b2d01d56146d196e2cc721d58cec7dc7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61

IBM i for Business Intelligence DB 2 Web Query Continues to Evolve! Paul Masschelein Senior IT Specialist paul_masschelein@be. ibm. com March, 2012 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § Demo § Q&A 2 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § Demo § Q&A 3 © 2011 IBM Corporation
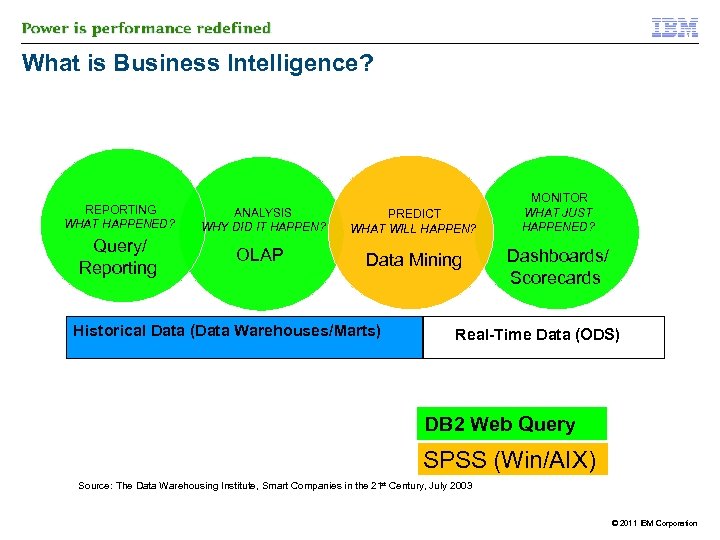
What is Business Intelligence? REPORTING WHAT HAPPENED? ANALYSIS WHY DID IT HAPPEN? PREDICT WHAT WILL HAPPEN? Query/ Reporting OLAP Data Mining Historical Data (Data Warehouses/Marts) MONITOR WHAT JUST HAPPENED? Dashboards/ Scorecards Real-Time Data (ODS) DB 2 Web Query SPSS (Win/AIX) Source: The Data Warehousing Institute, Smart Companies in the 21 st Century, July 2003 OS/EAI-Operation Systems/Enterprise Application Integrat © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § Demo § Q&A 5 © 2011 IBM Corporation
DB 2 Web Query for i q Leverage the latest query optimization technology q Value Licensing for existing Query/400 clients q Keep data in the database DB 2 for i q Capitalize on the analytical capabilities • Easily spot trends or exceptions in data with real time reports • Give Executives the means to track how the business is performing through intuitive Key Performance Indicator dashboards • Create self-service reporting environment that eliminates dependency on I/T • Provide data to spreadsheet aficionados painlessly and in real time • Execute and distribute reports in many different formats - on demand or scheduled – via e-mail or saved for later view • Integrate reports into existing applications for seamless access to data 6 © 2011 IBM Corporation

History § 2007 – Announce and delivery of V 1. 1. 0 – Offered “BASE” product as no charge upgrade to Query/400 § 2008 – Added Run Time User Enablement • Essentially unlimited user licensing – Removed SW Maintenance “after license” penalty • Try the product…. add SW Maintenance when you want w/o penalty – Added Report Broker and Software Development Kit • Automated report distribution and Web Services APIs § 2009 – Added SQL Server Adapter and Excel Client support • Seamlessly access data in Microsoft SQLServer and more powerful Excel interface § 2010 – Added Application Extensions allowing for more customization • • • Kick off reports from any interface (web or 5250) 5250 Report Extension Application Extension (generates URL that invokes a report) – Announced V 1. 1. 2 and Oracle JDEdwards Adapter § 2011 – – 7 Standard Edition SDK now includes Application Extension Latest Hot Fix (PTF Package) IBM i for BI Solution © 2011 IBM Corporation
BI is more than just a GUI Query Tool Fast, easy access to business information assets for query, reporting and analysis Authoring Tool “Intuitive” Reports & Graphs “Flexible delivery” Dashboards “Insightful” OLAP “Extensible” 8 © 2011 IBM Corporation

BI is more than just a GUI query tool: Data Issues § Not everyone understands the data. . only the original programmer knows! – Cryptic six character RPG fields – Data meaning buried in the field – If the first character is an “A”, the next 5 characters mean customer number – If the first character is a “B”, then it’s a company ID § Not everyone understand the table/file and data relationships – How do I join these 8 files? – How do I more easily roll up data by city/region/country/world? § Not everyone AGREES to the meaning of data – Accounting: 1+1 = 2 Sales: 1+1 = 3 ! § Not everyone understands complex date functions – Nor how every date is stored in different data TYPEs in the database § And no one wants to define these rules in EVERY single report This is where traditional reporting tools without a meta data layer fall short! 9 © 2011 IBM Corporation
Leveraging a Meta Data Layer to Shield Complexities of Database DB 2 Web Query Allows you to: § Standardize Field/Column Formats – Ex, use commas, set currency symbol, suppress leading zeros § Standardize/Decompose Date Fields – Ex: Integer defined as MMDDYYYY § Create Filters – Ex: Define a set of countries as “Europe” § Define JOINS and Dimensional Reporting § Create Business Views – Organize Columns/fields for easier report development § Define Stored Procedures, Views, UDFs to Meta Data Layer for some REALLY COOL function – Row/Column Level Security – Text Search Engine – Bring in weather report, local news and more © 2011 IBM Corporation
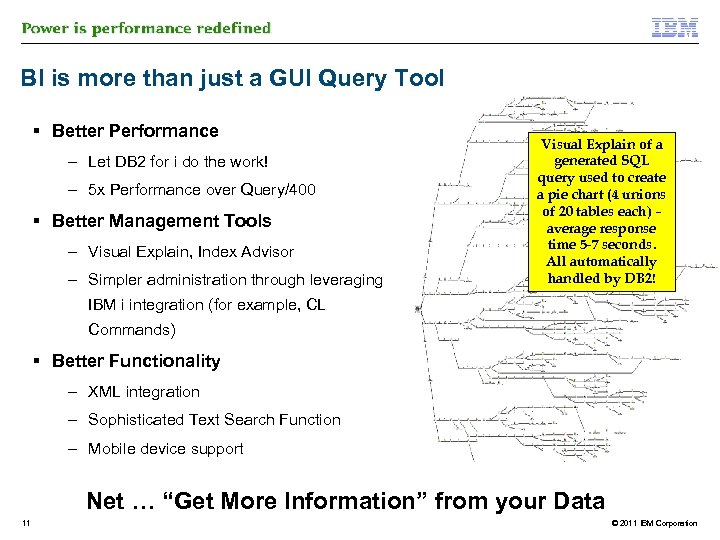
BI is more than just a GUI Query Tool § Better Performance – Let DB 2 for i do the work! – 5 x Performance over Query/400 § Better Management Tools – Visual Explain, Index Advisor – Simpler administration through leveraging Visual Explain of a generated SQL query used to create a pie chart (4 unions of 20 tables each) – average response time 5 -7 seconds. All automatically handled by DB 2! IBM i integration (for example, CL Commands) § Better Functionality – XML integration – Sophisticated Text Search Function – Mobile device support Net … “Get More Information” from your Data 11 © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM DB 2 Web Query for i Product Structure § Base Program Product Includes: – IBM i Web Reporting Server – Several Web Based authoring tools • RA, GA, Power Painter – Query/400 (5722 -QU 1) • Web Enable Query/400 Reports – BASE PRODUCT OFFERED AS NO CHARGE UPGRADE FROM QU 1 • Does not include Software Maintenance § Additional Features – Run Time User Enablement – Active Reports (Disconnected Analysis) – On Line Analytical Processing § DB 2 Web Query Report Broker (5733 -QU 3) – Automated Report Execution and Distribution § DB 2 Web Query SDK (5733 -QU 4) – Web Services to integrate reporting functions into applications/portals • Requires Meta Data provided with Developer Workbench § 5250 Reporting Extension – Developer Workbench – Lab Services asset – CL Command to • IT Tool for meta data execute reports in Batch or from 5250 – Adapter for MS SQL Server apps – Spreadsheet Client – JD Edwards Adapter © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § Demo § Q&A 13 © 2011 IBM Corporation

DB 2 Web Query Standard Edition § A pre-bundled set of software to make ordering easier. Includes: – DB 2 Web Query base product with n included users (5733 QU 2 *BASE) – – – – • n is 2 to 20, just as before, based on processor tier 4 additional user licenses (total licenses is 6 to 24) Run Time User License (essentially an unlimited run time user license) Active Technologies: Mobile Support OLAP Module: Analytical Reporting Developer Workbench: Meta Data Management and Dashboard Builder Spreadsheet Plug In Automated Report Scheduling and Distribution Application Integration Toolkit / SDK (Generate URL interface) § Generally Available (GA) on October 14, 2011 – Add additional users – Add JDE or SQL Server Adapter – Add 5250 Reporting Extension 14 © 2011 IBM Corporation
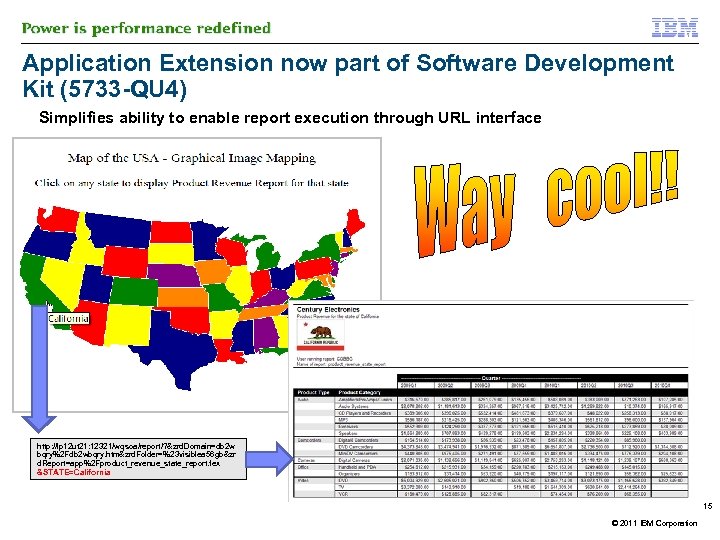
Application Extension now part of Software Development Kit (5733 -QU 4) Simplifies ability to enable report execution through URL interface http: //lp 12 ut 21: 12321/wqsoa/report/? &zrd. Domain=db 2 w bqry%2 Fdb 2 wbqry. htm&zrd. Folder=%23 visiblea 56 gb&zr d. Report=app%2 Fproduct_revenue_state_report. fex &STATE=California 15 © 2011 IBM Corporation
New Group PTF § Active Technologies (Active Reports) Mobile Platform Support – Download the Mobile Faves App § Meta Data Security Enhancements – more granular options for “DBA” or “user” § New CL Command CRTWQSYN to allow for creation (and refreshing) of meta data from command line § Application Extension (URL interface to run reports) now included in 5733 QU 4 Software Development Kit (SDK) – https: //www. ibm. com/developerworks/mydeveloperworks/wikis/home/wiki/W 516 d 8 b 60 d 32 c_4 fc 5_a 8 11_5 f 3 d 840 bf 524/page/Application%20 Extension § Various Info. Assist and HTML Composer (dashboard) enhancements Details here: https: //www. ibm. com/developerworks/mydeveloperworks/wikis/form/anonymous/api/library/96 f 36 e 44 -b 59 d-40 c 8 -8 efbe 3267 e 86 b 310/document/4 f 71713 c-3 eed-4 ab 4 -b 997 -48667 abb 1 c 78/attachment/05 d 67 df 8 -f 054 -4 a 93 -90312 ce 196 f 70 e 17/media/ibmwebquerynewfeatures 112. pdf 16 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Active Technologies for Mobile Web Apps § Ease of Use § Single-tap UI paradigm **new § Full gesture & screen rotation support **new § Embedded data analysis and visualization § Full offline data interactivity § Ease of Development § Dynamic device detection § Build once, fit in any device § § Industry Standard Send data with 128 -bit encryption Web Apps technology **new i. Phone App-like UI **new § Available in HTML or Flash **new Download i. Pad app: http: //itunes. apple. com/us/app/mobile-faves/id 406033421? mt=8 17 © 2011 IBM Corporation
Mobile Faves App © 2011 IBM Corporation

Query Modernization Service § Problem Statement: – – – 1000’s of Query/400 definitions Many are redundant but its not understood which ones Many are obsolete but we don’t know which ones Most are used to build extracts into another tool (spreadsheet, BI) Query/400 is old antiquated, cannot take advantage of the latest in DB 2 technology § Where do you start ? – Understand the Query/400 definitions: DISCOVER • What are the tables/files most often accessed? What are the fields being selected? What are the join criteria being established • IBM Lab Services has developed a “discovery” tool to help with this – Understand the Query/400 usage: ANALYZE • What queries are active? Which ones are obsolete? What is the end goal of the queries § Possible outcomes – Roadmap establishing a process and “best practices” for modernizing the queries – Education and getting started with DB 2 Web Query services – Prototyping 19 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § Demo § Q&A 20 © 2011 IBM Corporation
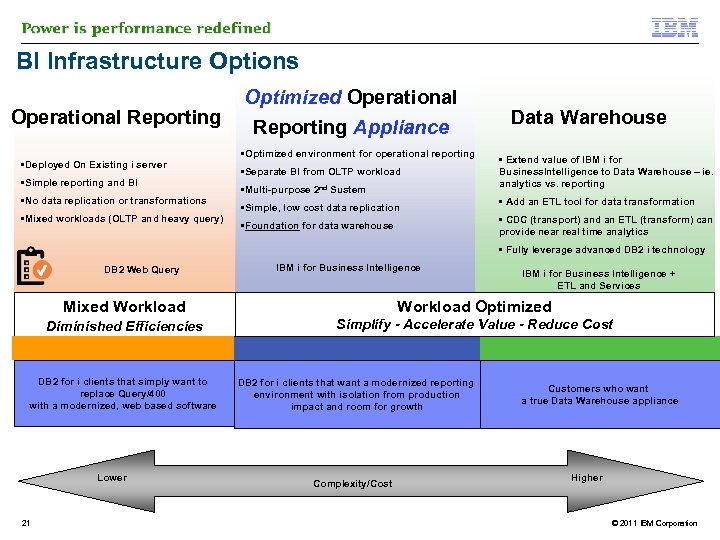
BI Infrastructure Options Operational Reporting • Deployed On Existing i server • Simple reporting and BI • No data replication or transformations • Mixed workloads (OLTP and heavy query) Optimized Operational Reporting Appliance • Optimized environment for operational reporting • Separate BI from OLTP workload • Multi-purpose 2 nd Sustem • Simple, low cost data replication Data Warehouse • Extend value of IBM i for Business. Intelligence to Data Warehouse – ie. analytics vs. reporting • Add an ETL tool for data transformation • CDC (transport) and an ETL (transform) can provide near real time analytics • Foundation for data warehouse • Fully leverage advanced DB 2 i technology DB 2 Web Query IBM i for Business Intelligence + ETL and Services Mixed Workload Optimized Diminished Efficiencies Simplify - Accelerate Value - Reduce Cost DB 2 for i clients that simply want to replace Query/400 with a modernized, web based software Lower 21 DB 2 for i clients that want a modernized reporting environment with isolation from production impact and room for growth Complexity/Cost Customers who want a true Data Warehouse appliance Higher © 2011 IBM Corporation
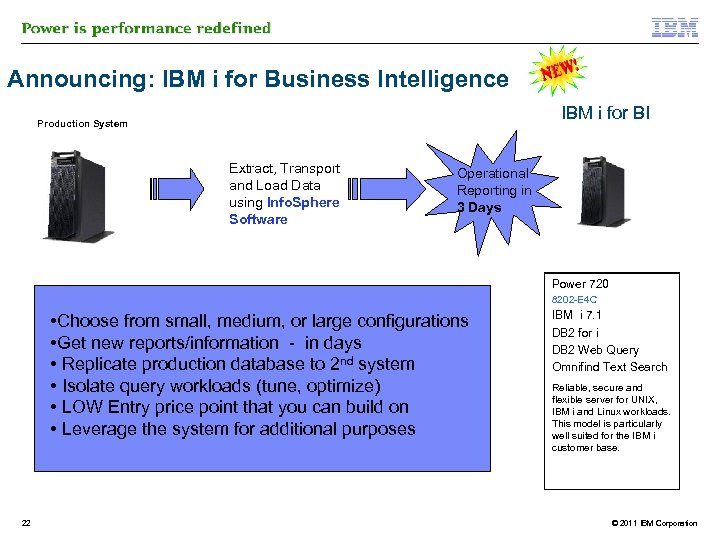
Announcing: IBM i for Business Intelligence IBM i for BI Production System Extract, Transport and Load Data using Info. Sphere Software Operational Reporting in 3 Days Power 720 8202 -E 4 C • Choose from small, medium, or large configurations • Get new reports/information - in days • Replicate production database to 2 nd system • Isolate query workloads (tune, optimize) • LOW Entry price point that you can build on • Leverage the system for additional purposes 22 IBM i 7. 1 DB 2 for i DB 2 Web Query Omnifind Text Search Reliable, secure and flexible server for UNIX, IBM i and Linux workloads. This model is particularly well suited for the IBM i customer base. © 2011 IBM Corporation
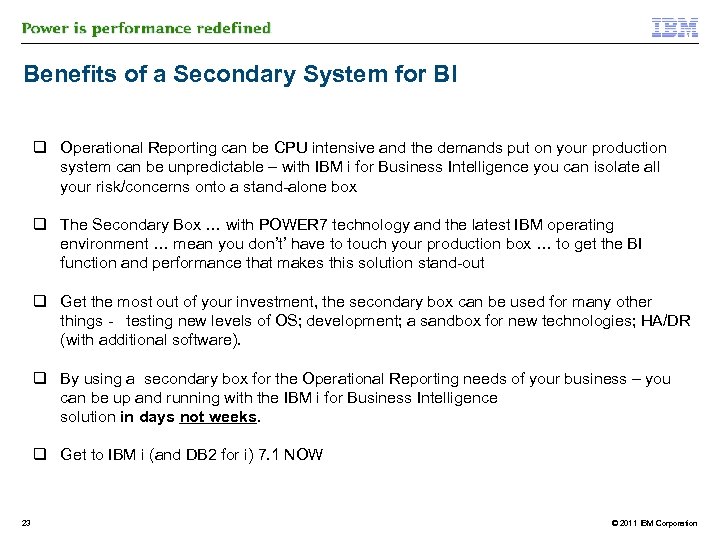
Benefits of a Secondary System for BI q Operational Reporting can be CPU intensive and the demands put on your production system can be unpredictable – with IBM i for Business Intelligence you can isolate all your risk/concerns onto a stand-alone box q The Secondary Box … with POWER 7 technology and the latest IBM operating environment … mean you don’t’ have to touch your production box … to get the BI function and performance that makes this solution stand-out q Get the most out of your investment, the secondary box can be used for many other things - testing new levels of OS; development; a sandbox for new technologies; HA/DR (with additional software). q By using a secondary box for the Operational Reporting needs of your business – you can be up and running with the IBM i for Business Intelligence solution in days not weeks. q Get to IBM i (and DB 2 for i) 7. 1 NOW 23 © 2011 IBM Corporation
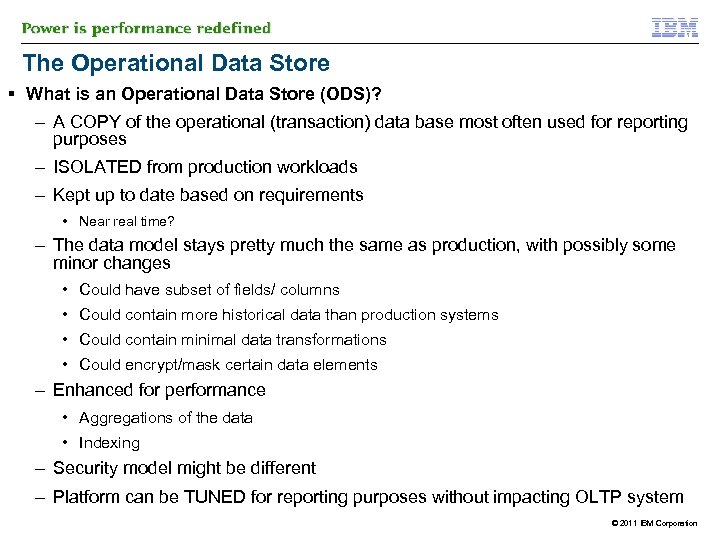
The Operational Data Store § What is an Operational Data Store (ODS)? – A COPY of the operational (transaction) data base most often used for reporting purposes – ISOLATED from production workloads – Kept up to date based on requirements • Near real time? – The data model stays pretty much the same as production, with possibly some minor changes • Could have subset of fields/ columns • Could contain more historical data than production systems • Could contain minimal data transformations • Could encrypt/mask certain data elements – Enhanced for performance • Aggregations of the data • Indexing – Security model might be different – Platform can be TUNED for reporting purposes without impacting OLTP system © 2011 IBM Corporation
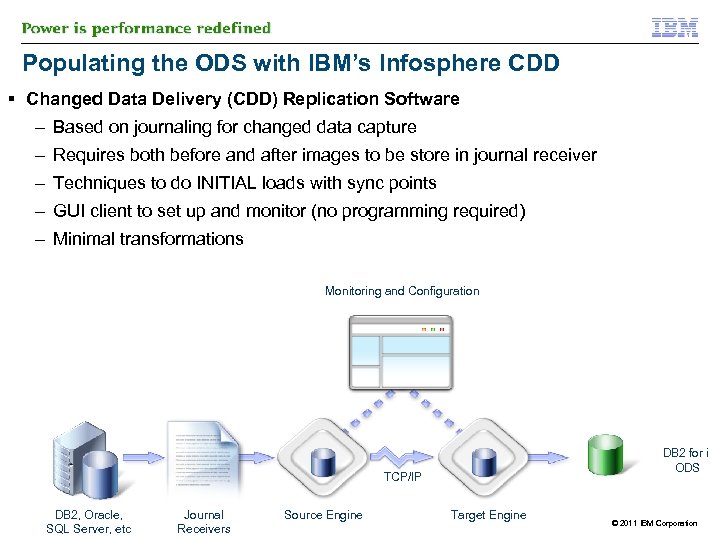
Populating the ODS with IBM’s Infosphere CDD § Changed Data Delivery (CDD) Replication Software – Based on journaling for changed data capture – Requires both before and after images to be store in journal receiver – Techniques to do INITIAL loads with sync points – GUI client to set up and monitor (no programming required) – Minimal transformations Monitoring and Configuration DB 2 for i ODS TCP/IP DB 2, Oracle, SQL Server, etc Journal Receivers Source Engine Target Engine © 2011 IBM Corporation
Small Solution q Small BI Edition (FC 4934) Power 720 Express (8202 -E 4 C) 1) 4 Cores Active/ 1 Core Licensed DB 2 Web Query for i 1) Defaults for Standard Edition Other Required BI Software 1) IBM i Proc License IBM i User Entitlements(15) One year of SWMA 2) i. Access Family 3) Omnifind Text Sch DB 2 4) DB 2 Symmetric Multi-proc 5) Rational Development Studio 6) Rational Developer for i q Info. Sphere Change Data Delivery: Order D 0 A 0 ZLL via Passport 1) 70 PVUs per core (One Core licensed - based on 12/2 promo) 26 © 2011 IBM Corporation
Medium Solution q Medium BI Edition (FC 4935) Power 720 Express (8202 -E 4 C) 1) 6 Cores Active / 2 Cores licensed (Includes entitlement for 3 Day Service voucher) Rack DB 2 Web Query for i 1) Defaults for Standard Edition Other Required BI Software: 1) IBM i Proc License IBM i User Entitlements(30) One year of SWMA 2) i. Access 3) Omnifind Text Sch DB 2 4) DB 2 Symmetric Multi-proc 5) Rational Development Studio 6) Rational Developer for I q Info. Sphere Change Data Delivery : Order D 0 A 0 ZLL via Passport 1) 70 PVUs per core (target box) (Two Cores ) 27 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Large Solution q Large BI Edition (FC 4936) Power 720 Express (8202 -E 4 C) 1) 6 Cores Active / 4 Cores Licensed (Includes entitlement for 3 Day Service voucher) Rack DB 2 Web Query for i 1) Defaults for Standard Edition Other Required Datamart Software: 1) IBM i Proc License IBM i User Entitlements(50) One year of SWMA 2) i. Access 3) Omnifind Text Sch DB 2 4) DB 2 Symmetric Multi-proc 5) Rational Development Studio 6) Rational Developer for i q Info. Sphere Change Data Delivery: Order D 0 A 0 ZLL via Passport 1) 70 PVUs per core (target box) (Four Cores licensed) 28 © 2011 IBM Corporation
IBM Info. Sphere Change Data Delivery Overview § CDD is a special license version of IBM’s Info. Sphere Change Data Capture (CDC) program – For our purposes, CDD = CDC § Provides near real time, batch, and refresh ETL across systems – Extracts the data directly from files or local or remote journals • Including the journal level control information such as job, user, program, etc. – Transforms data using basic functions and data lookups – Loads the data into an operational data store • Can be applied as soon as the changes are made in the primary system(s), changes rolled up into a batch processing window, or completely refreshed from the source • Can be used in point to point mode for data migration or for data consolidation from multiple origin systems to a single target § Consists of three components – Management Console – Windows based GUI to Access Server – Windows based server to setup and monitor data movement – CDC Server • Installed on both the source and target data systems for read and apply 29 © 2011 IBM Corporation
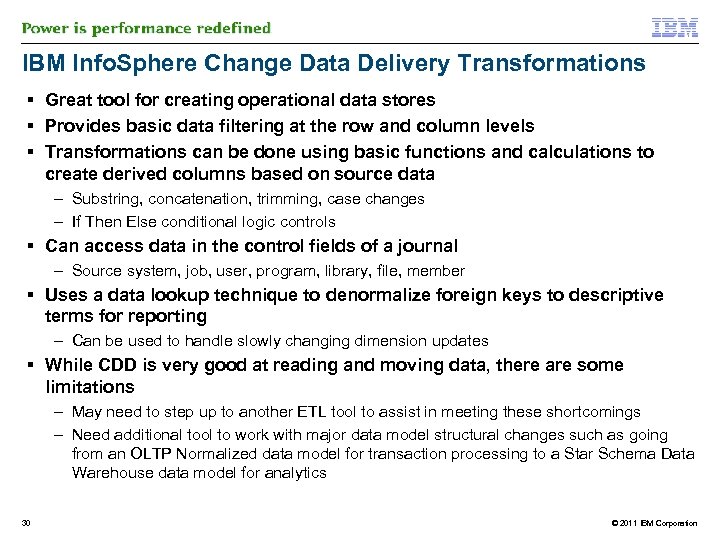
IBM Info. Sphere Change Data Delivery Transformations § Great tool for creating operational data stores § Provides basic data filtering at the row and column levels § Transformations can be done using basic functions and calculations to create derived columns based on source data – Substring, concatenation, trimming, case changes – If Then Else conditional logic controls § Can access data in the control fields of a journal – Source system, job, user, program, library, file, member § Uses a data lookup technique to denormalize foreign keys to descriptive terms for reporting – Can be used to handle slowly changing dimension updates § While CDD is very good at reading and moving data, there are some limitations – May need to step up to another ETL tool to assist in meeting these shortcomings – Need additional tool to work with major data model structural changes such as going from an OLTP Normalized data model for transaction processing to a Star Schema Data Warehouse data model for analytics 30 © 2011 IBM Corporation
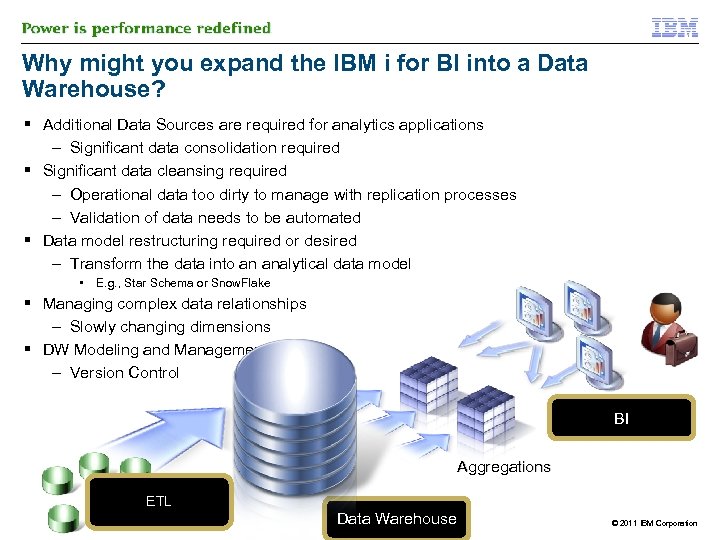
Why might you expand the IBM i for BI into a Data Warehouse? § Additional Data Sources are required for analytics applications – Significant data consolidation required § Significant data cleansing required – Operational data too dirty to manage with replication processes – Validation of data needs to be automated § Data model restructuring required or desired – Transform the data into an analytical data model • E. g. , Star Schema or Snow. Flake § Managing complex data relationships – Slowly changing dimensions § DW Modeling and Management tools – Version Control BI Aggregations ETL Data Warehouse © 2011 IBM Corporation
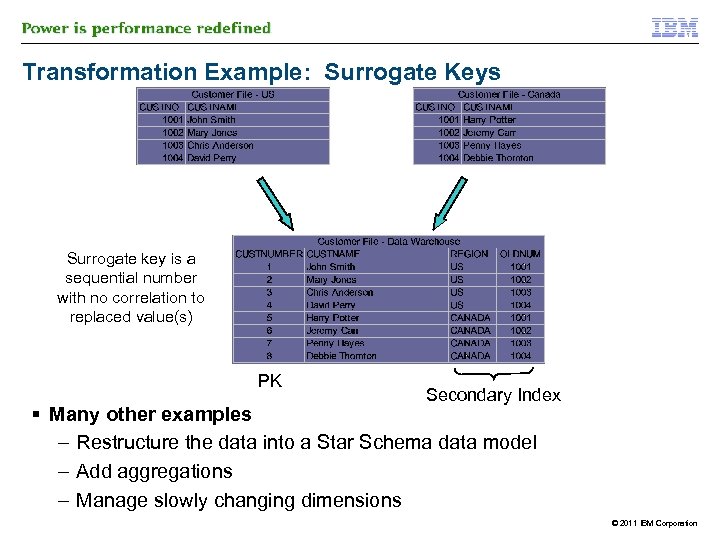
Transformation Example: Surrogate Keys Surrogate key is a sequential number with no correlation to replaced value(s) PK Secondary Index § Many other examples – Restructure the data into a Star Schema data model – Add aggregations – Manage slowly changing dimensions © 2011 IBM Corporation
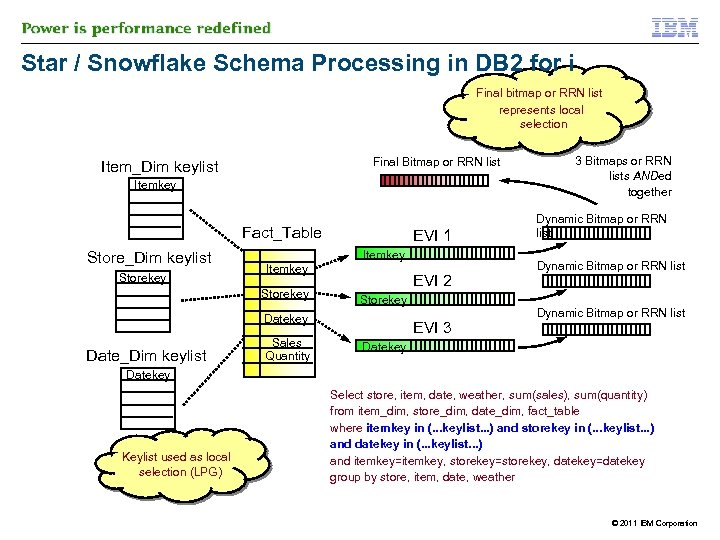
Star / Snowflake Schema Processing in DB 2 for i Final bitmap or RRN list represents local selection Final Bitmap or RRN list Item_Dim keylist Itemkey Fact_Table Store_Dim keylist Storekey EVI 1 Itemkey Storekey EVI 2 Storekey Date_Dim keylist Sales Quantity EVI 3 3 Bitmaps or RRN lists ANDed together Dynamic Bitmap or RRN list Datekey Keylist used as local selection (LPG) Select store, item, date, weather, sum(sales), sum(quantity) from item_dim, store_dim, date_dim, fact_table where itemkey in (. . . keylist. . . ) and storekey in (. . . keylist. . . ) and datekey in (. . . keylist. . . ) and itemkey=itemkey, storekey=storekey, datekey=datekey group by store, item, date, weather © 2011 IBM Corporation
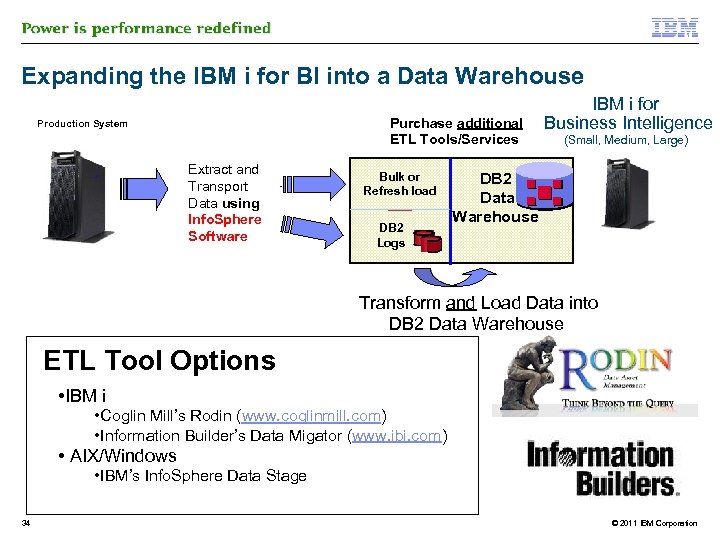
Expanding the IBM i for BI into a Data Warehouse Purchase additional ETL Tools/Services Production System Extract and Transport Data using Info. Sphere Software Bulk or Refresh load DB 2 Logs IBM i for Business Intelligence (Small, Medium, Large) DB 2 Data Warehouse Transform and Load Data into DB 2 Data Warehouse ETL Tool Options • IBM i • Coglin Mill’s Rodin (www. coglinmill. com) • Information Builder’s Data Migator (www. ibi. com) • AIX/Windows • IBM’s Info. Sphere Data Stage 34 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Why IBM i for Business Intelligence Reduce cost, complexity, and implementation time q Fully integrated to deliver high-performance business intelligence – start with Operational Reporting and grow into a Data Warehouse DB 2 Web Query for i q Engineered for rapid deployment with extract, transport, and loading of data from sourced systems that can be turned into business ready results in days – made possible through on-site no-charge services q Reduce cost of acquisition by up to 35% with discounted packaging q Built on a foundation of IBM i (includes DB 2 for i) , Info. Sphere Change Data Delivery, DB 2 Web Query for i and a Power 720 Express system … a fit-for purpose combination packaged to turn your data into information q Offers a range of business analytics capabilities including business intelligence reporting, analysis, and dashboards q Three solution sizes (Small, Medium, Large BI Editions) deliver broad scalability with DB 2 for i running on new POWER 7 technology serving up the needed performance with scalability to spare 35 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § Demo § Q&A 36 © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM DB 2 Web Query Installation § DB 2 Web Query 1. 1. 2 is the same for V 5 R 4, i 6. 1 and i 7. 1, but go i 7. 1( SQL engine , DB 2…. ) § Check prerequisites Ø See Info APAR II 14608 § Restore the DB 2 Web Query licensed program Ø Ø Ø Ø RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) – Base product RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(1) – Active Technologies RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(2) – OLAP enablement RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(3) – Developer Workbench (Reminder: This option is on a separate disc. ) RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(4) – Run Time User. Enablement RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(5) – Spreadsheet Client RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(6) - Adapter for Microsoft®SQL Server® RSTLICPGM(5733 QU 2) DEV(OPT 01) OPTION(7) - Adapter for Oracle’s JD Edwards § Set password for QWEBQRYADM Profile Ø CHGUSRPRF 5 QWEBQRYADM° PASSWORD(<yourpwd>) 37 © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM DB 2 Web Query Installation § Configure the features Ø Ø Ø Ø – § § Developer Workbench (Is installed on PC) Run Time User enablement Spreadsheet client Adapter for Microsoft SQL Server Adapter for Oracle’s JD Edwards Report Broker Application extension ( part of SDK) See install instructions on IBM® DB 2® Web Query for i™ 5733 QU 2 Install Instructions – Version 1. 1. 2 (2/14/2012 update) Add License Keys Install latest PTF Group for Web Query Ø Ø § Add Licensed Users Ø § WRKWEBQRY Option 5 Starting and Ending DB 2 Web Query Ø 38 See info APAR II 14608 Check for the PTF group that matches the release level WRKWEB QRY Opt 1 or STRWEBQRY/ENDWEBQRY © 2011 IBM Corporation

IBM DB 2 Web Query Installation § Check for the correct NLS configuration § In case of trouble…. Ø § Run the Web Query Health Checker Ø Ø Ø § 39 Check prereq and PTF Call the healthchecker : CALL QWEBQRY 77/CHKWEBQC Healthchecker checks file attributes, file authorities and environment Output in /tmp/webquery By the way : it is IBM Application Runtime Expert for i that does the job ! © 2011 IBM Corporation
IBM DB 2 Web Query Installation § 40 Healthchecker output…. © 2011 IBM Corporation
IBM DB 2 Web Query Installation § 41 Healthchecker output…. © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § Demo § Q&A 42 © 2011 IBM Corporation
IBM DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § § However you need Metadata to read from Query/400 § Similar process for Metadata on QRYDFN objects as on DB 2 tables § 43 DB 2 Web Query can run existng Query/400 reports without change and/or conversion process on the Query/400 object The process of creating metadata on a Query/400 runs the query at that time >> process can be longer © 2011 IBM Corporation
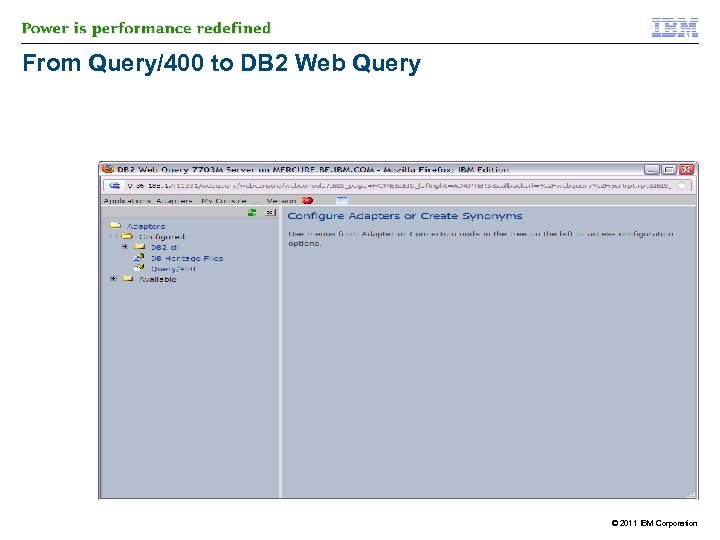
From Query/400 to DB 2 Web Query © 2011 IBM Corporation
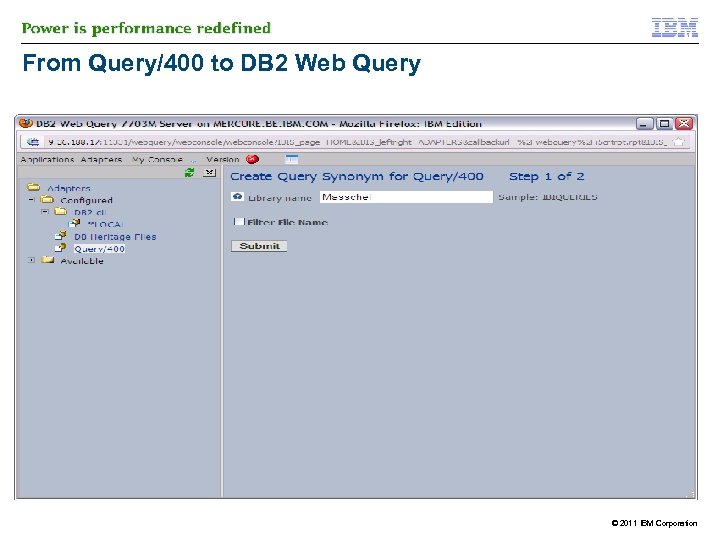
From Query/400 to DB 2 Web Query © 2011 IBM Corporation
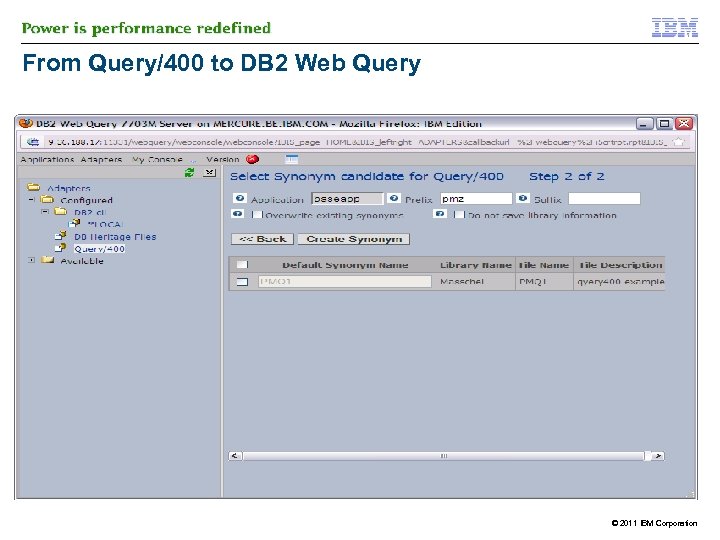
From Query/400 to DB 2 Web Query © 2011 IBM Corporation
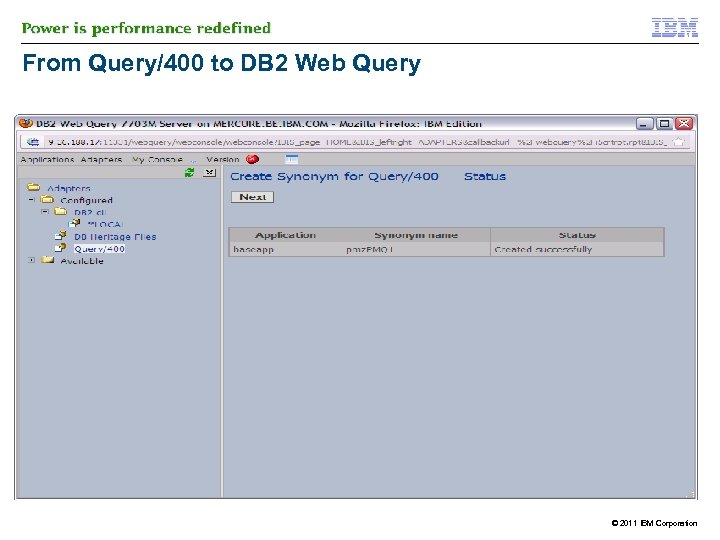
From Query/400 to DB 2 Web Query © 2011 IBM Corporation
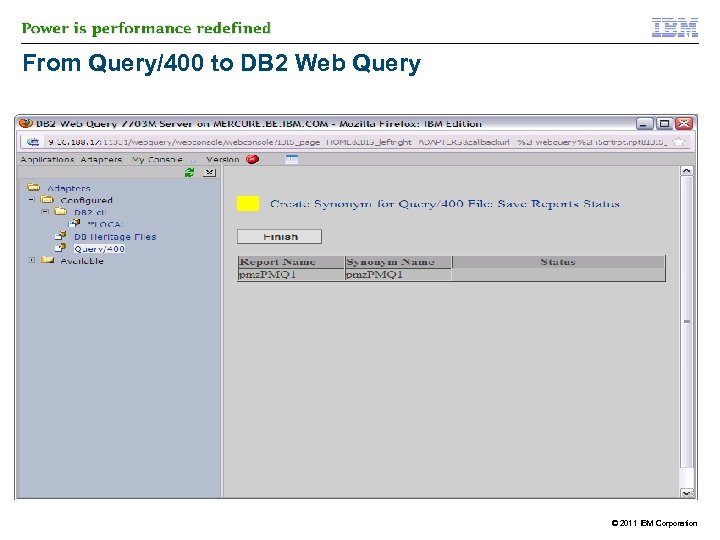
From Query/400 to DB 2 Web Query © 2011 IBM Corporation
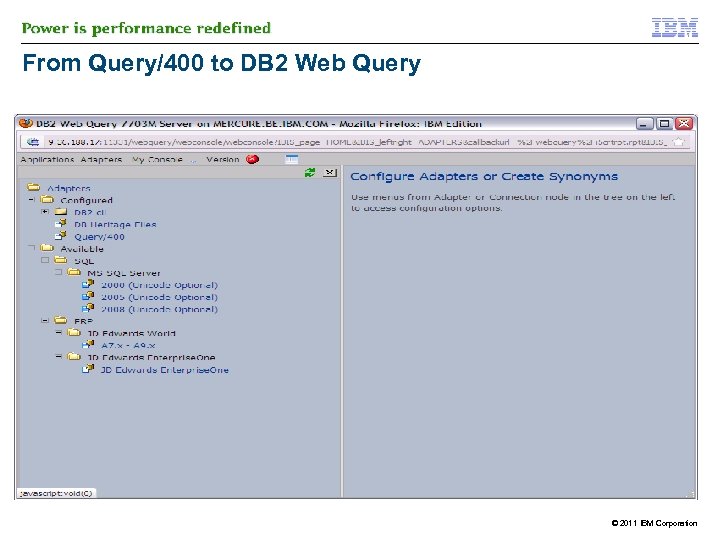
From Query/400 to DB 2 Web Query © 2011 IBM Corporation

Additional tools : Query/400 Discovery Tool § Used to DISCOVER Query/400 Query definitions (*QRYDFN) objects on system § Retrieves attributes of *QRYDFN and stores results in tables § Results, written into tables can be used for further analysis § ANALYZE: can be done with SQL, starting from the generated tables © 2011 IBM Corporation
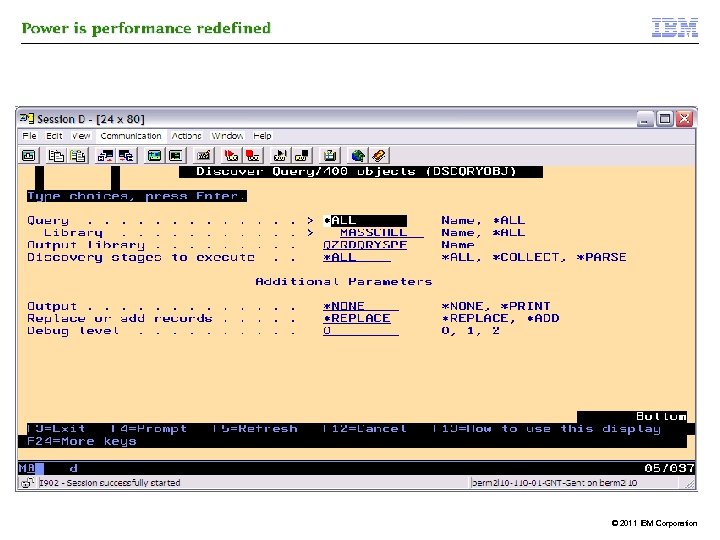
© 2011 IBM Corporation
© 2011 IBM Corporation
© 2011 IBM Corporation

Other “Best Practices” Guidance § IBM i for Business Intelligence Installation Services § DB 2 Web Query Getting Started Services* § Query/400 Modernization Services* § DB 2 for i Modernization Workshop(s) § DB 2 for i SQL Performance Workshop § DB 2 for i SQL Performance Health Check* § DB 2 for i Very Large Database (VLDB) Assessment* § DB 2 for i remote database administration and engineer services For more information, contact Mike Cain (cain@us. ibm. com) Or Doug Mack (mackd@us. ibm. com) © 2011 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Business Intelligence § DB 2 Web Query: the product § DB 2 Web Query Enhancements – Standard Edition – SDK Enhancements – PTF Package Enhancements – Query/400 Modernization Services § IBM i for BI Solution – The operational data store infrastructure – Expand into Data Warehousing § Installation § DB 2 Web Query and Query/400 § Demo § Q&A 55 © 2011 IBM Corporation

56 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Special notices This document was developed for IBM offerings in the United States as of the date of publication. IBM may not make these offerings available in other countries, and the information is subject to change without notice. Consult your local IBM business contact for information on the IBM offerings available in your area. Information in this document concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the suppliers of these products or other public sources. Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the suppliers of those products. IBM may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents. Send license inquires, in writing, to IBM Director of Licensing, IBM Corporation, New Castle Drive, Armonk, NY 10504 -1785 USA. All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only. The information contained in this document has not been submitted to any formal IBM test and is provided "AS IS" with no warranties or guarantees either expressed or implied. All examples cited or described in this document are presented as illustrations of the manner in which some IBM products can be used and the results that may be achieved. Actual environmental costs and performance characteristics will vary depending on individual client configurations and conditions. IBM Global Financing offerings are provided through IBM Credit Corporation in the United States and other IBM subsidiaries and divisions worldwide to qualified commercial and government clients. Rates are based on a client's credit rating, financing terms, offering type, equipment type and options, and may vary by country. Other restrictions may apply. Rates and offerings are subject to change, extension or withdrawal without notice. IBM is not responsible for printing errors in this document that result in pricing or information inaccuracies. All prices shown are IBM's United States suggested list prices and are subject to change without notice; reseller prices may vary. IBM hardware products are manufactured from new parts, or new and serviceable used parts. Regardless, our warranty terms apply. Any performance data contained in this document was determined in a controlled environment. Actual results may vary significantly and are dependent on many factors including system hardware configuration and software design and configuration. Some measurements quoted in this document may have been made on development-level systems. There is no guarantee these measurements will be the same on generallyavailable systems. Some measurements quoted in this document may have been estimated through extrapolation. Users of this document should verify the applicable data for their specific environment. Revised September 26, 2006 © 2011 IBM Corporation

Special notices (cont. ) IBM, the IBM logo, ibm. com AIX, AIX (logo), AIX 5 L, AIX 6 (logo), AS/400, Blade. Center, Blue Gene, Cluster. Proven, DB 2, ESCON, i 5/OS (logo), IBM Business Partner (logo), Intelli. Station, Load. Leveler, Lotus Notes, Operating System/400, OS/400, Partner. Link, Partner. World, Power. PC, p. Series, Rational, RISC System/6000, RS/6000, THINK, Tivoli (logo), Tivoli Management Environment, Web. Sphere, x. Series, z/OS, z. Series, Active Memory, Balanced Warehouse, Cache. Flow, Cool Blue, IBM Systems Director VMControl, pure. Scale, Turbo. Core, Chiphopper, Cloudscape, DB 2 Universal Database, DS 4000, DS 6000, DS 8000, Energy. Scale, Enterprise Workload Manager, General Parallel File System, , GPFS, HACMP/6000, HASM, IBM Systems Director Active Energy Manager, i. Series, Micro-Partitioning, POWER, Power. Executive, Power. VM (logo), Power. HA, Power Architecture, Power Everywhere, Power Family, POWER Hypervisor, Power Systems, Power Systems (logo), Power Systems Software (logo), POWER 2, POWER 3, POWER 4+, POWER 5+, POWER 6, POWER 6+, POWER 7, System i, System p 5, System Storage, System z, TME 10, Workload Partitions Manager and X-Architecture are trademarks or registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. If these and other IBM trademarked terms are marked on their first occurrence in this information with a trademark symbol (® or ™), these symbols indicate U. S. registered or common law trademarks owned by IBM at the time this information was published. Such trademarks may also be registered or common law trademarks in other countries. A full list of U. S. trademarks owned by IBM may be found at: http: //www. ibm. com/legal/copytrade. shtml. Adobe, the Adobe logo, Post. Script, and the Post. Script logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States, and/or other countries. Alti. Vec is a trademark of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. AMD Opteron is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Infini. Band, Infini. Band Trade Association and the Infini. Band design marks are trademarks and/or service marks of the Infini. Band Trade Association. Intel, Intel logo, Intel Inside logo, Intel Centrino logo, Celeron, Intel Xeon, Intel Speed. Step, Itanium, and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. IT Infrastructure Library is a registered trademark of the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency which is now part of the Office of Government Commerce. Java and all Java-based trademarks and logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Linear Tape-Open, LTO, the LTO Logo, Ultrium, and the Ultrium logo are trademarks of HP, IBM Corp. and Quantum in the U. S. and other countries. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries or both. Microsoft, Windows and the Windows logo are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries or both. Net. Bench is a registered trademark of Ziff Davis Media in the United States, other countries or both. SPECint, SPECfp, SPECjbb, SPECweb, SPECj. App. Server, SPEC OMP, SPECviewperf, SPECapc, SPEChpc, SPECjvm, SPECmail, SPECimap and SPECsfs are trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corp (SPEC). The Power Architecture and Power. org wordmarks and the Power and Power. org logos and related marks are trademarks and service marks licensed by Power. org. TPC-C and TPC-H are trademarks of the Transaction Performance Processing Council (TPPC). UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States, other countries or both. Other company, product and service names may be trademarks or service marks of others. Revised December 2, 2010 © 2011 IBM Corporation
Notes on benchmarks and values The IBM benchmarks results shown herein were derived using particular, well configured, development-level and generally-available computer systems. Buyers should consult other sources of information to evaluate the performance of systems they are considering buying and should consider conducting application oriented testing. For additional information about the benchmarks, values and systems tested, contact your local IBM office or IBM authorized reseller or access the Web site of the benchmark consortium or benchmark vendor. IBM benchmark results can be found in the IBM Power Systems Performance Report at http: //www. ibm. com/systems/p/hardware/system_perf. html. All performance measurements were made with AIX or AIX 5 L operating systems unless otherwise indicated to have used Linux. For new and upgraded systems, the latest versions of AIX were used. All other systems used previous versions of AIX. The SPEC CPU 2006, LINPACK, and Technical Computing benchmarks were compiled using IBM's high performance C, C++, and FORTRAN compilers for AIX 5 L and Linux. For new and upgraded systems, the latest versions of these compilers were used: XL C for AIX v 11. 1, XL C/C++ for AIX v 11. 1, XL FORTRAN for AIX v 13. 1, XL C/C++ for Linux v 11. 1, and XL FORTRAN for Linux v 13. 1. For a definition/explanation of each benchmark and the full list of detailed results, visit the Web site of the benchmark consortium or benchmark vendor. TPC SPEC LINPACK Pro/E GPC Volano. Mark STREAM SAP Oracle, Siebel, People. Soft Baan Fluent TOP 500 Supercomputers Ideas International Storage Performance Council http: //www. tpc. org http: //www. spec. org http: //www. netlib. org/benchmark/performance. pdf http: //www. proe. com http: //www. spec. org/gpc http: //www. volano. com http: //www. cs. virginia. edu/stream/ http: //www. sap. com/benchmark/ http: //www. oracle. com/apps_benchmark/ http: //www. ssaglobal. com http: //www. fluent. com/software/fluent/index. htm http: //www. top 500. org/ http: //www. ideasinternational. com/benchmark/bench. html http: //www. storageperformance. org/results Revised December 2, 2010 © 2011 IBM Corporation
Notes on HPC benchmarks and values The IBM benchmarks results shown herein were derived using particular, well configured, development-level and generally-available computer systems. Buyers should consult other sources of information to evaluate the performance of systems they are considering buying and should consider conducting application oriented testing. For additional information about the benchmarks, values and systems tested, contact your local IBM office or IBM authorized reseller or access the Web site of the benchmark consortium or benchmark vendor. IBM benchmark results can be found in the IBM Power Systems Performance Report at http: //www. ibm. com/systems/p/hardware/system_perf. html. All performance measurements were made with AIX or AIX 5 L operating systems unless otherwise indicated to have used Linux. For new and upgraded systems, the latest versions of AIX were used. All other systems used previous versions of AIX. The SPEC CPU 2006, LINPACK, and Technical Computing benchmarks were compiled using IBM's high performance C, C++, and FORTRAN compilers for AIX 5 L and Linux. For new and upgraded systems, the latest versions of these compilers were used: XL C for AIX v 11. 1, XL C/C++ for AIX v 11. 1, XL FORTRAN for AIX v 13. 1, XL C/C++ for Linux v 11. 1, and XL FORTRAN for Linux v 13. 1. Linpack HPC (Highly Parallel Computing) used the current versions of the IBM Engineering and Scientific Subroutine Library (ESSL). For Power 7 systems, IBM Engineering and Scientific Subroutine Library (ESSL) for AIX Version 5. 1 and IBM Engineering and Scientific Subroutine Library (ESSL) for Linux Version 5. 1 were used. For a definition/explanation of each benchmark and the full list of detailed results, visit the Web site of the benchmark consortium or benchmark vendor. SPEC http: //www. spec. org LINPACK http: //www. netlib. org/benchmark/performance. pdf Pro/E http: //www. proe. com GPC http: //www. spec. org/gpc STREAM http: //www. cs. virginia. edu/stream/ Fluent http: //www. fluent. com/software/fluent/index. htm TOP 500 Supercomputers http: //www. top 500. org/ AMBER http: //amber. scripps. edu/ FLUENT http: //www. fluent. com/software/fluent/fl 5 bench/index. htm GAMESS http: //www. msg. chem. iastate. edu/gamess GAUSSIAN http: //www. gaussian. com ANSYS http: //www. ansys. com/services/hardware-support-db. htm Click on the "Benchmarks" icon on the left hand side frame to expand. Click on "Benchmark Results in a Table" icon for benchmark results. ABAQUS http: //www. simulia. com/support/v 68_performance. php ECLIPSE http: //www. sis. slb. com/content/software/simulation/index. asp? seg=geoquest& MM 5 http: //www. mmm. ucar. edu/mm 5/ MSC. NASTRAN http: //www. mscsoftware. com/support/prod%5 Fsupport/nastran/performance/v 04_sngl. cfm STAR-CD www. cd-adapco. com/products/STAR-CD/performance/320/index/html NAMD http: //www. ks. uiuc. edu/Research/namd Revised December 2, 2010 HMMER http: //hmmer. janelia. org/ http: //powerdev. osuosl. org/project/hmmer. Altivec. Gen 2 mod © 2011 IBM Corporation

Notes on performance estimates r. Perf for AIX r. Perf (Relative Performance) is an estimate of commercial processing performance relative to other IBM UNIX systems. It is derived from an IBM analytical model which uses characteristics from IBM internal workloads, TPC and SPEC benchmarks. The r. Perf model is not intended to represent any specific public benchmark results and should not be reasonably used in that way. The model simulates some of the system operations such as CPU, cache and memory. However, the model does not simulate disk or network I/O operations. § r. Perf estimates are calculated based on systems with the latest levels of AIX and other pertinent software at the time of system announcement. Actual performance will vary based on application and configuration specifics. The IBM e. Server p. Series 640 is the baseline reference system and has a value of 1. 0. Although r. Perf may be used to approximate relative IBM UNIX commercial processing performance, actual system performance may vary and is dependent upon many factors including system hardware configuration and software design and configuration. Note that the r. Perf methodology used for the POWER 6 systems is identical to that used for the POWER 5 systems. Variations in incremental system performance may be observed in commercial workloads due to changes in the underlying system architecture. All performance estimates are provided "AS IS" and no warranties or guarantees are expressed or implied by IBM. Buyers should consult other sources of information, including system benchmarks, and application sizing guides to evaluate the performance of a system they are considering buying. For additional information about r. Perf, contact your local IBM office or IBM authorized reseller. ==================================== CPW for IBM i Commercial Processing Workload (CPW) is a relative measure of performance of processors running the IBM i operating system. Performance in customer environments may vary. The value is based on maximum configurations. More performance information is available in the Performance Capabilities Reference at: www. ibm. com/systems/i/solutions/perfmgmt/resource. html Revised April 2, 2007 © 2011 IBM Corporation
b2d01d56146d196e2cc721d58cec7dc7.ppt