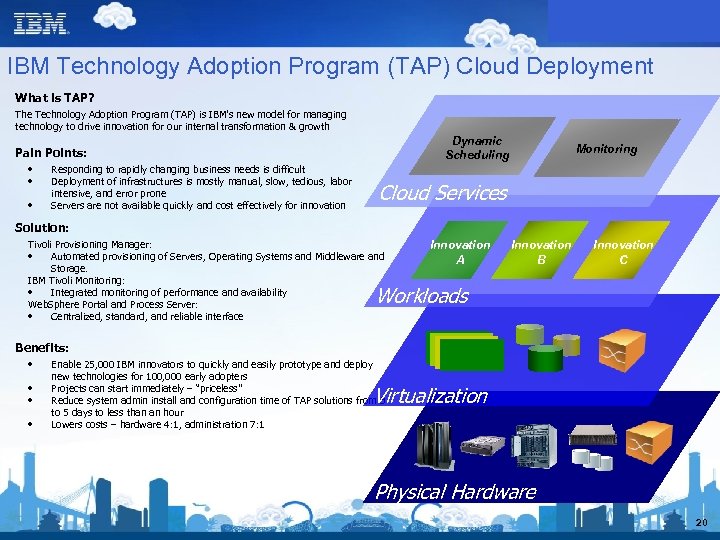
IBM Technology Adoption Program (TAP) Cloud Deployment What is TAP? The Technology Adoption Program (TAP) is IBM's new model for managing technology to drive innovation for our internal transformation & growth Dynamic Scheduling Pain Points: • • • Responding to rapidly changing business needs is difficult Deployment of infrastructures is mostly manual, slow, tedious, labor intensive, and error prone Servers are not available quickly and cost effectively for innovation Monitoring Cloud Services Solution: Tivoli Provisioning Manager: • Automated provisioning of Servers, Operating Systems and Middleware and Storage. IBM Tivoli Monitoring: • Integrated monitoring of performance and availability Web. Sphere Portal and Process Server: • Centralized, standard, and reliable interface Innovation A Innovation B Innovation C Workloads Benefits: • • Enable 25, 000 IBM innovators to quickly and easily prototype and deploy new technologies for 100, 000 early adopters Projects can start immediately – “priceless” Reduce system admin install and configuration time of TAP solutions from 3 to 5 days to less than an hour Lowers costs – hardware 4: 1, administration 7: 1 Virtual Application Server; Virtualization Physical Hardware 20
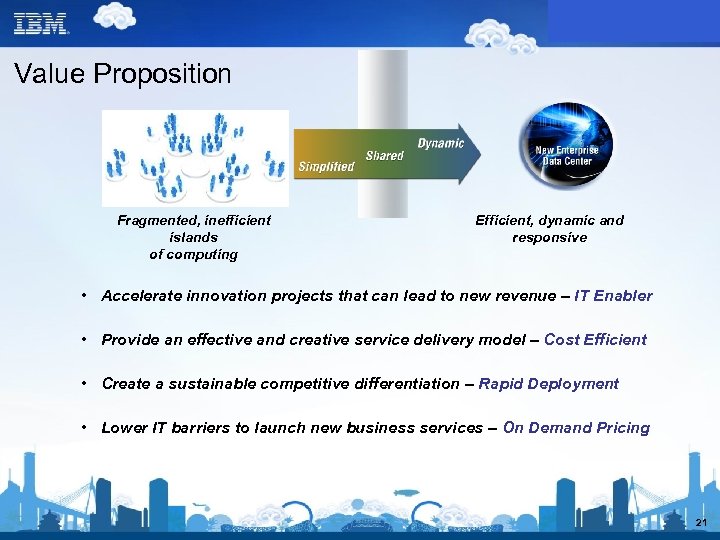
Value Proposition Fragmented, inefficient islands of computing Efficient, dynamic and responsive • Accelerate innovation projects that can lead to new revenue – IT Enabler • Provide an effective and creative service delivery model – Cost Efficient • Create a sustainable competitive differentiation – Rapid Deployment • Lower IT barriers to launch new business services – On Demand Pricing 21

22
df2f1987184ea019da2322206b340165.ppt