421d5bb8b47b9804edb31b1c2b3ad152.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
Hybrid MLN Multi-Level, Multi-Domain Hybrid Network Inter-Operation & Performance Joint Techs Winter Meeting February 12, 2007 Minneapolis, Minnesota US Dept. of Energy Office of Science Tom Lehman (USC/ISI) Nasir Ghani (Tenn Tech) Chin Guok (ESnet) Nagi Rao (ORNL) John Vollbrecht (Internet 2) John Moore (MCNC)
Outline • Project Overview • Multi-Layer, Multi-Domain Hybrid Network Issues/Investigation Areas • Hybrid Network Data. Plane(s) • Hybrid Network Control Plane(s) 2

Project Overview • Hybrid Multi-Layer Network Control Project • Funded by DOE Office of Science – Dr. Thomas D. Ndousse, Program Manager • Investigating issues associated with Multi-Layer, Multi-Domain Hybrid Networks from an architecture, data plane, and control plane perspective – Design and analysis – Experimentation and data collection – Modeling and simulation 3

Hybrid MLN Participants • Tennessee Tech University – Nasir Ghani – Qing Liu • Information Sciences Institute East – Tom Lehman – Xi Yang • Internet 2 – Rick Summerhill – John Vollbrecht – Andrew Lake • Oak Ridge National Laboratory – Nagi Rao • ESnet LBNL – Chin Guok 4
Hybrid Network Data Planes • Basic premise of hybrid networks is the availability of both best effort routed service and deterministic dedicated resource paths, i. e. , circuits • There are many technologies available over which to construct these circuits – IP router-based Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) “circuits” – Ethernet VLAN based “circuits” – SONET/SDH TDM “circuits” – Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) “circuits” 5
What Data Plane Technologies to Use? • What do you want to do with your circuits? – Dedicated bandwidth connections for deterministic file transfers? – Dedicated bandwidth & low jitter for instrument control or interactive applications? – Connector backhaul to your IP Network? – Traffic engineering of your IP Network? • Dynamic router-to-router circuits for traffic cut thru? – Computer to Computer communications? • Processor to memory? block data storage system access? – Setting up application specific topologies to create & optimize distributed application or data storage systems? 6
Data Plane Testing • Test characteristics/performances of “circuits” constructed via different technologies; and also “end-to-end paths” constructed via concatenation of individual circuits • Questions – – What is difference between the different technologies? How well does the concatenation/stitching work? How well does policing/shaping work at the edge? What happens to a flow that is policed/shaped at the ingress edge by the time it exits the egress edge? 7

More Questions • What are the performance characteristics (jitter, loss, latency) of circuits provisioned using individual data plane technologies? • What are the performance characteristics of end-to-end circuits constructed via concatenation of multiple individual circuits (spanning multiple data plane technologies & network domains) • What is the performance of an end-to-end circuit constructed via the hierarchical nesting of circuits at different technology levels? • How to quantify and characterize the performance of data plane technologies so that network designers and end-users can make decisions as to what is best suited to their needs and objectives? • Can analytical and simulation models be built to correlate empirical findings of real world data collection to a reasonably close degree? • Can these analytical/simulation models further predict performance in generalized hybrid networks and assist w. design efforts? 8
![Data Plane Testing • Circuit Descriptions – Circuit type: • network [accessframing: dataplane: accessframing] Data Plane Testing • Circuit Descriptions – Circuit type: • network [accessframing: dataplane: accessframing]](https://present5.com/presentation/421d5bb8b47b9804edb31b1c2b3ad152/image-9.jpg)
Data Plane Testing • Circuit Descriptions – Circuit type: • network [accessframing: dataplane: accessframing] – Circuit path: • network [ingressloc: transitnodes: egressloc] • Circuit Type: – network[accessframing: dataplane: accessframing] • Where the following values are possible for the above parameters: • Network - esnet, sdn, abilene, i 2 dsn, hopi, usn, dragon • Accessframing - ethernet, sonet (not included in this test plan), infiniband (not included in this test plan) • Dataplane - psc, pscq, l 2 sc, tdm, lsc (where pscq is a PSC path with Qo. S applied to the LSP) 9
Data Plane Testing Multi-Layer, Multi-Domain LSPs 10
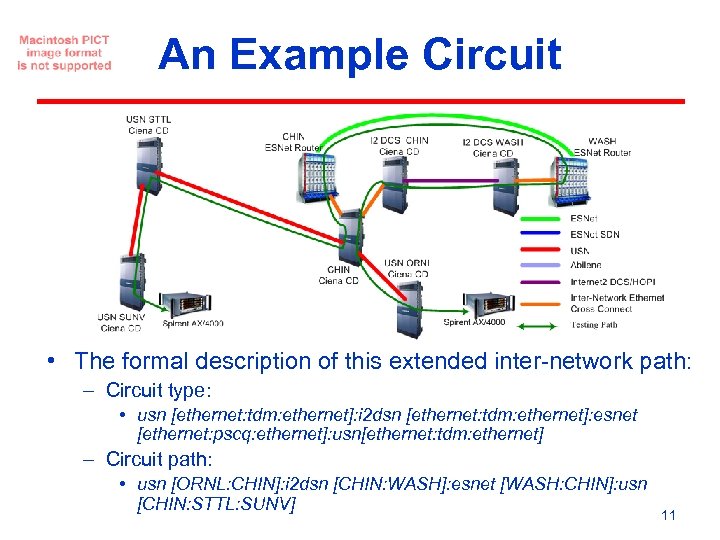
An Example Circuit • The formal description of this extended inter-network path: – Circuit type: • usn [ethernet: tdm: ethernet]: i 2 dsn [ethernet: tdm: ethernet]: esnet [ethernet: pscq: ethernet]: usn[ethernet: tdm: ethernet] – Circuit path: • usn [ORNL: CHIN]: i 2 dsn [CHIN: WASH]: esnet [WASH: CHIN]: usn [CHIN: STTL: SUNV] 11
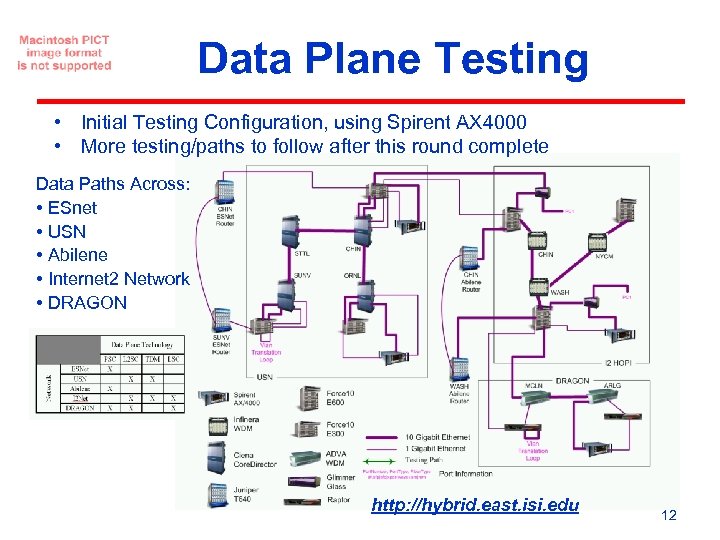
Data Plane Testing • Initial Testing Configuration, using Spirent AX 4000 • More testing/paths to follow after this round complete Data Paths Across: • ESnet • USN • Abilene • Internet 2 Network • DRAGON http: //hybrid. east. isi. edu 12
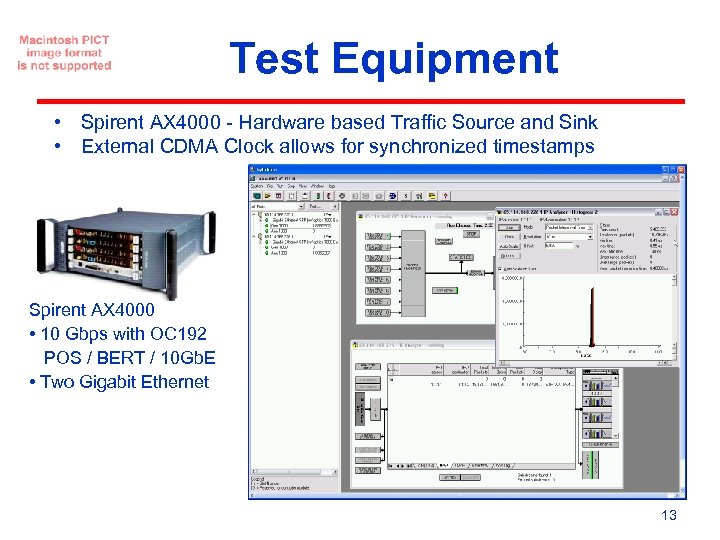
Test Equipment • Spirent AX 4000 - Hardware based Traffic Source and Sink • External CDMA Clock allows for synchronized timestamps Spirent AX 4000 • 10 Gbps with OC 192 POS / BERT / 10 Gb. E • Two Gigabit Ethernet 13
Modeling & Simulation OPNET Modeler. TM Environment Overview • Discrete event simulation • GUI interface, high re-use • Full C/C++ interface • Hierarchical modeling: Subnet-node-link-process “In-House” Development • MPLS/GMPLS control: RSVP-TE, OSPF-TE, PCE • Layer 2/3 data plane: IP/MPLS, VLAN • Full Layer 1 support: DWDM, SONET, GFP • Model any networks 14
Models Suite (Data Plane) • Layer 2/3 nodes (IP/MPLS, VLAN) – Generic modeling of T 640, E 300, others – Advanced I/O buffering design, policing, scheduling Status: MPLS completed (12/06), VLAN nearly done • Layer 1 nodes (SONET, DWDM) – SONET TSI, GFP edge mappings (model Ciena CDI) – DWDM cross-connects w. SONET framing Status: Completed (1/07) • End-systems & test applications – TCP & UDP file, TCPMON, UDPMON, ICMP-PING, ext. timestamps (SPIRENT tester) Status: All completed except TCPMON (12/06) 15

Simulation Test Plan • Current activities – Coding wrap-up, active development/testing of end-toend delay and jitter scenarios – Corroborating simulations with recent live tests on ESnet-USN, USN-Cheetah, USN-Hopi, etc – Gauge impact of SONET segments in e-2 -e path • Near term & future activities – Extrapolate out and simulate larger networks & domain mixtures (VLAN-SONET-MPLS) – Generate inputs for subsequent control plane development phase (i. e. , TE routing rule-sets) 16

Thank-You Questions & Comments ? Tom Lehman tlehman@isi. edu 17
421d5bb8b47b9804edb31b1c2b3ad152.ppt