fda7011a7898b19998617549778c8240.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23


IAEA, 09 -13 September 2013 “Current situation in Argentina related to management of Radioactive Waste and future plans for disposal” Daniela E. Alvarez Ph D. Department of Scientific and Technical Support, Division of Radiological Safety Assessments, Nuclear Regulatory Authority
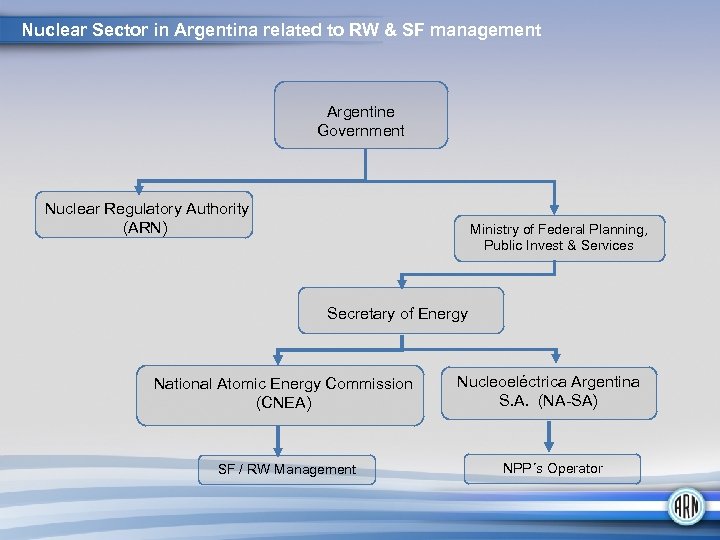
Nuclear Sector in Argentina related to RW & SF management Argentine Government Nuclear Regulatory Authority (ARN) Ministry of Federal Planning, Public Invest & Services Secretary of Energy National Atomic Energy Commission (CNEA) Nucleoeléctrica Argentina S. A. (NA-SA) SF / RW Management NPP´s Operator

Legal Framework - National Law Nº 24804 (1997) to regulate the Nuclear Activity CNEA SF and RW management responsibility + Research & Development + the National Government advisor - National Law Nº 25018 (1998) ARN to regulate and supervise nuclear activity (radiological and nuclear safety, physical protection and safeguards) to determine the Radioactive Waste Management Regime Propose National Radioactive Waste Management Program –PNGRR- and CNEA as the responsible for the compliance with a specific Strategic Plan for RW Management. - Nacional Law Nº 25279 (2001) Joint Convention on the Safety of Spent Fuel Management and on the Safety of Radioactive Waste Management
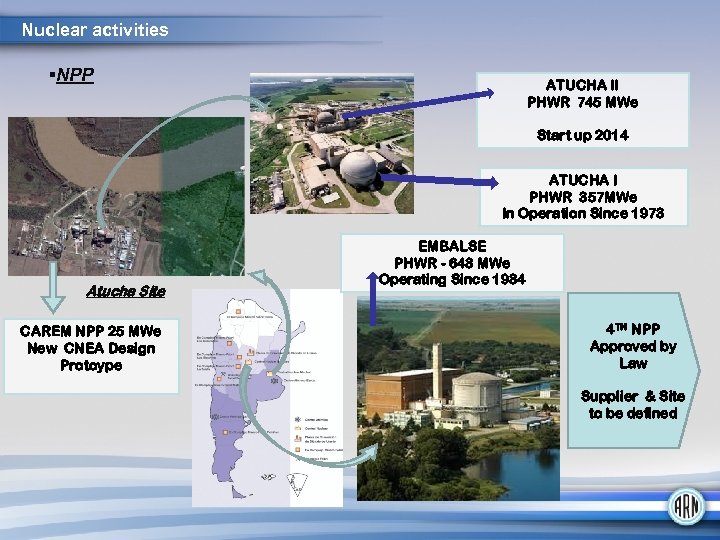
Nuclear activities NPP ATUCHA II PHWR 745 MWe Start up 2014 ATUCHA I PHWR 357 MWe In Operation Since 1973 Atucha Site CAREM NPP 25 MWe New CNEA Design Protoype EMBALSE PHWR - 648 MWe Operating Since 1984 4 TH NPP Approved by Law Supplier & Site to be defined

Nuclear activities Atomic Centres Ezeiza Atomic Center • Research Reactors • Fuel Cycle facilities • Other Nuclear Installations • Industrial & Medical Radioisotopes • Educational Institutions Bariloche Atomic Center Constituyentes Atomic Center

Nuclear activities - Argentine experience in Research Reactors: local and abroad - Radioisotopes Production: Co 60 (Industrial Use) Mo 99 I 131 others OPAL-Australia -Mining Sites: one in standby (Sierra Pintada) one in exploration stage (Cerro Solo) eight under remediation

Spent Fuel management policies - The National State is the owner of the radioactive fissile material contained in Spent Fuel from any origin - According to the Strategic Plan, decision on Reprocessing of SF is expected to be taken before 2030 --- underground geological laboratory started - Deep geological repository must be operative by the year 2060 - Meanwhile, NPP Operators are responsible for the SF Storage on Site until its transfer to CNEA

Radioactive Waste management policies - National State, through PNGRR, is Responsible for Safety Waste Management arising from nuclear energy applications, including waste from decommissioning of related facilities - Ensure safe management in order to protect the rights of present and future generations and the environment - Strategic Plan will by authorized, periodically reviewed and audited by Congress - Establish of a proper procedure to obtain and to manage the necessary financial resources - Establish the Waste Acceptance Criteria based on future repositories - Records Keeping of the inventories of radioactive waste and relevant documentation - Development of a Public Communication and Information Program

Spent Fuel management practices (NPP) Atucha I Nuclear Power Plant: decay and storage in water pools until the end of its operational life. Transference to interim dry storage is under development Embalse Nuclear Power Plant: six years decaying period in water pools and subsequent interim dry storage in concrete silos
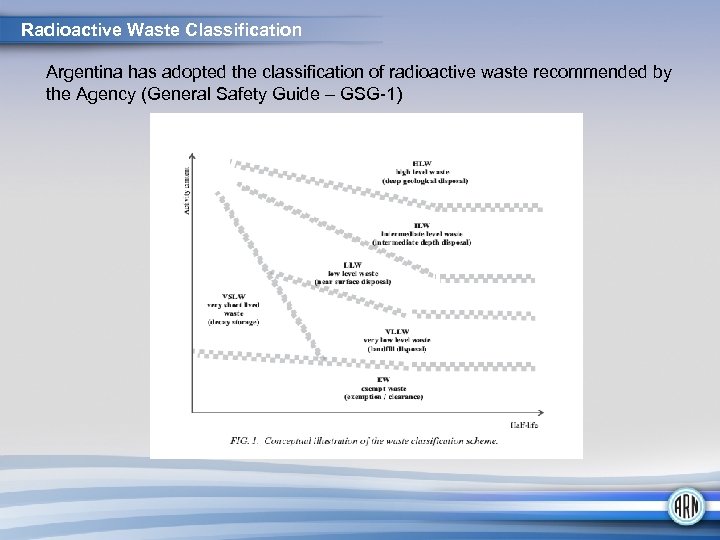
Radioactive Waste Classification Argentina has adopted the classification of radioactive waste recommended by the Agency (General Safety Guide – GSG-1)

Radioactive Waste management practices According to waste categories Low Level Disposable Waste NEAR SURFACE DISPOSAL - Solid waste, compacted in drums - Non compactable waste, conditioned in cement matrices - Low level liquid waste, concentrated and immobilized with cement in drums - Short Lived disused sealed sources, conditioned - Structural waste conditioned in cement matrix SYSTEM FOR DISPOSAL OF STRUCTURAL RADIOACTIVE WASTE AND SEALED SOURCES

Radioactive Waste management practices According to waste categories Low Level Disposable Waste (+ ILW) INTERIM STORAGE - Compacted Solid Waste and cemented liquid aqueous Waste - Non Compactable Waste, spent resins and filters - Disused sealed sources - Structural materials - Organic liquid Wastes INTERIM STORAGE OF SOURCES AND RADIOACTIVE WASTE

Radioactive Waste management practices According to waste categories Intermediate level disposable waste INTERIM STORAGE - Reactor internals from CNA I generated by maintenance - Alpha emitters contaminated waste - Long lived disused sealed sources - PT / CTI (CNE refurbishment)

Existing facilities - Radioactive Waste management EZEIZA RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT AREA - AGE ØLow Level Solid Radioactive Waste Treatment Facilities (**) ØDeposit for Interim Storage of Radioactive Sources and Waste ØHandling Yard and Storage of Items ØLong Term Storage Deposit ØSystem for Final Disposal of Structural Solid Radioactive Waste and Sealed Sources (*) ØSemi Containment System for Solid Radioactive Waste - trenches (*) ØSemi Containment System for Very Low Level Liquid Radioactive Waste and Very Short Periods - trenches (*) Semi Containment System for Solid Radioactive Waste (*)These facilities have finished their operation stage. (**)This facility is in a state of partial dismantling in order to expand its operations.

Existing facilities - Radioactive Waste management ATUCHA I NPP ØFacility for Immobilization by Cementation of Liquid Radioactive Waste and Noncompactable and Structural Solid Radioactive Waste ØTreatment & Conditioning of Solid Radioactive Waste System ØStorage Facilities for Solid Radioactive Waste ØStorage System for Mechanical Filters from the Reactors Primary Circuit ØStorage System for Spent Ionic Exchange Resin Beds ØDischarge System for Gaseous and Liquid Radioactive Waste New mechanical filters storage

Existing facilities - Radioactive Waste management EMBALSE NPP ØSystem for the Treatment & Conditioning of Solid Radioactive Waste ØStorage Facilities for Solid Radioactive Waste ØSpent Resin Storage Tanks ØLiquid Radioactive Waste Treatment System ØGaseous Radioactive Waste Treatment System -----------------------Ø Underground silos for filters and contaminated structurals Mechanical filters, activated and contaminated structurals storage

Plans Argentina has decided to build a near-surface monolithic repository with engineered barriers for low and some intermediate level radioactive waste The construction of final disposal systems near surface is foreseen, similar to those in operation in L’Aube (France) and El Cabril (Spain). This type of repository is based on the use of multiple and redundant barriers, completing the model with the application of approximately 300 years of institutional post-closure control. Waste will be immobilized in cement matrices and packed in 200 L drums and/or in special concrete containers At present, selection and characterization activities of an adequate site to locate the centralized repository are being carried out, which should be operational by the year 2023, in agreement with the schedule proposed in the draft of the last version of the Strategic Plan, prepared this year

Plans In the same site, a new low level radioactive waste final disposal (near-surface system) will be built, which should be operational by 2020 and which will replace the present systems located at AGE. It is also projected to dispose there the very low level RW, mainly originated from the dismantling of nuclear facilities With respect to High Level and/or Long Lived Waste generated in the final stage of the nuclear fuel cycle, spent fuel is temporarily stored until a decision is adopted on its reprocessing or final disposal The PEGRR foresees to perform studies for sitting, construction and operation of a Deep Geological Repository. The deadline to adopt a decision on the possible reprocessing or final disposal of the SF is 2030 Some duly treated and conditioned Low and Intermediate Level of Long Lived Radioactive Waste will also be disposed of in the deep geological repository According to PEGRR, the need to count with this type of repository is foreseen by 2060. Thus, the activities performed with reference to this topic have been included in the Research and Development activities of the PNGRR

Plans To continue with the development of activities of mathematical modeling of water flow in sedimentary and granitic matrix , taking into account different types of rock, which may be involved in a future repository Since studies conducive to determine the candidate sites continue, they imply a regional public acceptance, CNEA develops a plan on public communication of national scope as a stage prior to the formal acceptance of municipalities and provinces where new facilities could be located In order to select communication strategies, CNEA counted with IAEA assistance and other organizations in order to gain experiences of the field at an international level on the basis of a communication plan to a middle and long term
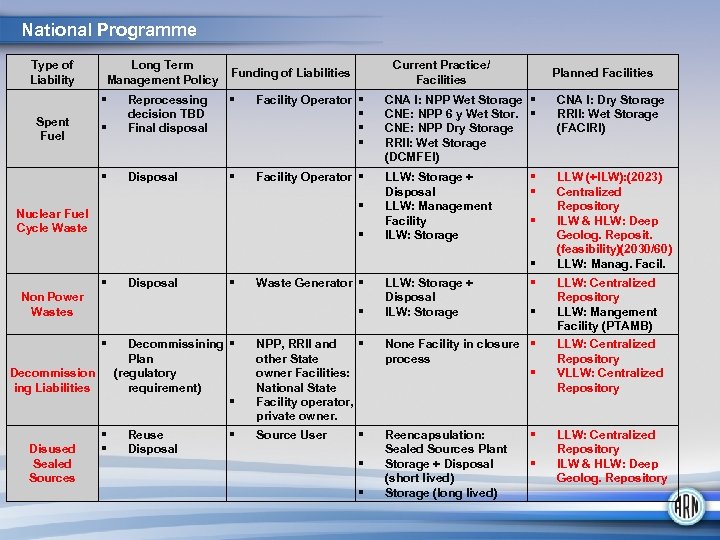
National Programme Type of Liability Long Term Management Policy Current Practice/ Facilities Funding of Liabilities Planned Facilities Facility Operator CNA I: NPP Wet Storage CNE: NPP 6 y Wet Stor. CNE: NPP Dry Storage RRII: Wet Storage (DCMFEI) Spent Fuel Reprocessing decision TBD Final disposal Disposal Facility Operator LLW: Storage + Disposal LLW: Management Facility ILW: Storage Nuclear Fuel Cycle Waste Disposal Waste Generator Non Power Wastes Decommission ing Liabilities Disused Sealed Sources Decommissining Plan (regulatory requirement) Reuse Disposal NPP, RRII and other State owner Facilities: National State Facility operator, private owner. Source User LLW: Storage + Disposal ILW: Storage None Facility in closure process Reencapsulation: Sealed Sources Plant Storage + Disposal (short lived) Storage (long lived) CNA I: Dry Storage RRII: Wet Storage (FACIRI) LLW (+ILW): (2023) Centralized Repository ILW & HLW: Deep Geolog. Reposit. (feasibility)(2030/60) LLW: Manag. Facil. LLW: Centralized Repository LLW: Mangement Facility (PTAMB) LLW: Centralized Repository VLLW: Centralized Repository ILW & HLW: Deep Geolog. Repository

IAEA, 09 -13 September 2013 THANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR YOUR ATENTION!!!

Autoridad Regulatoria Nuclear Av. del Libertador 8250 (C 1429 BNP) Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires, ARGENTINA Tel. : (+54) (011) 4125 -8436 Fax: (+54) (011) 4125 -8460 http: // www. arn. gob. ar E-Mail: dalvarez@arn. gob. ar
fda7011a7898b19998617549778c8240.ppt