 Humanism in English Language Teaching Mirasova Gulzhan & Turashova Moldir
Humanism in English Language Teaching Mirasova Gulzhan & Turashova Moldir
 Plan: 1) Humanistic language teaching 2)We can identify three main figures in this approach: Erikson Abraham Maslow Carl Rogers 3) Conclusion
Plan: 1) Humanistic language teaching 2)We can identify three main figures in this approach: Erikson Abraham Maslow Carl Rogers 3) Conclusion
 'Humanism' is one of those constructs that people argue about passionately. Instead of attempting to define it, perhaps it makes more sense to focus on some commonly agreed characteristics of humanism. These are: problem-solving, reasoning, free will, self- development, and co-operation.
'Humanism' is one of those constructs that people argue about passionately. Instead of attempting to define it, perhaps it makes more sense to focus on some commonly agreed characteristics of humanism. These are: problem-solving, reasoning, free will, self- development, and co-operation.
 “Humanistic Approach” is like this: (in language teaching) a term sometimes used for methods in which the following principles are considered important: a) development of human values b) growth in self-awareness and in the understanding of others c) sensitivity to human feelings and emotions d) active student involvement in learning and in the way learning takes place
“Humanistic Approach” is like this: (in language teaching) a term sometimes used for methods in which the following principles are considered important: a) development of human values b) growth in self-awareness and in the understanding of others c) sensitivity to human feelings and emotions d) active student involvement in learning and in the way learning takes place
 Role of Humanistic Approaches in Learner Motivation, including extrinsic and intrinsic, can be defined as the need or reason and urge to do something. Acquisition of any language involves motivation. In fact, I consider motivation as the first step in learning. In this part of my assignment I am going to explore the influence of humanistic approaches in creating motivation in learners of language.
Role of Humanistic Approaches in Learner Motivation, including extrinsic and intrinsic, can be defined as the need or reason and urge to do something. Acquisition of any language involves motivation. In fact, I consider motivation as the first step in learning. In this part of my assignment I am going to explore the influence of humanistic approaches in creating motivation in learners of language.
 Erikson’s theory Erikson's theory of psychosocial development is one of the best-known theories of personality in psychology. Much like Sigmund Freud, Erikson believed that personality develops in a series of stages. Unlike Freud's theory of psychosexual stages, Erikson's theory describes the impact of social experience across the whole lifespan.
Erikson’s theory Erikson's theory of psychosocial development is one of the best-known theories of personality in psychology. Much like Sigmund Freud, Erikson believed that personality develops in a series of stages. Unlike Freud's theory of psychosexual stages, Erikson's theory describes the impact of social experience across the whole lifespan.
 Main elements of Erikson's psychosocial stage theory is the development of ego identity
Main elements of Erikson's psychosocial stage theory is the development of ego identity
 EPIGENETIC PRINCIPLE 8 STAGES FROM BIRTH TO OLD AGE: each with a particular crisis STAGES /CHALLENGES PARENTS’/TEACHERS’ ATTITUDES
EPIGENETIC PRINCIPLE 8 STAGES FROM BIRTH TO OLD AGE: each with a particular crisis STAGES /CHALLENGES PARENTS’/TEACHERS’ ATTITUDES
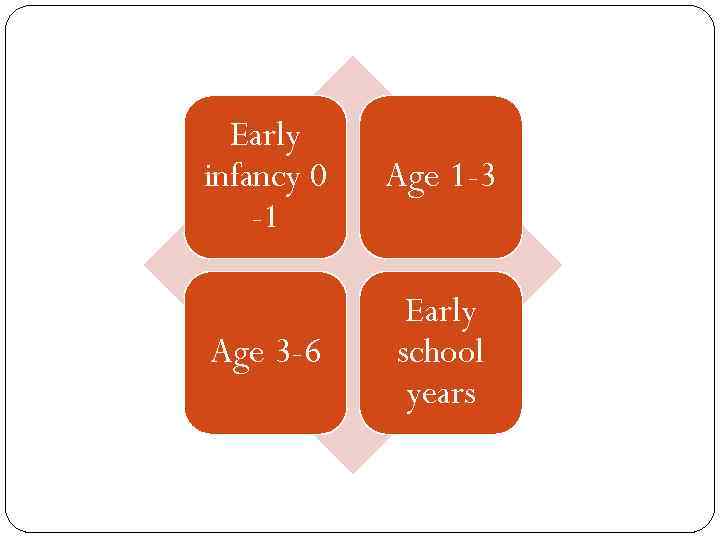 Early infancy 0 -1 Age 1 -3 Age 3 -6 Early school years
Early infancy 0 -1 Age 1 -3 Age 3 -6 Early school years
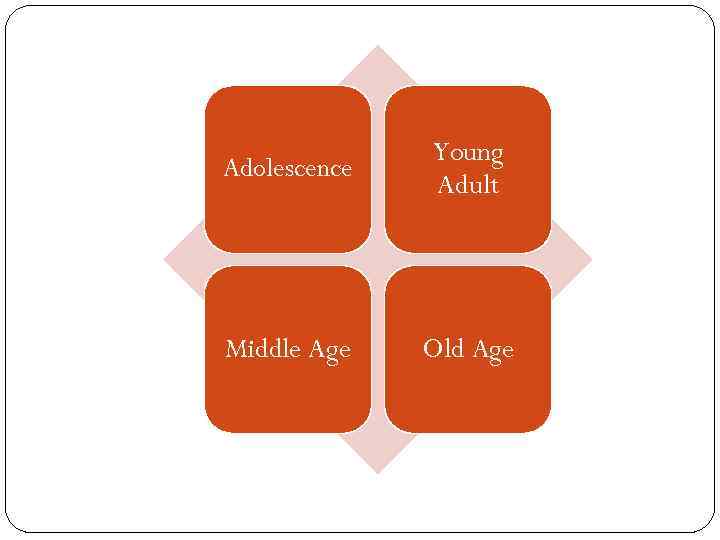 Adolescence Young Adult Middle Age Old Age
Adolescence Young Adult Middle Age Old Age
 Carl Roger's Theory Carl Rogers, another humanistic psychologist, proposed a theory called the person-centered theory.
Carl Roger's Theory Carl Rogers, another humanistic psychologist, proposed a theory called the person-centered theory.
 Rogers (1969) identified key elements if the humanistic approach to education. Human beings: have a natural potential for learning.
Rogers (1969) identified key elements if the humanistic approach to education. Human beings: have a natural potential for learning.
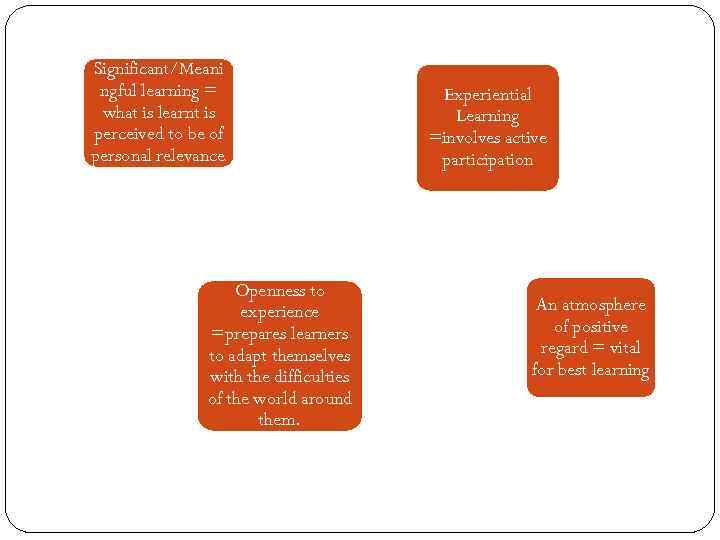 Significant/Meani ngful learning = what is learnt is perceived to be of personal relevance . Openness to experience =prepares learners to adapt themselves with the difficulties of the world around them. Experiential Learning =involves active participation An atmosphere of positive regard = vital for best learning
Significant/Meani ngful learning = what is learnt is perceived to be of personal relevance . Openness to experience =prepares learners to adapt themselves with the difficulties of the world around them. Experiential Learning =involves active participation An atmosphere of positive regard = vital for best learning
 Conclusion The thrust of humanism seems, to us , to be the ability to advance as a species through understanding and cooperation. This means that humanistic language teachers need to have a thorough grasp of both how people learn and what motivates them to learn. They need to shed the old image of the teacher being the fount of wisdom and replace it with the teacher as facilitator.
Conclusion The thrust of humanism seems, to us , to be the ability to advance as a species through understanding and cooperation. This means that humanistic language teachers need to have a thorough grasp of both how people learn and what motivates them to learn. They need to shed the old image of the teacher being the fount of wisdom and replace it with the teacher as facilitator.
 Thanks for Attention!
Thanks for Attention!