 • i • jm THE INFLUENCE OF ASCORBIC ACID ON NONSPECIFIC RESISTANCE OF THE BODY Performed: Gagarinova А. К, 2 nd year student group № 204 Scientific advisors: Litvinenko L. А. Кuzinа V. А.
• i • jm THE INFLUENCE OF ASCORBIC ACID ON NONSPECIFIC RESISTANCE OF THE BODY Performed: Gagarinova А. К, 2 nd year student group № 204 Scientific advisors: Litvinenko L. А. Кuzinа V. А.
 Ascorbic acid Synonyms : Vitamin C, Ascorbin, Ascorbit, Askorvit, Cantan etc. ; Ascorbic acid is lactone acid, similar in structure to glucose. Vitamin C is: • • • water-soluble; white crystalline powder with sour taste; quickly destroyed by high temperature and during prolonged storage of food;
Ascorbic acid Synonyms : Vitamin C, Ascorbin, Ascorbit, Askorvit, Cantan etc. ; Ascorbic acid is lactone acid, similar in structure to glucose. Vitamin C is: • • • water-soluble; white crystalline powder with sour taste; quickly destroyed by high temperature and during prolonged storage of food;
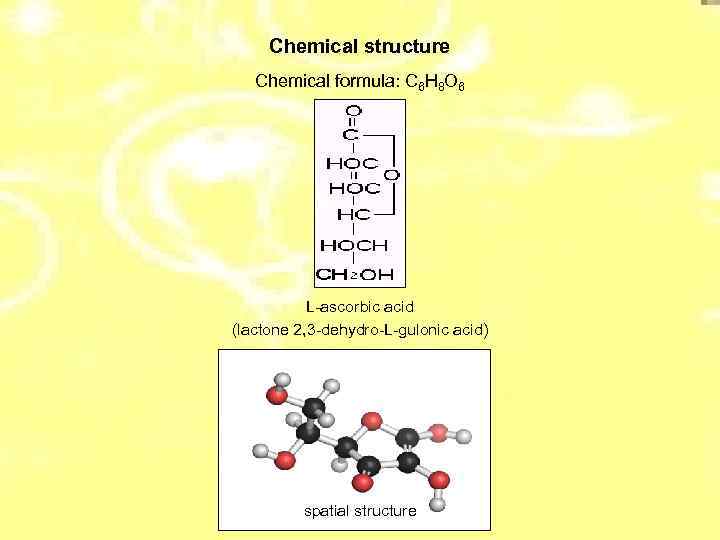 Chemical structure Chemical formula: C 6 H 8 O 6 L-ascorbic acid (lactone 2, 3 -dehydro-L-gulonic acid) spatial structure
Chemical structure Chemical formula: C 6 H 8 O 6 L-ascorbic acid (lactone 2, 3 -dehydro-L-gulonic acid) spatial structure
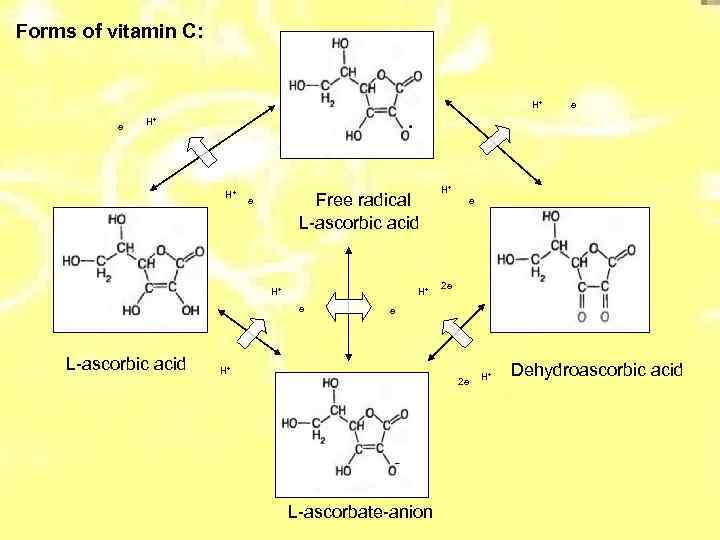 Forms of vitamin C: H+ e e H+ H+ Free radical L-ascorbic acid e H+ H+ e L-ascorbic acid H+ e 2 e e H+ 2 e L-ascorbate-anion H+ Dehydroascorbic acid
Forms of vitamin C: H+ e e H+ H+ Free radical L-ascorbic acid e H+ H+ e L-ascorbic acid H+ e 2 e e H+ 2 e L-ascorbate-anion H+ Dehydroascorbic acid
 A lot of animals can synthesize ascorbic acid from glucose. Еxception:
A lot of animals can synthesize ascorbic acid from glucose. Еxception:
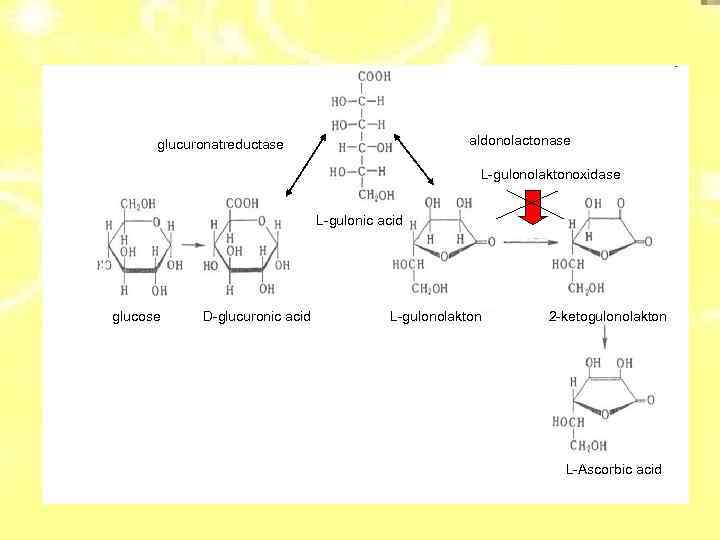 aldonolactonase glucuronatreductase L-gulonolaktonoxidase L-gulonic acid glucose D-glucuronic acid L-gulonolakton 2 -ketogulonolakton L-Ascorbic acid
aldonolactonase glucuronatreductase L-gulonolaktonoxidase L-gulonic acid glucose D-glucuronic acid L-gulonolakton 2 -ketogulonolakton L-Ascorbic acid
 The immune system Vitamin C promotes to increase production : • the production of leukocytes
The immune system Vitamin C promotes to increase production : • the production of leukocytes
 • the production of antibodies
• the production of antibodies
 • the production of interferon
• the production of interferon
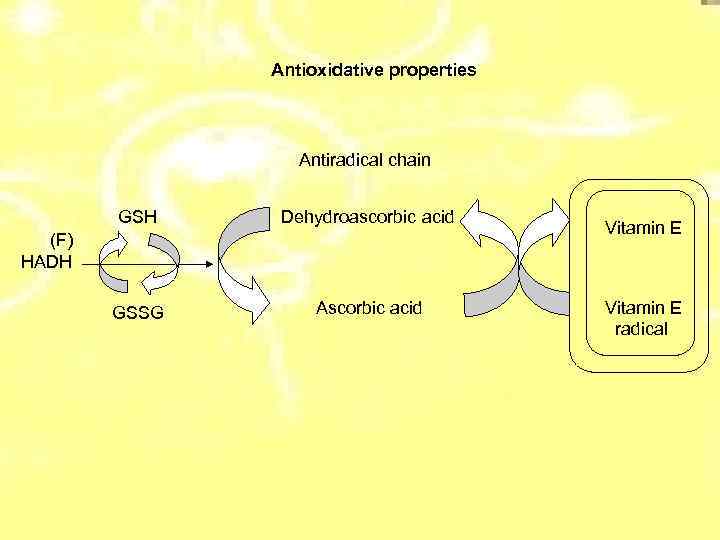 Antioxidative properties Antiradical chain GSH Dehydroascorbic acid GSSG Ascorbic acid (F) НАDH Vitamin E radical
Antioxidative properties Antiradical chain GSH Dehydroascorbic acid GSSG Ascorbic acid (F) НАDH Vitamin E radical
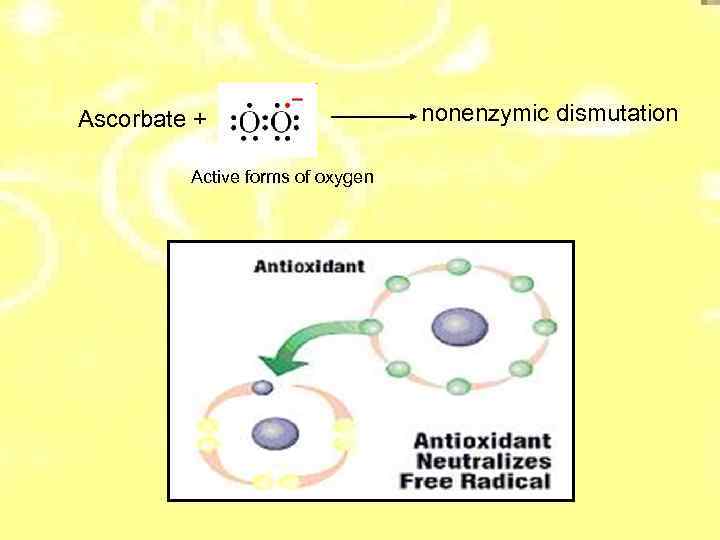 Аscorbate + Active forms of oxygen nonenzymic dismutation
Аscorbate + Active forms of oxygen nonenzymic dismutation
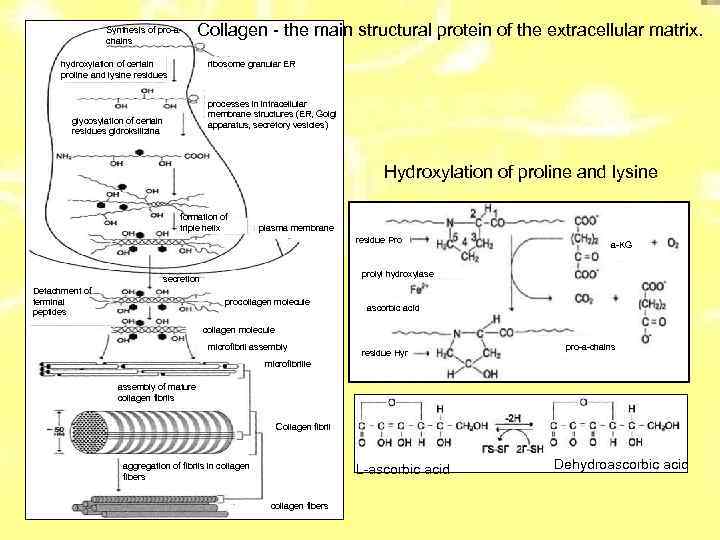 Synthesis of pro-achains Collagen - the main structural protein of the extracellular matrix. hydroxylation of certain proline and lysine residues ribosome granular ER processes in intracellular membrane structures (ER, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicles) glycosylation of certain residues gidroksilizina Hydroxylation of proline and lysine formation of triple helix plasma membrane residue Pro prolyl hydroxylase secretion Detachment of terminal peptides a-KG procollagen molecule ascorbic acid collagen molecule microfibril assembly residue Hyr pro-a-chains microfibrille assembly of mature collagen fibrils Collagen fibril aggregation of fibrils in collagen fibers L-ascorbic acid collagen fibers Dehydroascorbic acid
Synthesis of pro-achains Collagen - the main structural protein of the extracellular matrix. hydroxylation of certain proline and lysine residues ribosome granular ER processes in intracellular membrane structures (ER, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicles) glycosylation of certain residues gidroksilizina Hydroxylation of proline and lysine formation of triple helix plasma membrane residue Pro prolyl hydroxylase secretion Detachment of terminal peptides a-KG procollagen molecule ascorbic acid collagen molecule microfibril assembly residue Hyr pro-a-chains microfibrille assembly of mature collagen fibrils Collagen fibril aggregation of fibrils in collagen fibers L-ascorbic acid collagen fibers Dehydroascorbic acid
 Acute viral respiratory diseases (AVRD)
Acute viral respiratory diseases (AVRD)
 Linus Pauling and vitamin C 1970 28 February 1901 – 19 August 1994
Linus Pauling and vitamin C 1970 28 February 1901 – 19 August 1994
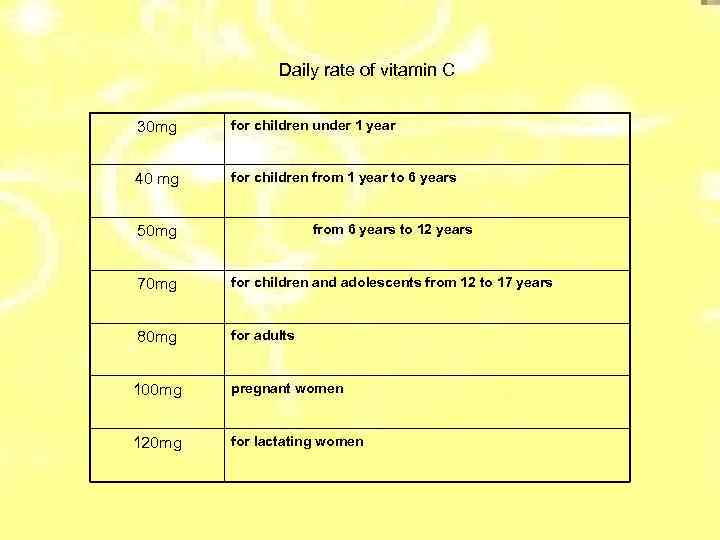 Daily rate of vitamin C 30 mg for children under 1 year 40 mg for children from 1 year to 6 years 50 mg from 6 years to 12 years 70 mg for children and adolescents from 12 to 17 years 80 mg for adults 100 mg pregnant women 120 mg for lactating women
Daily rate of vitamin C 30 mg for children under 1 year 40 mg for children from 1 year to 6 years 50 mg from 6 years to 12 years 70 mg for children and adolescents from 12 to 17 years 80 mg for adults 100 mg pregnant women 120 mg for lactating women
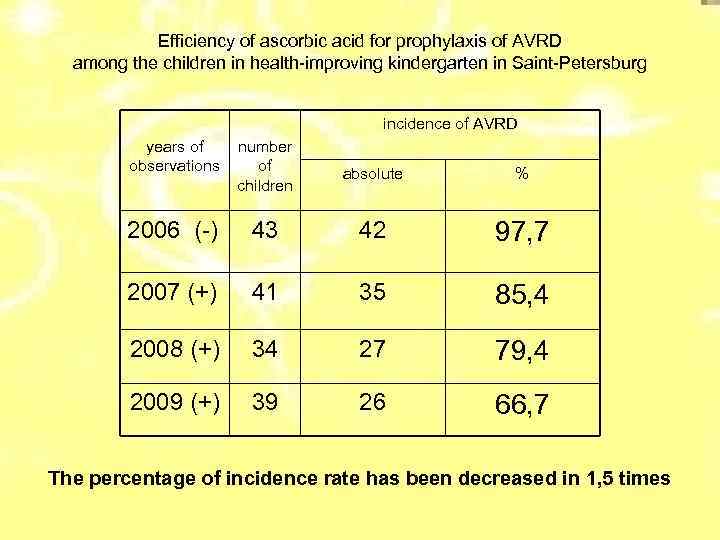 Efficiency of ascorbic acid for prophylaxis of AVRD among the children in health-improving kindergarten in Saint-Petersburg incidence of AVRD years of observations number of children absolute % 2006 (-) 43 42 97, 7 2007 (+) 41 35 85, 4 2008 (+) 34 27 79, 4 2009 (+) 39 26 66, 7 The percentage of incidence rate has been decreased in 1, 5 times
Efficiency of ascorbic acid for prophylaxis of AVRD among the children in health-improving kindergarten in Saint-Petersburg incidence of AVRD years of observations number of children absolute % 2006 (-) 43 42 97, 7 2007 (+) 41 35 85, 4 2008 (+) 34 27 79, 4 2009 (+) 39 26 66, 7 The percentage of incidence rate has been decreased in 1, 5 times
 Vitamin C in foods of plant origin (mg/100 g) 2400 40 450 30
Vitamin C in foods of plant origin (mg/100 g) 2400 40 450 30
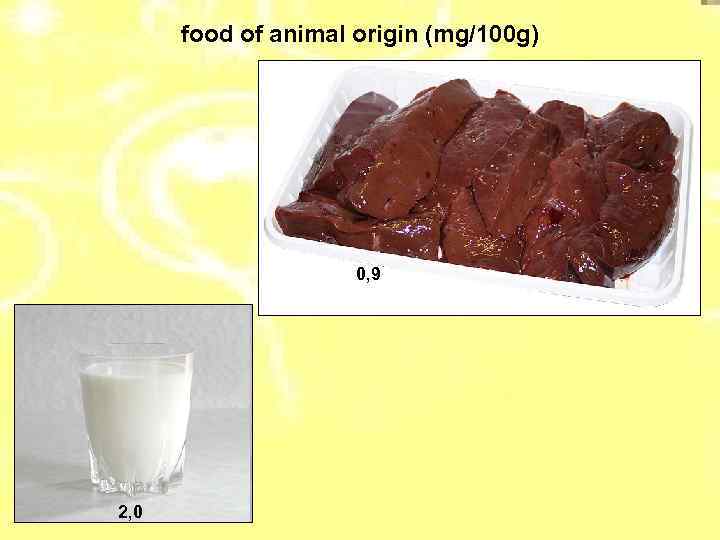 food of animal origin (mg/100 g) 0, 9 2, 0
food of animal origin (mg/100 g) 0, 9 2, 0
 Vitamin C under the microscope (an increase of 10 x and above)
Vitamin C under the microscope (an increase of 10 x and above)


