Urogenital.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
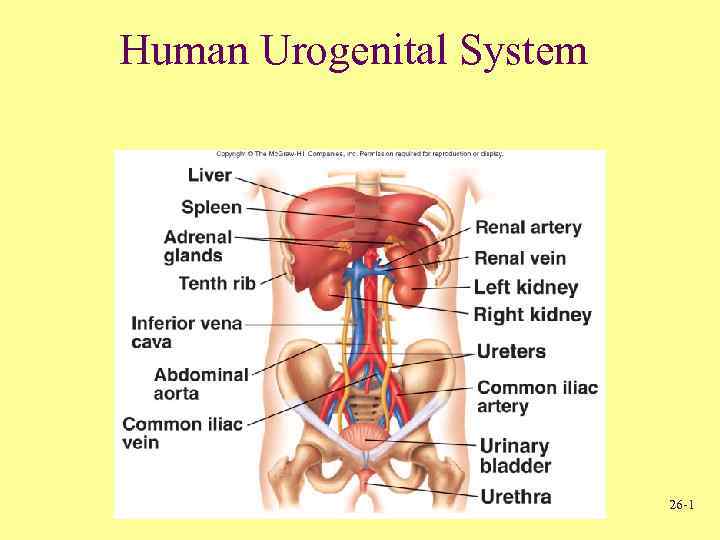 Human Urogenital System 26 -1
Human Urogenital System 26 -1
 Urogenital System Functions • Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites • Regulation of – blood volume and composition – concentration of blood solutes – p. H of extracellular fluid – blood cell synthesis • Synthesis of Vitamin D • Reproduction and sexual function 26 -2
Urogenital System Functions • Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites • Regulation of – blood volume and composition – concentration of blood solutes – p. H of extracellular fluid – blood cell synthesis • Synthesis of Vitamin D • Reproduction and sexual function 26 -2
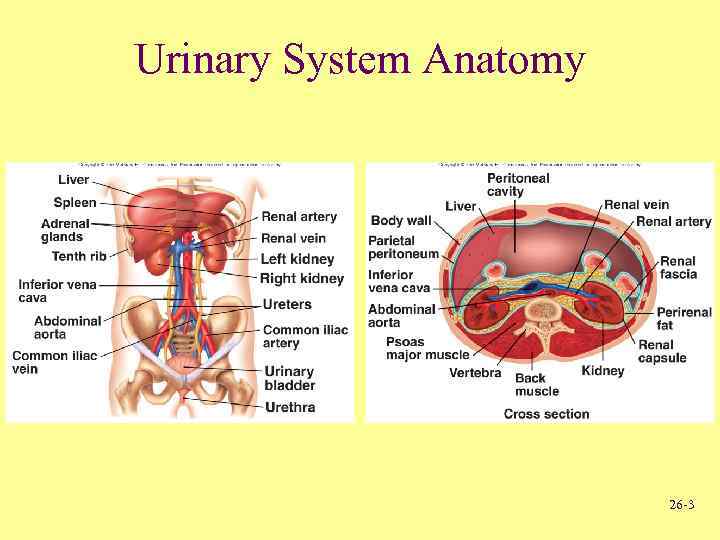 Urinary System Anatomy 26 -3
Urinary System Anatomy 26 -3
 Location and External Anatomy of Kidneys • Location – Lie behind peritoneum on posterior abdominal wall on either side of vertebral column – Lumbar vertebrae and rib cage partially protect – Right kidney slightly lower than left • External Anatomy – Renal capsule • Surrounds each kidney – Perirenal fat • Engulfs renal capsule and acts as cushioning and source of energy – Renal fascia • Anchors kidneys to abdominal wall, separates from abdomen – Hilum • Renal artery and nerves enter and renal vein and ureter exit kidneys 26 -4
Location and External Anatomy of Kidneys • Location – Lie behind peritoneum on posterior abdominal wall on either side of vertebral column – Lumbar vertebrae and rib cage partially protect – Right kidney slightly lower than left • External Anatomy – Renal capsule • Surrounds each kidney – Perirenal fat • Engulfs renal capsule and acts as cushioning and source of energy – Renal fascia • Anchors kidneys to abdominal wall, separates from abdomen – Hilum • Renal artery and nerves enter and renal vein and ureter exit kidneys 26 -4
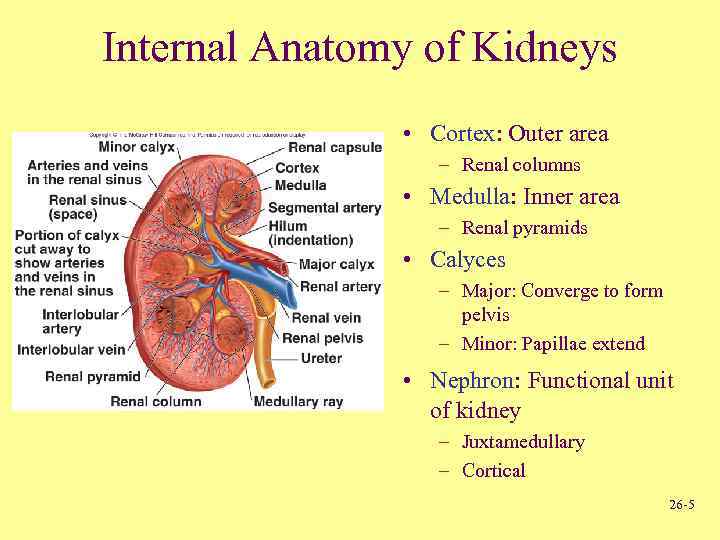 Internal Anatomy of Kidneys • Cortex: Outer area – Renal columns • Medulla: Inner area – Renal pyramids • Calyces – Major: Converge to form pelvis – Minor: Papillae extend • Nephron: Functional unit of kidney – Juxtamedullary – Cortical 26 -5
Internal Anatomy of Kidneys • Cortex: Outer area – Renal columns • Medulla: Inner area – Renal pyramids • Calyces – Major: Converge to form pelvis – Minor: Papillae extend • Nephron: Functional unit of kidney – Juxtamedullary – Cortical 26 -5
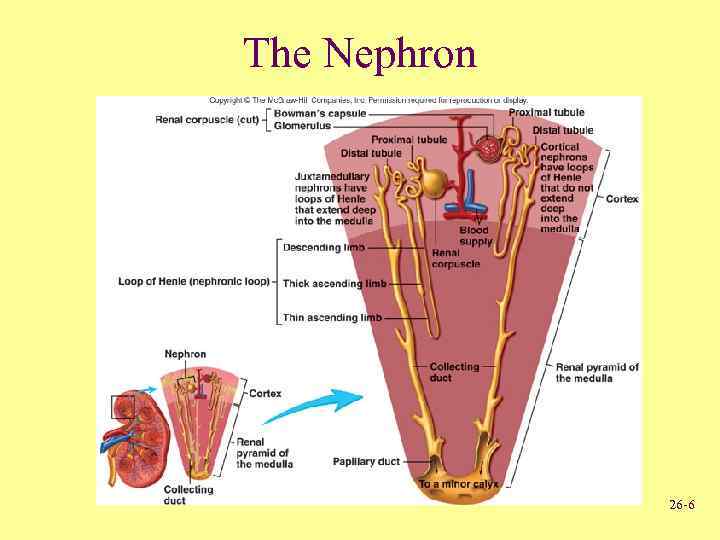 The Nephron 26 -6
The Nephron 26 -6
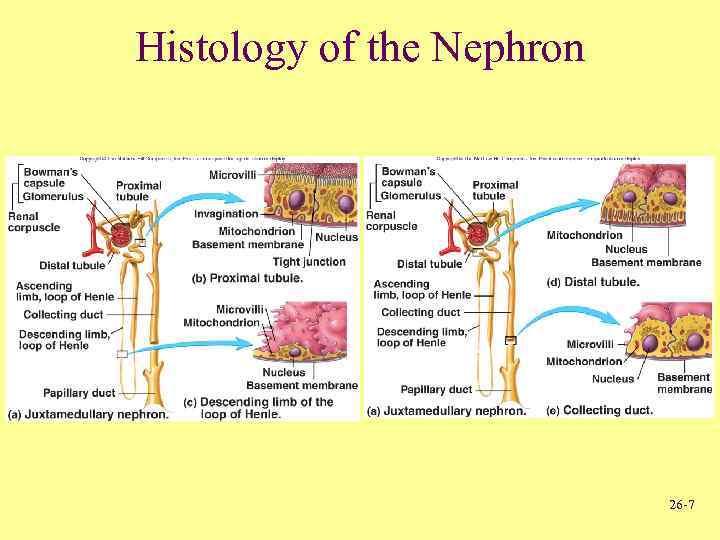 Histology of the Nephron 26 -7
Histology of the Nephron 26 -7
 Internal Anatomy of Kidneys • Renal corpuscle – Bowman’s or Renal capsule • Parietal layer • Visceral layer – Glomerulus • Network of capillaries goes into another capillary bed called the peritubular Capillaries - Arterioles – Afferent • Tubules – Proximal (convoluted) tubule – Loops of Henle • Descending limb • Ascending limb – Distal (convoluted) tubules • Collecting ducts • Blood to glomerulus – Efferent • Drains not into veinule but another arteriole 26 -8
Internal Anatomy of Kidneys • Renal corpuscle – Bowman’s or Renal capsule • Parietal layer • Visceral layer – Glomerulus • Network of capillaries goes into another capillary bed called the peritubular Capillaries - Arterioles – Afferent • Tubules – Proximal (convoluted) tubule – Loops of Henle • Descending limb • Ascending limb – Distal (convoluted) tubules • Collecting ducts • Blood to glomerulus – Efferent • Drains not into veinule but another arteriole 26 -8
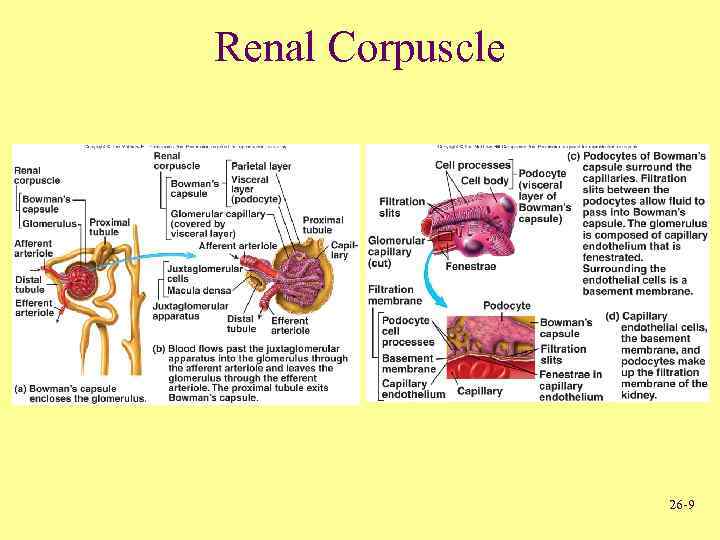 Renal Corpuscle 26 -9
Renal Corpuscle 26 -9
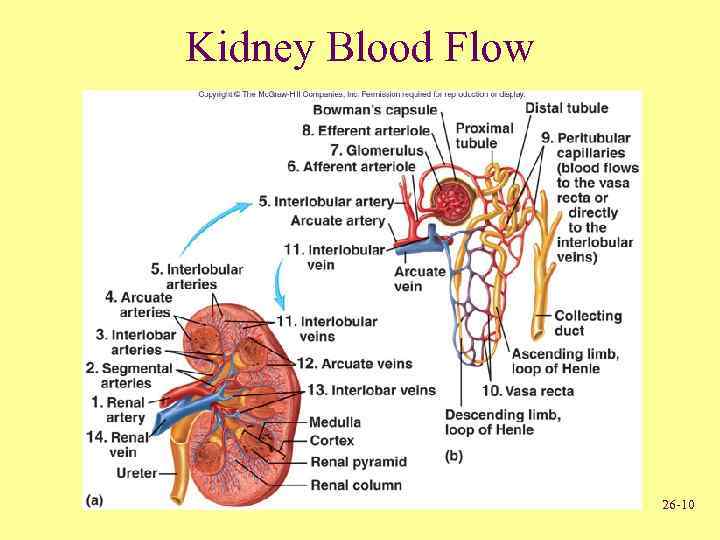 Kidney Blood Flow 26 -10
Kidney Blood Flow 26 -10
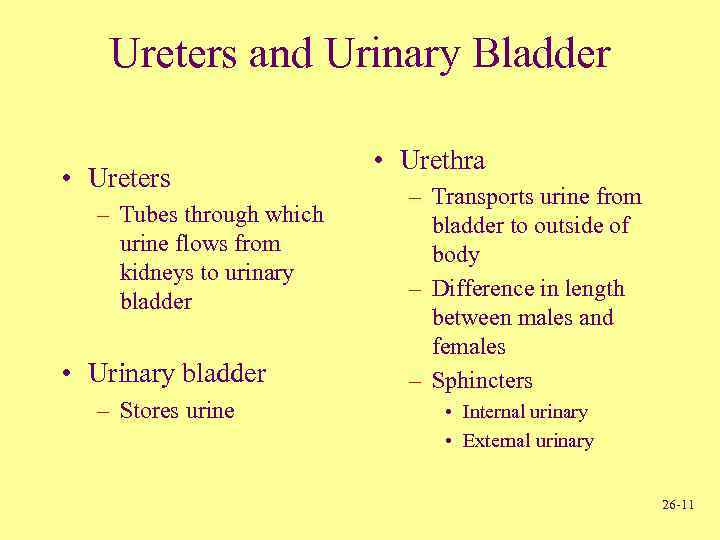 Ureters and Urinary Bladder • Ureters – Tubes through which urine flows from kidneys to urinary bladder • Urinary bladder – Stores urine • Urethra – Transports urine from bladder to outside of body – Difference in length between males and females – Sphincters • Internal urinary • External urinary 26 -11
Ureters and Urinary Bladder • Ureters – Tubes through which urine flows from kidneys to urinary bladder • Urinary bladder – Stores urine • Urethra – Transports urine from bladder to outside of body – Difference in length between males and females – Sphincters • Internal urinary • External urinary 26 -11
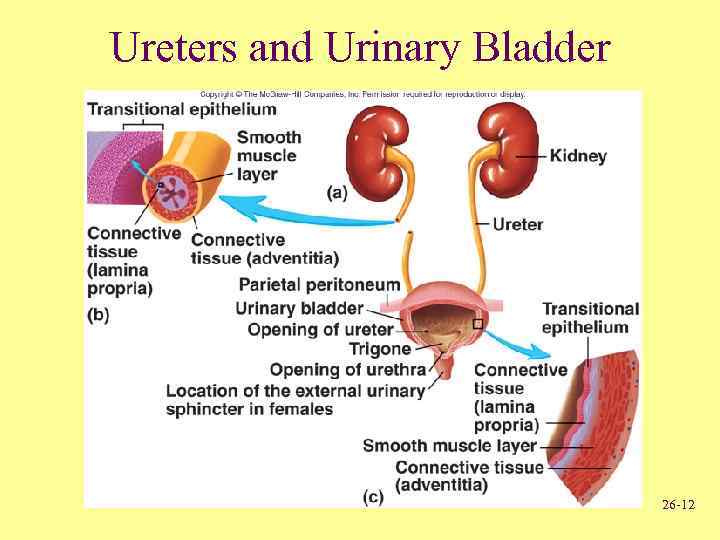 Ureters and Urinary Bladder 26 -12
Ureters and Urinary Bladder 26 -12
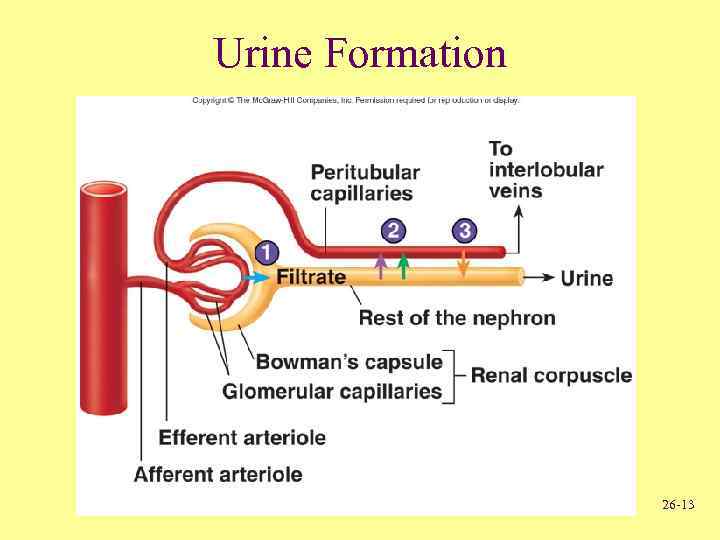 Urine Formation 26 -13
Urine Formation 26 -13
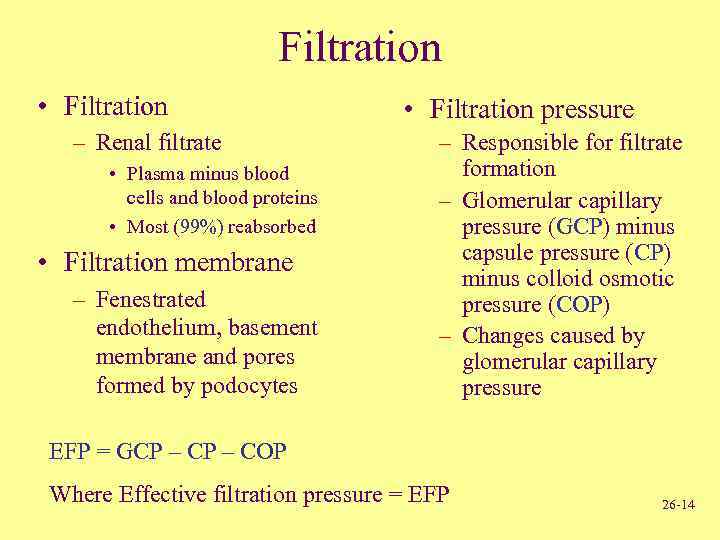 Filtration • Filtration – Renal filtrate • Plasma minus blood cells and blood proteins • Most (99%) reabsorbed • Filtration membrane – Fenestrated endothelium, basement membrane and pores formed by podocytes • Filtration pressure – Responsible for filtrate formation – Glomerular capillary pressure (GCP) minus capsule pressure (CP) minus colloid osmotic pressure (COP) – Changes caused by glomerular capillary pressure EFP = GCP – COP Where Effective filtration pressure = EFP 26 -14
Filtration • Filtration – Renal filtrate • Plasma minus blood cells and blood proteins • Most (99%) reabsorbed • Filtration membrane – Fenestrated endothelium, basement membrane and pores formed by podocytes • Filtration pressure – Responsible for filtrate formation – Glomerular capillary pressure (GCP) minus capsule pressure (CP) minus colloid osmotic pressure (COP) – Changes caused by glomerular capillary pressure EFP = GCP – COP Where Effective filtration pressure = EFP 26 -14
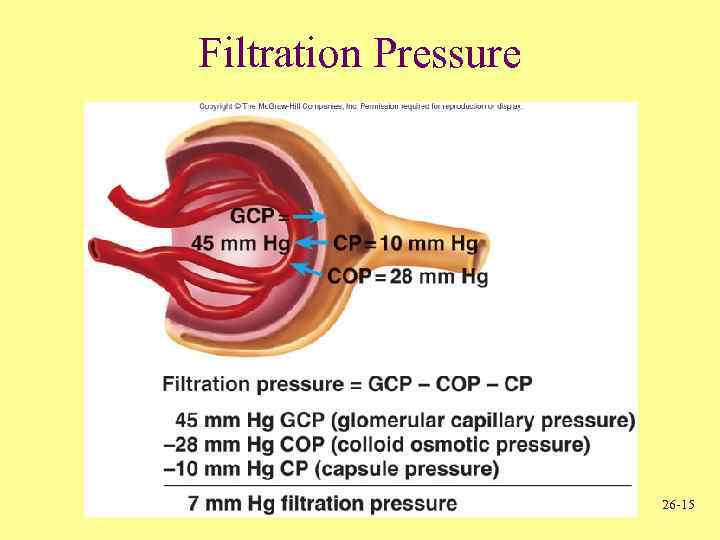 Filtration Pressure 26 -15
Filtration Pressure 26 -15
 Tubular Reabsorption • Reabsorption almost 90% takes place in Proximal • Substances transported tubule via – Passive transport – Active transport – Cotransport • Specialization of tubule segments • Distal tubule and collecting duct affected by hormones like ADH & Aldosterone – Active transport moves Na+ across nephron wall – Other ions and molecules moved by cotransport – Passive transport moves water, urea, lipid-soluble, nonpolar compounds 26 -16
Tubular Reabsorption • Reabsorption almost 90% takes place in Proximal • Substances transported tubule via – Passive transport – Active transport – Cotransport • Specialization of tubule segments • Distal tubule and collecting duct affected by hormones like ADH & Aldosterone – Active transport moves Na+ across nephron wall – Other ions and molecules moved by cotransport – Passive transport moves water, urea, lipid-soluble, nonpolar compounds 26 -16
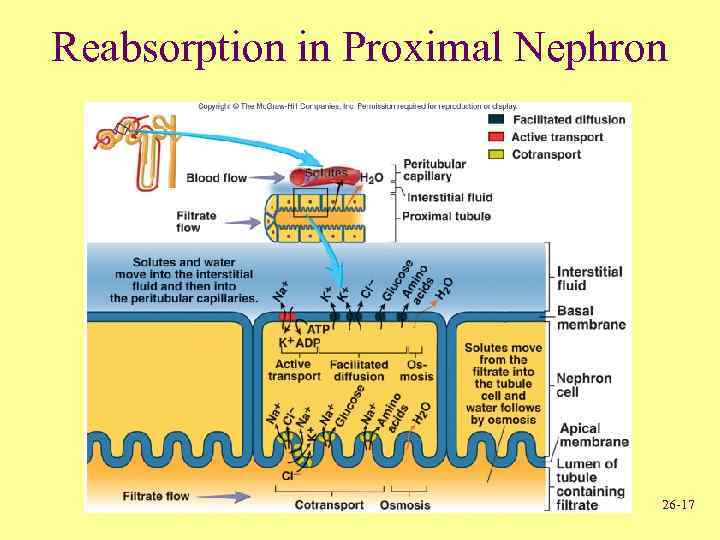 Reabsorption in Proximal Nephron 26 -17
Reabsorption in Proximal Nephron 26 -17
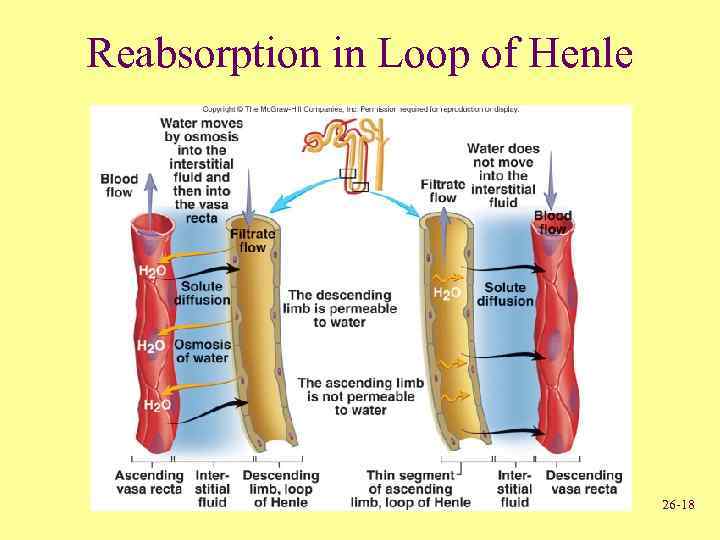 Reabsorption in Loop of Henle 26 -18
Reabsorption in Loop of Henle 26 -18
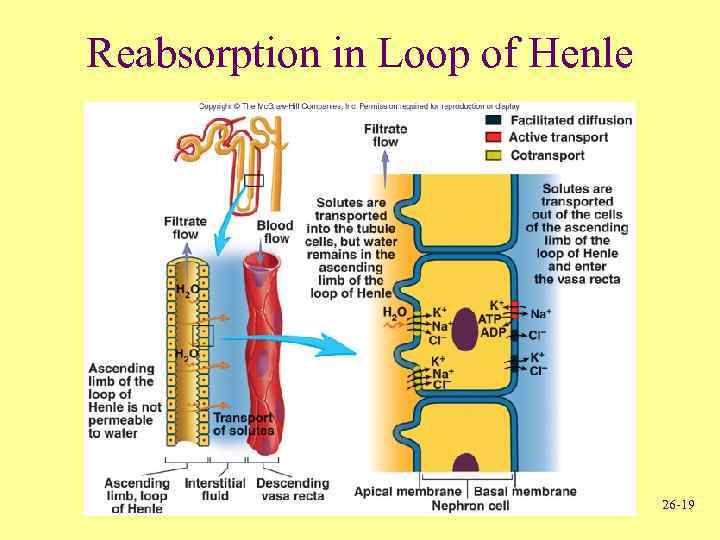 Reabsorption in Loop of Henle 26 -19
Reabsorption in Loop of Henle 26 -19
 Tubular Secretion • Substances enter proximal or distal tubules and collecting ducts • H+, K+ and some substances not produced in body are secreted by countertransport mechanisms 26 -20
Tubular Secretion • Substances enter proximal or distal tubules and collecting ducts • H+, K+ and some substances not produced in body are secreted by countertransport mechanisms 26 -20
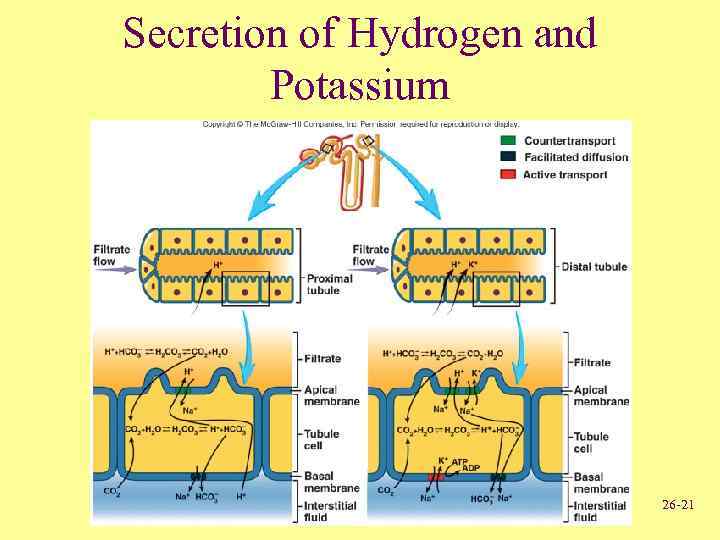 Secretion of Hydrogen and Potassium 26 -21
Secretion of Hydrogen and Potassium 26 -21
 Urine Production • In Proximal tubules – Na+ and other substances removed – Water follows passively – Filtrate volume reduced • In descending limb of loop of Henle – Water exits passively, solute enters – Filtrate volume reduced 15% • In ascending limb of loop of Henle – Na+, Cl-, K+ transported out of filtrate – Water remains • In distal tubules and collecting ducts – Water movement out regulated by ADH • If absent, water not reabsorbed and dilute urine produced • If ADH present, water moves out, concentrated urine produced 26 -22
Urine Production • In Proximal tubules – Na+ and other substances removed – Water follows passively – Filtrate volume reduced • In descending limb of loop of Henle – Water exits passively, solute enters – Filtrate volume reduced 15% • In ascending limb of loop of Henle – Na+, Cl-, K+ transported out of filtrate – Water remains • In distal tubules and collecting ducts – Water movement out regulated by ADH • If absent, water not reabsorbed and dilute urine produced • If ADH present, water moves out, concentrated urine produced 26 -22
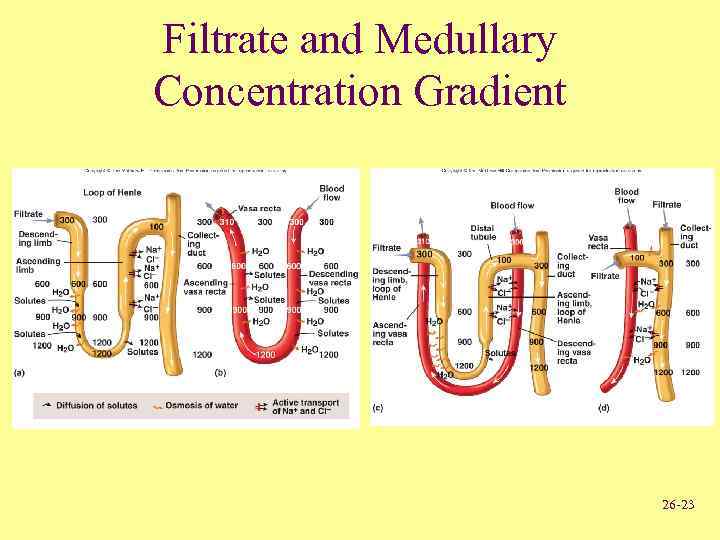 Filtrate and Medullary Concentration Gradient 26 -23
Filtrate and Medullary Concentration Gradient 26 -23
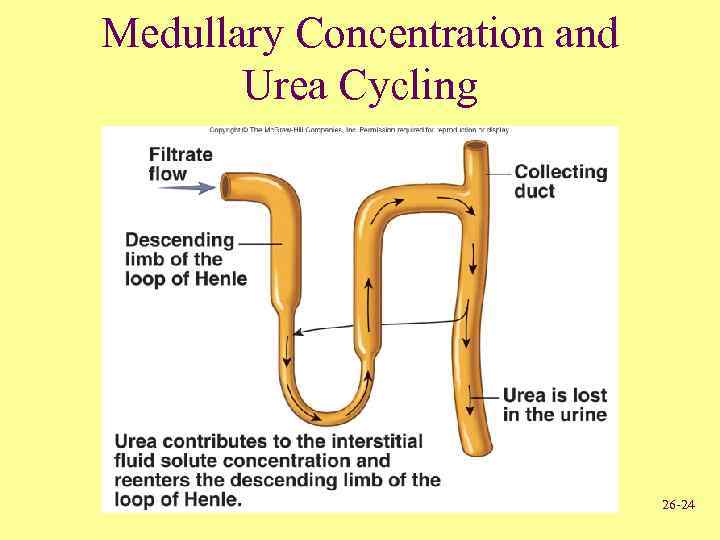 Medullary Concentration and Urea Cycling 26 -24
Medullary Concentration and Urea Cycling 26 -24
 Urine Concentration Mechanism • When large volume of water consumed – Eliminate excess without losing large amounts of electrolytes – Response is kidneys produce large volume of dilute urine • When drinking water not available – Kidneys produce small volume of concentrated urine – Removes waste and prevents rapid dehydration 26 -25
Urine Concentration Mechanism • When large volume of water consumed – Eliminate excess without losing large amounts of electrolytes – Response is kidneys produce large volume of dilute urine • When drinking water not available – Kidneys produce small volume of concentrated urine – Removes waste and prevents rapid dehydration 26 -25
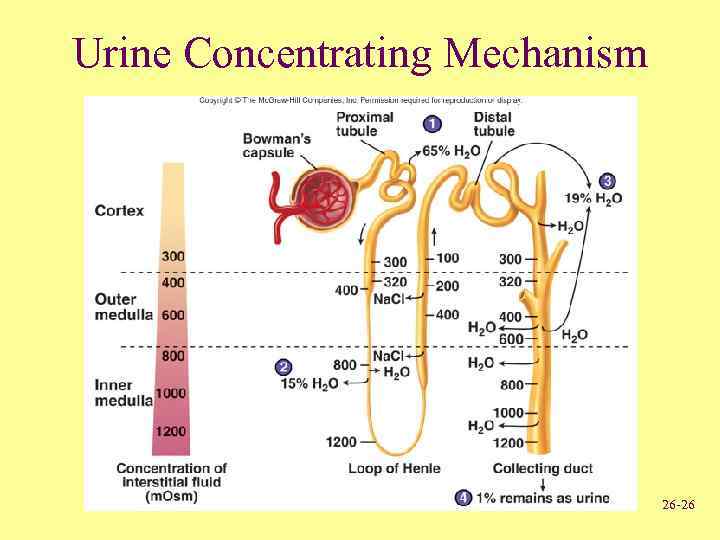 Urine Concentrating Mechanism 26 -26
Urine Concentrating Mechanism 26 -26
 Hormonal Mechanisms • ADH • Renin – Secreted by posterior – Produced by kidneys, pituitary causes production of – Increases water angiotensin II permeability in distal • Atrial natriuretic tubules and collecting ducts • Aldosterone – Produced in adrenal cortex – Affects Na+ and Cltransport in nephron and collecting ducts hormone – Produced by heart when blood pressure increases • Inhibits ADH production • Reduces ability of kidney to concentrate urine 26 -27
Hormonal Mechanisms • ADH • Renin – Secreted by posterior – Produced by kidneys, pituitary causes production of – Increases water angiotensin II permeability in distal • Atrial natriuretic tubules and collecting ducts • Aldosterone – Produced in adrenal cortex – Affects Na+ and Cltransport in nephron and collecting ducts hormone – Produced by heart when blood pressure increases • Inhibits ADH production • Reduces ability of kidney to concentrate urine 26 -27
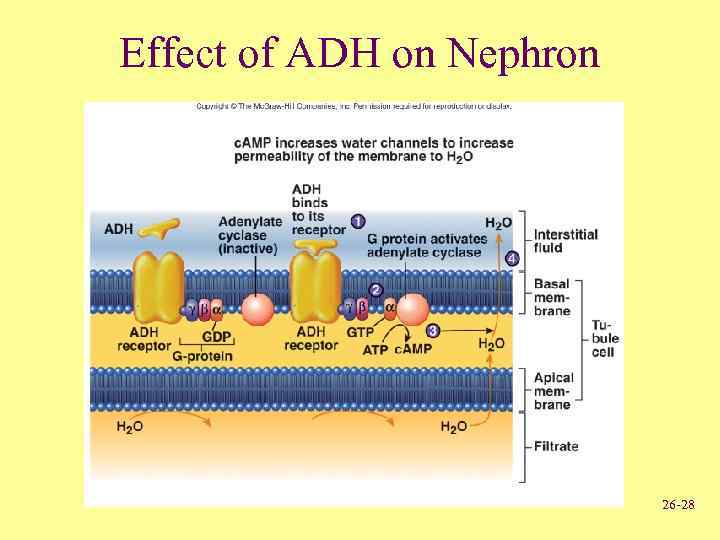 Effect of ADH on Nephron 26 -28
Effect of ADH on Nephron 26 -28
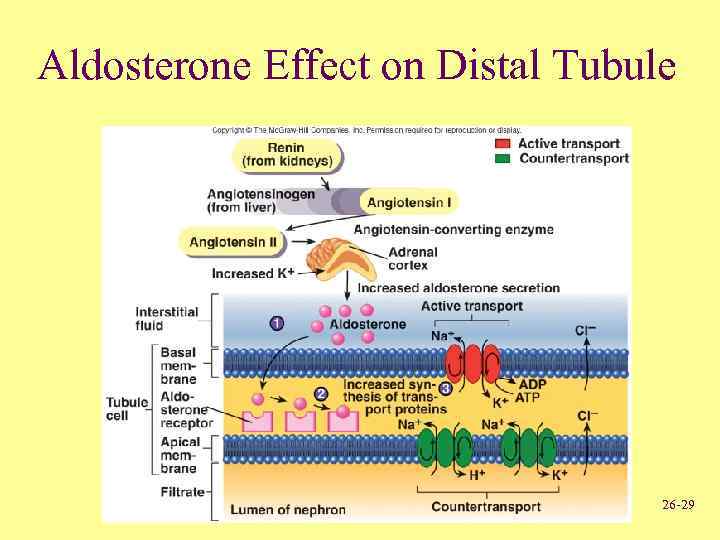 Aldosterone Effect on Distal Tubule 26 -29
Aldosterone Effect on Distal Tubule 26 -29
 Autoregulation and Sympathetic Stimulation • Autoregulation – Involves changes in degree of constriction in afferent arterioles – As systemic BP increased, afferent arterioles constrict and prevent increase in renal blood flow • Sympathetic stimulation – Constricts small arteries and afferent arterioles – Decreases renal blood flow 26 -30
Autoregulation and Sympathetic Stimulation • Autoregulation – Involves changes in degree of constriction in afferent arterioles – As systemic BP increased, afferent arterioles constrict and prevent increase in renal blood flow • Sympathetic stimulation – Constricts small arteries and afferent arterioles – Decreases renal blood flow 26 -30
 Clearance and Tubular Load • Plasma clearance – Volume of plasma cleared of a specific substance each minute – Used to estimate GFR – Used to calculate renal plasma flow – Used to determine which drugs or other substances excreted by kidney • Tubular load – Total amount of substance that passes through filtration membrane into nephrons each minute – Normally glucose is almost completed reabsorbed 26 -31
Clearance and Tubular Load • Plasma clearance – Volume of plasma cleared of a specific substance each minute – Used to estimate GFR – Used to calculate renal plasma flow – Used to determine which drugs or other substances excreted by kidney • Tubular load – Total amount of substance that passes through filtration membrane into nephrons each minute – Normally glucose is almost completed reabsorbed 26 -31
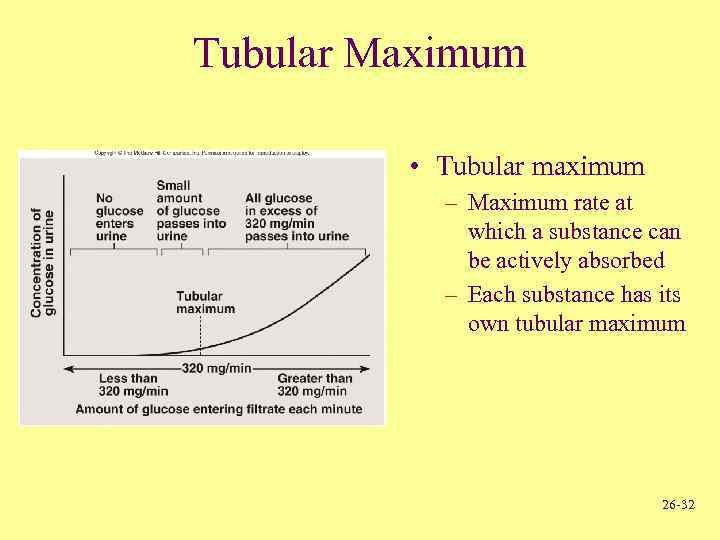 Tubular Maximum • Tubular maximum – Maximum rate at which a substance can be actively absorbed – Each substance has its own tubular maximum 26 -32
Tubular Maximum • Tubular maximum – Maximum rate at which a substance can be actively absorbed – Each substance has its own tubular maximum 26 -32
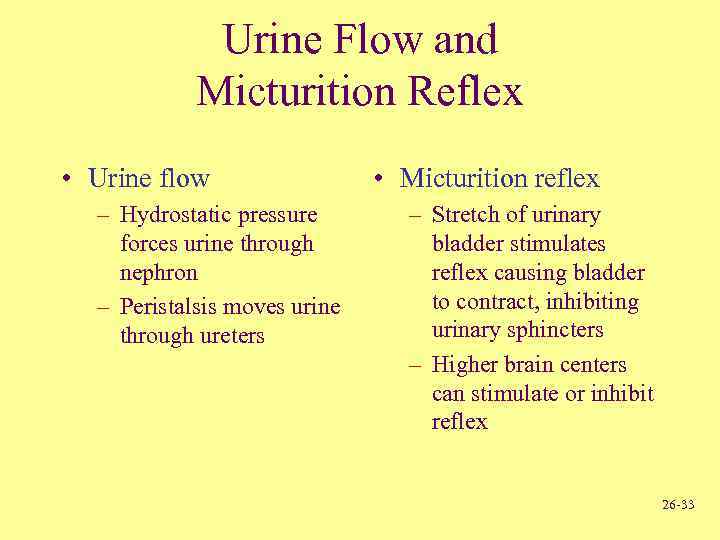 Urine Flow and Micturition Reflex • Urine flow – Hydrostatic pressure forces urine through nephron – Peristalsis moves urine through ureters • Micturition reflex – Stretch of urinary bladder stimulates reflex causing bladder to contract, inhibiting urinary sphincters – Higher brain centers can stimulate or inhibit reflex 26 -33
Urine Flow and Micturition Reflex • Urine flow – Hydrostatic pressure forces urine through nephron – Peristalsis moves urine through ureters • Micturition reflex – Stretch of urinary bladder stimulates reflex causing bladder to contract, inhibiting urinary sphincters – Higher brain centers can stimulate or inhibit reflex 26 -33
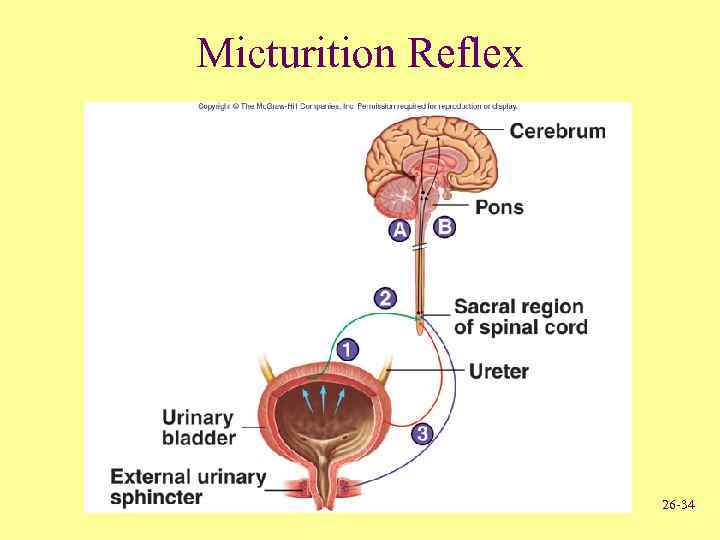 Micturition Reflex 26 -34
Micturition Reflex 26 -34
 Effects of Aging on Kidneys • Gradual decrease in size of kidney – Decrease in kidney size leads to decrease in renal blood flow • Decrease in number of functional nephrons • Decrease in renin secretion and vitamin D synthesis • Decline in ability of nephron to secrete and absorb 26 -35
Effects of Aging on Kidneys • Gradual decrease in size of kidney – Decrease in kidney size leads to decrease in renal blood flow • Decrease in number of functional nephrons • Decrease in renin secretion and vitamin D synthesis • Decline in ability of nephron to secrete and absorb 26 -35
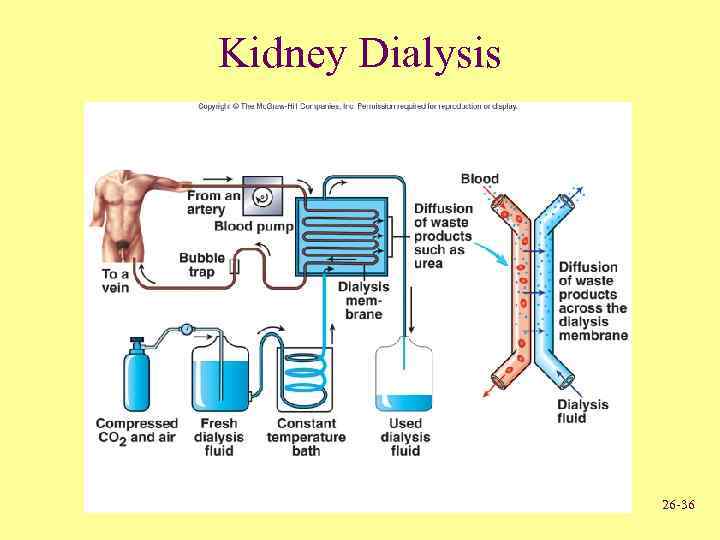 Kidney Dialysis 26 -36
Kidney Dialysis 26 -36


