 HW #2, Due Sep. 7 Chapter 2 P 7, P 12, P 16, PH 1, PH 2
HW #2, Due Sep. 7 Chapter 2 P 7, P 12, P 16, PH 1, PH 2
 This Lecture: Chapter 2 Geometric Optics Reading Assignment: All Chapter 2 By the way, what is refractive index? !!
This Lecture: Chapter 2 Geometric Optics Reading Assignment: All Chapter 2 By the way, what is refractive index? !!
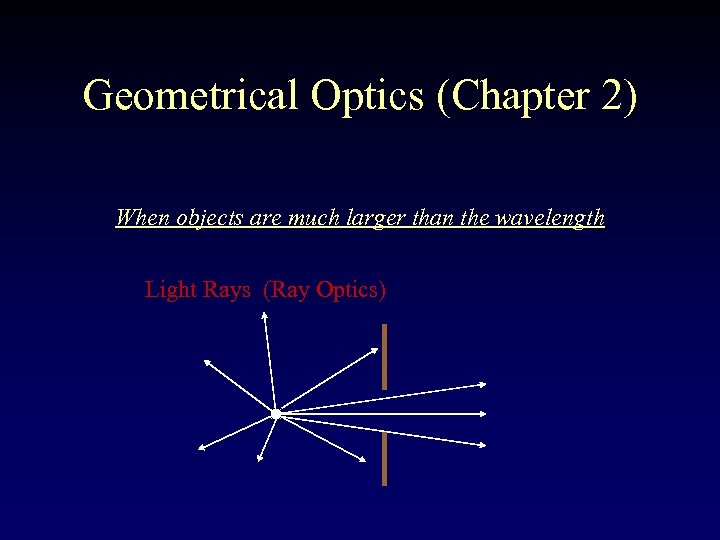 Geometrical Optics (Chapter 2) When objects are much larger than the wavelength Light Rays (Ray Optics)
Geometrical Optics (Chapter 2) When objects are much larger than the wavelength Light Rays (Ray Optics)
 Shadows *Shadow-point source http: //www. techxhome. com/lightsite/optics/shadows/point. Shadow. html *Shadow: Extended Source http: //www. techxhome. com/lightsite/optics/shadows/extended. Shadow. html
Shadows *Shadow-point source http: //www. techxhome. com/lightsite/optics/shadows/point. Shadow. html *Shadow: Extended Source http: //www. techxhome. com/lightsite/optics/shadows/extended. Shadow. html
 Solar Eclipse: Aug. 11 1999 SUN Moon Earth
Solar Eclipse: Aug. 11 1999 SUN Moon Earth
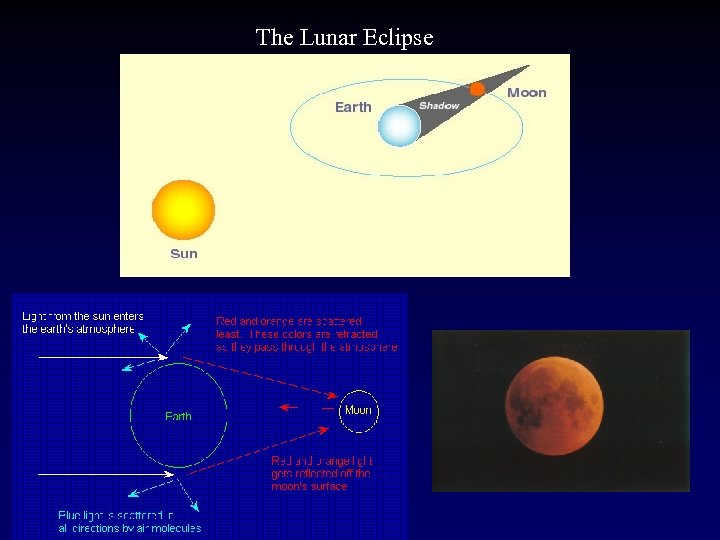 The Lunar Eclipse
The Lunar Eclipse
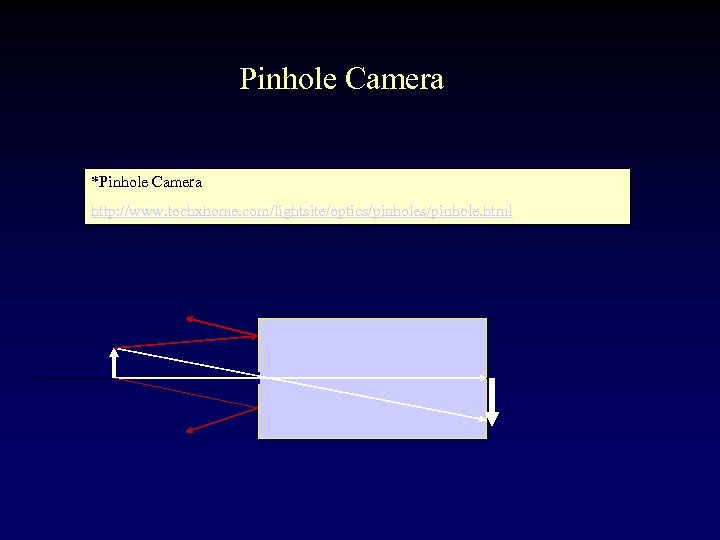 Pinhole Camera *Pinhole Camera http: //www. techxhome. com/lightsite/optics/pinhole. html
Pinhole Camera *Pinhole Camera http: //www. techxhome. com/lightsite/optics/pinhole. html
 Depth of Image and more 2 pinholes
Depth of Image and more 2 pinholes
 The effect of pinhole size
The effect of pinhole size
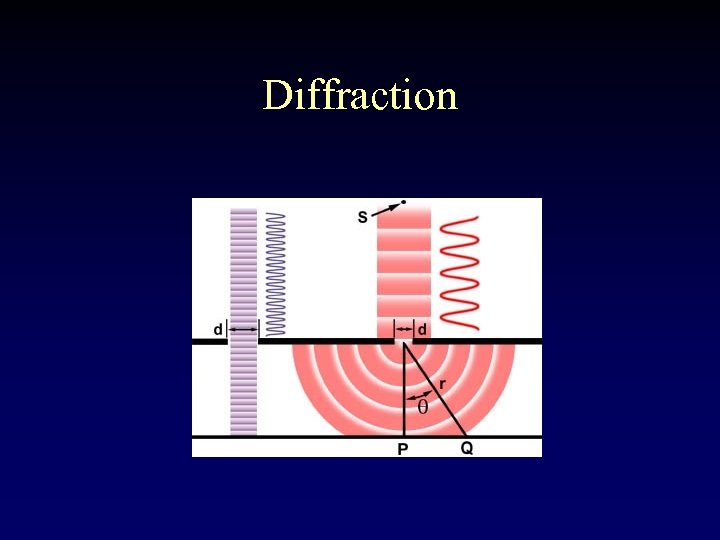 Diffraction
Diffraction
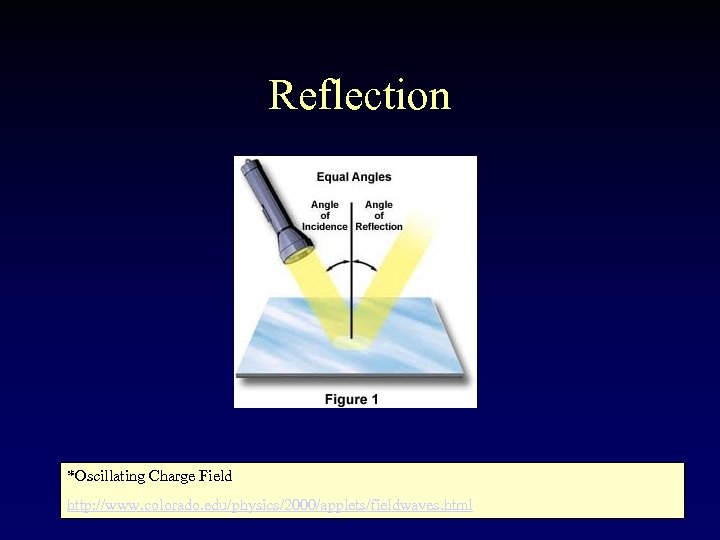 Reflection *Oscillating Charge Field http: //www. colorado. edu/physics/2000/applets/fieldwaves. html
Reflection *Oscillating Charge Field http: //www. colorado. edu/physics/2000/applets/fieldwaves. html
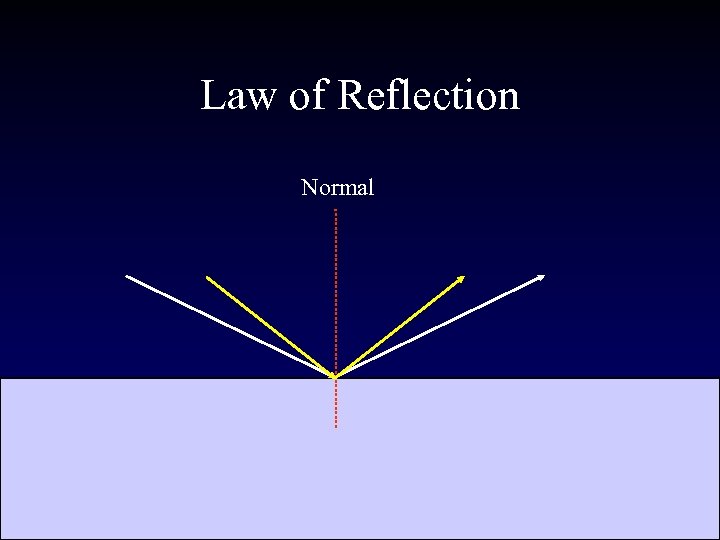 Law of Reflection Normal
Law of Reflection Normal
 Mirrors Why metals reflect light? Why do they appear certain color? Why can we listen to radio stations far away? • Silvered and half-silvered mirrors • First-surface and second-surface mirrors *Oscillating Charge Field http: //www. colorado. edu/physics/2000/applets/fieldwaves. html
Mirrors Why metals reflect light? Why do they appear certain color? Why can we listen to radio stations far away? • Silvered and half-silvered mirrors • First-surface and second-surface mirrors *Oscillating Charge Field http: //www. colorado. edu/physics/2000/applets/fieldwaves. html
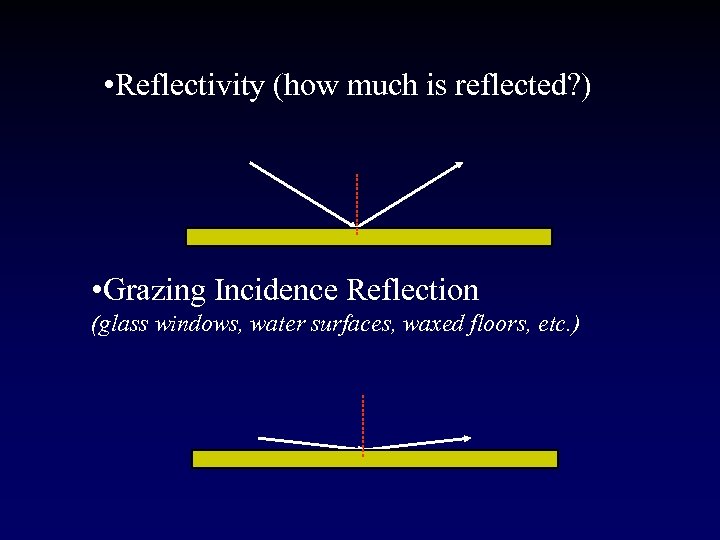 • Reflectivity (how much is reflected? ) • Grazing Incidence Reflection (glass windows, water surfaces, waxed floors, etc. )
• Reflectivity (how much is reflected? ) • Grazing Incidence Reflection (glass windows, water surfaces, waxed floors, etc. )
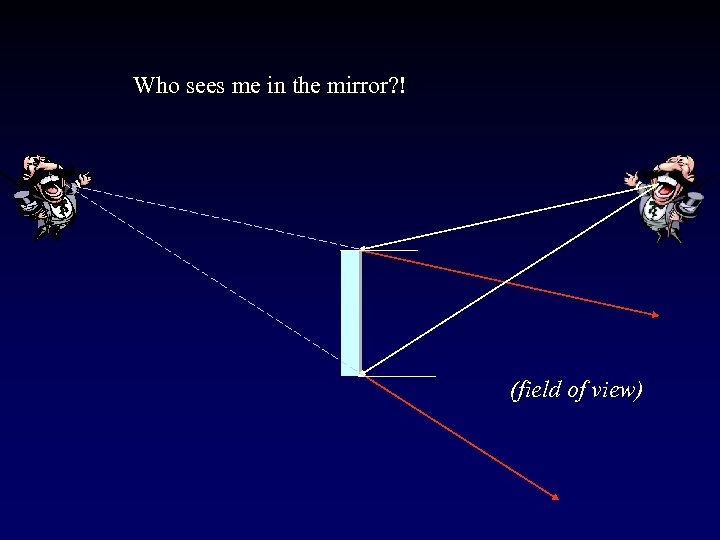 Who sees me in the mirror? ! (field of view)
Who sees me in the mirror? ! (field of view)
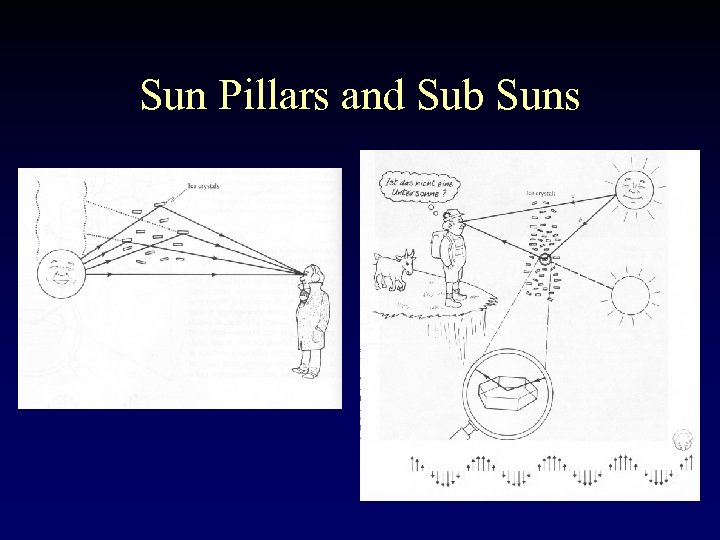 Sun Pillars and Sub Suns
Sun Pillars and Sub Suns
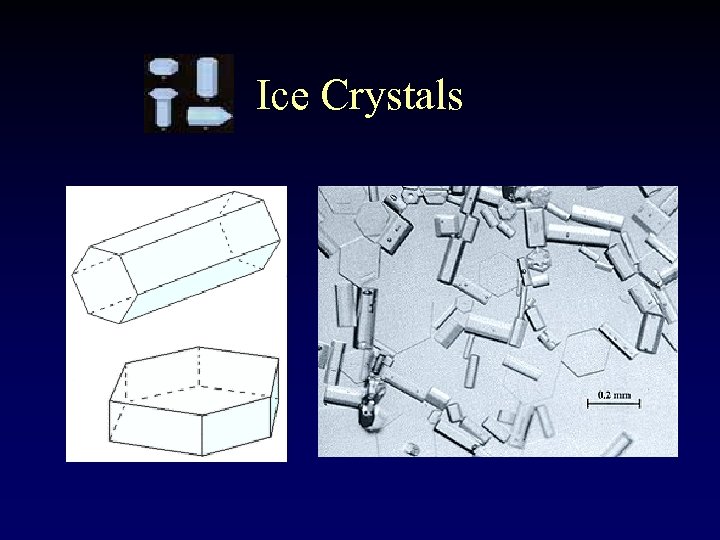 Ice Crystals
Ice Crystals
 Sub Sun A bright subsun looking downwards from 11, 000 m over Italy, late afternoon 18 th July 1995. The halo was intermittently visible over the southern and central parts of the country covered by a thin cirrus sheet. The halo elongated and contracted as the tilts of the plate crystal mirrors changed. Reflections from lakes and rivers shine through the cloud. Video by Les Cowley.
Sub Sun A bright subsun looking downwards from 11, 000 m over Italy, late afternoon 18 th July 1995. The halo was intermittently visible over the southern and central parts of the country covered by a thin cirrus sheet. The halo elongated and contracted as the tilts of the plate crystal mirrors changed. Reflections from lakes and rivers shine through the cloud. Video by Les Cowley.
 Sub Sun
Sub Sun
 http: //www. members. tripod. com/~regenbogen/englisch/atlas. htm
http: //www. members. tripod. com/~regenbogen/englisch/atlas. htm
 Sun Pillar
Sun Pillar
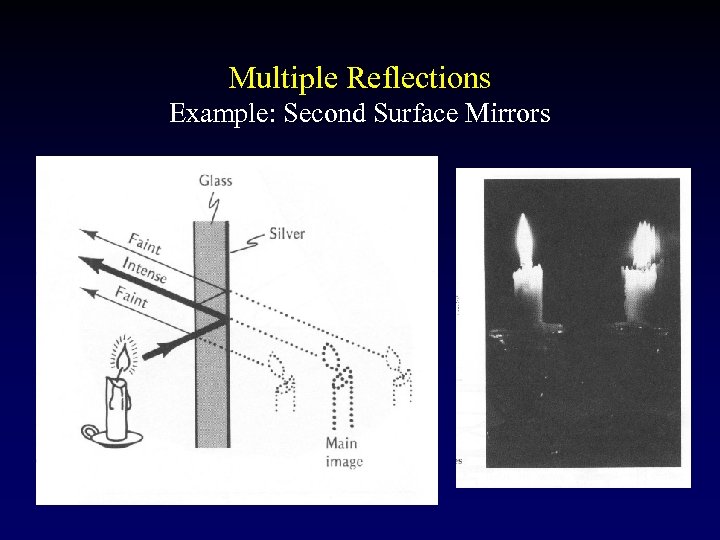 Multiple Reflections Example: Second Surface Mirrors
Multiple Reflections Example: Second Surface Mirrors
 Corner Reflectors
Corner Reflectors