dde6d0f08510a86ecfcd0e4a084e41ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

IBM DB 2 Data Analytics Accelerator Technology Exploration - User Group Road Show - Detroit Columbus Cincinnati - April 08 09 10 & Sturbridge June 19 © 2014 IBM Corporation 1
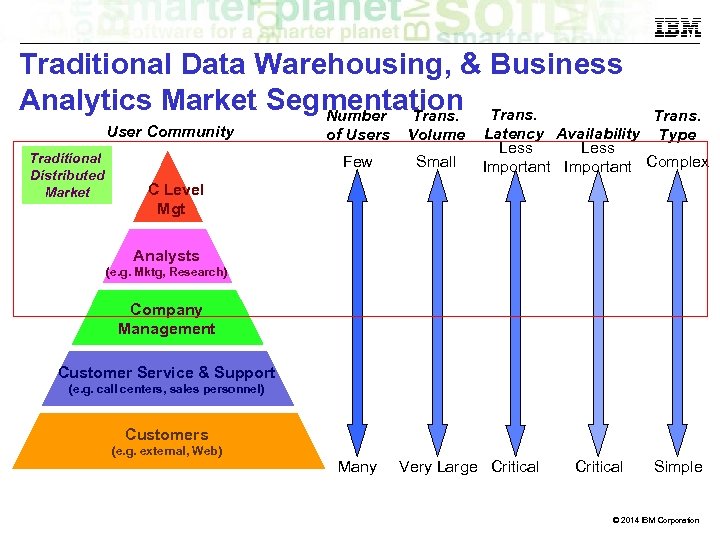
Traditional Data Warehousing, & Business Analytics Market Segmentation Trans. Number Trans. User Community Traditional Distributed Market of Users Volume Few Small Trans. Latency Availability Type Less Important Complex C Level Mgt Analysts (e. g. Mktg, Research) Company Management Customer Service & Support (e. g. call centers, sales personnel) Customers (e. g. external, Web) Many Very Large Critical Simple © 2014 IBM Corporation
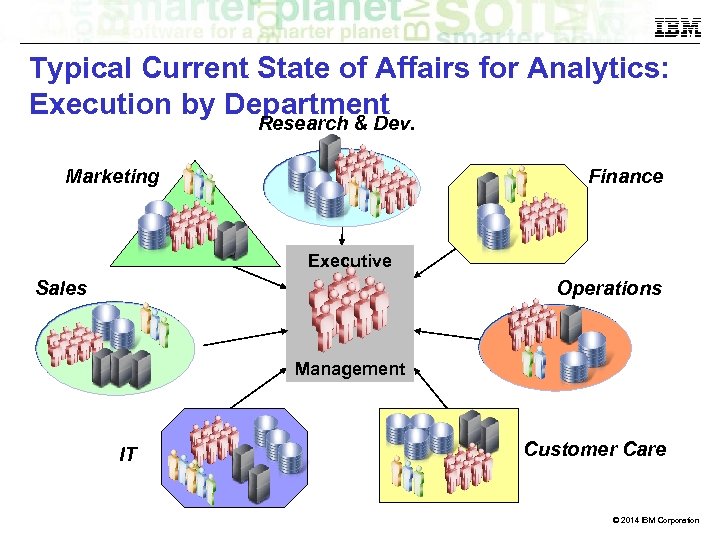
Typical Current State of Affairs for Analytics: Execution by Department Research & Dev. Marketing Finance Executive Sales Operations Finance Management IT 3 Customer Care © 2014 IBM Corporation
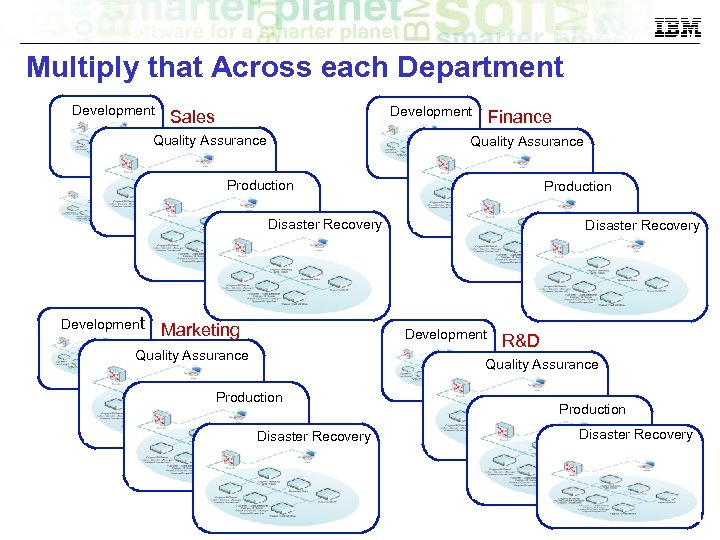
Multiply that Across each Department Development Sales Quality Assurance Finance Quality Assurance Production Disaster Recovery Development Marketing Disaster Recovery Development Quality Assurance R&D Quality Assurance Production Disaster Recovery © 2014 IBM Corporation
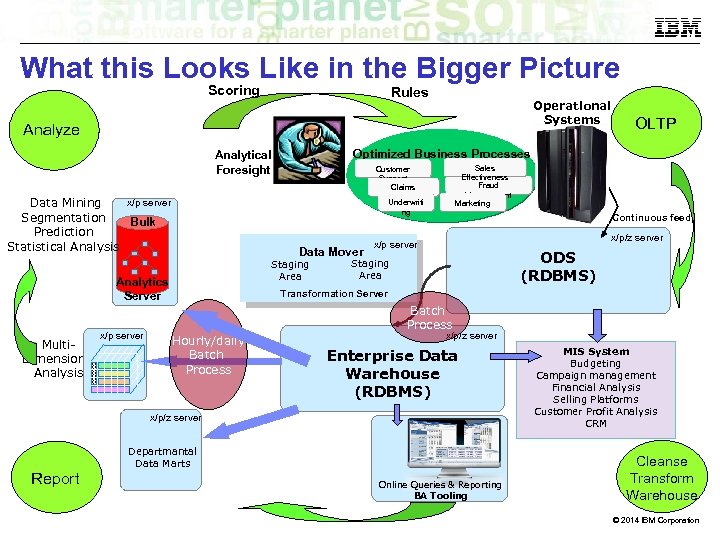
What this Looks Like in the Bigger Picture Scoring Rules Operational Systems Analyze Optimized Business Processes Analytical Foresight x/p server Data Mining Segmentation Bulk Prediction Statistical Analysis Multi. Dimensional Analysis x/p server Sales Effectiveness Fraud Management Marketing Customer Support Claims Processing Underwriti ng Data Mover Staging Area Analytics Server Continuous feed x/p/z server x/p server ODS (RDBMS) Staging Area Transformation Server Batch Process Hourly/daily Batch Process x/p/z server Enterprise Data Warehouse (RDBMS) x/p/z server Report OLTP Departmantal Data Marts Online Queries & Reporting BA Tooling MIS System Budgeting Campaign management Financial Analysis Selling Platforms Customer Profit Analysis CRM Cleanse Transform Warehouse © 2014 IBM Corporation

World’s Best Companies Run DB 2 for z/OS and System z Undisputed leader in total system availability, scalability, security and reliability Availability Zero downtime - maintenance and upgrades without service disruption. Hyperswap for storage availability and GDPS for unmatched disaster recovery Security Highest protection of business critical data and applications on Evaluation Assurance Level 5 (Common Criteria Security Certification) Scalability Unmatched Near-linear scalability through hardware-based System z Coupling Facility for DB 2 data sharing Performance CPU reductions out-of-the-box Integration Management integration, multi-platform integration and stack integration Efficiency Reduced infrastructure complexity through consolidation, automation and virtualization. Savings on software and environmental costs, reduce labor, energy and developmental costs © 2014 IBM Corporation
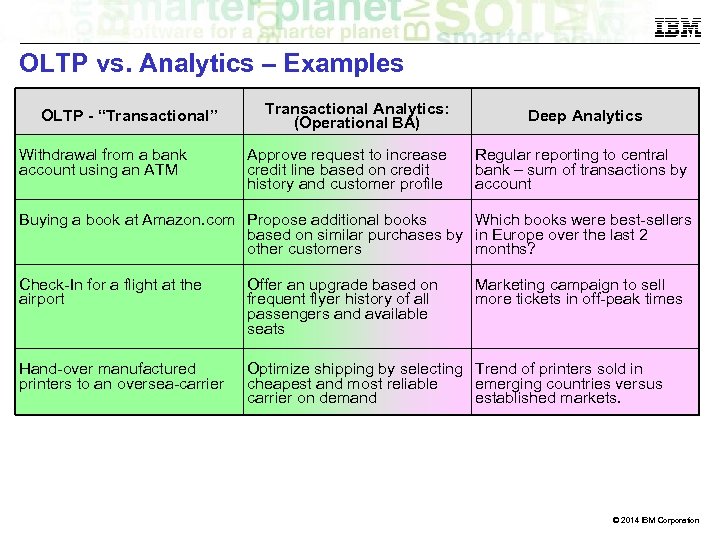
OLTP vs. Analytics – Examples OLTP - “Transactional” Withdrawal from a bank account using an ATM Transactional Analytics: (Operational BA) Approve request to increase credit line based on credit history and customer profile Deep Analytics Regular reporting to central bank – sum of transactions by account Buying a book at Amazon. com Propose additional books Which books were best-sellers based on similar purchases by in Europe over the last 2 other customers months? Check-In for a flight at the airport Offer an upgrade based on frequent flyer history of all passengers and available seats Marketing campaign to sell more tickets in off-peak times Hand-over manufactured printers to an oversea-carrier Optimize shipping by selecting Trend of printers sold in cheapest and most reliable emerging countries versus carrier on demand established markets. © 2014 IBM Corporation
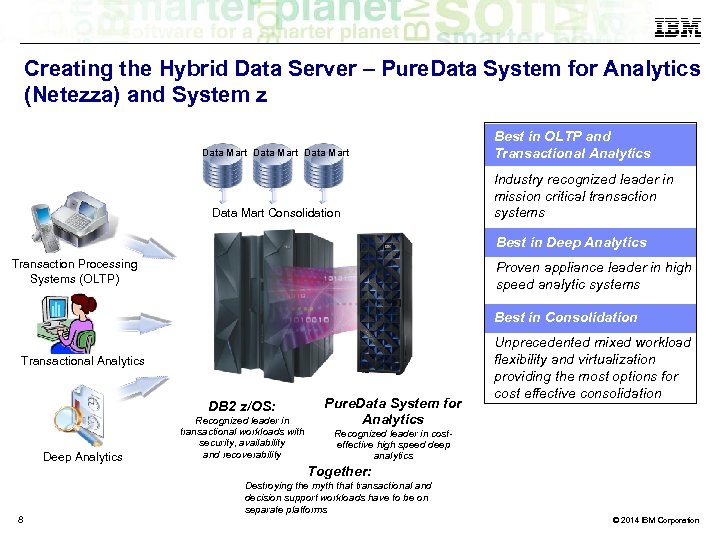
Creating the Hybrid Data Server – Pure. Data System for Analytics (Netezza) and System z Data Mart Consolidation Best in OLTP and Transactional Analytics Industry recognized leader in mission critical transaction systems Best in Deep Analytics Transaction Processing Systems (OLTP) Proven appliance leader in high speed analytic systems Best in Consolidation Transactional Analytics DB 2 z/OS: Deep Analytics 8 Recognized leader in transactional workloads with security, availability and recoverability Pure. Data System for Analytics Unprecedented mixed workload flexibility and virtualization providing the most options for cost effective consolidation Recognized leader in costeffective high speed deep analytics Together: Destroying the myth that transactional and decision support workloads have to be on separate platforms © 2014 IBM Corporation
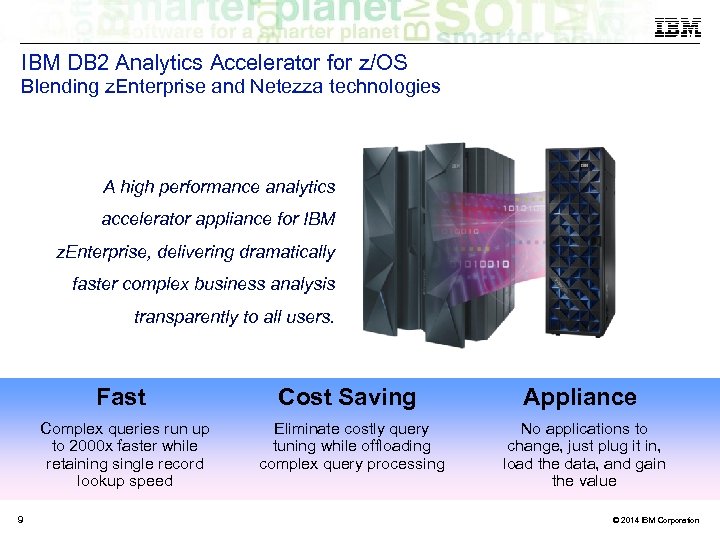
IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator for z/OS Blending z. Enterprise and Netezza technologies A high performance analytics accelerator appliance for IBM z. Enterprise, delivering dramatically faster complex business analysis transparently to all users. Fast Appliance Complex queries run up to 2000 x faster while retaining single record lookup speed 9 Cost Saving Eliminate costly query tuning while offloading complex query processing No applications to change, just plug it in, load the data, and gain the value © 2014 IBM Corporation

IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator for z/OS What is it? What is the value? What is it? The IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator is a dedicated workload optimized, appliance add-on to a DB 2 for z/OS environment that services long-running, complex queries. z Enterprise z 196, z 114, EC 12, BC 12 OLTP and Transactional Analytics IDAA Deep Analytics Breakthrough technology enabling new opportunities Extreme performance for complex analytics (aka Train of Thought Analysis) Improve price/performance for analytic workloads Minimize the need to create data marts for performance DB 2 for z/OS Transparent to DB 2 applications and users Highly secure environment for sensitive data analysis Versions Supported IDAA V 2 - DB 2 for z/OS V 9 & V 10 IDAA V 3 - DB 2 for z/OS V 10 & V 11 IDAA V 4 (GA 11/29) - DB 2 for z/OS V 10 & V 11 10 © 2014 IBM Corporation
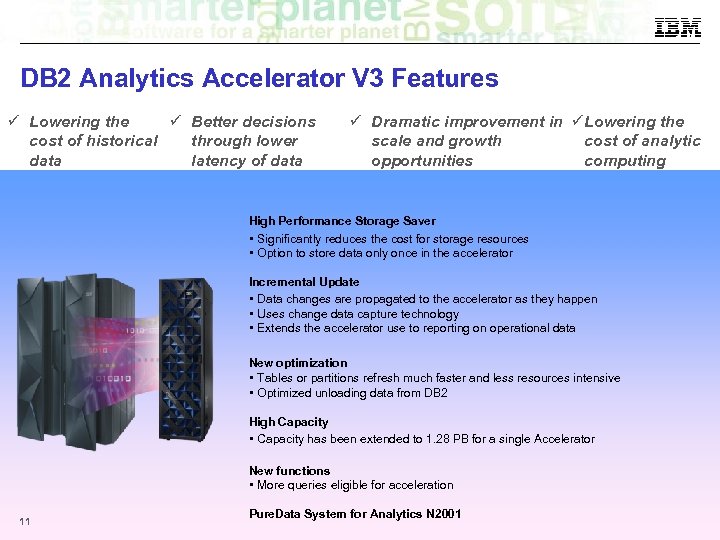
DB 2 Analytics Accelerator V 3 Features Lowering the Better decisions cost of historical through lower data latency of data Dramatic improvement in Lowering the scale and growth cost of analytic opportunities computing High Performance Storage Saver • Significantly reduces the cost for storage resources • Option to store data only once in the accelerator Incremental Update • Data changes are propagated to the accelerator as they happen • Uses change data capture technology • Extends the accelerator use to reporting on operational data New optimization • Tables or partitions refresh much faster and less resources intensive • Optimized unloading data from DB 2 High Capacity • Capacity has been extended to 1. 28 PB for a single Accelerator New functions • More queries eligible for acceleration 11 Pure. Data System for Analytics N 2001 © 2014 IBM Corporation
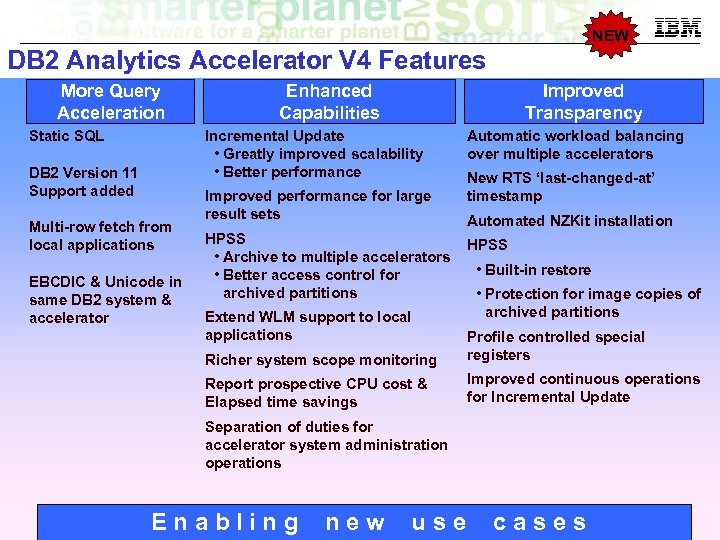
NEW DB 2 Analytics Accelerator V 4 Features More Query Acceleration Static SQL Enhanced Capabilities Improved Transparency Incremental Update • Greatly improved scalability • Better performance DB 2 Version 11 Support added Multi-row fetch from local applications EBCDIC & Unicode in same DB 2 system & accelerator Improved performance for large result sets HPSS • Archive to multiple accelerators • Better access control for archived partitions Extend WLM support to local applications Automatic workload balancing over multiple accelerators New RTS ‘last-changed-at’ timestamp Automated NZKit installation HPSS • Built-in restore • Protection for image copies of archived partitions Richer system scope monitoring Profile controlled special registers Report prospective CPU cost & Elapsed time savings Improved continuous operations for Incremental Update Separation of duties for accelerator system administration operations Enabling new use cases © 2014 IBM Corporation
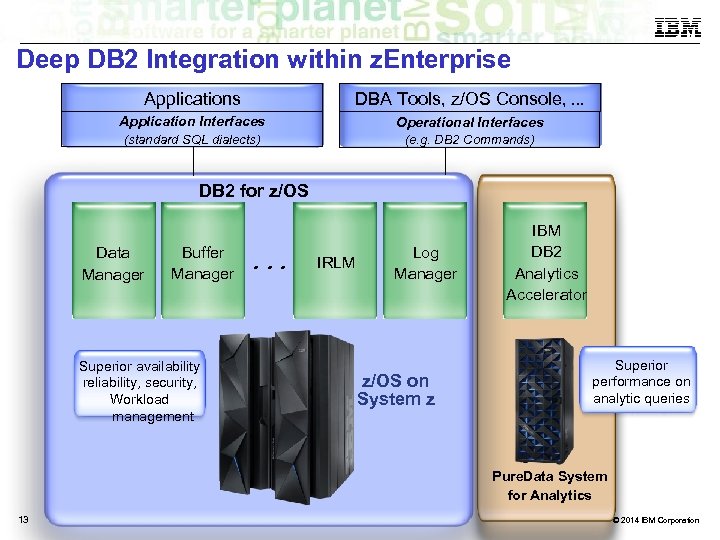
Deep DB 2 Integration within z. Enterprise Applications DBA Tools, z/OS Console, . . . Application Interfaces Operational Interfaces (standard SQL dialects) (e. g. DB 2 Commands) DB 2 for z/OS Data Manager Buffer Manager Superior availability reliability, security, Workload management . . . IRLM Log Manager z/OS on System z IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Superior performance on analytic queries Pure. Data System for Analytics 13 © 2014 IBM Corporation
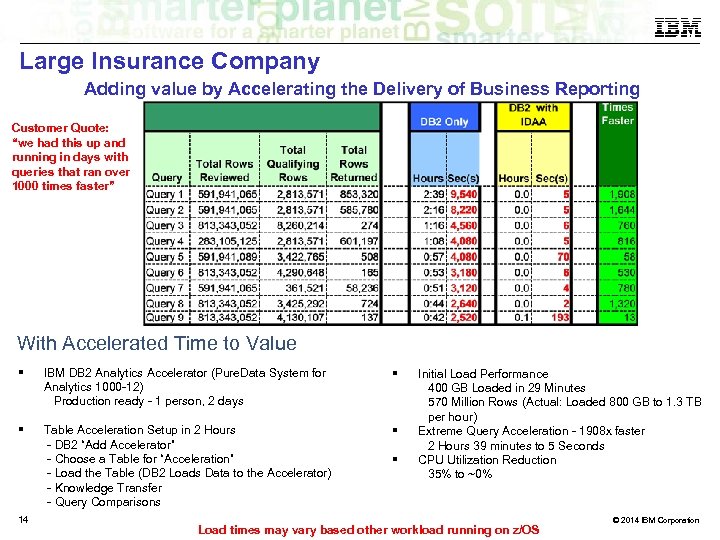
Large Insurance Company Adding value by Accelerating the Delivery of Business Reporting Customer Quote: “we had this up and running in days with queries that ran over 1000 times faster” With Accelerated Time to Value IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator (Pure. Data System for Analytics 1000 -12) Production ready - 1 person, 2 days Table Acceleration Setup in 2 Hours - DB 2 “Add Accelerator” - Choose a Table for “Acceleration” - Load the Table (DB 2 Loads Data to the Accelerator) - Knowledge Transfer - Query Comparisons 14 Initial Load Performance 400 GB Loaded in 29 Minutes 570 Million Rows (Actual: Loaded 800 GB to 1. 3 TB per hour) Extreme Query Acceleration - 1908 x faster 2 Hours 39 minutes to 5 Seconds CPU Utilization Reduction 35% to ~0% Load times may vary based other workload running on z/OS © 2014 IBM Corporation
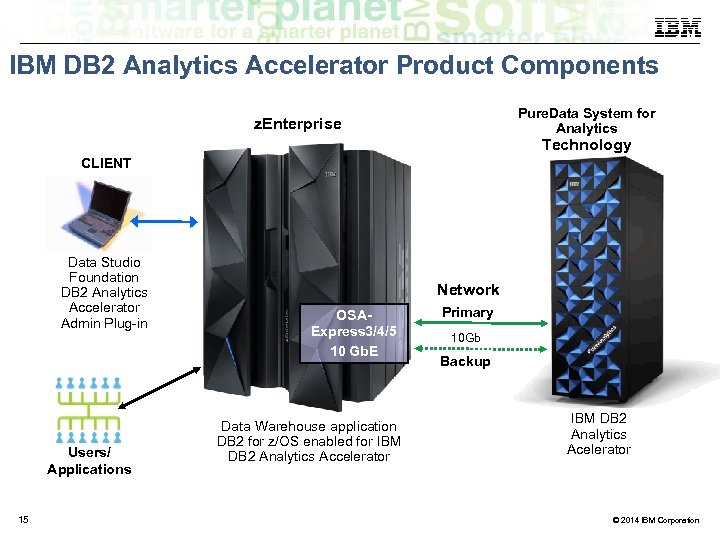
IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Product Components Pure. Data System for Analytics z. Enterprise Technology CLIENT Data Studio Foundation DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Admin Plug-in Users/ Applications 15 Network OSAExpress 3/4/5 10 Gb. E Data Warehouse application DB 2 for z/OS enabled for IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Primary 10 Gb Backup IBM DB 2 Analytics Acelerator © 2014 IBM Corporation
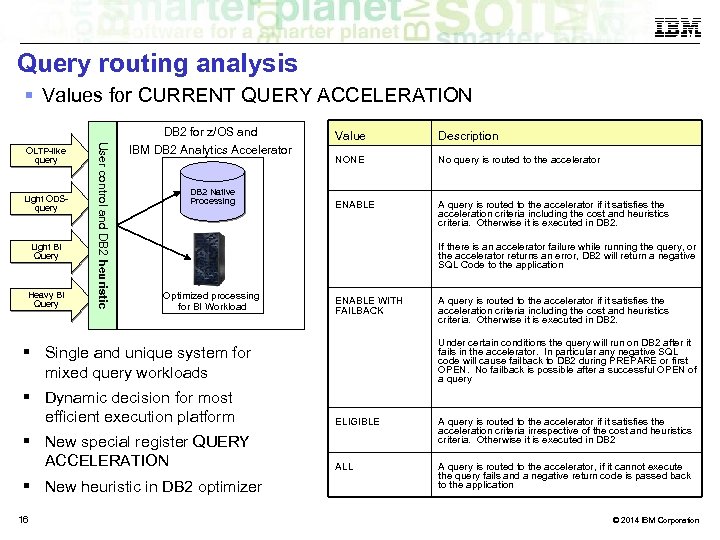
Query routing analysis Values for CURRENT QUERY ACCELERATION DB 2 for z/OS and Light ODSquery Light BI Query Heavy BI Query User control and DB 2 heuristic OLTP-like query IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator DB 2 Native Processing Value Description NONE No query is routed to the accelerator ENABLE A query is routed to the accelerator if it satisfies the acceleration criteria including the cost and heuristics criteria. Otherwise it is executed in DB 2. If there is an accelerator failure while running the query, or the accelerator returns an error, DB 2 will return a negative SQL Code to the application Optimized processing for BI Workload ENABLE WITH FAILBACK A query is routed to the accelerator if it satisfies the acceleration criteria including the cost and heuristics criteria. Otherwise it is executed in DB 2. Under certain conditions the query will run on DB 2 after it fails in the accelerator. In particular any negative SQL code will cause failback to DB 2 during PREPARE or first OPEN. No failback is possible after a successful OPEN of a query Single and unique system for mixed query workloads Dynamic decision for most efficient execution platform ELIGIBLE New special register QUERY ACCELERATION A query is routed to the accelerator if it satisfies the acceleration criteria irrespective of the cost and heuristics criteria. Otherwise it is executed in DB 2 ALL A query is routed to the accelerator, if it cannot execute the query fails and a negative return code is passed back to the application New heuristic in DB 2 optimizer 16 © 2014 IBM Corporation

Routing Criteria A query can be routed to Accelerator if is one of these types: The entire query can be accelerated, i. e. the unit of acceleration is a whole query – Individual query blocks are no longer units of acceleration – The whole query will either run in DB 2 or in the accelerator The associated cursor is not defined as a scrollable or a rowset cursor The query is defined as read-only The query is dynamic (V 4 will support static) The query is a SELECT statement. The private protocol is not in effect. Routing to Accelerator is considered more efficient for performance than to execute the query in DB 2 mainline – The decision is based on some heuristic rules 17 © 2014 IBM Corporation

Heuristic Routing Criteria – not just based on “elapsed time” … DB 2 Optimizer uses a set of rules to determine whether a given query is better off being executed in DB 2 core engine or routed to the accelerator, such as: – In general, typical OLTP access path patterns are not routed to the accelerator e. g. Equal unique access, One fetch access – If none of these: WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, aggregate functions is specified (i. e. all rows are to be returned), the query is not routed – Threshold specified by the DB 2 Profile (1) mechanism: • If all the tables referred in the query are “small”, the query is not routed ACCEL_TABLE_THRESHOLD determines total table cardinality for a query The default value is 1, 000 • If a “large” result set is expected, the query is not routed ACCEL_RESULTSIZE_THRESHOLD (number of rows) determines what is a “large” result set. The default value is -1, which means that this check is ignored • If estimated total cost for a query is treated as “short running”, the query is not routed ACCEL_TOTALCOST_THRESHOLD determines estimated total cost for a query The default value is 5, 000 (value is in milliseconds = 5 seconds) (1) http: //publib. boulder. ibm. com/infocenter/dzichelp/v 2 r 2/index. jsp? topic=/com. ibm. db 2 z 10. doc. perf/src/tpc/db 2 z_profiles. htm 18 • Recommendation: Use default values. Change only after rigorous testing! © 2014 IBM Corporation

Query Off-load Applicability Accelerator is based on Netezza which supports rich set of SQL and data types – BI tools such as Cognos has run on Netezza for years and will run on Accelerator as well Due to very large number of query types and SQL functions not all of them could be processed in V 3. Key restrictions include: – No static SQL (Lifted in V 4) – Not all DB 2 functions, No Mathematical functions such as SIN, COS, TAN. No advanced string functions such as HEX, POSITION, LOCATE, LEFT, OVERLAY No advanced OLAP functions such as RANK, ROLLUP, CUBE – No User Defined Functions – No correlated table expressions or recursive correlated table expressions – No correlated subquery in the SELECT list – Not UTF-16 and MIXED/DBCS EBCDIC – No multiple encoding schemes in the same statement – Not all DB 2 special registers: CURRENT PATH, SERVER, SQLID, SCHEMA, APPLICATION ENCODING SCHEME – Not all DB 2 data types: LOBs, ROWID, XML, DECFLOAT, BINARY None of these restrictions is a design problem, IBM plans to lift them in future releases based on customer feedback and needs 19 © 2014 IBM Corporation
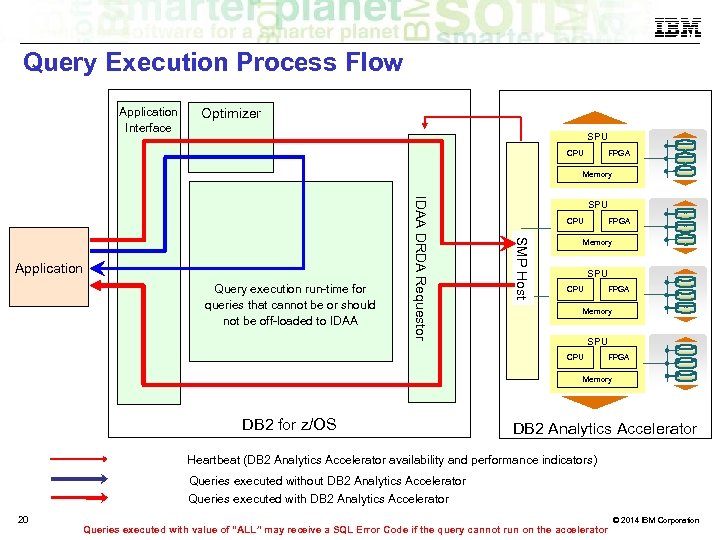
Query Execution Process Flow Application Interface Optimizer SPU CPU FPGA Memory SMP Host Query execution run-time for queries that cannot be or should not be off-loaded to IDAA DRDA Requestor Application SPU CPU FPGA Memory DB 2 for z/OS DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Heartbeat (DB 2 Analytics Accelerator availability and performance indicators) Queries executed without DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Queries executed with DB 2 Analytics Accelerator 20 Queries executed with value of “ALL” may receive a SQL Error Code if the query cannot run on the accelerator © 2014 IBM Corporation

Accelerator Administrative Stored Procedures 21 ACCEL_ADD_ACCELERATOR ACCEL_TEST_CONNECTION ACCEL_REMOVE_ACCELERATOR ACCEL_UPDATE_CREDENTIALS ACCEL_ADD_TABLES ACCEL_ALTER_TABLES ACCEL_REMOVE_TABLES ACCEL_GET_TABLES_INFO ACCEL_GET_TABLES_DETAILS ACCEL_LOAD_TABLES ACCEL_SET_TABLES_ACCELERATION ACCEL_SET_TABLES_REPLICATION ACCEL_CONTROL_ACCELERATOR ACCEL_UPDATE_SOFTWARE ACCEL_ARCHIVE_TABLES ACCEL_GET_QUERIES ACCEL_GET_QUERY_DETAILS ACCEL_GET_QUERY_EXPLAIN * For a list of the description of each stored procedure refer to the IDAA Stored Procedure Reference Manual © 2014 IBM Corporation
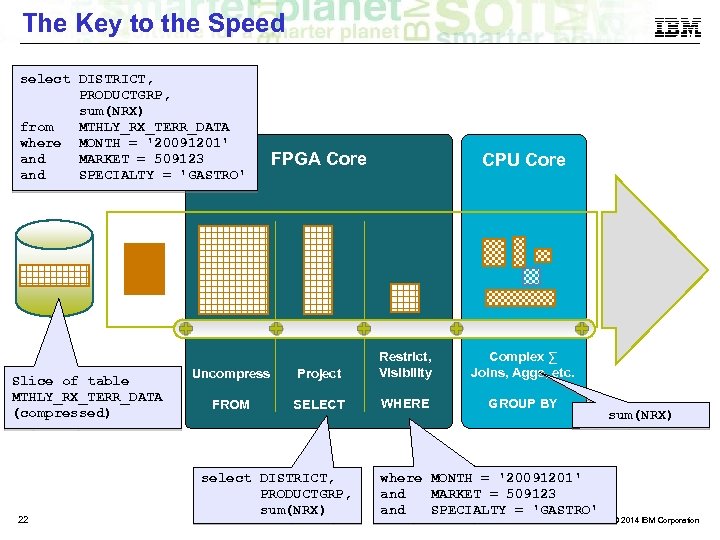
The Key to the Speed select DISTRICT, PRODUCTGRP, sum(NRX) from MTHLY_RX_TERR_DATA where MONTH = '20091201' and MARKET = 509123 and SPECIALTY = 'GASTRO' Slice of table MTHLY_RX_TERR_DATA (compressed) 22 FPGA Core CPU Core Uncompress Project Restrict, Visibility FROM SELECT WHERE select DISTRICT, PRODUCTGRP, sum(NRX) Complex ∑ Joins, Aggs, etc. GROUP BY where MONTH = '20091201' and MARKET = 509123 and SPECIALTY = 'GASTRO' sum(NRX) © 2014 IBM Corporation
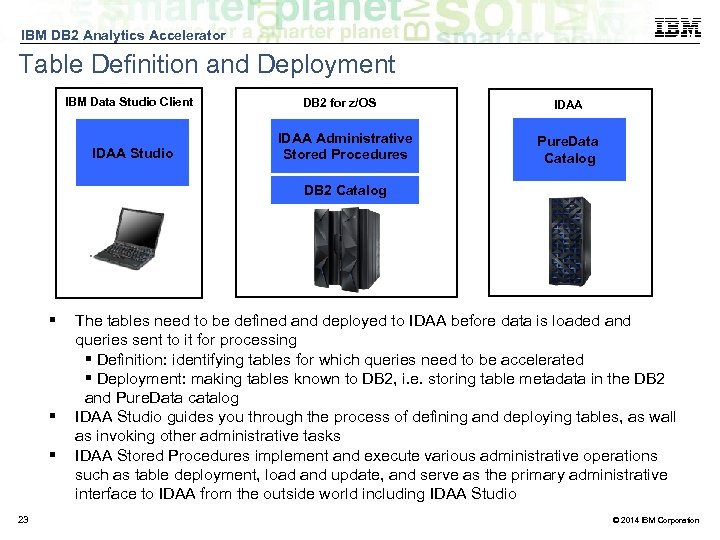
IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Table Definition and Deployment IBM Data Studio Client IDAA Studio DB 2 for z/OS IDAA Administrative Stored Procedures IDAA Pure. Data Catalog DB 2 Catalog 23 The tables need to be defined and deployed to IDAA before data is loaded and queries sent to it for processing Definition: identifying tables for which queries need to be accelerated Deployment: making tables known to DB 2, i. e. storing table metadata in the DB 2 and Pure. Data catalog IDAA Studio guides you through the process of defining and deploying tables, as wall as invoking other administrative tasks IDAA Stored Procedures implement and execute various administrative operations such as table deployment, load and update, and serve as the primary administrative interface to IDAA from the outside world including IDAA Studio © 2014 IBM Corporation
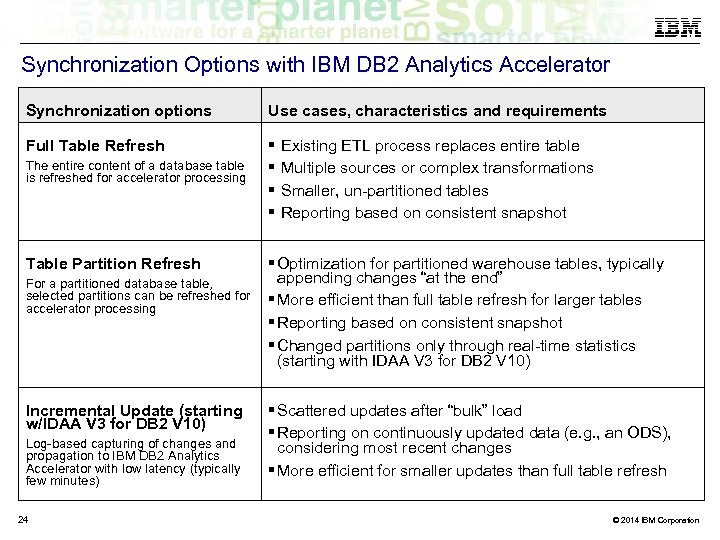
Synchronization Options with IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Synchronization options Use cases, characteristics and requirements Full Table Refresh The entire content of a database table is refreshed for accelerator processing Table Partition Refresh For a partitioned database table, selected partitions can be refreshed for accelerator processing Incremental Update (starting w/IDAA V 3 for DB 2 V 10) Log-based capturing of changes and propagation to IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator with low latency (typically few minutes) 24 Existing ETL process replaces entire table Multiple sources or complex transformations Smaller, un-partitioned tables Reporting based on consistent snapshot Optimization for partitioned warehouse tables, typically appending changes “at the end” More efficient than full table refresh for larger tables Reporting based on consistent snapshot Changed partitions only through real-time statistics (starting with IDAA V 3 for DB 2 V 10) Scattered updates after “bulk” load Reporting on continuously updated data (e. g. , an ODS), considering most recent changes More efficient for smaller updates than full table refresh © 2014 IBM Corporation
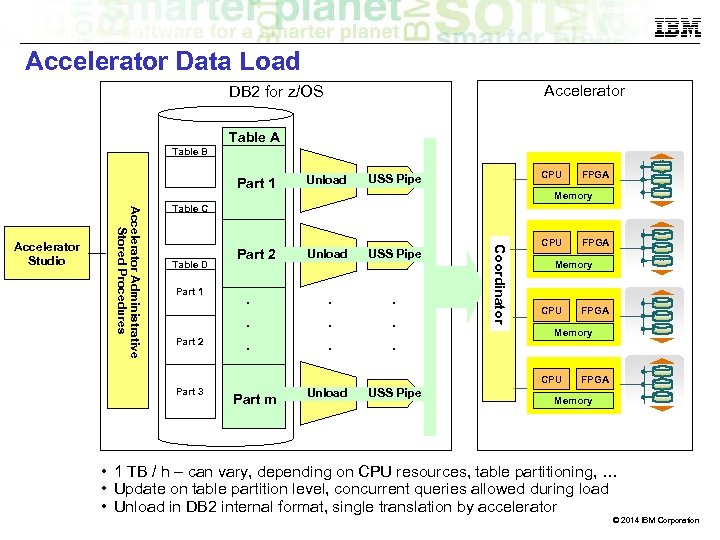
Accelerator Data Load Accelerator DB 2 for z/OS Table A Table B Unload Part 2 Unload USS Pipe . . . FPGA Memory Table C Table D Part 1 Part 2 . . . C o o r d i n a to r Accelerator Administrative Stored Procedures Accelerator Studio CPU USS Pipe Part 1 CPU Memory CPU Part m Unload USS Pipe FPGA Memory CPU Part 3 FPGA Memory • 1 TB / h – can vary, depending on CPU resources, table partitioning, … • Update on table partition level, concurrent queries allowed during load • Unload in DB 2 internal format, single translation by accelerator © 2014 IBM Corporation
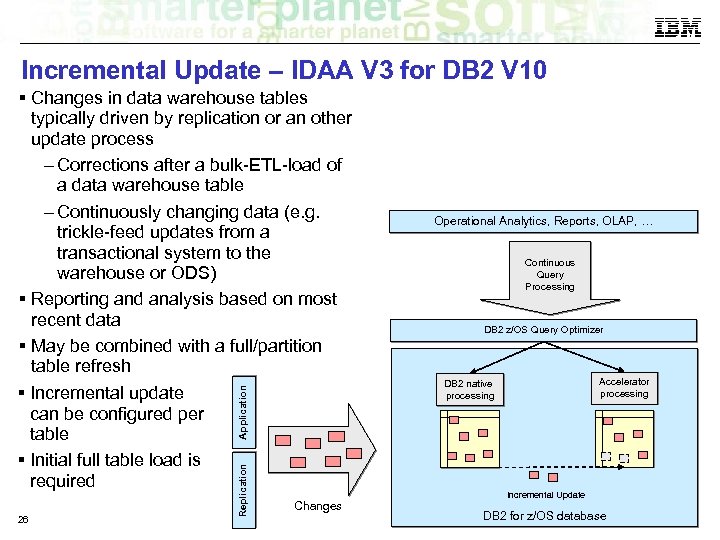
Incremental Update – IDAA V 3 for DB 2 V 10 26 Replication Application Changes in data warehouse tables typically driven by replication or an other update process – Corrections after a bulk-ETL-load of a data warehouse table – Continuously changing data (e. g. trickle-feed updates from a transactional system to the warehouse or ODS) Reporting and analysis based on most recent data May be combined with a full/partition table refresh Incremental update can be configured per table Initial full table load is required Changes Operational Analytics, Reports, OLAP, … Continuous Query Processing DB 2 z/OS Query Optimizer Accelerator processing DB 2 native processing Incremental Update DB 2 for z/OS database © 2014 IBM Corporation
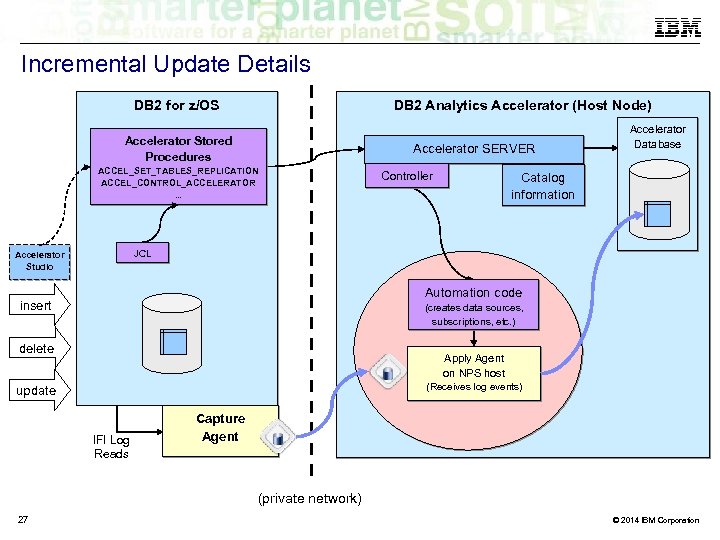
Incremental Update Details DB 2 Analytics Accelerator (Host Node) DB 2 for z/OS Accelerator Stored Procedures Accelerator SERVER ACCEL_SET_TABLES_REPLICATION ACCEL_CONTROL_ACCELERATOR. . . Controller Accelerator Database Catalog information JCL Accelerator Studio Automation code insert (creates data sources, subscriptions, etc. ) delete Apply Agent on NPS host (Receives log events) update IFI Log Reads Capture Agent (private network) 27 © 2014 IBM Corporation
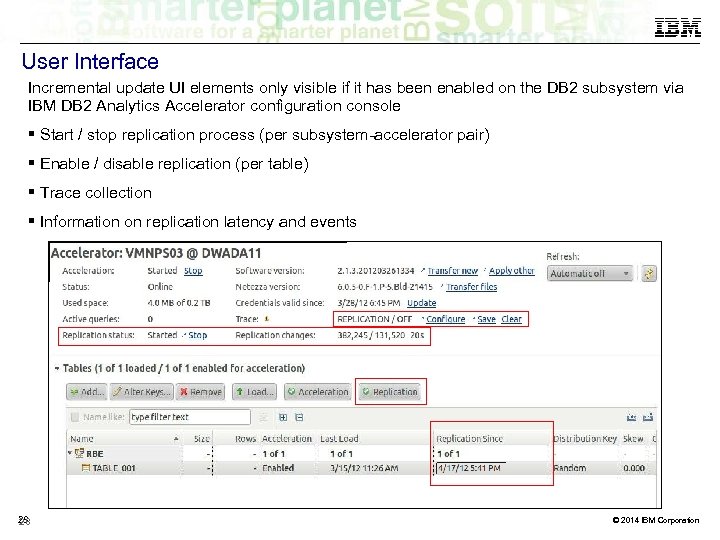
User Interface Incremental update UI elements only visible if it has been enabled on the DB 2 subsystem via IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator configuration console Start / stop replication process (per subsystem-accelerator pair) Enable / disable replication (per table) Trace collection Information on replication latency and events 28 28 © 2014 IBM Corporation
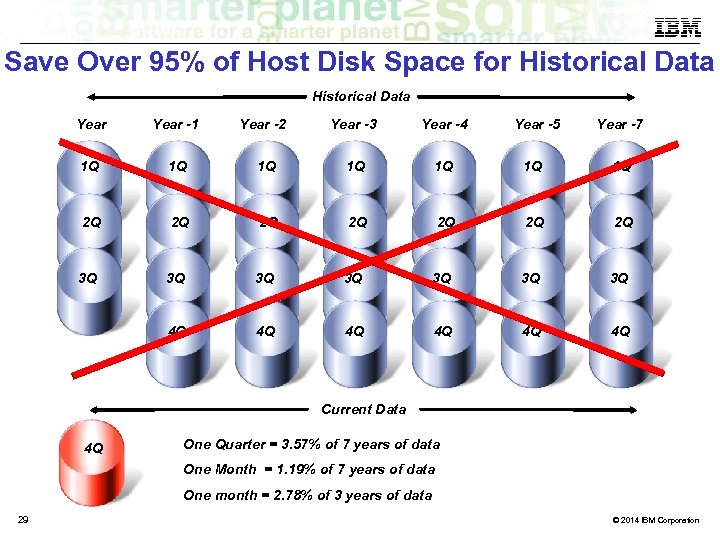
Save Over 95% of Host Disk Space for Historical Data Year -1 Year -2 Year -3 Year -4 1 Q 1 Q 2 Q 2 Q 3 Q Year -5 Year -7 3 Q 3 Q 3 Q 4 Q 4 Q 4 Q Current Data 4 Q One Quarter = 3. 57% of 7 years of data One Month = 1. 19% of 7 years of data One month = 2. 78% of 3 years of data 29 © 2014 IBM Corporation
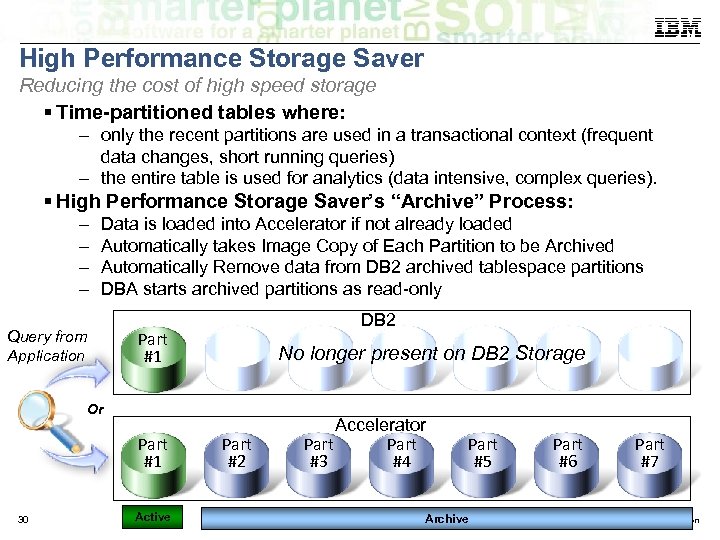
High Performance Storage Saver Reducing the cost of high speed storage Time-partitioned tables where: – only the recent partitions are used in a transactional context (frequent data changes, short running queries) – the entire table is used for analytics (data intensive, complex queries). High Performance Storage Saver’s “Archive” Process: – – Data is loaded into Accelerator if not already loaded Automatically takes Image Copy of Each Partition to be Archived Automatically Remove data from DB 2 archived tablespace partitions DBA starts archived partitions as read-only Query from Application DB 2 Part #1 No longer present on DB 2 Storage Or Part #1 30 Active Part #2 Accelerator Part #3 #4 Part #5 Archive Part #6 Part #7 © 2014 IBM Corporation
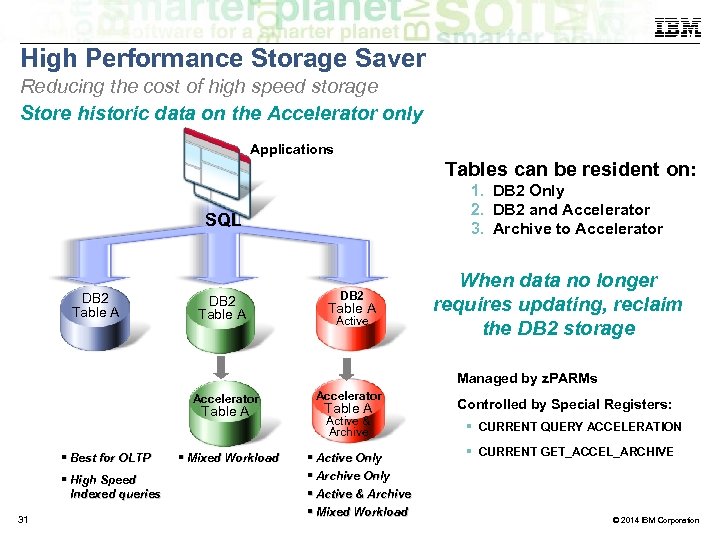
High Performance Storage Saver Reducing the cost of high speed storage Store historic data on the Accelerator only Applications Tables can be resident on: 1. DB 2 Only 2. DB 2 and Accelerator 3. Archive to Accelerator SQL DB 2 Table A Active When data no longer requires updating, reclaim the DB 2 storage Managed by z. PARMs Accelerator Table A Best for OLTP High Speed Indexed queries 31 Mixed Workload Accelerator Table A Active & Archive Active Only Archive Only Active & Archive Mixed Workload Controlled by Special Registers: CURRENT QUERY ACCELERATION CURRENT GET_ACCEL_ARCHIVE © 2014 IBM Corporation

Key Elements of the Implementation Approach • Older partitions are moved to IDAA and their data no longer exists in DB 2 • DB 2 is still solely responsible for the recovery and maintains all backups (copy images) • The most recent partitions exist in both DB 2 and IDAA • They are synchronized by existing means • Partition refresh or incremental update (replication-based propagation of changes) • Having the most recent partition in both, DB 2 and IDAA, provides IDAA-driven performance acceleration for analytical queries that access most recent partitions only • The data move process is encapsulated in a stored procedure • The stored procedure can be invoked directly or via IDAA Studio • The SQL statements do not change • The fact that some partitions have been moved to IDAA is transparent • By default, queries access only the data from the most recent partitions • The queries can be executed in DB 2 or IDAA based on the standard routing criteria • If all the data need to be accessed, one of the following mechanisms is used: • Setting a zparm which activates the 'all data' scope for the DB 2 subsystem/data sharing group. This way, none of the applications need to be changed (but this setting has global impact). • Setting a special register “CURRENT GET_ACCEL_ARCHIVE”, which allows switching between the 'all data' scope and the 'most recent data' scope at any time. This way the application can use both scopes within the same execution at choose scope at SQL statement level. 32 © 2014 IBM Corporation

Work Load Management - Usage scenarios • Workload Isolation: Ensure that the workload of one DB 2 subsystem doesn’t monopolize the resources of a shared accelerator. A development subsystem, attached to the same accelerator as a production subsystem, should not be able to drain all accelerator resources. • Query Prioritization: More important queries should be executed before and faster than less important queries that are sent from the same DB 2 subsystem against the accelerator. 33 © 2014 IBM Corporation

IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Instrumentation 34 © 2013 IBM Corporation
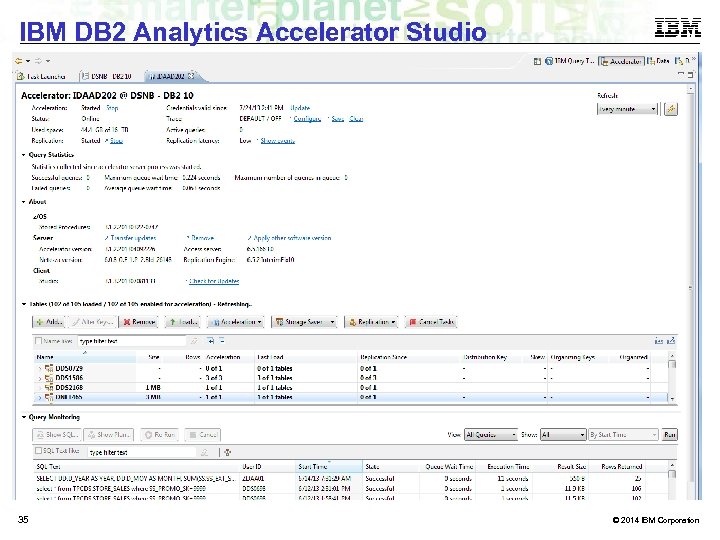
IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator Studio 35 © 2014 IBM Corporation
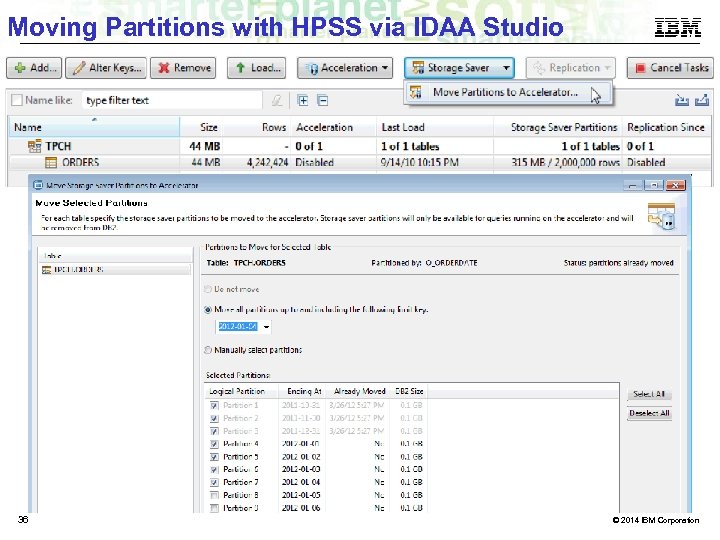
Moving Partitions with HPSS via IDAA Studio 36 © 2014 IBM Corporation
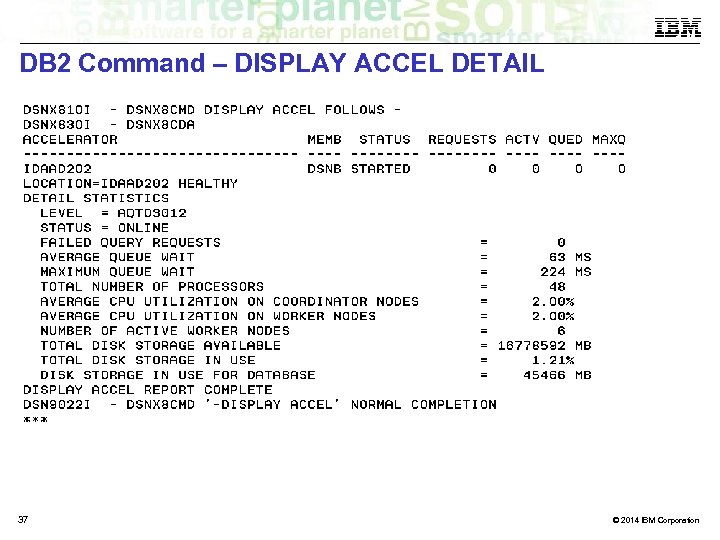
DB 2 Command – DISPLAY ACCEL DETAIL 37 © 2014 IBM Corporation
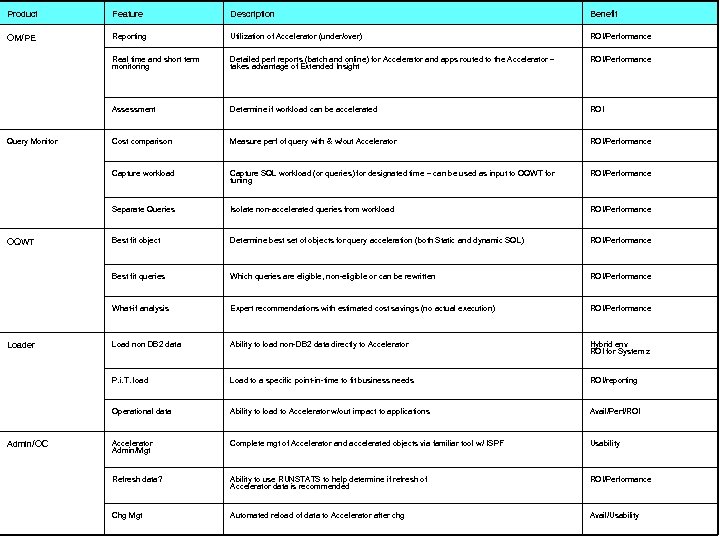
Product Feature Description Benefit OM/PE Reporting Utilization of Accelerator (under/over) ROI/Performance Real time and short term monitoring Detailed perf reports (batch and online) for Accelerator and apps routed to the Accelerator – takes advantage of Extended Insight ROI/Performance Assessment Determine if workload can be accelerated ROI Cost comparison Measure perf of query with & w/out Accelerator ROI/Performance Capture workload Capture SQL workload (or queries) for designated time – can be used as input to OQWT for tuning ROI/Performance Separate Queries Isolate non-accelerated queries from workload ROI/Performance Best fit object Determine best set of objects for query acceleration (both Static and dynamic SQL) ROI/Performance Best fit queries Which queries are eligible, non-eligible or can be rewritten ROI/Performance What-if analysis Expert recommendations with estimated cost savings (no actual execution) ROI/Performance Load non DB 2 data Ability to load non-DB 2 data directly to Accelerator Hybrid env ROI for System z P. i. T. load Load to a specific point-in-time to fit business needs ROI/reporting Operational data Ability to load to Accelerator w/out impact to applications Avail/Perf/ROI Accelerator Admin/Mgt Complete mgt of Accelerator and accelerated objects via familiar tool w/ ISPF Usability Refresh data? Ability to use RUNSTATS to help determine if refresh of Accelerator data is recommended ROI/Performance Chg Mgt Automated reload of data to Accelerator after chg Avail/Usability © 2014 IBM Corporation Query Monitor OQWT Loader Admin/OC
Product Documentation Links Information Center for IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator for z/OS V 3. 1 – http: //publib. boulder. ibm. com/infocenter/dzichelp/v 2 r 2/topic/com. ibm. datatools. aqt. doc/welcome/topics/idaa_start. html Quick Start Guide – http: //publibfp. dhe. ibm. com/epubs/pdf/h 1269820. pdf Installation Guide – http: //publibfp. dhe. ibm. com/epubs/pdf/h 1269830. pdf Stored Procedure Reference – http: //publibfp. dhe. ibm. com/epubs/pdf/h 1269840. pdf Analytics Accelerator Studio Users Guide – http: //publibfp. dhe. ibm. com/epubs/pdf/h 1269850. pdf Getting Started Guide – http: //publibfp. dhe. ibm. com/epubs/pdf/h 1269860. pdf Program Directory – http: //publibfp. dhe. ibm. com/epubs/pdf/i 1950060. pdf Redbook – Optimizing DB 2 Queries with IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator for z/OS – http: //www. redbooks. ibm. com/redpieces/abstracts/sg 248005. html? Open Redbook – Hybrid Analytics Solution using IBM DB 2 Analytics Accelerator for z/OS V 3. 1 – http: //www. redbooks. ibm. com/redpieces/abstracts/sg 248151. html? Open 39 © 2014 IBM Corporation

40 40 05/14/14 © 2014 IBM Corporation
dde6d0f08510a86ecfcd0e4a084e41ba.ppt