192d6fb14a883c15d4690991291cb6d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Hypobaric Chambers for Biological Life Support Research Michael Stasiak, Cara Ann Wehkamp, Jamie Lawson, and Michael Dixon Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility Department of Environmental Biology University of Guelph Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
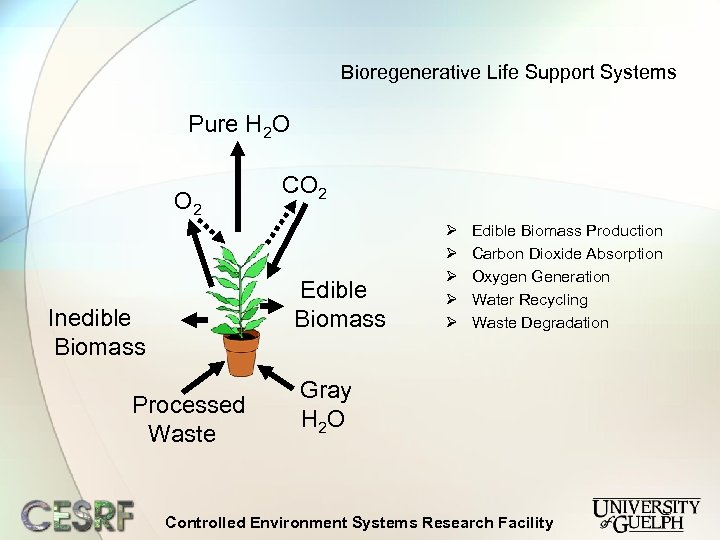
Bioregenerative Life Support Systems Pure H 2 O O 2 CO 2 Edible Biomass Inedible Biomass Processed Waste Ø Ø Ø Edible Biomass Production Carbon Dioxide Absorption Oxygen Generation Water Recycling Waste Degradation Gray H 2 O Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Plant Growth Structure on Mars Two options exist: Ø Earth atmospheric pressure - heavy and opaque Ø Reduced atmospheric pressure - light-weight and transparent material Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
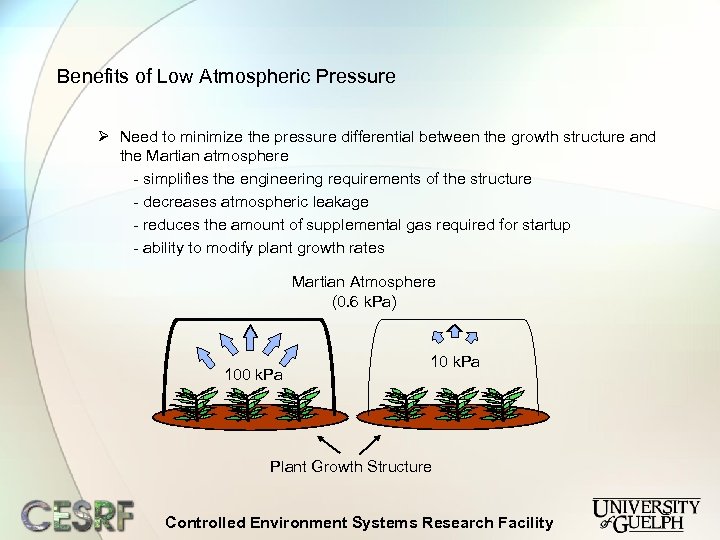
Benefits of Low Atmospheric Pressure Ø Need to minimize the pressure differential between the growth structure and the Martian atmosphere - simplifies the engineering requirements of the structure - decreases atmospheric leakage - reduces the amount of supplemental gas required for startup - ability to modify plant growth rates Martian Atmosphere (0. 6 k. Pa) 100 k. Pa 10 k. Pa Plant Growth Structure Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Summary Ø Mars is the best candidate for human exploration Ø Low pressure conditions may be advantageous to Martian habitation Ø Further investigation is required for the development of an atmospheric composition that allows for reduced pressure plant growth without compromising the plant production yields required for human life support Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
Hypobaric chambers: design and function Ø Chamber design Ø Data acquisition and control Ø Temperature and humidity Ø Pressure Ø Carbon dioxide and oxygen Ø Lighting Ø Nutrient delivery Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Hypobaric chamber design Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Five full canopy plant growth chambers 1. 0 x 1. 8 x 2. 5 m (WHD) 4500 litre volume Growing area of 1. 5 m 2 Highly closed systems with low leakage Internal surfaces 316 stainless steel 20. 5 mm laminate glass roof panels Viton sealing rings on doors and glass Fully automated Capable of maintaining low pressures Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
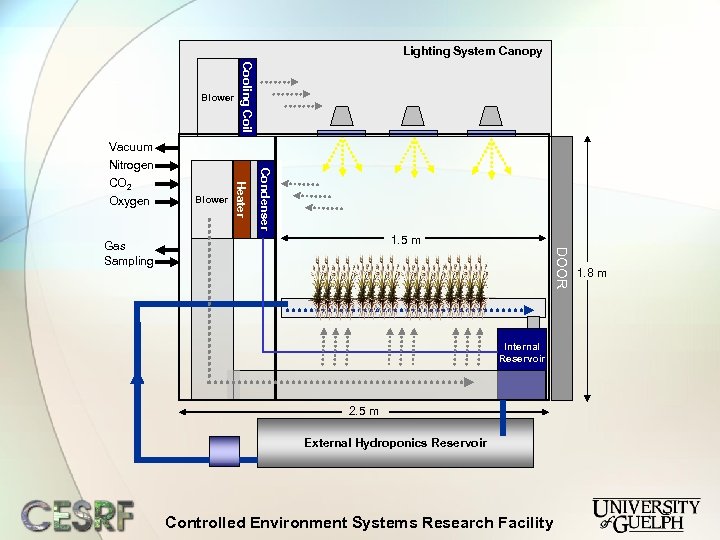
Lighting System Canopy Condenser Blower Heater Vacuum Nitrogen CO 2 Oxygen Cooling Coil Blower 1. 5 m DOOR Gas Sampling Internal Reservoir 2. 5 m External Hydroponics Reservoir Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility 1. 8 m

Data acquisition and control Ø Argus Control Systems Inc. Ø Distributed real-time control Ø Stand-alone microcontroller (Motorola 68 HC 811) on each chamber Ø Proprietary RS 485 communications network Ø Each hypobaric chamber operates independently Ø All sensor readings sampled once per second Ø Experimental data recorded once per minute (higher speeds available) Ø Operator interface provided through a PC-based system access and management program (Argus for Windows) Ø PC component is not used for real time control failure of the PC has no consequence on system control Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Temperature and humidity Ø Variable speed blower Ø Blower speed control coupled to pressure Ø Chilled water (4°C) and hot water (55°C) heat exchange coils Ø Cold exchange coil controlled to achieve required VPD setpoint Ø Hot exchange coil used to reheat cooled air to regulate final temperature setpoint Ø Two Honeywell 4139 T/RH sensors Ø Four Argus TN 2 temperature sensors (2 soil, 2 heat exchange) Ø Tipping bucket for evapotranspiration measurement Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
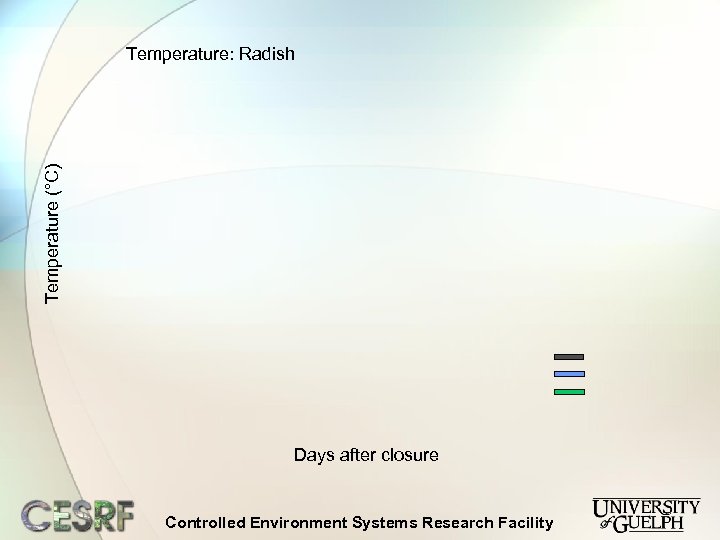
Temperature (°C) Temperature: Radish Days after closure Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

VPD (mb) Vapour pressure deficit: Radish Days after closure Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
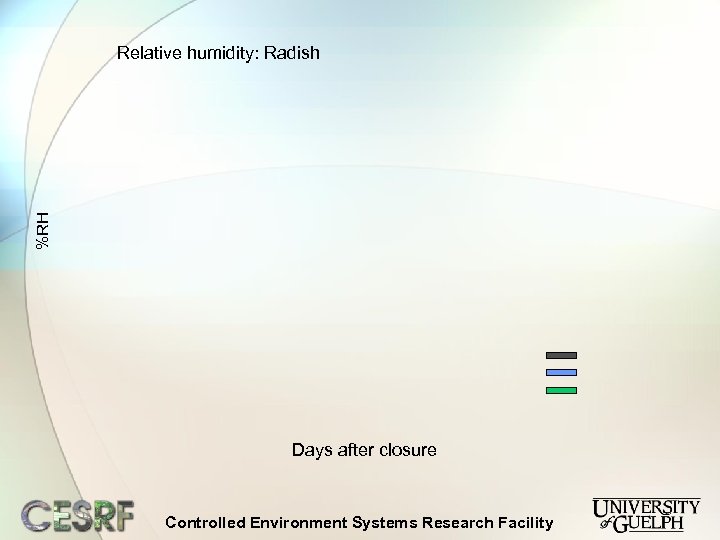
%RH Relative humidity: Radish Days after closure Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
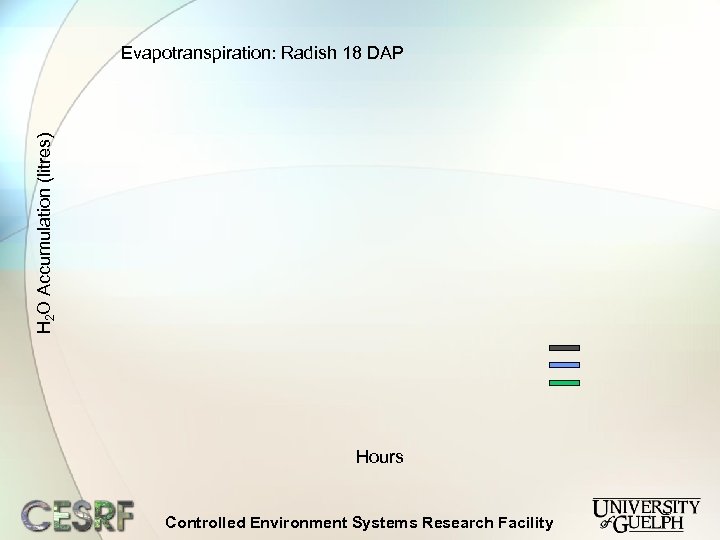
H 2 O Accumulation (litres) Evapotranspiration: Radish 18 DAP Hours Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Pressure Ø Ø Ø Ø Vacuum pump: Busch Vacuum Pressure sensors: Pribusin Inc Control Valve: Swagelok Control range +/- 0. 1 k. Pa Pressure control ambient to 0. 01 k. Pa Systems not designed for pressurization Leakage rate less than 1% per day Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
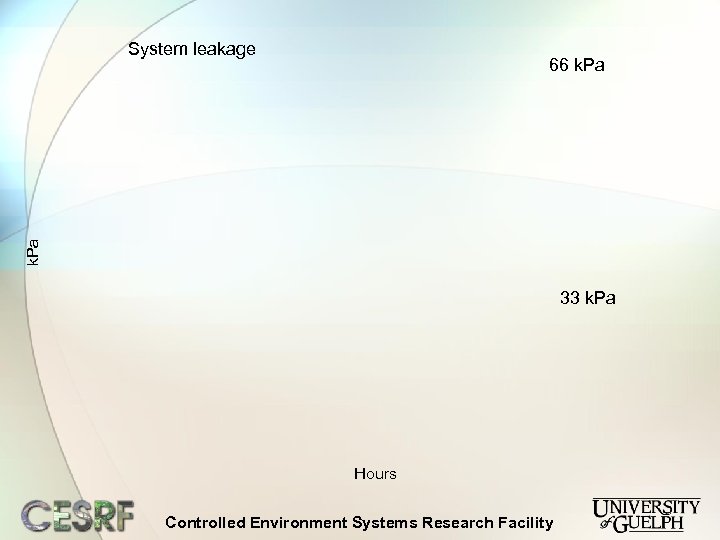
System leakage k. Pa 66 k. Pa 33 k. Pa Hours Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
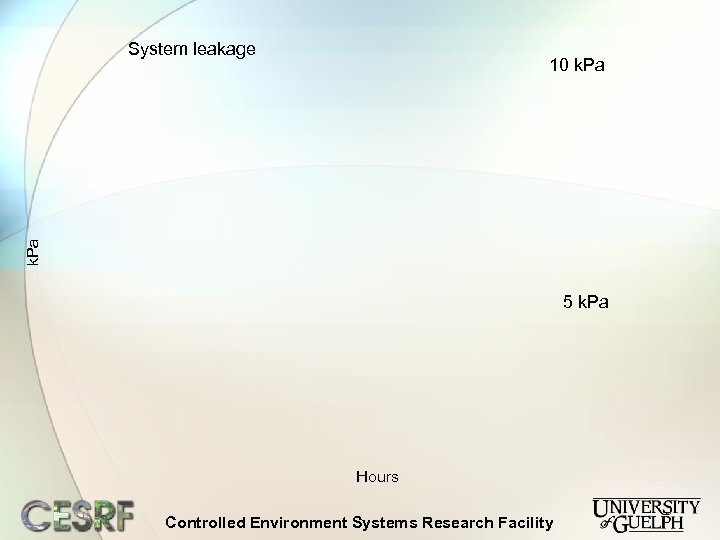
System leakage k. Pa 10 k. Pa 5 k. Pa Hours Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

k. Pa Pressure: Radish Days after closure Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
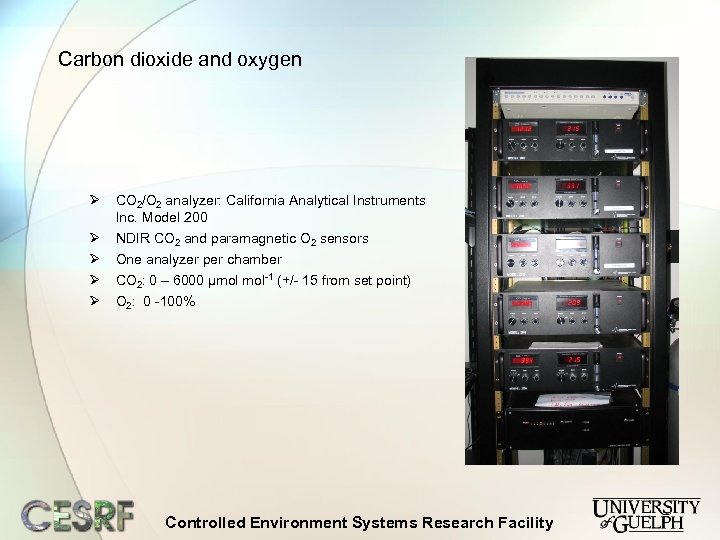
Carbon dioxide and oxygen Ø CO 2/O 2 analyzer: California Analytical Instruments Inc. Model 200 Ø Ø NDIR CO 2 and paramagnetic O 2 sensors One analyzer per chamber CO 2: 0 – 6000 µmol mol-1 (+/- 15 from set point) O 2: 0 -100% Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
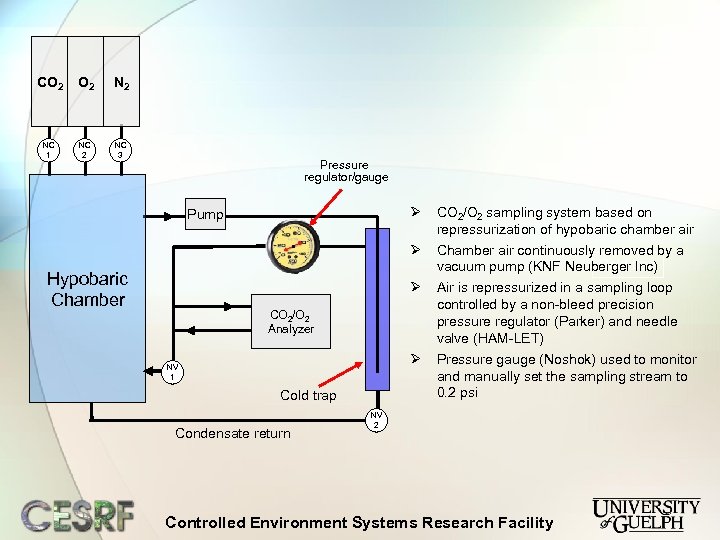
CO 2 N 2 NC 1 NC 2 NC 3 Pressure regulator/gauge Ø Hypobaric Chamber CO 2/O 2 sampling system based on repressurization of hypobaric chamber air Ø Pump Chamber air continuously removed by a Cold Inc) vacuum pump (KNF Neuberger trap Air is repressurized in a sampling loop controlled by a non-bleed precision pressure regulator (Parker) and needle valve (HAM-LET) Pressure gauge (Noshok) used to monitor and manually set the sampling stream to 0. 2 psi Ø CO 2/O 2 Analyzer Ø NV 1 Cold trap Condensate return NV 2 Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
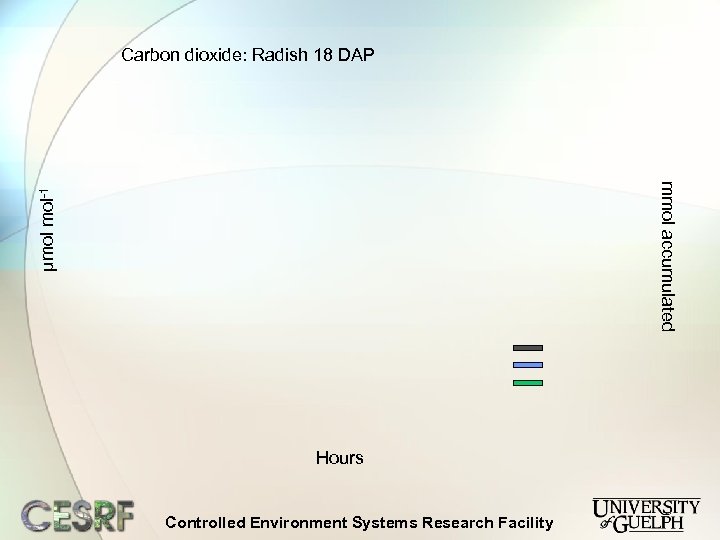
Carbon dioxide: Radish 18 DAP µmol mol-1 mmol accumulated Hours Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
Percent oxygen Oxygen: Radish 18 DAP Hours Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Lighting Ø Ø Ø six 1000 watt HPS lamps (P. L. Light Systems) per chamber Maximum irradiation intensity at highest bench level approximately 1500 μmol m-2 s-1 PAR Externally mounted lighting canopy cooled with chilled water heat exchanger coupled to a blower Two Li. Cor PAR sensors continuously monitor irradiation lighting schedule automated and under control of the Argus Control System. Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
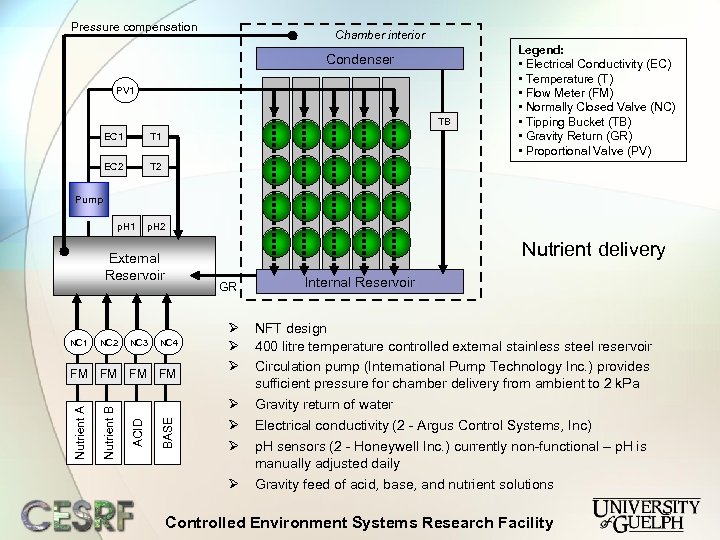
Pressure compensation Chamber interior Condenser PV 1 TB EC 1 T 1 EC 2 Legend: • Electrical Conductivity (EC) • Temperature (T) • Flow Meter (FM) • Normally Closed Valve (NC) • Tipping Bucket (TB) • Gravity Return (GR) • Proportional Valve (PV) T 2 Pump p. H 1 p. H 2 Nutrient delivery External Reservoir GR FM FM BASE NC 4 ACID NC 3 Nutrient B NC 2 Nutrient A NC 1 Ø Ø Ø Ø Internal Reservoir NFT design 400 litre temperature controlled external stainless steel reservoir Circulation pump (International Pump Technology Inc. ) provides sufficient pressure for chamber delivery from ambient to 2 k. Pa Gravity return of water Electrical conductivity (2 - Argus Control Systems, Inc) p. H sensors (2 - Honeywell Inc. ) currently non-functional – p. H is manually adjusted daily Gravity feed of acid, base, and nutrient solutions Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Electrical conductivity (m. S) EC: Radish Days after planting Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Nutrient delivery Ø Ø Removable tray system Pump truck to move crop to harvest lab Quick-connect couplings for water delivery Gravity return to external tank Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility

Acknowledgements Controlled Environment Systems Research Facility
192d6fb14a883c15d4690991291cb6d3.ppt