4ac6d8097e7c53623c096c9ceac08bec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 97
 Hydrogen Fuel Cells Kayla Heffron Daniel Choi
Hydrogen Fuel Cells Kayla Heffron Daniel Choi
 Produced/Obtained ¡ Hydrogen doesn’t exist as a gas on earth. Therefore, hydrogen has to be separated from other elements. Hydrogen atoms can be separated from water, biomass, or natural gas molecules. The two most common methods for producing hydrogen are steam reforming and electrolysis (water splitting). Scientists have discovered that even some algae and bacteria give off hydrogen.
Produced/Obtained ¡ Hydrogen doesn’t exist as a gas on earth. Therefore, hydrogen has to be separated from other elements. Hydrogen atoms can be separated from water, biomass, or natural gas molecules. The two most common methods for producing hydrogen are steam reforming and electrolysis (water splitting). Scientists have discovered that even some algae and bacteria give off hydrogen.
 Steam Reforming cont. ¡ ¡ ¡ Steam reforming is currently the cheapest method of producing hydrogen and accounts for about 95% of the hydrogen produced in the United States. This method is used to separate hydrogen atoms from carbon atoms in methane. (CH 4) Unfortunately this process emits greenhouse gases linked with global warming.
Steam Reforming cont. ¡ ¡ ¡ Steam reforming is currently the cheapest method of producing hydrogen and accounts for about 95% of the hydrogen produced in the United States. This method is used to separate hydrogen atoms from carbon atoms in methane. (CH 4) Unfortunately this process emits greenhouse gases linked with global warming.
 Electrolysis cont. Electrolysis is a process that splits hydrogen from water. ¡ It emits no emissions ¡ Currently a very expensive process but new technologies are currently being developed. ¡
Electrolysis cont. Electrolysis is a process that splits hydrogen from water. ¡ It emits no emissions ¡ Currently a very expensive process but new technologies are currently being developed. ¡
 Uses for energy ¡ ¡ ¡ About 9 million metric tons of hydrogen are produced in the United States annually, enough to power 20 -30 million cars or 5 -8 million homes. Most of this hydrogen is produced in three States: California, Louisiana, and Texas. Nearly all of hydrogen is used in refining, treating metals and processing foods. NASA is a primary user of hydrogen. Hydrogen batteries, called fuel cells, power the shuttle’s electrical systems. The only by-product is pure water, which the crew uses as drinking water. Hydrogen is also used to fuel cars. There are currently 200 -300 hydrogen fueled cars. They store hydrogen gas or liquid on board and convert the hydrogen into electricity for the motor using a fuel cell. Only a few of these vehicles burn the hydrogen directly (producing almost no pollution).
Uses for energy ¡ ¡ ¡ About 9 million metric tons of hydrogen are produced in the United States annually, enough to power 20 -30 million cars or 5 -8 million homes. Most of this hydrogen is produced in three States: California, Louisiana, and Texas. Nearly all of hydrogen is used in refining, treating metals and processing foods. NASA is a primary user of hydrogen. Hydrogen batteries, called fuel cells, power the shuttle’s electrical systems. The only by-product is pure water, which the crew uses as drinking water. Hydrogen is also used to fuel cars. There are currently 200 -300 hydrogen fueled cars. They store hydrogen gas or liquid on board and convert the hydrogen into electricity for the motor using a fuel cell. Only a few of these vehicles burn the hydrogen directly (producing almost no pollution).
 Renewable or nonrenewable? ¡ Hydrogen is renewable in the sense that petroleum we use is a hydrocarbon compound. When we burn hydrogen it turns into vapor and goes up and comes down as precipitation. Since hydrogen comes as precipitation we can also form it compared to petroleum which takes millions of years to produce. Despite being a renewable source the methods to extracting hydrogen needs the use of non -renewable sources.
Renewable or nonrenewable? ¡ Hydrogen is renewable in the sense that petroleum we use is a hydrocarbon compound. When we burn hydrogen it turns into vapor and goes up and comes down as precipitation. Since hydrogen comes as precipitation we can also form it compared to petroleum which takes millions of years to produce. Despite being a renewable source the methods to extracting hydrogen needs the use of non -renewable sources.
 Environmental Problems ¡ ¡ ¡ 90 percent of all hydrogen would come from non-renewable resources like oil, natural gas, and other fossil fuels. Once it is used in a car, only water vapor and heat would be expelled from the car. This cycle of burning fossil fuels will release carbon dioxide, which is the primary cause of global warming. Many scientists think that since hydrogen is extracted from fossil fuels the environmental impact outweighs the benefit of a clean-burning energy provider.
Environmental Problems ¡ ¡ ¡ 90 percent of all hydrogen would come from non-renewable resources like oil, natural gas, and other fossil fuels. Once it is used in a car, only water vapor and heat would be expelled from the car. This cycle of burning fossil fuels will release carbon dioxide, which is the primary cause of global warming. Many scientists think that since hydrogen is extracted from fossil fuels the environmental impact outweighs the benefit of a clean-burning energy provider.
 What countries use this? Japan, North America, Germany and the UK are potentially looking into using hydrogen fuel cells. ¡ No country uses hydrogen fuel cells as of now. ¡
What countries use this? Japan, North America, Germany and the UK are potentially looking into using hydrogen fuel cells. ¡ No country uses hydrogen fuel cells as of now. ¡
 Advantages Mass production costs would be low because they have a simple construction. ¡ It is more energy efficient than gasoline-fueled automobiles. They produce far less pollution. ¡ Fuel cells combine the best of internal combustion engines and batteries. ¡
Advantages Mass production costs would be low because they have a simple construction. ¡ It is more energy efficient than gasoline-fueled automobiles. They produce far less pollution. ¡ Fuel cells combine the best of internal combustion engines and batteries. ¡
 Disadvantages Currently, fuel cells are very expensive. ¡ They are energy users because it costs more to make the hydrogen than is earned by using hydrogen in fuel cells. ¡ Fuel cells only last 1/5 th as long as would be needed to make them cost effective. ¡
Disadvantages Currently, fuel cells are very expensive. ¡ They are energy users because it costs more to make the hydrogen than is earned by using hydrogen in fuel cells. ¡ Fuel cells only last 1/5 th as long as would be needed to make them cost effective. ¡
 Citaiton ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //hotcellularphone. com/handsets/sprint-nextel-toexpand-hydrogen-fuel-cell-deployment/ http: //www. columbia. edu/~ajs 120/hydrogen/web-pages/hfuel-cell-disadv. html http: //www. sciencebase. com/science-blog/fuel-cell-hydrogeneconomy. html http: //www. pbs. org/newshour/science/hydrogen/environment. html http: //www. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=hydrogen_ho me-basics http: //wiki. answers. com/Q/Is_hydrogen_renewable http: //www. alternative-energy-news. info/hydrogen-fuel-cellbikes/ http: //alfin 2100. blogspot. com/2006/07/hydrogen-notefficient-for-energy. html http: //techtickerblog. com/2006/07/27/h-racer-hydrogen-fuelcell-car/
Citaiton ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //hotcellularphone. com/handsets/sprint-nextel-toexpand-hydrogen-fuel-cell-deployment/ http: //www. columbia. edu/~ajs 120/hydrogen/web-pages/hfuel-cell-disadv. html http: //www. sciencebase. com/science-blog/fuel-cell-hydrogeneconomy. html http: //www. pbs. org/newshour/science/hydrogen/environment. html http: //www. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=hydrogen_ho me-basics http: //wiki. answers. com/Q/Is_hydrogen_renewable http: //www. alternative-energy-news. info/hydrogen-fuel-cellbikes/ http: //alfin 2100. blogspot. com/2006/07/hydrogen-notefficient-for-energy. html http: //techtickerblog. com/2006/07/27/h-racer-hydrogen-fuelcell-car/
 By: Reggie Kilmer Hydropower
By: Reggie Kilmer Hydropower
 Production/Use/Who ¡ ¡ Hydropower is the power that is produced from the force of moving water. The force that is used is produced by the kinetic ¡ energy of the water. ¡ It accounted for 6% of total U. S. electricity generation and 67% of generation from renewable in 2008. France, England, Canada, and Russia have also implemented the use of this energy.
Production/Use/Who ¡ ¡ Hydropower is the power that is produced from the force of moving water. The force that is used is produced by the kinetic ¡ energy of the water. ¡ It accounted for 6% of total U. S. electricity generation and 67% of generation from renewable in 2008. France, England, Canada, and Russia have also implemented the use of this energy.
 Hydropower & The Environment ¡ ¡ A reservoir and operation of the dam can also change the natural water temperatures, chemistry, flow characteristics, and silt loads, all of which can lead to significant changes. Reservoirs may cover important natural areas, agricultural lands, archeological sites and cause the relocation of people. Greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide and methane, maybe released into the atmosphere. This may happen due to the fact that dead things and waste may sit in the stagnant water and cause the release of these gases. A dam to create a reservoir may obstruct migration of fish to their upstream spawning areas. It may also harm or kill the fish as they pass trough the dam.
Hydropower & The Environment ¡ ¡ A reservoir and operation of the dam can also change the natural water temperatures, chemistry, flow characteristics, and silt loads, all of which can lead to significant changes. Reservoirs may cover important natural areas, agricultural lands, archeological sites and cause the relocation of people. Greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide and methane, maybe released into the atmosphere. This may happen due to the fact that dead things and waste may sit in the stagnant water and cause the release of these gases. A dam to create a reservoir may obstruct migration of fish to their upstream spawning areas. It may also harm or kill the fish as they pass trough the dam.
 Chart of Use Percent/What 48. 6% for irrigation 17. 4 % for hydropower 12. 7% for water supply 10. 0% for food control 5. 3% for recreation 0. 6% for navigation and fish farming 5. 4% others
Chart of Use Percent/What 48. 6% for irrigation 17. 4 % for hydropower 12. 7% for water supply 10. 0% for food control 5. 3% for recreation 0. 6% for navigation and fish farming 5. 4% others
 Advantages 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Once a dam is constructed, electricity can be produced at a constant rate. If electricity is not needed, the sluice gates can be shut, stopping electricity generation. The water can be saved for use another time when electricity demand is high. Dams are designed to last many decades and so can contribute to the generation of electricity for many years. The lake that forms behind the dam can be used for water sports and leisure / pleasure activities. Often large dams become tourist attractions in their own right. The lake's water can be used for irrigation purposes.
Advantages 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Once a dam is constructed, electricity can be produced at a constant rate. If electricity is not needed, the sluice gates can be shut, stopping electricity generation. The water can be saved for use another time when electricity demand is high. Dams are designed to last many decades and so can contribute to the generation of electricity for many years. The lake that forms behind the dam can be used for water sports and leisure / pleasure activities. Often large dams become tourist attractions in their own right. The lake's water can be used for irrigation purposes.
 Disadvantages 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dams are extremely expensive to build and must be built to a very high standard. The high cost of dam construction means that they must operate for many decades to become profitable. The flooding of large areas of land means that the natural environment is destroyed. People living in villages and towns that are in the valley to be flooded, must move out. This means that they lose their farms and businesses. In some countries, people are forcibly removed so that hydro-power schemes can go ahead. Although modern planning and design of dams is good, in the past old dams have been known to be breached, the dam gives under the weight of water in the lake. This has led to flooding and death.
Disadvantages 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dams are extremely expensive to build and must be built to a very high standard. The high cost of dam construction means that they must operate for many decades to become profitable. The flooding of large areas of land means that the natural environment is destroyed. People living in villages and towns that are in the valley to be flooded, must move out. This means that they lose their farms and businesses. In some countries, people are forcibly removed so that hydro-power schemes can go ahead. Although modern planning and design of dams is good, in the past old dams have been known to be breached, the dam gives under the weight of water in the lake. This has led to flooding and death.
 Bibliography http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm ? page=hydropower_home-basics ¡ http: //www. technologystudent. com/ener gy 1/hydr 2. htm ¡
Bibliography http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm ? page=hydropower_home-basics ¡ http: //www. technologystudent. com/ener gy 1/hydr 2. htm ¡
 Petroleum Joe Bogle Garrett Wright
Petroleum Joe Bogle Garrett Wright
 How is petroleum obtained? ¡ ¡ ¡ Petroleum is extracted by taking crude oil from the ground and refining it at refineries Uses separation, conversion, and treatment to determine what the oil will be made into based on the density and the octane Deposits of crude oil are trapped deep within the earth’s crust under land sea High-tech equipment drills up to seven miles deep Saudi Arabia Canada, Russia and Middle East have large deposits Energy is produced by burning the petroleum
How is petroleum obtained? ¡ ¡ ¡ Petroleum is extracted by taking crude oil from the ground and refining it at refineries Uses separation, conversion, and treatment to determine what the oil will be made into based on the density and the octane Deposits of crude oil are trapped deep within the earth’s crust under land sea High-tech equipment drills up to seven miles deep Saudi Arabia Canada, Russia and Middle East have large deposits Energy is produced by burning the petroleum
 Uses Petroleum makes up 37. 3% of energy use in USA ¡ Used mainly in transportation and manufacturing ¡ Petrochemicals Gases, Gasoline, Aviation fuel, heating oil, diesel fuel, naphtha solvent, grease and wax, and asphalt depending on the density of the section of the crude oil ¡
Uses Petroleum makes up 37. 3% of energy use in USA ¡ Used mainly in transportation and manufacturing ¡ Petrochemicals Gases, Gasoline, Aviation fuel, heating oil, diesel fuel, naphtha solvent, grease and wax, and asphalt depending on the density of the section of the crude oil ¡
 Nonrenewable Energy World uses 26, 000, 000 barrels per year ¡ At this rate there is enough for 40 -93 years. ¡ Oil fields already discovered have 1, 000, 000 barrels available ¡
Nonrenewable Energy World uses 26, 000, 000 barrels per year ¡ At this rate there is enough for 40 -93 years. ¡ Oil fields already discovered have 1, 000, 000 barrels available ¡
 Problems with use and acquisition Environmental costs not put in market price ¡ Land disruption, water disruption, and degradation of wildlife for acquisition ¡ Accounts for 43% of global CO 2 emissions from burning ¡ Can cause water pollution (BP) ¡ Global warming from CO 2 affects all wildlife ¡
Problems with use and acquisition Environmental costs not put in market price ¡ Land disruption, water disruption, and degradation of wildlife for acquisition ¡ Accounts for 43% of global CO 2 emissions from burning ¡ Can cause water pollution (BP) ¡ Global warming from CO 2 affects all wildlife ¡
 What countries use Petroleum
What countries use Petroleum
 Advantages ¡ Low cost, ample supply, high net energy yield, easily transported between countries, technology is well developed, efficient distribution system
Advantages ¡ Low cost, ample supply, high net energy yield, easily transported between countries, technology is well developed, efficient distribution system
 Disadvantages ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Need to find a substitute in the next fifty years Cars are not very efficient and it is the most common mean of transportation A lot of energy is lost Large government subsidies Low price encourages waste Politically unstable countries profit and oppress the people OPEC controls the prices
Disadvantages ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Need to find a substitute in the next fifty years Cars are not very efficient and it is the most common mean of transportation A lot of energy is lost Large government subsidies Low price encourages waste Politically unstable countries profit and oppress the people OPEC controls the prices
 Sites we plagiarized ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //perotcharts. com/category/charts/e nergy-charts/ Living in the Environment- the book http: //www. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=oil_home-basics http: //www. energy. gov/energysources/oil. htm http: //www. alaska-in-pictures. com/oil-rig -with-crew-boats-3218 -pictures. htm http: //knowledgenews. net/moxie/todaysk nowledge/a-barrel-of-oil-refined. shtml
Sites we plagiarized ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //perotcharts. com/category/charts/e nergy-charts/ Living in the Environment- the book http: //www. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=oil_home-basics http: //www. energy. gov/energysources/oil. htm http: //www. alaska-in-pictures. com/oil-rig -with-crew-boats-3218 -pictures. htm http: //knowledgenews. net/moxie/todaysk nowledge/a-barrel-of-oil-refined. shtml
 Mehrunnisa Ali Eshani Brahmbhatt Solid Biomass
Mehrunnisa Ali Eshani Brahmbhatt Solid Biomass
 Produced/Obtained Ø Ø Ø Produced by organic material from plants and animals. Stored energy from sun. Located in the air.
Produced/Obtained Ø Ø Ø Produced by organic material from plants and animals. Stored energy from sun. Located in the air.
 Uses Ø Generates: ü ü ü Ø Heat Electricity Steam Users in US: ü ü ü Industries Electric power producers Commercial businesses
Uses Ø Generates: ü ü ü Ø Heat Electricity Steam Users in US: ü ü ü Industries Electric power producers Commercial businesses
 Renewable/Nonrenewable? Ø Ø Renewable Types of biomass: ü Crops (corn, sugarcane, etc) ü Wood (most common) ü Garbage ü Landfill gas ü Alcohol fuels ü Manure
Renewable/Nonrenewable? Ø Ø Renewable Types of biomass: ü Crops (corn, sugarcane, etc) ü Wood (most common) ü Garbage ü Landfill gas ü Alcohol fuels ü Manure
 Environmental Problems Pollution in the air due to excessive amount of carbon dioxide ¡ Climate change ¡ Saving trees ¡
Environmental Problems Pollution in the air due to excessive amount of carbon dioxide ¡ Climate change ¡ Saving trees ¡
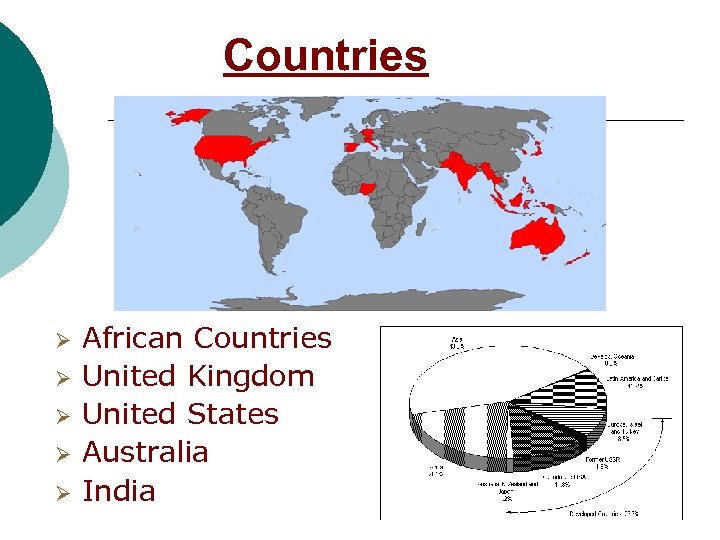 Countries Ø Ø Ø African Countries United Kingdom United States Australia India
Countries Ø Ø Ø African Countries United Kingdom United States Australia India
 Advantages Ø Ø Ø Plants that are targeted produce photosynthesis to even out carbon dioxide in the environment when they are grown. Sustainable cultivation Harvesting Available throughout the world Efficient, possible, and clean burning
Advantages Ø Ø Ø Plants that are targeted produce photosynthesis to even out carbon dioxide in the environment when they are grown. Sustainable cultivation Harvesting Available throughout the world Efficient, possible, and clean burning
 Limitations/Disadvantages Ø Ø Air Pollution Releases carbon dioxide Cost more to produce than conventional crude oil resources. Contributes to Global Warming
Limitations/Disadvantages Ø Ø Air Pollution Releases carbon dioxide Cost more to produce than conventional crude oil resources. Contributes to Global Warming
 Bibliography http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=biomass_home-basics ¡ http: //www. inforse. org/europe/dier et/Biomass/wood 1 rozloyeniesvet. gif ¡ http: //www. futureenergyevents. co m/biomass/wpcontent/uploads/2009/03/chart-ofcountries-at-biomass-world 20093. png ¡ http: //www. seps. sk/zp/fond/dieret/ biomass. html ¡
Bibliography http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=biomass_home-basics ¡ http: //www. inforse. org/europe/dier et/Biomass/wood 1 rozloyeniesvet. gif ¡ http: //www. futureenergyevents. co m/biomass/wpcontent/uploads/2009/03/chart-ofcountries-at-biomass-world 20093. png ¡ http: //www. seps. sk/zp/fond/dieret/ biomass. html ¡
 Daniela & Jennifer Wind Energy
Daniela & Jennifer Wind Energy
 Wind Energy Caused by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun. ¡ Wind energy is produced by wind turbines. ¡ It is obtained by the wind continuously causing the turbines to move and produce more wind energy. -” The wind flows over the blades creating lift, like the effect on airplane wings” ¡
Wind Energy Caused by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun. ¡ Wind energy is produced by wind turbines. ¡ It is obtained by the wind continuously causing the turbines to move and produce more wind energy. -” The wind flows over the blades creating lift, like the effect on airplane wings” ¡
 Locations Map of U. S. Wind Resources Map of U. S. Wind Capacity Wind Turbines in the Ocean *The top five wind power producing States with the most wind production were Texas, Iowa, California, Minnesota, and Washington. They were put on land, but now are more popular out in the ocean so they don’t cause disturbances. *It is successful in Europe. Holland*
Locations Map of U. S. Wind Resources Map of U. S. Wind Capacity Wind Turbines in the Ocean *The top five wind power producing States with the most wind production were Texas, Iowa, California, Minnesota, and Washington. They were put on land, but now are more popular out in the ocean so they don’t cause disturbances. *It is successful in Europe. Holland*
 Renewable ¡ Wind is a renewable energy source that does not pollute, so some people see it as a good alternative to fossil fuels.
Renewable ¡ Wind is a renewable energy source that does not pollute, so some people see it as a good alternative to fossil fuels.
 Environmental Issues There people who oppose putting turbines just offshore, near the coastlines, because they think the wind turbines will spoil the view of the ocean. ¡ They also kill birds and bats. ¡
Environmental Issues There people who oppose putting turbines just offshore, near the coastlines, because they think the wind turbines will spoil the view of the ocean. ¡ They also kill birds and bats. ¡
 Advantages Economic Once the infrastructure is established, it does not have any expenses. ¡ Easily expanded ¡ Moderate to high net energy yield ¡ Quick construction ¡ moderate capital cost ¡ Environmental • Land below turbines can be used to grow crops or graze livestock • Can be used at sea • No CO 2 emissions • High efficiency
Advantages Economic Once the infrastructure is established, it does not have any expenses. ¡ Easily expanded ¡ Moderate to high net energy yield ¡ Quick construction ¡ moderate capital cost ¡ Environmental • Land below turbines can be used to grow crops or graze livestock • Can be used at sea • No CO 2 emissions • High efficiency
 Disadvantages Economic ¡ ¡ Environmental costs not included in market price Noise wind located near populated areas Environmental • Steady winds needed • Plastic components produced from oil • High land use for wind farm • Visual pollution • Kills birds and bats
Disadvantages Economic ¡ ¡ Environmental costs not included in market price Noise wind located near populated areas Environmental • Steady winds needed • Plastic components produced from oil • High land use for wind farm • Visual pollution • Kills birds and bats
 Bibliography http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=about_sources_of_ener gy-basics ¡ http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=2 ¡
Bibliography http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=about_sources_of_ener gy-basics ¡ http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=2 ¡
 Geothermal Energy Dallas Fitzgibbon Tyler Smith
Geothermal Energy Dallas Fitzgibbon Tyler Smith
 Production and Location ¡ ¡ ¡ Created in Earth’s core by the slow decay of radioactive particles Naturally occuring hydrothermal resources are called geothermal reservoirs. Wells are drilled and temperature tested to find said geothermal reservoirs. Hot springs, volcanoes, fumaroles, and geysers, near tectonic plates (such as the Ring of Fire) Western States and Hawaii
Production and Location ¡ ¡ ¡ Created in Earth’s core by the slow decay of radioactive particles Naturally occuring hydrothermal resources are called geothermal reservoirs. Wells are drilled and temperature tested to find said geothermal reservoirs. Hot springs, volcanoes, fumaroles, and geysers, near tectonic plates (such as the Ring of Fire) Western States and Hawaii
 Uses ¡ ¡ Direct – mineral springs for bathing, cooking and heating from ancient cultures until today Heating buildings through District Heating Systems (hot water pumped from center directly into buildings) This form of heating is used in 95% of Reykjavik, Iceland is majorilly used in California Industrially -- food dehydration, gold mining, and milk pasteurizing
Uses ¡ ¡ Direct – mineral springs for bathing, cooking and heating from ancient cultures until today Heating buildings through District Heating Systems (hot water pumped from center directly into buildings) This form of heating is used in 95% of Reykjavik, Iceland is majorilly used in California Industrially -- food dehydration, gold mining, and milk pasteurizing

 Non-Renewable or Renewable! ¡ Only 0. 4% of total U. S energy use ¡
Non-Renewable or Renewable! ¡ Only 0. 4% of total U. S energy use ¡
 Enviromental Problems ¡ ¡ ¡ Geothermal power plants do not burn fuel to generate electricity, so their emission levels are very low. Geothermal plants use scrubber systems to clean the air of hydrogen sulfide that is naturally found in the steam and hot water. Geothermal plants emit 97% less acid raincausing sulfur compounds than are emitted by fossil fuel plants. Almost 100% of the visible, airborne effluent seen rising from geothermal plants is water vapor. Geothermal energy has the smallest land use of any major power generation technology. Among the cheapest power providers around and getting cheaper with every project.
Enviromental Problems ¡ ¡ ¡ Geothermal power plants do not burn fuel to generate electricity, so their emission levels are very low. Geothermal plants use scrubber systems to clean the air of hydrogen sulfide that is naturally found in the steam and hot water. Geothermal plants emit 97% less acid raincausing sulfur compounds than are emitted by fossil fuel plants. Almost 100% of the visible, airborne effluent seen rising from geothermal plants is water vapor. Geothermal energy has the smallest land use of any major power generation technology. Among the cheapest power providers around and getting cheaper with every project.
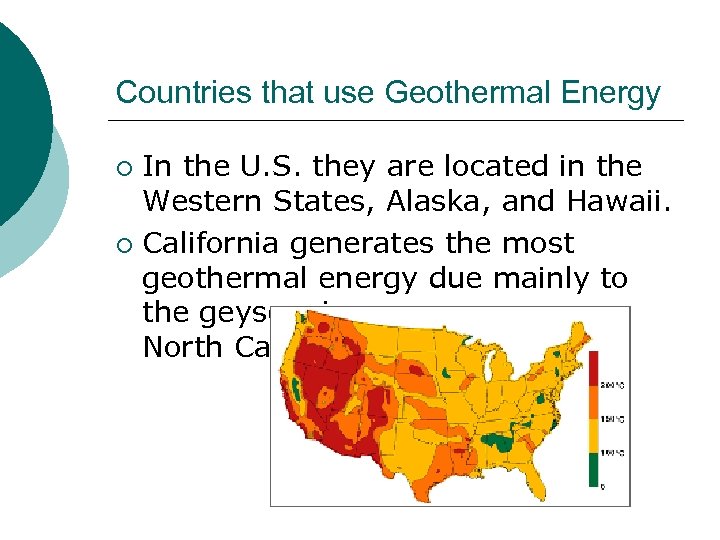 Countries that use Geothermal Energy In the U. S. they are located in the Western States, Alaska, and Hawaii. ¡ California generates the most geothermal energy due mainly to the geysers in North Ca. ¡
Countries that use Geothermal Energy In the U. S. they are located in the Western States, Alaska, and Hawaii. ¡ California generates the most geothermal energy due mainly to the geysers in North Ca. ¡
 Advantages ¡ ¡ ¡ Geothermal resources may outlast the sun. A constant energy source Temperatures underground remain fairly constant There is enough thermal nuclear energy in our Earth to fuel the engines of civilization for billions of years. Very energy efficient and eviromentally sound
Advantages ¡ ¡ ¡ Geothermal resources may outlast the sun. A constant energy source Temperatures underground remain fairly constant There is enough thermal nuclear energy in our Earth to fuel the engines of civilization for billions of years. Very energy efficient and eviromentally sound
 Disadvantages Geothermal power is primarily available where hot magma finds its way close to the surface and heats ground water to usable temperatures above 212 F. ¡ Fairly expensive ¡ Lack of easily attainable magma suitable for geothermal energy ¡ Excessive drilling ¡
Disadvantages Geothermal power is primarily available where hot magma finds its way close to the surface and heats ground water to usable temperatures above 212 F. ¡ Fairly expensive ¡ Lack of easily attainable magma suitable for geothermal energy ¡ Excessive drilling ¡
 Works Cited ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //www. google. com/imgres? imgurl=http: //www. geoberg. de/text/geology/07020205. jpg&imgrefurl=https: //duncanscie nce 9. wikispaces. com/Geothermal%2 BEnergy&usg=__Lza. Ds. D 95 Xu. Omiw 0 w. Od. Vs. Xj. BHr. Us=&h=434&w=500&sz=26&hl=en& start=15&sig 2=F 5_qg. Ql. A 4 HJI 9 n. ZL 4 jcvaw&zoom=1&tbnid=d WHHQK 4 Sktu. P 6 M: &tbnh=129&tbnw=152&ei=Pri. TOs. Rk. M 69 A_j. B 4 M 4 O&prev=/images%3 Fq%3 DGeothermal% 2 Benergy%26 um%3 D 1%26 hl%3 Den%26 client%3 Dfirefoxa%26 sa%3 DN%26 rls%3 Dorg. mozilla: en. US: official%26 biw%3 D 1024%26 bih%3 D 549%26 tbs%3 Disch: 10%2 C 513&um=1&itbs=1&iact=rc&dur=403&oei=dni. TIPCGYT 78 Ab 0 kp. GHDg&esq=7&page=2&ndsp=15&ved=1 t: 429, r: 5, s: 15&tx=77&ty=58&biw=1024&bih=549 http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=geothermal_ home-basics http: //www. energy. gov/energysources/renewables. htm http: //www. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=geothermal_ home-basics geothermal. id. doe. gov/
Works Cited ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //www. google. com/imgres? imgurl=http: //www. geoberg. de/text/geology/07020205. jpg&imgrefurl=https: //duncanscie nce 9. wikispaces. com/Geothermal%2 BEnergy&usg=__Lza. Ds. D 95 Xu. Omiw 0 w. Od. Vs. Xj. BHr. Us=&h=434&w=500&sz=26&hl=en& start=15&sig 2=F 5_qg. Ql. A 4 HJI 9 n. ZL 4 jcvaw&zoom=1&tbnid=d WHHQK 4 Sktu. P 6 M: &tbnh=129&tbnw=152&ei=Pri. TOs. Rk. M 69 A_j. B 4 M 4 O&prev=/images%3 Fq%3 DGeothermal% 2 Benergy%26 um%3 D 1%26 hl%3 Den%26 client%3 Dfirefoxa%26 sa%3 DN%26 rls%3 Dorg. mozilla: en. US: official%26 biw%3 D 1024%26 bih%3 D 549%26 tbs%3 Disch: 10%2 C 513&um=1&itbs=1&iact=rc&dur=403&oei=dni. TIPCGYT 78 Ab 0 kp. GHDg&esq=7&page=2&ndsp=15&ved=1 t: 429, r: 5, s: 15&tx=77&ty=58&biw=1024&bih=549 http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=geothermal_ home-basics http: //www. energy. gov/energysources/renewables. htm http: //www. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=geothermal_ home-basics geothermal. id. doe. gov/
 By: Alaina and Justina Block: 3
By: Alaina and Justina Block: 3
 Production of Energy • Nuclear Power is gained from Nuclear Fission. • Nuclear Fission involves the split of atoms into smaller particles that release energy. • Uranium is the fuel. It is nonrenewable but very common. • U-235 is the particular type of Uranium used by nuclear plants due to the easy splitting of its atoms. Although Uranium is easily obtained U-235 is a rare. • Uranium is mined in the Western part of the USA.
Production of Energy • Nuclear Power is gained from Nuclear Fission. • Nuclear Fission involves the split of atoms into smaller particles that release energy. • Uranium is the fuel. It is nonrenewable but very common. • U-235 is the particular type of Uranium used by nuclear plants due to the easy splitting of its atoms. Although Uranium is easily obtained U-235 is a rare. • Uranium is mined in the Western part of the USA.
 Nuclear Fuel Cycle
Nuclear Fuel Cycle
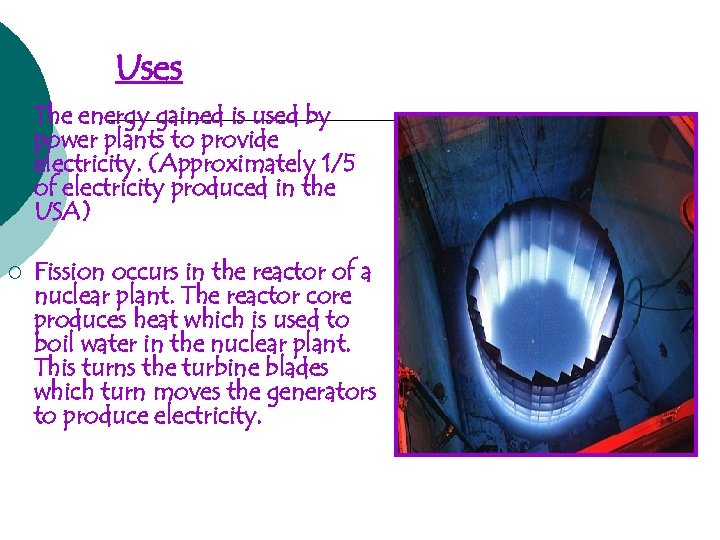 Uses ¡ The energy gained is used by power plants to provide electricity. (Approximately 1/5 of electricity produced in the USA) ¡ Fission occurs in the reactor of a nuclear plant. The reactor core produces heat which is used to boil water in the nuclear plant. This turns the turbine blades which turn moves the generators to produce electricity.
Uses ¡ The energy gained is used by power plants to provide electricity. (Approximately 1/5 of electricity produced in the USA) ¡ Fission occurs in the reactor of a nuclear plant. The reactor core produces heat which is used to boil water in the nuclear plant. This turns the turbine blades which turn moves the generators to produce electricity.
 Uranium ¡ Nonrenewable ¡ The current consumption rate of uranium is 67, 000 tonnes per year based on this uranium resources will last 42 years. ¡ If the military inventory of uranium as a secondary resources is added to the level of uranium resources it accumulates to (4. 8 million tonnes). This is expected to last 72 years if capacity does not increase by a six – fold.
Uranium ¡ Nonrenewable ¡ The current consumption rate of uranium is 67, 000 tonnes per year based on this uranium resources will last 42 years. ¡ If the military inventory of uranium as a secondary resources is added to the level of uranium resources it accumulates to (4. 8 million tonnes). This is expected to last 72 years if capacity does not increase by a six – fold.
 Environmental Issues ¡ ¡ NO Carbon Dioxide is produced however large amounts of energy are required to mine and enrich the uranium resource. Radioactive Waste – Waste is harmful to human health and consists of two levels. High Level such as reactor fuel and Low level such as Mill tailings (contain radium that produces radio active gas). Include tools used, protective clothing e. t. c Uncontrolled Nuclear reactions can cause high levels of radioactivity and contaminate the air and water.
Environmental Issues ¡ ¡ NO Carbon Dioxide is produced however large amounts of energy are required to mine and enrich the uranium resource. Radioactive Waste – Waste is harmful to human health and consists of two levels. High Level such as reactor fuel and Low level such as Mill tailings (contain radium that produces radio active gas). Include tools used, protective clothing e. t. c Uncontrolled Nuclear reactions can cause high levels of radioactivity and contaminate the air and water.
 Where It’s Used ¡ There are now over 440 commercial nuclear power reactors operating in 30 countries ¡ They provide about 14% of the world's electricity as continuous, reliable baseand their efficiency is increasing.
Where It’s Used ¡ There are now over 440 commercial nuclear power reactors operating in 30 countries ¡ They provide about 14% of the world's electricity as continuous, reliable baseand their efficiency is increasing.


 Disadvantages of Nuclear Power Advantages of Nuclear Fission ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ The waste is extremely dangerous Any small accident at a plant could be devastating ¡ Costs are high to build ¡ plants Could be targets for ¡ terrorist attacks The same technology used ¡ for nuclear energy can be used for nuclear weapons Nuclear energy uses uranium as fuel. Uranium is a limited resource It is possible to generate a high amount of electrical energy in one single plant Emits relatively low amounts of carbon dioxide Running costs of a plant are relatively cheap Reduces dependence on foreign oil Generally very efficient and reliable
Disadvantages of Nuclear Power Advantages of Nuclear Fission ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ The waste is extremely dangerous Any small accident at a plant could be devastating ¡ Costs are high to build ¡ plants Could be targets for ¡ terrorist attacks The same technology used ¡ for nuclear energy can be used for nuclear weapons Nuclear energy uses uranium as fuel. Uranium is a limited resource It is possible to generate a high amount of electrical energy in one single plant Emits relatively low amounts of carbon dioxide Running costs of a plant are relatively cheap Reduces dependence on foreign oil Generally very efficient and reliable
 ¡ ¡ ¡ result of a flawed reactor design operated by poorly trained employee Two Chernobyl plant workers died on the night of the accident, and a further 28 people died within a few weeks as a result of acute radiation poisoning. Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) was originally diagnosed in 237 people on-site and involved with the clean-up and it was later confirmed in 134 cases.
¡ ¡ ¡ result of a flawed reactor design operated by poorly trained employee Two Chernobyl plant workers died on the night of the accident, and a further 28 people died within a few weeks as a result of acute radiation poisoning. Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) was originally diagnosed in 237 people on-site and involved with the clean-up and it was later confirmed in 134 cases.

 Works Cited ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //www. world-nuclear. org/info/inf 01. html http: //www. eia. doe. gov/emeu/aer/pecss_diagram. html http: //timeforchange. org/pros-and-cons-ofnuclear-power-and-sustainability http: //wanttoknowit. com/advantages-of-nuclearpower/ http: //www. associatedcontent. com/article/30290 2/disadvantages_of_nuclear_energy. html http: //www. worldnuclear. org/info/chernobyl/inf 07. html http: //www. fraw. org. uk/mei/papers/oies_article. h tml http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=n uclear_home-basics http: //www. eia. doe. gov/cneaf/nuclear/page/intro. html
Works Cited ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ http: //www. world-nuclear. org/info/inf 01. html http: //www. eia. doe. gov/emeu/aer/pecss_diagram. html http: //timeforchange. org/pros-and-cons-ofnuclear-power-and-sustainability http: //wanttoknowit. com/advantages-of-nuclearpower/ http: //www. associatedcontent. com/article/30290 2/disadvantages_of_nuclear_energy. html http: //www. worldnuclear. org/info/chernobyl/inf 07. html http: //www. fraw. org. uk/mei/papers/oies_article. h tml http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energy. cfm? page=n uclear_home-basics http: //www. eia. doe. gov/cneaf/nuclear/page/intro. html
 Natural Gas Rafi Javaid Seth Murdoch
Natural Gas Rafi Javaid Seth Murdoch
 How is the energy produced/obtained? ¡ ¡ ¡ Geologists study the structure and processes of the earth. They locate the rocks that are likely to contain gas and oil deposits. They use seismic surveys that help them to find the right places to drill the wells. Then, they study a chosen area of rocks and if the area looks promising, they start drilling. Once the gas is found, it flows up through the well to the surface of the ground and into large pipelines. Some of these areas are on land, but may of them are offshore, which is deep in the ocean.
How is the energy produced/obtained? ¡ ¡ ¡ Geologists study the structure and processes of the earth. They locate the rocks that are likely to contain gas and oil deposits. They use seismic surveys that help them to find the right places to drill the wells. Then, they study a chosen area of rocks and if the area looks promising, they start drilling. Once the gas is found, it flows up through the well to the surface of the ground and into large pipelines. Some of these areas are on land, but may of them are offshore, which is deep in the ocean.
 Natural Gas Uses ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Natural gas is used for many different things: Heating Buildings Heating Water Cooking Drying Clothes Outdoor Lights Water Heaters Fireplace Logs Energy from natural gas accounts for 24 percent of total energy consumed in the U. S, making it a vital component of the nation’s energy supply.
Natural Gas Uses ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Natural gas is used for many different things: Heating Buildings Heating Water Cooking Drying Clothes Outdoor Lights Water Heaters Fireplace Logs Energy from natural gas accounts for 24 percent of total energy consumed in the U. S, making it a vital component of the nation’s energy supply.
 Renewable or Nonrenewable? ¡ ¡ Natural Gas is a nonrenewable source. With the present rate of consumption, we are more likely to run out in less than a hundred years. However, there are lots of places where this resource can be found and we don’t know where all of them are. Considering the fact that new locations are being found and more reserves are being opened could mean that it can last us way longer than expected. There really is no answer to this question until we extract all of the natural gas from this planet.
Renewable or Nonrenewable? ¡ ¡ Natural Gas is a nonrenewable source. With the present rate of consumption, we are more likely to run out in less than a hundred years. However, there are lots of places where this resource can be found and we don’t know where all of them are. Considering the fact that new locations are being found and more reserves are being opened could mean that it can last us way longer than expected. There really is no answer to this question until we extract all of the natural gas from this planet.
 Environmental Problems ¡ ¡ Natural gas uses can cause air pollution. Because natural gas contains methane, air pollution is common. It can leak into the atmosphere from wells, storage tanks, and pipelines. That can result in smog and air quality. That can cause acid rain.
Environmental Problems ¡ ¡ Natural gas uses can cause air pollution. Because natural gas contains methane, air pollution is common. It can leak into the atmosphere from wells, storage tanks, and pipelines. That can result in smog and air quality. That can cause acid rain.
 Countries/Areas that have implemented the use of natural gas ¡ ¡ The throughout the United States, natural gas is used in heating systems and some appliances. Coastal and some inland states use natural gas to produce electricity. Larger, more developed nation such as the United States and countries in the European Union use the most natural gas The majority of the natural gas is used in industry, residential and commercial buildings, as well as to produce electricity.
Countries/Areas that have implemented the use of natural gas ¡ ¡ The throughout the United States, natural gas is used in heating systems and some appliances. Coastal and some inland states use natural gas to produce electricity. Larger, more developed nation such as the United States and countries in the European Union use the most natural gas The majority of the natural gas is used in industry, residential and commercial buildings, as well as to produce electricity.
 Graph
Graph
 Advantages of Natural Gas ¡ ¡ Natural Gas is the cleanest of all fossil fuels. Natural gas is readily available and 99% of the gas that the United States uses comes from North America and 84% is domestic. It is very efficient in transportation and energy conversion. It is very useful, whether it be for heating a home, heating water, or gas ovens and stoves.
Advantages of Natural Gas ¡ ¡ Natural Gas is the cleanest of all fossil fuels. Natural gas is readily available and 99% of the gas that the United States uses comes from North America and 84% is domestic. It is very efficient in transportation and energy conversion. It is very useful, whether it be for heating a home, heating water, or gas ovens and stoves.
 Disadvantages of Natural Gas ¡ ¡ It is Highly flammable. It is toxic if inhaled in large amounts. It's a Non. Renewable resource. It is creating cavities in the Earth.
Disadvantages of Natural Gas ¡ ¡ It is Highly flammable. It is toxic if inhaled in large amounts. It's a Non. Renewable resource. It is creating cavities in the Earth.
 Works Cited http: //www. naturalgas. org/environ ment/naturalgas. asp ¡ http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=natural_gas_home ¡ http: //www. naturalgas. org/overvie w/uses. asp ¡ http: //todaysfacilitymanager. com/fa cilityblog/wpcontent/uploads/natural-gas_5. jpg ¡
Works Cited http: //www. naturalgas. org/environ ment/naturalgas. asp ¡ http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=natural_gas_home ¡ http: //www. naturalgas. org/overvie w/uses. asp ¡ http: //todaysfacilitymanager. com/fa cilityblog/wpcontent/uploads/natural-gas_5. jpg ¡
 OCEAN THERMAL BY SHELLY & GRACE
OCEAN THERMAL BY SHELLY & GRACE
 What is OTEC? ¡ Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) converts solar radiation into electric power l l Oceans are the world’s largest solar energy collector and storage system l ¡ Makes use of Oceans’ temperature differences in each layer to produce energy (thermal gradient) “ 23 million square miles of tropical seas absorb an amount of solar radiation equal in heat content to about 250 billion barrels of oil. If less than one-tenth of one percent of this stored solar energy could be converted into electric power, it would supply more than 20 times the total amount of electricity consumed in the United States on any given day. “ Located in tropical islands that depend on imported fuel
What is OTEC? ¡ Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) converts solar radiation into electric power l l Oceans are the world’s largest solar energy collector and storage system l ¡ Makes use of Oceans’ temperature differences in each layer to produce energy (thermal gradient) “ 23 million square miles of tropical seas absorb an amount of solar radiation equal in heat content to about 250 billion barrels of oil. If less than one-tenth of one percent of this stored solar energy could be converted into electric power, it would supply more than 20 times the total amount of electricity consumed in the United States on any given day. “ Located in tropical islands that depend on imported fuel
 How is energy obtained? ¡ Open Cycle l ¡ Closed Cycle l l ¡ warm surface water is placed in a low-pressure container and boils. Vapors are turned into electrical energy by the turbine. The vapors (pure freshwater now since salts are left in the container) turn into liquid from exposure to temperature of deep ocean water Fluids with low boiling points are used to rotate a turbine (engine that extracts energy from liquid and vapors) to produce electricity Warm surface water is pumped through a heat exchanger where low boiling point is vaporized. Electrical energy is extracted from the vapor by the turbine. Cold deep water is pumped through another heat exchanger and turns vapor back into a liquid. Recycled. Hybrid Cycle l l combination of open and closed cycle Warm surface water enters low-pressure container, evaporated into steam, steam vaporizes low boiling point fluid, produces electricity by turbine.
How is energy obtained? ¡ Open Cycle l ¡ Closed Cycle l l ¡ warm surface water is placed in a low-pressure container and boils. Vapors are turned into electrical energy by the turbine. The vapors (pure freshwater now since salts are left in the container) turn into liquid from exposure to temperature of deep ocean water Fluids with low boiling points are used to rotate a turbine (engine that extracts energy from liquid and vapors) to produce electricity Warm surface water is pumped through a heat exchanger where low boiling point is vaporized. Electrical energy is extracted from the vapor by the turbine. Cold deep water is pumped through another heat exchanger and turns vapor back into a liquid. Recycled. Hybrid Cycle l l combination of open and closed cycle Warm surface water enters low-pressure container, evaporated into steam, steam vaporizes low boiling point fluid, produces electricity by turbine.
 Type of energy source and uses RENEWABLE ¡ Provides electricity at very little environmental cost ¡
Type of energy source and uses RENEWABLE ¡ Provides electricity at very little environmental cost ¡
 Environmental Problems ¡ Too many OTEC plants in a certain area can disrupt marine life due to constant pumping of sea water ¡ Temperature can be affected as well ¡ Plants must be spaced appropriately to prevent problems with marine life and temperature
Environmental Problems ¡ Too many OTEC plants in a certain area can disrupt marine life due to constant pumping of sea water ¡ Temperature can be affected as well ¡ Plants must be spaced appropriately to prevent problems with marine life and temperature

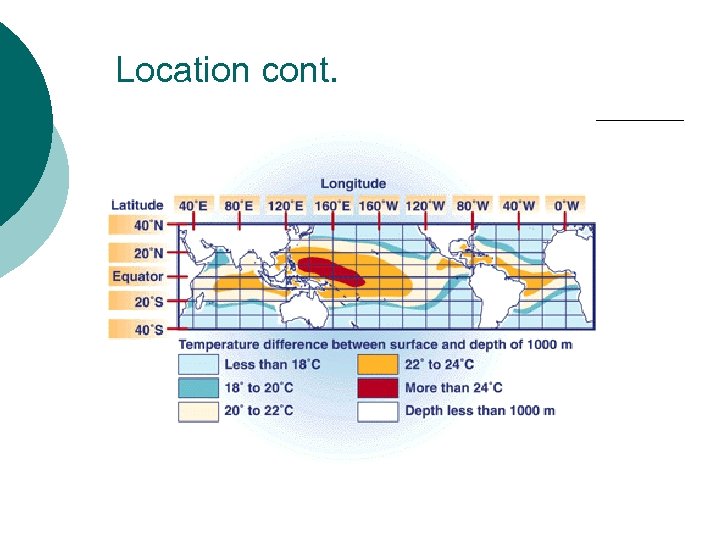
 Location ¡ ¡ Specific requirements on where OTEC plants can be located l temp of warm surface water must differ 20 degrees C from temp of cold deep water l cold water must be 1000 meters below surface Bodies of water that meet requirement found between latitudes 20 deg N and 20 deg S. Countries: USA, Australia, 29 territories, 66 developing countries Plants are built in tropical islands that heavily depend on expensive imported oil
Location ¡ ¡ Specific requirements on where OTEC plants can be located l temp of warm surface water must differ 20 degrees C from temp of cold deep water l cold water must be 1000 meters below surface Bodies of water that meet requirement found between latitudes 20 deg N and 20 deg S. Countries: USA, Australia, 29 territories, 66 developing countries Plants are built in tropical islands that heavily depend on expensive imported oil
 Location cont.
Location cont.
 Advantages ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Helps produce Hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol Produces desalinated water Air conditioning for nearby buildings Refrigeration Increased aquaculture Chilled soil agriculture Renewable No combustion/waste products
Advantages ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Helps produce Hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol Produces desalinated water Air conditioning for nearby buildings Refrigeration Increased aquaculture Chilled soil agriculture Renewable No combustion/waste products
 Limitations ¡ ¡ ¡ Not easy finding an area to build OTEC plant Constant pumping of seawater might disrupt marine life Money l Lots of money required to build large-scale plants and many private firms are not willing to invest.
Limitations ¡ ¡ ¡ Not easy finding an area to build OTEC plant Constant pumping of seawater might disrupt marine life Money l Lots of money required to build large-scale plants and many private firms are not willing to invest.
 Bibliography http: //www. energysavers. gov/rene wable_energy/ocean/index. cfm/myt opic=50010 ¡ http: //www. nrel. gov/otec/what. html ¡ http: //www. nrel. gov/otec/design_lo cation. html ¡ http: //www. nrel. gov/otec/benefits. h tml ¡
Bibliography http: //www. energysavers. gov/rene wable_energy/ocean/index. cfm/myt opic=50010 ¡ http: //www. nrel. gov/otec/what. html ¡ http: //www. nrel. gov/otec/design_lo cation. html ¡ http: //www. nrel. gov/otec/benefits. h tml ¡
 SOLAR ENERGY By: Andre Ching and Jon Pratt
SOLAR ENERGY By: Andre Ching and Jon Pratt
 HOW IS IT PRODUCED AND OBTAINED systems use focusing mirrors and metal plates to capture the sun’s energy. ¡ The radiation is absorbed by the black plates then transferred. ¡ Solar fields are located usually in areas with a lot of sunlight. Usually in dry areas. ¡
HOW IS IT PRODUCED AND OBTAINED systems use focusing mirrors and metal plates to capture the sun’s energy. ¡ The radiation is absorbed by the black plates then transferred. ¡ Solar fields are located usually in areas with a lot of sunlight. Usually in dry areas. ¡
 USES Heat water ¡ Heat up pools ¡ Power a house ¡ Heat a house ¡
USES Heat water ¡ Heat up pools ¡ Power a house ¡ Heat a house ¡
 RENEWABLE OR NONRENEWABLE Solar energy is renewable because the sun never runs out at least for a while. ¡ Due to an increase in green house gases and the polar ice caps, more sunlight is reflected. Even though solar energy is renewable the amount that comes in fluctuates ¡
RENEWABLE OR NONRENEWABLE Solar energy is renewable because the sun never runs out at least for a while. ¡ Due to an increase in green house gases and the polar ice caps, more sunlight is reflected. Even though solar energy is renewable the amount that comes in fluctuates ¡
 SOLAR ENERGY ACQUISITION ¡ With the acquirement of solar energy there is no environmental problems with it. All it is using sunlight from the sun.
SOLAR ENERGY ACQUISITION ¡ With the acquirement of solar energy there is no environmental problems with it. All it is using sunlight from the sun.
 WHERE IS IT PRODUCED ¡ The main area of the united states where the solar energy is absorbed and produced is in the Mojave desert in southern California.
WHERE IS IT PRODUCED ¡ The main area of the united states where the solar energy is absorbed and produced is in the Mojave desert in southern California.
 ADVANTAGES It is clean ¡ Renewable ¡ Abundant ¡ Cheaper to have ¡
ADVANTAGES It is clean ¡ Renewable ¡ Abundant ¡ Cheaper to have ¡
 DISADVANTAGES ¡ ¡ Expensive to install Only work in places with abundant sunlight. Doesn’t work at night Solar cells produce only D. C current. So when it switches from D. C to A. C it loses some energy
DISADVANTAGES ¡ ¡ Expensive to install Only work in places with abundant sunlight. Doesn’t work at night Solar cells produce only D. C current. So when it switches from D. C to A. C it loses some energy
 BIBLIOGRAPHY http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=about_sources_of_ener gy-basics ¡ http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=2 ¡ http: //www. eia. doe. gov/emeu/aer/ pecss_diagram. html ¡ http: //www. energy. gov/energysour ces/index. htm ¡
BIBLIOGRAPHY http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=about_sources_of_ener gy-basics ¡ http: //tonto. eia. doe. gov/kids/energ y. cfm? page=2 ¡ http: //www. eia. doe. gov/emeu/aer/ pecss_diagram. html ¡ http: //www. energy. gov/energysour ces/index. htm ¡


