0ef53841b3fae924a4f419fe7d799991.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

IBM DB/2 UDB vs ORACLE Andrei Solntsev, Aprill 2003

5 aastat tagasi • IBM • Oracle • Informix • Sys. Base Vähendasid klientide olemasolevate süsteemide arendamise võimalused 1

• Internet Täna • 24 x 7 x 365 • kaugajaline partner • IBM • Oracle • Microsoft • NCR Tera. Data • Tõkestatud skaleeruvus • ainult keskkondades Windows NT/2000 • Ebakindel tulevik • Tagasihoidlik koht äriturul 2

• Internet Täna • 24 x 7 x 365 • kaugajaline partner • IBM • Oracle • Microsoft • NCR Tera. Data • Tõkestatud skaleeruvus • ainult keskkondades Windows NT/2000 • Ebakindel tulevik • Tagasihoidlik koht äriturul

DB/2 ja Oracle: Ühised muudatused • Internet-tehnoloogiad: • Java • XML • . . . • Klasteriseerimine • Usaldusväärsus • Arhitektuuri täiustamine 3
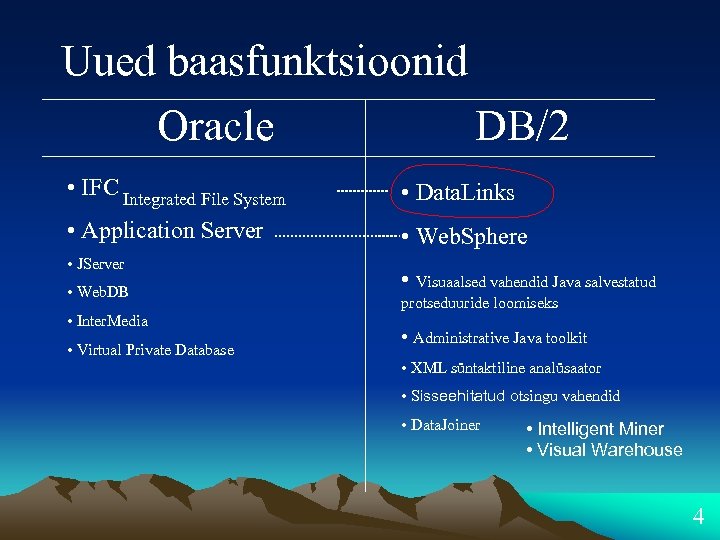
Uued baasfunktsioonid Oracle DB/2 • IFC Integrated File System • Data. Links • Application Server • Web. Sphere • JServer • Web. DB • Inter. Media • Virtual Private Database • Visuaalsed vahendid Java salvestatud protseduuride loomiseks • Administrative Java toolkit • XML süntaktiline analüsaator • Sisseehitatud otsingu vahendid • Data. Joiner • Intelligent Miner • Visual Warehouse 4

Data. Links data in files no longer needs to be imported into the database
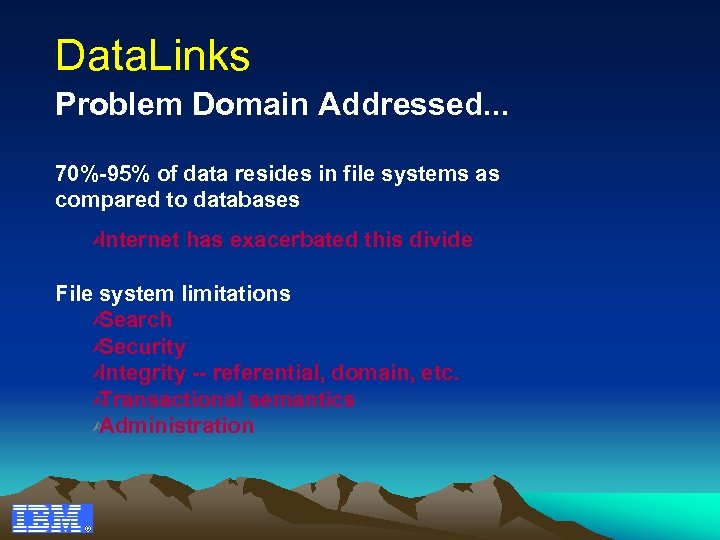
Data. Links Problem Domain Addressed. . . 70%-95% of data resides in file systems as compared to databases Ù Internet has exacerbated this divide File system limitations Ù Search Ù Security Ù Integrity -- referential, domain, etc. Ù Transactional semantics Ù Administration
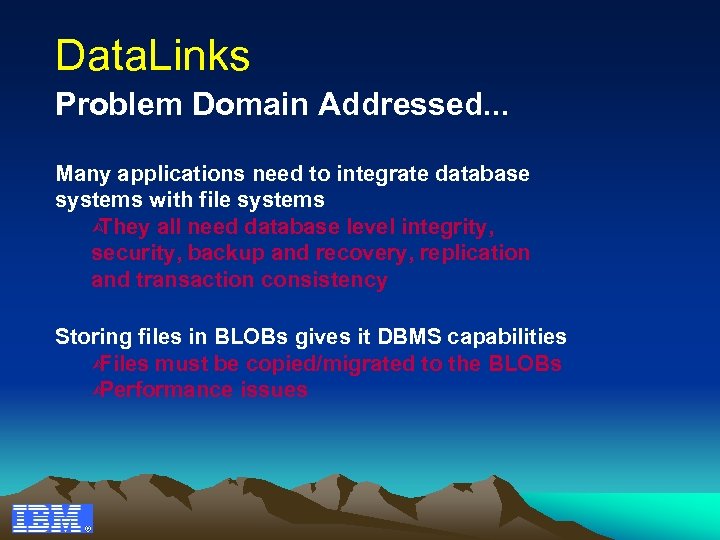
Data. Links Problem Domain Addressed. . . Many applications need to integrate database systems with file systems Ù They all need database level integrity, security, backup and recovery, replication and transaction consistency Storing files in BLOBs gives it DBMS capabilities Ù Files must be copied/migrated to the BLOBs Ù Performance issues
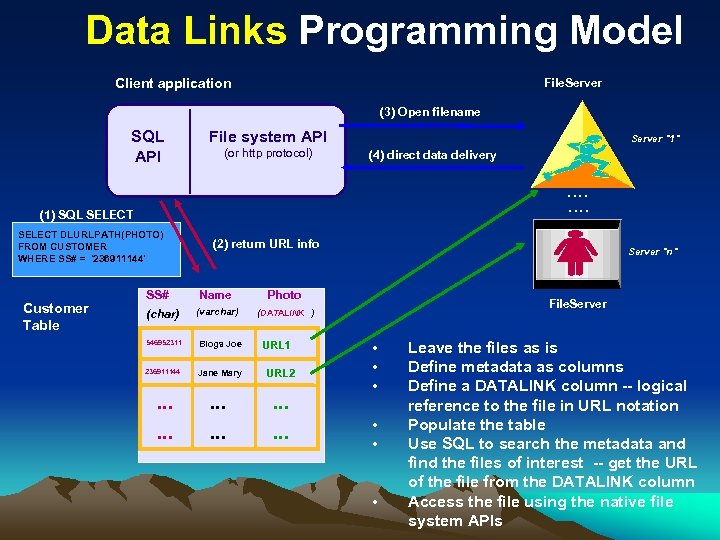
Data Links Programming Model Client application File. Server (3) Open filename SQL API File system API (or http protocol) Server "1" (4) direct data delivery . . . . (1) SQL SELECT DLURLPATH(PHOTO) FROM CUSTOMER WHERE SS# = '236911144' Customer Table SS# (char) (2) return URL info Name Photo (varchar) (DATALINK ) 546952311 Blogs Joe 236911144 Jane Mary URL 2 . . . . Server "n" URL 1 File. Server • • • Leave the files as is Define metadata as columns Define a DATALINK column -- logical reference to the file in URL notation Populate the table Use SQL to search the metadata and find the files of interest -- get the URL of the file from the DATALINK column Access the file using the native file system APIs
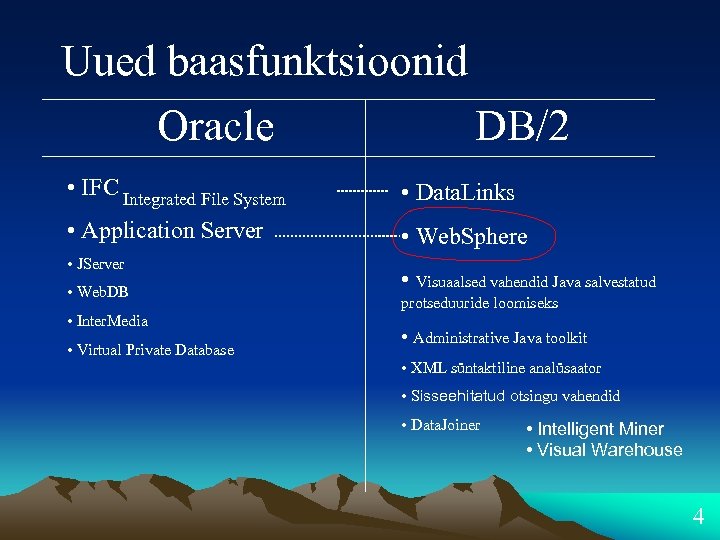
Uued baasfunktsioonid Oracle DB/2 • IFC Integrated File System • Data. Links • Application Server • Web. Sphere • JServer • Web. DB • Inter. Media • Virtual Private Database • Visuaalsed vahendid Java salvestatud protseduuride loomiseks • Administrative Java toolkit • XML süntaktiline analüsaator • Sisseehitatud otsingu vahendid • Data. Joiner • Intelligent Miner • Visual Warehouse 4
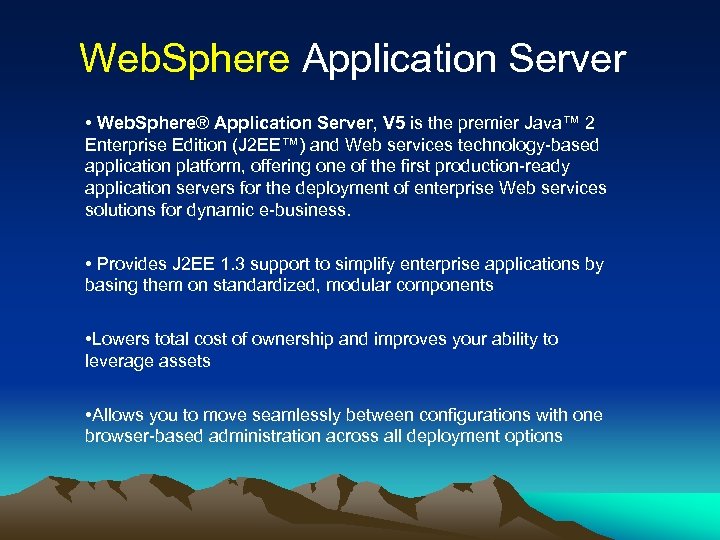
Web. Sphere Application Server • Web. Sphere® Application Server, V 5 is the premier Java™ 2 Enterprise Edition (J 2 EE™) and Web services technology-based application platform, offering one of the first production-ready application servers for the deployment of enterprise Web services solutions for dynamic e-business. • Provides J 2 EE 1. 3 support to simplify enterprise applications by basing them on standardized, modular components • Lowers total cost of ownership and improves your ability to leverage assets • Allows you to move seamlessly between configurations with one browser-based administration across all deployment options
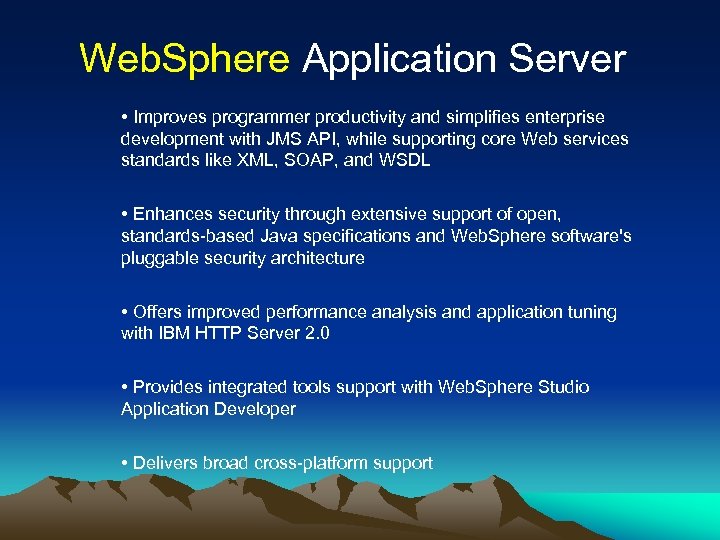
Web. Sphere Application Server • Improves programmer productivity and simplifies enterprise development with JMS API, while supporting core Web services standards like XML, SOAP, and WSDL • Enhances security through extensive support of open, standards-based Java specifications and Web. Sphere software's pluggable security architecture • Offers improved performance analysis and application tuning with IBM HTTP Server 2. 0 • Provides integrated tools support with Web. Sphere Studio Application Developer • Delivers broad cross-platform support
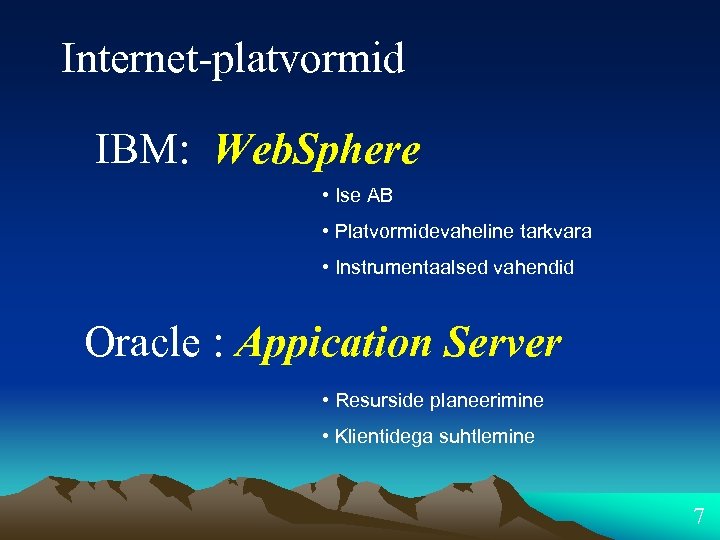
Internet-platvormid IBM: Web. Sphere • Ise AB • Platvormidevaheline tarkvara • Instrumentaalsed vahendid Oracle : Appication Server • Resurside planeerimine • Klientidega suhtlemine 7
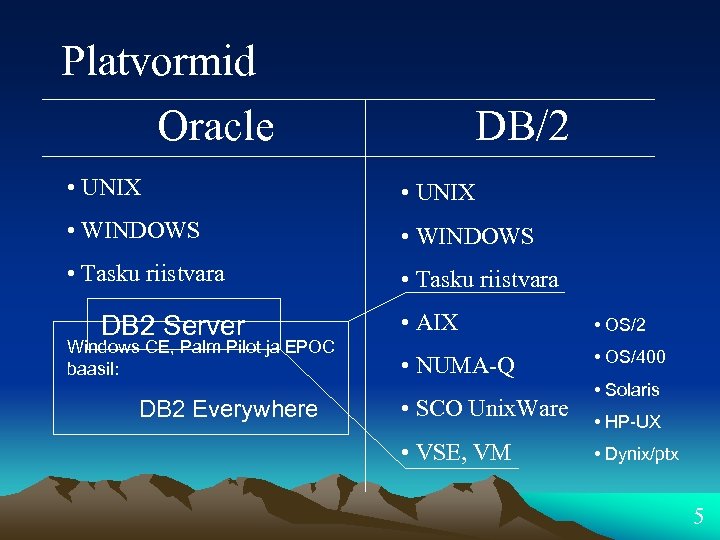
Platvormid Oracle DB/2 • UNIX • WINDOWS • Tasku riistvara DB 2 Server Windows CE, Palm Pilot ja EPOC baasil: DB 2 Everywhere • AIX • OS/2 • NUMA-Q • OS/400 • SCO Unix. Ware • VSE, VM • Solaris • HP-UX • Dynix/ptx 5

Arhitektuur IBM: DB 2 UDB eraldi iga keskonna jaoks Oracle : ühine süsteem, adapteerimine 6

Usaldatavus IBM: DB 2 UDB EEEExtended Edition Enterprise • Suured klasterid • Massilise parallelismi realiseerimine HP + Oracle: Parallel Failsafe • Klasteriseerimine 8
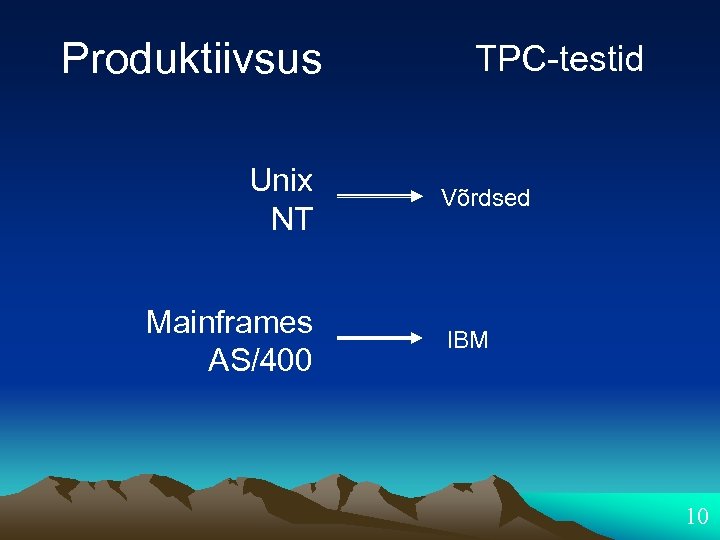
Produktiivsus Unix NT Mainframes AS/400 TPC-testid Võrdsed IBM 10
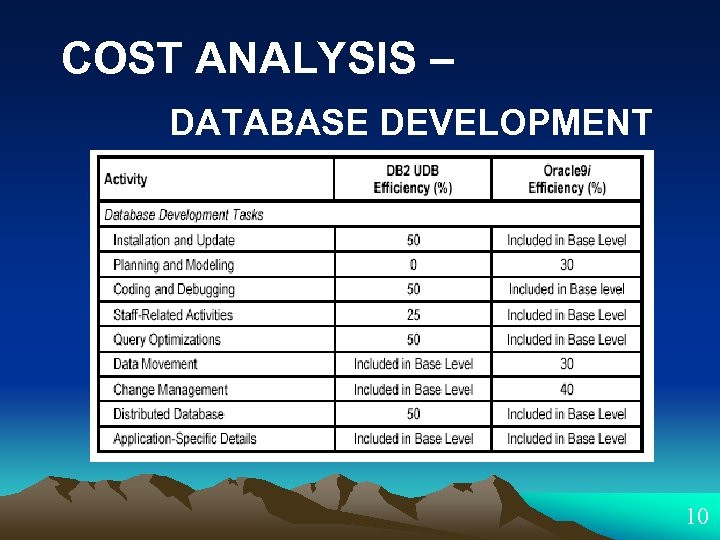
COST ANALYSIS – DATABASE DEVELOPMENT 10
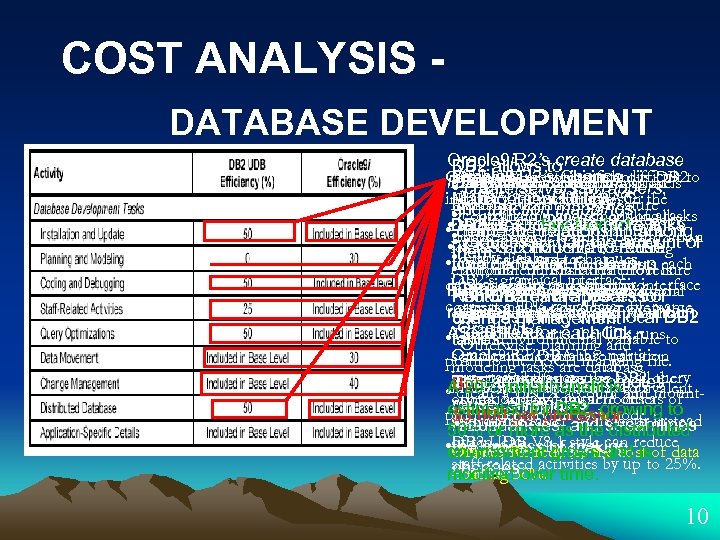
COST ANALYSIS DATABASE DEVELOPMENT Oracle 9 i. R 2’sto create database DB 2 Both: allows notoriously difficult to Oracle 9 i. R 2 mostimage with theis Oracle 9 i. R 2’s significant link syntaxis V 8. 1 ESE • Probablyservers, wrappers, DB 2’s UDB Change is DB 2 single-system attending meetings • DB 2 cost-based optimization create parallel load, Utility install. mature: advantagesetc. the UDB V 8. 1’s fast load, in Installing Feature Management Database Partitioning. RAC: morefunction mappings and • Coding and management of all centralized Debugging category, coordinating and scheduling tasks DB 2: raw tofast loader!toamong • requires a bitrelationshipfiles requires devices for all comore • nodes along more work links define the createof • create complete settheoptimization more the newhalf • where conducive to reuse. reduces amount • locate data in its. Development of is less by shared-nothing them Table techniques, • create an comprehensive lists each Copy ASCII filecleanup strategies and to that • • Center’s installation effort is time dedicated environment, this extra procedure automated DB 2’s graphical interface: interface database aobjectandsingle-partition the • functionalityin Oracle 9 i. R 2 of Furthermore, therange of special not required andsuperior to cover broader Center Non-DB 2 data appears • Data Warehouse process automates a a corresponding however. overthan requires level of automation name environment, raw were local DB 2 situations, they device -give it asto create and maintain greater 50% advantage file users if change management Oracle 9 i. R 2. each CD, runs ASCII environmental variable Oracle 9 i. R 2 • The an files for the link. to set DBA planning and tables. inserts Otherwise, Oracle 9 i. R 2: DBA mapping setup onthe database partition - guides one point to the ASCII through a file. modeling tasks are database server, and then copies DB 2 query insequence of steps. the to all the certain instances This architecture promotes But: initial benefit is • Transportable hence, and Acreate a UNIX account equivalent 20% independent and. Tablespaces mount • others, adding complete orders of operation can logical nodes as reuse, DBMSs. estimated for DB 2, growing to for botheliminates point directory on– one node instead each hour $3, 000 per appropriate. processor magnitude faster and streamlines redundancies, the distributed 50% or more as of ten, etc. all DB 2 process nodes can • Oracle 9 i. R 2 V 8. 1 style andreduce replicate to grows the UDB reduces the cost environment of making isof data staff related activities by up to 25%. changes. -loading over modified 30%. time. 10
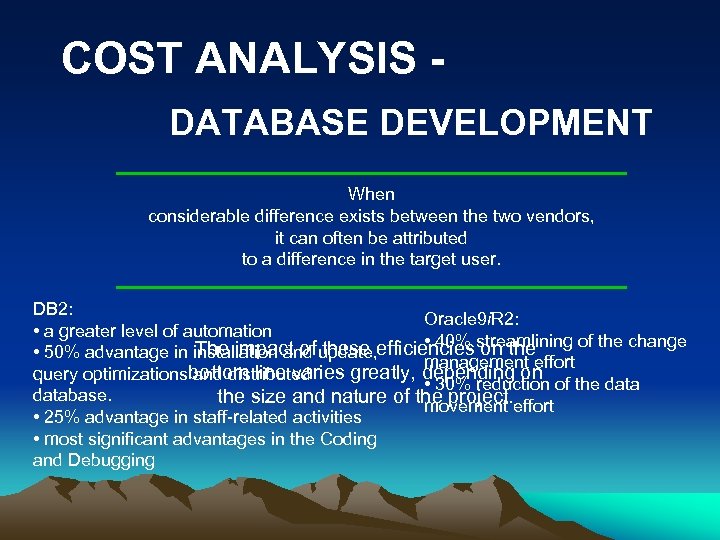
COST ANALYSIS DATABASE DEVELOPMENT When considerable difference exists between the two vendors, it can often be attributed to a difference in the target user. DB 2: Oracle 9 i. R 2: • a greater level of automation • 40% streamlining of the change The impact of these • 50% advantage in installation and update, efficiencies on the management effort query optimizations bottom line varies greatly, depending on and distributed • 30% reduction of the database. the size and nature of the project. effort movement • 25% advantage in staff-related activities • most significant advantages in the Coding and Debugging
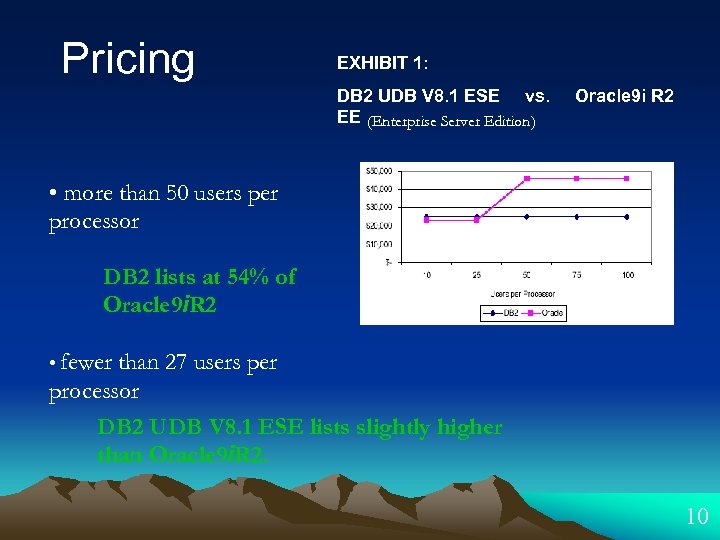
Pricing EXHIBIT 1: DB 2 UDB V 8. 1 ESE vs. EE (Enterprise Server Edition) Oracle 9 i R 2 • more than 50 users per processor DB 2 lists at 54% of Oracle 9 i. R 2 • fewer than 27 users per processor DB 2 UDB V 8. 1 ESE lists slightly higher than Oracle 9 i. R 2. 10
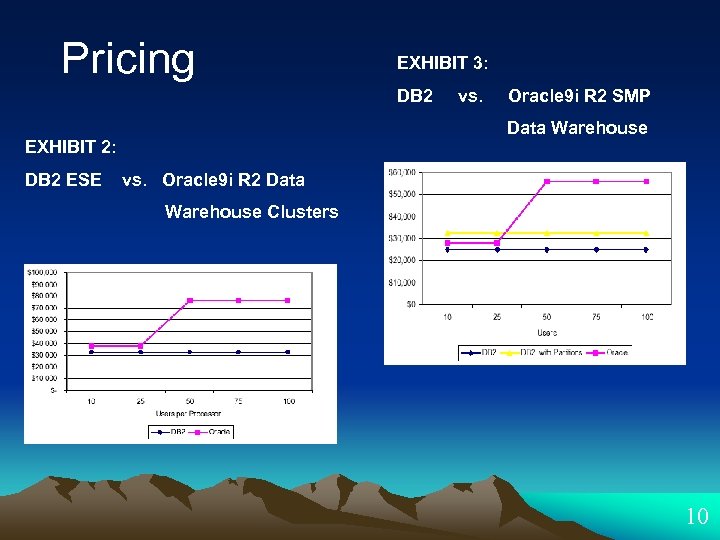
Pricing EXHIBIT 3: DB 2 Oracle 9 i R 2 SMP Data Warehouse EXHIBIT 2: DB 2 ESE vs. Oracle 9 i R 2 Data Warehouse Clusters 10
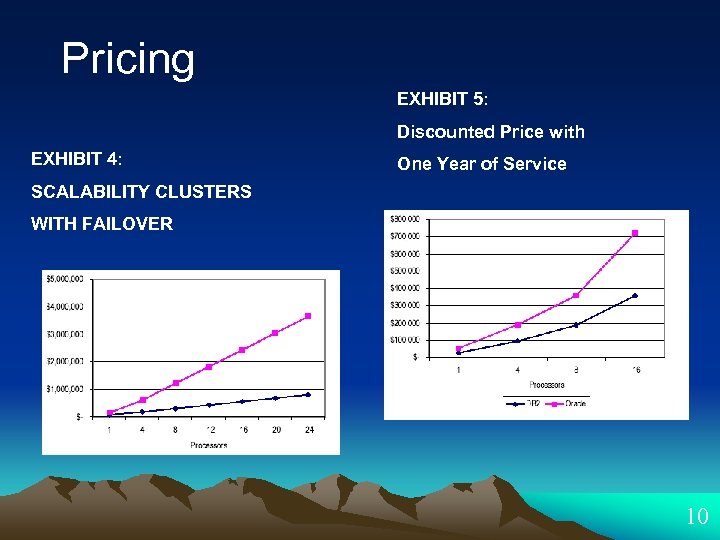
Pricing EXHIBIT 5: Discounted Price with EXHIBIT 4: One Year of Service SCALABILITY CLUSTERS WITH FAILOVER 10

Kokkuvõte While the two products provide functionally equivalent technologies, they vary significantly in total cost

Kokkuvõte Although the weights of these expense categories may vary by customer environments and applications, DB 2’s advantages suggest that it is the more economical choice over a five-year period for almost all scenarios.

Kasutatud linke: 1. http: //www-3. ibm. com/software/data/db 2/udb/ 2. http: //www. almaden. ibm. com/cs/datalinks/ 3. http: //www. citforum. ru/seminars/cbd 2001/day_1_1_ibm. shtml 10
0ef53841b3fae924a4f419fe7d799991.ppt